Efficacy Evaluation of Civil-Works Mud as Soil Matrix Modified by Organic Amendments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Measurement
2.5. The Assessment of SQI
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
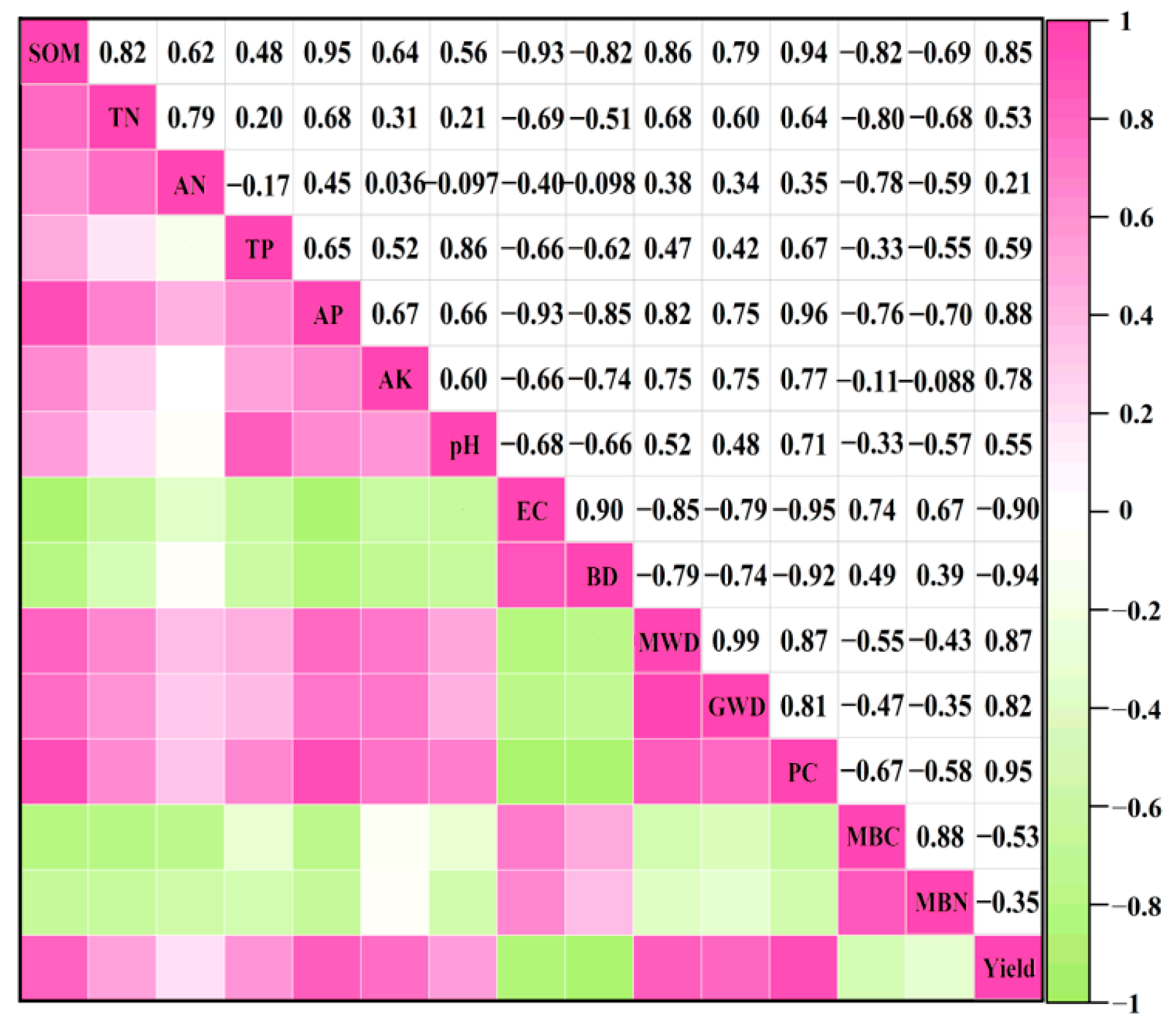
3.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Matrix Properties
3.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Crop
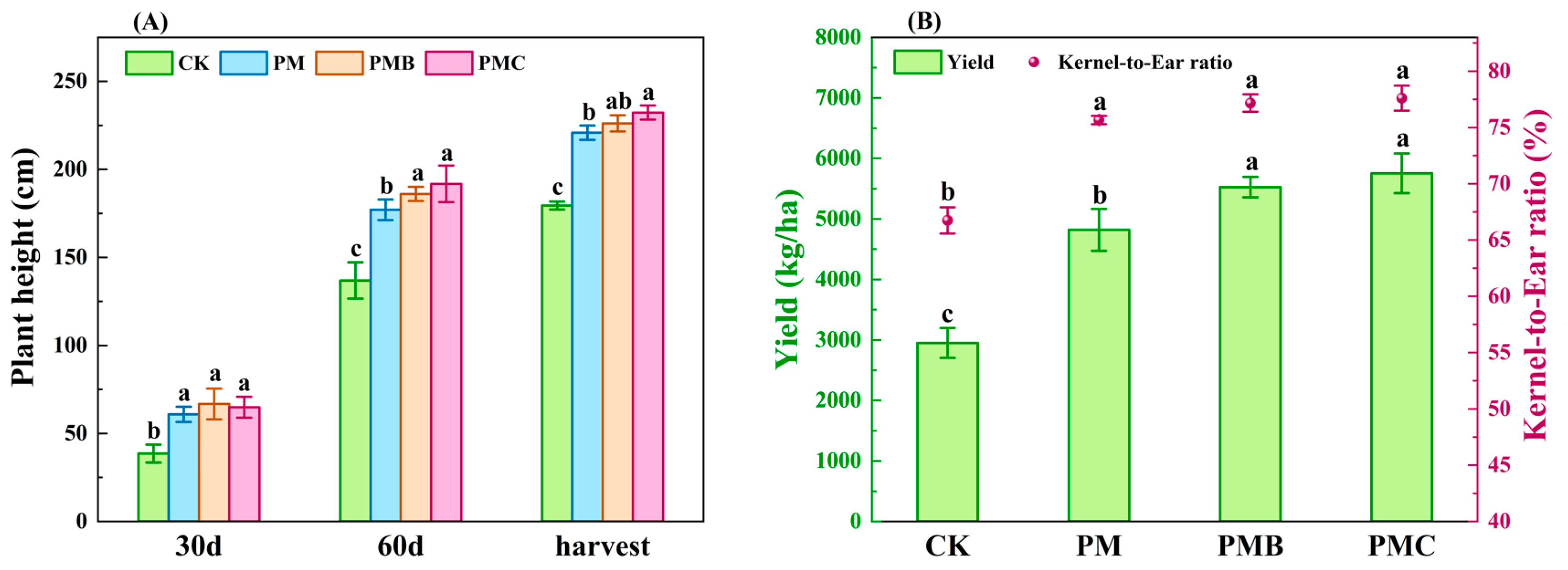
3.2.1. Plant Height and Yield
3.2.2. Safety Evaluation of Corn
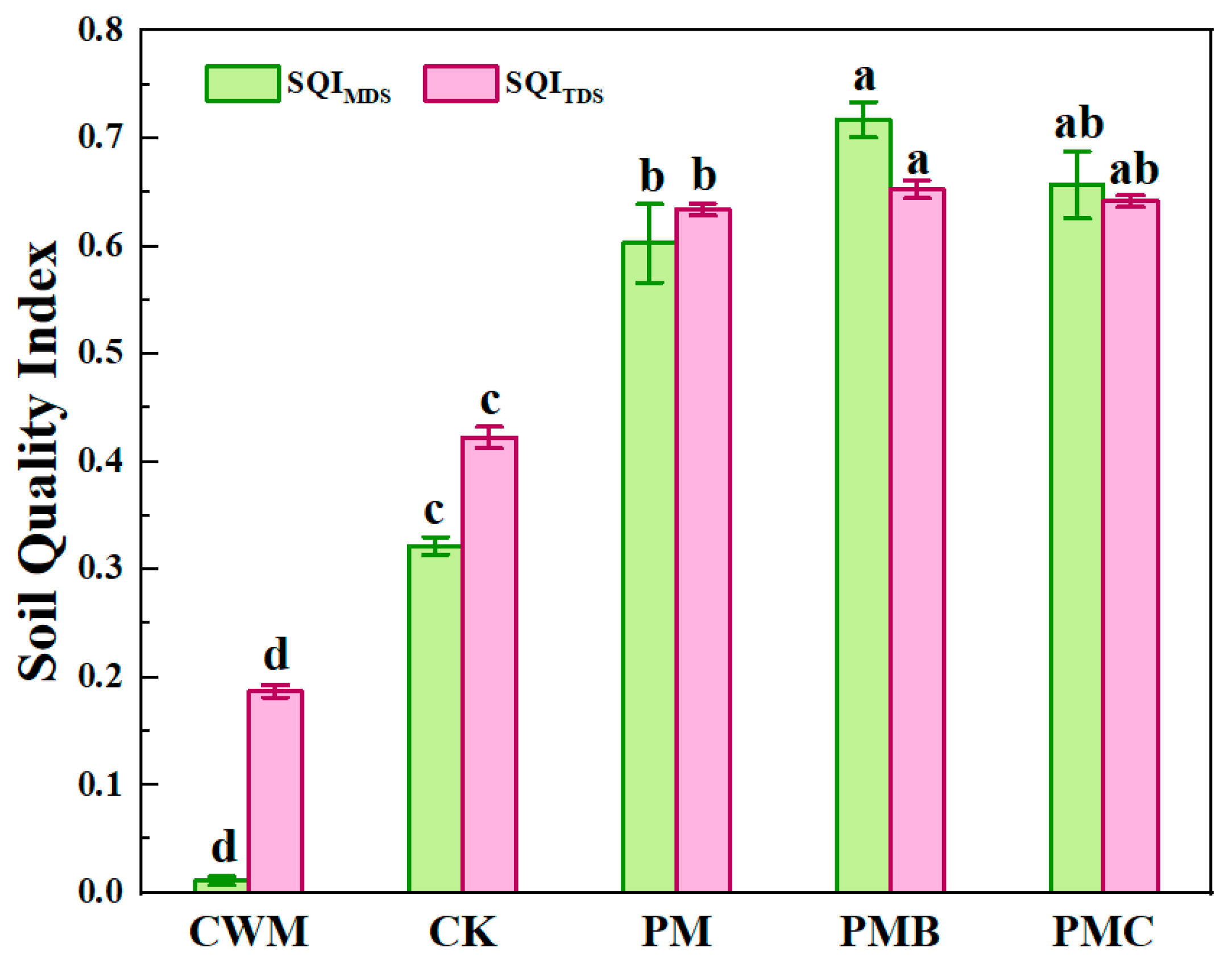
3.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Quality Index (SQI)
3.3.1. Determination of Total Data Set (TDS) and Minimum Data Set (MDS)
3.3.2. Soil Quality Index (SQI) Calculation
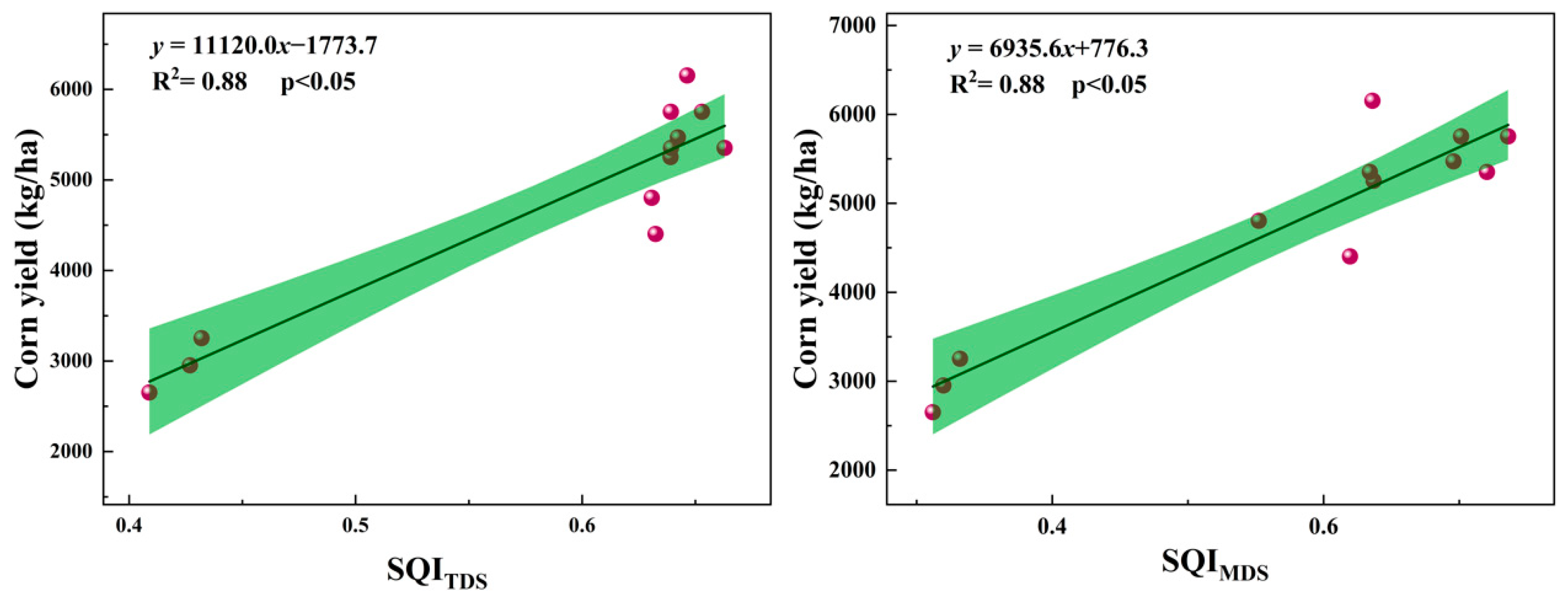
3.4. Relationship Between Crop Yield and SQI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GB T 50145-2007; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for Engineering Classification of Soils. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 6–14.
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Fu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Xie, Y. Evaluating the feasibility of muck from slurry shield tunnels as a growth medium for landscaping. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2022, 72, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, S.; Katra, I.; Argaman, E.; Ben-Hur, M. Erodibility of waste (Loess) soils from construction sites under water and wind erosional forces. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 616, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellopede, R.; Brusco, F.; Oreste, P.; Pepino, M. Main aspects of tunnel muck recycling. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. Investigations on the preparation of ceramsite from petrochemical excess sludge. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1008884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Lin, S.; Liu, G. Study on the Preparation of biochar ceramsite based on sewage sludge and the characterization of its properties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; An, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Song, Z. Safety and environmental protection application of high performance solid waste unburned ceramsite and its lightweight high strength concrete. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 40, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, A.M. Plants, soils, and climate. Science 2019, 366, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzel, K.; Renger, M.; Sauerbrey, R.; Wessolek, G. Soil physical characteristics of peat soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Wang, D.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Z. Optimizing the formulation of coal gangue planting substrate using wastes: The sustainability of coal mine ecological restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 143, 105669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Luan, D.; Tai, Z.; Deng, J.; Han, J.; Zhou, Y. Effects of different substrate ratios on the growth and physiology of Sequoia sempervirens container seedlings. Compos. Sci. Util. 2019, 27, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, X.; Huang, D.; Shang, J.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Liu, K. The mixed addition of biochar and nitrogen improves soil properties and microbial structure of moderate-devere fegraded alpine grassland in Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 765041. [Google Scholar]
- Mengqi, Z.; Shi, A.; Ajmal, M.; Ye, L.; Awais, M. Comprehensive review on agricultural waste utilization and high-temperature fermentation and composting. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2021, 13, 5445–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.; Yi, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, P.; Peng, X. Does animal manure application improve soil aggregation? Insights from nine long-term fertilization experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.; Ali, S.; Ilyas, M.; Riaz, M.; Akhtar, K.; Ali, K.; Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Khan, I.; Shah, S.; et al. Enhancing phosphorus availability, soil organic carbon, maize productivity and farm profitability through biochar and organic-inorganic fertilizers in an irrigated maize agroecosystem under semi-arid climate. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 37, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q. Influence of straw amendment on soil physicochemical properties and crop yield on a consecutive mollisol slope in northeastern China. Water 2018, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valani, G.P.; Vezzani, F.M.; Cavalieri-Polizeli, K.M.V. Soil quality: Evaluation of on-farm assessments in relation to analytical index. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Bai, Z.; Guo, D.; Chen, M. Develop a soil quality index to study the results of Black Locust on soil quality below different allocation patterns. Land 2021, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB22 T 2073-2014; Jilin Provincial Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Technical Specification for Safety Production Standardization of Small and Micro Industrial Enterprises. Jilin Provincial Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision: Changchun, China, 2014; pp. 2–9.
- Chen, F.Y. High yield cultivation techniques for corn in Youjiang District, Baise City. South China Agric. 2025, 19, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; Chinese Agriculture Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 14–245. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Cong, P.; Kuang, S.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Song, W. Long-term excessive application of K2SO4 fertilizer alters bacterial community and functional pathway of tobacco-planting soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1005303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Huang, L.; Shao, M. Vertical distribution of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus in the critical zone on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 166, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Li, C.; Zhu, F.; Luo, X.; Feng, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, C.; Hatrley, W.; Xue, S. Effect of potentially toxic elements on soil multifunctionality at a lead smelting site. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NY T 1121.6-2006; Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Soil Testing—Part 6: Method for Determination of Soil Organic Matter. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 1–3.
- Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xia, R.; Zhong, K. The fate of Cd in soils with various particle sizes: Characteristics, speciation distribution and influencing factors. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 113, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Liu, K.; Dou, P.; Li, J.; Wang, K. The changes in soil microorganisms and soil chemical properties affect the heterogeneity and stability of soil aggregates before and after grassland conversion. Agriculture 2022, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, W. Deep Rock Mechanics: From Research to Engineering, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 483–487. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Yao, H.; Huang, C. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2006, 6, 981–988. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D. Selecting the minimum data set and quantitative soil quality indexing of alkaline soils under different land uses in northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; China Environmental Publishing Group. Soil Environmental Quality—Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1–3.
- GB 2762-2022; National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. National Food Safety Standard—Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 1–12.
- Zhang, M.; Riaz, M.; Zhang, L.; El-Desouki, Z.; Jiang, C. Biochar induces changes to basic soil properties and bacterial communities of different soils to varying degrees at 25 mm rainfall: More effective on acidic soils. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindhadevi, K.; Chinnathambi, A.; Obaid, S.A. An investigation on the conversion of infertile soil into fertile soil using crop waste as a remedial (compost) approach and its influence on Vigna mungo biometric and biomolecule profile. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Shu, A.; Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Effects of long-term fertilization with different substitution ratios of organic fertilizer on paddy soil. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, B.; Recous, S.; Darwis, D.; Robin, D. Interactions between decomposition of plant residues and nitrogen cycling in soil. Plant Soil 1996, 181, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, N.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z.; Cheng, Y. The influence of long-term animal manure and crop residue application on abiotic and biotic N immobilization in an acidified agricultural soil. Geoderma 2019, 337, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, Z.R.; Schmidt, A.M.; Woodbury, B.; Eskridge, K.M.; Durso, L.; Li, X. Corn stalk residue may add antibiotic-resistant bacteria to manure composting piles. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Sun, W.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, R. Reducing antibiotic resistance genes, integrons, and pathogens in dairy manure by continuous thermophilic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeiss, S.; Gleixner, G.; Antonietti, M. Effect of biochar amendment on soil carbon balance and soil microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Sanchez-Monedero, M.A.; Gomez, I. Influence of particle size of municipal solid waste amendments and presence or absence of Eisenia fetidaon soil greenhouse gases emission. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Effects of composite soil conditioner on soil properties and corn yield in a saline-alkali soil. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Han, L.; Wu, L. Effects of exogenous organic materials on the yield of double cropping rice, soil fertility and soil quality. J. China Agric. Univ. 2024, 29, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Polakowski, C.; Sochan, A.; Ryżak, M.; Beczek, M.; Mazur, R.; Majewska, K.; Turski, M.; Bieganowski, A. Measurement of soil dry aggregate size distribution using the laser diffraction method. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 211, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, J.; et al. Soil aggregates stability and storage of soil organic carbon respond to cropping systems on black soils of northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Giani, L. Water-stable aggregates, glomalin-related soil protein, and carbohydrates in a chronosequence of sandy hydromorphic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, T.; Ludynia, A. Permeability coefficient of low permeable soils as a single-variable function of soil parameter. Water 2019, 11, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, G.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; Jiang, G. Effects of Straw mulching thickness on the soil health in a temperate organic vineyard. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, T.D.; Bulletti, L.; Capecchi, E.; Viola, A.L.; Piccinino, D.; Piscopo, V. Perspectives of using lignin as additive to improve the permeability of in-situ soils for barrier materials in landfills. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.; Hu, F.; Zou, Y.; Du, B.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, J. Effects of combined application of chemical and organic fertilizer on soil bulk density, pH, and carbon and nitrogen metabolism in ratooning rice fields. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2023, 31, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Yang, Y.; Guan, P.; Geng, L.; Ma, L.; Di, H.; Liu, W.; Li, B. Remediation of organic amendments on soil salinization: Focusing on the relationship between soil salts and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, R.; Si, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Luo, R.; Wang, Y. The growth and ion absorption of Sesbania (Sesbania cannabina) and Hairy Vetch (Vicia villosa) in saline soil under improvement measures. Plants 2024, 13, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Saleem, M.H.; Yasin, G.; Mumtaz, S.; Qureshi, F.F.; Ali, B.; Ercisli, S.; Alhag, S.K.; Ahmed, A.E.; Vodnar, D.C.; et al. Individual and combinatorial effects of SNP and NaHS on morpho-physio-biochemical attributes and phytoextraction of chromium through Cr-stressed spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 973740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yan, D. Warming suppresses microbial biomass but enhances N recycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 131, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Dosage |
|---|---|
| CK | without any organic amendments |
| PM | 22,500 kg/ha of pig manure |
| PMB | 16,875 kg/ha of pig manure + 4950 kg/ha of biochar |
| PMC | 16,875 kg/ha of pig manure + 7200 kg/ha of corn straw |
| Indicators | CWM | CK | PM | PMB | PMC | ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | ||||||
| SOM (g/kg) | 2.47 ± 0.04 d | 2.29 ± 0.03 e | 6.23 ± 0.09 a | 5.35 ± 0.09 c | 5.66 ± 0.04 b | <0.01 |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.25 ± 0.02 d | 0.34 ± 0.02 c | 0.42 ± 0.01 a | 0.38 ± 0.01 b | 0.38 ± 0.01 b | <0.01 |
| AN (mg/kg) | 0.38 ± 0.01 d | 6.83 ± 0.10 c | 11.25 ± 0.37 a | 7.56 ± 0.31 b | 7.43 ± 0.15 b | <0.01 |
| TP (g/kg) | 0.40 ± 0.02 c | 0.43 ± 0.01 bc | 0.45 ± 0.02 b | 0.53 ± 0.02 a | 0.49 ± 0.02 ab | <0.01 |
| AP (mg/kg) | 11.84 ± 0.31 c | 20.58 ± 0.31 b | 27.82 ± 0.64 a | 27.95 ± 0.88 a | 27.76 ± 1.02 a | <0.01 |
| AK (mg/kg) | 21.95 ± 1.49 d | 30.37 ± 1.91 c | 38.51 ± 2.06 b | 38.33 ± 2.27 b | 51.55 ± 2.79 a | <0.01 |
| pH | 8.54 ± 0.07 a | 8.11 ± 0.05 c | 8.21 ± 0.03 bc | 8.29 ± 0.06 b | 8.27 ± 0.05 b | <0.01 |
| EC (us/cm) | 521.78 ± 10.88 a | 232.99 ± 11.31 b | 141.41 ± 7.83 c | 123.83 ± 6.67 c | 134.00 ± 9.75 c | <0.01 |
| BD (g/cm3) | 1.63 ± 0.03 a | 1.56 ± 0.02 b | 1.45 ± 0.02 c | 1.41 ± 0.02 cd | 1.38 ± 0.02 d | <0.01 |
| MWD | 1.06 ± 0.01 c | 1.41 ± 0.02 b | 1.49 ± 0.02 a | 1.48 ± 0.01 a | 1.51 ± 0.01 a | <0.01 |
| GMD | 0.52 ± 0.01 c | 0.89 ± 0.02 b | 0.97 ± 0.03 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 0.99 ± 0.01 a | <0.01 |
| PC (cm/d) | 6.40 ± 0.02 e | 25.57 ± 0.83 d | 121.54 ± 2.67 c | 130.75 ± 1.47 b | 142.56 ± 1.87 a | <0.01 |
| Indicators | CK | PM | PMB | PMC | Limit Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd (μg/kg) | 25.53 ± 1.03 | 18.03 ± 0.42 | 12.47 ± 0.34 | 17.70 ± 0.45 | <100 |
| Hg (μg/kg) | 4.23 ± 0.26 | 3.86 ± 0.28 | 3.35 ± 0.16 | 3.96 ± 0.31 | <20 |
| As (μg/kg) | 210.5 ± 15.3 | 198.3 ± 16.7 | 175.6 ± 13.5 | 156.3 ± 12.8 | <500 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 26.96 ± 2.24 | 27.69 ± 2.49 | 25.36 ± 2.15 | 26.26 ± 1.68 | <50 |
| Pb (μg/kg) | 46.23 ± 3.52 | 46.59 ± 3.88 | 40.36 ± 2.96 | 42.36 ± 3.45 | <200 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | <1 |
| Indicators | PC1 | PC2 | Communality | Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOM | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.94 | 11.90 |
| TN | 0.79 | 0.50 | 0.87 | 2.82 |
| AN | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.82 | 5.81 |
| TP | 0.77 | 0.25 | 0.66 | 4.12 |
| AP | 0.88 | 0.46 | 0.99 | 5.12 |
| AK | 0.87 | 0.21 | 0.81 | 5.56 |
| pH | −0.16 | −0.93 | 0.89 | 4.96 |
| EC | −0.78 | −0.62 | 0.99 | 21.92 |
| BD | −0.92 | −0.23 | 0.91 | 8.44 |
| MWD | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.99 | 4.59 |
| GWD | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.98 | 4.63 |
| PC | 0.98 | 0.14 | 0.98 | 10.08 |
| MBC | 0.22 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 5.18 |
| MBN | 0.13 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 4.87 |
| Eigenvalue | 7.77 | 4.90 | ||
| Variance (%) | 55.50 | 35.03 | ||
| Cumulative variance (%) | 55.50 | 90.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, J.; Yin, J.; Zhong, K.; Gu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, H.; Pang, X.; Zhang, C. Efficacy Evaluation of Civil-Works Mud as Soil Matrix Modified by Organic Amendments. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101056
Su Y, Zhang Q, Tang J, Yin J, Zhong K, Gu J, Xiong Z, Wu H, Pang X, Zhang C. Efficacy Evaluation of Civil-Works Mud as Soil Matrix Modified by Organic Amendments. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101056
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yuan, Qian Zhang, Junwei Tang, Juanjuan Yin, Kai Zhong, Jingying Gu, Zicong Xiong, Haile Wu, Xingzhi Pang, and Chaolan Zhang. 2025. "Efficacy Evaluation of Civil-Works Mud as Soil Matrix Modified by Organic Amendments" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101056
APA StyleSu, Y., Zhang, Q., Tang, J., Yin, J., Zhong, K., Gu, J., Xiong, Z., Wu, H., Pang, X., & Zhang, C. (2025). Efficacy Evaluation of Civil-Works Mud as Soil Matrix Modified by Organic Amendments. Agriculture, 15(10), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101056






