Spider Web DNA Metabarcoding Provides Improved Insight into the Prey Capture Ability of the Web-Building Spider Tetragnatha keyserlingi Simon (Araneae: Tetragnathidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Investigation
2.2. Collection of T. keyserlingi and Its Webs
2.3. Specimen Preprocessing and DNA Extraction
2.4. DNA Amplification and Sequencing Protocol
2.5. Sequence Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
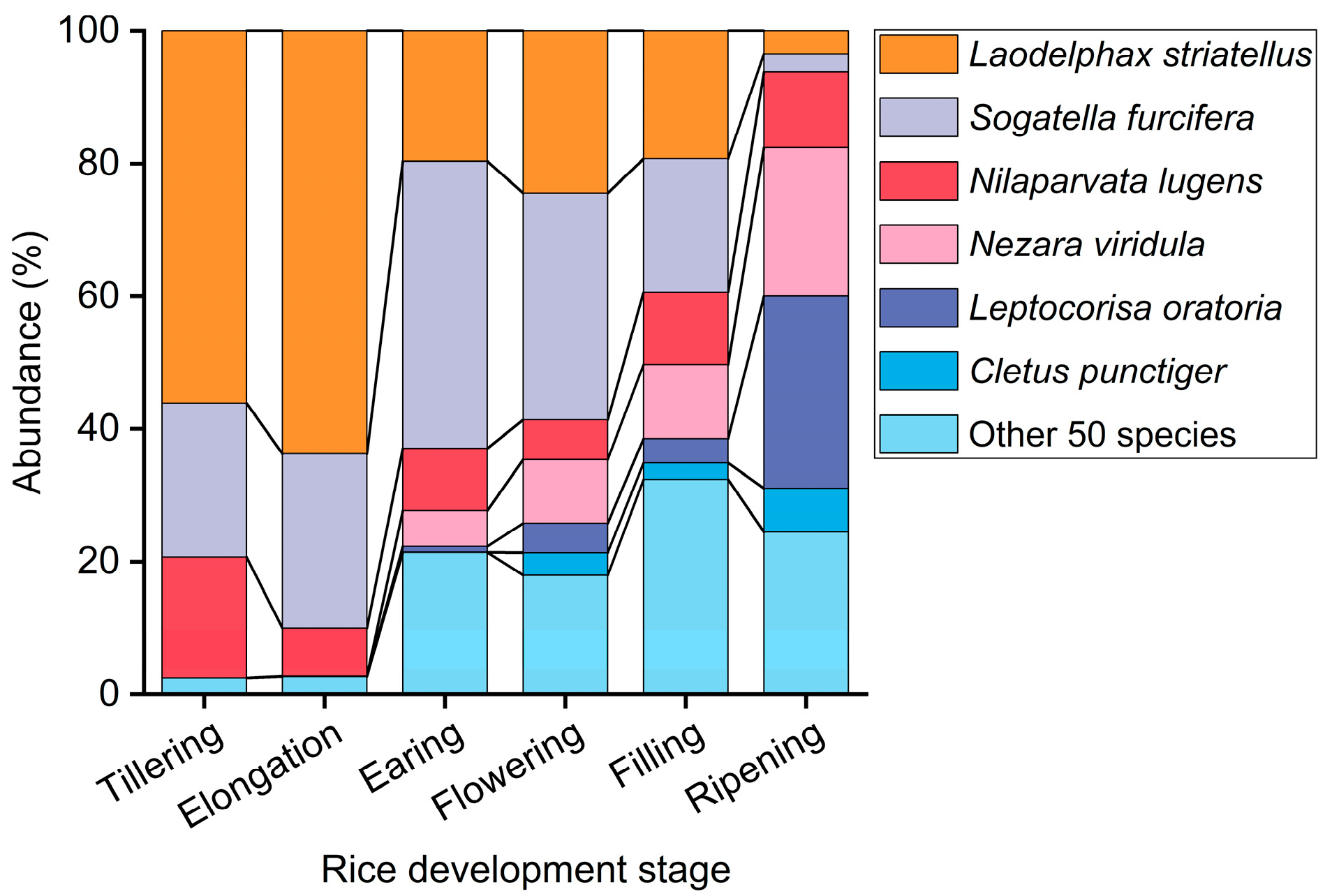
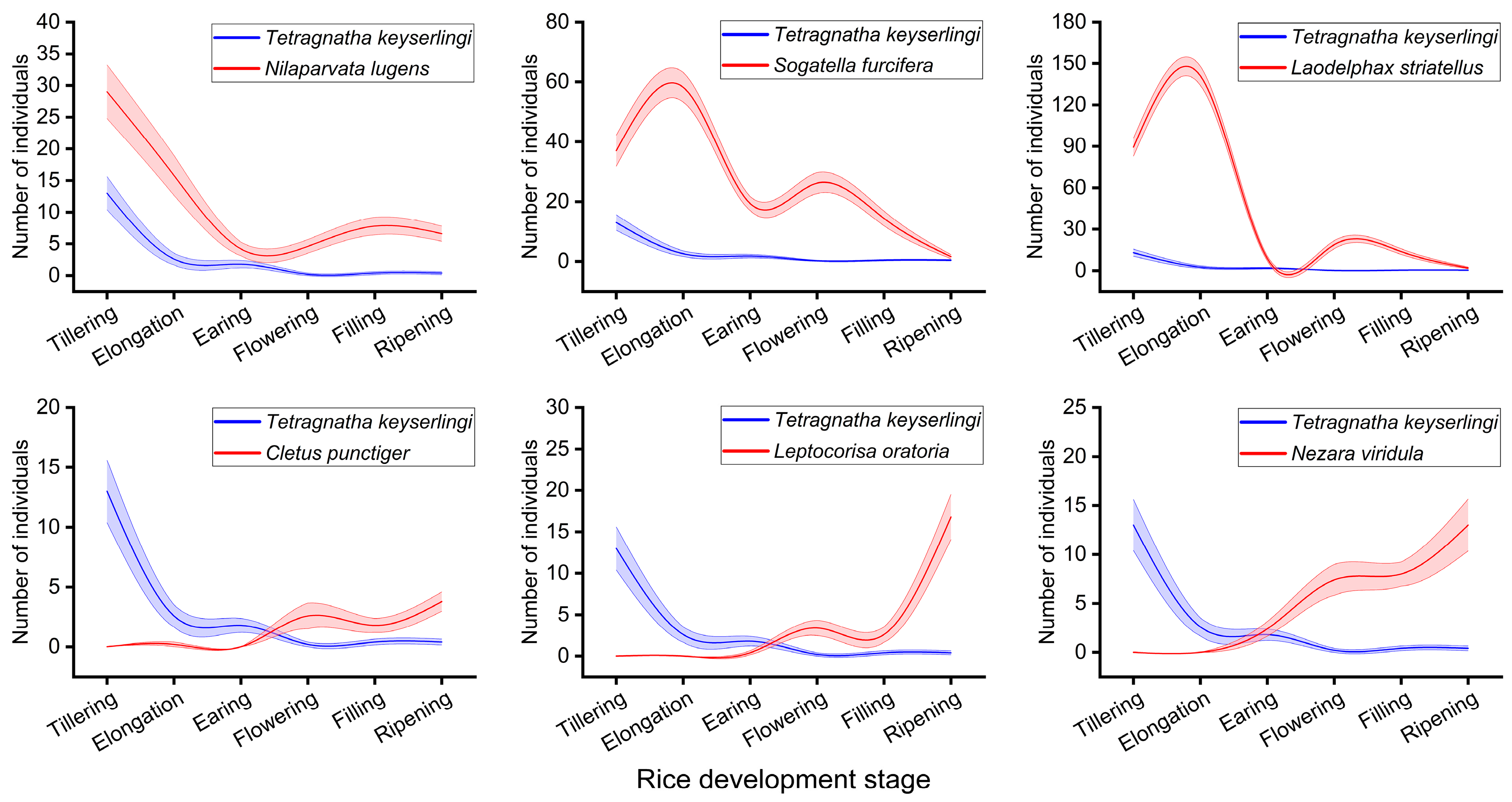
3.1. Population Dynamic Relationships Between T. keyserlingi and Major Rice Pests
3.2. Dietary DNA Metabarcoding Analysis of T. keyserlingi
3.2.1. Species Taxon Assignment
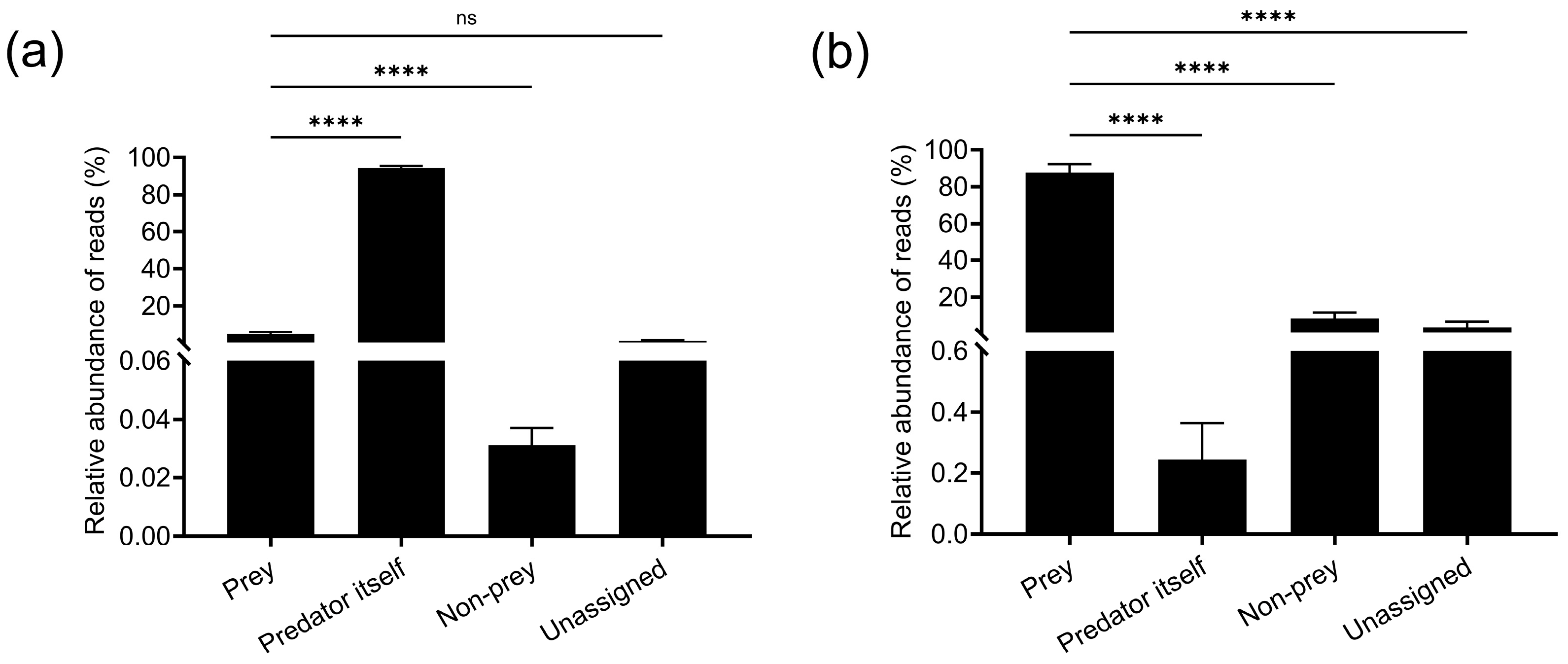
3.2.2. Evaluation of Prey Taxon Assignment Efficiency
3.2.3. Comparison of Prey Species Richness Between Spider Opisthosoma and Spider Webs
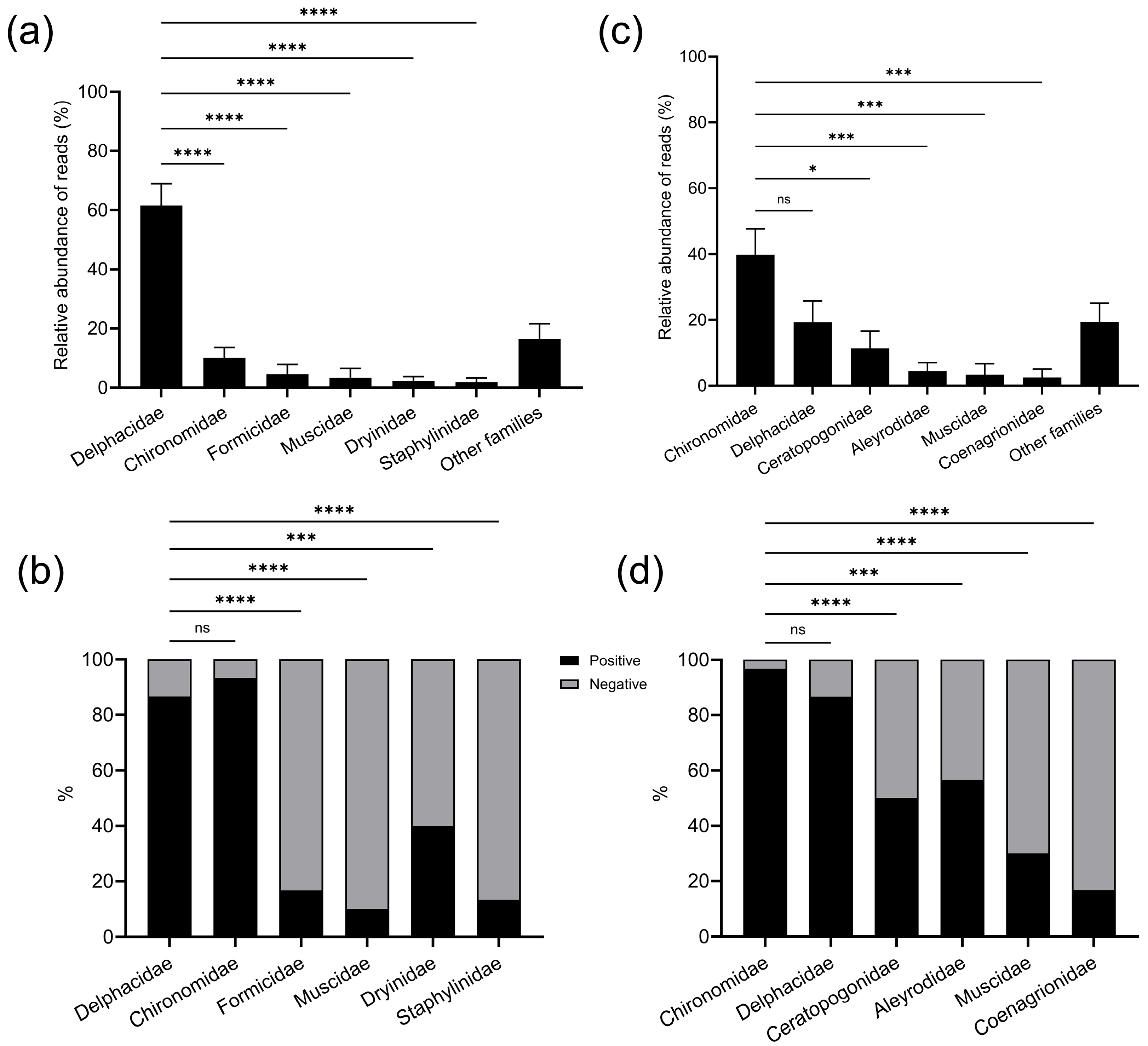
3.2.4. Composition of Prey Identified from Spider Opisthosoma and Spider Webs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boldorini, G.X.; McCary, M.A.; Romero, G.Q.; Mills, K.L.; Sanders, N.J.; Reich, P.B.; Michalko, R.; Gonçalves-Souza, T. Predators control pests and increase yield across crop types and climates: A meta-analysis. Proc. R. Soc. B 2024, 291, 20232522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyffeler, M.; Benz, G. Spiders in natural pest control: A review. J. Appl. Entomol. 1987, 103, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalko, R.; Pekár, S.; Entling, M.H. An updated perspective on spiders as generalist predators in biological control. Oecologia 2019, 189, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Qiao, F.; Zhu, Z.R.; Cheng, J.A. Development and preliminary application of a triplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for evaluating predation on three planthoppers in a rice ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Agnarsson, I.; Chen, J. Molecular identification of spiders preying on Empoasca vitis in a tea plantation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Main predators of insect pests: Screening and evaluation through comprehensive indices. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirodin, A.; Simmons, A.M.; Legaspi, J.C.; Grabarczyk, E.E.; Toews, M.D.; Roberts, P.M.; Chong, J.-H.; Snyder, W.E.; Schmidt, J.M. Can generalist predators control Bemisia tabaci? Insects 2020, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Spider Catalog. Available online: http://wsc.nmbe.ch (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Yang, H.; Peng, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, B.; Xie, C.; Wang, Z. Rice field spiders in China: A review of the literature. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Yang, T.; Xu, X.; Zhong, Y. A checklist of spiders in tea plantations of China. Biodivers. Data J. 2020, 8, e60143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Song, X.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, C. Field investigation- and dietary metabarcoding-based screening of arthropods that prey on primary tea pests. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, J.R.; Premila, K.S. Species composition and quantitative analysis of Tetragnathid spiders, Tetragnathidae (Araneae) in rice fields. Int. J. Fauna Biol. Stud. 2016, 3, 158–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.X.; Pan, W.J.; Chen, L.L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Pan, H.C. The complete mitochondrial genome of stretch spider Tetragnatha maxillosa (Araneae: Tetragnathidae). Mitochondrial DNA A 2016, 27, 3469–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandumula, N. Rice production in Asia: Key to global food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 88, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Wang, G.H.; Zhu, Z.R.; Tang, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, F.; Heong, K.L.; Cheng, J. Spider (Araneae) predations on white-backed planthopper Sogatella furcifera in subtropical rice ecosystems, China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackledge, T.A. Prey capture in orb weaving spiders: Are we using the best metric? J. Arachnol. 2011, 39, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyffeler, M.; Sunderland, K.D. Composition, abundance and pest control potential of spider communities in agroecosystems: A comparison of European and US studies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 95, 579–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksongmuang, V.; Michalko, R.; Petcharad, B.; Bumrungsri, S. Changes in community composition and prey capture of web-building spiders during rice field development. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2024, 79, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelix, R.F. Biology of Spiders, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saksongmuang, V.; Miyashita, T.; Maneerat, T.; Bumrungsri, S. Population dynamics and prey composition of Tetragnatha spiders (Araneae: Tetragnathidae) in semi-organic rice fields, Songkhla Province, southern Thailand. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 725–733. [Google Scholar]
- Salomon, M. The natural diet of a polyphagous predator, Latrodectus hesperus (Araneae: Theridiidae), over one year. J. Arachnol. 2011, 39, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafage, D.; Elbrecht, V.; Cuff, J.P.; Steinke, D.; Hambäck, P.A.; Erlandsson, A. A new primer for metabarcoding of spider gut contents. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra Ramirez, D.; Guevara, G.; Franco Pérez, L.M.; van Der Meijden, A.; González-Gómez, J.C.; Carlos Valenzuela-Rojas, J.; Quiroga, C.F.P. Deciphering the diet of a wandering spider (Phoneutria boliviensis; Araneae: Ctenidae) by DNA metabarcoding of gut contents. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 5950–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Song, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, C.; Shi, A. A comparative analysis of spider prey spectra analyzed through the next-generation sequencing of individual and mixed DNA samples. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 15444–15454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, A.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. DNA barcoding for ecologists. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompanon, F.; Deagle, B.E.; Symondson, W.O.; Brown, D.S.; Jarman, S.N.; Taberlet, P. Who is eating what: Diet assessment using next generation sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1931–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefair, J.E.; Clare, E.L. Barcoding the food chain: From Sanger to high-throughput sequencing. Genome 2016, 59, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, A.; Haran, J.; Benoit, L.; Galan, M.; Brévault, T. DNA metabarcoding as a tool for disentangling food webs in agroecosystems. Insects 2020, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krehenwinkel, H.; Kennedy, S.; Pekár, S.; Gillespie, R.G. A cost-efficient and simple protocol to enrich prey DNA from extractions of predatory arthropods for large-scale gut content analysis by Illumina sequencing. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toju, H.; Baba, Y.G. DNA metabarcoding of spiders, insects, and springtails for exploring potential linkage between above- and below-ground food webs. Zool. Lett. 2018, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñol, J.; San Andrés, V.; Clare, E.L.; Mir, G.; Symondson, W.O.C. A pragmatic approach to the analysis of diets of generalist predators: The use of next-generation sequencing with no blocking probes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuff, J.P.; Kitson, J.J.; Hemprich-Bennett, D.; Tercel, M.P.; Browett, S.S.; Evans, D.M. The predator problem and PCR primers in molecular dietary analysis: Swamped or silenced; depth or breadth? Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñol, J.; Mir, G.; Gómez-Polo, P.; Agustí, N. Universal and blocking primer mismatches limit the use of high-throughput DNA sequencing for the quantitative metabarcoding of arthropods. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, J.P.; Nevill, P.; Bateman, P.W.; Campbell, M.A.; Allentoft, M.E. Spider webs capture environmental DNA from terrestrial vertebrates. iScience 2024, 27, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorič, M.; Kutnjak, D.; Bačnik, K.; Gostinčar, C.; Pecman, A.; Ravnikar, M.; Kuntner, M. Spider webs as eDNA samplers: Biodiversity assessment across the tree of life. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2534–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabarczyk, E.E.; Querejeta, C.M.; Tillman, P.G.; Wallace, R.D.; Barnes, B.F.; Meinecke, C.D.; Villari, C.; Gandhi, K.J.K.; LaForest, J.; Elliott, M.; et al. DNA metabarcoding analysis of three material types to reveal Joro spider (Trichonephila clavata) trophic interactions and web capture. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1177446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Hernández, N.; Athey, K.; Tonzo, V.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Arnedo, M.; Harwood, J.D. Molecular gut content analysis of different spider body parts. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.W.; Ji, Y.; Emerson, B.C.; Wang, X.; Ye, C.; Yang, C.; Ding, Z. Biodiversity soup: Metabarcoding of arthropods for rapid biodiversity assessment and biomonitoring. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, M.; Yang, J.Y.; Meyer, C.P.; Mills, S.C.; Agudelo, N.; Ranwez, V.; Boehm, J.T.; Machida, R.J. A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Bambaradeniya, C.N.B.; Edirisinghe, J.P. Composition, structure and dynamics of arthropod communities in a rice agro-ecosystem. Cey. J. Sci. (Biol. Sci.) 2009, 37, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, G.F.; Westbrook, J.K.; Brown, V.A.; Eldridge, M.; Federico, P.; Kunz, T.H. Bats track and exploit changes in insect pest populations. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollot, G.; Duyck, P.F.; Lefeuvre, P.; Lescourret, F.; Martin, J.F.; Piry, S.; Canard, E.; Tixier, P. Cover cropping alters the diet of arthropods in a banana plantation: A metabarcoding approach. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llaneza, L.; López-Bao, J.V. Indirect effects of changes in environmental and agricultural policies on the diet of wolves. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2015, 61, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpurua, O.; Budinski, I.; Georgiakakis, P.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Ibañez, C.; Mata, V.; Rebelo, H.; Russo, D.; Szodoray-Parádi, F.; Zhelyazkova, V.; et al. Agriculture shapes the trophic niche of a bat preying on multiple pest arthropods across Europe: Evidence from DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhadi-Marín, J.; Pereira, J.A.; Sousa, J.P.; Santos, S.A. Distribution of the spider community in the olive grove agroecosystem (Portugal): Potential bioindicators. Agr. For. Entomol. 2020, 22, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyffeler, M.; Birkhofer, K. An estimated 400–800 million tons of prey are annually killed by the global spider community. Sci. Nat. 2017, 104, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyffeler, M. Ecological impact of spider predation: A critical assessment of Bristowe’s and Turnbull’s estimates. Bull. Br. Arachnol. Soc. 2000, 11, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Venturino, E.; Isaia, M.; Bona, F.; Chatterjee, S.; Badino, G. Biological controls of intensive agroecosystems: Wanderer spiders in the Langa Astigiana. Ecol. Complex. 2008, 5, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefler, C.D.; Chen, A.; Jakob, E.M. The potential of a jumping spider, Phidippus clarus, as a biocontrol agent. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phartale, N.N.; Bhede, B.V.; Patait, D.D.; Kadam, T.A.; Gyananath, G. Pest control potential of four predatory spiders from soybean fields. J. Entomol. Res. 2019, 43, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhou, X.Z.; Bi, S.D.; Zou, Y.D.; Ma, F.; Cheng, X.N.; Ke, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, H. The dominant species of predatory natural enemies of three kinds of planthoppers and impact of pesticides on natural enemies in paddy field. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuff, J.P.; Drake, L.E.; Tercel, M.P.; Stockdale, J.E.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Bell, J.R.; Vaughan, I.P.; Müller, C.T.; Symondson, W.O. Money spider dietary choice in pre- and post-harvest cereal crops using metabarcoding. Ecol. Entomol. 2021, 46, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.E.; Cuff, J.P.; Young, R.E.; Marchbank, A.; Chadwick, E.A.; Symondson, W.O. An assessment of minimum sequence copy thresholds for identifying and reducing the prevalence of artefacts in dietary metabarcoding data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Amir, A.; Hyde, E.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Song, S.J.; Knight, R. Tracking down the sources of experimental contamination in microbiome studies. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krehenwinkel, H.; Kennedy, S.R.; Adams, S.A.; Stephenson, G.T.; Roy, K.; Gillespie, R.G. Multiplex PCR targeting lineage-specific SNPs: A highly efficient and simple approach to block out predator sequences in molecular gut content analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalko, R.; Uhrinec, M.; Khum, W.; Sentenská, L. The benefits of intraguild predation for a top predator spider. Ecol. Entomol. 2021, 46, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Wang, N.Y.; Jiang, J.W. Ecological significance of neutral insects as nutrient bridge for predators in irrigated rice arthropod community. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 1995, 11, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Toft, S.; Wise, D.H. Growth, development, and survival of a generalist predator fed single- and mixed-species diets of different quality. Oecologia 1999, 119, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yuan, H.; Lu, Y. Predation by generalist arthropod predators on Apolygus lucorum (Hemiptera: Miridae): Molecular gut-content analysis and field-cage assessment. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Song, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.; Yang, T.; Zhang, S. Spider Web DNA Metabarcoding Provides Improved Insight into the Prey Capture Ability of the Web-Building Spider Tetragnatha keyserlingi Simon (Araneae: Tetragnathidae). Agriculture 2025, 15, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121235
Sun J, Song X, Wang B, Chen D, Yang T, Zhang S. Spider Web DNA Metabarcoding Provides Improved Insight into the Prey Capture Ability of the Web-Building Spider Tetragnatha keyserlingi Simon (Araneae: Tetragnathidae). Agriculture. 2025; 15(12):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121235
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jie, Xuhao Song, Bin Wang, Dongmei Chen, Tingbang Yang, and Shichang Zhang. 2025. "Spider Web DNA Metabarcoding Provides Improved Insight into the Prey Capture Ability of the Web-Building Spider Tetragnatha keyserlingi Simon (Araneae: Tetragnathidae)" Agriculture 15, no. 12: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121235
APA StyleSun, J., Song, X., Wang, B., Chen, D., Yang, T., & Zhang, S. (2025). Spider Web DNA Metabarcoding Provides Improved Insight into the Prey Capture Ability of the Web-Building Spider Tetragnatha keyserlingi Simon (Araneae: Tetragnathidae). Agriculture, 15(12), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121235





