Spatial and Temporal Variations of Climate Resources during the Growing Season of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methods and Measurement Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Variation Characteristics of Heat Resources during the Growth Duration of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province
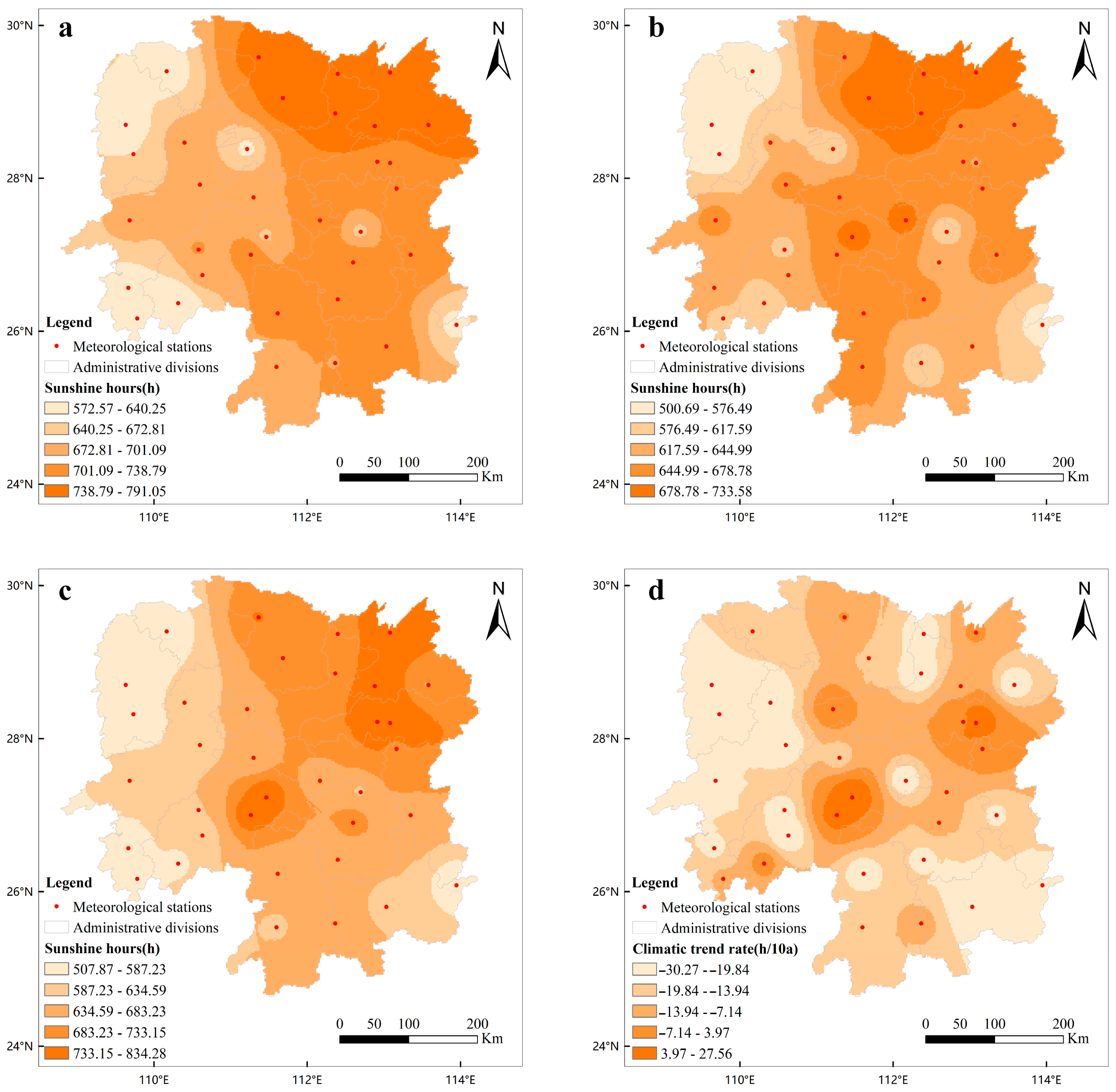
3.2. Variation Characteristics of Sunshine Resources during the Growth Duration of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province
3.3. Variation Characteristics of Rainfall Resources during the Growth Duration of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province
3.4. The Varying Characteristics of Heat, Sunlight, and Rainfall Resources during Different Growth Stages of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Redden, R.J.; Hatfield, J.L.; Prasad, P.V.; Ebert, A.W.; Yadav, S.S.; O’Leary, G.J. Temperature, climate change, and global food security. In Temperature and Plant Development; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Geng, S. Impacts of climate change on agriculture and adaptive strategies in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Schlenker, W.; Costa-Roberts, J. Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 2011, 333, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, F. The central trend in crop yields under climate change in China: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, T.; Von Braun, J. Climate change impacts on global food security. Science 2013, 341, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Wang, D.Y.; Fang, F.P.; Zeng, X.K.; Liao, X.Y. Food safety and rice production in China. Res. Agric. Mod. 2005, 26, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.F.; Fang, F.P. Report on the Development of China’s Rice Industry in 2021; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2021; ISBN 9787511655783. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.C.; Ji, L.; Li, F.B.; Feng, J.F.; Fang, F.P. Situation and strategies of rice industry development in China. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2022, 41, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, P.J.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Song, S.; Tao, F.L. Is yield increase sufficient to achieve food security in China? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 0222167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.P.; Wang, G.Y. Key fingings and assessment results of IPCC WGI fifth assessment report. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2013, 35, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.X.; Wang, X.Z.; Guo, J.P.; Zhao, Y.X.; Huang, J.F. The temporal-spatial dynamic analysis of China rice production. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2012, 45, 3473–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.F.; Wang, Y.L. Analysis of characteristics of temporal and spatial variation of rice production in the world. China Rice 2021, 27, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Cheng, L.L.; Tong, Q.M.; Liu, Y. Impact of climate change on rice yield and its regional heterogeneity in China. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2019, 35, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laza, M.R.C.; Sakai, H.; Cheng, W.; Tokida, Y.; Peng, S.B.; Hasegawa, T. Differential response of rice plants to high night temperatures imposed at varying developmental phases. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209–210, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, R.; Yu, X.; Grün, C. Climate change, risk and grain yields in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.H.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.Q.; Tian, L.; Zhou, X.B.; Tao, G. Effects of high air temperature on rice grain quality and yield under field condition. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Rotter, R.P. Variability in crop yields associated with climate anomalies in China over the past three decades. Reg. Environ. Change 2016, 16, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Z.; Reimund, P.R. Separating out the influence of climatic trend, fluctuations, and extreme events on crop yield: A case study in Hunan province, China. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 4469–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P. Advances in impacts of climate change on agricultural production in China. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2015, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Huang, S.E.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q. Spatial-temporal characteristics of thermal respirces and its influence on the growth of double cropping rice in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river, China. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2016, 27, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Liu, A.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wu, K.T. Dynamic variations of heat injury on rice in Hubei province under climate change. Meteorol. Disaster Reduct. Res. 2013, 36, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.B.; Lou, W.P. Impact of climate warming on the distribution of thermal resources in the lower-middle reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Nat. Resour. 2013, 28, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Data Website of National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online: https://data.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Ni, Y.N. Hunan provincial bureau of statistics Hunan. In Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, N.Y.; Grassini, P.; Yang, H.S.; Huang, J.L.; Cassman, K.G.; Peng, S.B. Closing yield gaps for rice self-sufficiency in China. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.K.; Jin, Z.Q. Impacts of climate change and its variability on rice production in the middle and lower valley of the Yangtze river, China. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2009, 23, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jiang, S.D.; Yang, S.B.; Tian, X.Y. Changes of agricultural climate resources during rice growing season in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2020, 36, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Luo, Y.; Liang, H.; Ma, S.K. Spatial and temporal variation of total solar radiation in China in recent 50 years. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.D.; Jiang, T.; Ren, G.Z.; Chen, Z.H. Observed trends of precipitation extremes in the Yangtze river basin during 1960 to 2004. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2006, 2, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Liu, F.X.; Zhai, J.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Jiang, T. Variation characteristics of extreme precipitation in the Yangtze river basin under the global warming 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C. Meteorol. Sci. 2019, 39, 540–547. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.F.; Liu, X.B.; Deng, W. Changes in agricultural meteorological elements in Hunan and their impact on main crops. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2009, 1, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Xue, J.F.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.D.; Chen, B.; Hu, S.J.; Zhang, H.L. Sensitivity analysis of double-rice yield under climate change in Hunan province. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Yang, X.G.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.F. Changes of China agricultural climate resources under the background of climate change. VIII. Change characteristics of heat resources during the growth period of double cropping rice in Jiangxi Province. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y. Modern Climate Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Technology; Meteorological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Yang, X.G.; Xie, W.J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Dong, C.Y.; Sun, S. Tendency of use efficiency of rice growth season in southern China under the background of global warming. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 46, 4399–4415. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.J.; Liu, X.J.; Huang, F.; Jiang, H.Y.; Chao, W.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of spatial interpolation methods for daily meteorological elements. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.G.; Dai, S.W.; Wang, W.F. Spatial temporal change characteristics of agricultural climate resources in middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 2912–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.L.; Liu, B.; Zhong, H.L. Impact of global warming on the rice cultivable area in Southern China in 1961–2009. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2011, 7, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.B.; Shen, S.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.X.; Xu, Y.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.W. Impacts of climate changes on rice production in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Agron. Sin. 2010, 36, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Wei, X. Global warming over 1960–2009 did increase heat stress and reduce cold stress in the major rice-planting areas across China. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 59, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X. Climate warming over the past three decades has shortened rice growth duration in China and cultivar shifts have further accelerated the process for late rice. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, G.; Long, Z.W.; Chen, C.Q. Impacts of recent temperatures rise on double-rice phenology across southern China. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2019, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H. A Simulation Study on Rice Productivity under Future Climate Change. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agriculture University, Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, G.S.; Kaur, M.; Kaushik, P. Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture and Its Mitigation Strategies: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wei, D.Q. Study on the Crop Suitability and Planting Structure Optimization in Typical Grain Production Areas under the Influence of Human Activities and Climate Change: A Case Study of the Naoli River Basin in Northeast China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R. Modern Global Climate Change. Science 2003, 302, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Tang, Z.G.; Li, C.K.; Chen, H.; Peng, H.H.; Wang, X.R. Extraction and analysis of spatiotemporal variation of rice planting area in Hunan province based on MODIS time-series data. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2020, 32, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, L.Y.; Zhan, W.X.; Xiao, J.F.; Liu, Y.; Jin, L.X.; Deng, W. Geographical spatial differentiation characteristics of double-season rice in Hunan province based on remote sensing data products. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2023, 5, 82–87+93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
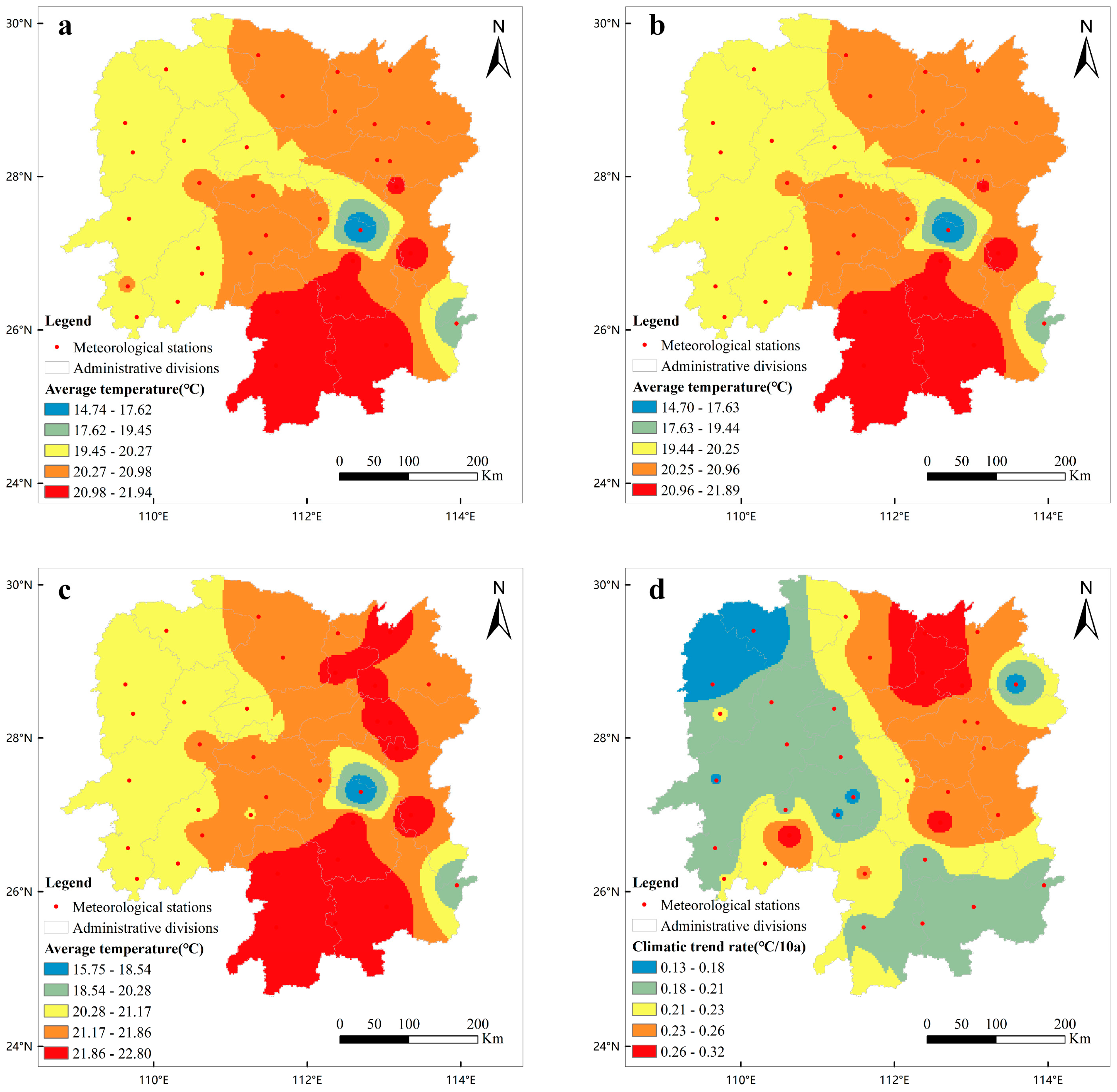
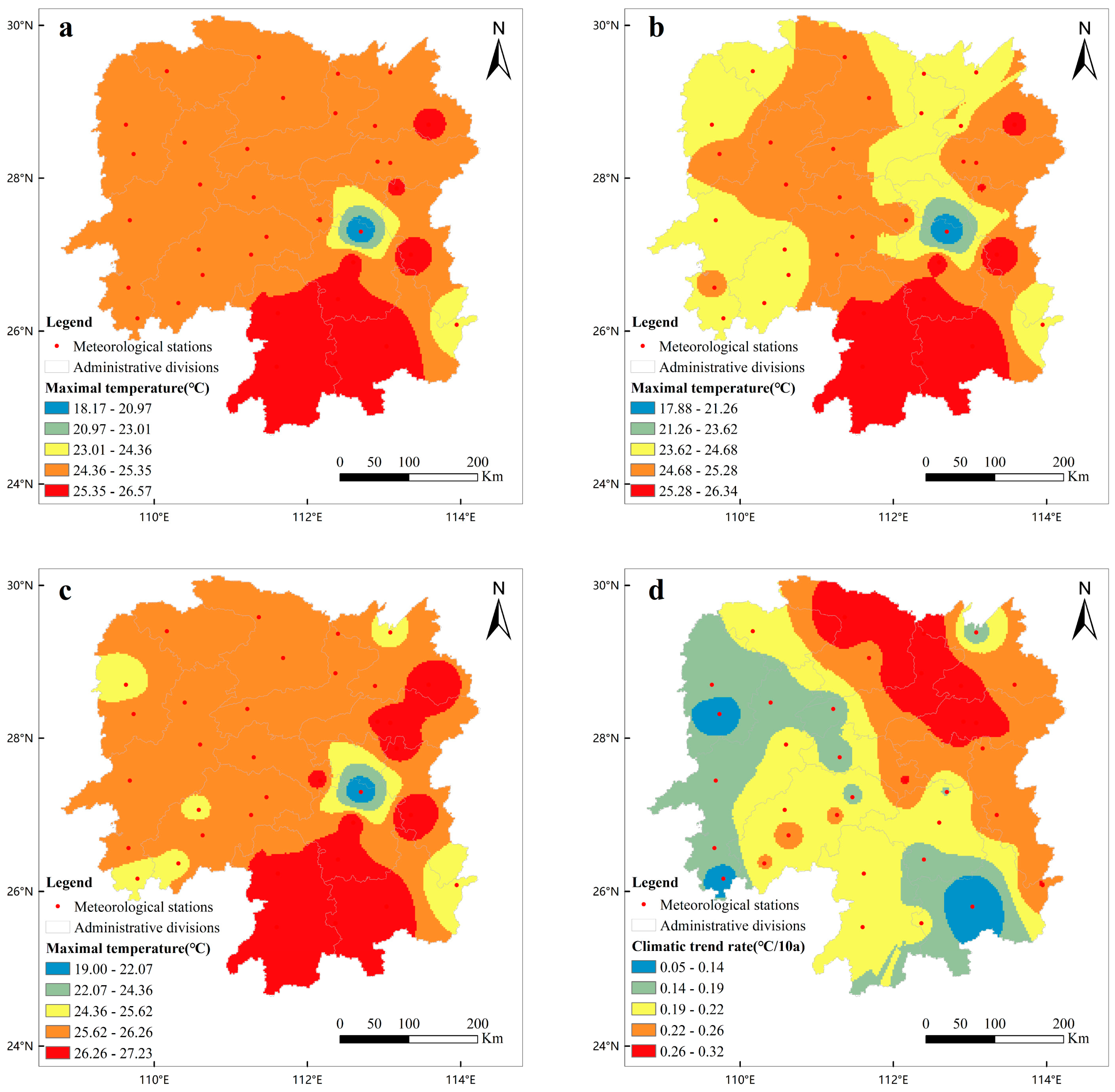
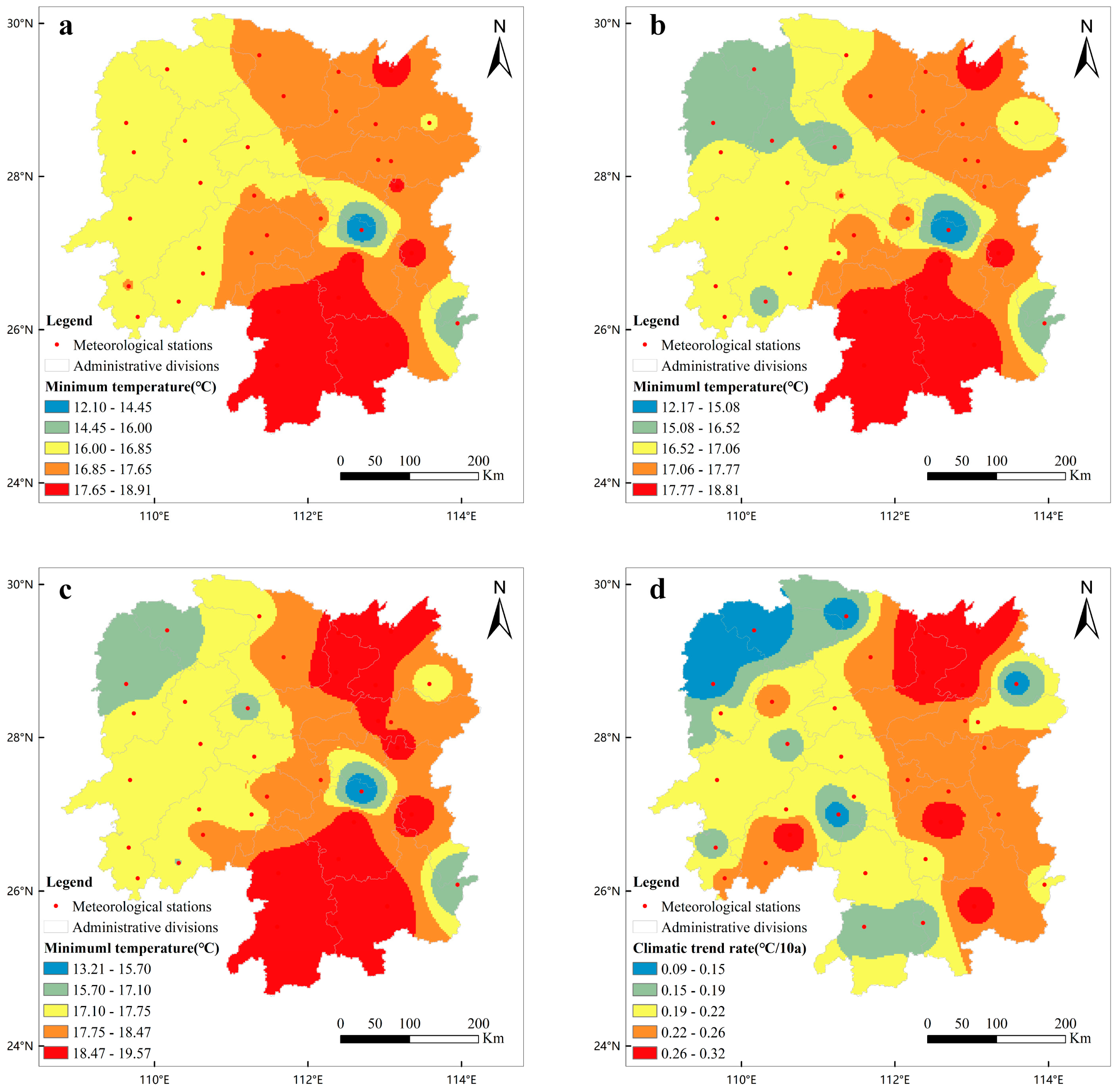
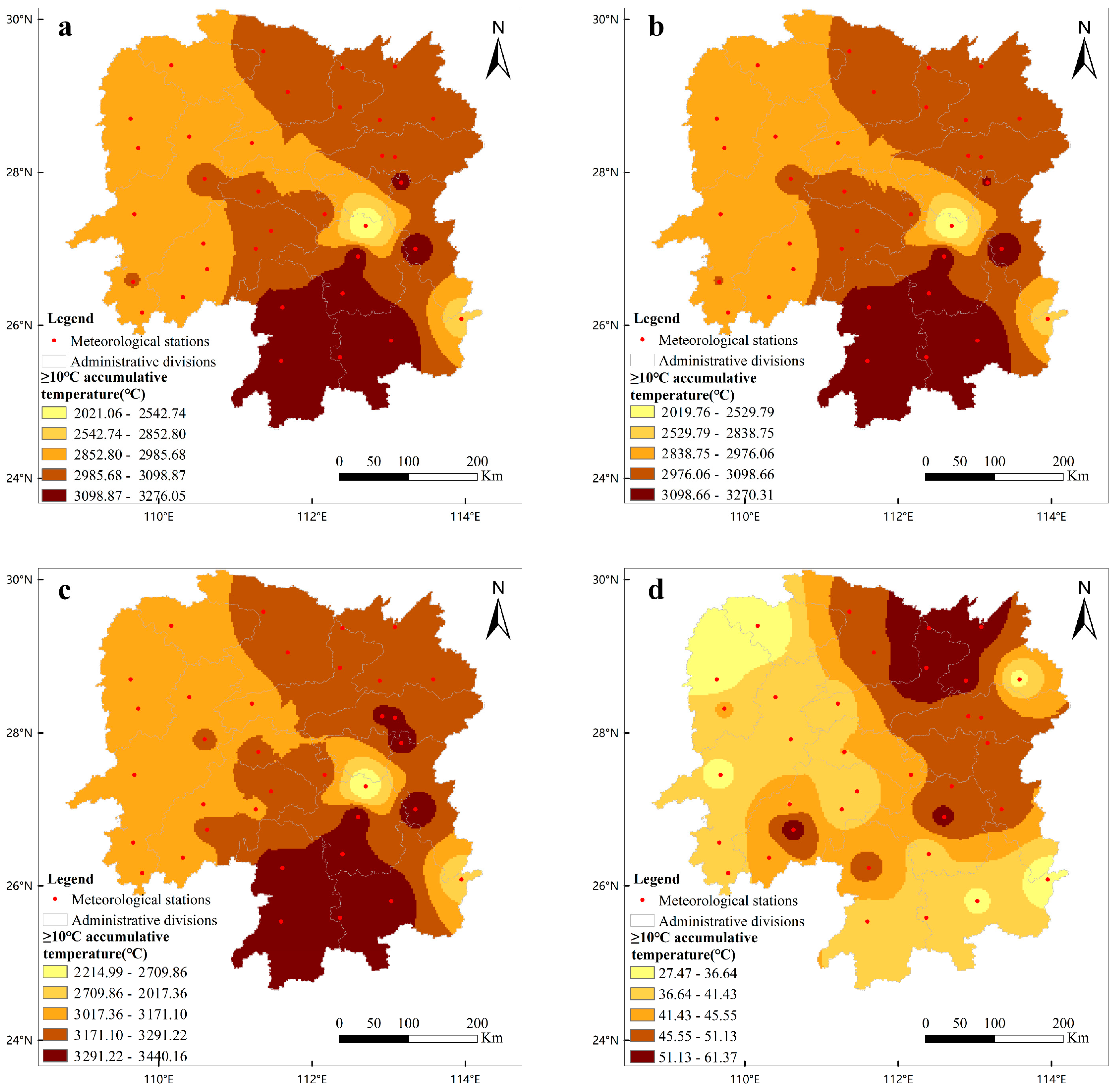

| Periods of Time | Average Temperature (°C) | Climatic Trend Rate (°C/10a) | Maximal Temperature (°C) | Climatic Trend Rate (°C/10a) | Minimum Temperature (°C) | Climatic Trend Rate (°C/10a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961–1980 | 20.40 b | −0.31 c | 24.93 b | −0.52 c | 17.01 b | −0.06 b |
| 1981–2000 | 20.37 b | 0.18 b | 24.77 c | 0.15 a | 17.08 b | 0.24 a |
| 2001–2020 | 21.36 a | 0.35 a | 25.92 a | 0.06 b | 17.90 a | 0.27 a |
| Periods of Time | ATe (°C) | Climatic Trend Rate (°C/10a) | Sunshine Hours (h) | Climatic Trend Rate (h/10a) | Precipitation (mm) | Climatic Trend Rate (mm/10a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961–1980 | 3004.66 b | −71.02 c | 698.45 a | −60.57 b | 869.42 a | 9.89 c |
| 1981–2000 | 2998.84 b | 39.01 b | 640.48 b | −31.73 a | 866.70 a | 117.87 a |
| 2001–2020 | 3192.86 a | 73.36 a | 658.14 b | −60.43 b | 873.33 a | 34.13 b |
| Meteorological Factor | Periods of Time | Sowing- Seedling Stage | Transplanting- Tillering Stage | Booting Stage | Heading Stage | Filling and Ripening Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAT (°C) | 1961–1980 | 12.62 b | 18.73 b | 22.74 b | 24.84 b | 26.48 a |
| 1981–2000 | 12.58 b | 18.92 b | 22.81 b | 24.69 b | 26.57 a | |
| 2001–2020 | 12.90 a | 19.65 a | 23.10 a | 25.19 a | 26.74 a | |
| Climatic trend rate (°C/10a) | 0.17 B | 0.40 A | 0.16 B | 0.15 B | 0.11 C | |
| DATmax (°C) | 1961–1980 | 17.17 b | 22.32 b | 26.55 a | 28.63 b | 30.47 a |
| 1981–2000 | 17.06 b | 22.49 b | 26.41 a | 28.08 c | 30.21 a | |
| 2001–2020 | 17.53 a | 23.13 a | 26.74 a | 29.05 a | 30.74 a | |
| Climatic trend rate (°C/10a) | 0.16 B | 0.35 A | 0.08 C | 0.18 B | 0.16 B | |
| DATmin (°C) | 1961–1980 | 9.42 b | 14.63 c | 18.58 c | 20.78 b | 22.87 b |
| 1981–2000 | 9.56 ab | 14.91 b | 18.79 b | 21.02 a | 23.01 ab | |
| 2001–2020 | 9.73 a | 15.47 a | 19.14 a | 21.02 a | 23.14 a | |
| Climatic trend rate (°C/10a) | 0.13 BC | 0.37 A | 0.24 B | 0.10 C | 0.16 B | |
| ATe (°C) | 1961–1980 | 277.43 b | 556.79 ab | 592.42 b | 646.52 b | 691.27 b |
| 1981–2000 | 273.53 b | 543.85 b | 594.56 b | 648.21 b | 692.03 b | |
| 2001–2020 | 296.82 a | 590.96 a | 610.53 a | 666.58 a | 702.78 a | |
| Climatic trend rate (°C/10a) | 8.43 B | 14.86 A | 7.87 B | 8.72 B | 5.00 C |
| Meteorological Factor | Periods of Time | Sowing-Seedling Stage | Transplanting and Tillering Stage | Booting Stage | Heading Stage | Filling and Ripening Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunshine hours (h) | 1961–1980 | 102.58 a | 160.49 b | 158.76 a | 84.93 a | 188.45 a |
| 1981–2000 | 100.42 b | 158.43 b | 143.64 b | 79.63 b | 183.56 ab | |
| 2001–2020 | 98.43 c | 164.23 a | 148.82 b | 78.14 b | 177.48 b | |
| Climatic trend rate (°C/10a) | −1.80 B | 2.51 A | −7.37 C | −2.74 B | −5.64 C | |
| Precipitation (mm) | 1961–1980 | 167.81 a | 239.71 a | 185.65 b | 96.04 a | 179.29 b |
| 1981–2000 | 169.77 a | 231.67 b | 185.61 b | 95.43 ab | 180.56 b | |
| 2001–2020 | 159.49 b | 234.65 b | 197.71 a | 93.56 b | 192.13 a | |
| Climatic trend rate (°C/10a) | −3.62 D | −2.20 C | 3.94 A | −1.08 B | 5.13 A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, A.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Climate Resources during the Growing Season of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091514
He A, Li J, Long J, Ai Z, Zhang P, Guo X. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Climate Resources during the Growing Season of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province. Agriculture. 2024; 14(9):1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091514
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Aibin, Jiebing Li, Jirui Long, Zhiyong Ai, Peiguang Zhang, and Xiayu Guo. 2024. "Spatial and Temporal Variations of Climate Resources during the Growing Season of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province" Agriculture 14, no. 9: 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091514
APA StyleHe, A., Li, J., Long, J., Ai, Z., Zhang, P., & Guo, X. (2024). Spatial and Temporal Variations of Climate Resources during the Growing Season of Early-Season Rice in Hunan Province. Agriculture, 14(9), 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091514





