Abstract
Previous studies have demonstrated that slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) treatment can enhance rice seed growth and promote the accumulation of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a bioactive compound. However, the underlying mechanisms remain unexplored. This study systematically investigated the effects of pH and available chlorine concentration (ACC) of SAEW on rice seed germination and GABA biosynthesis. The changing trends were monitored within 7 days. The results revealed that the treatment group with moderate pH (S2, pH 5.74 ± 0.04) showed significantly higher GABA accumulation (71.27 ± 0.45 mg/100 g) compared with S1 (pH 5.04 ± 0.03) and S3 (pH 6.38 ± 0.04) (p < 0.05). Furthermore, a positive correlation was observed between ACC levels and GABA accumulation, suggesting that ACC plays a crucial regulatory role in rice seed germination. These findings were further substantiated by monitoring the enzymatic activity of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) throughout the germination process. Notably, while higher ACCs negatively impacted rice seed growth, pH variations within the tested range showed no adverse effects on seed development. The results show that optimal SAEW parameters, considering both pH and ACC, should be carefully determined for practical applications in rice seed production.
1. Introduction
Rice is the staple food for over 3.5 billion people worldwide (accounting for nearly half of the world’s population), especially in developing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, where about 90% of the output is concentrated [1]. It is primarily categorized into two types: Indica rice and Japonica rice, each exhibiting distinct growth characteristics, quality traits, and cultivation methodologies. Rice is rich in carbohydrates, as well as essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals [2]. Owing to its abundant nutritional profile, rice has not only become a focal point in numerous health-related studies but is also recognized for its various health benefits [3]. Consequently, rice and its derived products have garnered significant attention in both agricultural and scientific research domains.
In recent years, the escalating demand for healthy and nutritious foods has positioned rice as a preferred choice. Research indicates that during the germination process, the nutritional content of rice is enhanced, particularly through the increase in bioactive compounds such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and its digestibility is also improved [4]. However, rice seeds are susceptible to microbial contamination during germination, especially when traditional water sources like tap water are utilized. This issue has prompted extensive research into methods to inhibit microbial growth and ensure safe germination. Common treatment approaches include physical techniques such as steam, high-pressure electric fields, and ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, as well as the application of natural preservatives or chemical substances [5]. While these methods can mitigate microbial contamination, they may occasionally adversely affect seed germination rates and vitality, and may pose health risks to users. Therefore, the development of a safer and more effective rice seed treatment technology is imperative.
Electrolyzed water (EW), particularly mildly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW), has been widely acknowledged as a promising seed treatment method for rice. Compared with strongly acidic electrolyzed water, SAEW, with a pH range of 5.0–6.5 and an available chlorine concentration (ACC) of 10–50 mg/L, has been extensively applied in agricultural product preservation due to its mild disinfection effect and minimal impact on human health and the environment [6,7]. Studies have demonstrated that SAEW can significantly reduce microbial contamination in various agricultural products, including rice, while maintaining their quality and safety. SAEW has proven effective in inhibiting pathogenic microorganisms such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus aureus [8,9]. Beyond its role in ensuring agricultural product safety, SAEW has also exhibited significant effects in promoting rice seed germination and enhancing the accumulation of beneficial compounds [10]. For instance, during the germination of brown rice, researchers found that SAEW reduced microbial load and promoted GABA accumulation [11]. Another study illustrated that SAEW treatment was an effective method to enhance the accumulation of GABA and antimicrobial capacity in germinated brown millet [12]. Moreover, previous research has confirmed that SAEW can promote the dual accumulation of GABA and rutin in rice seeds [13]. However, existing studies only suggest that SAEW promotes GABA accumulation by activating glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), and which specific parameters of SAEW affect GABA accumulation remains unclear.
This study investigates how specific SAEW parameters (pH and ACC) affect seed growth, GABA accumulation, and GAD enzyme activity during rice seed germination.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this study, “Nipponbare” rice seeds were utilized as experimental samples. The seeds were harvested on 10 September 2023, in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. Post-harvest, the rice seeds were sealed in plastic bags and stored at 4 °C until further use. The standard GABA used in the experiments was procured from Sigma-Aldrich (Louis, MI, USA). All chemicals employed were of analytical grade, and distilled water was used throughout this study.
2.2. Preparation of Treatment Solutions
SAEW was prepared using a flow electrolysis instrument (non-membrane electrolytic cell, model MS303D, Meisheng Company, Shaoxing, China) under varying operating conditions [14]. The pH value of SAEW was measured using a pH meter (model PHSJ-3F, Leici Company, Shanghai, China), and the ACC was determined via the iodometric method. The pH values and ACCs of SAEW are detailed in Table 1. Specifically, treatment groups S1, S2, and S3 exhibited similar ACC ranges but differed in pH values, whereas treatment groups S4 and S5 had similar pH values but differed in ACCs. Deionized water was employed as the control group.

Table 1.
Physical and chemical parameters of SAEW.
2.3. Production of Rice Seeds
Initially, the rice seeds were rinsed three times with SAEW of the corresponding parameters. Subsequently, the seeds were soaked in SAEW of varying concentrations or deionized water (used as the control) at 25 °C for 12 h. After soaking, the seeds were removed and dried at 25 °C for 12 h. Following this, the seeds were re-immersed in the corresponding solution and soaked for an additional 12 h at 25 °C before being removed. The seeds were then placed in plastic germination trays (115 × 115 mm), with 100 seeds per tray, 5 trays in each treatment group, and incubated in a constant temperature and humidity chamber set to 25 ± 1 °C and 85 ± 2% relative humidity, respectively. Over the subsequent 7 days, the corresponding treatment solution was sprayed onto the seeds at scheduled intervals (5 mL/12 h), and the effects of SAEW on seed germination were monitored.
On days 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7, the GABA content and GAD activity of the rice seeds were measured. Concurrently, daily assessments of germination rate, shoot length, and 100-grain weight were conducted as morphological indicators.
2.4. Determination of GABA
When measuring the GABA content, the test samples were pre-treated with liquid nitrogen and ground into a powder. A 0.50 g sample of freeze-dried powder is then added to 5 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid solution, shaken for 1 min using a vortex mixer, and incubated at 40 °C for 2 h to extract GABA. The sample is then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 15 min, and the supernatant is collected and filtered through a 0.45 µm filter. Finally, the GABA content in the filtrate is determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (Agilent Technologies Co., Ltd., Santa Clara, CA, USA, Agilent 1290 infinityII), and the results are expressed as the mass of GABA per 100 g of sample (g/100 g).
2.5. Evaluation of GAD Activity
The methodology for GABA extraction and activity determination was adapted from the protocol established by Bai et al. [15] with necessary modifications.
Initially, 1 g of lyophilized sample was homogenized with 5 mL of potassium phosphate buffer (0.1 mol/L, pH 5.8) supplemented with β-mercaptoethanol (2 mmol/L), EDTA (2 mmol/L), and pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (0.2 mmol/L). The mixture was subsequently homogenized in an ice bath and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 15 min using a refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf Centrifuge 5425, Hamburg, Germany). The resulting supernatant, designated as crude GAD extract, was collected and its volume standardized to 5 mL by the addition of the aforementioned potassium phosphate buffer.
For enzymatic activity assessment, 400 μL of the crude GAD extract was combined with 200 μL of substrate solution (1% glutamic acid, pH 5.8) and incubated at 40 °C for 20 min. The enzymatic reaction was terminated by heating the mixture to 90 °C for 5 min. GABA quantification was performed as previously described. GAD activity was quantitatively defined as the amount of enzyme required to catalyze the formation of 1 μmol of GABA per hour under standard assay conditions at 40 °C.
2.6. Morphological Measurements of the Rice Seeds
The shoot length of germinated rice was measured using a digital caliper (Mitutoyo, Japan), with 100 randomly selected samples from each treatment group being analyzed. For 100-grain weight determination, an electronic analytical balance (Sartorius BSA224S, accuracy ±0.0001 g, Sartorius, Göttingen, Germany) was employed, with 100 samples randomly selected from each treatment group. Germination rate was calculated as the percentage of germinated seeds relative to the total number of seeds in each treatment group. All measurements were performed in triplicate to ensure data reliability.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All experimental treatments were performed in triplicate (biological repetition). Data obtained from independent replicate trials for each treatment were combined, and statistical parameters including mean values and standard deviations were calculated. Statistical analysis was performed using Duncan’s multiple range test implemented in SPSS software (version 26.0 for Windows, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The threshold for statistical significance was established at p < 0.05 for all comparative analyses.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of SAEW with Different pH or ACC on the Germination Rate of Rice Seeds
SAEW with varying pH levels and ACC, serving as an environmental stress factor, may influence seed germination [16,17]. Consequently, samples from the initial 7-day period were collected to assess germination rates, with the results presented in Table 2. The data revealed that all experimental groups exhibited a germination rate of 0% during the first two days of the germination period, suggesting that rice seeds remained dormant under all treatment conditions. However, significant differences in germination rates were observed between SAEW-treated groups and the control group from days 3 to 7 (p < 0.05).

Table 2.
Germination rate of rice seeds treated by SAEW.
For SAEW treatments with comparable ACC levels (approximately 30 mg/L) but differing pH values, results of the statistical analysis showed no significant differences in germination rates (p > 0.05). This indicates that pH variation within SAEW of similar ACC (approximately 30 mg/L) does not significantly affect rice seed germination. A notable observation emerged when comparing SAEW treatments with similar pH values (approximately 5.7) but varying ACCs. The treatment with 30 mg/L ACC demonstrated the highest germination rates from day 3 to day 7 (63.41–94.45%, p < 0.05), suggesting that this ACC represents the optimal range for promoting rice seed germination in SAEW with a pH of approximately 5.7.
3.2. Effect of SAEW with Different pH or ACC on the Length of Rice Seeds During Germination
Shoot length serves as a reliable indicator of rice seed growth status. In this investigation, shoot length measurements were initiated from day 3, with the results presented in Figure 1. The data demonstrated a consistent increase in shoot length across both experimental treatment groups and the control group. As illustrated in Figure 1a, the three treatment groups with comparable ACC levels (approximately 30 mg/L) but varying pH values exhibited longer shoot lengths compared with the control group on day 7. However, the influence of different pH values on shoot length was statistically insignificant (p > 0.05), indicating that pH variation within SAEW does not adversely affect shoot growth.
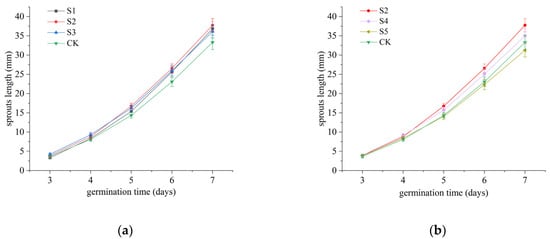
Figure 1.
Effects of SAEW with varying pH values on rice seed shoot elongation. (a) Three SAEW treatments with comparable ACCs (approximately 30 mg/L) but distinct pH values (5.04 ± 0.03, 5.74 ± 0.04, and 6.38 ± 0.04, respectively) were evaluated. (b) Three SAEW treatments with similar pH values (approximately 5.7) but different ACCs (10.2 ± 0.3, 30.1 ± 0.4, and 50.3 ± 0.5 mg/L) were analyzed to monitor shoot length variations during germination. Deionized water served as the negative control. All experiments were conducted in triplicate (n = 3), and the results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
Figure 1b reveals that the S2 treatment group (ACC approximately 30 mg/L) achieved a final shoot length of 37.75 mm, representing a 7.3–17.3% increase compared with other SAEW treatment groups and 1.13 times that of the control group. Conversely, the S5 treatment group demonstrated inhibited shoot growth. These findings suggest that at a consistent pH value (approximately 5.7), SAEW with an optimal ACC (approximately 30 mg/L) effectively promotes shoot growth.
3.3. Effect of SAEW with Different pH or ACC on the Hundred-Grain Weight of Rice Seeds During Germination
During the initial stages of germination, the embryo undergoes elongation and swelling through water absorption, ultimately rupturing the seed coat. Thus, water uptake plays a critical role in this process, and changes in 100-grain weight serve as a reliable indicator of this phenomenon. Previous studies have demonstrated that SAEW (pH 5.83, ACC 20.3 mg/L) can enhance the 100-grain weight of rice seeds; however, comprehensive investigations into the effects of SAEW’s pH and ACC variations remain limited [13]. In this study, the 100-grain weight was measured daily, and the results are presented in Figure 2. Overall, the 100-grain weight of all five treatment groups and the control group exhibited a consistent upward trend.
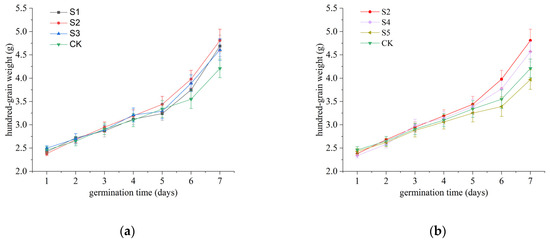
Figure 2.
Effects of SAEW with varying pH values on 100-grain weight during rice seed germination. (a) Three SAEW treatments with comparable ACCs (approximately 30 mg/L) but distinct pH values (5.04 ± 0.03, 5.74 ± 0.04, and 6.38 ± 0.04) were investigated. (b) Three SAEW treatments with similar pH values (approximately 5.7) but different ACCs (10.1 ± 0.2, 30.3 ± 0.4, and 50.2 ± 0.5 mg/L) were examined. Deionized water served as the negative control in this experiment. All treatments were performed in triplicate (n = 3), and the results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
As illustrated in Figure 2a, on day 7 of germination, the S1, S2, and S3 treatment groups showed 100-grain weights that were 0.48, 0.60, and 0.40 g higher, respectively, than the control group (4.21 g). However, no significant differences were observed among the S1, S2, and S3 treatment groups (p > 0.05), indicating that variations in SAEW pH did not significantly influence the 100-grain weight.
Additionally, as shown in Figure 2b, no significant differences were detected among the four treatment groups prior to day 5 of germination (p > 0.05). However, from day 6 onward, the S2 treatment group (3.98–4.81 g) demonstrated significantly higher 100-grain weights compared with the other groups, maintaining the highest levels throughout the observation period. This was followed by the S4 treatment group (3.77–4.57 g). In contrast, the S5 treatment group exhibited consistently lower 100-grain weights (3.39–3.97 g) from day 6 onward, which were significantly lower than those of the control group (3.55–4.21 g) (p < 0.05).
3.4. Effect of pH and ACC of SAEW on GABA Content of Germinated Rice During Germination
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid), a non-protein amino acid widely distributed in various organisms, exhibits significant biological activity [18]. It plays a beneficial role in multiple physiological processes, including blood pressure reduction [19], immunity enhancement [20], oxidative stress alleviation [21], and anti-obesity effects [22]. Extensive research has demonstrated that the GABA content increases during the germination of various grains, such as brown rice [23], soybeans [24], and buckwheat [25]. However, the mechanism underlying GABA accumulation in rice seeds during germination has attracted our attention. Therefore, we investigated this mechanism by examining the effects of SAEW’s pH and ACC on GABA accumulation.
During the germination process, samples were collected every two days to analyze changes in the GABA content in rice seeds treated with SAEW of varying pH and ACC levels. The results, presented in Figure 3, reveal that the GABA content continuously increased until day 5, reaching a peak before declining. This trend differed from that of the control group, where the GABA content peaked before day 3 and then gradually decreased. Figure 3a illustrates the effect of SAEW with different pH values on the GABA content. Notably, the GABA content in all treatment groups exceeded that of the control group. Under similar ACC conditions (approximately 30 mg/L), the maximum GABA content in the treatment groups, in descending order, was as follows: S2 (16.17–71.27 mg/100 g) > S1 (19.45–57.27 mg/100 g) > S3 (15.18–50.87 mg/100 g). Meanwhile, as shown in Figure 3b, the GABA content in the S4 treatment group (14.97–38.37 mg/100 g) was slightly lower than that of the control group (13.75–39.45 mg/100 g), whereas the GABA content in the S2 (16.17–71.27 mg/100 g) and S5 (17.58–83.47 mg/100 g) treatment groups was significantly higher than that of the control group (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that under similar pH conditions (approximately 5.7), higher ACC levels (50.46 ± 0.18 mg/L) in SAEW significantly promote GABA accumulation.
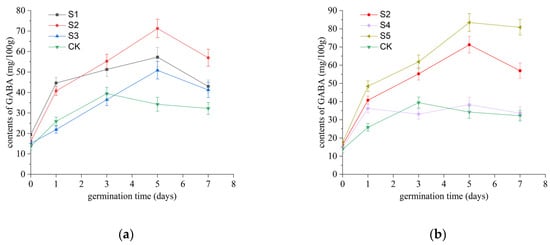
Figure 3.
Effects of SAEW with different pH values on γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) accumulation in germinating rice seeds. (a) Three SAEW treatments with equivalent ACCs (approximately 30 mg/L) but varying pH values (5.04 ± 0.03, 5.74 ± 0.04, and 6.38 ± 0.04) were analyzed. (b) Three SAEW treatments with comparable pH values (approximately 5.7) but distinct ACCs (10.2 ± 0.2, 30.3 ± 0.4, and 50.1 ± 0.5 mg/L) were evaluated. Deionized water served as the negative control throughout the experiment. All treatments were conducted in triplicate (n = 3), and the results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
3.5. Effect of pH and ACC of SAEW on GAD Activity of Germinated Rice During Germination
Endogenous enzymes are synthesized or activated during seed germination, facilitating the degradation of plant proteins into small molecules, which leads to significant GABA accumulation [26,27]. For instance, glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) catalyzes the decarboxylation of glutamate to produce GABA [28]. Various stress factors, including high temperature, hypoxia, freezing, and drought, have been shown to enhance GAD activity [29,30]. Therefore, SAEW may similarly function as a stress factor, promoting GABA accumulation through analogous mechanisms. Additionally, variations in the pH and ACC of SAEW may influence GAD activity, making the evaluation of GAD activity essential for elucidating the mechanism of GABA accumulation.
As illustrated in Figure 4, changes in GAD activity for each treatment group on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 are presented. For treatment groups S1, S2, and S3 (with similar ACC but varying pH values), it is evident that as the pH increases from 5.04 ± 0.03 to 6.38 ± 0.04, GAD activity gradually decreases, with all groups exhibiting higher GAD activity than the control group. An exception is treatment group S2 (pH 5.74 ± 0.04), which demonstrated a peak in GAD activity on day 5 (14.11 U), aligning with the observed changes in the GABA content during this period. Thus, under similar ACC conditions (approximately 30 mg/L), a moderate pH (around 5.70) maximizes GAD activation, thereby promoting GABA accumulation. Furthermore, for treatment groups S2, S4, and S5 (with similar pH values but different ACC levels), it was observed that during seed germination, GAD activity followed this descending order: S5 (17.23–38.41 U) > S2 (14.11–31.72 U) > control group (6.80–23.03 U) > S4 (5.81–22.50 U). This indicates that under similar pH conditions (approximately 5.70), as the ACC of SAEW increases from 10.14 ± 0.14 to 50.46 ± 0.18 mg/L, higher ACC levels correspond to higher GAD activity. This conclusion is consistent with the observed trends in the GABA content.
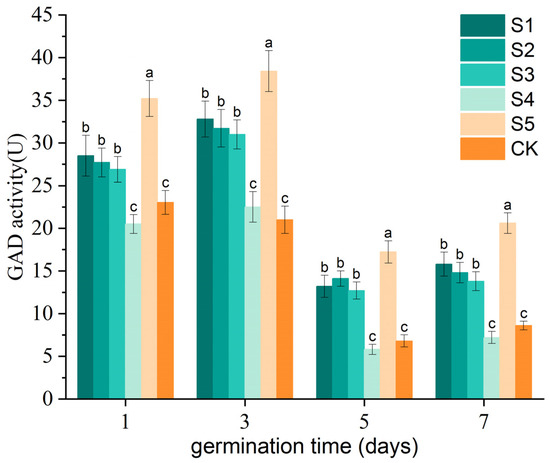
Figure 4.
The temporal changes in glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) activity in germinating rice seeds were monitored under different treatment conditions (SAEW treatments and deionized water as control) at 1, 3, 5, and 7 days post-treatment. Three treatment groups (S1, S2, and S3) maintained comparable ACCs (approximately 30 mg/L) but exhibited distinct pH values (5.04 ± 0.03, 5.74 ± 0.04, and 6.38 ± 0.04, respectively). Conversely, another set of treatment groups (S2, S4, and S5) showed similar pH values (approximately 5.7) but significantly varied in ACCs (30.1 ± 0.4, 10.2 ± 0.3, and 50.3 ± 0.5 mg/L, respectively). All experimental treatments were conducted in triplicate (n = 3), and the results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistically significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05) are indicated by different superscript letters.
4. Discussion
In this study, SAEWs with a near-neutral pH range (5.0–6.5) and a low ACC (10–50 mg/L) was utilized to enhance seed germination. The research evaluated the effects of SAEW’s pH and ACC on rice seed growth and GABA accumulation. The results demonstrated that, under SAEW treatments with varying pH values and similar ACC (approximately 30 mg/L), treatment group S2 (pH 5.74 ± 0.04) exhibited superior GABA accumulation compared with treatment groups S1 (pH 5.04 ± 0.03) and S3 (pH 6.38 ± 0.04). Moreover, within the ACC range of 10.14 ± 0.14 to 50.46 ± 0.18 mg/L, higher ACC levels (under similar pH conditions of approximately 5.7) led to increased GABA accumulation, highlighting the significant role of ACC in the rice seed germination process. These findings were further corroborated by the analysis of GAD activity during germination.
However, within the ACC range of 10.14 ± 0.14 to 50.46 ± 0.18 mg/L, samples from treatment group S2 (ACC 29.96 ± 0.12 mg/L) maintained higher germination rates, shoot lengths, and 100-grain weights during germination, outperforming the other two treatment groups with similar pH (approximately 5.70) (p < 0.05). In contrast, treatment group S5 (ACC 50.46 ± 0.18 mg/L) exhibited inferior performance compared with the control group, demonstrating an inhibitory effect. This indicates that when the ACC level is too high, SAEW has an inhibitory effect on the growth of rice seeds. In terms of seed germination rate, this finding contrasts with the results reported by Zhang et al. [31], who demonstrated that electrolyzed oxidizing water (EOW) with a pH of 6.5 exhibited superior effects on radish seed germination compared with pH 5.5 treatment at similar ACC levels (25 mg/L). This discrepancy may be attributed to interspecies variation. In terms of seed sprout length, results of the comparative analysis reveal similarities in the response of SAEW-treated brown rice, mung bean, and buckwheat seeds. For instance, SAEW application with 20 mg/L ACC significantly enhanced mung bean sprout shoot length compared with 30 mg/L ACC treatment, with both concentrations outperforming the control group during the 70–120 h germination period [32]. However, in millet with a 72 h germination period, lower ACC (15 mg/L) resulted in shorter shoots compared with higher ACC (30 mg/L) treatment [12]. Conversely, broccoli exhibited decreased shoot length with increasing SAEW ACCs (10–40 mg/L), with all SAEW treatments inhibiting growth relative to the control group [33]. These findings underscore the critical importance of selecting appropriate SAEW ACCs for optimizing shoot growth in germinating vegetables. In terms of the hundred-grain weight of seeds, these results align with the observations of Li et al., who reported that broccoli sprouts irrigated with SAEW (pH 5.5, ACC 10–50 mg/L) exhibited lower fresh weights compared with tap water treatment, with fresh weight progressively decreasing as ACCs increased [33]. Therefore, the ACC of SAEW applied during seed germination is a critical factor in maintaining the weight and commercial value of germinating vegetables.
Additionally, no significant differences were observed in the 100-grain weight, shoot length, or germination rate among treatment groups S1, S2, and S3 (with similar pH), indicating that SAEW’s pH does not adversely affect rice seed growth. This finding aligns with the conclusions of Liu et al., who reported that SAEW with ACCs ranging from 10 to 30 mg/L enhanced mung bean sprout germination, with moderate ACC levels (20 mg/L) yielding the highest germination rates [32]. These findings collectively underscore the regulatory role of ACC in SAEW-mediated seed germination. Therefore, in rice production applications, SAEW with appropriate pH and ACC levels should be employed to improve germination quality and GABA content in rice seeds during sprouting.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.H. and L.W.; methodology, T.H.; software, T.H. and F.C.; validation, T.H.; formal analysis, T.H.; investigation, T.H.; resources, L.W.; data curation, T.H. and F.C.; writing—original draft preparation, T.H.; writing—review and editing, T.H., H.C., C.L., M.X., and L.W.; visualization, T.H.; supervision, L.W.; project administration, L.W.; funding acquisition, L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFD2301605), awarded to Liyan Wu.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to the Rice Research Institute of Shenyang Agricultural University for providing the experimental site and equipment for this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ACC | available chlorine concentration |
| EW | electrolyzed water |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| GAD | activating glutamate decarboxylase |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| ND | not detected |
| SAEW | slightly acidic electrolyzed water |
| SD | standard deviation |
| UV | ultraviolet |
References
- Wang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Asseng, S.; Harrison, M.T.; Tang, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, K.; Luo, Z.K.; Wang, E.L.; Chang, J.F.; et al. Rice yield stability and its determinants across different rice-cropping systems in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2025, 364, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Oh, S.D.; Lee, S.K.; Chang, A.; Park, S.U.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.K. Metabolic profiling characterizes the genetic diversity of genetically modified and conventional rice. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 18, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Fu, W.T.; Xiao, L.Y.; Wei, Z.J.; Han, L.H. Nutrition, health benefits, and processing of sand rice (Agriophyllum squarrosum): Comparisons with quinoa and buckwheat. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 7060–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.C.; Xu, J.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Hua, D.; Zhang, H.J.; He, Y.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Tang, A.; Liu, H.; Sun, J. A multi-omics study revealed the effect of pulsed light treatment on germinated brown rice: Promotion of sprouting efficiency and gamma-aminobutyric acid enrichment. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.E.; Ding, T.; Oh, D.H. Inactivation effect of newly developed low concentration electrolyzed water and other sanitizers against microorganisms on spinach. Food Control 2010, 21, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa-Zacharia, A. Application of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water as a Potential Sanitizer in the Food Industry. J. Food Qual. 2024, 2024, 5559753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.Q.; Chen, X.Z.; Li, M.L.; Lin, M.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, H.T. Slightly acidic electrolyzed water treatment improves the quality and storage properties of carambola fruit. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, K.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.B.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhou, C.S.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.C. Ultrasonic synergistic slightly acidic electrolyzed water processing to improve postharvest storage quality of Chinese bayberry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 101, 106668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.M.; Zang, Y.; Mo, Q.N.; Yuan, X.Y.; Shu, D.Q.; Zhang, G.S.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, R.X.; Bing, S.; et al. Effect of combined electrolyzed reduced water and slightly acidic electrolyzed water spraying on the control of Salmonella, eggshell quality, and shelf life of eggs during storage. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, F.; Eskandari, M.; Oh, D.H. Application of slightly acidic electrolyzed water and ultrasound for microbial decontamination of kashk. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Chen, X.; Shabbir, U.; Chelliah, R.; Oh, D.H. Effect of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on amino acid and phenolic profiling of germinated brown rice sprouts and their antioxidant potential. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 157, 113119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Hao, J.X.; Liu, X.G.; Liu, H.J.; Ning, Y.W.; Cheng, R.H.; Tan, B.; Jia, Y.M. Effect of the treatment by slightly acidic electrolyzed water on the accumulation of γ-aminobutyric acid in germinated brown millet. Food Chem. 2015, 186, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.X.; Wu, T.J.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.J. Dual effects of slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) treatment on the accumulation of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and rutin in germinated buckwheat. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.R.; Quan, Y.; Liu, S.K.; Hao, J.X. Effectiveness of ultrasound (US) and slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) treatments for removing Listeria monocytogenes biofilms. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 112, 107190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.Y.; Chai, M.Q.; Gu, Z.X.; Cao, X.H.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.L. Effects of components in culture medium on glutamate decarboxylase activity and γ-aminobutyric acid accumulation in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) during germination. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Xue, F.; Ma, S.H.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, D.D.; Hao, J.X. Contribution of slightly acidic electrolytic water (SAEW) to food safety, nutrients enrichment, and allergenicity reduction of peanut sprouts. J. Food Process Preserv. 2022, 46, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Liu, W.F.; Chen, Y.Q.; Yang, G.J.; Xia, X.D.; Cao, Y.F. The application of slightly acidic electrolyzed water in pea sprout production to ensure food safety, biological and nutritional quality of the sprout. Food Control 2019, 104, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.D.; Xiao, H.Y.; Guo, C.L.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.J. Effects of exogenous gamma-aminobutyric acid on α-amylase activity in the aleurone of barley seeds. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, K.; Sakakibara, H.; Yokoyama, D.; Uehara, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Sakono, M. Consumption of Salted Pickles of Sun-dried Radish Roots (Raphanus sativus cv. YR-Hyuga-Risou) Attenuates Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.S.; Ji, T.; Wang, C.Q.; Shi, Q.H.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, J.W.; Gong, B. High-nitrogen-induced γ-aminobutyric acid triggers host immunity and pathogen oxidative stress tolerance in tomato and Ralstonia solanacearum interaction. New Phytol. 2024, 244, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.Q.; Zhang, H.B.; Liu, S.Q.; Li, H.Q.; Huo, Y.Z.; Guo, K.W.; Xu, Z.S.; Zhang, H.H. Exogenous γ-glutamic acid (GABA) induces proline and glutathione synthesis in alleviating Cd-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative damage in tobacco leaves. J. Plant Interact. 2021, 16, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, T.; Braga, J.D.; Chen, S.Y.; Thongngam, M.; Chartkul, M.; Yanaka, N.; Kumrungsee, T. Synergistic effects of peripheral GABA and GABA-transaminase inhibitory drugs on food intake control and weight loss in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1487585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Q.; Geng, C.X.; Gu, Z.X. Activation and Tempering on -Aminobutyric Acid Accumulation and Distribution in Brown Rice. J. Food Process Preserv. 2016, 40, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Xing, C.C.; Zhang, L.J.; Xu, T.; Fang, F.; Wang, F.Z. Accumulating mechanism of -aminobutyric acid in soybean (Glycine max L.) during germination. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onozawa, G.; Ishikawa, D.; Tanji, H.; Fujii, T. The kinetic analysis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production in buckwheat after high hydrostatic pressure. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2024, 30, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Wei, Q.L.; Chen, J.H.; Cao, S.F.; Luo, M.; Qian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.Y.; Shao, X.F.; Xu, F. Identification analysis of GAD gene family, and the role of BoGAD 5 in GABA enrichment in broccoli sprouts. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 1643–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.F.; Gao, L.; Chen, X.Y. Unraveling the Potential of γ-Aminobutyric Acid: Insights into Its Biosynthesis and Biotechnological Applications. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.J.; Wei, X.B.; Liu, H.Y.; Fang, H.T. Site-directed mutagenesis improves the practical application of L-glutamic acid decarboxylase in Escherichia coli. Eng. Life Sci. 2023, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravier, E.; Godefroidt, T.; Nguyen, H.H.; van der Kant, R.; Lemmens, E.; Deleu, L.J.; Gebruers, K.; Schymkowitz, J.; Rousseau, F.; Delcour, J.A. Sodium glutamate and glutamic acid decarboxylase as alternative for classical chemical leavening in wheat (pan)cake batter systems. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 110, 103638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.Q.; Cheng, C.; Fang, W.M. Effects of the inhibitor of glutamate decarboxylase on the development and GABA accumulation in germinating fava beans under hypoxia-NaCl stress. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 20456–20461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cao, W.; Hung, Y.C.; Li, B. Application of electrolyzed oxidizing water in production of radish sprouts to reduce natural microbiota. Food Control 2016, 67, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, D.C.; He, X.L.; Nirasawa, S.; Tatsumi, E.; Liu, H.J. The relationship between antioxidant enzymes activity and mungbean sprouts growth during the germination of mungbean seeds treated by electrolyzed water. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 74, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Hao, J.X.; Song, S.H.; Nirasawa, S.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Liu, H.J. Effect of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on bioactive compounds and morphology of broccoli sprouts. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).