Effects of Catch Crops Cultivated for Green Manure on Soil C and N Content and Associated Enzyme Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment Description
2.2. Soil Sampling and Sample Preparation
2.3. Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Content
2.4. Determination of Enzymatic Activity and Soil Respiration
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
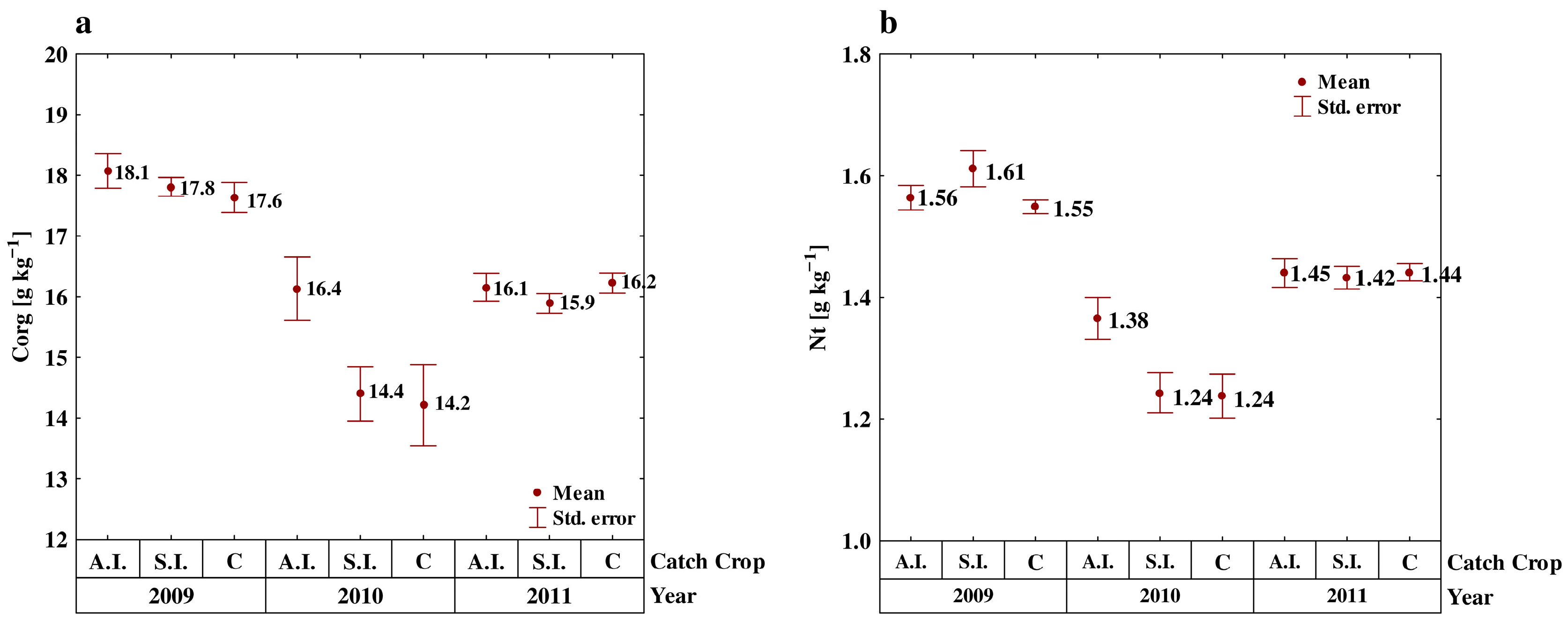
3.1. Soil Carbon and Nitrogen
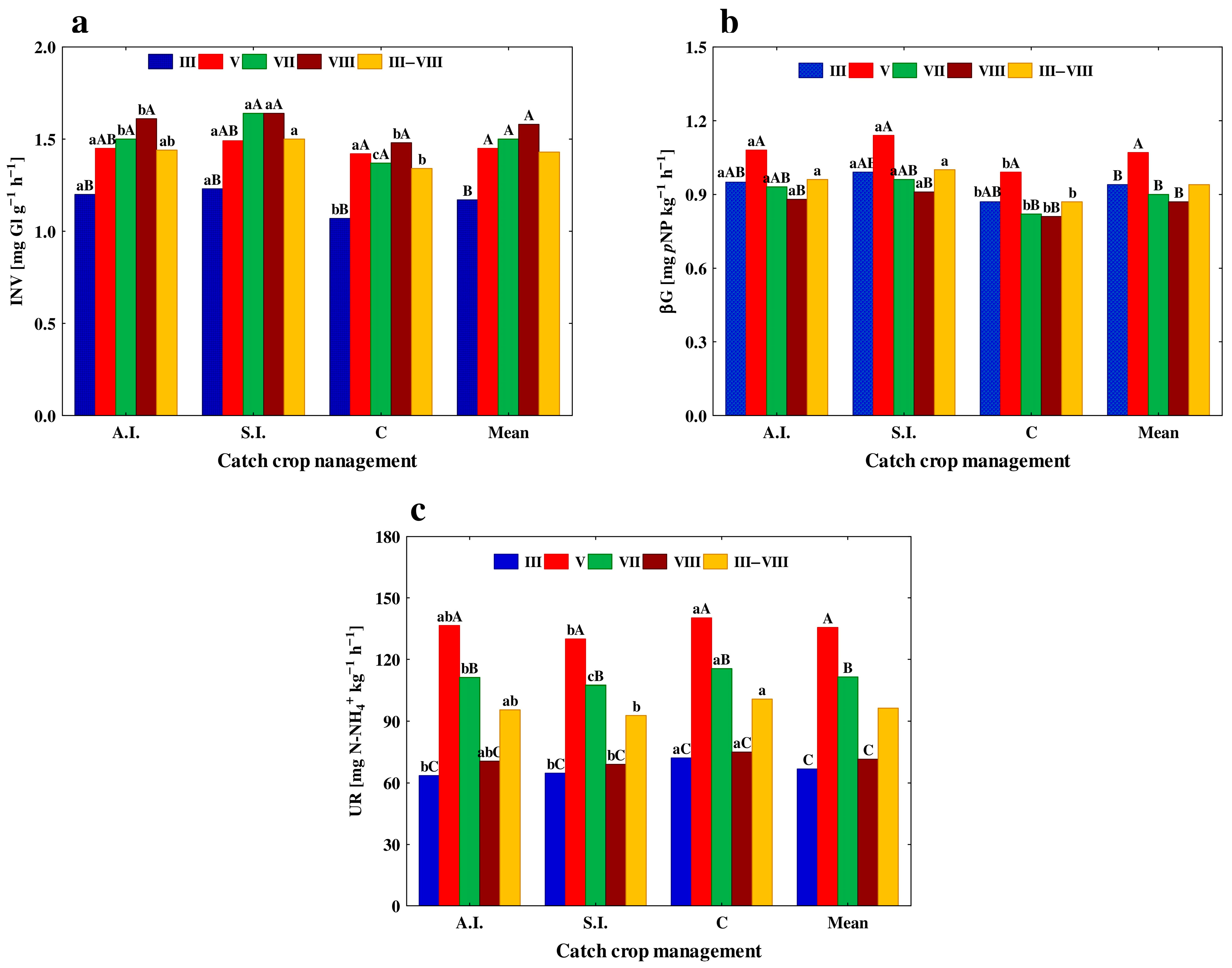
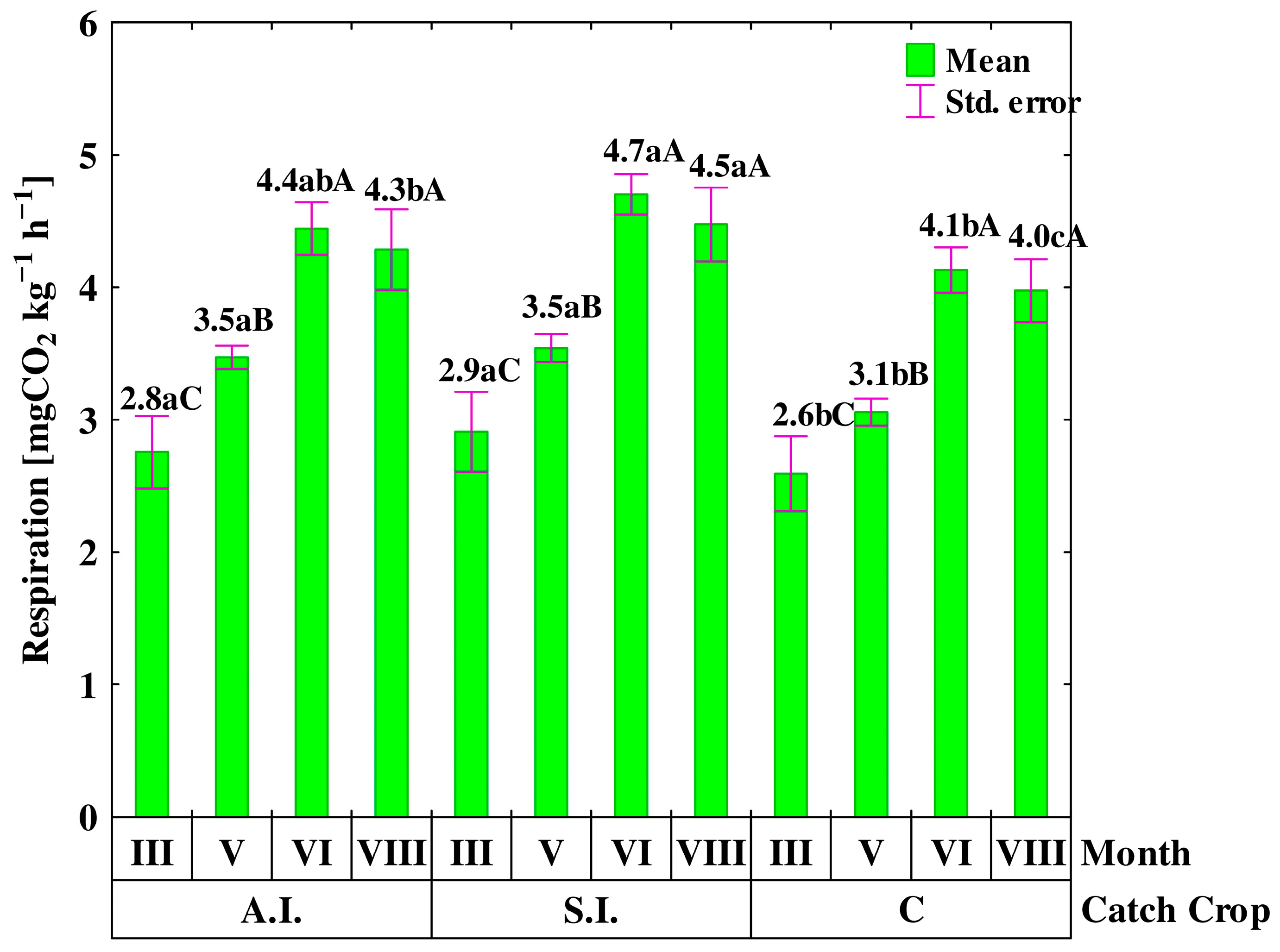
3.2. C- and N-Cycling Enzyme Activities and Soil Respiration
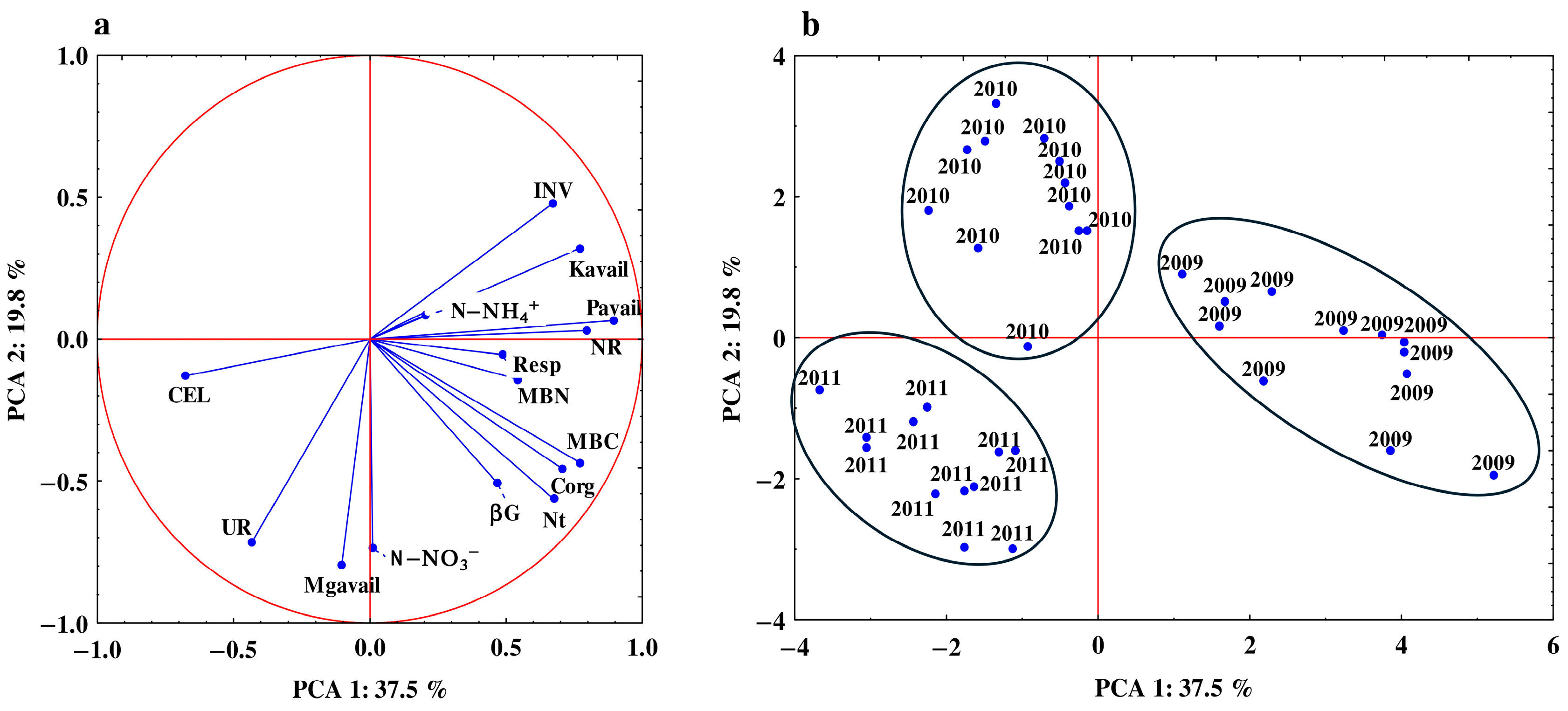
3.3. Relationship between the Studied Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Carbon and Nitrogen
4.2. The Effect of Catch Crops on Soil Microbial and Enzymatic Properties
4.3. Autumn vs. Spring Incorporation of Field Pea
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, P.; Laor, Y.; Raviv, M.; Medina, S.; Saadi, I.; Kransnovsky, A.; Vager, M.; Levy, G.J.; Bar-Tal, A.; Borisover, M. Green manure as part of organic management cycle: Effects on changes in organic matter characteristics across the soil profile. Geoderma 2017, 305, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Ge, J. Green Manure Return Strategies to Improve Soil Properties and Spring Maize Productivity under Nitrogen Reduction in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, N.; Karbout, N.; Dhaouadi, L.; Bouajila, A. Global Landscape of Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen in the Soils of Oasis Ecosystems in Southern Tunisia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barel, J.M.; Kuyper, T.W.; Paul, J.; de Boer, W.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; De Deyn, G.B. Winter cover crop legacy effects on litter decomposition act through litter quality and microbial community changes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P. Distribution of extracellular enzymes in soils: Spatial heterogeneity and determining factors at various scales. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Dick, R.P. Soil enzyme activity: A brief history and biochemistry as a basis for appropriate interpretations and meta-analysis. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Długosz, A. Significance of the enzymes associated with soil C and N transformation. In Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling in Soil; Datta, R., Meena, R.S., Pathan, S.I., Ceccherini, M.T., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020; pp. 339–437. [Google Scholar]
- Gunina, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Sugars in soil and sweets for microorganisms: Review of origin, content, composition and fate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lase, E.R.K.; Giyanto Santosa, D.A. Isolation, identification, and analysis of the invertase-producing bacteria abundance in sugarcane rhizosphere soil with different plant productivity levels. Biodiversitas 2021, 22, 3156–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Kelkar, A.; Baraniya, D.; Molaei, A.; Moulick, A.; Meena, R.; Formanek, P. Enzymatic degradation of lignin in soil: A review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Ekenler, M.; Senwo, Z.N. Significance of Enzyme Activities in Soil Nitrogen Mineralization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Cheng, X. Soil nitrogen-hydrolyzing enzyme activity and stoichiometry following a subtropical land use change. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4277–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Długosz, J.; Gryta, A.; Frąc, M. Responses of N-Cycling Enzyme Activities and Functional Diversity of Soil Microorganisms to Soil Depth, Pedogenic Processes and Cultivated Plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utobo, E.B.; Tewari, L. Soil enzymes as bioindicators of soil ecosystem status. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, B. Effects of soil management regimes on biochemical properties of a loess soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 15, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Tsai, C.F.; Rekha, P.D.; Ghate, S.D.; Huang, H.Y.; Hsu, Y.H.; Liaw, L.L.; Young, C.C. Agricultural management practices influence the soil enzyme activity and bacterial community structure in tea plantations. Bot. Stud. 2021, 62, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Razavi, B. Spatio-temporal distribution of enzyme activities with covered and mixed straw incorporation. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2024, Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024. EGU24-1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, I.K. Nitrate leaching under spring barley is influenced by the presence of a ryegrass catch crop: Results from a lysimeter experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 111, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Wilczewski, E. Assessment of soil nitrogen and related enzymes as influenced by the incorporation time of field pea cultivated as a catch crop in Alfisol. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8425–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, M.; Franchini, J.; Brandao-Junior, C.; Kaschuk, G.; Souza, A.R. Soil microbial activity and crop sustainability in a long-term experiment with three soil-tillage and two crop-rotation systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschuk, G.; Alberton, O.; Hungria, M. Three decades of soil microbial biomass studies in Brazilian ecosystems: Lessons learned about soil quality and indications for improving sustainability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doltra, J.; Olesen, J.E. The role of catch crops in the ecological intensification of spring cereals in organic farming under Nordic climate. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 44, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, E.B.; Acosta-Martinez, V. Cover Crops and Compost Influence Soil Enzymes during Six Years of Tillage-Intensive, Organic Vegetable Production. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.; Ebelhar, S.A.; Lang, J.M. Long-term effects of cover crops on crop yields, soil organic carbon stocks and sequestration. Open J. Soil Sci. 2014, 4, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, E.E.; Wickings, K.; McDaniel, M.D.; Robertson, G.P.; Grandy, A.S. Cover crop root contributions to soil carbon in a no-till corn bioenergy cropping system. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ghahramani, A.; Ali, A.; Erbacher, A. Cover cropping impacts on soil water and carbon in dryland cropping system. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014; Update 2015; International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczewski, E.; Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Lemańczyk, G. Influence of catch crop on soil properties and yield of spring barley. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2014, 8, 391–408. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M.; Mulvaney, C.S. Nitrogen—Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 2; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeny, D.R., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 594–624. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis—Advanced Course: A Manual of Methods Useful for Instruction and Research in Soil Chemistry, Physical Chemistry of Soils, Soil Fertility, and Soil Genesis, 2nd ed.; UW-Madison Libraries Parallel Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinsen, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Mueller, T. The fumigation-extraction method to estimate soil microbial biomass: Calibration of the kEN value. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashour, I.I.; Sayegh, A.H. Methods of Analysis for Soils of Arid and Semi-Arid Regions; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United States: Rome, Italy, 2007; 128p. [Google Scholar]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Glucosidases and galactosidases in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinner, F.; von Mersi, W. Xylanase-, CM-cellulase- and invertase activity in soil: An improved method. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Gerber, H. Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonia. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E. Enzymes Involved in Nitrogen Metabolism. In Methods in Soil Biology; Scinner, F., Ohlinger, R., Kandeler, E., Margesin, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 163–184. [Google Scholar]
- Isermeyer, H. Eine einfache Methode zur Bestimmung der Bodenatmung und der Karbonate im Boden. Z. Pflanzenernährung Düngung Bodenkd. 1952, 56, 26–38. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaullah, M.; Mujtaba, A.; Haider, G.; ur Rehman, H.; Mubeen, F. Mitigation and actions toward nitrogen losses in Pakistan. In Nitrogen Assessment; Pakistan as a Case-Study; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; Volume 8, pp. 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhofer-Walzl, K.; Rasmussen, J.; Høgh-Jensen, H.; Eriksen, J.; Søegaard, K.; Rasmussen, J. Nitrogen transfer from forage legumes to nine neighbouring plants in a multi-species grassland. Plant Soil 2012, 3350, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárceles Rodríguez, B.; Durán Zuazo, V.H.; Soriano Rodríguez, M.; García-Tejero, I.F.; Gálvez Ruiz, B.; Repullo-Ruibérriz de Torres, M.A.; Ordóñez-Fernández, R.; Carbonell-Bojollo, R.M.; Cuadros Tavira, S. Legumes protect the soil erosion and ecosystem. Adv. Legumes Sustain. Intensif. 2022, 13, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczewski, E.; Sadkiewicz, J.; Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Gałęzewski, L. Change of Plant Nutrients in Soil and Spring Barley Depending on the Field Pea Management as a Catch Crop. Agriculture 2021, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, F.J.; Nielsen, D.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Vigil, M.F.; Lyon, D. Cover Crop and Irrigation Effects on Soil Microbial Communities and Enzymes in Semiarid Agroecosystems of the Central Great Plains of North America. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, D.; Alcantara dos Santos, C.; Toledo Bernel, L.P.; Andrade, G.; Nogueira, M.A. Identifying indicators of C and N cycling in a clayey Ultisol under different tillage and uses in winter. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 76, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacomo, M.; Montemuro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskulska, I.; Romaneckas, K.; Jaskulski, D.; Gałęzewski, L.; Breza-Boruta, B.; Dębska, B.; Lemanowicz, J. Soil properties after eight years of the use of strip-till one-pass technology. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, L.; Yin, Q.; Nie, L. Effect of in situ incorporation of three types of green manure on soil quality, grain yield and 2-acetyl-1-pyrrolline content in tropical region. Crop Environ. 2022, 1, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, M.; Benito, M.; Rodriguez, I.; Masaguer, A. Effect of five forage legume covers on soil quality at the Eastern plains of Venezuela. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 49, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mohapatra, A.; Sahu, K.; Panday, D.; Ghimire, D.; Maharjan, B. Nitrogen dynamics as a function of soil types, compaction, and moisture. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, N.; Kumar, M.; Mohan, S.; Azzam, R. Influence of organic matter and solute concentration on nitrate sorption in batch and diffusion-cell experiments. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5283–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinari, S.; Mancinelli, R.; Campiglia, E.; Grego, S. Chemical and biological indicators of soil quality in organic and conventional farming systems in Central Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, C.; Condron, L.M.; Stewart, A.; Di, H.J.; O’Callaghan, M. Influence of organic and mineral amendments on microbial soil properties and processes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 35, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegarescu, G.; Reintam, E.; Tõnutare, T. Cover crop residues effect on soil structural stability and phosphatase activity. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdel, E. Soil Enzyme Activities Affecting by Different Tillage Systems and Cover Crops Following Corn Cultivation. J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Wilczewski, E. Influence of field pea (Pisum sativum L.) as catch crop cultivated for green manure on soil phosphorus and P-cycling enzyme activity. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.H. Microbial Eco-Physiological Indicators to Assess Soil Quality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 98, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Cheng, K.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Bian, R.; Zang, X.; Xia, S.; et al. Topsoil microbial biomass carbon pool and the microbial quotient under distinct land-use types across China: A data synthesis. Soil Sci. Environ. 2023, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Abaidoo, R.C.; Iwuafor, E.N.O.; Olufajo, O.O.; Sanginga, N. Rotation effects of grain legumes and fallow on maize yield, microbial biomass and chemical properties of an Alfisol in the Nigerian savanna. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.; Domsch, K.H. Application of eco-physiological quotients (qCO2 and qD) on microbial biomasses from soils of different cropping histories. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlauskiené, A.; Maikšténiené, S. The effect of cover crop and straw applied for manuring on spring barley yield and agrochemical soil properties. Zemdirbyste-Agric. 2010, 97, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, R.P. A review: Long-term effects of agricultural systems on soil biochemical and microbial parameters. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1992, 40, 25–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Horwath, W.R.; Joergensen, R.G.; Ludwig, B. Pathways of nitrogen utilization by soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Hwang, H.Y.; Kim, G.W.; Kim, P.J.; Das, S. Microbial responses to temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in a dry fallow cover cropping and submerged rice mono-cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 128, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.R.; Bridges, W.C., Jr.; Narayanan, S. Fall–winter cover crops promote soil health and weed control in the southeastern clayey soils. Agron. J. 2023, 115, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsky, S.B.; Ryan, M.R.; Teasdale, J.R.; Curran, W.S.; Reberg-Horton, C.S.; Spargo, J.T.; Wells, M.S.; Keene, C.L.; Moyer, J.W. Overcoming weed management challenges in cover crop–based organic rotational no-till soybean production in the east-ern United States. Weed Technol. 2013, 27, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vann, R.A.; Reberg-Horton, S.C.; Edmisten, K.L.; York, A.C. Implications of cereal rye/crimson clover management for conventional and organic cotton producers. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, J.; Olsen, J.E.; Petersen, B.M.; Hansen, E.M. Long-term fate of nitrogen uptake in catch crops. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 25, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczewski, E.; Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Lemańczyk, G. Properties of Alfisol and yield of spring barley as affected by catch crop. Zemdirbyste-Agric. 2015, 102, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczewski, E. The efficiency of nitrogen fertilization of spring wheat depending on seasonal rainfall. Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2013, 3, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnecker, J.; Baldoszti, L.; Gündler, P.; Pleitner, M.; Sandén, T.; Simon, E.; Spiegel, F.; Spiegel, H.; Urbina Malo, C.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; et al. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial growth, respiration, biomass, and carbon use efficiency in temperate soils. Geoderma 2023, 440, 116693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E.; Barea, J.M.; McNeill, A.M.; Prigent-Combaret, C. Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, A.T.; Sundqvist, M.K.; Henning, J.A.; Newman, G.S.; Moore, J.A.M.; Cregger, M.A.; Moorhead, L.C.; Patterson, C.M. Direct and indirect effects of climate change on soil microbial and soil microbial-plant interactions: What lies ahead? Ecosphere 2015, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delttedesco, E.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Piepho, H.-P.; Antonielli, L.; Potsch, E.M. Soil microbial community structure and function mainly respond to indirect effects in a multifactorial climate manipulation experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinweg, J.M.; Dukes, J.S.; Paul, E.A.; Wallenstein, M.D. Microbial responses to multi-factor climate change: Effects on soil enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Years | Sampling Month | & Autumn Incorporation | Spring Incorporation | Control | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | ^ March | 350.0 #ab*B | 424.2 aA | 338.7 bB | 371.0 AB |
| May | 387.0 abA | 409.6 aA | 361.9 bA | 386.2 A | |
| June | 358.8 bB | 413.7 aA | 330.8 bB | 367.8 B | |
| August | 357.6 bB | 389.1 aB | 322.3 cB | 356.3 B | |
| Mean | 363.3 b | 409.1 a | 338.4 c | 370.3 | |
| 2010 | March | 306.8 aB | 274.3 bC | 232.5 cC | 271.2 B |
| May | 303.9 aB | 305.9 aA | 266.5 bA | 291.8 A | |
| June | 326.3 aA | 290.9 abB | 229.8 bC | 282.3 AB | |
| August | 301.3 aB | 286.0 bB | 241.3 cB | 276.2 B | |
| Mean | 309.6 a | 289.3 a | 242.5 b | 280.4 | |
| 2011 | March | 269.3 aB | 274.6 aB | 199.0 bC | 247.6 C |
| May | 314.0 abA | 362.3 aA | 294.5 bA | 323.6 A | |
| June | 271.7 abB | 266.5 aB | 197.5 bC | 245.2 C | |
| August | 324.1 aA | 380.5 aA | 234.3 bB | 313.0 B | |
| Mean | 294.8 b | 321.0 a | 231.3 c | 282.4 | |
| 2009–2011 | March | 308.7 aB | 324.3 aB | 255.4 bB | 296.1 B |
| May | 335.0 bA | 359.0 aA | 307.6 cA | 333.9 A | |
| June | 318.9 aAB | 323.7 aB | 252.7 bB | 298.4 B | |
| August | 327.7 aA | 351.9 aA | 266.0 bB | 315.2 AB | |
| Mean | 322.6 a | 339.7 a | 270.4 b | 310.9 |
| Sampling Month | & Autumn Incorporation | Spring Incorporation | Control | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ^ March | 68.4 #b*A | 80.0 aA | 45.3 cB | 64.6 A |
| May | 66.9 bA | 74.0 aB | 52.3 cA | 64.4 A |
| June | 67.2 aA | 60.0 bC | 51.4 cA | 59.5 A |
| August | 68.7 aA | 60.2 bC | 53.4 cA | 60.8 A |
| Mean | 67.8 a | 68.6 a | 50.6 b | 62.3 |
| Years | Sampling Month | & Autumn Incorporation | Spring Incorporation | Control | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | ^ March | 0.91 #a*B | 1.04 aB | 0.68 bA | 0.88 B |
| May | 1.31 aA | 1.13 aB | 0.66 bA | 1.03 B | |
| June | 1.45 bA | 2.62 aA | 0.67 cA | 1.58 A | |
| August | - | - | - | - | |
| Mean | 1.22 b | 1.60 a | 0.67 c | 1.16 | |
| 2010 | March | 0.61 aC | 0.65 aC | 0.35 bC | 0.54 C |
| May | 1.65 abA | 2.03 aA | 1.16 bB | 1.61 B | |
| June | 1.35 aAB | 1.40 aB | 1.32 aA | 1.36 A | |
| August | 1.16 aB | 0.87 bC | 1.49 aA | 1.17 BC | |
| Mean | 1.19 a | 1.24 a | 1.08 b | 1.17 | |
| 2011 | March | 0.62 aB | 0.31 bC | 0.40 bC | 0.44 BC |
| May | 1.67 abA | 2.34 aA | 1.02 bA | 1.68 A | |
| June | 0.21 bC | 0.17 bC | 0.30 aC | 0.23 C | |
| August | 0.88 aB | 0.82 aB | 0.86 aB | 0.85 B | |
| Mean | 0.85 a | 0.91 a | 0.65 b | 0.80 | |
| 2009–2011 | March | 0.71 aC | 0.67 aC | 0.48 bC | 0.62 C |
| May | 1.54 abA | 1.83 aA | 0.95 bAB | 1.44 A | |
| June | 1.00 abB | 1.40 aB | 0.76 bB | 1.05 B | |
| August | 1.02 abB | 0.85 bC | 1.18 aA | 1.02 B | |
| Mean | 1.07 a | 1.19 a | 0.84 b | 1.03 |
| Years | Sampling Month | & Autumn Incorporation | Spring Incorporation | Control | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | ^ March | 13.6 #a*B | 13.3 aB | 7.77 bB | 11.6 B |
| May | 47.4 aA | 32.2 bA | 26.6 cA | 35.5 A | |
| June | 12.1 aB | 9.33 bB | 10.4 bB | 10.6 B | |
| August | - | - | - | - | |
| Mean | 24.4 a | 18.3 b | 14.9 c | 19.2 | |
| 2010 | ^ March | 8.43 aAB | 9.92 aA | 7.42 bB | 8.59 A |
| May | 9.47 aA | 6.91 bB | 8.29 abA | 8.22 A | |
| June | 8.18 aAB | 8.29 aAB | 8.32 aA | 8.26 A | |
| August | 6.62 aB | 6.13 bB | 5.95 bB | 6.23 B | |
| Mean | 8.18 a | 7.81 b | 7.50 b | 7.83 | |
| 2011 | March | 12.8 bC | 17.7 aC | 11.5 bC | 14.0 C |
| May | 58.7 aA | 54.6.aA | 31.0 bA | 48.1 A | |
| June | 24.6 bB | 37.1 aB | 20.7 bB | 27.5 B | |
| August | 14.0 aC | 14.7 aC | 10.9 bC | 13.2 C | |
| Mean | 27.5 a | 31.0 a | 18.5 b | 25.7 | |
| 2009–2011 | March | 11.6 aBC | 13.6 aC | 8.88 bC | 11.4 BC |
| May | 38.5 aA | 31.2 bA | 21.9 cAB | 30.5 A | |
| June | 15.0 abB | 18.2 aB | 13.1 bB | 15.4 B | |
| August | 6.87 bC | 10.4 aC | 8.44 abA | 8.57 C | |
| Mean | 18.0 a | 18.4 a | 13.1 b | 16.5 |
| Years | Sampling Month | & Autumn Incorporation | Spring Incorporation | Control | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | ^ March | 2.69 #a*B | 2.52 aB | 2.25 bC | 2.49 B |
| May | 9.30 aA | 10.2 aA | 6.78 bA | 8.76 A | |
| June | 8.63 aA | 8.06 aA | 5.10 bB | 7.26 A | |
| August | 3.29 aB | 3.09 aB | 2.94 aC | 3.11 B | |
| Mean | 5.98 a | 5.97 a | 4.27 b | 5.41 | |
| 2010 | March | 2.54 aB | 2.74 aB | 2.24 aB | 2.50 B |
| May | 3.82 abA | 4.03 aA | 3.62 bA | 3.82 A | |
| June | 3.11 aA | 3.05 aB | 2.26 bB | 2.81 B | |
| August | 1.83 aB | 1.94 aC | 1.55 bC | 1.77 C | |
| Mean | 2.83 a | 2.94 a | 2.41 a | 2.73 | |
| 2011 | March | 4.14 aC | 4.42 aBC | 4.09 aB | 4.22 BC |
| May | 5.05 aB | 5.04 aB | 4.29 bB | 4.80 B | |
| June | 3.84 aC | 3.76 aC | 2.78 bC | 3.46 C | |
| August | 6.41 bA | 7.41 aA | 6.34 bA | 6.72 A | |
| Mean | 4.86 ab | 5.16 a | 4.38 b | 4.80 | |
| 2009–2011 | ^ March | 3.12 aC | 3.23 aC | 2.86 aC | 3.07 C |
| May | 6.06 aA | 6.42 aA | 4.90 bA | 5.79 A | |
| June | 5.19 aB | 4.96 ab | 3.38 bBc | 4.51 B | |
| August | 3.84 abC | 4.15 aB | 3.61 bB | 3.87 BC | |
| Mean | 4.55 a | 4.69 a | 3.69 b | 4.31 |
| Years | Sampling Month | & Autumn Incorporation | Spring Incorporation | Control | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | ^ March | 2.60 #a*B | 2.28 aC | 2.53 aB | 2.47 C |
| May | 5.84 aA | 6.90 aA | 5.70 aA | 6.15 A | |
| June | 4.99 aA | 5.34 aB | 4.66 aA | 5.00 B | |
| August | 4.84 aA | 4.59 aB | 4.21 aAB | 4.55 B | |
| Mean | 4.57 a | 4.78 a | 4.28 a | 4.54 | |
| 2010 | March | 7.38 abB | 8.22 Ba | 6.10 bB | 7.23 B |
| May | 7.61 abB | 8.37 aB | 6.94 bB | 7.64 B | |
| June | 13.2 aA | 13.5 aA | 10.7 bA | 12.5 A | |
| August | 13.1 aA | 13.3 aA | 10.6 bA | 12.3 A | |
| Mean | 10.3 a | 10.9 a | 8.58 b | 9.92 | |
| 2011 | March | 23.1 aA | 22.9 aA | 18.2 bA | 21.7 A |
| May | 7.64 aC | 7.59 aC | 6.65 bC | 7.30 C | |
| June | 13.2 aB | 13.5 aB | 10.7 bB | 12.4 B | |
| August | 8.44 aC | 8.21 aC | 8.33 aC | 8.33 C | |
| Mean | 13.1 a | 13.1 a | 11.0 b | 12.4 | |
| 2009–2011 | March | 11.3 aA | 11.1 aA | 8.94 bA | 10.4 A |
| May | 7.03 aB | 7.62 aB | 6.43 aB | 7.03 B | |
| June | 10.4 aA | 10.76 aA | 8.64 bA | 10.0 A | |
| August | 8.81 aAB | 8.76 aAB | 7.74 aAB | 8.44 AB | |
| Mean | 9.39 a | 9.57 a | 7.94 b | 8.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Wilczewski, E. Effects of Catch Crops Cultivated for Green Manure on Soil C and N Content and Associated Enzyme Activities. Agriculture 2024, 14, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060898
Piotrowska-Długosz A, Wilczewski E. Effects of Catch Crops Cultivated for Green Manure on Soil C and N Content and Associated Enzyme Activities. Agriculture. 2024; 14(6):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060898
Chicago/Turabian StylePiotrowska-Długosz, Anna, and Edward Wilczewski. 2024. "Effects of Catch Crops Cultivated for Green Manure on Soil C and N Content and Associated Enzyme Activities" Agriculture 14, no. 6: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060898
APA StylePiotrowska-Długosz, A., & Wilczewski, E. (2024). Effects of Catch Crops Cultivated for Green Manure on Soil C and N Content and Associated Enzyme Activities. Agriculture, 14(6), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060898







