Reducing Mineral Fertilizer Can Improve the Soil Quality and Increase the Wheat Yield and Nutrient Utilization Efficiency: The Fertilizing Effect of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Determination Items and Methods
2.3.1. Yield Measurement
2.3.2. Determination of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.3.3. Calculation of Fertilizer Utilization Rate and Fertilizer Partial Productivity
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Growth, Yield, Yield Components
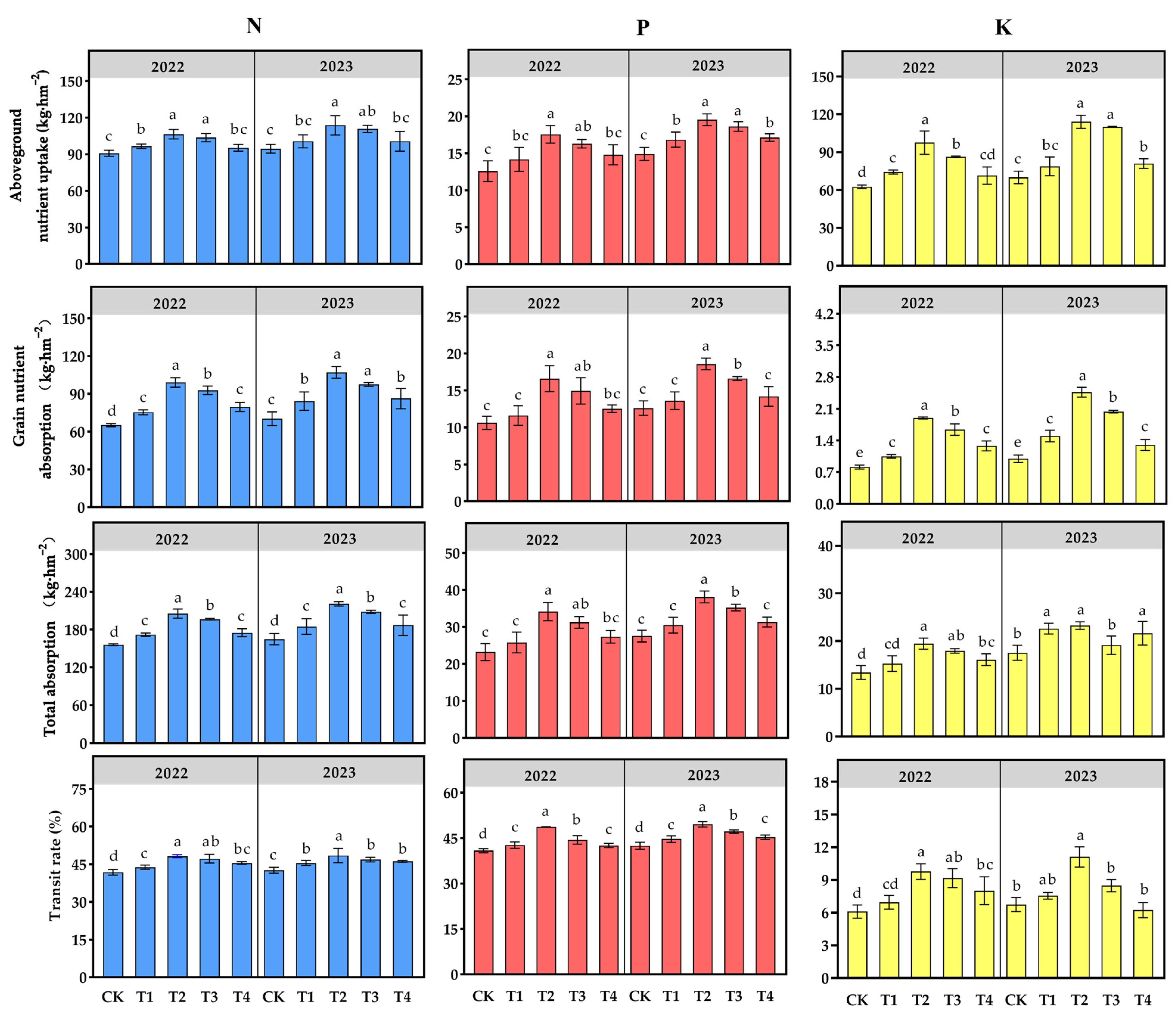
3.2. Nutrient Uptake and Utilization Efficiency
3.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Nutrients
3.4. Correlation Analysis Among All Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. Replacing Chemical Fertilizers with Organic Fertilizers Increases Wheat Yield
4.2. Replacing Chemical Fertilizers with Organic Fertilizers Can Increase Wheat Yield by Improving Nutrient Uptake and Transportation
4.3. Organic Fertilizer Replacing Chemical Fertilizer Promotes Wheat Nutrient Uptake by Increasing Soil Nutrient Content and Reducing pH
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y. After-effects of straw and straw-derived biochar application on crop growth, yield, and soil properties in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) -maize (Zea mays L.) rotations: A four-year field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Tan, G.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J. Effects of cover crops and nitrogen fertilization on soil physical properties, carbon and nitrogen fractions, and winter wheat yield in the Chinese loess plateau: A 4-year field experiment. Field Crops Res. 2024, 312, 109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, S.; Fan, J.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer derived from agricultural waste resources on soil properties and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield in semi-humid drought-prone regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamnie Asrade, D.; Kulhánek, M.; Černý, J.; Sedlář, O.; Balík, J. Effects of long-term mineral fertilization on silage maize monoculture yield, phosphorus uptake and its dynamic in soil. Field Crops Res. 2022, 280, 108476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitsopoulos, M.L.; Burgess, P.J.; Sakrabani, R.; Holden, A.; Saini, H.; Kirui, C. Modelling the effects of soil organic content and pH on the yield responses of tea to nitrogen fertilizer. Agric. Syst. 2023, 212, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Sheoran, S.; Prakash, D.; Yadav, D.B.; Yadav, P.K.; Jat, M.K. Long-term application of organic manures and chemical fertilizers improve the organic carbon and microbiological properties of soil under pearl millet-wheat cropping system in North-Western India. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilian, Y.; Amiri, M.B.; Tavassoli, A.; Caballero-Calvo, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Replacing chemical fertilizers with organic and biological ones in transition to organic farming systems in saffron (Crocus sativus) cultivation. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Wu, S.; Meng, Q.; Feng, H.; Siddique, K.H.M. Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions by replacing inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer in wheat–maize rotation systems in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Saeed, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Xu, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, P.; Hu, C.; et al. Manure replacing synthetic fertilizer improves crop yield sustainability and reduces carbon footprint under winter wheat–summer maize cropping system. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Shu, A.; Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Effects of long-term fertilization with different substitution ratios of organic fertilizer on paddy soil. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Hao, X.; Shi, F.; Li, N.; Tian, Y.; Han, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Luo, H. Improving cotton productivity and nutrient use efficiency by partially replacing chemical fertilizers with organic liquid fertilizer under mulched drip irrigation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 216, 118731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Ma, L.; Zheng, F.; Tan, D. Enhancing Maize Yield and Nutrient Utilization through Improved Soil Quality under Reduced Fertilizer Use: The Efficacy of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizer. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryan, S.; Gulab, G.; Hashemi, T.; Habibi, S.; Kakar, K.; Habibi, N.; Amin, M.W.; Sadat, M.I.; Zahid, T.; Zerak, A. Pre-spike emergence nitrogen fertilizer application as a strategy to improve floret fertility and production efficiency in wheat. Field Crops Res. 2024, 319, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Gong, M.; Wang, R. Effects of organic and inorganic fertilizer ratio on wheat nutrient utilization and soil fertility in wheat-maize rotation system. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Dongxu, Z.; Danzhu, H.; Jinlong, Y.; Liyun, F.; Zhiyuan, W.; Yanhua, L.; Haili, Y.; Yongming, C.; Junling, Z. Effect of organic fertilizer replacing chemical fertilizer on wheat growth and soil nutrients. Chinese J. Ecol. 2024, 43, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.A.; Abbott, L.K.; Solaiman, Z.M.; Mawson, P.R.; Waite, I.S.; Jenkins, S.N. Complementary effect of zoo compost with mineral nitrogen fertilisation increases wheat yield and nutrition in a low-nutrient soil. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.; Lu, W.; Hou, Z.; Li, J. Commercial organic fertilizer substitution increases wheat yield by improving soil quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, C. Multiple soil quality assessment methods for evaluating effects of organic fertilization in wheat-maize rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 150, 126929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Yu, T.; Zang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y. Manure replacement of chemical fertilizers can improve soil quality in the wheat-maize system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 200, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cao, H.; Huang, M.; Bao, M.; Qiu, W.; Liu, J. Winter wheat yield and soil critical phosphorus value response to yearly rainfall and P fertilization on the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 296, 108921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Ding, W.; Zou, G.; He, P. Effects of chicken manure substitution for mineral nitrogen fertilizer on crop yield and soil fertility in a reduced nitrogen input regime of North-Central China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1050179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei-dan, L.; Jun-hua, L.; Tong, L.; Li-li, C.; Lei, Z.; Shuo-kang, L. Effects of different organic fertilizer replacement rates on wheat yield and soil nutrients over three consecutive years. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2021, 27, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y. Long-term straw mulching with nitrogen fertilization increases nutrient and microbial determinants of soil quality in a maize–wheat rotation on China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.; Hou, Z.; Li, J. Organic substitution contrasting direct fertilizer reduction increases wheat productivity, soil quality, microbial diversity and network complexity. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.; Siebers, N.; Merbach, I.; Seidel, S.J.; Herbst, M. Simulation of soil phosphorus dynamics and crop yield for organic and mineral fertilization treatments at two long-term field sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Sun, N.; Meersmans, J.; Longdoz, B.; Colinet, G.; Xu, M.; Wu, L. Impacts of climate change on crop production and soil carbon stock in a continuous wheat cropping system in southeast England. Agriculture. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 365, 108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Tian, X.; Ye, X. Integrated mulching and nitrogen management strategies influence carbon footprint and sustainability of wheat production on the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 297, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Niu, W.; Ma, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Legacy effects of wheat season organic fertilizer addition on microbial co-occurrence networks, soil function, and yield of the subsequent maize season in a wheat-maize rotation system. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.-R.; Xu, Y.; Virk, A.L.; Liu, M.; Pei, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, C. Organic fertilizer substitution benefits microbial richness and wheat yield under warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liu, X. Combined application of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers increases soil organic carbon storage in cropland soils. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 168, 127607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gao, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Phosphorus fertilizer input threshold shifts bacterial community structure and soil multifunctionality to maintain dryland wheat production. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 243, 106174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fu, D.; Li, T.; Yuan, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Duan, C. Temporal variations of N and P losses via surface runoff from Chinese farmland after fertilisation. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sadras, V.O.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Sun, B.; Hu, C.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S. Responses of winter wheat yield and soil organic carbon to long-term (1990–2021) fertilization regimes under inter-annual weather variation in the Loess Plateau. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 157, 127189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, X.; Tou, C.; Luo, Z.; Ma, C.; Huang, W.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, F. Exploring phosphorus fertiliser management in wheat production. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 153, 127063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, M.; Xing, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, X. Reduction of nitrogen fertilizer and simultaneously application of organic fertilizer optimizes yield, water productivity and nitrogen metabolism of spring maize by improving soil properties in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yue, X.; Liang, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, N. Micro-moistening irrigation combined with bio-organic fertilizer: An adaptive irrigation and fertilization strategy to improve soil environment, edible Rose yield, and nutritional quality. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 196, 116487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, Y.; Shang, L.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Wang, D. Supplemental irrigation at the jointing stage of late sown winter wheat for increased production and water use efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Wei, Q.; Zheng, L.; Rui, Z.; Niu, M.; Gao, C.; Guan, X.; Wang, T.; Xiong, S. Adaptability of wheat to future climate change: Effects of sowing date and sowing rate on wheat yield in three wheat production regions in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, C.; Xu, M.; Cheng, B.; Zhuang, M. Key technologies improvements promote the economic-environmental sustainability in wheat production of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 141230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yang, S.; Luan, C.-s.; Wu, Q.; Lin, L.-l.; Li, X.-x.; Che, Z.; Zhou, D.-b.; Dong, Z.-r.; Song, H. Partial organic substitution for synthetic fertilizer improves soil fertility and crop yields while mitigating N2O emissions in wheat-maize rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, Y.; He, W.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Chen, H.; Fan, M. Soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality after 13-year of organic and nitrogen fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Ding-yi, Z.; Li, W.; Ping-ping, M.; Juan, Z.; Jiao-ai, W. The mechanism of different combinations of organic and N, P fertilizers increasing yield of dryland wheat. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2017, 23, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, F.; Ronchetti, G.; Dentener, F.; van der Velde, M.; van den Berg, M.; Lugato, E. Quantifying the impact of an abrupt reduction in mineral nitrogen fertilization on crop yield in the European Union. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Year | Soil Type | pH | Unit Weight (g·cm−3) | Total Nitrogen (g·kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg·kg−1) | Rapidly Available Potassium (mg·kg−1) | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | Fine loam | 7.95 | 1.03 | 1.07 | 34.50 | 195.00 | 11.60 |
| 2023 | Fine loam | 7.45 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 38.20 | 153.58 | 27.10 |
| Treatment | Chemical Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Rate (kg/Hectare) | Nutrient Dosage (kg·hm−2) | Application Rate (kg/Hectare) | Nutrient Dosage (kg·hm−2) | |||||
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | |||
| CK | 600.00 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 36.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| T1 | 600.00 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 36.00 | 3000 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 30.00 |
| T2 | 540.00 | 108.00 | 108.00 | 32.40 | 6000 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 60.00 |
| T3 | 480.00 | 96.00 | 96.00 | 28.80 | 6000 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 60.00 |
| T4 | 420.00 | 84.00 | 84.00 | 25.20 | 6000 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 60.00 |
| Year | Treatment | Plant Height (cm) | Grains Per Spike | Spike Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Yield (kg/ha) | Biological Yield (kg/ha) | Economic Coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | CK | 64.25 d | 35.63 d | 63.11 d | 39.17 c | 3998.83 c | 10,568.91 b | 0.38 c |
| T1 | 67.06 cd | 37.20 c | 65.70 c | 40.79 b | 4429.67 b | 10,893.07 b | 0.41 abc | |
| T2 | 74.53 a | 40.58 a | 69.37 a | 42.97 a | 5167.77 a | 11,928.85 a | 0.44 a | |
| T3 | 71.90 ab | 39.05 b | 68.35 ab | 41.68 b | 5048.67 a | 11,779.86 a | 0.43 ab | |
| T4 | 69.84 bc | 37.55 c | 66.66 bc | 40.80 b | 4412.00 b | 10,972.28 b | 0.40 bc | |
| 2023 | CK | 66.60 d | 36.30 b | 66.52 b | 40.17 c | 4132.17 c | 10,902.25 b | 0.38 b |
| T1 | 69.40 cd | 38.43 ab | 68.36 ab | 41.47 bc | 4696.33 b | 10,993.07 b | 0.43 a | |
| T2 | 77.20 a | 41.19 a | 71.29 a | 44.30 a | 5534.44 a | 12,295.52 a | 0.45 a | |
| T3 | 75.90 ab | 42.43 ab | 70.13 a | 43.35 ab | 5248.67 a | 11,979.86 a | 0.44 a | |
| T4 | 72.27 c | 38.88 ab | 68.63 ab | 42.47 abc | 4512.00 bc | 11,172.28 b | 0.41 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo, P.; He, Q.; Lan, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H. Reducing Mineral Fertilizer Can Improve the Soil Quality and Increase the Wheat Yield and Nutrient Utilization Efficiency: The Fertilizing Effect of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizers. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121294
Bo P, He Q, Lan Y, Li J, Liu H, Li X, Wang H. Reducing Mineral Fertilizer Can Improve the Soil Quality and Increase the Wheat Yield and Nutrient Utilization Efficiency: The Fertilizing Effect of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizers. Agriculture. 2025; 15(12):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121294
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo, Ping, Qingyang He, Yubin Lan, Jiankun Li, Haiteng Liu, Xinlong Li, and Huizheng Wang. 2025. "Reducing Mineral Fertilizer Can Improve the Soil Quality and Increase the Wheat Yield and Nutrient Utilization Efficiency: The Fertilizing Effect of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizers" Agriculture 15, no. 12: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121294
APA StyleBo, P., He, Q., Lan, Y., Li, J., Liu, H., Li, X., & Wang, H. (2025). Reducing Mineral Fertilizer Can Improve the Soil Quality and Increase the Wheat Yield and Nutrient Utilization Efficiency: The Fertilizing Effect of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizers. Agriculture, 15(12), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121294





