Abstract
This study aims to improve the performance of wood–plastic composites (WPCs) composed of cotton stalk powder and residual film particles. Additionally, it aims to promote the efficient utilization of cotton stalk biochar. The composites were prepared using modified cotton stalk biochar and xylem powder as the matrix, maleic anhydride grafted high-density polyethylene (MA-HDPE) as the coupling agent, and polyethylene (PE) residual film particles as the filler. The WPCs were fabricated through melt blending using a twin-screw extruder. Mechanical properties were evaluated using a universal testing machine and texture analyzer, Shore D hardness was measured using a durometer, and microstructure was analyzed using a high-resolution digital optical microscope. A systematic investigation was conducted on the effect of biochar content on material properties. The results indicated that modified biochar significantly enhanced the mechanical and thermal properties of the WPCs. At a biochar content of 80%, the material achieved optimal performance, with a hardness of 57.625 HD, a bending strength of 463.159 MPa, and a tensile strength of 13.288 MPa. Additionally, thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity decreased to 0.174 W/(m·K) and 0.220 mm2/s, respectively, indicating improved thermal insulation properties. This research provides a novel approach for the high-value utilization of cotton stalks and residual films, offering a potential solution to reduce agricultural waste pollution in Xinjiang and contributing to the development of low-cost and high-performance WPCs with wide-ranging applications.
1. Introduction
Biochar, a low-cost porous material, has recently shown great potential for improving the mechanical and thermophysical properties of WPCs [1]. Compared with natural fibers, biochar loses some polar functional groups during high-temperature pyrolysis, reducing its polarity. This property enhances interfacial adhesion between wood flour and non-polar plastics such as polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP), thus improving the overall performance of WPCs [2]. Extensive research has been conducted globally to explore the application potential and optimization strategies of biochar in WPCs. For instance, Pudełko et al. [3] incorporated biochar into polylactic acid composites, significantly improving water absorption, hardness, and thermomechanical properties. Similarly, Das et al. [4] demonstrated that biochar reinforcement effectively enhanced the mechanical strength of lignocellulosic polymer composites. Collectively, these studies highlight biochar as a cost-effective and high-performance reinforcing agent for WPCs.
Cotton stalk (CS) is an essential renewable biomass resource with important implications for sustainable agriculture and carbon emission reduction. According to the International Cotton Advisory Committee (ICAC), global cotton production is expected to reach 25.26 million tons in 2024, a 4.7% increase from the previous year, corresponding to an estimated cotton stalk output of approximately 126 million tons [5]. In China, a major cotton-producing region, cotton production is expected to reach 6.36 million tons in 2024, resulting in an estimated cotton stalk output of 31.8 million tons, with Xinjiang accounting for about 94% of national cotton production [6,7]. As cotton cultivation expands, cotton stalk production continues to rise, making it an important agricultural waste resource. However, the resource utilization of cotton stalks faces numerous challenges. Currently, cotton stalks are mostly shredded and returned to the field or burned. However, their high fiber content often causes pest and disease issues after shredding [8]. Additionally, burning cotton stalks not only wastes resources but also contributes significantly to air and environmental pollution [9]. In recent years, introducing cotton stalk biochar into WPCs has effectively improved the material’s mechanical strength and thermal stability, providing new solutions for the high-value utilization of cotton stalks [10,11].
In Xinjiang, large-scale plastic film mulching technology has improved crop yields and growth rates to some extent, but the low recycling rate of polyethylene (PE) plastic films has resulted in serious “white pollution” [12,13,14,15]. Statistics show that Xinjiang generates 255,000 tons of waste residual film annually, with an average residual film amount of about 3798 kg per hectare, and it can reach up to 5716.5 kg [16,17]. PE plastic films are difficult to degrade naturally and pose potential threats to crop growth, soil ecology, and the human environment [18,19]. Currently, the plastic pellets recovered from residual films are generally characterized by poor mechanical properties, complex processing, and low economic benefits, leading to insufficient enthusiasm among recycling enterprises and difficulty in effectively curbing residual film pollution [20]. Although current PE residual film recycling technologies face challenges, research indicates that using waste films as fillers in WPCs has significant research value and application prospects. Particularly, optimizing interface bonding and performance enhancement could provide new pathways for resource utilization.
Although prior studies have explored cotton stalk biochar in WPCs, the synergistic use of cotton stalks and PE residual films—particularly in enhancing interfacial bonding and optimizing composite performance via modified biochar—remains underexplored. This study introduces modified cotton stalk biochar and PE residual film particles into the WPC system to develop composites with superior mechanical and thermal properties. By optimizing the formulation and processing conditions, the overall performance is significantly enhanced. This research offers a novel approach for high-value utilization of cotton stalks and PE films, addressing agricultural waste and film pollution in Xinjiang and promoting resource recycling and environmental protection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Equipment
In this study, “Tarim-2” cotton stalks were collected from the 11th Regiment Farm in Alar City, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China, and air-dried under natural conditions after harvesting. Waste PE residual films were collected from the 12th Regiment Farm in the same city. The recycled residual films were cleaned to remove impurities and then dried. MA-HDPE was purchased from Dongguan Shanyi Plastics Co., Ltd. (Dongguan, China). The KH570 silane coupling agent was supplied by Zhengzhou Yaying Chemical Products Co., Ltd. (Zhengzhou, China). Anhydrous ethanol (99.9% purity) was obtained from Lianyungang Letong Chemical Trading Co., Ltd. (Lianyungang, China).
Various instruments were employed throughout the preparation and characterization of the cotton stalk-based composites. A KRD-SX3-15-13 muffle furnace (Shandong Keruida Electric Furnace Co., Ltd., Jinan, China; max. 1000 °C, ±2 °C accuracy) was used for biochar preparation. Microstructural features were analyzed using a JT-200A high-resolution digital optical microscope (Shenzhen Jingtuo Youcheng Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China; 130× magnification). Mechanical properties such as compressive and flexural strengths were measured using a TMS-PRO texture analyzer (Beijing Yingsheng Hengtai Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), while a PT-307A gantry universal material testing machine (Guangdong Dongguan Beidou Instrument Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China) was used for tensile testing. Additional equipment included a PT-412S-72B high-temperature aging chamber (Guangdong Dongguan Beidou Instrument Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China) for material preprocessing and a CA200 contact angle meter (Guangdong Dongguan Beidou Instrument Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China) for surface wettability analysis. Composite hardness was assessed using a type D Shore durometer (Deqing Shengtai Xin Electronics Co., Ltd., Huzhou, China). For composite fabrication, a crusher (Guangdong Dongguan JiuTong Machinery Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China), SHR5L high-speed mixer (Guangdong Dongguan JiuTong Machinery Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China), and SZ20 conical twin-screw extruder (Guangdong Dongguan JiuTong Machinery Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China) were employed. Finally, thermal conductivity was evaluated using an HNB-DRS2 tester (Xiamen Senbei Technology Co., Ltd., Xiamen, China).
2.2. Preparation and Pretreatment of Cotton Stalk Biochar
2.2.1. Preparation and Testing of Cotton Stalk Biochar at Different Temperatures
Cotton stalks were initially cleaned, naturally air-dried, then cut into 40–60 mm segments and oven-dried at 105 °C to a constant weight for moisture removal. Their physicochemical properties were subsequently analyzed. The cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin contents were determined via the Van Soest method using an ANKOM DELTA fiber analyzer (Model: DELTAJ; ANKOM Technology, Macedon, NY, USA). Total nitrogen was measured using the Kjeldahl method after H2SO4–H2O2 digestion, while total potassium and phosphorus were determined by flame photometry and UV spectrophotometry, respectively, following the same digestion. The chemical properties and nutrients of the cotton stalks are shown in Table 1 [21,22].

Table 1.
The chemical properties and nutrients of cotton stalks.
Fifty grams of dried cotton stalk segments was accurately weighed and placed into a sealed iron container. Prior to sealing, the cotton stalks were manually compacted to increase material density and minimize the presence of oxygen within the container, thereby establishing a low-oxygen environment conducive to pyrolysis. To further reduce oxygen ingress, three layers of aluminum foil were laid along the interior walls of the iron container. Additionally, the container opening was sealed with aluminum foil and tightly secured with iron wire.
The biochar resulting from pyrolysis at 250 °C and 300 °C was insufficiently carbonized, potentially affecting measurements. Thus, only samples from 350–600 °C pyrolysis were analyzed further. The carbon yields for the CS350, CS400, CS450, CS500, CS550, and CS600 biochars were 39.9%, 42.4%, 40.4%, 35.8%, 33.1%, and 32.6%, respectively, with the highest yield obtained at 400 °C. Yield declined at higher temperatures due to devolatilization, consistent with Afif et al. [23].
The compressive strength of the biochar samples was evaluated using a TMS-PRO texture analyzer. As presented in Table 2, the CS350 biochar exhibited the highest mechanical performance, with average longitudinal and transverse compressive strengths of 1.879 MPa and 1.479 MPa, respectively, based on three independent trials. Although the CS400 biochar achieved the highest carbon yield, its compressive strength was lower than that of the CS350 biochar. To confirm the statistical significance of these differences, Tukey’s honest significant difference (HSD) test was conducted. The results indicated that the compressive strength of the CS350 biochar was significantly greater than that of the other samples (p < 0.05), validating its selection as the optimal reinforcement material. Taking into account both pyrolysis efficiency and mechanical properties, the CS350 biochar was selected for use in the subsequent fabrication of wood–plastic composites.

Table 2.
Compressive strength of six groups of cotton stalk charcoal.
2.2.2. Modification and Pretreatment of CS350 Cotton Stalk Biochar
To improve interfacial compatibility with the polymer matrix, the CS350 biochar was modified using KH570 silane coupling agent [23]. KH570 enhances adhesion while preserving the biochar’s structure [24,25]. A solution containing 20% KH570, 70% anhydrous ethanol, and 10% distilled water was prepared. The biochar was immersed and stirred in a 30 °C water bath for 12 h, and then filtered and washed with anhydrous ethanol to remove residual reagents.
The modified biochar was dried at 45 °C for 4.5 h and ground into 60 mesh powder, producing hydrophobic, surface-modified biochar. The modification process is shown in Figure 1.
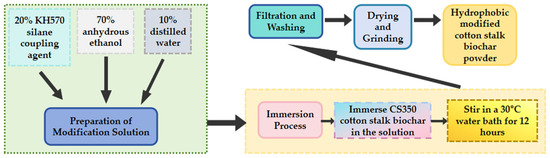
Figure 1.
The process flow of cotton stalk biochar modification.
2.3. Pretreatment of Cotton Stalks, Residual Films, and Composite Material Preparation
The mechanical properties of wood–plastic composites (WPCs) depend largely on the strength of the plant fibers, the plastic matrix, and their interfacial bonding [26]. Cotton stalks, rich in cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, offer excellent reinforcement potential. Among their components, the xylem—with its higher lignin content—provides superior mechanical strength and antioxidant capacity, enhancing rigidity and compressive resistance [27]. Therefore, cotton stalk xylem was selected as the matrix material for this study, as its composition is better suited to improving composite durability and strength compared to the whole stalk, which includes lower-lignin tissues such as the phloem.
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), commonly used in Xinjiang for agricultural films [28,29], was chosen as the filler due to its excellent thermal insulation properties [30,31].
2.3.1. Pretreatment of Cotton Stalks and Preparation of Residual Film Particles
Cotton stalks were washed to remove surface dust and soil, and then air-dried naturally. After removing the phloem and pith, the xylem was retained, cut into ~50 mm segments, and oven-dried at 105 °C to a constant weight. The dried xylem was ground with a high-speed pulverizer and sieved to 60 mesh to obtain fine powder.
Due to prolonged field exposure, residual plastic films often carry soil and impurities, which can compromise composite performance. Thus, thorough cleaning and decontamination were conducted, followed by air-drying. The cleaned film was heat-treated at 185 °C for 1.5 h in a thermal aging chamber, water-cooled, pressed into sheets, and pulverized into fine particles. The pretreatment procedures for cotton stalks and residual film are shown in Figure 2.
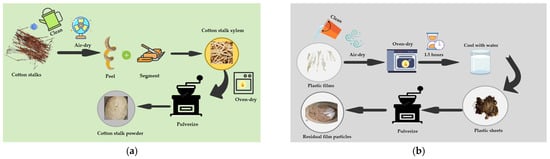
Figure 2.
Pretreatment of cotton stalks and preparation of residual film particles. Note: (a) Preparation workflow of cotton stalk xylem powder. (b) Preparation workflow of residual film particles.
2.3.2. Preparation of Composite Boards
In this study, cotton stalk xylem powder and modified cotton stalk biochar powder were blended to form a matrix, which was then combined with polyethylene (PE) residual film particles and maleic anhydride grafted high-density polyethylene (MA-HDPE) to fabricate wood–plastic composite (WPC) boards. To assess the effect of biochar content on composite properties, six groups were prepared with biochar proportions of 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% in the mixed wood powder (Table 3). The mixed wood powder, residual film particles, and MA-HDPE were combined at a mass ratio of 46%:50%:4% and uniformly mixed. The experimental procedure is shown in Figure 3a.

Table 3.
Material Formulation of Six Groups of Wood–Plastic Panels.
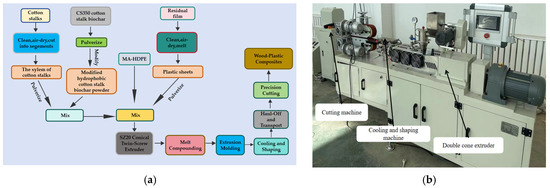
Figure 3.
(a) Experimental workflow for the preparation of wood–plastic composites. (b) The SZ20 conical twin-screw extruder in wood–plastic composite fabrication. Note: The SZ20 conical twin-screw extruder (operating temperature 150–180 °C) is used for feeding, melt blending, extrusion molding, and cooling of wood–plastic composites.
The blended materials were first mixed in a high-speed mixer at 160 °C for 6 min, and then cooled and fed into a preheated SZ20 conical twin-screw extruder. The main machine, feeding, and drawing frequencies were set to 19 Hz, 4 Hz, and 5 Hz, respectively. Die zone temperatures were maintained at 175 °C (Zone 1) and 165 °C (Zone 2), while barrel zone temperatures were set at 170 °C (Feeding), 180 °C (Melting), and 175 °C (Metering) to ensure optimal extrusion conditions.
Figure 3b shows the SZ20 conical twin-screw extruder used for fabricating wood–plastic composite (WPC) boards. The process includes: (1) feeding the blended material into the extruder for melt compounding and extrusion through an 80 mm × 3 mm flat die to form continuous boards; (2) cooling and shaping via water-cooled steel plates before traction; and (3) precision cutting to the required dimensions. Six groups of WPC boards were prepared using this method, as shown in Figure 4.
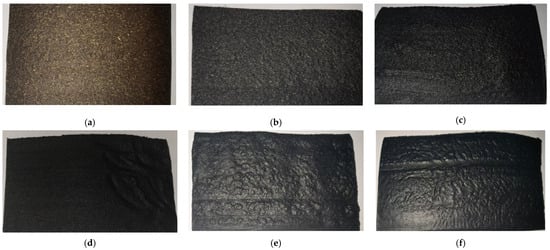
Figure 4.
Physical images of six groups of wood–plastic panels. Note: (a) 0% charcoal wood–plastic panels. (b) 20% charcoal wood–plastic panels. (c) 40% charcoal wood–plastic panels. (d) 60% charcoal wood–plastic panels. (e) 80% charcoal wood–plastic panels. (f) 100% charcoal wood–plastic panels.
2.4. Performance Testing and Characterization of Wood–Plastic Composites
To comprehensively evaluate the cotton stalk-residual film wood–plastic composite boards, this study tested their density, microstructure, wettability, water absorption, mechanical properties, thermal properties, and hardness. An overview of the measurement methods and standards is provided below.
2.4.1. Density Measurement
Samples measuring 3 mm × 10 mm × 80 mm were cut from the boards, weighed, and the density was calculated using Equation (1). Five parallel tests were performed for each group, and the average value was reported.
where ρ is the density (g/cm3); m is the mass (g); and a, b, and h are the length, width, and height (mm), respectively.
2.4.2. Microstructure Observation
The surface morphology of cotton stalk biochar and WPC boards was observed using a JT-200A high-resolution digital optical microscope. With suitable magnification, brightness, and contrast, the microstructures of six board groups were recorded, and samples carbonized at different temperatures were comparatively analyzed.
2.4.3. Contact Angle and Surface Energy Measurement
The six types of boards were cut into thin slices measuring 10 mm × 10 mm × 2 mm. The contact angle was measured using a CA200 research-type optical contact angle meter (23 °C, relative humidity 55%), and the surface energy was subsequently calculated.
2.4.4. Water Absorption Measurement
The water absorption test was conducted in accordance with the national standard for wood–plastic flooring, GB/T 24508-2020 Wood–Plastic Flooring [32]. The water absorption rate was calculated at regular intervals using Equation (2):
where X is the water absorption rate (%), m0 is the initial mass (g), and mt is the mass after immersion (g).
2.4.5. Tensile Strength Test
The tensile strength was tested according to GB/T 1040.1-2018 [33] using a PT-307A gantry-type universal testing machine. Three defect-free samples were tested for each group, and the average value was reported.
2.4.6. Bending Performance Test
The three-point bending performance of the composite materials was tested according to GB/T 9341-2008 [34] using a TMS-PRO texture analyzer. Three specimens were tested for each group, and the average value was reported.
2.4.7. Thermal Physical Property Parameter Measurement
Samples with a diameter of 30 mm, a thickness of 2 mm, and a smooth surface were placed in the HNB-DRS2 thermal conductivity tester. The thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity were measured at an ambient temperature of 25 °C.
2.4.8. Hardness Measurement
Smooth-surfaced board samples were prepared, and the hardness was measured by applying a vertical pressure using a Shore D durometer. The value was recorded once the needle stabilized. Each group was tested three times, and the average value was taken.
Besides, Origin 2024 (Origin Lab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA) was used to process the experimental data. This software facilitated curve fitting, statistical analysis, and graphical visualization, ensuring accurate interpretation and clear presentation of the results.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Density Analysis
Figure 5 shows the density variation of the wood–plastic composites (WPCs) with increasing cotton stalk biochar (CSB) content from 0% to 100%. The densities at 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% CSB were 0.883 ± 0.032, 0.91 ± 0.061, 1.03 ± 0.046, 1.13 ± 0.026, 1.31 ± 0.066, and 1.29 ± 0.085 g/cm3, respectively (n = 5 per group). A continuous increase was observed up to 80% CSB, followed by a slight decrease at 100%. This trend was primarily attributed to synergistic interfacial interactions between CSB and the polymer matrix (PE residual film, MA-HDPE, and cotton stalk xylem powder), where physical adsorption (e.g., van der Waals forces) and chemical bonding (e.g., hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl and carboxyl groups) restricted polymer chain mobility and reduced the free volume, thereby enhancing density [35,36]. Additionally, the microporous structure of CSB (Figure 6 and Figure 7) contributed to void filling and matrix compaction [10]. However, excessive CSB content (100%) led to particle agglomeration (10–50 μm, Figure 7f), weakened interfacial adhesion and increasing porosity (Figure 6f), resulting in a slight density decline. One-way ANOVA confirmed a statistically significant difference between the 80% and 100% groups (p < 0.05), aligning with Patti et al. [37], who emphasized the importance of uniform filler dispersion in maintaining composite density.
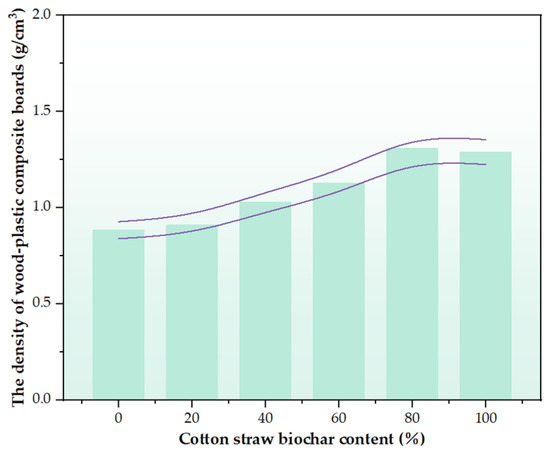
Figure 5.
Experimental results of density testing of six groups of wood–plastic panels.
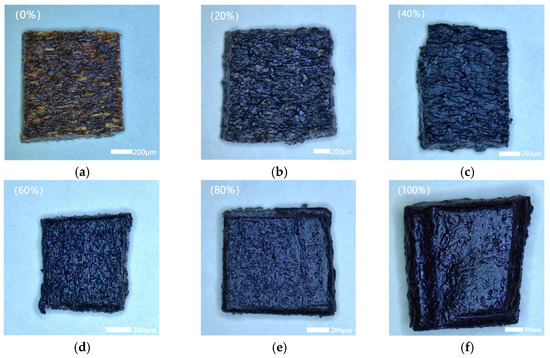
Figure 6.
Surface microstructures of wood–plastic composites with different cotton stalk biochar contents at 50× magnification. Note: (a) 0% cotton stalk biochar. (b) 20% cotton stalk biochar. (c) 40% cotton stalk biochar. (d) 60% cotton stalk biochar. (e) 80% cotton stalk biochar. (f) 100% cotton stalk biochar.
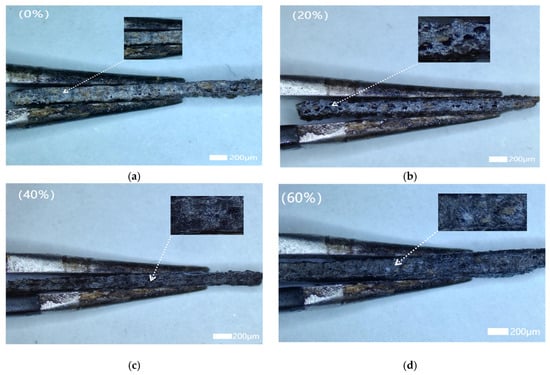
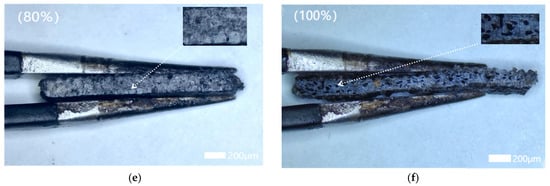
Figure 7.
Cross-sectional microstructures of wood–plastic composites with different cotton stalk biochar contents at 50× magnification. Note: (a) 0% cotton stalk biochar. (b) 20% cotton stalk biochar. (c) 40% cotton stalk biochar. (d) 60% cotton stalk biochar. (e) 80% cotton stalk biochar. (f) 100% cotton stalk biochar.
3.2. Surface Microstructure of Wood–Plastic Composites
Figure 6 and Figure 7 illustrate the surface and cross-sectional microstructures of the composites with varying modified cotton stalk biochar (CSB) contents. As CSB increased from 0% to 100%, the surface color transitioned from brown to black, reflecting progressive CSB integration. At low CSB levels (0–20%), exposed wood fibers dominated, resulting in rough surfaces due to incomplete particle coverage. Optimal CSB content (40–80%) yielded smoother surfaces through uniform dispersion and effective pore filling, while 100% CSB induced particle agglomeration and localized roughness. Cross-sectional analysis revealed compact structures with minimal pores for the 0%, 60%, and 80% CSB groups, correlating with enhanced density (1.31 ± 0.066 g/cm3 at 80% CSB) and peak hardness (57.625 HD). Conversely, the 20% and 100% CSB samples exhibited larger voids and loose structures (density: 1.29 ± 0.085 g/cm3 at 100% CSB), suggesting that excessive CSB content led to uneven particle dispersion and weak interfacial bonding, resulting in increased porosity and deterioration of water resistance and mechanical strength [38].
Structural variations induced by different CSB contents directly impacted composite functionality. Within the 40–80% CSB range, well-dispersed particles strengthened interfacial interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonding between CSB and matrix components), reduced porosity, and enhanced hydrophobicity, thereby improving water resistance and mechanical strength. By contrast, insufficient (0–20%) or excessive (100%) CSB disrupted particle–matrix compatibility, resulting in pore formation or particle agglomeration that increased water absorption and weakened structural integrity. These results underscore the critical importance of controlling the CSB content and dispersion to achieve optimal density, low water uptake, and superior mechanical performance. The composites containing 40–80% CSB demonstrated a favorable balance of structural compactness and durability, making them well suited for moisture-prone agricultural applications. This work offers valuable insights for designing sustainable wood–plastic composites with enhanced performance in humid environments.
3.3. Hardness Analysis of WPCs
Figure 8 presents the effect of modified cotton stalk biochar (CSB) content on the Shore D hardness of the wood–plastic composite boards made from cotton stalk and residual film particles. The Shore D hardness values at CSB contents of 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% were 46.875 ± 2.25 HD, 47.375 ± 4.31 HD, 51.125 ± 2.78 HD, 51.750 ± 2.96 HD, 57.625 ± 3.22 HD, and 54.875 ± 3.61 HD, respectively (n = 3 per group). Hardness increased steadily up to 80% CSB, peaking at 57.625 HD, before slightly decreasing to 54.875 HD at 100% CSB. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated a statistically significant difference in hardness between the 80% CSB group (57.625 HD) and the 100% CSB group (54.875 HD) (p < 0.05).
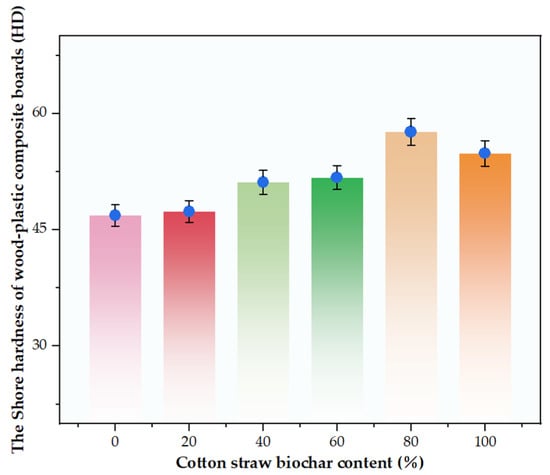
Figure 8.
Shore hardness of six groups of wood–plastic panels.
The change in Shore D hardness of the composite materials was mainly regulated by the effect of CSB content on the interface interaction. In the 0–80% CSB range, hydrogen bonding between CSB-OH and MA-HDPE-COOH groups, combined with mechanical interlocking and coupling effects, effectively restricted molecular chain mobility and improved stress transfer [39,40]. However, at 100% CSB, agglomeration (Figure 7f) formed 10–50 μm loose regions (arrows), weakening interfacial bonding and increasing porosity—consistent with the literature on filler dispersion effects [41]. Although controlled particle size (60 mesh, ~45 μm) and optimized mixing (160 °C, 6 min) reduced dispersion variability, local porosity and cutting direction still led to ±1.5 HD fluctuations. Overall, 60–80% CSB yielded the best hardness via chemical–mechanical synergy, while higher contents compromised performance. Thus, for agricultural applications demanding durable materials, the CSB content should remain below 80% to ensure uniform dispersion and interfacial integrity.
3.4. Water Absorption Analysis of Wood–Plastic Materials
Figure 9a demonstrates that the water absorption behavior of the wood–plastic composites (WPCs) was strongly influenced by the content of modified cotton stalk biochar (CSB). At low CSB contents (0% to 20%), water uptake increased progressively over time, reaching 1.84% (0% CSB) and 2.44% (20% CSB) after 120 h. This behavior was primarily attributed to insufficient pore filling and weak interfacial bonding, which resulted in microstructural defects that facilitated capillary-driven moisture ingress along the filler–matrix interface [42]. Although a slight increase in density was observed (from 0.883 to 0.910 g/cm3), the overall packing efficiency remained suboptimal relative to the added filler amount. This was further supported by the nearly unchanged Shore D hardness values (46.9 to 47.4 HD), indicating limited improvements in interfacial adhesion and mechanical integration. As a result, while pore tortuosity may have increased, the lack of effective matrix encapsulation and bonding failed to restrict moisture transport through interconnected pathways. By contrast, at moderate CSB levels (40–80%), significant reductions in water absorption were observed, reflecting improved interfacial compatibility and structural compactness, as discussed below.
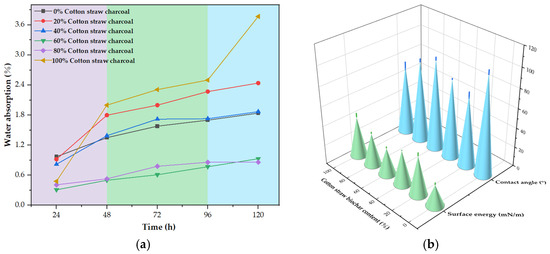
Figure 9.
Effect of cotton stalk biochar (CSB) content on the water resistance of wood–plastic composites. Note: (a) Water absorption of six groups of composite panels. (b) Experimental evaluation of hydrophobicity in six wood–plastic composites.
As the CSB content increased to 40–80%, water absorption decreased significantly (40%: 1.87%, 60%: 0.93%, 80%: 0.89%). Similar hydrogen bonding mechanisms were proposed by Zhang et al. [43], who observed that biochar–MA-HDPE composites exhibited enhanced mechanical properties and reduced water absorption due to improved interfacial adhesion. Although no direct chemical analysis was provided in their study, the concurrent trends in mechanical performance, moisture resistance, and morphological compactness strongly support the role of interfacial hydrogen bonding. These synergistic effects, coupled with CSB’s intrinsic hydrophobicity, created a compact microstructure with minimized capillary pathways, as confirmed by microscopy. This composition range represented the optimal window for moisture resistance.
By contrast, 100% CSB content resulted in a sharp rise in water absorption (3.77%), due to particle agglomeration and insufficient polymer encapsulation. These agglomerates formed loosely packed, interconnected porous regions that allowed moisture penetration (Figure 8 and Figure 9). The partial hydrophilicity of CSB further accelerated water uptake. While previous studies have discussed biochar’s role in WPC moisture resistance [44], this study highlights 40–80% CSB as the optimal range for balancing hydrophobicity and interfacial bonding. To ensure long-term durability in applications such as outdoor decking and agricultural substrates, both the CSB content and dispersion quality must be carefully controlled. Future work should focus on quantitative pore structure analysis to refine processing parameters for scalable production.
3.5. Contact Angle and Surface Energy Analysis
Figure 9b and Figure 10 systematically elucidate the nonlinear evolution of wettability in the wood–plastic composites (WPCs) with varying modified cotton stalk biochar (CSB) contents. One-way ANOVA confirmed statistically significant differences among groups (F = 28.7, p < 0.01), with post hoc Tukey tests revealing three distinct wettability regimes governed by interfacial architecture and capillary dynamics.
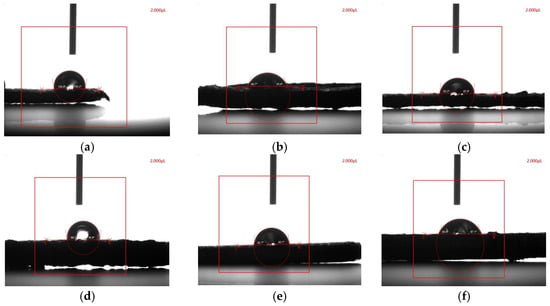
Figure 10.
Typical seat-drop diagrams of six wood–plastic composites with different cotton stalk biochar (CSB) contents. Note: (a) 0% cotton stalk biochar. (b) 20% cotton stalk biochar. (c) 40% cotton stalk biochar. (d) 60% cotton stalk biochar. (e) 80% cotton stalk biochar. (f) 100% cotton stalk biochar.
At low CSB contents (0–20%), the composites exhibited limited moisture resistance, primarily due to weak interfacial bonding and enhanced capillary effects. Although the 0% CSB sample showed a relatively high contact angle of 102.634°, its water absorption after 120 h reached 1.84%, indicating that intrinsic matrix hydrophobicity alone could not prevent moisture ingress. At 20% CSB, the water absorption increased further to 2.44%, while the contact angle decreased sharply to 72.894° and surface energy rose to 39.910 mN/m. These changes were attributed to exposed hydrophilic -OH groups on CSB surfaces and the formation of continuous water pathways due to insufficient matrix encapsulation, which collectively enhanced water penetration.
With increased CSB contents (40–80%), the composites achieved improved water resistance. Water absorption decreased to 1.87%, 0.93%, and 0.89% at 40%, 60%, and 80% CSB, respectively. This improvement coincided with an increase in contact angle (80.784° to 92.991°) and a decrease in surface energy (34.993 to 27.368 mN/m), as shown in Figure 9b. These properties reflected the formation of a denser and more uniform microstructure, where well-dispersed CSB particles were fully encapsulated by the polymer matrix. Additionally, silane modification enhanced compatibility and further reduced the polar surface component, effectively impeding water infiltration.
However, at 100% CSB content, the composite structure deteriorated significantly. Water absorption surged to 3.77%, while the contact angle decreased to 70.907° and the surface energy increased to 41.141 mN/m. This sharp decline in performance was caused by severe particle agglomeration and the absence of continuous polymer coverage, which resulted in the formation of interconnected macropores. These regions facilitated rapid moisture uptake, negating the benefits of CSB’s inherent hydrophobicity. Despite this, the observed trends across different CSB loadings provide practical guidance for tailoring WPC materials to suit agricultural applications such as water-saving substrates or biodegradable films.
3.6. Analysis of Tensile Properties of Six Groups of Wood–Plastic Materials
Figure 11a shows the effect of CSB content on the tensile properties of the wood–plastic composites. As the CSB content increased from 0% to 80%, the tensile strength rose from 8.896 ± 0.194 MPa to 13.288 ± 0.201 MPa, and the tensile modulus increased from 20.451 ± 0.446 MPa to 45.184 ± 2.417 MPa. However, at 100% CSB, both values declined to 10.830 ± 0.372 MPa and 37.851 ± 0.981 MPa, respectively. One-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) confirmed significant improvement within the 0–80% range, especially between 60% and 80%.
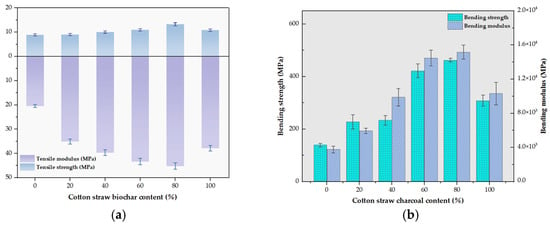
Figure 11.
The mechanical performance testing of six groups of wood–plastic compositesirostructure. Note: (a) Tensile strength and tensile modulus of different wood–plastic composites. (b) Comparison of flexural properties of six groups of WPC lumber.
Within the 0–80% CSB content range, strong interfacial synergy was achieved between cotton stalk biochar (CSB) and the matrix (polyethylene residual film, maleic anhydride-grafted HDPE, and cotton stalk xylem powder). Uniform dispersion of CSB and xylem powder facilitated effective void filling, enhancing the composite’s rigidity and tensile strength. The hydroxyl and carboxyl groups on the CSB surface enabled dense interfacial bonding with MA-HDPE via hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces, which restricted polymer chain mobility and improved stress transfer. This mechanism was consistent with previous findings [41], showing that at 60–80% CSB, tensile stress distribution became more uniform, significantly improving mechanical performance.
However, at 100% CSB content, microstructural analysis (Figure 7f) revealed severe particle agglomeration and increased local porosity. These defects, along with insufficient polymer encapsulation, created loose regions (~10–50 μm) that acted as stress concentrators, accelerating crack initiation and propagation. Statistical analysis (p < 0.05) confirmed that both tensile strength and modulus increased significantly with CSB content up to 80%, with a strong positive correlation between them (r = 0.836), reflecting effective reinforcement synergy. By contrast, the property degradation at 100% CSB further highlighted the critical role of optimized content and uniform dispersion. Notably, the 60–80% CSB group exhibited superior tensile performance and interfacial bonding compared to previously reported rice husk biochar/HDPE and bamboo charcoal/WPC systems [44,45].
From an application standpoint, wood–plastic composites with enhanced tensile properties are highly suitable for outdoor, agricultural, and humid environment applications. To ensure reliable performance, industrial production is recommended to maintain the CSB content within 60–80%. Further improvements could involve surface modification, particle size control, and co-dispersants to ensure homogeneous dispersion of CSB within the matrix. Additionally, future research should employ dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) to quantitatively assess hydrogen bonding stability and transfer efficiency, providing a solid theoretical foundation for large-scale manufacturing.
3.7. Analysis of Bending Properties of Six Groups of Wood–Plastic Materials
Figure 11b presents the effect of CSB content on bending strength and flexural modulus, while Figure 12 displays the cross-sectional microstructure after bending tests. As the CSB content increased from 0% to 80%, the bending strength improved from 139.133 ± 6.859 MPa to 463 ± 7 MPa, and the flexural modulus rose from 3757.112 MPa to 15,180.933 MPa, with optimal performance at 60–80% CSB. However, at 100% CSB, both properties declined to 308.333 ± 20.841 MPa and 10,311.333 MPa, respectively.
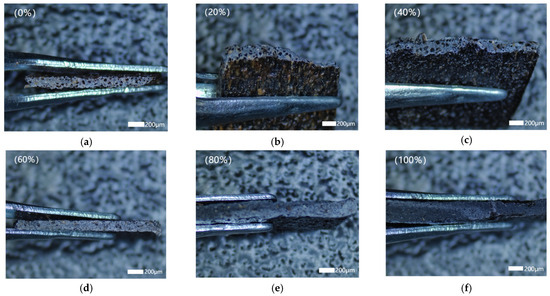
Figure 12.
Microscopic morphology of fracture surfaces of wood–plastic composites with different cotton stalk biochar contents. Note: (a) 0% cotton stalk biochar. (b) 20% cotton stalk biochar. (c) 40% cotton stalk biochar. (d) 60% cotton stalk biochar. (e) 80% cotton stalk biochar. (f) 100% cotton stalk biochar.
The enhanced flexural performance of the composites within the 0–80% CSB range primarily resulted from the synergistic effect of uniform CSB dispersion and strong interfacial bonding with the polymer matrix (PE residual film, MA-HDPE, and cotton stalk xylem powder). Finely dispersed CSB particles effectively filled voids in the matrix, reducing pore size and limiting stress concentration zones that would otherwise facilitate crack initiation and propagation. Additionally, surface hydroxyl and carboxyl groups on CSB enabled hydrogen bonding and van der Waals interactions with the matrix, improving interfacial adhesion and stress transfer efficiency by restricting molecular mobility. These mechanisms aligned with prior findings [41] reporting that improved interfacial compatibility led to enhanced mechanical behavior at intermediate CSB contents.
However, at 100% CSB, microstructural observations (Figure 7f) revealed significant particle agglomeration and the formation of large, loosely packed regions that undermined interfacial integrity. This increased porosity created weak points that promoted early crack growth, resulting in reduced bending strength and modulus [38,39]. One-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) confirmed significant improvements in flexural properties from 0% to 80% CSB, with a strong positive correlation between bending strength and modulus (r = 0.991). The notable performance drop at 100% CSB further emphasized the detrimental effect of overloading filler. Thus, maintaining the CSB content within the 60–80% range, combined with optimized dispersion strategies (e.g., surface modification, particle size control), is crucial for achieving high mechanical strength and structural durability in wood–plastic composites [46,47].
3.8. Thermophysical Characterization of Wood–Plastic Materials
Figure 13 shows that both the thermal conductivity and diffusivity of the wood–plastic composites peaked at 40% CSB content, then declined significantly with further increase, indicating 40% as a critical threshold for thermal performance.
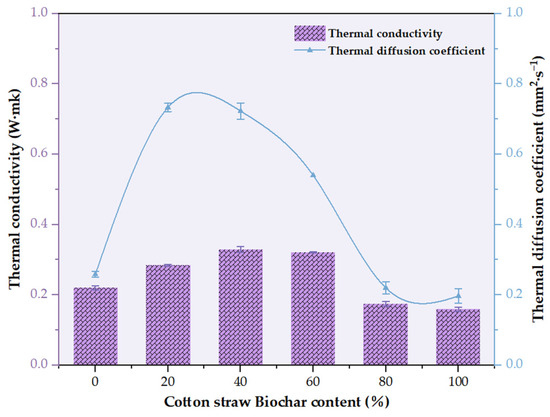
Figure 13.
Thermophysical properties of six groups of composite plates.
The thermophysical properties of the wood–plastic composites were closely governed by the content of modified cotton stalk biochar (CSB). Within the 0–40% CSB range, the thermal conductivity increased steadily from 0.220 ± 0.005 to 0.329 ± 0.008 W/(m·K), accompanied by a rise in thermal diffusivity to 0.733 ± 0.012 mm2/s. This improvement was primarily due to the formation of continuous and efficient heat conduction pathways facilitated by the uniform dispersion of CSB particles with inherently high thermal conductivity. Strong interfacial bonding between CSB and the polymer matrix (residual PE, MA-HDPE, and cotton stalk xylem powder) enhanced phonon transport, reduced thermal resistance, and optimized heat transfer. Additionally, moderate CSB content helped to fill internal voids, increasing structural compactness and promoting uniform heat distribution, ultimately improving the material’s thermal performance [48].
However, when the CSB content exceeded 40%, particularly in the 80–100% range, the thermal conductivity and diffusivity decreased markedly, with values dropping to 0.159 ± 0.005 W/(m·K) and 0.197 ± 0.021 mm2/s, respectively. This decline was mainly attributed to increased porosity and particle agglomeration, which disrupted heat conduction pathways and introduce air-filled micro-defects with low thermal conductivity (~0.026 W/(m·K)) [49,50]. The resulting heterogeneity reduced interfacial contact and impeded heat carrier migration. These findings aligned with previous reports on the negative correlation between porosity and effective thermal conductivity in porous composites [50]. Therefore, the CSB content must be carefully optimized based on functional requirements: ~40% CSB is recommended for thermal management applications, while 80–100% is more suitable for insulation purposes. Balancing the CSB content and improving dispersion and microstructure are key to tailoring composite performance for specific end uses.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that the CSB content significantly affected the microstructure and mechanical and thermal properties of the wood–plastic composites (WPCs). Incorporating 60–80 wt% CSB effectively enhanced mechanical performance by improving interfacial bonding and filling matrix pores, resulting in optimized stress distribution and increased tensile and flexural strength. By contrast, 80–100 wt% CSB offered superior thermal insulation due to increased porosity and reduced thermal conductivity, despite diminished mechanical performance. Notably, thermal conductivity peaked at 40 wt% CSB (0.329 ± 0.005 W/(m·K)) before declining due to agglomeration and pore formation (>15% porosity at 100 wt%). Thus, 60–80 wt% CSB is suitable for load-bearing agricultural applications (e.g., greenhouse supports), while 80–100 wt% CSB is better suited for thermal insulation. To further enhance performance, KH570 surface treatment or nano-filler incorporation is recommended. Future work may focus on hybrid filler systems (e.g., nanoclay/CSB) to achieve balanced improvements in mechanical and thermal properties for sustainable agricultural applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.S., X.L. (Xiaoyun Lian), J.R., X.Z. and X.L. (Xiaoqing Lian); Methodology, Z.S., J.R., X.W. and X.Z.; Software, Z.S. and X.L. (Xiaoqing Lian); Validation, Z.S., J.R., X.L. (Xiaoyun Lian) and X.L. (Xiaoqing Lian); Formal analysis, Z.S., J.R., X.Z. and X.W.; Investigation, Z.S.; Resources, J.R.; Data curation, Z.S. and X.L. (Xiaoyun Lian); Writing—original draft, Z.S. and J.R.; Writing—review & editing, Z.S., X.L. (Xiaoyun Lian), J.R., X.Z., X.W. and X.L. (Xiaoqing Lian); Supervision, X.W., J.R. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Programme of the First Division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, Alar City (Grant No. 2022ZB04), and the Southern Xinjiang Residual Film Recycling and Resource Utilisation Experimental Demonstration (Grant No. NYHXGG, 2023AA401). We sincerely thank these funding organizations for their generous support, which was crucial to the successful completion of our research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, K.; Remón, J.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, W. Recent Advances in the Preparation and Application of Biochar Derived from Lignocellulosic Biomass: A Mini Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Farooq, A.; Lee, D.; Seo, M.W.; Jung, S.C.; Hussain, M.; Khan, M.A.; Jeon, B.H.; Jang, S.H.; Choi, Y.J.; et al. Green conversion of wood plastic composites: A study on gasification with an activated bio-char catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 54, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudełko, A.; Postawa, P.; Stachowiak, T.; Malińska, K.; Dróżdż, D. Waste derived biochar as an alternative filler in biocomposites-mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of biochar added biocomposites. Polymers 2020, 278, 123850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.; Tamrakar, S.; Kiziltas, A.; Xie, X. Incorporation of biochar to improve mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of polymer composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Cotton Advisory Committee (ICAC). Cotton Market Report. Available online: https://www.icac.org (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Ou, M.; Gao, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhuo, L.; Ma, Y. Development and characterization of polymer composites with cotton straw fiber derived from agricultural wastes. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 16304–16316. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Report on Cotton Production in 2023; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Liang, F.; Li, B.; Vogt, R.D.; Mulder, J.; Song, H.; Chen, J.; Guo, J. Straw return exacerbates soil acidification in major Chinese croplands. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Hu, S.; Xiang, J.; Sun, L.; Su, S.; An, S. Study on the gas evolution and char structural change during pyrolysis of cotton stalk. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 97, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Hamawand, I.; Sandell, G.; Pittaway, P.; Chakrabarty, S.; Yusaf, T.; Chen, G.; Seneweera, S.; Al-Lwayzy, S.; Bennett, J.; Hopf, J. Bioenergy from Cotton Industry Wastes: A Review and Potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 435–448. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Xu, W.; Gu, M.; Yao, H.; Pu, S.; Hu, K. Characteristics of cotton stalk charcoal and its effect on soil organic carbon mineralisation in grey desert soil. J. Ecol. 2019, 39, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Standing Committee of the 14th People’s Congress of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Regulations on the Management of Agricultural Mulch in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Duan, X.; Gu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zha, S.; Chen, X. Natural aging and adsorption/desorption behaviors of polyethylene mulch films: Roles of film types and exposure patterns. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, X.G.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, C.R. Current situation of residual film pollution in farmland and prevention and control strategies in Xinjiang. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H. Evaluation of Film Residue Pollution and Analysis of Influencing Factors in Farmland in Southern Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Q.Q.; Tang, Q.X.; Wu, F.Q.; Lin, T.; He, W.Q.; Yan, C.R.; Yang, Z.L. Analysis of Cotton Growth, Development, and Benefits Based on Degradable Mulch Film Coverage in Xinjiang. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2019, 36, 649–655. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.X.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.S.; Jia, H.T.; Huai, G.L.; Sun, C.; Qiao, X.Y. Study on biodegradation of field residual film by Macrocephalus macrocephalus. Hans J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 10, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Li, W.B.; Wang, P.Y.; Tao, H.Y.; Zhou, R.; Cui, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, T.; Zhao, X.Z.; Wang, Y.B.; et al. Farmers’ participation into the recovery of waste agricultural plastic film: An application of the Theory of Planned Behavior. Waste Manag. 2023, 169, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R. Investigation and Analysis of the Current Situation of Regional Distribution of Residual Film Pollution in Cotton Fields in Aksu Region, Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2016; pp. 26–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, R.Q.; Chen, X.G.; Zhang, B.C.; Meng, H.W.; Jiang, P.; Peng, X.B.; Kan, Z.; Li, W.M. Problems and countermeasures of the current status of residual film recycling methods and resource reuse in cotton fields in Xinjiang. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.P.; He, C.X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.Y. Comparison of seawater corrosion resistance of four plant fibre/high density polyethylene wood-plastic composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 36, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Response of Cotton Stalks Crushed and Returned to the Field for Decomposition and Soil Fertility. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2024; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Afif, R.; Anayah, S.S.; Pfeifer, C. Batch pyrolysis of cotton stalks for evaluation of biochar energy potential. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Fei, P.; Jin, W.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Z. Enhancing the performance of starch-based wood adhesive by silane coupling agent (KH570). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.; Xiao, Z. Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.; Rencoret, J.; Chemetova, C.; Gominho, J.; Gutierrez, A.; Del Rio, J.C.; Pereira, H. Lignin composition and structure differs between xylem, phloem and phellem in Quercus suber L. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1612. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, W.; Jin, Y.; Wu, W. Exploring the relationship between lignin structure and antioxidant property using lignin model compounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136786. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L. Study on the Effects of Polyethylene, the Main Component of Environmentally Degradable Mulch Film, on Soil and Crops. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Normal University, Sichuan, China, 2010; pp. 4–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Effects of Different Films on Cotton Growth and Residual Film Recycling. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2023; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeilzade, R.; Stainslavovich, K.A.; Jandaghian, M.H.; Hosseini, L.S.R.; Saleh, L.H.; Zarghampour, S. Correlation of structure, rheological, thermal, mechanical, and optical properties in low density polyethylene/linear low density polyethylene blends in the presence of recycled low density polyethylene and linear low density polyethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, P.; Silva, M.H.; Cavalcanti, S.N.; Freitas, D.M.; Araújo, J.P.; Oliveira, A.D.; Mélo, T.J. Rheological properties of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene and high-density polyethylene/low-density polyethylene blends. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 2321–2343. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 24508-2020; Wood—Plastic Composite Flooring. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 1040.1-2018; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 1: General Principles. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 9341-2008; Plastics—Determination of Flexural Properties. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Cui, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, S.; Bai, R.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Wei, H. Research on the Adsorption Mechanism and Performance of Cotton Stalk-Based Biochar. Molecules 2024, 29, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hangargi, S.; Swamy, A.; Raj, R.G.; Aruna, M.; Venkatesh, R.; Madhu, S.; Al Obaid, S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Kalam, M.A. Enhancement of Kevlar fiber-polypropylene composite by the inclusions of cotton stalk and granite particle: Characteristics study. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 30305–30314. [Google Scholar]
- Patti, A.; Russo, P.; Acierno, D.; Acierno, S. The effect of filler functionalization on dispersion and thermal conductivity of polypropylene/multi wall carbon nanotubes composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 94, 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Kalderis, D.; Michailidis, N.; Maravelakis, E.; Saltas, V.; Bolanakis, N.; Papadakis, V.; Spiridaki, M.; Argyros, A. Reinforced HDPE with optimized biochar content for material extrusion additive manufacturing: Morphological, rheological, electrical, and thermomechanical insights. Biochar 2024, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, J.; Peng, Y.; Cao, J. Versatile biochar for wood-plastic composites: Improving mechanical properties, dimensional and thermal stability. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 10349–10364. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xiao, Y.W. Key Node Identification Method Based on Binary Entropy and Van der Waals Force Between Neighboring Nodes. J. Air Force Eng. Univ. 2024, 25, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Cai, H.Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.B.; Yi, W.M. Effect of Carbon Content on the Properties of Charcoal/Polypropylene Composites. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Huang, J.; Xie, L.; Feng, C.; Na, H.; Wang, N.; Zhu, J. Water absorption of biomass fillers to impact the degradation of poly (butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate) composites. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 3990–4001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Xu, H.; Lu, W.; Ren, X.; Cai, H.; Lei, H.; Huo, E.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, M.; et al. Biochar filled high-density polyethylene composites with excellent properties: Towards maximizing the utilization of agricultural wastes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 146, 112185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Peng, H.; Li, S.; Yang, X.; Li, H.; Xing, Z.; Xian, Y. Effect of biochar content and particle size on mechanical and water absorption properties of landsca waste/polylactic acid composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 223, 120163. [Google Scholar]
- Yusof, A.A.M.Y.; Mustapa, M.S.; Ariffin, A.H.; Ibrahim, M.R.; Masirin, M.I.M.; Siswanto, W.A.; Yoshiharu, M. The Effect of Bamboo Charcoal Powder on the Tensile Strength of Wood Plastic Composite. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2022, 1075, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, P.; Jayabalakrishnan, D.; Balaji, V.; Bhaskar, K.; Maridurai, T.; Prakash, V.A. Mechanical, tribology, dielectric, thermal conductivity, and water absorption behaviour of Caryota urens woven fibre-reinforced coconut husk biochar toughened wood-plastic composite. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzkopf, M.; Muszyński, L.; Hammerquist, C.C.; Nairn, J.A. Micromechanics of the internal bond in wood plastic composites: Integrating measurement and modeling. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 997–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ciarla, R.; Boonkird, A.; Raza, S.; Nguyen, T.; Zhou, J.; Osti, N.C.; Mamontov, E.; Jiang, Z.; Zuo, X.B.; et al. Defects vibrations engineering for enhancing interfacial thermal transport in polymer composites. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadp651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, J. Highly thermally conductive polymer composite enhanced by constructing a dual thermal conductivity network. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 5734–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jeong, S.; Cho, W.; Ryu, J.; Zhang, B.; Crovella, P.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Wie, J.J.; Yoo, C.G. Green co-solvent-assisted one-pot synthesis of high-performance flexible lignin polyurethane foam. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156142. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).