Lactic Acid Bacteria from Bombyx mori Frass: Probiotic Properties and Antagonistic Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
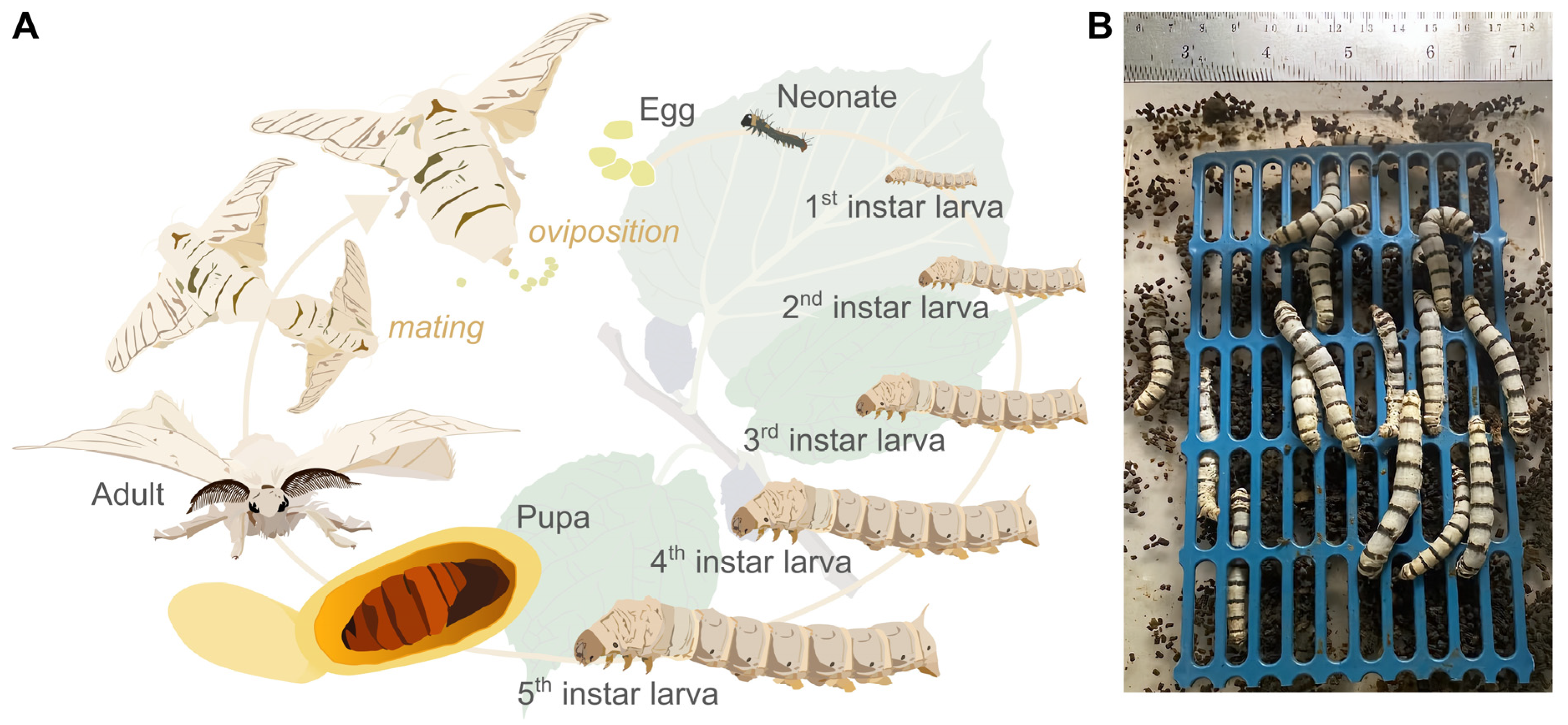
2.1. Silkworm Rearing and Harvesting of Fresh Faeces
2.2. Isolation of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) and Assessment of Acid Tolerance
2.3. Gram Staining and Catalase Test
2.4. Haemolytic Activity
2.5. Bile Salt Tolerance Assay
2.6. Cell Surface Hydrophobicity Assay
2.7. Evaluation of LAB Isolates against Bacteria Pathogens
2.8. Sensitivity of LAB to Antibiotics
2.9. Colony PCR, Sanger Sequencing, and Taxonomic Identification
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological and Physiological Study of Lactic Acid Bacteria
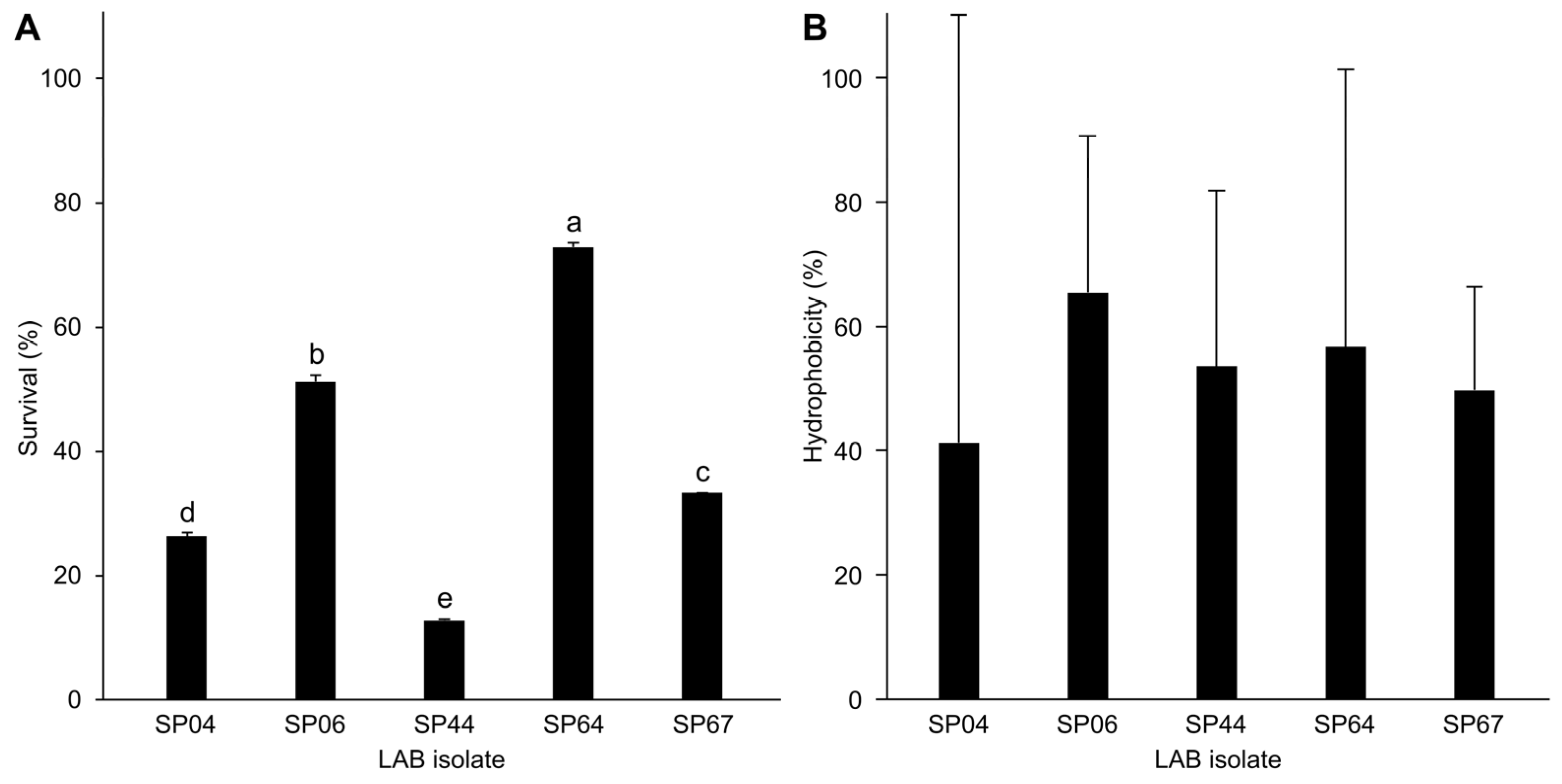
3.2. Haemolytic Activity, Bile Salt Tolerance, and Cell Surface Hydrophobicity
3.3. Selected LAB Isolates against Bacterial Pathogens
3.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
3.5. Genetic Identification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J.; Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision; Agricultural Development Economics Division, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, R.; Klammsteiner, T.; Kong, X.; Yan, B.; Mihai, F.-C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Kumar Awasthi, M. Recent Trends and Advances in Composting and Vermicomposting Technologies: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanboonsong, Y.; Jamjanya, T.; Durst, P.B. Six-Legged Livestock: Edible Insect Farming, Collection and Marketing in Thailand; RAP Publication; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific: Bangkok, Thailand, 2013; ISBN 978-92-5-107578-4. [Google Scholar]
- Orihara, Y.; Hamamoto, H.; Kasuga, H.; Shimada, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Sekimizu, K. A Silkworm–Baculovirus Model for Assessing the Therapeutic Effects of Antiviral Compounds: Characterization and Application to the Isolation of Antivirals from Traditional Medicines. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto, H.; Kurokawa, K.; Kaito, C.; Kamura, K.; Manitra Razanajatovo, I.; Kusuhara, H.; Santa, T.; Sekimizu, K. Quantitative Evaluation of the Therapeutic Effects of Antibiotics Using Silkworms Infected with Human Pathogenic Microorganisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Duan, H.; Wang, J.; Yan, W. Silkworm Pupae: A Functional Food with Health Benefits for Humans. Foods 2022, 11, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banday, M.T.; Adil, S.; Sheikh, I.U.; Hamadani, H.; Qadri, F.I.; Sahfi, M.E.; Sait, H.S.A.W.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Salem, H.M.; Taha, A.E.; et al. The Use of Silkworm Pupae (Bombyx mori) Meal as an Alternative Protein Source for Poultry. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2023, 79, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Lee, D.-G.; Yeon, S.-W.; Kwon, H.-S.; Ko, J.-H.; Shin, D.-J.; Park, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Bang, M.-H.; Baek, N.-I. Isolation of Megastigmane Sesquiterpenes from the Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) Droppings and Their Promotion Activity on HO-1 and SIRT1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łochyńska, M.; Frankowski, J. The Biogas Production Potential from Silkworm Waste. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łochyńska, M.; Frankowski, J. Impact of Silkworm Excrement Organic Fertilizer on Hemp Biomass Yield and Composition. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Zande, E.M.; Wantulla, M.; Van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M. Soil Amendment with Insect Frass and Exuviae Affects Rhizosphere Bacterial Community, Shoot Growth and Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio of a Brassicaceous Plant. Plant Soil 2023, 495, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimolmangkang, S.; Somkhanngoen, C.; Sukrong, S. Potential Pharmaceutical Uses of the Isolated Compounds from Silkworm Excreta. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013, 41, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Tulp, M.; Bohlin, L. Unconventional Natural Sources for Future Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Gu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, K. Silkworm Feces Extract Improves Iron Deficiency Anemia via Suppressing Hepcidin Expression and Promoting Iron-Regulatory Proteins Expression. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50378–50388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelagund, S.; Ingalhalli, S.; Savanurmath, C.; Hinchigeri, S.; Hiremath, M. Purification and Characterization of Antiviral Protein from Silkworm Fecal Matter. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 5, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, D.; Wang, G.; Dong, Z.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, P. Comparative Fecal Metabolomes of Silkworms Being Fed Mulberry Leaf and Artificial Diet. Insects 2020, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-García, A.; Álvarez-Cervantes, J. The Gut Microbiota of Insects: A Potential Source of Bacteria and Metabolites. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2024, 44, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Fu, Y.; Liu, H. Isolation and Characterization of Enzyme-Producing Bacteria of the Silkworm Larval Gut in Bioregenerative Life Support System. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 116, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unban, K.; Klongklaew, A.; Kodchasee, P.; Pamueangmun, P.; Shetty, K.; Khanongnuch, C. Enterococci as Dominant Xylose Utilizing Lactic Acid Bacteria in Eri Silkworm Midgut and the Potential Use of Enterococcus hirae as Probiotic for Eri Culture. Insects 2022, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruva, T.; Vankadara, S.; Ramasamy, S.; Lingaiah, K. Identification of Potential Probiotics in the Midgut of Mulberry Silkworm, Bombyx mori through Metagenomic Approach. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.-L.; Zhang, S.-X.; Chen, Z.-H.; Tao, H.; Li, X.; Qiu, J.-F.; Cui, W.-Z.; Sima, Y.-H.; Cui, W.-Z.; Xu, S.-Q. Differences in Gut Microbiota between Silkworms (Bombyx mori) Reared on Fresh Mulberry (Morus alba Var. Multicaulis) Leaves or an Artificial Diet. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26188–26200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gómez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A. Probiotic Mechanisms of Action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarner, F. Probiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 39, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lähteinen, T.; Malinen, E.; Koort, J.M.K.; Mertaniemi-Hannus, U.; Hankimo, T.; Karikoski, N.; Pakkanen, S.; Laine, H.; Sillanpää, H.; Söderholm, H.; et al. Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus Isolates Originating from Porcine Intestine and Feces. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Shigwedha, N.; Zhang, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L. Probiotic Effects and Metabolic Products of Enterococcus faecalis LD33 with Respiration Capacity. Foods 2022, 11, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Atya, A.K.; Drider-Hadiouche, K.; Ravallec, R.; Silvain, A.; Vachee, A.; Drider, D. Probiotic Potential of Enterococcus faecalis Strains Isolated from Meconium. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Progress in the Application of Enterococcus faecium in Animal Husbandry. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1168189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, P.K.; Trivedi, D.; Thakore, K.; Chaudhary, H.; Giri, S.S.; Seshadri, S. Isolation and Characterization of Probiotic Properties of Lactobacilli Isolated from Rat Fecal Microbiota. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Clogston, J.D.; Neun, B.W.; Hall, J.B.; Patri, A.K.; McNeil, S.E. Method for Analysis of Nanoparticle Hemolytic Properties in Vitro. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2180–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, N.P.; Saliba, L.; Deiana, P. Functional and Safety Characterization of Autochthonous Lactobacillus paracasei FS103 Isolated from Sheep Cheese and Its Survival in Sheep and Cow Fermented Milks during Cold Storage. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, D. Assessing the Safety and Probiotic Characteristics of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus X253 via Complete Genome and Phenotype Analysis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiocchi, F.; Porcellato, D.; Limonta, L.; Picozzi, C.; Vigentini, I.; Locatelli, D.P.; Foschino, R. Insect Frass in Stored Cereal Products as a Potential Source of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis for Sourdough Ecosystem. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidreza, T.; Fatemeh, T.; Hossein, M.; Mojtaba, Z.; Mahmood, S.; Parvin, S. Potential Probiotic of Lactobacillus johnsonii LT171 for Chicken Nutrition. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 5833–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausova, G.; Hyrslova, I.; Hynstova, I. In Vitro Evaluation of Adhesion Capacity, Hydrophobicity, and Auto-Aggregation of Newly Isolated Potential Probiotic Strains. Fermentation 2019, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, U.; Lücke, F.K. Antibacterial Activity of Lactobacillus sake Isolated from Meat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, M.P.; Hermans, K.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Lebeer, S.E.; Vanderleyden, J.; De Keersmaecker, S.C.J. Identification and Characterization of Starter Lactic Acid Bacteria and Probiotics from Columbian Dairy Products. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing by a Standardized Single Disk Method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchwińska, K.; Gwiazdowska, D. Isolation and Probiotic Potential of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Swine Feces for Feed Additive Composition. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Balcázar, J.L.; García, Y.; Halaihel, N.; Vendrell, D.; De Blas, I.; Merrifield, D.L.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I. Identification and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), with Inhibitory Activity against Lactococcus garvieae: Trout Endogenous LAB Antagonise L. garvieae. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, R.; Sahu, R.K.; Das Gupta, D.; Saikia, M.; Borthakur, S.; Majumder, M.; Mech, S.; Thapa, M.; Dutta, P.; Kalita, J. Recycling of Protein Rich Silk Industry Waste for Potential Food and Therapeutic Application. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praeg, N.; Klammsteiner, T. Primary study on frass fertilizers from mass-reared insects: Species variation, heat treatment effects, and implications for soil application at laboratory scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insam, H.; Klammsteiner, T.; Gómez-Brandòn, M. Biology of Compost. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 522–532. ISBN 978-0-12-409548-9. [Google Scholar]
- Menconi, A.; Kallapura, G.; Latorre, J.D.; Morgan, M.J.; Pumford, N.R.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez, G. Identification and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria in a Commercial Probiotic Culture. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2014, 33, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimee, G.; Halami, P.M. Emerging Resistance to Aminoglycosides in Lactic Acid Bacteria of Food Origin—An Impending Menace. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibi, N.; Aouini, R.; Borgo, F.; Ben Said, L.; Ferrario, C.; Dziri, R.; Boudabous, A.; Torres, C.; Ben Slama, K. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence of Faecal Enterococci Isolated from Food-Producing Animals in Tunisia. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Muhammad, A.; Zhang, F.; Lu, X. Features and Colonization Strategies of Enterococcus faecalis in the Gut of Bombyx mori. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 921330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, N.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lu, X. The Gut Commensal Bacterium Enterococcus faecalis LX10 Contributes to Defending against Nosema bombycis Infection in Bombyx mori. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.; Alonso, C.A.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; León-Sampedro, R.; Del Campo, R.; Coque, T.M. Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterococcus spp. of Animal Origin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kumar, D.; Liu, B.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, L.; Liang, Z.; Kuang, S.; et al. Effects of BmCPV Infection on Silkworm Bombyx mori Intestinal Bacteria. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellozza, S.; Saviane, A.; Tettamanti, G.; Squadrin, M.; Vendramin, E.; Paolucci, P.; Franzetti, E.; Squartini, A. Identification of Enterococcus mundtii as a Pathogenic Agent Involved in the “Flacherie” Disease in Bombyx mori L. Larvae Reared on Artificial Diet. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 106, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Joop, G. Probiotic Enterococcus mundtii Isolate Protects the Model Insect Tribolium castaneum against Bacillus thuringiensis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebeci, A.; Gürakan, C. Properties of Potential Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Strains. Food Microbiol. 2003, 20, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti, B.; Agazzi, A.; Bersani, C.; De Dea, P.; Pecorini, C.; Pirani, S.; Rebucci, R.; Savoini, G.; Stella, S.; Stenico, A.; et al. Screening of Species-Specific Lactic Acid Bacteria for Veal Calves Multi-Strain Probiotic Adjuncts. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; Reale, A.; Sorrentino, E.; Grazia, L.; Pacifico, S.; Coppola, R. Bile Salt and Acid Tolerance of Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strains Isolated from Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazireh, H.; Shariati, P.; Azimzadeh Jamalkandi, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Boroumand, M.A. Isolation of Novel Probiotic Lactobacillus and Enterococcus Strains from Human Salivary and Fecal Sources. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 597946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Re, B.; Sgorbati, B.; Miglioli, M.; Palenzona, D. Adhesion, Autoaggregation and Hydrophobicity of 13 Strains of Bifidobacterium longum. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Ahire, J.J.; Pawar, S.P.; Chaudhari, B.L.; Chincholkar, S.B. Comparative Accounts of Probiotic Characteristics of Bacillus spp. Isolated from Food Wastes. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Lohrasbi, V.; Abdi, M.; Mirkalantari, S.; Esghaei, M.; Kashanian, M.; Oshaghi, M.; Talebi, M. The Probiotic Properties and Potential of Vaginal Lactobacillus spp. Isolated from Healthy Women against Some Vaginal Pathogens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, B.; Wityk, P.; Gałęcka, M.; Michalik, M. The Many Faces of Enterococcus spp.—Commensal, Probiotic and Opportunistic Pathogen. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servin, A.L. Antagonistic Activities of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria against Microbial Pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 405–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, C.; Mugo-Kamiri, L.; Upfold, J.K. Bugs in Bugs: The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in Maintenance of Health in Mass-Reared Insects. Insects 2022, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LAB Isolate | Pathogenic Bacteria [⌀ mm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | Staphylococcus aureus | Salmonella typhimurium | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |
| SP04 | 5.3 ± 0.5 (+) | 12.8 ± 1.0 (+++) | 19.8 ± 0.8 (+++) | 14.5 ± 0.0 (+++) |
| SP06 | 4.8 ± 0.3 (+) | 12.8 ± 0.8 (+++) | 18.5 ± 1.4 (+++) | 14.2 ± 0.3 (+++) |
| SP44 | 13.1 ± 0.3 (+++) | 4.2 ± 0.5 (+) | 14.2 ± 0.5 (+++) | 6.6 ± 0.4 (++) |
| SP64 | 12.9 ± 0.5 (+++) | 7.3 ± 0.4 (++) | 19.7 ± 1.1 (+++) | 11.3 ± 0.4 (++) |
| SP67 | 17.9 ± 0.9 (+++) | 9.0 ± 0.3 (++) | 16.3 ± 0.3 (+++) | 13.3 ± 0.7 (+++) |
| LAB Isolate | Antibiotic Susceptibility Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | Chloramphenicol | Gentamicin | Penicillin | Tetracycline | |
| SP04 | 27.3 ± 1.9 (S) | 20.7 ± 1.0 (S) | 12.2 ± 0.3 (R) | 19.5 ± 1.3 (S) | 23.3 ± 0.8 (S) |
| SP06 | 29.2 ± 0.3 (S) | 20.3 ± 0.8 (S) | 12.3 ± 0.6 (R) | 19.8 ± 0.6 (S) | 23.8 ± 2.4 (S) |
| SP44 | 28.0 ± 0.5 (S) | 20.0 ± 1.0 (S) | 13.3 ± 0.6 (I) | 19.3 ± 0.6 (S) | 23.3 ± 0.8 (S) |
| SP64 | 27.7 ± 1.5 (S) | 19.5 ± 0.9 (S) | 12.8 ± 1.4 (R) | 18.8 ± 0.3 (S) | 22.7 ± 0.8 (S) |
| SP67 | 27.8 ± 0.8 (S) | 20.0 ± 0.0 (S) | 12.3 ± 0.6 (R) | 20.3 ± 1.0 (S) | 19.3 ± 4.6 (S) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suraporn, S.; Cansee, S.; Hupfauf, S.; Klammsteiner, T. Lactic Acid Bacteria from Bombyx mori Frass: Probiotic Properties and Antagonistic Activities. Agriculture 2024, 14, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060924
Suraporn S, Cansee S, Hupfauf S, Klammsteiner T. Lactic Acid Bacteria from Bombyx mori Frass: Probiotic Properties and Antagonistic Activities. Agriculture. 2024; 14(6):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060924
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuraporn, Siripuk, Sopa Cansee, Sebastian Hupfauf, and Thomas Klammsteiner. 2024. "Lactic Acid Bacteria from Bombyx mori Frass: Probiotic Properties and Antagonistic Activities" Agriculture 14, no. 6: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060924
APA StyleSuraporn, S., Cansee, S., Hupfauf, S., & Klammsteiner, T. (2024). Lactic Acid Bacteria from Bombyx mori Frass: Probiotic Properties and Antagonistic Activities. Agriculture, 14(6), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060924






