Abstract
Soil acidification is a significant threat to agricultural sustainability, particularly in paddy fields, where acidic conditions can limit crop productivity and soil health. This study aimed to explore the combined effects of alkaline amendments—lime, magnesia, and silicon fertilizer—on the acid-neutralizing capacity (ANC) of paddy soils and the rice yield, with the objective of identifying effective strategies to mitigate soil acidification and enhance agricultural productivity. From 2018 to 2021, a four-year field trial in Hunan tested lime, magnesia, and silicon fertilizers. Soil samples (0–20 cm depth) were collected once post-harvest in 2021 to evaluate the cumulative treatment effects. After four years, the control soil pH was 6.12. Lime and light magnesia treatment increased it to 6.70 and 6.99, respectively. Silicon fertilizer showed no significant difference (pH 6.05). ANC analysis revealed the following anti-acidification capacity ranking: light magnesia > lime > control > silicon fertilizer. Light magnesia boosted the rice yield by 13.02% over the control. Statistical analyses indicated a significant positive correlation between the soil acid-neutralizing capacity and pH (ANC4.0 = 7.53 × pH − 30.00, R2adj = 0.70; ANC5.0 = 6.96 × pH − 37.49, R2adj = 0.58). The rice yield was correlated with exchangeable magnesium (yield = 0.42 × Ex-Mg + 24.54, R2adj = 0.44). The continuous application of lime and light magnesia enhanced the nutrient availability and soil anti-acidification, with light magnesia also improving the rice yield. These findings provide insights to aid in enhancing soil quality and agricultural productivity in acid-affected regions.
1. Introduction
Under the dual pressures of global population growth and climate change, ensuring a stable food supply has become an urgent global issue [1]. The United Nations projects that the global population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050, with the fastest growth occurring in the least developed countries [2]. This rapid population increase, combined with the adverse effects of climate change, poses significant challenges to food security. Rice, as a staple crop for nearly half of the global population, plays a crucial role in maintaining food security [3]. However, rice production is particularly vulnerable to climate change, with studies indicating potential yield declines of up to 9% by 2080–2100 [4].
In Southern China, acidic red soil covers about 22.7% of the total land area [5]. This region, with its unique geographical and climatic conditions, is both a major rice-producing area and a primary location for acidic soils [6]. Soil acidification reduces soil nutrient availability [7] and inhibits microbial activity, affecting rice growth and development [8]. Therefore, using alkaline materials to amend acidic soil in Southern China to boost the rice yield is critical for national food security [9].
The primary cause of soil acidification in southern regions is long-term rainfall and nutrient cycling during crop growth [2]. Acidic substances in rainwater lower the soil pH, while crops deplete soil calcium and magnesium, worsening acidification [10]. The application of nitrogen fertilizers increases the soil exchangeable acidity dominated by aluminum, reduces the exchangeable alkaline ions, and accelerates the rate of acidification [11]. This acidification process not only affects soil health but also poses a significant threat to rice yields and quality [2].
Calcium, magnesium, and silicon fertilizers provide essential nutrients, improve the soil structure, and increase the soil’s resistance to acidification [10]. Studies have shown that these fertilizers effectively raise the soil pH, increase base ions, and reduce exchangeable aluminum, thereby mitigating soil acidity [12]. For example, Ji et al. [13] demonstrated that silicon, calcium, potassium, and magnesium fertilizers effectively raised the soil pH, increased base ions, and reduced exchangeable aluminum, thus mitigating soil acidity. These fertilizers also improve hybrid rice’s tillering, material accumulation, and yield by increasing the effective tillers and dry matter accumulation [14].
The soil acid-neutralizing capacity is a crucial indicator of soil’s anti-acidification ability. Meng et al. [15] found that the acid-neutralizing capacity calculated using a quadratic polynomial provided greater precision than the traditional acid-buffering capacity when evaluating soil anti-acidification. Research has shown that lime application raises the soil pH and neutralizes soil acidity [16,17,18]. Ming et al. [16] reported that higher amendment dosages enhanced soil nutrient availability and organic matter. Alkaline amendments support nutrient cycling, enhance exchangeable cations such as calcium and magnesium, and improve the soil structure [19,20,21], promoting nutrient absorption by crops [22]. Lu et al. [23] noted that regular lime supplementation can improve soil conditions.
The severe acidification of paddy soil significantly impacts rice yields and quality. However, existing studies on the soil acid-neutralizing capacity in rice paddies often focus on short-term effects, with a limited emphasis on the cumulative impacts under prolonged amendment application. Given the critical importance of addressing soil acidification to ensure sustainable rice production, this study aimed to evaluate the long-term effects of alkaline amendments—lime, light magnesia, and silicon fertilizer—in mitigating soil acidification and enhancing the rice yield in acidic paddy soils. We hypothesized that the application of these alkaline amendments will significantly improve the soil ANC and rice yield by enhancing nutrient availability and the soil structure. To test this hypothesis, we conducted a four-year field trial (2018–2021) in Hunan, China, under a rice–rice–fallow system. Soil samples were collected from the 0–20 cm layer at the end of the trial (October 2021) to assess cumulative changes in soil nutrient availability, ANC, and the rice yield. The findings of this study are expected to provide valuable insights into the efficacy of alkaline amendments in improving soil quality and crop productivity under prolonged acidic conditions, supporting their practical application in agriculture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The experimental site was located in Hongqiao Village, Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province (27°31′ N, 113°10′ E, elevation 50 m). Zhuzhou lies within a subtropical monsoon climate zone, characterized by four distinct seasons, abundant rainfall, and ample sunlight. The frost-free period exceeds 286 days per year, and the annual average temperature ranges from 16 °C to 18 °C, creating ideal conditions for crop growth. Consequently, Zhuzhou is a major grain-producing area in Hunan and a critical national grain base.
2.2. Experimental Design
The experiment was conducted using a completely randomized design. Four treatments—conventional fertilization (CK), lime (L), light magnesia (LM), and silicon fertilizer (SS)—were randomly assigned to 12 plots (3 replicates per treatment). Each plot measured 33 m2 and was separated by 30-cm-high cement ridges with independent drainage and irrigation systems to prevent cross-contamination. The allocation of treatments to plots was fully randomized to ensure spatial independence.
The cropping system followed a rice–rice–fallow rotation. Early rice (variety Zhongjiazao No. 17) was transplanted in April and harvested in early July, while late rice (variety C Liangyou 87) was transplanted in mid-July and harvested in late October. Both the early and late rice yields were measured separately for each treatment, and the total annual yield (sum of early and late rice) is reported in this manuscript. Before transplantation, fertilizers were applied at the following rates: urea (214.5 kg·ha−1, 98.67 kg N·ha−1), superphosphate (687 kg·ha−1, 82.44 kg P2O5·ha−1), and potassium chloride (138 kg·ha−1, 82.8 kg K2O·ha−1). After the resumption of green growth, additional urea (142.5 kg·ha−1, 65.55 kg N·ha−1) and potassium chloride (138 kg·ha−1, 82.8 kg K2O·ha−1) were applied. The amendment dosages were based on equal alkali amounts: lime (CaO content ≥70%) at 1500 kg·ha−2, light magnesia (MgO content ≥99%) at 750 kg·ha−2, and silicon fertilizer (containing 30% Na2O and 30% SiO2) at 1500 kg·ha−2. The amendments were evenly spread on the soil surface three days before the base fertilizer application and then incorporated using a rotary tiller. All treatments received the same daily management, including water management and pest/disease control, following local farming practices.
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
In October 2021 (after four years of treatment application), composite soil samples were collected from the 0–20 cm plough layer of each plot using a stainless-steel auger. The “S-shaped” multi-point sampling method was used to collect soil from the 0–20 cm depth across each plot, ensuring representative coverage of the experimental area. Samples were sieved through a 2 mm sieve, air-dried, and cleared of roots and impurities before being sealed for soil chemical property analysis.
2.4. Analytical Methods
The basic physicochemical properties of the soil (0–20 cm plowing layer) in the experimental paddy field are summarized in Table 1. The soil was classified as acidic paddy soil (pH < 6.5, Hydragric Anthrosols, Chinese Soil Taxonomy) with moderate fertility. The total organic carbon (TOC) and nutrient content was analyzed following standardized protocols, and all methodologies adhered to national or industry-specific guidelines.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of the experimental paddy soil (0–20 cm depth).
Additional Methodological Details: Exchangeable hydrogen (Ex-H) and aluminum (Ex-Al) were extracted with 1 M KCl and quantified by neutralization titration according to the acidic soil analysis guidelines [20]. Exchangeable basic cations (Ex-K, Ex-Na, Ex-Ca, Ex-Mg) were extracted with 1 M ammonium acetate (pH 7.0) and measured via atomic absorption spectrophotometry, adhering to the agricultural soil exchangeable cation protocol. Total exchangeable bases (SEB) and base saturation (BS) were calculated as the sum of Ex-K, Ex-Na, Ex-Ca, and Ex-Mg and their proportions relative to the cation-exchange capacity (CEC, Table 1), respectively [25].
Meng et al. [15] found that the acid-neutralizing capacity calculated using a quadratic polynomial provides greater precision than the traditional acid-buffering capacity when evaluating soil anti-acidification. The acid titration curve was derived using the equation
where c represents the initial pH, and a and b are the quadratic and linear coefficients, respectively. ANC4.0 and ANC5.0 represent the amount of acid required to lower the pH to the reference levels of 4.0 and 5.0, respectively. Soil ABC reflects the molar mass of acid needed to decrease the pH by one unit. When setting the target pH (y) to 5.0 or 4.0 in Equation (1), the corresponding value of x (acid added, mmol H+·kg−1 soil) represents the acid-neutralizing capacity (ANC) required to lower the pH to the respective reference levels. Setting y = c − 1 allows the calculation of the soil acid-buffering capacity (ABC) (mmol H+·kg−1 soil).
Freshly harvested rice grains were oven-dried at 70 °C to a constant weight, and the yield was calculated based on 14% moisture content, following the national standard protocol for grain yield measurement [26].
2.5. Data Processing
Data were subjected to preliminary analysis using Excel 2019 and SPSS 22.0. The preliminary analysis included descriptive statistics to summarize the basic characteristics of the data. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to assess the differences among treatments, followed by multiple comparisons (LSD) to determine significant differences between treatments.
The Mantel test was used to evaluate the correlations between the soil acid-neutralizing capacity (ANC), acid-buffering capacity (ABC), rice yield, and various environmental factors (such as soil pH, exchangeable cations, etc.). The Mantel test is a non-parametric method that assesses the correlation between two distance matrices by calculating the Mantel statistic and performing random permutations (999 times) to test the significance of the correlation. In this study, we constructed distance matrices for soil properties and environmental factors and used the Mantel test to assess their correlations.
Graphs were created using the Origin 2022 software to visualize the results. Regression models were developed to explore the relationships between the soil properties (e.g., pH, exchangeable magnesium) and rice yield, and the adjusted R2 values are reported to indicate the goodness of fit.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Nutrient Content in Paddy Soil
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and organic matter are essential nutrient indicators in paddy soil, playing a crucial role in rice growth and development. As shown in Table 2, compared to CK, the TN content was significantly increased in all treatments, with the highest TN content observed in SS at 2.21 g·kg−1 (F (3,8) = 4.30, p = 0.044). The TP and TK content did not show significant differences across treatments (F (3,8) = 1.21, p = 0.367, for TP; F (3,8) = 3.00, p = 0.095, for TK). The AN content was significantly higher in the L, LM, and SS treatments than in CK (F (3,8) = 6.29, p = 0.017), following the order LM > SS > L > CK. The AP content was higher in the LM treatment, followed by L and SS, while CK had the lowest AP content (F (3,8) = 18.61, p < 0.001). SOM followed the order SS > LM > L > CK, with the SS treatment exhibiting the highest SOM content at 42.5 g·kg−1, which was significantly greater than that of CK (F (3,8) = 2.42, p = 0.141).

Table 2.
Changes in nutrient content in paddy soil under different treatments.
3.2. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Soil Exchangeable Cations
Table 3 shows that the exchangeable hydrogen (Ex-H) and aluminum (Ex-Al) content in the CK and SS treatments was significantly higher than in the L and LM treatments (F (3,8) = 27.14, p < 0.001, for Ex-H; F (3,8) = 0.751, p = 0.552, for Ex-Al). The Ex-K content was the highest under the LM treatment and lowest under the SS treatment (F (3,8) = 2.32, p = 0.152). Ex-Na was the highest under SS, at 0.51 cmol·kg−1, significantly higher than in the other treatments (F (3,8) = 25.979, p < 0.001). The Ex-Ca content was significantly higher under the L treatment, reaching 10.99 cmol·kg−1, followed by CK and SS, while LM had the lowest Ex-Ca content (F (3,8) = 20.353, p < 0.001). Ex-Mg was significantly higher under LM, followed by SS, with L and CK showing the lowest content (F (3,8) = 2166.26, p < 0.001). In terms of total exchangeable bases (SEB), those of the L and LM treatments were significantly higher than in CK and SS, with the order being LM > L > CK > SS. Base saturation (BS) was also significantly higher in L and LM than in CK and SS.

Table 3.
Changes in exchangeable cations in rice paddy soil under different treatments.
3.3. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Soil pH, Acid-Buffering Capacity (ABC), and Acid-Neutralizing Capacity (ANC)
Figure 1 illustrates the differences in the soil pH, ABC, and ANC across treatments. The pH levels followed the order LM > L > SS > CK, with a pH of 6.99 for LM, 6.70 for L, 6.05 for SS, and 6.12 for CK. The pH values for the L and LM treatments were significantly higher than that of CK, while the pH under SS was not significantly different from that of CK. Soil ABC and ANC indicate the soil’s resistance to acidification and its neutralizing capacity [26]. As shown in Figure 1b, ABC was lower following the L and LM treatments but higher under SS, with no significant difference from CK. ANC followed the opposite trend, being higher after the L and LM treatments and lower under SS. Both the ANC4.0 and ANC5.0 measurements consistently followed the pattern LM > L > CK > SS, suggesting that the L and LM treatments effectively mitigated soil acidification.
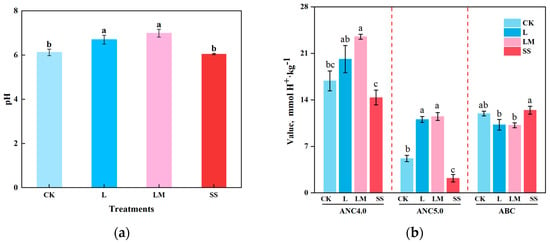
Figure 1.
The variations in the pH values, acid-neutralizing capacity (ANC), and acid-buffering capacity (ABC) under different treatment conditions. (a) The trend of pH value changes; (b) the trend of changes in ANC and ABC. Lowercase letters indicate significant differences between conventional fertilization (CK), lime (L), light magnesium (LM), and silicon fertilizer (SS) (p < 0.05).
3.4. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Rice Yield
The rice yield is a direct measure of the efficacy of different acidification remediation strategies. As shown in Figure 2, the rice yield was 13.02% higher under the LM treatment and 4.43% higher under the SS treatment compared to CK, reaching 7.16 t·ha−2 and 6.61 t·ha−2, respectively, compared to CK (6.33 t·ha−2). Conversely, the L treatment resulted in a 2.83% reduction in yield, with a yield of 6.15 t·ha−2. Among the treatments, the yield under LM was significantly higher than under CK and L, demonstrating the beneficial effect of light magnesium oxide on rice yields.
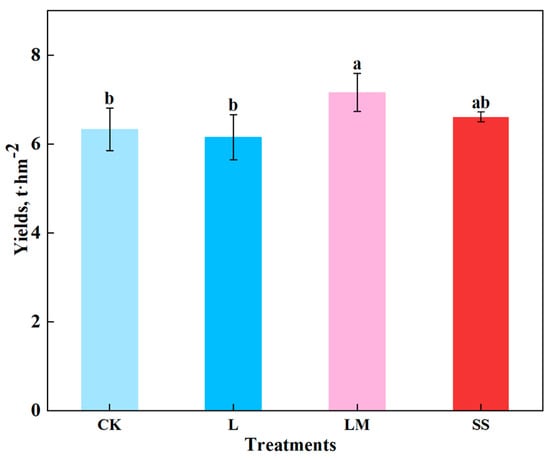
Figure 2.
Changes in rice yield under different treatments. Lowercase letters indicate significant differences between conventional fertilization (CK), lime (L), light magnesium (LM), and silicon fertilizer (SS) (p < 0.05).
3.5. Relationships Between Soil Acid-Neutralizing Capacity, Acid-Buffering Capacity, and Rice Yield and Environmental Factors
The relationships between the soil ABC, ANC, and rice yield and environmental factors were assessed using a Mantel test, as shown in Figure 3. The results of the Mantel experiment showed that there was a significant positive correlation between exchangeable magnesium and the rice yield. The correlations with other factors were not significant. Soil ABC was positively correlated with Ex-H and Ex-Na but negatively correlated with the pH, ANC4.0, and ANC5.0. In contrast, ANC4.0 and ANC5.0 were negatively correlated with Ex-H and Ex-Na and positively correlated with the pH. Additionally, ANC4.0 was positively correlated with AP, Ex-K, and Ex-Mg.
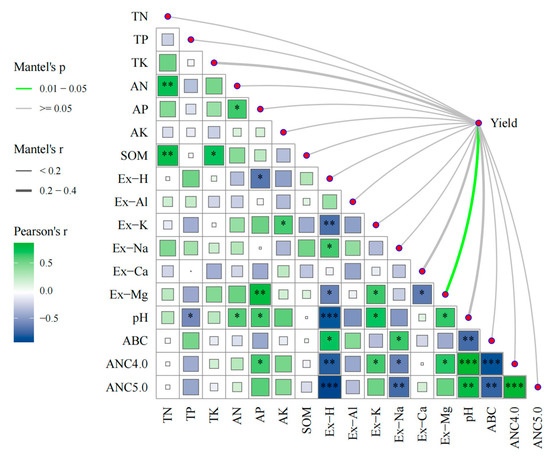
Figure 3.
Mantel test analysis of correlations between rice yield and soil environmental factors. Green lines represent significant positive correlations (Mantel’s 0.01 < p < 0.05), and gray lines represent significant negative correlations (Mantel’s p ≥ 0.05). Symbols *, **, and *** indicate significant differences, with p < 0.05, <0.01, and <0.001, respectively.
In Figure 4, ABC shows a negative linear regression relationship with the pH (R2adj = 0.48, t = 6.16, F (1,10) = 11.28, p = 0.007), with no significant regression effect observed for Ex-Ca and Ex-Mg. Both ANC4.0 and ANC5.0 demonstrated significant positive regression relationships with the pH, modeled as follows: ANC4.0 = 7.53 × pH − 30.00 (R2adj = 0.70, t = 5.22, F (1,10) = 27.29, p < 0.001) and ANC5.0 = 6.96 × pH − 37.49 (R2adj = 0.58, t = 3.32, F (1,10) = 15.91, p = 0.003). ANC4.0 also exhibited a positive regression relationship with Ex-Mg (R2adj = 0.38, t = 13.32, F (1,10) = 7.80, p = 0.019). No significant relationship was found between ANC4.0 and Ex-Ca. Figure 5 indicates a non-significant positive regression trend between the rice yield and pH. However, the yield showed a significant negative regression relationship with Ex-Ca (yield = −0.70 × Ex-Ca + 31.5, R2adj = 0.41, F (1,10) = 8.56, p = 0.015) and a significant positive regression relationship with Ex-Mg (yield = 0.42 × Ex-Mg + 24.54, R2adj = 0.44, F (1,10) = 9.64, p = 0.011).
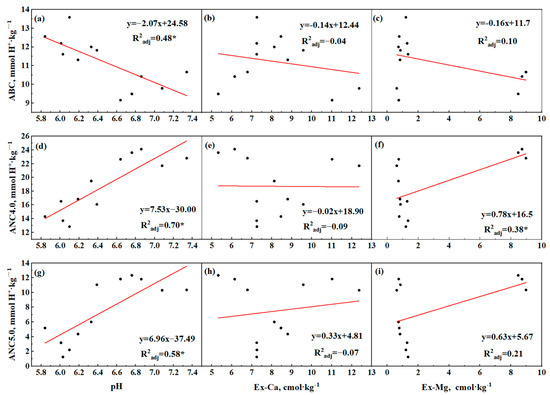
Figure 4.
(a–c) Regression relationships among soil acid-buffering capacity (ABC) and pH, exchangeable calcium (Ex-Ca), and exchangeable magnesium (Ex-Ma) and (d–i) regression relationships among acid-neutralizing capacity (ANC) and pH, exchangeable calcium (Ex-Ca), and exchangeable magnesium (Ex-Ma). Symbols * represents a statistically significant regression relationship (p < 0.05).
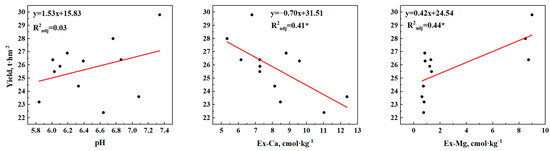
Figure 5.
Regression relationships between rice yield and pH, exchangeable calcium (Ex-Ca), and exchangeable magnesium (Ex-Ma). Symbols * represents a statistically significant regression relationship (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Exchangeable base cations in soil, such as Na+, Ca2+, K+, and Mg2+, are essential for nutrient cycling, pH regulation, and soil structure stability, contributing to the soil cation exchange capacity [27]. Studies have shown that soils with higher levels of exchangeable base cations generally exhibit a higher ANC [28], as these cations help to neutralize acidic substances, boosting the soil’s buffering capacity and creating a more favorable environment for crop growth [29]. In this study, we observed significant changes in the soil exchangeable base cation content after applying L, LM, and SS. These amendments, which contained high calcium, magnesium, and sodium levels, directly increased the exchangeable base cation concentrations in the soil [30]. Among them, L and LM were particularly effective, raising the exchangeable base cations by 25.8% and 58.4%, respectively. This aligns with the findings of Ji et al. [13], who reported that the continuous application of alkaline mineral fertilizers over four years reduced soil acidification by releasing exchangeable base cations, with higher application rates showing greater improvements. Zhang et al. [1] also demonstrated that applying alkaline residues to acidic tea plantation soils significantly increased the soil pH, exchangeable base cations, and base saturation while maintaining a balanced supply of calcium and magnesium. Similarly, Zhang et al. [31] found that soil amendments increased the exchangeable base cation levels by 45.18–46.16%, with lime proving to be the most effective, consistent with our results. Calcium and magnesium help to replenish alkaline components lost due to acidification, thus maintaining the soil nutrient balance, while silicon can react with acidic substances in the soil, reducing active acids and increasing the soil pH [13]. However, in this study, the silicon fertilizer had a less significant effect on exchangeable base cations. Although silicon fertilizer primarily supplies Na+, its contribution to exchangeable base cations was less noticeable than that of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Overall, lime, light magnesium oxide, and silicon fertilizer effectively increased the exchangeable base cations in the soil, with light magnesium oxide having the greatest impact, followed by lime, while silicon fertilizer had a comparatively minor effect.
In this study, applying L and LM significantly improved the soil pH and ANC (Figure 1), helping to prevent soil acidification and enhance the soil’s acid–base balance. Liu et al. [27] found that lime neutralized the active acids and potential acidity in the soil, thereby alleviating acidification. Lime can also produce hydroxides that neutralize aluminum toxicity and increase calcium ions in the soil, which displace hydrogen ions on soil colloids, further enhancing the soil’s acid-neutralizing capacity [32]. Blake et al. [33] suggested that the primary reason for declining ANC is the leaching of calcium and magnesium ions. Therefore, as alkaline substances, lime and light magnesia react with acidic components in the soil, boosting the calcium and magnesium levels and thereby improving the soil ANC. In contrast, the silicon fertilizer had a limited effect on the soil pH and ANC. Although the silicon fertilizer helped to maintain a stable pH and prevent further acidification, its lower ANC indicates that it was less effective in neutralizing acidic substances than lime and light magnesia. This may be due to the higher solubility of silicon fertilizer in the soil, which allows it to react with other soil components to form insoluble silicate colloids, thereby reducing the availability of ion exchange sites needed for acid neutralization [34]. The soil acid-buffering capacity (ABC) is often used to assess a soil’s resistance to acidification [15]. Luo et al. [35] found that the ABC was positively correlated with the initial pH, carbonate content, and cation exchange capacity. In this study, however, we observed a negative correlation between the ABC and pH, consistent with the findings of Meng et al. [15]. This is because, in soils treated with lime and light magnesium oxide, the pH was significantly higher than in the CK and silicon fertilizer treatments. Furthermore, statistically small differences in the acid-buffering capacity are biologically consequential. For example, in Halomonas bioreactors, a pH drop of 0.2 units activated stress-responsive promoters, amplifying indigo production by 100% through dynamic gene regulation [36]. In soils with a pH < 7, less acid is required to lower the pH by one unit. The ANC was positively correlated with exchangeable calcium and magnesium, further confirming the roles of the pH and exchangeable base cations in maintaining the soil acid–base balance and resistance to acidification.
The soil acid-neutralizing capacity (ANC) and buffering capacity (ABC) are critical indicators complementing the pH to assess soil’s resistance to acidification. The ANC quantifies the acid required to lower the soil pH to a reference level (e.g., 4.0), reflecting long-term acid resistance, while the ABC measures the acid needed per pH unit decrease, indicating the short-term buffering stability. Both parameters are linked to soil ion exchange processes, indirectly revealing treatment-induced variations in the ion exchange capacity. Integrating the pH, ANC, and ABC enables a comprehensive evaluation of a soil’s acid resistance mechanisms and buffering performance. These results highlight the importance of base cations in supporting the soil pH and improving its resistance to acidification. In conclusion, applying amendments effectively increased the soil ANC, enhancing its resistance to acidification.
In this study, all treatments significantly increased the soil total nitrogen, alkaline nitrogen, and available phosphorus, with the light magnesia treatment having the most potent effect, which was linked to the increase in soil pH. Previous studies have shown that amendments significantly boost alkaline nitrogen and available phosphorus, making these nutrients more accessible to plants [37]. In acidic soils, a large proportion of the available phosphorus is absorbed and fixed, making it difficult for plants to absorb. Increasing the soil pH reduces phosphorus adsorption by iron and aluminum oxides, thus enhancing the phosphorus availability [27]. Tang et al. [38] reported that higher amendment application rates increased the total nitrogen and alkaline nitrogen levels. Similarly, Li et al. [39] found that applying bio-organic amendments raised the alkaline nitrogen levels by 66.8–148.6%. The silicon fertilizer treatment notably increased the soil organic matter, promoting organic matter accumulation. Higher organic matter levels improve the soil fertility and structure [40] and enhance water retention, nutrient availability, and crop yields [41].
Interestingly, under the light magnesia treatment, both the exchangeable magnesium in the soil and the rice yield increased significantly (Table 3 and Figure 2), and we observed a strong positive correlation between the rice yield and exchangeable magnesium (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Wang et al. [42] analyzed data from 30 different crops across various countries and found that magnesium fertilization increased the crop yield by an average of 8.5%. Huang et al. [43] surveyed the magnesium status of red soils in Jiangxi and Hunan Provinces in China, revealing that 61.9% of soils had available magnesium content below 20 mg·kg−1, indicating a low magnesium supply capacity. According to Zhang et al. [44], paddy soils are considered magnesium-deficient when the exchangeable magnesium is less than 50 mg·kg−1, and it is magnesium-rich when it exceeds 120 mg·kg−1. In our study, the application of calcined powder significantly raised the exchangeable magnesium content to a high level, while the soils under other treatments remained magnesium-deficient.
Low levels of exchangeable magnesium in acidic soils, coupled with the frequent neglect of magnesium fertilizer application by farmers, result in chronic magnesium deficiency, which often becomes a significant limiting factor for crop production [27]. Under such conditions, applying magnesium fertilizers can substantially increase the rice biomass and yield [45]. However, long-term magnesium supplementation can lead to changes in soil microbial communities and nutrient cycling, which may affect other essential nutrients [46]. Additionally, excessive magnesium application could potentially lead to soil compaction or an altered soil structure if not managed properly [47].
Notably, while lime effectively prevented soil acidification, its impact on the rice yield was less favorable. This may be due to several factors, including potential competitive inhibition from calcium. Excessive calcium from lime can inhibit the uptake of other cations, such as magnesium and potassium, which are critical for rice growth [17]. Additionally, raising the soil pH excessively can lead to nutrient imbalances and reduced yields [48,49,50]. Future studies should optimize the lime application rates to avoid such trade-offs and ensure balanced nutrient availability. In conclusion, applying soil amendments effectively improved the nutrient availability and rice yield in acidic paddy soils, with light magnesium oxide being particularly effective in increasing the available phosphorus and rice yield. These findings provide scientific evidence supporting the use of soil amendments in agricultural practices to enhance crop yields.
5. Conclusions
The application of alkaline amendments, particularly light magnesium and lime, significantly enhanced the exchangeable base cations and improved the soil acid-neutralizing capacity in acidic paddy soils. These treatments effectively mitigated soil acidification and increased the nutrient availability. Notably, light magnesia increased the soil pH from 6.12 (control) to 6.99, while lime raised it to 6.70. Both treatments also significantly boosted the rice yield, with light magnesium offering 13.02% higher yields than the control. These results highlight the importance of base cations in maintaining the soil pH and enhancing its resistance to acidification. This study provides scientific evidence supporting the use of alkaline amendments in agricultural practices to improve the soil quality and enhance crop productivity, particularly in regions with acidic soils. Our findings suggest that light magnesium and lime are effective tools in mitigating soil acidification and improving rice yields, thereby contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. Future research should focus on long-term experiments to assess the sustained impacts of alkaline amendments on soil properties and crop productivity over multiple seasons. This will help in understanding the long-term dynamics of soil acidification and the persistence of the benefits observed in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. (Zedong Long); methodology, Z.L. (Zedong Long) and M.S.; software, Z.L. (Zedong Long), J.Z. and Q.F.; formal analysis, M.S. and Z.L. (Zunchang Luo); validation, Z.L. (Zunchang Luo); investigation, Z.L. (Zedong Long), G.S. and Y.Z.; resources, Z.L. (Zedong Long) and T.Y.; data curation, Z.L. (Zedong Long) and G.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L. (Zedong Long) and T.Y.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. (Zedong Long) and T.Y.; visualization, H.D. and G.S.; supervision, Z.L. (Zedong Long) and T.Y.; project administration, G.S. and H.D.; funding acquisition, Z.L. (Zedong Long) and G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Project of the National Key Research and Development Program (2023YFD1901105), the Project of the Hunan Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Fund (2024CX38), and the Project of the Key Research and Development Program of Hunan Province (2023NK2027).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, Q.; de Vries, W.; Ros, G.H.; Chen, X.; Muneer, M.A.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L. Effects of soil amendments on soil acidity and crop yields in acidic soils: A world-wide meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, J.; Newman, K.; Mayhew, S. Population dynamics and climate change: What are the links? J. Public Health-UK 2010, 32, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, K.M.; Shaalan, A.M.; AbouEl-Soud, G.M.; El-Dalil, M.A.; Marei, A.M.; El-Moneim, D.A.; El-Banna, A.A.; Lamlom, S.F.; Abdelghany, A.M. Comprehensive quality profiling and multivariate analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars: Integrating physical, cooking, nutritional, and micronutrient characteristics for enhanced varietal selection. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Camac, J.; Robinson, A.; Kompas, T. Predicting changes in agricultural yields under climate change scenarios and their implications for global food security. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q. Exploiting Resource Advantage and Innovating Research and Development Potential for Social and Economic Development in Red Soil Region of Southern China—In Celebration of the 30th Anniversary of the Establishment of Ecological Experiment Station of Red Soil, Chineses Academy of Sciences. Soils 2015, 47, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pan, X.; Ma, H.; Dong, X.; Che, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, R. Scientific Issues and Strategies of Acid Soil Use in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Fanin, N.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Du, G.; Hu, F.; Jiang, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, M. Nutrient-induced acidification modulates soil biodiversity-function relationships. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Bao, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X. Research Progresses on Soil Acidification and its effects on Soil-Microrganism-Crop Systems in Agricultural Soil. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 55, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, R. Effects of Liming and Dicyandiamide (DCD) Application on Soil pH and Nitrification of Acidic Red Soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2021, 58, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, H.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Lan, X.; Chen, J. Effects of fertilizer of calcium silicon magnesium potassium on the dynamics of soil acidity and exchangeable base cation in paddy field of southern China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S. Intensified soil acidification from chemical N fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 15, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Lei, M.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, H.; Du, H. In vitro tungsten bioaccessibility in Chinese residential soils: Implications for human health risk assessments and soil screening level derivation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Lan, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, X. Effect of Si-Ca-K-Mg Fertilizer Remedying Acid Paddy Soil in South China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2019, 56, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AShen, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, N.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Ma, P.; AEr, L.; Liao, X.; Zhang, K. Effects of Silicon, Calcium, Potassium and Magnesium Fertilizer and Density on Rice Yield Formatio. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Li, T.; Shi, Z.; Cai, J.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, Y. Effects of fertilization and water addition on soil acid neutralizing capacity in an old-field grassland. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, R.; Wan, F.; Na, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Tan, W.; Wu, Y. Effect of Soil Acid Reduction and Fertilizer Cultivation Under Conditioner Application: Meta-analysis Based on Acid Soil Improvement Studies in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2025, 62, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yin, Z.-r.; Sheng, H.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, P. Response of microbial community, enzyme activity, and physicochemical property in paddy soil to continuous organic fertilizer and lime amendments. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sun, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, H.; Lei, M.; Du, H. Association of tungsten with aluminosilicate mineral colloids and silicotungstates in soil porewaters: Insights into the unexpectedly high tungsten mobility in soil. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2025, 389, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Pan, Q.; He, X. Research progress of soil amelioration of acidified soil by soil amendments. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Li, D.; Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Shah, A.; Liu, L.; Feng, G.; Zhang, H. Soil potassium regulation by initial K level and acidification degree when subjected to liming: A meta-analysis and long-term field experiment. Catena 2023, 232, 107408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Ran, Y.; Tan, Y.; Peacock, C.L.; Du, H. Arsenite and arsenate binding to ferrihydrite organo-mineral coprecipitate: Implications for arsenic mobility and fate in natural environments. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Soil Nutrient Transformation and Bioavailability of Arsenic and Lead in Contaminated Soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 332–339+345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Nie, J.; Zhou, X.; Xie, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, H. Effect of Long-term Fertilization and Lime Application on Soil Acidity of Reddish Paddy Soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2016, 53, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Wadoux, A.M.C.; Akoeb, E.N.; Sabrina, T. Precocious 19th century soil carbon science. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 22, e00306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H. (Eds.) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3: Chemical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 3543.5-1995; Rules for Agricultural Seed Testing—Verification of Genuineness and Varietal Purity. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 1995.
- Liu, F.; Fang, C.; Yu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Cao, W.; Nie, J.; Tu, N. Effects of Green Manure, Rice Straw Return and Lime Combination on Soil Acidity and Rice Yield. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2024, 61, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Xu, M.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Z. Evaluation of Acid-neutralizing Capacity of Topsoil in Croplands Using Quadratic Curve Fitting. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ros, G.H.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, M.; Wen, S.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, F.; de Vries, W. Major drivers of soil acidification over 30 years differ in paddy and upland soils in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.R.; DeSutter, T.M.; Daigh, A.L.M.; Meehan, M.A.; Derby, N. Effects of calcium amendments on hydraulic conductivity and sodium content of brine-impacted soils. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2024, 7, e20556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Miliang, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhang, M.; Tian, M. Effects of different amendments application on remediation of acidic soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Xie, G. Organic Carbon and Acidity and Alkalinity of Orchard Soils in Typical Geomorphic Areas of Zhejiang and Countermeasures for Improving Soil Quality. J. Agric. 2023, 13, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, D.; Boyce, M.C.; Stock, W.D.; Horwitz, P. Fire in Organic-Rich Wetland Sediments: Inorganic Responses in Porewater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.F.; Ahmed, O.H.; Jalloh, M.B.; Omar, L.; Kwan, Y.M.; Musah, A.A.; Poong, K.H. Soil Nutrient Retention and pH Buffering Capacity Are Enhanced by Calciprill and Sodium Silicate. Agronomy 2022, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.T.; Nelson, P.N.; Li, M.H.; Cai, J.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.G.; Yang, S.; Wang, R.Z.; Wang, Z.W.; Wu, Y.N.; et al. Contrasting pH buffering patterns in neutral-alkaline soils along a 3600 km transect in northern China. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 7047–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.N.; Li, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, Y.H.; Liu, K.X.; Gan, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.W.; Deng, R.Z.; et al. Developing Quorum Sensing-Based Collaborative Dynamic Control System in Halomonas TD01. Adv. Sci. 2025, 2408083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Guan, H.; Lu, J.; Xu, W. Effects of Biochar on Physicochemical Properties of Dry Land Acid Red Soil. Soils 2020, 52, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xiang, B.; Tan, T. Effect of biochar and bentonite on physicochemical properties of sandy soil in northwestern Liaoning province. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, S.; Cheng, F.; Li, J.; Tong, M.; Ding, C. Effects of biological organic amendments on soil quality in tidal flat of Suaeda heteroptera wetland in Liaohe estuarine. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, T.C.; Incerti, G.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A.; Mazzoleni, S.; Bonanomi, G. Linking organic matter chemistry with soil aggregate stability: Insight from 13C NMR spectroscopy. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2018, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, D.; Dai, Q.; Gui, J.; Chen, J.; Fu, Y. Effect of Returning Straw on Transfer and Accumulation of Cd in Soil-rice System: Research Progress. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2018, 34, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hassan, M.U.; Nadeem, F.; Wu, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Magnesium Fertilization Improves Crop Yield in Most Production Systems: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 01727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, F.; Xu, M.; Qing, D.; Gao, J.; Zhu, Y. Status of magnesium and the techniques of application of magnesium fertilizer in the red earth region. Soil Fertil. Sci. 2000, 5, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Han, T.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Wen, S.; Zhang, H. Distribution characteristics of effective medium and micronutrient element contents in paddy soils of China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Ren, T.; Lu, J. Soil available magnesium status and effects of magnesium application on rapeseed yield in main producing area of China. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2021, 40, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joris, P.J.; Plat, J.; Bakker, S.J.; Mensink, R.P. Effects of long-term magnesium supplementation on endothelial function and cardiometabolic risk markers: A randomized controlled trial in overweight/obese adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, G.; Dzupina, A.; Alhmadi, H.B.; Magomedova, A.; Siddiqui, Z.; Mehdi, A.; Hadi, N.; Mehdi, A. Magnesium matters: A comprehensive review of its vital role in health and diseases. Cureus 2024, 16, e71392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lin, B.; Rao, G.; Dai, W.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Song, H.; Tang, S.; et al. Effects of Straw Returning with Lime on SOC and Carbon Pool Management in Acidic Paddy Soil. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 5813–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.D.; Conyers, M.K.; Helyar, K.R.; Lisle, C.J.; Poile, G.J.; Cullis, B.R. Long-term surface application of lime ameliorates subsurface soil acidity in the mixed farming zone of south-eastern Australia. Geoderma 2019, 338, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Tu, N.; Fang, C.; Yi, Z.; Yang, J.; Tan, Z.; Li, P.; Dong, Y. Effects of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers with zinc fertilizer and lime on yield and soil nutrient characteristics of double croping rice. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).