Parameter Optimization Design and Experimental Validation of a Header for Electric Rice Reaper Binders Employed in Hilly Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
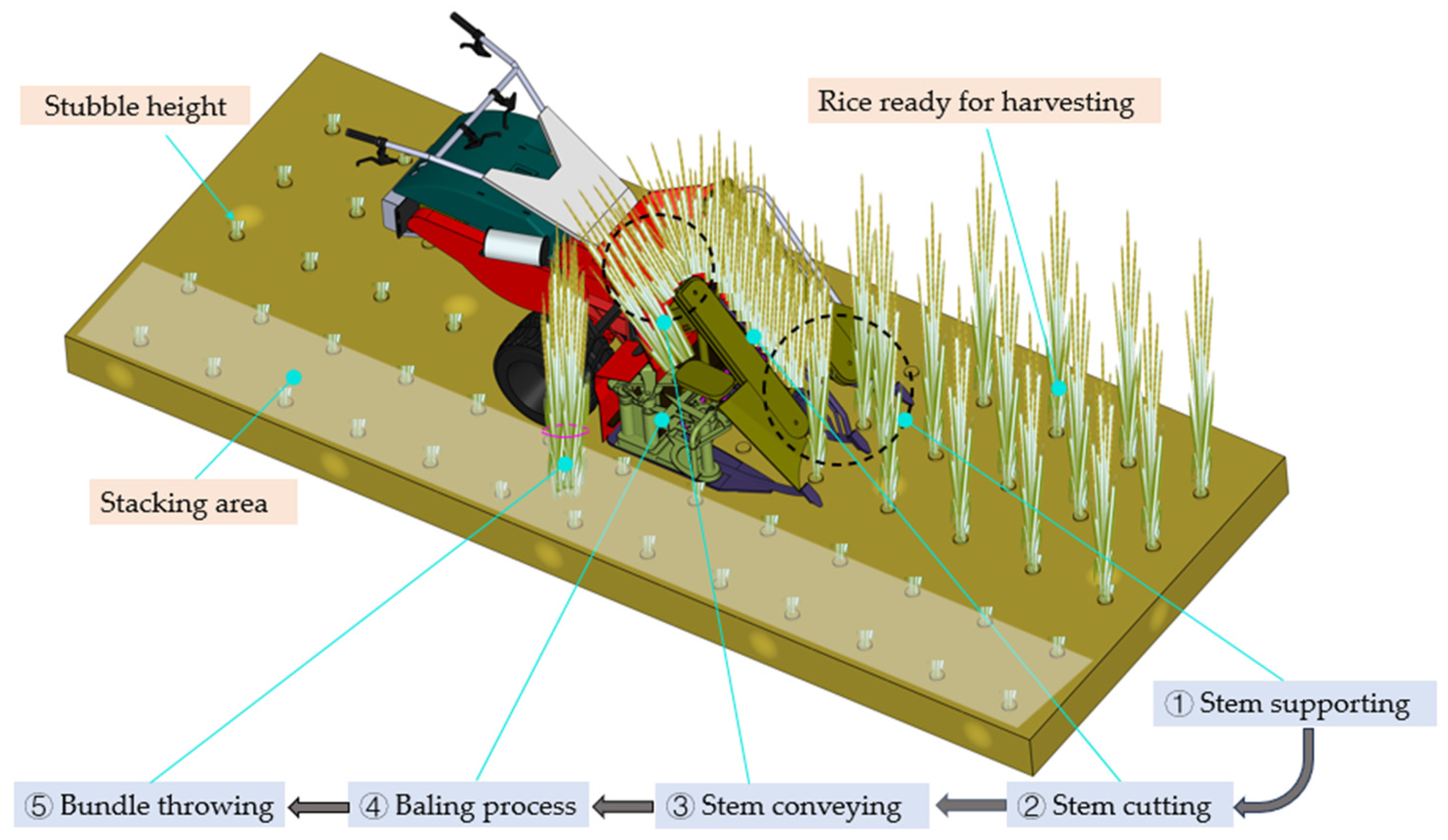
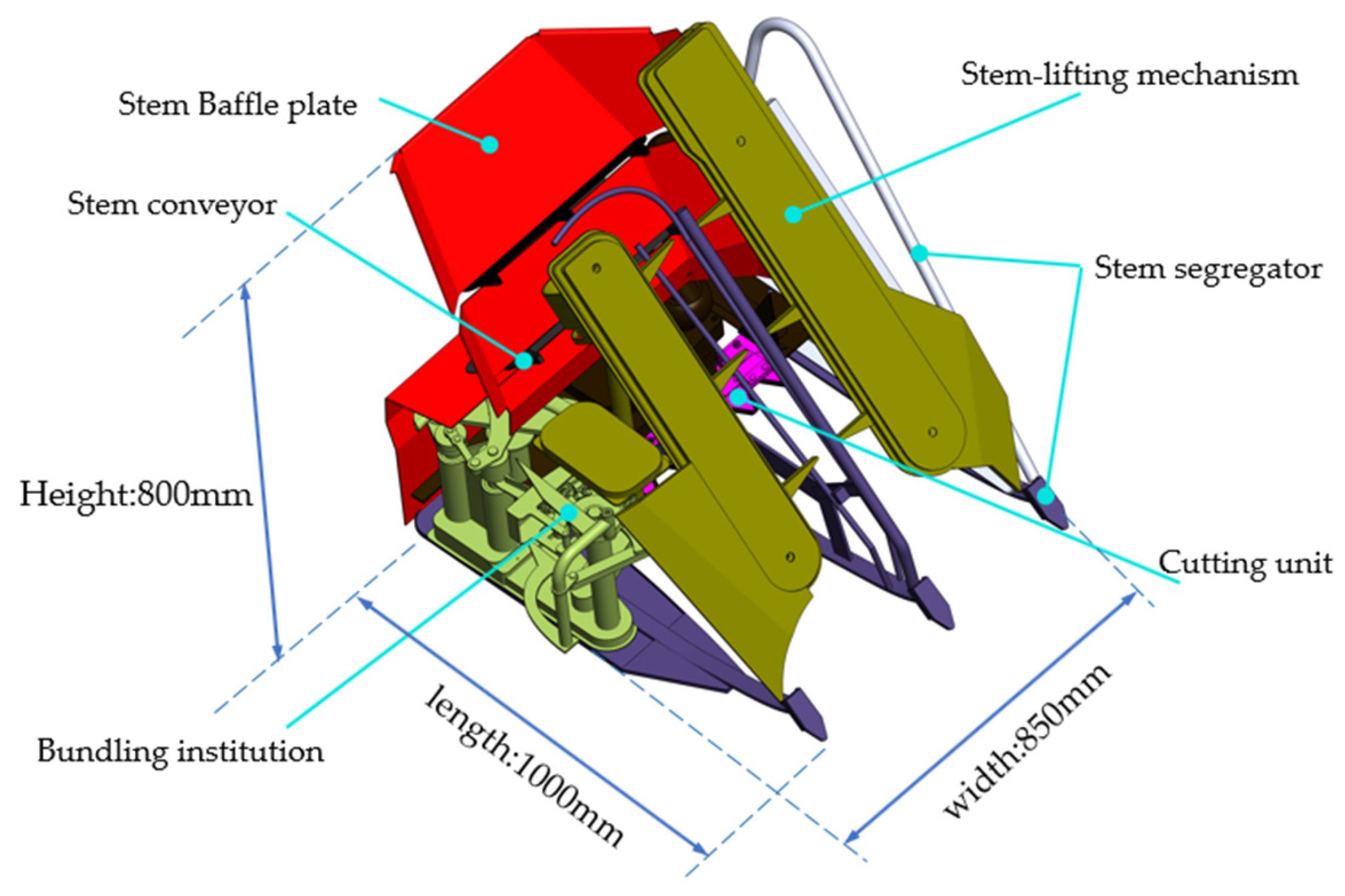
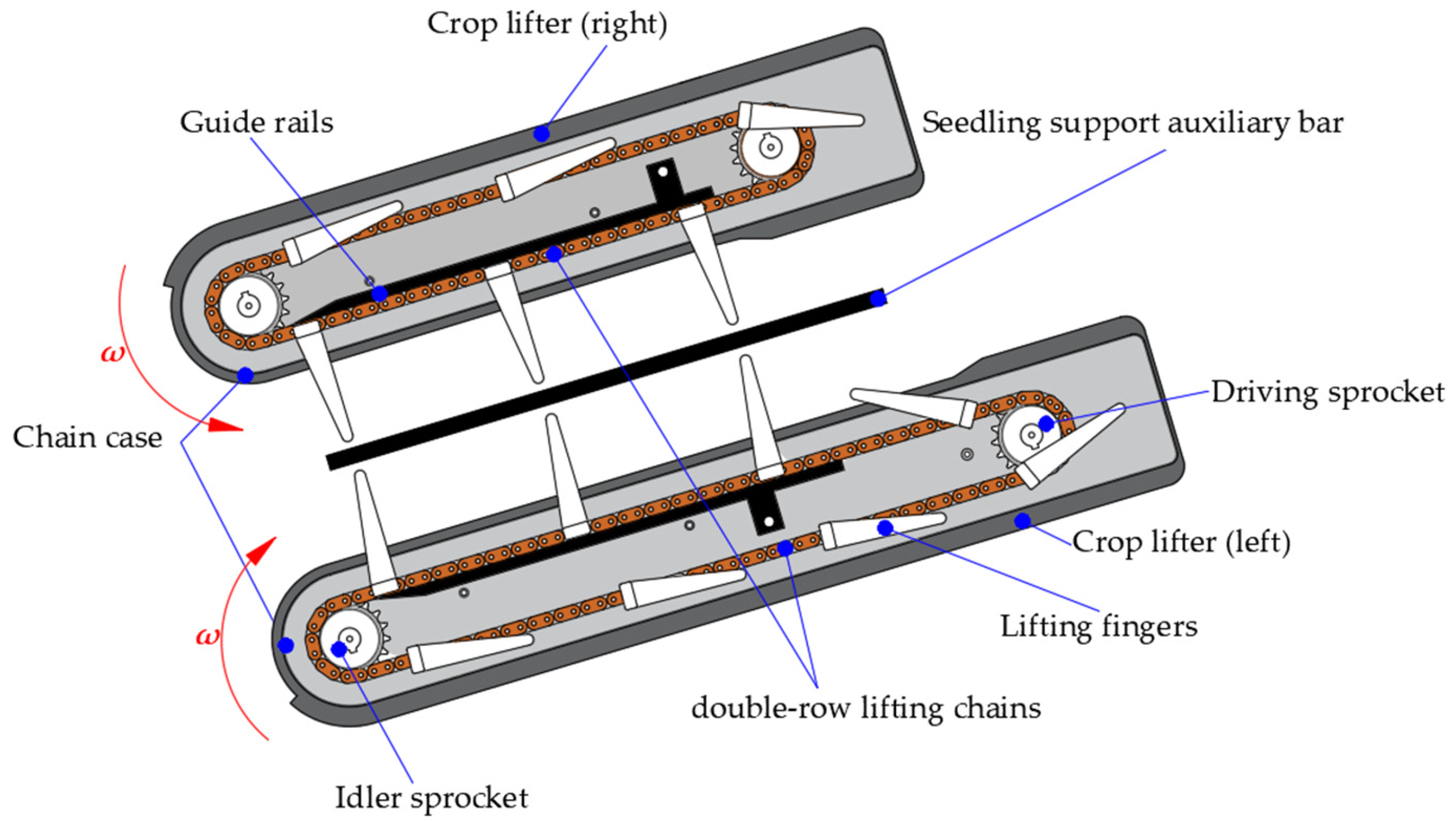
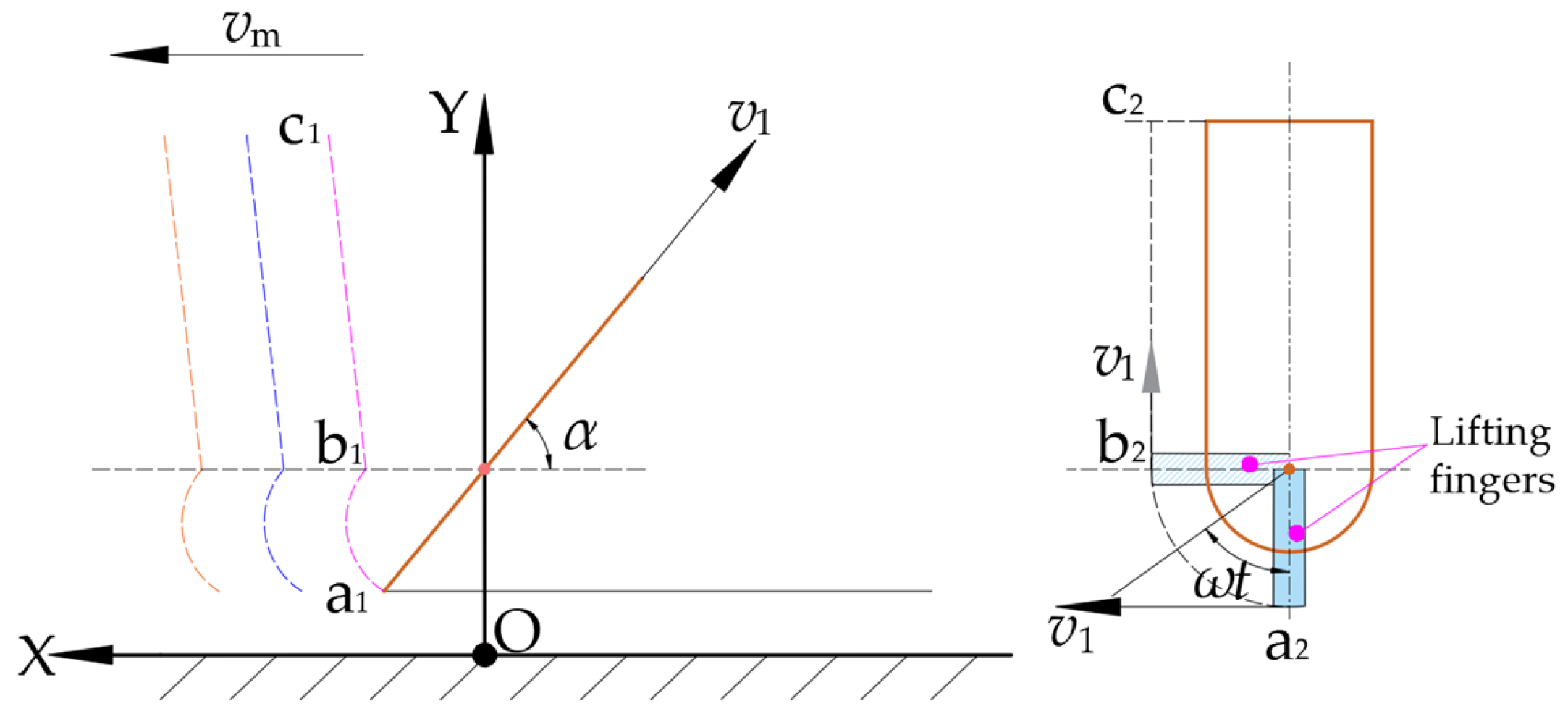
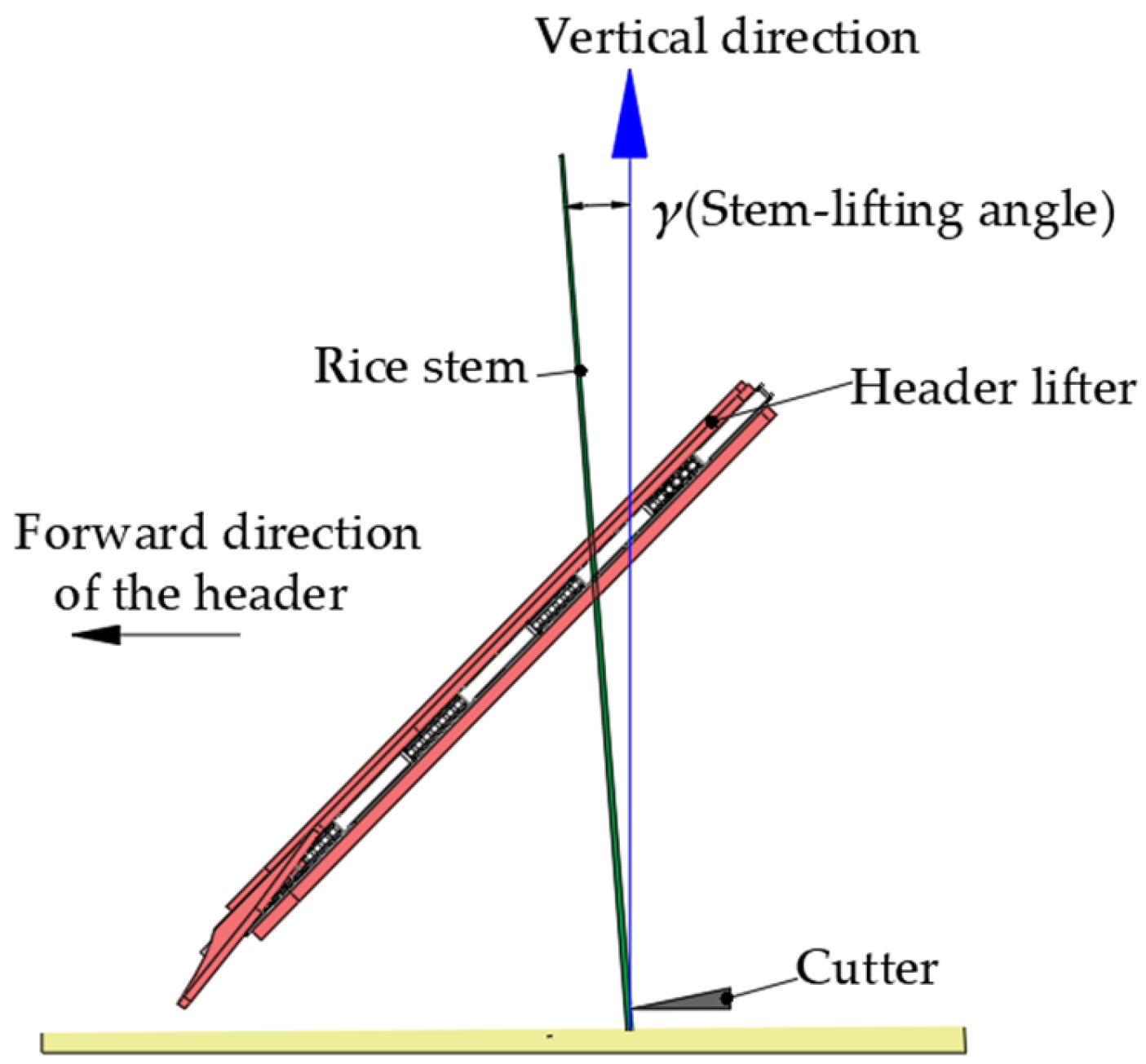
2.1. Working Principle of Header Stem-Lifting Mechanism
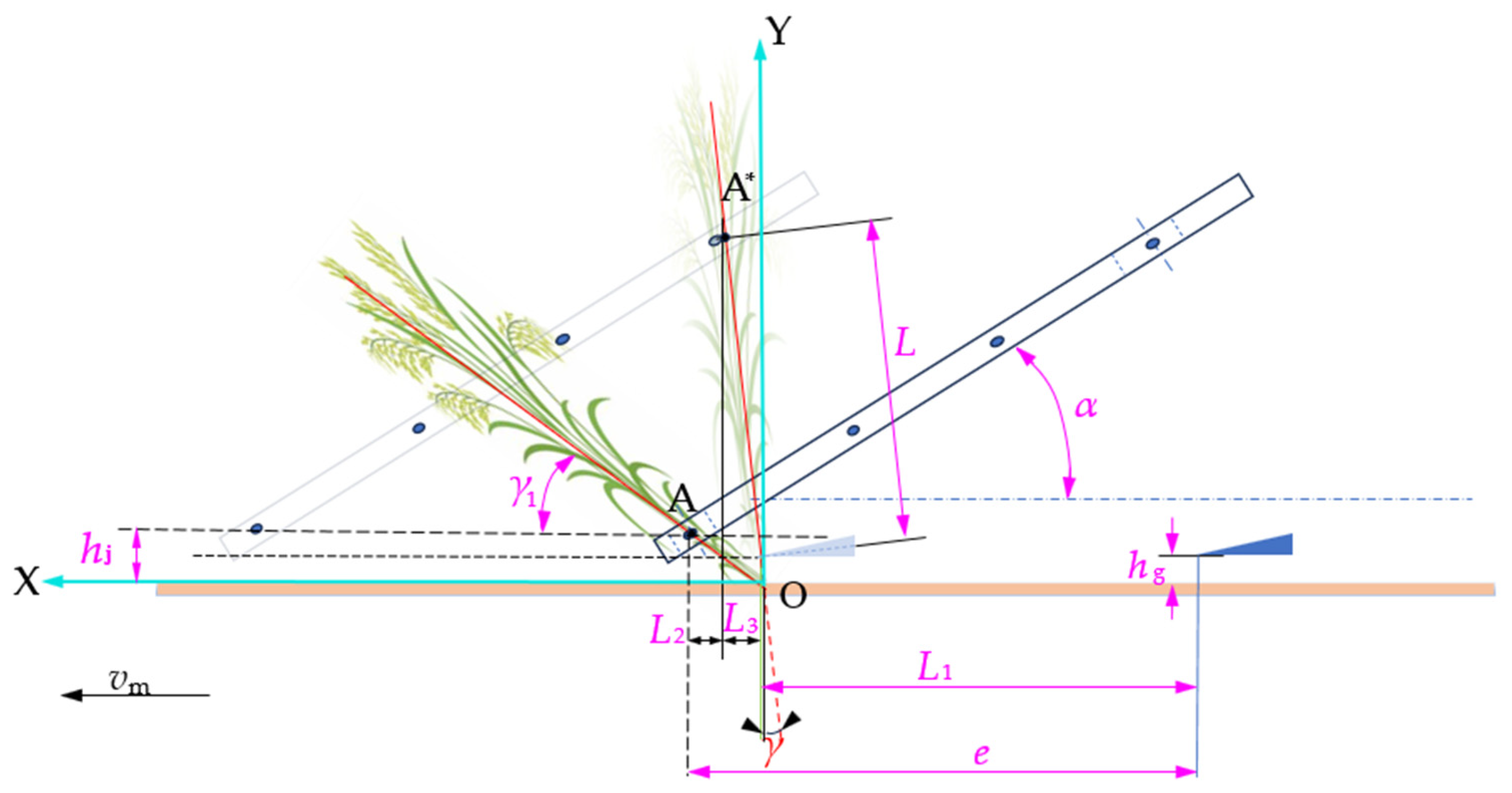
2.2. Analysis of Stem-Lifting Process
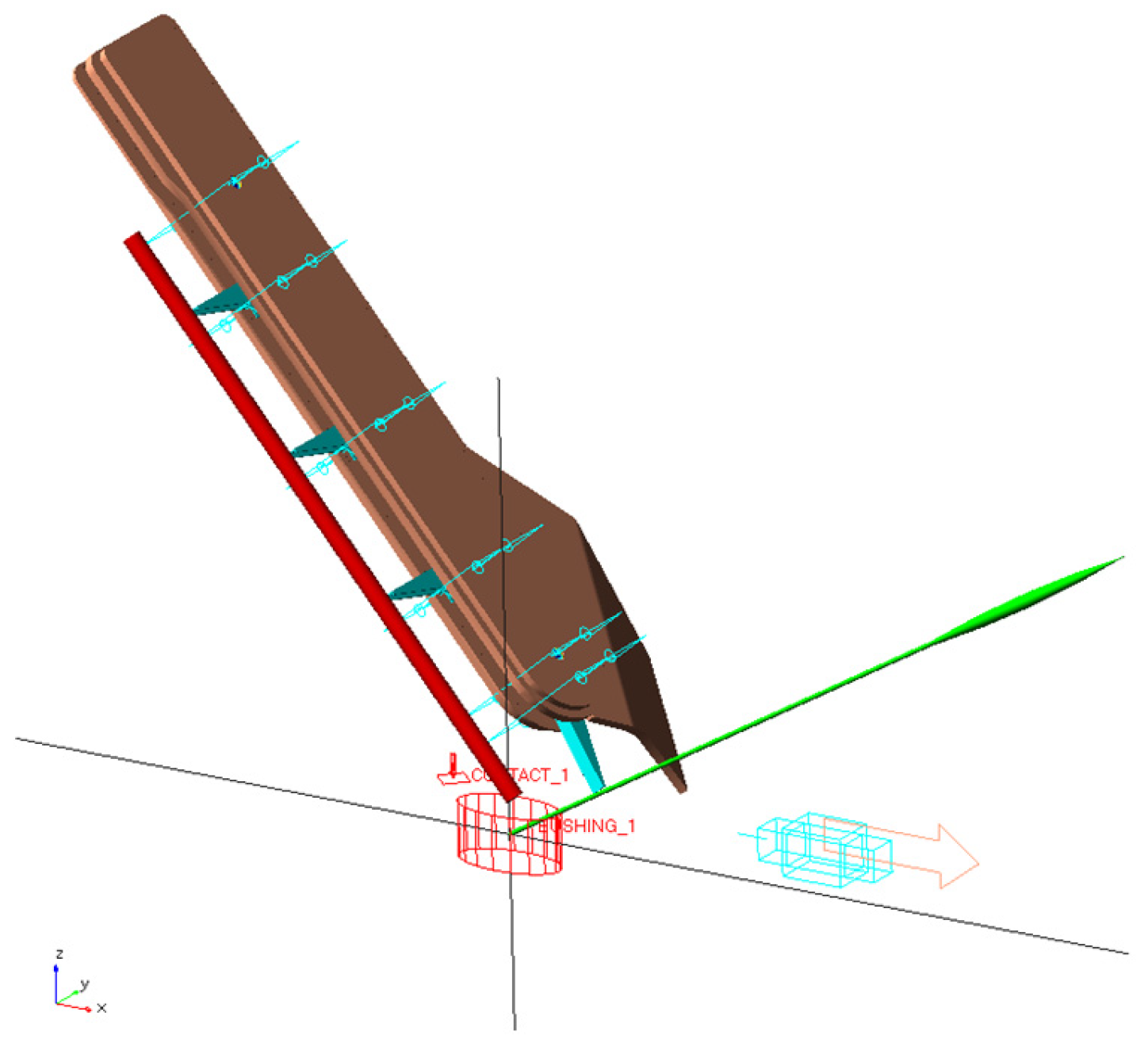
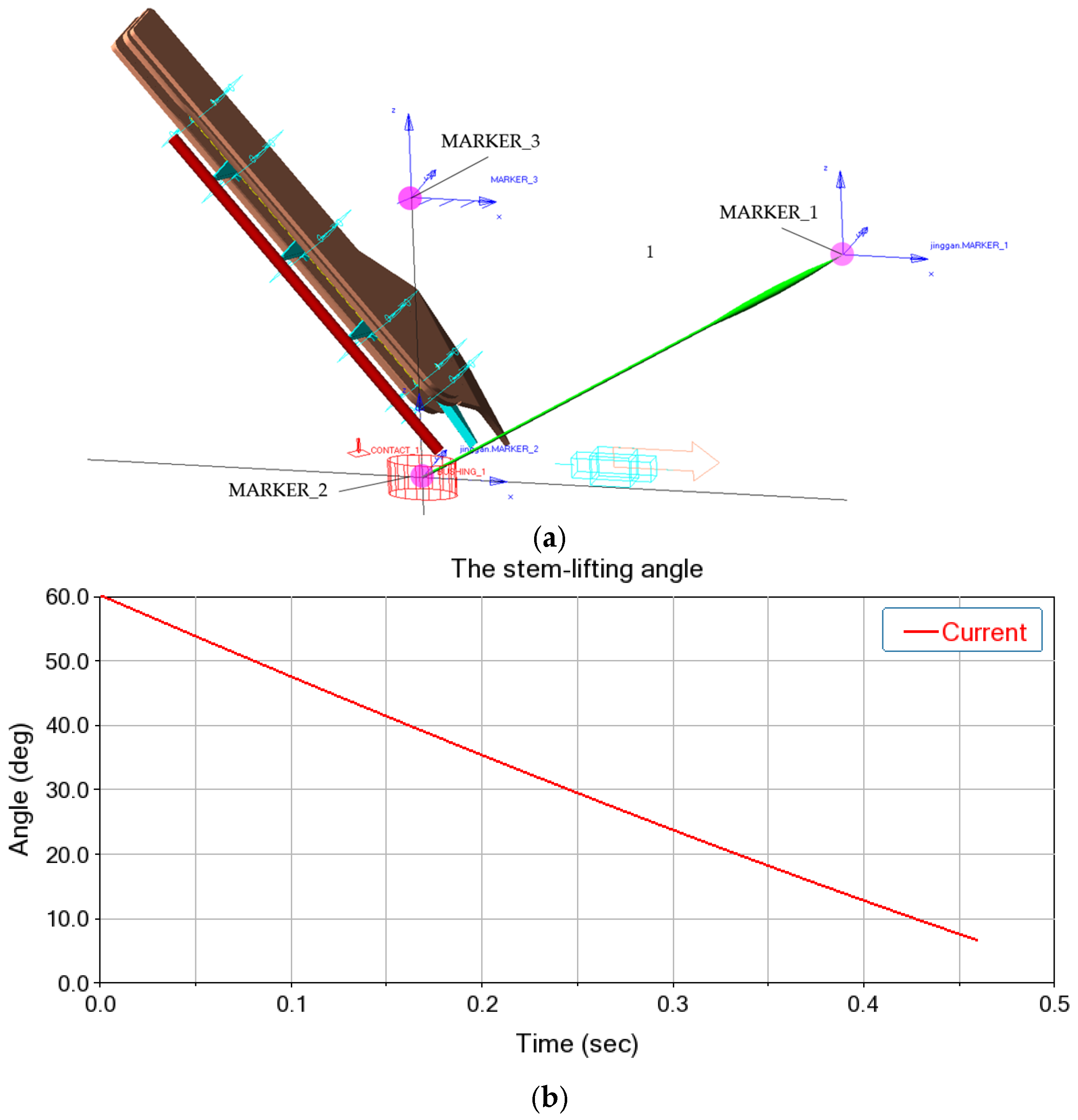
2.3. Dynamic Simulation Model of Header Stem-Lifting Mechanism
2.4. Box–Behnken Simulation Experimental Method
2.4.1. Experimental Factors and Levels
2.4.2. Evaluation Index
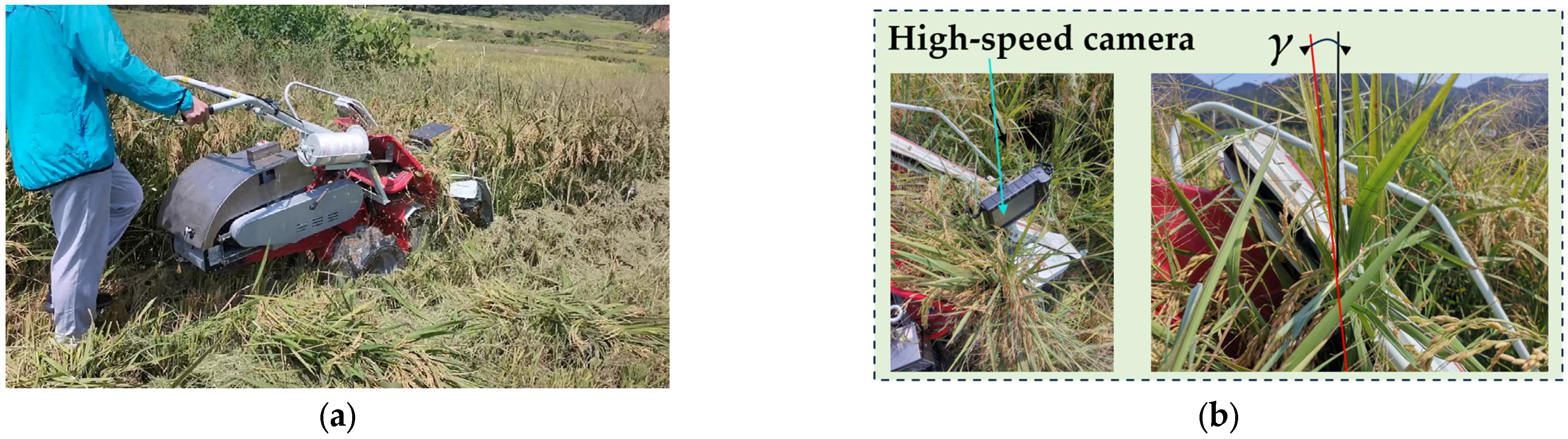
2.5. Field Experimental Method
3. Results
3.1. Regression Prediction Model for Lifting Performance
3.2. ANOVA Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Interaction Effects on Evaluation Index
4.2. Parameter Optimization
4.3. Field Experimental Results and Analysis
4.4. Improvement Directions
4.4.1. Comparative Analysis with Similar Studies
4.4.2. Limitations
4.4.3. Economic Evaluation and Engineering Application Prospects
5. Conclusions
- The theoretical analysis allowed us to identify the critical factors influencing stem-lifting performance, i.e., the stem-lifting speed ratio coefficient, the cutter installation position, and the header tilt angle, alongside their operational ranges. A multibody dynamic simulation model of the stem-lifting mechanism was developed by using the ADAMS platform, which enabled the visualization and analysis of the lifting process.
- A Box–Behnken experimental design was adopted to develop a regression model with the stem-lifting angle as the response variable, quantitatively correlating the operational parameters with performance. Notably, it can be seen from the p value in the analysis of variance table that the interaction between the cutter installation position and the header tilt angle showed no significant effect on the test index, whereas all other factors and interactions exhibited statistically significant impacts.
- Optimization based on response surface methodology yielded the optimal parameter combination, i.e., a stem-lifting speed ratio coefficient of 2.14, a cutter installation position of 258.79 mm, and a header tilt angle of 62.63°, achieving a theoretical stem-lifting angle of 2.36°. Field validation confirmed a measured stem-lifting angle of 2.44°, corresponding to a relative error of 3.39%. Concurrently, the harvesting loss rate was experimentally determined to be 0.59%, demonstrating a 49.6% reduction compared with pre-optimization levels. These outcomes verify the accuracy of the simulation model and the practical efficacy of the optimized header. The enhanced design not only fulfills operational requirements but also provides a viable technical solution for mechanized rice harvesting on hilly terrains, addressing critical challenges in regional agricultural productivity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| RSM | response surface methodology |
References
- Duppala, M.; Srinivas, T.; Rao, L.V.S.; Suneetha, Y.; Sundaram, R.M.; Prasannakumari, V.; Satyanaryana, P.V.; Abdulfiyaz, R.; Raveendra, C.H.; Singh, G. Marker-Assisted Pedigree Breeding to Enhance Resistance Against Bacterial Blight, Blast, And Tolerance to Low Soil Phosphorus in the Indian Elite Rice Cultivar Mtu1121. Cereal Res. Commun. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Deere. John Deere China Official Home Page. Available online: https://www.deere.com.cn/zh/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- CLAAS. CLAAS Group China Official Home Page. Available online: https://www.claas.com/zh-cn/agricultural-machinery/combines (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Case IH. Case IH (China) Co., Ltd. Official Home Page. Available online: https://www.caseih-china.cn/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Hu, B.; Wang, R. Structural Parameter Optimization of Combine Harvester Cutting Bench. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter, D.C.; Giles, D.K.; Downey, D. Autonomous Robotic Weed Control Systems: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 61, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashi, F. Collision Vibration Characteristics with Interspace in Knife Driving System of Combine Harvester. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2012, 5, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, J.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, L. Structural Design and Testing of a Corn Header for Soybean–Corn Intercropping. Agriculture 2025, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Dai, F.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Pan, H.; Chen, J. Analysis of the Anti-Winding Mechanism for the Interaction Between Flax Stem and Harvest Header in Hilly Area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, C.; Zong, W.; Huang, X.; Ma, L.; Lian, G. Optimization of Clamping and Conveying Device for Sunflower Oil Combine Harvester Header. Agriculture 2021, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Jin, C.; Zhang, F.; Kang, D.; Hu, M. Design and Experiment of 4LZG-3.0 Millet Combine Harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, W.; Rong, K.; Hong, H.; Zhang, G. Development and Testing of the Adaptive Control System for Profiling Grain Header. Agriculture 2025, 15, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liao, Z.; Shi, S.; Dai, J.; Yuan, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z. Design and Testing of a 2-DOF Adaptive Profiling Header for Forage Harvesters. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, S.; Jia, H.; Qu, M.; Xiang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Zou, Z. Design and Experiment of Header Height Adaptive Adjustment System for Maize (Zeamays L.) Harvester. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Li, K.; Hu, Y.; Pan, B.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Q.; Tang, Z. Design and Experimentation of the Millet Combine Harvester Header. Machines 2024, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawatharani, R.; Bandara, M.; Senevirathne, D. Influence of Cutting Height and Forward Speed on Header Losses in Rice Harvesting. Int. J. Agric. For. Plant. 2016, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zareei, S.; Pour, S.A.; Moghaddam, M.; Sahrayan, H. Optimum Setting of Combine Header for Wheat Harvesting Using Taguchi Method. Res. Crop. 2012, 13, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Leis, K.; Zeng, Z. Retrofitting and Testing of a Pull-Type Small-Grain Combine Harvester. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zeng, S.; Chen, X. Vortex Cleaning Device for Rice Harvester: Design and Bench Test. Agriculture 2024, 14, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y. Dynamic load distribution property of transmission system during rice harvesting process. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2024, 16, 16878132231224175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Sun, W.; Yang, R. Simulation and Optimization of a Self-Cleaning Device for the Header of a Rice Seed Harvester Using Fluent–EDEM Coupling. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zeng, S.; Chen, X. Design and Experiment of Adaptive Profiling Header Based on Multi-Body Dynamics–Discrete Element Method Coupling. Agriculture 2024, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Liao, Q.; Wan, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L.; Liao, Y. Design and Experiment of Self-propelled Six-row Harvester for Oilseed Rape Shoot. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- China Academy of Agricultural Mechanization Sciences (Ed.) Agricultural Machinery Design Manual (Lower Volume); China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 877–1028. ISBN 978-7-80233-335-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y. Design and Test of Boat-Type Harvesting Platform for Deep-Water Paddy Field. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X. The Design of Small Wheat and Cereal Grain Combine Harvester and Baler. Agric. Technol. Equip. 2021, 13–14+17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. (Ed.) Agricultural Mechanics; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 155–195. ISBN 7-109-08403-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Dun, G. Optimization of Parameters for Soybean Lifter Based on Dynamic Simulation of Virtual Prototype. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; He, J.; Fang, D.; Du, X.; Xu, F. Dynamic Simulation Test and Analysis of Cerasus humilis Lifting Branches Based on ADAMS. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 10, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Yang, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Liao, Q.; Ren, W. Design and Experiment of Seed Hill-seeding Centralized Metering Device for Rapeseed. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C. Research and Experiment on the Stripping Mechanism of Concave Combs and Increasing Flow Header for Stripping Prior to Cutting. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, H.; Du, J.; Zheng, K.; Li, Y. Calibration and Verification of Flexible Rice Straw Model by Discrete Element Method. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 174–184. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 24686-2009; Rice Reaper and Binder. Standardization Admi-nistration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2009.
- NY/T 498-2013; Combine Harvester—Operating Quality. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Xin, S.; Zhao, W.; Shi, L.; Dai, F.; Feng, B.; Yan, Z.B.; Lv, D.Y. Design and Experiments of the Clamping and Conveying Device for the Vertical Roller Type Corn Harvesting Header. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 34–43. [Google Scholar]




| Name | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rice stem | Poisson’s ratio | 0.4 |
| Elastic modulus (Mpa) | 320 | |
| Density (kg/m3) | 222 | |
| Steel | Poisson’s ratio | 0.29 |
| Elastic modulus (Mpa) | 2.06 × 108 | |
| Density (kg/m3) | 7800 | |
| ABS | Poisson’s ratio | 0.394 |
| Elastic modulus (Mpa) | 200 | |
| Density (kg/m3) | 1060 | |
| Rice stem–steel contact coefficient | Static friction coefficient | 0.46 |
| Rolling friction coefficient | 0.03 | |
| Rice stem–ABS contact coefficient | Static friction coefficient | 0.41 |
| Rolling friction coefficient | 0.3 |
| Horizontal Coded Value | Stem-Lifting Speed Ratio Coefficient, kb | Cutter Installation Position, e (mm) | Header Tilt Angle, α (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 1.56 | 230 | 50 |
| 0 | 1.85 | 265 | 60 |
| 1 | 2.14 | 300 | 70 |
| Test No. | kb | e (mm) | α (°) | γ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.56 | 230 | 60 | 11.239 |
| 2 | 2.14 | 230 | 60 | 3.478 |
| 3 | 1.56 | 300 | 60 | 7.565 |
| 4 | 2.14 | 300 | 60 | 4.836 |
| 5 | 1.56 | 265 | 50 | 6.153 |
| 6 | 2.14 | 265 | 50 | 7.653 |
| 7 | 1.56 | 265 | 70 | 14.003 |
| 8 | 2.14 | 265 | 70 | 5.458 |
| 9 | 1.85 | 230 | 50 | 6.43 |
| 10 | 1.85 | 300 | 50 | 5.871 |
| 11 | 1.85 | 230 | 70 | 10.669 |
| 12 | 1.85 | 300 | 70 | 8.552 |
| 13 | 1.85 | 265 | 60 | 2.011 |
| 14 | 1.85 | 265 | 60 | 1.934 |
| 15 | 1.85 | 265 | 60 | 2.443 |
| 16 | 1.85 | 265 | 60 | 2.653 |
| 17 | 1.85 | 265 | 60 | 1.848 |
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 204.53 | 9 | 22.73 | 72.58 | <0.0001 ** |
| kb | 38.43 | 1 | 38.43 | 122.74 | <0.0001 ** |
| e | 3.12 | 1 | 3.12 | 9.95 | 0.0161 * |
| α | 19.77 | 1 | 19.77 | 63.13 | <0.0001 ** |
| kbe | 6.33 | 1 | 6.33 | 20.22 | 0.0028 ** |
| kbα | 25.23 | 1 | 25.23 | 80.56 | <0.0001 ** |
| eα | 0.6068 | 1 | 0.6068 | 1.94 | 0.2065 |
| kb2 | 26.72 | 1 | 26.72 | 85.32 | <0.0001 ** |
| e2 | 18.26 | 1 | 18.26 | 58.33 | 0.0001 ** |
| α2 | 55.18 | 1 | 55.18 | 176.21 | <0.0001 ** |
| Residual | 2.19 | 7 | 0.3131 | ||
| Lack of fit | 1.7 | 3 | 0.5666 | 4.6 | 0.0871 |
| Error | 0.4922 | 4 | 0.123 | ||
| Total | 206.72 | 16 |
| Test Number | Optimized Theoretical Value (°) | Experimental Value (°) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.51 | 6.36 | |
| 2 | 2.47 | 4.66 | |
| 3 | 2.36 | 2.28 | 3.39 |
| 4 | 2.38 | 0.85 | |
| 5 | 2.56 | 8.47 | |
| Average value | 2.36 | 2.44 | 3.39 |
| No. | Mass Loss Per Square Meter, Wq1 (g) | Natural Shedding Mass, Wz1 (g) | Rice Mass Per Square Meter, Wd (g) | Harvesting Loss Rate, Ws1 (%) | Pre-Improvement Field Trial Results (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.15 | 913.57 | 0.55 | ||
| 2 | 9.37 | 3.12 | 909.49 | 0.69 | 1.17 |
| 3 | 7.91 | 911.92 | 0.53 | ||
| Average value | 8.48 | 3.12 | 911.66 | 0.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Bao, D.; Liang, Z.; Yan, C.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Zheng, S. Parameter Optimization Design and Experimental Validation of a Header for Electric Rice Reaper Binders Employed in Hilly Regions. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121242
Ren J, Bao D, Liang Z, Yan C, Wu J, Wu X, Zheng S. Parameter Optimization Design and Experimental Validation of a Header for Electric Rice Reaper Binders Employed in Hilly Regions. Agriculture. 2025; 15(12):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121242
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jinbo, Difa Bao, Zhi Liang, Chongsheng Yan, Junbo Wu, Xinhui Wu, and Shuhe Zheng. 2025. "Parameter Optimization Design and Experimental Validation of a Header for Electric Rice Reaper Binders Employed in Hilly Regions" Agriculture 15, no. 12: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121242
APA StyleRen, J., Bao, D., Liang, Z., Yan, C., Wu, J., Wu, X., & Zheng, S. (2025). Parameter Optimization Design and Experimental Validation of a Header for Electric Rice Reaper Binders Employed in Hilly Regions. Agriculture, 15(12), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121242





