Balancing Productivity and Environmental Sustainability in Pomelo Production Through Controlled-Release Fertilizer Optimization
Abstract
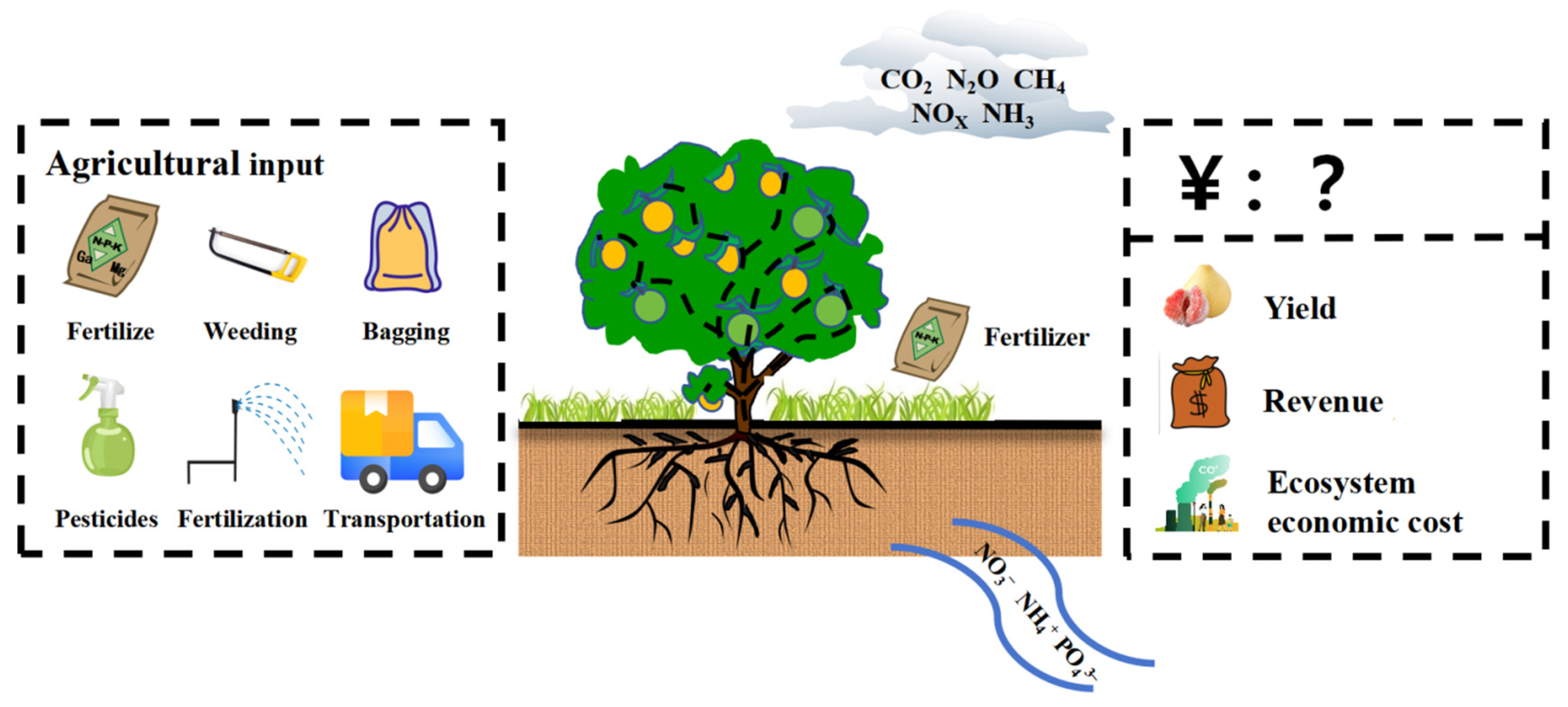
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Indicator Measurement
2.3.1. Collection of Honey Pomelo Fruit and Soil Samples
2.3.2. Determination of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Environmental Footprints and Economic Evaluation
2.4.1. System Boundaries and Functional Unit
2.4.2. Economic Benefits and Environmental Costs of Pomelo Production
2.5. Comprehensive Evaluation and Structural Equation Modeling
2.5.1. Construction of the Comprehensive Evaluation Index System and Entropy Weight Method Calculation
2.5.2. PLS-SEM
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Different Fertilization Regimes on Pomelo Yield
3.2. Effects of Different Fertilization Regimes on Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Economic Benefits and Environmental Costs Under Different Fertilization Regimes

3.4. Effects of Different Fertilization Regimes on the Environmental Footprint of Pomelo Orchards
3.5. Responses of PFPN and Environmental Footprints to Different Fertilization Regimes in Pomelo Orchards
3.6. Mechanisms of Different Fertilization Regimes on the EEB of Pomelo Orchards
3.7. Comprehensive Evaluation of Economic and Ecological Benefits of Different Fertilization Regimes in Pomelo Orchards
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Optimized Fertilization on Pomelo Yield
4.2. Effects of Optimized Fertilization on Soil Physicochemical Properties in Pomelo Orchards
4.3. Effects of Optimized Fertilization on Economic Benefits
4.4. Effects of Optimized Fertilization on EEB of Pomelo Orchards
4.5. Effects of Optimized Fertilization on the Environmental Footprint of Pomelo Production
4.6. Comprehensive Performance Evaluation and Optimal Fertilization Strategy Based on CEI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Tables
| Source | Unit | Emission Factor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic N fertilizer | t CO2-eq t−1 | 8.3 | [30] |
| Synthetic P2O5 fertilizer | t CO2-eq t−1 | 2.33 | [31] |
| Synthetic K2O fertilizer | t CO2-eq t−1 | 0.66 | [31] |
| Pesticide | t CO2-eq t−1 | 18 | [32] |
| Diesel fuel | t CO2-eq t−1 | 3.7 | [33] |
| Fruit bag | t CO2-eq t−1 | 1.54 | [33] |
| Synthetic N fertilizer | kg NH3 kg−1 | 0.01110 | [34] |
| Synthetic P2O5 fertilizer | kg NH3 kg−1 | 0.00100 | [34] |
| Synthetic K2O fertilizer | kg NH3 kg−1 | 0.00484 | [34] |
| Pesticide | kg NH3 kg−1 | 0.00119 | [34] |
| Fruit bag | kg NH3 kg−1 | 0.00001 | [35] |
| Synthetic P2O5 fertilizer | kg P kg−1 | 0.00001090 | [34] |
| Pesticide | kg P kg−1 | 0.00059579 | [34] |
| Fruit bag | kg P kg−1 | 0.00000029 | [35] |
Appendix B. Figures




Appendix C. Calculation Methods for Economic and Environmental Indicators
Appendix C.1. Economic and Environmental Benefit Calculation
Appendix C.1.1. Economic Benefits
Appendix C.1.2. Environmental Economic Cost
Appendix C.2. Environmental Footprint
Appendix C.2.1. Estimation of Carbon Footprint (CF)
Appendix C.2.2. Estimation of Nitrogen Footprint (NF)
Appendix C.2.3. Estimation of Phosphorus Footprint (PF)
References
- Luo, Z.W.; Tao, J.X.; Hou, K.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, Y.W.; Guo, J.X. Optimized nutrient management improves fruit yield and fertilizer use efficiency and reduces carbon emissions in pomelo production. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Jiang, Y.; Song, B.; Wu, Z.; Yan, X.; He, Z.; Ye, D.; Ou, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, L. Reduced Fertilization and Magnesium Supplementation: Modulating Fruit Quality in Honey Pomelo (Citrus maxima (Burm.) Merr.). Plants 2024, 13, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Low N apparent surplus with higher rice yield under long-term fertilizer postponing in the rice-wheat cropping system. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Shah, F.; Wu, W. Environmental and socio-economic performance of intensive farming systems with varying agricultural resource for maize production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lin, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of fertilizer reduction control in Zhejiang Province. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.-L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.-L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Xu, M.; Li, R.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Reis, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; et al. Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer use for more grain and less pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, X.; Muneer, M.A.; Weng, X.; Cai, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.; et al. Pomelo green production on acidic soil: Reduce traditional fertilizers, but do not ignore magnesium. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 948810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Assinck, F.B.; Heinen, M.; Oenema, O. Water and nitrogen use efficiencies in citrus production: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 222, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, G.; Xiao, R.; Hou, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Yuan, P.; Tian, F.; Yin, L.; Zhu, H.; et al. An appropriate amount of straw replaced chemical fertilizers returning reduced net greenhouse gas emissions and improved net ecological economic benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Javed, T.; Hussain, S.; Guo, S.; Guo, R.; Yang, L.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z.; Shah, A.A.; et al. Maize/peanut rotation intercropping improves ecosystem carbon budget and economic benefits in the dry farming regions of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, F. Integrating environmental footprints and ecosystem economic performance to evaluate nitrogen management in intensive drip-irrigated potato production. Agric. Syst. 2024, 221, 104110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Qian, R.; Naseer, M.A.; Han, F.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z.; Chen, X.; Ren, X. Integrated straw-derived biochar utilization to increase net ecosystem carbon budget and economic benefit and reduce the environmental footprint. Field Crops Res. 2024, 307, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U.; Zhang, W.; Ruan, S.; Chen, X. Integrated assessment of agronomic, environmental and ecosystem economic benefits of blending use of controlled-release and common urea in wheat production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S. Winter legume-rice rotations can reduce nitrogen pollution and carbon footprint while maintaining net ecosystem economic benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ma, Y.; Kong, K.; Muneer, M.A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, Z.; Ma, C.; Zheng, C.; et al. Mitigating life-cycle environmental impacts and increasing net ecosystem economic benefits via optimized fertilization combined with lime in pomelo production in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Dong, Z.; Liu, B.; Xiong, H.; Guo, C.; Lakshmanan, P.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Can citrus production in China become carbon-neutral? A historical retrospect and prospect. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 348, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- ISO 14040:2006; Environmental Management−Life Cycle Assessment−Principles and Framework. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- ISO 14044:2006; Environmental Management−Life Cycle Assessment−Requirements and Guidelines. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Schiermeier, Q. Prices plummet on carbon market. Nature 2009, 457, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.A.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.A.; Zheng, H.; Yan, H.M.; Huang, H. Studies on the external costs of and the optimum use of nitrogen fertilizer based on the balance of economic and ecological benefits in the paddy field system of the Dongting Lake area. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2006, 39, 2031–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Yan, X. Ecologically optimal nitrogen application rates for rice cropping in the Taihu Lake region of China. Sustain. Sci. 2012, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yan, X. Comparison of statistical models for predicting cost effective nitrogen rate at rice-wheat cropping systems. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L. Nitrogen Fertilizer Demand and Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Potential Under Nitrogen Limiting Conditions for Chinese Agriculture Production. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. 2014 Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.D. Study on the Characteristics of Carbon Cycle in Citrus Orchard Ecosystem. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Wang, X.K.; Han, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Duan, X.; Zheng, H.; Miao, H. Soil carbon sequestrations by nitrogen fertilizer application, straw return and no-tillage in China’ s cropland. Global Change Biol. 2009, 15, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R. Research on One-Time Controlled-Release Fertilization of High-Yield Grapefruit Orchards. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.K. Estimation of greenhouse gases emission factors of China’ s nitrogen, phosphate and potash fertilizers. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6371–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Gao, W.S.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.Q.; Sui, P. Reducing agricultural carbon footprint through diversified crop rotation systems in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 76, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Qiu, R.Z. Estimation of energy consumption and carbon emissions of China’s pulp and paper industry. China pulp. Pap. 2014, 33, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, T.; Kägi, T.; Blaser, S. Life Cycle Inventories of Agricultural Production Systems, Final Report Ecoinvent v2.0; Agrosope Reckenholz-Tänikon Research Station: Zürich, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shen, X.; Zhang, T.; Ji, C.; Yuan, X.; Hong, J. Energy and carbon coupled water footprint analysis for straw pulp paper production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Yu, J.; Zheng, X.; Qu, F.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H. N2O emissions from an apple orchard in the coastal area of Bohai Bay, China. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 164732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.F.; Jiang, Y.M.; Wei, S.C.; Fang, X.J. Nitrogen balance under different N application rates in young apple orchards. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2011, 17, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.; Wang, F.; Qin, W.; Zhang, F.; Oenema, O. Modeling nutrient flows in the food chain of China. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wesenbeeck, C.F.A.; Keyzer, M.A.; Van Veen, W.C.M.; Qiu, H. Can China’s overuse of fertilizer be reduced without threatening food security and farm incomes? Agric. Syst. 2021, 190, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Peng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhuge, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H. Effect of bag-controlled release fertilizer on nitrogen loss, greenhouse gas emissions, and nitrogen applied amount in peach production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Hou, P.; Xue, L.; Yang, L.; Ding, Y. Lower dose of controlled/slow release fertilizer with higher rice yield and N utilization in paddies: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2023, 294, 108879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunović, I.; Filipović, V. Mulch as a nature-based solution to halt and reverse land degradation in agricultural areas. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 34, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, T.B.; Mazzoncini, M.; Bàrberi, P.; Antichi, D.; Silvestri, N. Fifteen years of no till increase soil organic matter, microbial biomass and arthropod diversity in cover crop-based arable cropping systems. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.; Xie, S.; Zheng, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Mo, M. Long-term effects of living grass mulching on soil and water conservation and fruit yield of citrus orchard in south China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 252, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Cheng, M.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Zou, Y.; Chau, H.W.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X. Coupling effects of water and fertilizer on yield, water and fertilizer use efficiency of drip-fertigated cotton in northern Xinjiang, China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 219, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.; Lu, W.; Hou, Z.; Li, J. Commercial organic fertilizer substitution increases wheat yield by improving soil quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Muneer, M.A.; Li, J.; Hou, W.; Ma, C.; Jiao, J.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, L.; Zheng, C. Integrated nutrient management significantly improves pomelo (Citrus grandis) root growth and nutrients uptake under acidic soil of southern China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Bi, R.; Song, M.; Wang, B.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Z. Optimizing organic substitution: Balancing carbon sequestration and priming effects of a six-year field experiment for sustainable vegetable production. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 44, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, P.; Yang, C.; Lu, S. Effects of oyster shell powder and lime on availability and forms of phosphorus and enzyme activity in acidic paddy soil. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2022, 43, 5224–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Chen, S.; Ke, L.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X. Cover crops restore declining soil properties and suppress bacterial wilt by regulating rhizosphere bacterial communities and improving soil nutrient contents. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 238, 126505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, T.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Shankar, A.; Saxena, A.; Tiwari, A.; Maturi, K.C.; Solanki, M.K.; Singh, V.; Eissa, M.A.; et al. Role of calcium nutrition in plant Physiology: Advances in research and insights into acidic soil conditions-A comprehensive review. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 210, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.Y.; Ni, N.; Nkoh, J.N.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, W.R.; Pan, X.Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Xu, R.-K.; Qian, W. Biochar retards Al toxicity to maize (Zea mays L.) during soil acidification: The effects and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Jia, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, L.-T.; Chen, L.S. Regulation of magnesium and calcium homeostasis in citrus seedlings under varying magnesium supply. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 204, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Ji, Z.; Yan, X.; Kong, K.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Muneer, M.A.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L. Reducing aluminum is the key nutrient management strategy for ameliorating soil acidification and improving root growth in an acidic citrus orchard. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 1681–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, W.; Muneer, M.A.; Ji, Z.; Tong, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L. Integrated use of lime with Mg fertilizer significantly improves the pomelo yield, quality, economic returns and soil physicochemical properties under acidic soil of southern China. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 290, 110502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Z. Synthesis of a slow-release fertilizer composite derived from waste straw that improves water retention and agricultural yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, S.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, J.; Guo, J.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, L. Combined effects of irrigation level and fertilization practice on yield, economic benefit and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated greenhouse tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xue, J.; Yu, E.; Wei, H.; Xu, K.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, H. One-time fertilization of controlled-release urea with compound fertilizer and rapeseed cake maintains rice grain yield and improves nitrogen use efficiency under reduced nitrogen conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1281309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Zabaloy, M.C.; Guan, K.; Villamil, M.B. Do cover crops benefit soil microbiome? A meta-analysis of current research. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X. Optimizing fertilizer use for sustainable food systems: An evaluation of integrated water-fertilizer system adoption among cotton farmers in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1310426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.C.; Peng, W.T.; Li, J.; Liao, H. Functional dissection and transport mechanism of magnesium in plants. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, X.; Xiao, H.; Toan, N.S.; Liao, B.; Wu, X.; Hu, R. Leaching is the main pathway of nitrogen loss from a citrus orchard in Central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 356, 108559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.B.; Van Meter, K.J.; Byrnes, D.K.; Van Cappellen, P.; Brouwer, R.; Jacobsen, B.H.; Jarsjö, J.; Rudolph, D.L.; Cunha, M.C.; Nelson, N.; et al. Managing nitrogen legacies to accelerate water quality improvement. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Qian, W.; He, M.; Chen, P.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Z. Nitrogen losses from soil as affected by water and fertilizer management under drip irrigation: Development, hotspots and future perspectives. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Coupling effects of phosphate fertilizer type and drip fertigation strategy on soil nutrient distribution, maize yield and nutrient uptake. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 290, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenveld, T.; Kohn, Y.Y.; Gross, A.; Lazarovitch, N. Optimization of nitrogen use efficiency by means of fertigation management in an integrated aquaculture-agriculture system. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.J.; Tian, Y.; He, M.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Lyu, Q.; Xie, R.J.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Deng, L.; Yi, S.L. Effects of chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer application on soil properties, citrus growth physiology, and yield. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.A.; Morgan, K.T.; Hamido, S.A.; Kadyampakeni, D.M. Effect of essential nutrients on roots growth and lifespan of huanglongbing affected citrus trees. Plants 2020, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Ge, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xu, B.; Luo, W.; Jiang, H.; Gu, B.H.; Chang, J. Atmospheric reactive nitrogen in China: Sources, recent trends, and damage costs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9420–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.Y.; Shen, G.X.; Gu, H.R.; Pugliese, M.; Gullino, M.L. Effects of drip fertigation management on nutrient losses and pear production at Chongming Dongtan in Yangtze River Estuary, China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 396, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Sorrenti, G.; Panzacchi, P.; George, E.; Tonon, G. Biochar reduces short-term nitrate leaching from a horizon in an apple orchard. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| N (kg ha−1) | P2O5 (kg ha−1) | K2O (kg ha−1) | MgO (kg ha−1) | CaO (kg ha−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1084 | 914 | 906 | 0 | 0 |
| B | 1084 | 914 | 906 | 0 | 0 |
| C | 250 | 0 | 200 | 100 | 400 |
| D | 250 | 0 | 200 | 100 | 400 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Gao, G.; Yu, J.; Zhan, R.; Yang, H.; He, Z.; Dong, B.; Fan, J.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, S.; et al. Balancing Productivity and Environmental Sustainability in Pomelo Production Through Controlled-Release Fertilizer Optimization. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131367
Zhang Z, Gao G, Yu J, Zhan R, Yang H, He Z, Dong B, Fan J, Fang Y, Zeng S, et al. Balancing Productivity and Environmental Sustainability in Pomelo Production Through Controlled-Release Fertilizer Optimization. Agriculture. 2025; 15(13):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131367
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zetian, Guangzhao Gao, Jinghui Yu, Runzhi Zhan, Hongyu Yang, Zhengjia He, Bin Dong, Jindun Fan, Yina Fang, Sisi Zeng, and et al. 2025. "Balancing Productivity and Environmental Sustainability in Pomelo Production Through Controlled-Release Fertilizer Optimization" Agriculture 15, no. 13: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131367
APA StyleZhang, Z., Gao, G., Yu, J., Zhan, R., Yang, H., He, Z., Dong, B., Fan, J., Fang, Y., Zeng, S., Xuan, X., Wang, S., Wu, L., Yang, W., & Guo, L. (2025). Balancing Productivity and Environmental Sustainability in Pomelo Production Through Controlled-Release Fertilizer Optimization. Agriculture, 15(13), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131367




