Abstract
As a typical agricultural waste, the resource utilization of corn stover (CS) plays a crucial role in the coordinated optimization of ecological and economic benefits. In order to enhance the utilization of CS resources, Lentilactobacillus (L.) buchneri (LB) and different proportions of Artemisia argyi (AA) were added to CS to investigate the impact of additives on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of corn stover silage (CSS). This study revealed that the separate addition of AA or LB in CS effectively improved the silage quality and aerobic stability. Specifically, LB exhibited the lowest pH value of 3.72 at 90 d of fermentation, while the NH3-N content was 0.07 g/kg DM during the anaerobic fermentation stage and 0.19 g/kg DM during the aerobic exposure stage (p < 0.05). Mixing 30% AA increased the lactic acid content, lowered the pH, maintained a higher relative abundance of Lactobacillus, and reduced mycotoxin levels. In terms of aerobic stability, all AA-treated groups demonstrated superior performance compared to the LB treatment. Additionally, it was observed, that in the 30% AA group, Candida exhibited the highest relative abundance. Importantly, the addition of AA upregulated carbohydrate metabolism and lipid metabolism during the ensiling process, and their relative abundances remained high during aerobic exposure. Fully utilizing CS resources as feed to provide fiber and nutrients for ruminants can not only reduce the pressure on forage demand but meet the development needs of “grain-saving” animal husbandry, which is conducive to solving the contradictions of “human–animal competition for food” and “human animal competition for land”.
1. Introduction
Agricultural waste refers to the organic materials discarded during agricultural production activities and primarily includes crop straw and animal manure [1]. Research shows that the total annual amount of agricultural waste reaches 1.75 × 109 tons, with crop stover (CS) being the largest component at 9.93 × 108 tons, accounting for 56.82% of the total [2]. China is the world’s second-largest corn producer, in 2022, the theoretical amount of CS resources in China was 340 million tons. However, a large amount of stover is being burned or discarded, causing resource waste and environmental pollution including increased greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, water pollution, and land degradation [3,4,5]. The eco-friendly use of agricultural waste through recycling, low-carbon and efficiency methods, will cut pollution and boost sustainability development [6,7,8,9].
Compared with wheat and rice straw, CS has the highest digestible nutrient content, superior crude protein (CP) and calcium contents, a relatively reduced amount of crude fiber and a higher nutritional value. However, the lignocellulosic matrix in CS adversely affects palatability [10]. At present, the main methods for degrading CS include physical, chemical and microbial treatments [11,12]. Biological treatments that use microorganisms or enzyme systems to decompose lignin, increase the contact area between microorganisms and lignin and improve the degradation effect, have low energy consumption and do not create pollution [12]. Silage can maintain the juice and nutrients of forage grass for a long time; therefore, it is a favorable method for preserving forage, alleviating the shortage of forage in winter and spring and ensuring animals have access to forage year-round [13]. During ensiling, microorganisms compete with each other for nutrients. Stover mainly relies on lactic acid bacteria (LAB) attached to the stover for fermentation, LAB produces organic acid, which increases the acidity of the silage and enhances its sour aroma, inhibiting the unwanted microorganisms that are intolerant to low pHs [14]. Therefore, the synergistic effects between additional microorganisms and epiphytic LAB on forage have become the key to research in the area of feed.
The prophylactic and growth-promoting use of antibiotics in intensive livestock production has led to the development of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), representing a serious threat to public health [15]. Finding and promoting effective green alternative antibiotic products is an effective measure to address the growing demand for meat consumption, food shortages and environmental pollution worldwide. Research has shown that adding microorganism, enzyme and microorganism–enzyme composite preparations influence the optimized fermentation parameters and nutrition profiles upon feed utilization and effectively reduce cellulose content, enhancing aerobic stability and increasing the utilization rate of renewable resources [16,17,18]. Meanwhile, it reduces the transmission of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) [19]. Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) contains abundant bioactive compounds (e.g., polysaccharides and volatile oils). These bioactive substances interact with microbial cellular structures, disrupting bacterial and fungal cell walls as well as genetic material (DNA) [20]. Artemisia argyi (AA) is a traditional herbaceous plant widely distributed across Asia, commonly utilized as both a medicinal herb and functional food [21,22]. AA contains numerous bioactive compounds including essential oils, polysaccharides, flavonoids, organic acids and terpenoids [20,23], most of which exhibit various biological activities such as antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antiviral, antiallergic, anti-aging and hypolipidemic properties [24,25,26,27]. Extensive research has demonstrated that AA as a feed additive effectively lowers pH, increases lactic and acetic acid content, improves aerobic stability and significantly reduces levels of mycotoxins (including AFB1, DON, ZEN, OA and FB) [28,29,30,31]. Studies also indicate that AA can modulate gastrointestinal microbiota and mitigate inflammatory responses in animals [24].
This study investigated the feasibility of using CS as silage fermentation feedstock by adding different additives to CS and examining its fermentation quality, aerobic stability and mycotoxins so as to provide technical guidance for the sustainable utilization of agricultural residues and to promote circular agricultural practices through the efficient value-added conversion of crop byproducts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Forage Acquisition and Ensiling Protocol
In September 2022, corn stover (CS, Zhengdan 958 variety) collected from Xingyang, Henan, and whole-crop AA was made of Artemisia argyi (Tangyin Beiai variety) harvested in Anyang, Henan, were both chopped into 1–2 cm segments for subsequent processing.
Lentilactobacillus (L.) buchneri, supplied by China Agricultural University, was initially grown in MRS broth at 37 °C for 12 h. After incubation, the bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation (12,000× g, 10 min, 4 °C) and resuspended in distilled water to obtain a suspension with an optical density (OD600) of 0.80.
The experiment comprised five treatment groups shows in Table 1.

Table 1.
Treatment groups (w/w).
After adjusting moisture content to 65%, 300 g samples were vacuum-sealed in polyethylene bags (25 × 35 cm) using a P-290 sealer (Shineye, Dongguan, China), with three replicates per group. Silages were stored at ambient temperature (16–35 °C) for 90 days (d), followed by aerobic exposure for 1, 3, 5 and 7 d after unsealing. Fermentation characteristics, nutritional components, and microbial community composition were determined at each exposure interval.
2.2. Silage Fermentation Characteristics, Nutritional Components and Microbial Community Composition
For analytical measurements, 10 g samples collected at 90 d of ensiling and on days 1, 3, 5 and 7 of aerobic exposure were homogenized with 90 mL of sterile water. The homogenate was filtered through four-layered cheesecloth for pH and ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) determination [32]. Organic acid (lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid) analysis required additional filtration through a 0.22 μm membrane prior to HPLC quantification [33]. Microbial enumeration was followed Pang et al. [34], where serial dilutions (10−1–10−5) were prepared and plated using the spread-plate technique.
Dry matter (DM) content was analyzed by oven-drying 100 g samples at 65 °C for 48 h. Following AOAC guidelines [35], subsequent measurements included water-soluble carbohydrates (WSC), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), acid detergent fiber (ADF) and crude protein (CP) concentrations [28,29].
2.3. Aerobic Stability
Aerobic stability was assessed following the modified protocol of Hu et al. [36]. For each treatment group, 300 g silage samples per bag were transferred into 5 kg plastic containers and maintained under aerobic conditions at ambient temperature (18–22 °C). The temperature was monitored using a data logger positioned at the sample center, with recordings taken at 30 min intervals and subsequently averaged over 2 h periods. To ensure proper aeration while preventing contamination and moisture loss, all samples were covered with sterile double-layered coarse cotton cloth.
2.4. Toxin Contents Determination
The concentrations of major mycotoxins Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), Zearalenone (ZEN) and Fumonisin (FB) were quantified using commercial ELISA kits (Ameko Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) following the manufacturer’s protocols.
2.5. Bacterial and Fungi Community Analyses
Genomic DNA was extracted from 10 g frozen samples by homogenization with 40 mL sterile water, followed by filtration through four-layer sterile cheesecloth. The residue was washed thrice with sterile water to maximize microbial recovery. After centrifugation (12,000× g, 15 min, 4 °C), purified DNA was subjected to PCR amplification. The V4 region amplicons were sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq platform (paired-end) (BGI Genomics Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) with barcode multiplexing. Raw sequences were quality-filtered to discard low-quality reads, and the retained high-quality data were processed into tags via overlap assembly. Tags were clustered into Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) at 97% similarity and taxonomically annotated using a reference database.
Microbial community composition was evaluated at both phylum and genus taxonomic levels through sequence alignment against the Silva database (90% confidence threshold). Alpha diversity metrics, including the Chao1 richness estimator and Shannon diversity index, were computed at the OTU level to assess sample-specific species complexity. Beta diversity patterns were visualized via principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) to illustrate structural variations within bacterial and fungal communities. Additionally, Spearman rank correlation analysis with heatmap visualization was employed to examine potential associations between microbial taxa and fermentation metabolites.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Fermentation characteristics, nutritional components and microbial community composition data were statistically processed using IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Treatment differences were evaluated through Duncan’s multiple range tests, with significance thresholds set at p < 0.05 (significant) and p < 0.01 (highly significant). For correlation analyses between fermentation parameters and microbial community dynamics, paired t-tests were conducted with distinct significance markers: * p < 0.05, and ** p < 0.01.
3. Results
3.1. Properties of Raw Substrates
The initial characteristics of CS and AA prior to fermentation are presented in Table 2. Both materials exhibited pH values above 5.00; AA had NH3-N, lactic acid and acetic acid contents of 0.41, 20.21 and 6.38 g/kg DM, respectively, while none were detected in CS. The LAB counts in both fresh samples were around 5.42 lg cfu/g FM, while unwanted microorganisms totaled 5.07 lg cfu/g FM for almost all samples (except for clostridia in CS). The DM content of AA was 43.62% higher than that of CS; in contrast, CS contained significantly more WSC at 195.69 g/kg DM compared to AA. For fiber components, CS showed values of both NDF at 600.59 g/kg DM and ADF at 573.24 g/kg DM than AA. However, AA demonstrated superior crude protein content at 109.62 g/kg DM relative to CS.

Table 2.
Properties of raw substrates (Mean ± SD, n = 3).
3.2. Silage Fermentation Characteristics, Nutritional Components and Microbial Community Composition
3.2.1. Fermentation Characteristics
Table 3 demonstrates the absence of propionic and butyric acid during both the anaerobic fermentation and aerobic exposure phases. After 90 d of fermentation, the pH value of the LB group was the lowest, being significantly lower than that of the CS, 60% AA and 90% AA groups (p < 0.05). The LB group also exhibited significantly reduced NH3-N levels compared to the 60% and 90% AA groups (p < 0.05). Notably, 30% AA contained elevated concentrations of lactic and acetic acids relative to other treatments, though these differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). As the duration of aerobic exposure increased, both pH and NH3-N showed an increasing trend. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the NH3-N content in the LB treatment group was 0.19 g/kg DM, which was significantly lower than for all AA treatment groups (p < 0.05). Additionally, the 30% AA group had higher lactic acid and acetic acid contents compared to other treatment groups, at 140.91 and 14.52 g/kg DM, respectively, with a significantly lower pH of 3.88 than the other treatment groups (p < 0.05).

Table 3.
Characteristics of fermentation in corn stover silage during both ensiling and aerobic exposure periods.
3.2.2. Nutritional Components
Table 4 displays the dynamic variations in nutritional constituents throughout the 90 d of fermentation and the subsequent aerobic exposure period. Notably, the DM, WSC and CP contents of CS increased with the proportion of AA addition, while the NDF and ADF contents decreased with the increasing addition of AA. In parallel, an extended aerobic duration led to the incremental elevation of DM contents. Following 90 d fermentation and 7 d aerobic exposure, all AA groups exhibited significantly elevated WSC and CP levels compared to the CS controls and LB group (p < 0.05), demonstrating dose-dependent enhancement with increasing AA supplementation. Notably, the WSC and CP contents in CS decreased at the fastest rate during the aerobic exposure phase. Throughout the 90 d of fermentation and subsequent aerobic exposure period, both NDF and ADF contents of each group exhibited progressive declines, with minimum values recorded on d 7 of aerobic exposure; the NDF contents of the AA addition groups demonstrated significantly reduced values compared to both CS and LB groups (p < 0.05), while the ADF content, although not significant, was also lower than that of the CS and LB groups (p > 0.05).

Table 4.
Nutritional components in corn stover silage during both ensiling and aerobic exposure periods.
3.2.3. Microbial Community Composition
Table 5 demonstrates that the 30% AA treatment achieved maximal LAB proliferation at 9.85 lg cfu/g FM by the end of the 90 d fermentation period. During the progressive aerobic exposure, all treatment groups exhibited population growth among coliform bacteria, aerobic bacteria, bacilli, clostridia and yeast. However, after 7 d of aerobic exposure, the 30% AA treatment maintained significantly reduced counts of coliform bacteria, bacilli, clostridia and yeast relative to other groups (p < 0.05). Additionally, the 30% AA group had the highest content of LAB, measuring 7.77 lg cfu/g FM.

Table 5.
Microbial community composition in corn stover silage during both ensiling and aerobic exposure periods (lg cfu/g FM).
3.3. Aerobic Stability Analysis
As shown in Figure 1, when CS was fermented for 90 d, all treatment groups were below ambient temperature. With the extension of aerobic exposure time, the temperature of all treatment groups showed varying degrees of increase. When exposed aerobically for 5 d, the temperature of CS was higher than the ambient temperature, with an aerobic stabilization time of 128 h; when exposed aerobically for 7 d, the temperature of LB was higher than the ambient temperature, with an aerobic stabilization time of 162 h; and the group with AA addition maintained a temperature lower than the ambient temperature throughout the entire aerobic exposure stage.
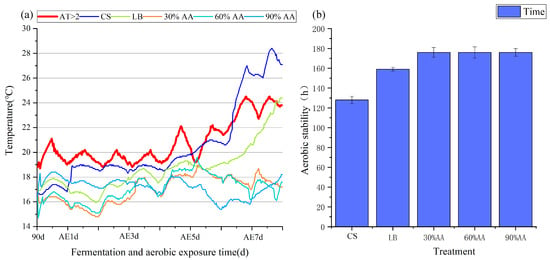
Figure 1.
Changes in temperature (a) and aerobic stability (b) were monitored. AE1 d, AE3 d, AE5 d and AE7 d, aerobic exposure for 1, 3, 5 and 7 days after ensiling 90 days, respectively.
3.4. Toxin Contents
As shown in Table 6, the levels of three types of fungal toxins increase with the extension of aerobic exposure time. After 90 d of fermentation, all treatment groups maintained toxin concentrations compliant with the regulatory thresholds established in the “Feed Hygiene Standards for Fermented Feed Fungal Toxin Content” with the 30% AA group exhibiting non-significantly lower toxin levels than the other treatments. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the levels of AFB1, ZEN and FB in the 30% AA treatment group were still at the lowest levels (p < 0.05), measuring 3.68 μg/kg DM, 0.44 mg/kg DM and 2.67 mg/kg DM, respectively.

Table 6.
Changes in toxin levels during fermentation and aerobic exposure stages.
3.5. Microbial Community Succession from Fresh Forage to Ensiled Product
3.5.1. Analysis of Microbiota Biodiversity
The microbial Alpha diversity indices are presented in Figure 2. Concerning the bacterial community (Figure 2a,b) of the fresh samples, the statistical analysis revealed that the CS samples possessed significantly elevated Chao and Shannon indices in comparison with the AA-treated samples. After 90 d of fermentation, the LB group had the highest Chao index, but all the AA treatment groups exhibited Chao indices at lower levels with no significant differences; the Shannon index of the 30% AA group was the lowest. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the Chao index of the 90% AA group was significantly lower than that of the other treatment groups, with the LB group having the lowest Shannon index followed by the 30% AA group. Concerning the fungal community (Figure 2c,d) in fresh samples, the Chao and Shannon indices of AA were higher than those of the CS group. After 90 d of fermentation, the Chao index was highest for the 90% AA group and the Shannon index was lowest for the 30% AA group. On the 7th d of aerobic exposure, the Shannon index was lowest for the 30% AA and highest for the LB group.
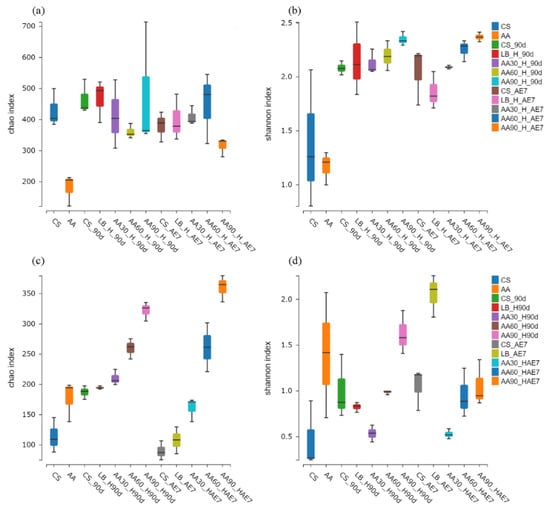
Figure 2.
Bacterial (a,b) and fungal (c,d) community alpha diversity dynamics were monitored across the ensiling period and following aerobic exposure stage. AE7 d, aerobic exposure for 7 days after ensiling 90 days.
The results of the PCoA analysis at the OTU level are presented in Figure 3. Concerning the bacterial community (Figure 3a), before fermentation, there was a considerable distance between the CS and AA groups in the fresh samples, indicating a significant difference in bacterial community structure. After 90 d of fermentation, the distance between the CS and LB groups was smaller, suggesting a higher level of similarity in microbial composition. The 30% AA had a greater distance from all other treatment groups, indicating substantial differences in microbial species. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the distance between all AA treatment groups was smaller, demonstrating a convergence in bacterial community structure at a notable distance from the CS and LB treatment groups. Concerning the fungal community (Figure 3b), there was a smaller distance between the CS and AA groups in the fresh samples, indicating a higher level of similarity in fungal community structure. By the 90 d of fermentation, the distance between all the treatment groups was smaller, suggesting a similar fungal community structure. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the groups with AA addition were at a greater distance from the CS and LB groups, indicating a significant difference in their fungal community structure.
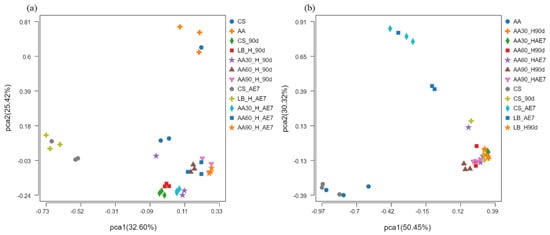
Figure 3.
Bacterial (a) and fungal (b) community β–diversity analyzed via PCoA at OTU level across ensiling and aerobic exposure phases. AE7 d, aerobic exposure for 7 days after ensiling 90 days.
3.5.2. Microbial Community Abundance
The microbial phylum distribution depicted in Figure 4a. In the fresh samples, before fermentation, both the CS and AA groups were dominated by Proteobacteria. After 90 d of fermentation, all experimental groups demonstrated elevated Firmicutes prevalence, with the highest relative abundance found in the 90% AA group (40.23%), followed by the 30% AA group with a relative abundance of 37.56%. Over time and with increasing aerobic exposure, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria increased in the CS and LB groups, becoming the dominant microbes. The relative abundance of Firmicutes in all AA treatment groups increased compared to the 90 d of fermentation, with the 30% AA group having the highest relative abundance of Firmicutes, at 48.52%, among all the treatment groups.
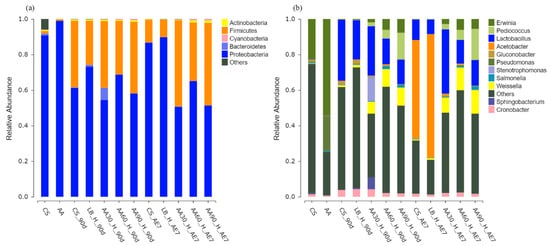
Figure 4.
Bacterial community composition at phylum (a) and genus (b) taxonomic levels. AA30, AA60 and AA90, corn stover mixed with 30%, 60% and 90% Artemisia argyi, respectively; AE7 d, aerobic exposure for 7 days after ensiling 90 days.
Figure 4b displays the bacterial taxonomic distribution at the genus level. Erwinia was the dominant microorganism in the fresh samples of the CS and AA groups, while Pseudomonas also had a relatively high abundance in the fresh sample AA groups. Following the 90 d fermentation period, Lactobacillus became the predominant microorganism in the LB and CS groups. All AA-treated groups were dominated by Lactobacillus, Pediococcus and Weissella. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the CS and LB groups displayed marked reductions in Lactobacillus populations accompanied by an increase in Acetobacter to the dominant prevalence. In the 30% AA group, the proportion of Lactobacillus was the highest at 36.14%, demonstrating a statistically significant superiority compared to all other treatment groups (p < 0.05).
Figure 5a illustrates the fungal phylum levels, showing that the dominant microorganisms in the fresh samples of the CS and AA groups were Basidiomycota. After 90 d of fermentation, the relative abundance of Ascomycota increased in all treatment groups, although the relative abundance of Basidiomycota in the 90% AA group was significantly higher than in all other treatment groups (p < 0.05). Following 7 d of aerobic exposure, the relative abundance of Ascomycota in all treatment groups showed a non-significant increase.
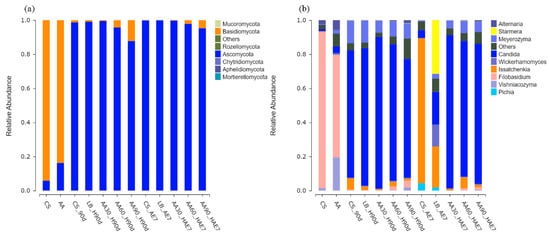
Figure 5.
Fungal community composition at phylum (a) and genus (b) taxonomic levels. AE7 d, aerobic exposure for 7 days after ensiling 90 days.
The genus-level fungal distributions are shown in Figure 5a. The main microorganism in the fresh samples of the CS and AA groups was Filobasidium. After 90 d of fermentation, all treatment groups were dominated by the genus Candida, with the highest relative abundance found in the 30% AA group. With prolonged aerobic exposure, the relative abundance of Issatchenkia in the CS and LB groups increased, becoming the dominant genus in the CS group, and an increase in the relative abundance of Pichia was also observed. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the primary microorganism in the AA-treated group remained Candida, with the highest relative abundance of Candida found in the 30% AA group, specifically.
3.5.3. Genus Level Microbial Associations with Fermentation Dynamics
At the bacterial genus level (Figure 6a), significant inverse relationships were observed between Lactobacillus and Weissella abundance and pH (p < 0.01), while these genera demonstrated positive associations with lactic acid and acetic acid concentrations (p < 0.01). Notably, both genera exhibited significant negative correlations with AFB1, ZEN and FB levels (p < 0.01). Stenotrophomonas exhibited a negative correlation with pH (p < 0.05), a non-significant positive correlation with acetic acid and a non-significant negative correlation with AFB1, ZEN and FB. The genus Acetobacter exhibited a non-significant positive correlation with pH and acetic acid.
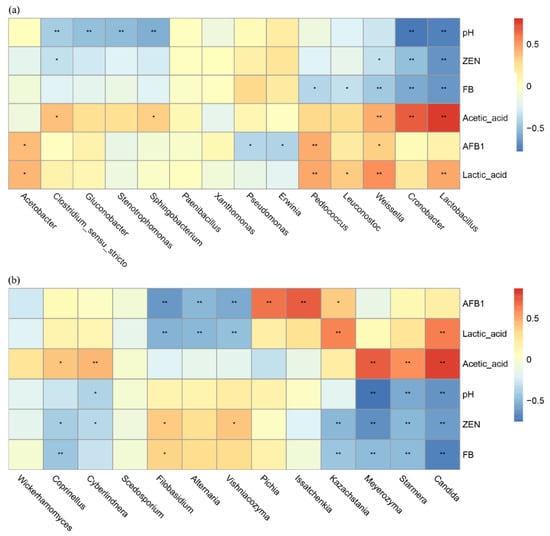
Figure 6.
Genus level microbial associations with fermentation dynamics: bacteria (a) and fungi (b). Positive correlations are shown in red, and negative correlations are shown in blue. * means p < 0.05 and ** means p < 0.01.
For fungi at the taxonomic level (Figure 6b), Candida demonstrated an inverse relationship with pH (p < 0.01) while exhibiting positive associations with both lactic and acetic acid production (p < 0.01). This genus negatively correlated with ZEN and FB (p < 0.01). Issatchenkia populations displayed a modest pH-independent increase (non-significant) along with a strong positive response to AFB1 presence (p < 0.01), but a non-significant negative correlation with acetic acid. Pichia abundance was strongly influenced by AFB1 levels (p < 0.01) and exhibited weakly positive, though statistically insignificant, co-occurrence patterns with both ZEN and FB.
3.6. Bacterial of Functional Prediction on KEGG
As shown in Figure 7, in the functional annotation of KEGG level 1 (a), all treatment groups during the ensiling and aerobic exposure stages had the highest relative abundance annotated to metabolic functions. In the functional annotation of KEGG level 2 (b), for the metabolic pathway of cofactors and vitamins, the relative abundance for the fresh materials in the CS and AA groups in fresh materials was approximately 12.09% each. After 90 d of fermentation, this relative abundance decreases in all treatment groups. With an increasing amount of aerobic exposure time, both the CS and LB groups showed an increasing trend in relative abundance, reaching 12.81% and 13.99%, respectively, while the 30% AA group had the lowest relative abundance (10.69%). Regarding lipid metabolism, the relative abundance in the CS and LB groups was 5.03% and 5.11%, respectively. After 90 d of fermentation, the relative abundance increased in all treatment groups, with 30% AA having the highest relative abundance (8.18%). After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the relative abundance decreased for CS (5.98%) and LB (5%), while 30% AA still had the highest relative abundance (8.12%). Regarding the carbohydrate metabolism pathway, during the 90 d of fermentation, the relative abundance for all the treatment groups was higher than that for the fresh samples. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the relative abundance decreased for the CS and LB groups, and there was no significant difference in relative abundance for the AA groups compared to the abundance following the 90 d fermentation stage.
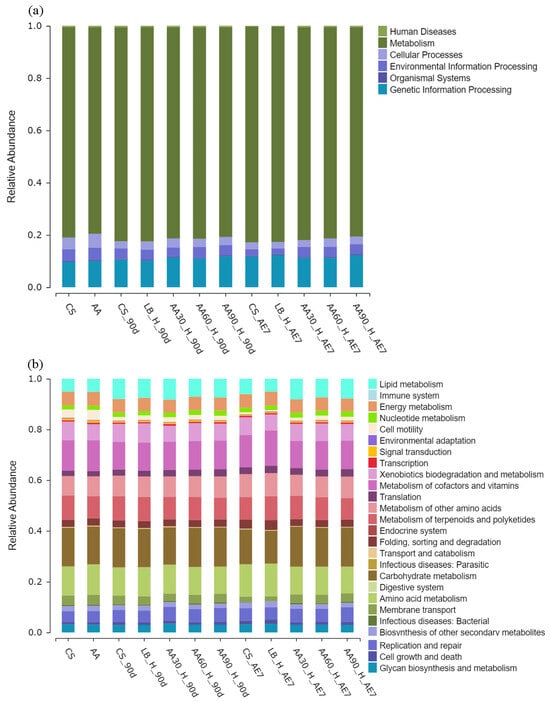
Figure 7.
Bacterial of functional prediction on KEGG level 1 (a) and level 2 (b).
4. Discussion
Actively promoting the use of CS as feed represents an efficacious approach to enhancing the efficiency of the comprehensive utilization efficiency of CS. The utilization of CS as feed is not only limited by the conditions of the stover itself; generally, fermentation efficiency is predominantly determined by the physicochemical properties of the substrate and the metabolic activity of the autochthonous microbial consortium. In the present investigation, the DM content of fresh samples of CS and AA was 32.66% and 47.87%, respectively, with CS falling within the optimal DM range (30–35%) for high-quality silage production [37]. The WSC content of fresh samples of CS and AA totaled 195.69 g/kg DM and 127.58 g/kg DM, respectively. The high WSC content in CS is sufficient for supporting the growth of LAB and other microorganisms [38,39]. A microbial analysis revealed LAB counts exceeded 5.42 log cfu/g FM in both materials, thereby meeting the minimum requirement for lactic acid fermentation [40]. However, the simultaneous presence of substantial coliform bacteria, aerobic bacteria and mycotoxins (with zearalenone levels exceeding the limits specified in China’s Feed Hygiene Standard GB 13078-2017) [41] poses significant preservation challenges. Therefore, the application of additives is crucial for effectively inhibiting the proliferation of harmful microorganisms, reducing mycotoxin contamination, enhancing fermentation efficiency, optimizing silage quality parameters and preventing post-fermentation aerobic deterioration.
During anaerobic fermentation, LAB metabolizes WSC to produce lactic acid, resulting in decreased pH levels that effectively suppressed the proliferation of undesirable microorganisms. Therefore, silage pH serves as a critical parameter for assessing silage quality, which can reflect the degree of feed fermentation [42]. When the pH of the feed is less than 4.2, it can provide an acidic environment for the beneficial fermentation of bacteria such as lactic acid bacteria, suppress the proliferation and reproduction of adverse microbial populations, promote fermentation and increase the content of lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, etc., and also extend the feed’s shelf life. After 90 d of fermentation, the pH of all treatment groups was below 4.00, while the lactic acid content was above 63.00 g/kg DM. Recent studies have indicated that butyric acid can serve as one of the criteria for evaluating silage fermentation quality, with butyric acid content of >0.3% DM leading to an 11–15% decrease in dry matter intake (DMI) in ruminants [43]. During the present investigation, no butyric acid was detected. This suggests that ensiling CS agricultural waste with the addition of AA can effectively promote lactic acid fermentation within CS while enhancing the resource utilization efficiency of agricultural waste. With prolonged aerobic exposure, all treatment groups exhibited distinct characteristics of quality deterioration: both the pH and NH3-N contents increased significantly, while lactic acid and acetic acid contents decreased markedly. These changes primarily stem from the following two interrelated biological processes: First, aerobic microorganisms (predominantly yeasts and molds) proliferate rapidly upon air exposure, generating substantial metabolic heat through the decomposition of substrates including WSC, organic acids and proteins, which not only accelerates the volatilization of organic acids but also disrupts the acid-base balance of the system [44,45]. Second, the sharp rise in NH3-N content indicates significant protein degradation, which according to previous studies [34], is mainly caused by the deamination activity of Clostridium and the amino acid metabolism induced by coliform bacteria [46]. These findings provide important insights into the microbiological mechanisms underlying post-opening quality changes in silage.
After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the 30% AA group displayed optimal fermentation characteristics, namely the lowest pH value (3.88) coupled with high levels of lactic acid and acetic acid (totaling 140.91 and 14.92 g/kg DM, respectively). This protective effect likely stems from various active components in AA (such as essential oils and flavonoids [21,22,23]), which, through their antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, effectively inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms such as coliform bacteria, aerobic bacteria, bacilli, clostridia and yeasts during aerobic exposure, thereby reducing nutrient loss [24,25,26,27,33,34]. Furthermore, Chinese herbal medicine has long been applied as a feed additive in animal husbandry production, playing a significant role in livestock and poultry health, promoting growth and development and improving reproductive ability [47]. The results of this study demonstrate that the addition of AA significantly improved both the fermentation quality and nutritional value of silage. With increasing AA supplementation levels, the CP content exhibited a significant increase (p < 0.05), which was primarily attributed to the inherently high initial CP content (109.62 g/kg DM) of AA as a raw material. Concurrently, the NH3-N content exhibited a dose-dependent increasing trend, which was consistent with findings reported by Pang et al. [48]. After 90 d of fermentation, the DM content of the 30% AA group reached the standard required for high-quality silage (25–35%), with DM preservation rates increasing proportionally with levels of AA addition, which aligned with results from Wang et al. [28,29,30]. Furthermore, AA supplementation significantly reduced the ADF and NDF content in the feed (p < 0.05), which may have a significant effect on improving animal feed intake and digestibility [49].
Temperature serves as a crucial indicator for evaluating silage aerobic stability, with a 2 °C increase above ambient temperature signaling the onset of aerobic deterioration [50]. Aerobic stability, defined as the duration (in hours) that silage maintains stability upon air exposure [51], is compromised when oxygen triggers mold and yeast proliferation. These microorganisms generate substantial metabolic heat through nutrient utilization, accelerating silage spoilage [13]. While chemical additives like pyroligneous acid have been shown to enhance Napier grass’s silage stability to 76 h [52], this study revealed significant improvements over 90 d of fermentation when the CS was supplemented with AA. The control CS group and the LB treatment groups demonstrated stability periods of 128 h and 162 h, respectively, whereas all the AA-treated groups maintained stability for over 7 d (168 h). These results demonstrate that AA not only significantly enhances silage aerobic stability but also offers superior safety as a natural feed additive compared to conventional chemical treatments.
Environmental factors (e.g., temperature and pH) and physiological conditions can affect the synthesis of fungal toxins [52]. Mold can grow and proliferate between 10 and 40 °C and at pH values between 4.0 and 8.0 [53,54]. Therefore, favorable ensiling conditions are important for reducing fungal toxin production. Fusarium ear rot is one of the most common diseases seen in corn plants, and ZEN and FB are commonly found in corn and its by-products [55]. Silages containing ZEN and FB can result in adverse effects for ruminants, including infertility, reduced milk production, excessive estrogen levels and mild liver disease [56]. After 90 d of ensiling, the contents of ZEN and FB in all the treatment groups decreased, with the lowest content found in the 30% AA group; the AFB1 content was also the lowest in the 30% AA group. This may be because the low pH and anaerobic conditions inhibited the growth of Fusarium [56]. With the increasing duration of aerobic exposure, the content of fungal toxins (AFB1, ZEN, FB) in all treatment groups increased, as oxidative stress often induces the toxin production of various fungi [57]. Thus, the growth of yeast and mold is accompanied by the production of fungal toxins, leading to the aerobic deterioration of the silage during the aerobic exposure process. By the 7th d of aerobic exposure, the content of the three fungal toxins was still the lowest in the 30% AA group. One explanation for this phenomenon is that, while maintaining a lower pH, AA promotes the release and transformation of its active components after fermentation, enhances the biological utilization of herbs and improves the nutritional value and functionality of herbs [58]. Through extensive research on AA, it has been found that as a feed additive, AA effectively lowers pH, increases the content of lactic acid and acetic acid, improves aerobic stability and significantly reduces levels of mycotoxins (AFB1, DON, ZEN, OA, and FB) [28,29,30]. Studies have also shown that AA can regulate gastrointestinal microbiota and enhance meat growth performance and stability; replacing stover with AA in the diet of sheep can significantly increase their intake, rumen fermentation and internal digestion rates [59].
Alpha diversity reflects the microbial abundance (Chao index) and species diversity (Shannon index) of a single sample, while beta diversity elucidates the differences in microbial communities within silage [60]. Regarding the fresh samples, the Alpha diversity of CS was higher than that of AA. This may be because CS has a higher moisture content (64.79%) and contains nutrients suitable for microbial growth [42]. After 90 d of fermentation, the Chao index of bacteria in all the AA treatment groups was at a relatively low level, possibly due to anaerobic and acidic conditions inhibiting microbial growth. The Shannon index of the 30% AA group was the lowest, indicating its low species diversity. Polley et al. [61] have reported that microbial community diversity is lower when dominant bacteria are abundant. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the Shannon index of the LB group was the lowest, possibly due to the dominance of Acetobacter. At the fungal level, in fresh samples, both the Chao and Shannon indices of AA were higher than in CS, indicating the existence of a rich fungal community within AA. Both after 90 d of fermentation and 7 d of aerobic exposure, the lowest Shannon index values were exhibited by the 30% AA group, because Candida was the dominant fungus with the highest relative abundance. Regarding Beta diversity, both for bacteria and fungi, the microbial community structure of all the AA groups was similar after 90 d of fermentation and 7 d of aerobic exposure, indicating that there were similar mechanisms at play. Fluctuations in microbial communities may explain the differences in silage quality [29]. However, there were significant differences in microbial community structure between the CS and AA groups after 90 d of fermentation and 7 d of aerobic exposure, indicating poor aerobic stability.
Fresh CS and AA were both annotated with Proteobacteria at the bacterial phylum level, which has been proven to contain a large category of pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella enteritidis, Vibrio cholerae, Helicobacter pylori and many other well-known species [62,63]. After 90 d of fermentation, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria decreased in all treatment groups, while the relative abundance of Firmicutes increased. Many well-known probiotics come from Firmicutes, such as Lactobacillus, Faecalibacterium and Roseburia [64]. Over the 7 d of aerobic exposure, the relative abundance of Firmicutes decreased in the CS and LB groups, while the relative abundance of Proteobacteria increased. This may be due to the poor aerobic stability of CS and AA-treated silage after exposure to air, leading to the increased growth of aerobic microorganisms. In this study, the Firmicutes in the AA addition group still maintained a high relative abundance, with the highest relative abundance found in the 30% AA group, specifically. This may be because the acidic environment and active substances present in AA, such as essential oils and flavonoids, inhibited the growth of aerobic microorganisms. This corresponds to the lower pH (3.88), higher lactic acid content (140.91 g/kg DM) and acetic acid content (14.52 g/kg DM), and lower count of spoilage microorganisms found in the 30% AA group.
At the bacterial genus level, after 90 d of fermentation, all treatment groups were mainly dominated by Lactobacillus, with the AA addition group also containing Pediococcus and Weissella, which are beneficial probiotics for gut health, indicating good fermentation quality. With a prolonged duration of aerobic exposure, the relative abundance of Lactobacillus decreased in the CS and LB groups, while Acetobacter became the main microorganism in both groups. Acetobacter is a facultative aerobic bacterium that easily causes the aerobic deterioration of silage [65]. After 7 d of aerobic exposure, the relative abundance of Lactobacillus was highest in the 30% AA group, which was positively correlated with the lowest pH and highest lactic acid content, indicating better fermentation quality. Research has shown that adding AA to feed is positively correlated with total flavonoids in AA and the relative abundance of Lactobacillus and Weissella genera [28], suggesting that adding AA to feed can not only inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms but also increase the relative abundance of Lactobacillus and Weissella genera.
Regarding the fungal communities of the fresh samples before fermentation, both CS and AA were dominated by the phylum Basidiomycota. After 90 d of fermentation, the dominant phylum in all treatment groups was found to be Ascomycota. Studies have shown that Ascomycota has a high relative abundance in silage feed, followed by Basidiomycota [66,67]. During aerobic exposure, the relative abundance of Basidiomycota increased with the addition of AA but decreases compared to the relative abundance at 90 d of fermentation. This indicates that the addition of AA affects the fungal community structure of silage feed; this is also consistent with the results of the PCoA analysis, which showed larger differences in community composition between the AA groups and the CS and LB groups. At the genus level, after 90 d of fermentation, the dominant genus in all treatment groups was Candida. Research has found that after establishing anaerobic conditions in silage feed, the microbial community in yeast is mainly composed of fermentative species belonging to the genus Candida and the genus Pichia [68]. During aerobic exposure, the main microorganisms in CS and LB transition from Candida to Issatchenkia, with CS having the highest relative abundance. This indicates that CS and LB have poor aerobic stability, with an active fungal community. Studies have shown that Issatchenkia is considered the most significant fungus associated with the aerobic deterioration of silage [66]. In the correlation analysis, Issatchenkia exhibited a highly significant positive correlation with AFB1 (p < 0.01) and a non-significant positive correlation with pH. This further illustrates that Issatchenkia disrupts the aerobic stability of silage feed, causing an increase in pH and thereby leading to aerobic deterioration and the production of AFB1, which poses a significant threat to the livestock industry.
When exposed to aerobic conditions for 7 d, the dominant genus in the AA-added group was still Candida. Candida is a controversial fungus. Research has shown that as a lactic acid-assimilating yeast, it easily degrades lactic acid into CO2 and H2O within silage feed, generating heat and causing the aerobic deterioration of the silage [68,69]. Of particular note, the findings of this study demonstrated that, following the supplementation of 30% AA, although the relative abundance of Candida was the highest, this treatment group exhibited optimal fermentation characteristics: it maintained the lowest pH level (3.88) while showing significantly higher lactic acid (140.91 g/kg DM) and acetic acid (14.52 g/kg DM) contents than the other treatment groups (p < 0.05). This seemingly paradoxical phenomenon suggests that Candida may exhibit metabolic properties under AA-specific conditions that differ from our conventional understanding. Furthermore, in the correlation analysis, Candida exhibited a negative correlation with pH (p < 0.01) and a positive correlation with lactic acid and acetic acid (p < 0.01), as well as a negative correlation with ZEN and FB (p < 0.01). These results are similar to those of Chen et al. [70] and Pang et al. [48]. Under acidic conditions (pH < 4.5), yeast cells undergo autolysis and release essential nutrients including B vitamins (e.g., B12, thiamine and riboflavin), amino acids and nucleotides that promote LAB growth [71]. This metabolic cross-feeding explains the observed symbiotic relationship between Candida and Lactobacillus, which maintained co-dominant status during the 7 d of aerobic exposure in this study. Candida and Lactobacillus have proven to be beneficial in improving food flavor, promoting acid production and enhancing quality [72,73,74]. Candida utilis has been listed as an intentional additive in silage [75]. Our finding that Candida may positively influence fermentation quality and potentially exhibit synergistic effects with Lactobacillus could represent a key contribution to silage fermentation research. Therefore, the mechanism of Candida’s impact on the quality and aerobic stability of silage requires further in-depth research. During 7 d of aerobic exposure, Pichia appeared in both the CS and LB groups, with the highest relative abundance found in the CS group. Pichia also showed a highly significant positive correlation with AFB1 (p < 0.01) and a non-significant positive correlation with ZEN and FB. However, Pichia was not found in any of the AA addition groups. This indicates that the addition of AA can effectively inhibit the growth of Pichia and reduce the production of fungal toxins.
Next-generation sequencing serves as a robust analytical platform that enables both the assessment of microbial community composition/diversity and the prediction of metabolic capabilities, offering essential data for functional microbiome characterization [76]. In this study, regarding the predicted bacterial community KEGG functions, carbohydrate metabolism, cofactor and vitamin metabolism and lipid metabolism were the main metabolic pathways for silage metabolism, similarly to the results of Wang et al. [77]. Fermentation for 90 d resulted in higher relative abundances of carbohydrate metabolism and lipid metabolism in all treatment groups than in the fresh samples. Studies have shown that the relative abundance of total LAB in the microbial community affects the abundance of carbohydrate metabolism pathways [78]. In the present investigation, an increase in the relative abundance of Lactobacillus was observed in silage with a high abundance of the carbohydrate metabolism pathway. Under anaerobic fermentation conditions, lipids in silage may be degraded by Lactobacillus into metabolites such as fatty acids and glycerol, leading to an increase in the relative abundance of the lipid metabolism pathway [79]. As the aerobic exposure time increases, the relative abundances of the carbohydrate metabolism and lipid metabolism pathways in the CS and LB groups decrease, while remaining at higher levels in the AA-treated groups. This may be due to the significant growth and reproduction of Acetobacter induced after silage is exposed to air, leading to a decrease in the relative abundance of Lactobacillus. Similar observations were reported in the study by Zhao et al. [80]. After 90 d of fermentation, the relative abundance of the cofactors and vitamins metabolism pathway was lower than in fresh samples, but it was upregulated during aerobic exposure. It is difficult to explain this phenomenon, and similar results have been reported in other studies [77,81,82]. Therefore, some believe that using specific LAB inoculants can upregulate the metabolism of cofactors and vitamins in Napier grass silage [77]. In conclusion, both carbohydrate metabolism and lipid metabolism can reflect the impact of AA addition on the quality and aerobic stability of silage feed.
5. Conclusions
This study provides innovative approaches for the value-added utilization of corn stover, an agricultural waste product. Specifically, the respective additions of LB and of 30% Artemisia argyi mixed to CS for ensiling enhanced the silage quality by increasing the lactic acid content, reducing the pH value, inhibiting unwanted microorganisms, lowering the NH3-N and mycotoxin content, improving the aerobic stability and maintaining a relatively high abundance of Lactobacillus. The optimized silage technology not only provides a sustainable management solution for agricultural waste by converting corn stover into high-value-added feed but also promotes environmentally friendly agricultural production practices.
Author Contributions
Designed experiments, P.Z., H.P. and L.W.; carried out experiments, P.Z.; analyzed experimental results, P.Z., G.W., X.L., Y.M., K.G., S.Z. and Z.T.; wrote and edited the manuscript, P.Z. and H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Qinghai Province Key R&D and Transformation Plan of China (Grant no. 2023-NK-141) and Independent Selection of Basic Research Business Expenses, Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine (No. 2024-MKY-P01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dai, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; et al. Utilizations of agricultural waste as adsorbent for the removal of contaminants: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Zheng, T.; Wang, P.; Hao, L.; Wang, Y. Fast microwave-assisted preparation of a low-cost and recyclable carboxyl modified lignocellulose-biomass jute fiber for enhanced heavy metal removal from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Begho, T. Crop residue burning in South Asia: A review of the scale, effect, and solutions with a focus on reducing reactive nitrogen losses. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Niu, Y.; Mukherjee, S.; Abou-Elwafa, S.F.; Nguyen, N.S.H.; Al Aboud, N.M.; Wang, Y.; Pu, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A comprehensive review on agricultural waste utilization through sustainable conversion techniques, with a focus on the additives effect on the fate of phosphorus and toxic elements during composting process. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 942, 173567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Yakoob, M.; Shah, M.P. Agricultural waste management strategies for environmental sustainability. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yu, P.; Xu, X. Straw utilization in China-status and recommendations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses on fermentation dynamics, structural and nonstructural carbohydrate composition and in vitro ruminal fermentation of rice straw silage. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, H.; Yan, K. Selective production of phenol-rich bio-oil from corn straw waste by direct microwave pyrolysis without extra catalyst. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 700887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.; Dong, H.; Yin, F. Improving production of lactic acid and volatile fatty acids from dairy cattle manure and corn straw silage: Effects of mixing ratios and temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Hong, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, J. Lactic acid bacteria strains selected from fermented total mixed rations improve ensiling and in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics of corn stover silage. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Shao, T. Silage fermentation characteristics of Napiergrass harvested at various times on a sunny day. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Xing, Y.; Pian, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Improving the quality of rice straw silage with Moringa oleifera leaves and propionic acid: Fermentation, nutrition, aerobic stability and microbial communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 299, 122579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Yin, X.; Zhang, J. Changes of the fermentation quality and microbial community during re-ensiling of sweet corn stalk silage. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 21, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Jara, D.; Rivera-Gomis, J.; Tornel, J.A.; Jordán, M.J.; Martínez-Conesa, C.; Pablo, M.J.C. Oregano essential oil and purple garlic powder effects on intestinal health, microbiota indicators and antimicrobial resistance as feed additives in weaning piglets. Animals 2023, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laugalis, J.; Jatkauskas, J.; Vrotniakiene, V.; Zelvyte, R.; Makauskas, S. Effect of inoculation on silage quality and rumen fermentation in dairy cows. Med. Weter. 2007, 63, 1057–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Filya, I.; Muck, R.E.; Contreras-Govea, F.E. Inoculant effects on alfalfa silage: Fermentation products and nutritive value. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 5108–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, J. Fermentation profile, aerobic stability, and microbial community dynamics of corn straw en-siled with Lactobacillus buchneri PC-C1 and Lactobacillus plantarum PC1-1. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 270, 127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zou, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, N.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W. Effects of pyroligneous acid on diversity and dynamics of antibiotic resistance genes in alfalfa silage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0155422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Bi, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, D. Chemical constituents and biological activities of Artemisia argyi H. Lév. Vaniot. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Tu, P.; Zeng, W. Sesquiterpene lactone from Artemisia argyi induces gastric carcinoma cell apoptosis via activating NADPH oxidase/ reactive oxygen species/mitochondrial pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 837, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Liao, M.; Hu, R.; Deng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y. Artemisia argyi water extract promotes selenium uptake of peach seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1014454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Shi, B.; Sun, D.; Chen, H.; Tong, M.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X.; Yan, S. Effects of dietary supplementation of Artemisia argyi aqueous extract on antioxidant indexes of small intestine in broilers. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Kim, C.E.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.O.; Hiep, N.T.; Lee, D.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kang, K. Protective effect of Artemisia argyi and its flavonoid constituents against contrast-induced cytotoxicity by iodixanol in LLC-PK1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lu, S.; Du, H.; Cao, Y. Antioxidant capacity of flavonoids from Folium Artemisiae argyi and the molecular mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, F.; Peng, S.; Ou, Y.; He, B.; Li, Y.; Lin, Q. Effects of Artemisia argyi powder on egg quality, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal development of roman laying hens. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 902568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yao, Q.; OuYang, X.; Yao, L.; Yajie, L.; Chang, H.; Rui, H.; Xin, H.; Hao, W.; Rui, Z.; et al. The mechanism study of moxa combustion products on regulating vascular endothelial function in atherosclerotic mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 1303978. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Tan, Z.; Gu, L.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Variation of microbial community and fermentation quality in corn silage treated with lactic acid bacteria and Artemisia argyi during aerobic exposure. Toxins 2022, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, Z.; Wu, G.; Wang, L.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of whole-crop wheat silage treated by lactic acid bacteria and Artemisia argyi during ensiling and aerobic exposure. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1004495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, Z.; Wu, G.; Wang, L.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Investigation on fermentation characteristics and microbial communities of wheat straw silage with different proportion Artemisia argyi. Toxins 2023, 15, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Son, Y.J.; Ha, I.J.; Erdenebileg, S.; Jung, D.S.; Song, D.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.M.; Nho, C.W. Artemisia argyi extract alleviates inflammation in a DSS-induced colitis mouse model and enhances immunomodulatory effects in lymphoid tissues. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effects of wilting and Lactobacillus plantarum addition on the fermentation quality and microbial community of Moringa oleifera leaf silage. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Qin, G.; Tan, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Natural populations of lactic acid bacteria associated with silage fermentation as determined by phenotype, 16S ribosomal RNA and recA gene analysis. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Official Methods of Analysis; AOAC: Rockville, ML, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Schmidt, R.J.; McDonell, E.E.; Klingerman, C.M.; Kung, L., Jr. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 or Lactobacillus plantarum MTD-1 on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silages ensiled at two dry matter contents. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyader, J.; Baron, V.; Beauchemin, K. Corn forage yield and quality for silage in short growing season areas of the canadian prairies. Agronomy 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, E.; Chouinard, P.Y.; Allard, G.; Lapierre, H.; Pellerin, D. Milk from forage as affected by carbohydrate source and degradability with alfalfa silage-based diets. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigh, P.M.; Parker, J.W.G. Effect of silage additives and wilting on silage fermentation, digestibility and intake, and on liveweight change of young cattle. Grass Forage Sci. 2010, 40, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R. Inoculation of Silage and Its Effects on Silage Quality; US Dairy Forage Res Center: Madison, WI, USA, 1996.
- GB 13078-2017; Hygienical standard for feeds. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (AQSIQ), Standardization Administration of China (SAC), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonka, B.N.; Tao, S.; Dahl, G.E.; Spurlock, D.M. Genetic regulation of prepartum dry matter intake in Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 8195–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.C.; Cunha, C.S.; Fernandes, J.O. Prevalent mycotoxins in animal feed: Occurrence and analytical methods. Toxins 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.H.; Swanepoel, N.; Heguy, J.M.; Price, T.; Meyer, D.M. Shrink losses in commercially sized corn silage piles: Quantifying total losses and where they occur. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542 PtA, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Zhou, P.; Yue, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Cai, Y. Fermentation characteristics, chemical composition, and aerobic stability in whole crop corn silage treated with lactic acid bacteria or Artemisia argyi. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tan, Z.; Gu, L.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Dynamics changes of microorganisms community and fermentation quality in soybean meal prepared with lactic acid bacteria and Artemisia argyi through fermentation and aerobic exposure processes. Foods 2022, 11, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Choe, K.; Yoo, H.H. Review on a traditional herbal medicine, eurycoma longifolia jack (Tongkat Ali): Its traditional uses, chemistry, evidence-based pharmacology and toxicology. Molecules 2016, 21, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Sun, X.; Kong, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Cao, Z.; Li, S. Comparison of ruminal degradability, indigestible neutral detergent fiber, and total-tract digestibility of three main crop straws with Alfalfa hay and corn silage. Animals 2021, 11, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Fang, X.; Feng, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Silage fermentation, bacterial community, and aerobic stability of total mixed ration containing wet corn gluten feed and corn stover prepared with different additives. Animals 2022, 10, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Renaud, J.; Apper, E. Microbiota succession during aerobic stability of maize silage inoculated with Lentilactobacillus buchneri NCIMB 40788 and Lentilactobacillus hilgardii CNCM-I-4785. Microbiol. Open 2021, 10, e1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qu, H.; Bai, S.; Yan, L.; You, M.; Gou, W.; Li, P.; Gao, F. Effect of wet sea buckthorn pomace utilized as an additive on silage fermentation profile and bacterial community composition of alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlow, L.W.; Hagler, W.M. Mycotoxins in Dairy Cattle: Occurrence, Toxicity, Prevention and Treatment. 2005. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=747bd5debc896a5cc6c7f9db722f507f&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Magan, N.; Aldred, D. Post-harvest control strategies: Minimizing mycotoxins in the food chain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gxasheka, M.; Wang, J.; Tyasi, T.L.; Gao, J. Scientific understanding and effects on ear rot diseases in maize production: A review. Int. J. Soil Crop Sci. 2015, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Martinez-Tuppia, C.; Queiroz, O.C.M.; Jiang, Y.; Drouin, P.; Wu, F.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Mycotoxins in silage: Occurrence, effects, prevention, and mitigation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverberi, M.; Ricelli, A.; Zjalic, S.; Fabbri, A.A.; Fanelli, C. Natural functions of mycotoxins and control of their biosynthesis in fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Qu, C.; Dong, X.; Shen, M.R.; Ni, J. Preparation regularity of Chinese patent medicine in Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2022, 47, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.S.; Jin, S.K.; Kang, S. Effects of feeding mugwort powder on meat composition and sensory characteristics in gilt. Hangug Chugsan Sigpum Haghoeji = Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2009, 29, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Shao, T.; Tao, X.; Yuan, X. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality and mycotoxins concentrations of corn silage infested with mycotoxigenic fungi. Toxins 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, H.W.; Wilsey, B.J.; Derner, J.D. Dominant species constrain effects of species diversity on temporal variability in biomass production of tallgrass prairie. Oikos 2007, 116, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzatti, G.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Gibiino, G.; Binda, C.; Gasbarrini, A. Proteobacteria: A common factor in human diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9351507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Sichel, S.R.; Salama, N.R. Bent bacteria: A comparison of cell shape mechanisms in proteobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 457–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Nie, Q.; He, H.; Tan, H.; Geng, F.; Ji, H.; Hu, J.; Nie, S. Gut firmicutes: Relationship with dietary fiber and role in host homeostasis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 12073–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, M.; Yin, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Hao, J. Characterization of mycotoxins and microbial community in whole-plant corn ensiled in different silo types during aerobic exposure. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1136022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Gu, Q.; Liang, M.; Mu, S.; Zhou, B.; Huang, F.; Lin, B.; Zou, C. Analysis of the correlation between bacteria and fungi in sugarcane tops silage prior to and after aerobic exposure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Oude Elferink, S.J.W.H.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. Silage Sci. Technol. 2003, 42, 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Xu, D.; Xie, D.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Effects of antibacterial peptide-producing Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus buchneri on fermentation, aerobic stability, and microbial community of alfalfa silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W. Improving the quality of Napier grass silage with pyroligneous acid: Fermentation, aerobic stability, and microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1034198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyirifo, D.S.; Wamalwa, M.; Otwe, E.P.; Galyuon, I.; Runo, S.; Takrama, J.; Ngeranwa, J. Metagenomics analysis of cocoa bean fermentation microbiome identifying species diversity and putative functional capabilities. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Q. Influence of Lactobacillus/Candida fermentation on the starch structure of rice and the related noodle features. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewara, O.A.; Ogunbanwo, S.T. Acid stress responses of Lactobacillus amylovorus and Candida kefyr isolated from fermented sorghum gruel and their application in food fermentation. Can. J. Microbiol. 2022, 68, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, X.; Li, C.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X. Mixed fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum, Bifidobacteriµm animalis subsp. lactis and Candida utilis improves the fermentation quality of Hong Suan Tang. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134488. [Google Scholar]
- Buerth, C.; Tielker, D.; Ernst, J.F. Candida utilis and Cyberlindnera (Pichia) jadinii: Yeast relatives with expanding applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6981–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Effect of storage time on the fermentation quality, bacterial community structure and metabolic profiles of Napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum.) silage. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 204, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: Ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Tang, N.; Liu, R.; Gong, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, M. The relationship between flavor formation, lipid metabolism, and microorganisms in fermented fish products. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5685–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Dynamics of phyllosphere microbiota and chemical parameters at various growth stages and their contribution to anaerobic fermentation of Pennisetum giganteum. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0228822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Franco, M.; Ding, Z.; Hao, L.; Ke, W.; Wang, M.; Xie, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, L. Effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis on fermentation, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts of whole-plant corn silage. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Changes in the fermentation products, taxonomic and functional profiles of microbiota during high-moisture sweet sorghum silage fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 967624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).