Abstract
In the field of crop research, the study of roots involves many challenges, particularly the lack of effective methods for identifying crop roots. To deal with this problem, this study proposes a solution strategy: in applying strontium to crop leaves, the roots of different crops are distinguished. In this study, we applied strontium ions to the leaves of hydroponically grown wheat, and these strontium ions were partially absorbed by the leaves and transported to the roots. Therefore, the strontium concentration of roots was significantly increased through the foliar application of strontium. After mixing the treated wheat with the untreated wheat root, the greater the biomass of the wheat root applied with strontium ions, the higher the strontium concentration in the mixed root. Based on this phenomenon, we can establish the relationship between wheat root biomass and strontium concentration in mixed roots through linear fitting. Furthermore, we can also use the relationship between root biomass and root length to establish the correlation between strontium concentration in mixed roots and the root length of wheat with strontium ions. After measuring the strontium concentration of the mixed roots to be distinguished, the root biomass and root length of wheat applied with strontium ions can be calculated according to the equation obtained through linear fitting. The accuracy of this method was verified through a comparison with the actual value and the existing root staining method. The results show that the coefficient of determination (R2) of the root biomass estimation equation obtained through linear fitting reached 0.83, which is statistically significant (p < 0.01). The Pearson correlation coefficient with the measured value was more than 0.9, showing a very high correlation and significance. The root length estimation equation derived from the relationship between the root biomass, strontium concentration and root length was compared with the real root length value and the root length value obtained using the staining method. The Pearson correlation coefficient also exceeded 0.8 and reached a statistically significant level (p < 0.01). This study confirms that strontium ions can be absorbed and transported to roots through wheat leaves and successfully developed a new method for predicting the length of wheat roots, providing an effective new tool for wheat root research.
1. Introduction
At present, the interaction between crop roots is a concern of agricultural workers. As the main organ for plants to obtain water and nutrients, roots not only respond to water and nutrients in the soil [1] but also to the roots of other plants in the soil [2] so as to make adjustments to the supply of soil moisture and nutrients and establish their own advantages in a competitive environment [3]. An in-depth understanding of the interaction between plant roots is conducive to not only a better understanding of the competitive strategies of different species in natural ecological communities, enabling improved ecological protection and ecological restoration, but also a better understanding of the mechanism of the efficient utilization of crop water and nutrients in farmland ecosystems. It is the theoretical basis for the establishment of the efficient management of farmland nutrients and environmentally friendly agricultural cultivation technology systems [4,5,6]. In order to study root interactions between plants, it is necessary to effectively distinguish the specific sources of entangled roots. However, there is no effective method for effectively distinguishing the sources of roots. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out research on methods to effectively distinguish root sources [7].
The majority of previous plant research has focused on the aboveground part of the plant rather than the root system. Consequently, research methods for studying roots are limited, and previous methods for studying plant or crop roots have primarily focused on root morphology and structure, such as the excavation method [8], in-growth core method [9], trench profile method [10], rhizobox method [11], minirhizotrons method [12], ground-penetrating radar [13], nuclear magnetic resonance imaging [14], and so on. There are also methods for distinguishing root sources, such as using DNA nucleic acid information, but quantitative PCR technology is costly and difficult to implement, which is not conducive to the effective and rapid development of related research [15]. Murakami [7] proposed a staining method to distinguish root sources, which involved introducing organic dye into root cells through a plant catheter using the external pressure method. In pressing different dyes into two different plants, the roots of two interacting crops can be distinguished. This method requires high pressure to be maintained for a long time during the dyeing process and requires the catheter to be sealed with the root. Therefore, this method is ineffective for plants with soft stems and poor lignification, or plants with hollow stems, such as wheat. Predecessors have also used isotopes to explore competition for soil resources [16], but their research purposes were different from those of root identification. For example, Brigit et al. applied stable isotopes (13C, 15N) to leaves for a study on ecology in an ecological environment [17]. J. D. Quinlan et al. closed the plant leaves and provided 14CO2 in an enclosed space to study the growth process of wheat [18]. In addition, Fox et al. [19] and Bonanomi et al. [20] injected isotope ions into the ground to elucidate the activity depth of plant roots.
Foliar fertilizer is a conventional agricultural operation [21]. Metal ions in foliar fertilizers such as calcium, magnesium, copper, iron and zinc can quickly enter vascular tissue through leaf stomata and transport and distribute throughout crops [22,23]. Therefore, we assume that applying metal ions on the leaf surface of the crop results in the absorption of these ions through the leaf surface and transportation to the plant root system, resulting in the metal ion concentration of the plant root being higher than that of the plant without metal ions on the leaf surface. According to this feature, we can distinguish the source of the root system. When selecting metal ions, it is necessary to select metal ions with lower concentrations in soil or water. At the same time, metal ions routinely used in foliar fertilizers are easily disturbed, such as the application of medium and trace elements in crop production. When we apply metal ions to crop leaves to distinguish roots, we cannot clearly know whether the metal ions in crop roots come from fertilizers or what we use as markers. Since most metal isotope ions are radioactive and harmful to the environment and testers, we focused on selecting elements from the first main group with similar chemical properties to potassium (K) and the second main group with similar chemical properties to calcium (Ca). We evaluated some metal ions, including lithium (Li), cesium (Cs), strontium (Sr) and barium (Ba). Among these options, strontium (Sr) is easier to obtain and has a lower price and higher cost–performance ratio. At the same time, this study found that plants can absorb strontium ions through calcium ion channels [24]. Burger proved that plants can absorb strontium through leaves and transport strontium to roots [25].
Previous studies on strontium have mainly focused on the harm of radioactive strontium to plants and the phytoremediation of radioactive strontium pollution [25]. Research indicates that adding high concentrations of strontium in soil or a hydroponic solution inhibits plant root growth, reduces the chlorophyll concentration, and so on [26,27,28]. However, unlike with other metal ions, plants will die from poisoning at extremely high strontium concentrations (about 1%) [29]. Strontium ions compete with calcium ions to bind to the same receptor sites on the biofilm and inhibit the absorption of calcium. In the natural state, more than 90% of the absorption of calcium by crops depends on the root system. Therefore, adding strontium directly to the root system’s contact points, such as in a hydroponic solution or soil, poses the greatest toxic potential to plants. When strontium is applied to leaves, the strontium absorbed by plants will be reduced, and the competition with calcium will also be reduced. Then, the toxicity potential of strontium will be reduced [30]. At the same time, the toxicity of strontium is also related to the duration of strontium stress. Studies have shown that the toxicity of strontium increases with the increase in the duration of strontium stress [31]. Under the same strontium concentration, treatment for 7 days will affect the growth of roots, while treatment for 1–2 days has little effect on roots [32]. Therefore, the above research indicates that strontium was a suitable metal ion for our experiment. Accordingly, we verified the idea through hydroponic experiments. Our goals were to (1) prove that a sufficient amount of strontium can be detected in the roots after the leaves are coated with strontium; (2) establish a method to estimate root biomass and root length using the concentration of strontium in roots, referred to as the root length biomass estimation method; (3) verify the feasibility of the estimation method using the measured method; (4) and verify the feasibility of the estimation method using root staining. The successful establishment of this method will provide strong support for the study of root interaction between plants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Materials
The wheat variety ‘Luohan 11’ was used as the test object in this study. Wheat was cultured using hydroponics in three stages. The germination period (3 d), growth period (15 d) and smear period (1 d–5 d) were carried out in the natural environment of the laboratory. (1) Germination stage: Whole wheat seeds were soaked in 5% hydrogen peroxide for 5 min to eliminate the bacteria on the seed epidermis, and then the wheat ventral groove was placed downward in a Petri dish with filter paper. Deionized water was added to the Petri dish, but the water level was kept below the wheat seeds to ensure their respiration. The samples were cultured in shade for 3 days at a laboratory temperature of 28 °C. (2) Growth period: After growing to 3–5 cm, the wheat seedlings were moved into a porous hydroponic tank, and a wheat seedling was placed in each hole and fixed with a sponge. Then, they were placed into a controllable environment incubator (GZX-150B; Shanghai Kuntian Laboratory Instrument Co., Ltd.; Shanghai, China). The environmental conditions of the incubator were controlled at 26 °C during the light period and 22 °C during the dark period. The light cycle was 10 h of light every 16 h, the light intensity was 300 μmol/(m2 · s), and the humidity was maintained at 60%. Hoagland nutrient solution was added to the hydroponic pool for culture. The pH of the nutrient solution was adjusted to 6.5, and the nutrient solution was replaced every 3 days for a total of 15 days [33]. (3) Spreading period: Wheat with uniform growth was selected, and strontium ions were applied. SrCl2 · 6H2O was used to provide Sr2+, preparing a 10 mmol L−1 Sr2+ solution [27]. A surfactant, polyoxyethylene fatty 377 alcohol, was added at 1 mL L−1 to increase the strontium uptake. The fronts and backs of the leaves were completely wet, but not so much strontium solution was used that it dripped from the leaves. Strontium solution was applied at 6 p.m. every 24 h. In the process of smearing, the upper and lower leaves of wheat were dripped with a rubber dropper, and then the strontium solution was uniformly smeared on the leaves with a glass slide. A total of 3 leaves were smeared. That is, each plant consumed 0.3 mL of strontium solution every 24 h, which was applied for 5 days in total. Deionized water was smeared as a control. After each application, wheat samples were left for 24 h before being retrieved. Then, the roots and shoots of wheat were immersed in a 1.0 M CaCl2 solution for 2 min to remove Sr2+ ions from the surface [34]. Finally, the wheat samples were placed in a refrigerator at minus 80 degrees Celsius for future use.
2.2. Effect of Foliar Application of Strontium Solution on Strontium Concentration in Roots
In this part of the experiment, the number of smears was set as the treatment variable, and there were 6 treatment groups, that is, 5 cycles of smear and blank were carried out, with each smear being performed 24 h after the previous smear. Each treatment group retained enough roots for testing. Each treatment group was repeated three times, making up a total of 18 samples. The strontium concentration in different parts (including leaves, stems and roots) of the wheat plants after 5 cycles of strontium application was determined. This was repeated 3 times. The cup root samples were placed in an oven at 105 degrees Celsius for half an hour and then dried to a constant weight at 80 degrees Celsius. Weighed by one ten thousandth of the balance, after weighing, the samples were crushed into powder with a pestle and mortar. Perchloric acid and nitric acid (1:4) were used for wet digestion. Then, the concentration of strontium was determined using an atomic absorption spectrometer (AA240FS-GTA120; Varian; Melbourne, Australia). The flame method was employed using spectrr AA software (5.1 version). The following conditions were utilized: flame type, air/acetylene; air flow (r), 3.50 (L min−1); acetylene flow (c), 1.50 (L min−1); equal current, 10 mA; wavelength, 460.7 nm; slit, 0.5 nm; measurement method, integral. In analyzing the concentration of strontium in the wheat roots after each round of sampling, the number of smears was determined to elucidate the difference between the concentration of strontium in the roots of strontium plants and the concentration of strontium in the roots of deionized water plants.
After the wheat leaves were smeared 5 times, the leaves, stems and roots of the wheat were removed, and the strontium concentration of each part of the wheat was determined using the above method, which was repeated 3 times. The transport of strontium in wheat leaves after smearing strontium in wheat was observed. After 5 rounds of smearing, the strontium concentration in the nutrient solution was determined to elucidate the background value.
2.3. Study of the Relationship between the Root Strontium Concentration and Biomass and Root Length and Establishment of the Estimation Method
In this part of the experiment, we defined the wheat leaves smeared with strontium ions as plant A and the wheat leaves smeared with deionized water (control) as plant B. The roots of plants A and B were mixed according to different biomass ratios shown in Table 1. Each mixed group was treated as a treatment, and each treatment was repeated three times. Before mixing, in using a root scanner (Epson Perfection V850 Pro; Seiko Epson Corporation; South Jakarta, Republic of Indonesia) and Winrhizo software (WinRhizo Pro 2009; 32 Bits Version; Regent Co., Ltd.; Quebec, QC, Canada), the root lengths of plant A wheat and plant B wheat in each group were measured, respectively. Then, the strontium concentration of each group of roots after mixing was measured according to the method outlined in Section 2.2. Under the 9 mixed ratios, with the increase in the proportion of roots of plant A, the biomass and root length of plant A also increased. Due to the high strontium concentration in the roots of plant A, the strontium concentration also increased with the increase in the proportion of plant A. The biomass and root length of plant A were linearly regressed, and Equation (1) for estimating the biomass of plant A in mixed roots was obtained. Then, the biomass and root length were linearly regressed to obtain Equation (2), which was used to assess the wheat biomass and root length. In considering the biomass, Equations (1) and (2) were combined to obtain Equation (3), which was used to estimate the root length with a varying strontium concentration. The three equations are as follows:
yb = axsr + b
yrl = cxb + d
yrl = d + c (axsr + b)

Table 1.
Mixed group.
In Equation (1), yb represents the biomass, and xsr represents the strontium concentration. In Equation (2), yrl represents the root length; xb represents the biomass; and a, b, c, and d are constants to be measured.
2.4. The Estimation Method Was Verified using Measured Values
In order to verify the accuracy of the root length biomass estimation method, we took out a batch of roots and grouped them proportionally according to the method outlined in Section 2.3. The root length value was scanned using root scanner and Winrhizo software to obtain the true value of the root length and biomass, and then the strontium concentration of mixed roots in each group was determined according to the method outlined in Section 2.2. The measured strontium concentration was substituted into the equation obtained using the linear regression in Section 2.3 to estimate the biomass and root length.
2.5. The Estimation Method Was Verified Using the Root Dyeing Method
In order to verify the accuracy and precision of the root length biomass method, we compared the dyeing method with the root length biomass method. In Toshifumi’s dyeing method, the stem is required to have a certain strength, but because wheat has a hollow stem, it is difficult to carry out pressure staining, so we used in vitro staining for the simulation. The specific methods were as follows: after the application was completed, the roots of plant A were removed, and methylene blue was soaked and stained for 30 min. The wheat roots were dyed blue as a dyeing treatment, resulting in plant A being dyed and containing a high concentration of strontium. The roots of plant B were not stained, and the roots of plants A and B were randomly taken out for mixing. After mixing, the total root length was scanned using root scanner and Winrhizo software. The color was classified using Winrhizo software; the root length with blue staining was recorded as the root length for the dyeing method, while the root length without coloration was considered the root length for other plants. After completion, the blue wheat roots were picked out and placed in a cool place for 2 h to remove moisture from the root surface, and then the fresh weight was weighed as the biomass of the dyeing method. The two roots were mixed again. The strontium concentration in the mixed roots was measured according to the method outlined in Section 2.2, and the strontium concentration was substituted into the equation of the estimated biomass and root length outlined in Section 2.3 to obtain the estimated biomass and root length. The estimated plant A biomass and root length were compared with the biomass and root length obtained via staining, and its accuracy and the accuracy of the biomass root length estimation method were observed.
2.6. Data Analysis
R software (4.1.2 version) was used for significance analyses, regression analyses and correlation analyses and the mapping of the above data.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Strontium Coating on Leaves on Strontium Concentration in Roots
Figure 1a illustrates that with an increasing number of applications, the strontium concentration in wheat roots progressively rises. A one-way ANOVA and multiple comparison tests were conducted to assess the strontium concentration in the roots after each application. The results show that the concentration of strontium was significantly higher than that of the control after two treatments. After five treatments, the concentration of strontium reached the maximum, and the concentration of strontium in wheat roots increased by four to five times compared with the control. In order to ensure the accuracy of the estimation and effectively distinguish the roots, we chose the wheat roots smeared for 5 days as the test material.
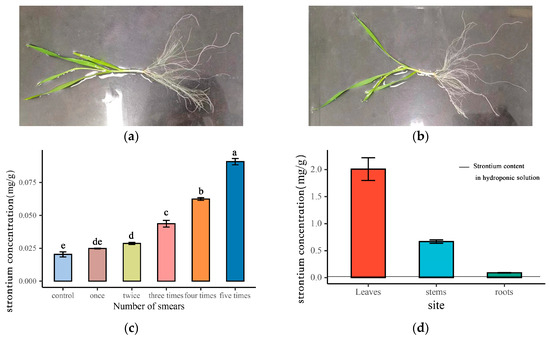
Figure 1.
Strontium concentration of wheat after smearing strontium: (a) state of the leaves after applying strontium for 5 days (plant A); (b) control state of the leaves after applying deionized water (plant B); (c) change in strontium in wheat roots with the number of smears, Different lowercase letters in the figure represent significant differences; (d) strontium concentration in different parts of wheat.
It can be seen from Figure 1b that the concentration of strontium in wheat leaves was the highest, reaching 2.01 mg g−1. The concentration of strontium transferred from leaves to stems was 0.67 mg g−1, accounting for 33.33% of the leaves. The concentration of strontium transferred to roots was 0.09 mg g−1, accounting for 4.5% of the leaves and 13.43% of the stems. The concentration of strontium in the nutrient solution was 0.013 mg L−1 after 5 days of smearing.
3.2. Establishment of the Estimation Method: The Relationship between the Strontium Concentration and the Root Length and Biomass
It can be seen from Figure 2a that there is a good correlation between the root biomass of wheat from plant A and the strontium concentration of the mixed roots. The slope of the equation obtained through linear fitting was 1.31, the intercept was 0, and the coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.83, which is statistically significant (p < 0.01). The obtained Equation (1) is as follows:
yb = 1.31xsr
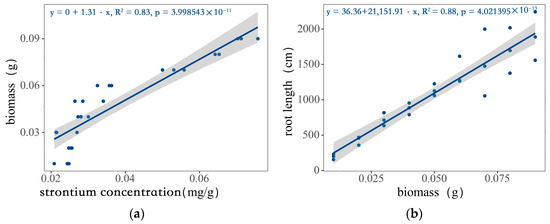
Figure 2.
The relationship between the biomass and the strontium concentration and root length: (a) the relationship between root biomass of wheat from plant A and root strontium concentration after mixing; (b) the relationship between biomass and root length.
In the formula, xsr represents the strontium concentration, and yb represents the biomass.
In Figure 2b, the relationship between the root biomass and root length of the wheat is expressed. The slope of the equation obtained through linear fitting was 21,151.91, the intercept was 36.36, and the coefficient of determination was 0.88, which is statistically significant (p < 0.01). The obtained equation is as follows:
yrl = 36.36 + 21,151.91xb
In the formula, xb represents the biomass, and yrl represents the root length.
In considering the biomass, Equations (4) and (5) were combined to obtain Equation (6), predicting the root length with strontium can be achieved as follows:
yrl = 36.36 + 27,709xsr
In the formula, yrl denotes the root length, and xsr denotes the strontium concentration.
3.3. The Estimation Method Was Validated Using Measured Values
It can be seen from Figure 3a,b that the results obtained using the biomass estimation equation are not much different from the real values, and there is a strong correlation between the two (the Pearson correlation coefficient is greater than 0.8). A t-test indicated that the correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (p < 0.01). It was proved that the biomass estimation equation is viable.
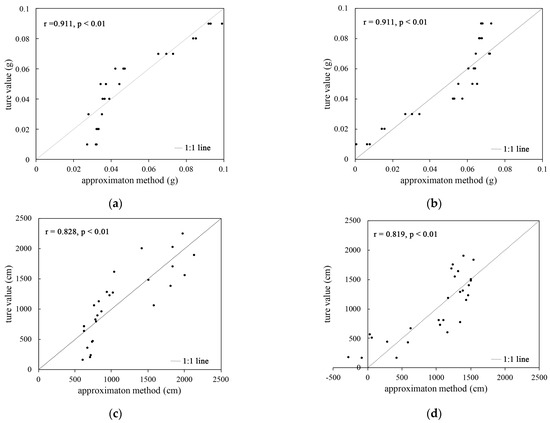
Figure 3.
Comparative analysis of the correlation between the biomass root length estimation method and real value: (a) the correlation between the biomass estimation method from plant A and the true value; (b) the correlation between the biomass estimation and the true value from plant B; (c) the correlation between the root length estimation and the true value derived from plant A; (d) the correlation between the root length estimation and the true value derived from plant B.
Figure 3c,d show that the results obtained from the root length estimation equation are generally similar to the real values, and some scatter points show that the estimated values are too large or too small. The Pearson correlation coefficient was greater than 0.8. The t-test indicated that the correlation was significant at the 0.01 level (p < 0.01), which proved that the root length estimation equation could be used.
3.4. Root Length Comparison between Dyeing Method and Estimation Method
From Figure 4, it can be seen that the root length value obtained using the root length estimation equation is generally similar to the root length value obtained using the dyeing method. There is a strong correlation between the two, and the Pearson correlation coefficient was greater than 0.8. A t-test showed that at the 0.01 level, the correlation between the two is significant and statistically significant.
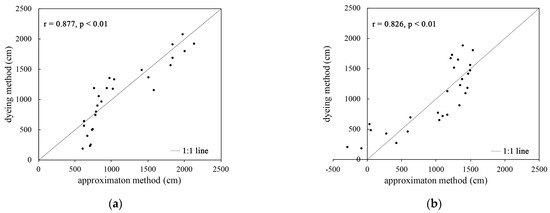
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis of the biomass root length estimation method and the root length value obtained using the dyeing method: (a) the correlation between root length derived from plant A and root length with color in the dyeing method; (b) the correlation between the root length derived from plant B and the root length without color in the dyeing method.
4. Discussion
The roots of adjacent crops are affected by many factors and adapt in ways that are more conducive to their own growth [35]. Agricultural technicians need to understand the growth of crop roots in order to facilitate the design and cultivation of more suitable varieties or optimize the utilization efficiency of farmland nutrient resources, which is crucial for maximizing food production [36]. However, due to the concealment of roots, it is not easy to observe them, and because most crop roots are similar, it is difficult to observe the sources of roots. Therefore, in the farmland ecosystem, research on breeding varieties or optimizing the utilization efficiency of farmland nutrient resources from the aspects of root cooperation or competition is limited. This paper provides an effective technical means for this research. Through smearing strontium on wheat leaves, it was verified that strontium will be absorbed by wheat and transported to the roots, which is consistent with previous research results [25,37].
In this study, the strontium concentration in the stems accounted for 33.33% of the strontium concentration in the leaves, and the strontium concentration in the roots accounted for 4.5% of the leaves and 13.43% of the stems. These findings differ from those obtained in previous studies [38,39]; this may be attributed to the types of crops used being different and the period of strontium use being inconsistent. In previous studies [40], 0.01% of the stable strontium applied to the leaves was transferred to the roots; however, 0.6% of strontium was transferred to roots in this study, which was significantly higher than in previous studies. The reason for this is that we added surfactants to the strontium solution used, so that the leaves could be wet for a long time after smearing the strontium solution, thereby increasing the permeability of strontium. However, this study did not evaluate other surfactants. The surfactants we used were still the basic type, and the amount of transfer shown in the application of this study was not too high. However, looking forward to the future, if we find a surfactant with a higher transfer efficiency, it will undoubtedly greatly promote the absorption of strontium by the leaves, thus theoretically increasing the amount of transfer from the leaves to roots. It is expected that the estimation accuracy will be significantly improved. Of course, this will require later tests to verify.
Based on this, we proposed a method for estimating the root length biomass of a wheat plant in the mixed root using strontium. This method was verified with the real value and the root length value obtained using the dyeing method. We found that the data point deviated from the 1:1 line, which may be due to the uneven distribution of strontium in the main roots and lateral roots and may also be due to the uneven distribution of wheat leaves. However, although some data points deviated from the 1:1 line, the Pearson coefficient exceeded 0.8, the correlation was strong, and the t-test indicated a very significant level (p < 0.01).
Compared with the dyeing method, the root length biomass estimation method has a wider range of applications. This method is suitable not only for lignified stems but also for non-lignified stems or hollow stems. It is worth noting that Toshifumi’s dyeing method cannot stain root hairs or dry or damaged roots [7], and the dyeing method in this study entailed staining wheat roots in vitro. Due to the limitations of the experimental materials, Toshifumi’s dyeing method cannot be fully replicated, and dry or injured roots could also be stained. This increases the accuracy of the dyeing method and is closer to the true value. At the same time, this method uses steady-state strontium, which is friendly to both the experimenters and the environment [25]. Compared with PCR [15], this method is simple and low-cost. In theory, this method could be used for crops other than wheat, but if the root morphology of other crops is significantly different from that of wheat, the equations of biomass, root length and strontium concentration will need to be re-established to ensure accuracy when estimating root length and biomass. Although this method has not been verified for other crops, it has shown effectiveness in the wheat seedling stage.
The transport mechanism of strontium in wheat is not yet fully understood. The detailed process of how strontium ions are effectively transported to plant roots remains to be further explored, particularly after the leaves are smeared with strontium ions. This study not only involved the transport pathway of strontium ions in plants but also necessitated exploring its accumulation mechanism to fully elucidate this complex process.
5. Conclusions
This paper provides a new perspective and method for the study of crop roots, especially wheat roots. In smearing strontium ions on wheat leaves, the root length and biomass of a certain plant in multiple wheat mixed roots can be effectively estimated, which provides a powerful tool for future research on wheat roots. Similarly, the potential application value of this method cannot be ignored, especially in the study of crop root competition, breeding of excellent varieties, and improvement of crop fertilization. With further research, this method may play a greater role in plant root research and crop research in the future, providing additional insights and guidance for solving related problems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F. and X.X.; methodology, S.F., X.X. and Z.S.; software, S.F. and D.L.; validation, S.F., D.L. and Y.T.; formal analysis, S.F. and X.X.; data curation, S.F., D.L. and Y.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F., X.X., Z.S. and D.L.; writing—review and editing, S.F., X.X., Z.S., D.L. and Y.T.; visualization, S.F. and D.L.; supervision, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Freschet, G.T.; Pagès, L.; Iversen, C.M.; Comas, L.H.; Rewald, B.; Roumet, C.; Klimešová, J.; Zadworny, M.; Poorter, H.; Postma, J.A.; et al. A Starting Guide to Root Ecology: Strengthening Ecological Concepts and Standardising Root Classification, Sampling, Processing and Trait Measurements. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 973–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semchenko, M.; Saar, S.; Lepik, A. Plant Root Exudates Mediate Neighbour Recognition and Trigger Complex Behavioural Changes. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Li, D.; Di, N.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Xi, B.; Coleman, M. Stand Development Modifies Effects of Soil Water Availability on Poplar Fine-Root Traits: Evidence from a Six-Year Experiment. Plant Soil 2022, 480, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakumova, M.; Zobel, K.; Lepik, A.; Semchenko, M. Plasticity in Plant Functional Traits Is Shaped by Variability in Neighbourhood Species Composition. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Dresbøll, D.B.; Thorup-Kristensen, K. Naturally Coloured Roots as a Tool for Studying Root Interactions in Mixed Cropping. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabal, C.; Martínez-García, R.; de Castro Aguilar, A.; Valladares, F.; Pacala, S.W. The Exploitative Segregation of Plant Roots. Science 2020, 370, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Shimano, S.; Kaneda, S.; Nakajima, M.; Urashima, Y.; Miyoshi, N. Multicolor Staining of Root Systems in Pot Culture. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2006, 52, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo-Danso, S.D.; Prescott, C.E.; Smith, A.R. Methods for Estimating Root Biomass and Production in Forest and Woodland Ecosystem Carbon Studies: A Review. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 359, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, S.; Reinsch, T.; Loges, R.; Hasler, M.; Taube, F. Comparison of Ingrowth Core and Sequential Soil Core Methods for Estimating Belowground Net Primary Production in Grass–Clover Swards. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeght, J.-L.; Rewald, B.; Pierret, A. How to Study Deep Roots—And Why It Matters. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 56547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Monnier, Y.; Mao, Z.; Lobet, G.; Maeght, J.-L.; Ramel, M.; Stokes, A. An Evaluation of Inexpensive Methods for Root Image Acquisition When Using Rhizotrons. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewald, B.; Meinen, C. Plant Roots and Spectroscopic Methods—Analyzing Species, Biomass and Vitality. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 66166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, G.H. A Device for the Observation of Root Growth in the Soil. Nature 1937, 139, 966–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugfelder, D.; Kochs, J.; Koller, R.; Jahnke, S.; Mohl, C.; Pariyar, S.; Fassbender, H.; Nagel, K.A.; Watt, M.; van Dusschoten, D. The Root System Architecture of Wheat Establishing in Soil Is Associated with Varying Elongation Rates of Seminal Roots: Quantification Using 4D Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 2050–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oram, N.J.; Ravenek, J.M.; Barry, K.E.; Weigelt, A.; Chen, H.; Gessler, A.; Gockele, A.; de Kroon, H.; van der Paauw, J.W.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; et al. Below-Ground Complementarity Effects in a Grassland Biodiversity Experiment Are Related to Deep-Rooting Species. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmatiski, A.; Beard, K.H. Root Niche Partitioning among Grasses, Saplings, and Trees Measured Using a Tracer Technique. Oecologia 2013, 171, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, B.; Drapela, T.; Wanek, W.; Schmidt, O.; Frank, T.; Zaller, J.G. A Simple Method for In Situ-labelling with 15N and 13C of Grassland Plant Species by Foliar Brushing. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 2, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.D.; Sagar, G.R. An autoradiographic study of the movement of 14C-Labelled assimilates in the developing wheat plant. Weed Res. 1962, 2, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.L.; Lipps, R.C. A Comparison of Stable Strontium and P32 as Tracers for Estimating Alfalfa Root Activity. Plant Soil 1964, 20, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Rietkerk, M.; Dekker, S.C.; Mazzoleni, S. Negative Plant–Soil Feedback and Positive Species Interaction in a Herbaceous Plant Community. Plant Ecol. 2005, 181, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, C.; Pina, C.M.; Müller, N.; Lara, L.A.; Melo Rodriguez, G.; Orlando, F.; Schoelkopf, J.; Fernández, V. Mineral Particles in Foliar Fertilizer Formulations Can Improve the Rate of Foliar Uptake. Plants 2023, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, L.; Du, Y.; Hampton, M.A.; Nguyen, A.V.; Huang, L.; Rudolph, V.; Xu, Z.P. Potential Foliar Fertilizers with Copper and Zinc Dual Micronutrients in Nanocrystal Suspension. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, V.; Pimentel, C.; Bahamonde, H.A. Salt Hydration and Drop Drying of Two Model Calcium Salts: Implications for Foliar Nutrient Absorption and Deposition. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2020, 183, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Qiu, N.; Zhang, W.; Du, M.; Fang, X.; Zhou, F. Research progress on plant biological effects of strontium. Plant Physiol. J. 2022, 58, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.; Lichtscheidl, I. Strontium in the Environment: Review about Reactions of Plants towards Stable and Radioactive Strontium Isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1458–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Wang, D.; Kaleri, A.R.; Baloch, S.B.; Brtnicky, M.; Kucerik, J.; Mustafa, A. Physiological Responses and Phytoremediation Abilities of Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L.) under Cesium and Strontium Contaminated Soils. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Kang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, N.; Chen, M.; Zhou, F. The Biological Effects of Strontium (88Sr) on Chinese Cabbage. Plant Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tang, Y.L.; Ao, J.; Wang, D. Effects of Strontium on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Oilseed Rape Seedlings. Russ J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 59, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Pemberton, R.; Li, P. Bioindicating Potential of Strontium Contamination with Spanish Moss Tillandsia usneoides. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 152, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyen, C.; Roblin, G. Uptake and Translocation of Strontium in Hydroponically Grown Maize Plants, and Subsequent Effects on Tissue Ion Concentration, Growth and Chlorophyll a/b Ratio: Comparison with Ca Effects. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 68, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyen, C.; Roblin, G. Occurrence of Interactions between Individual Sr2+- and Ca2+-Effects on Maize Root and Shoot Growth and Sr2+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ Concentrations, and Membrane Potential: Consequences on Predicting Sr2+-Impact. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, B.; Fu, K.; Li, C.; Li, C. Comparative Analysis of Combined Phosphorus and Drought Stress-Responses in Two Winter Wheat. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, C.C.; Whipker, B.E.; McCall, I.; Garzón, J. Characterization of nutrient disorders of lettuct in silica sand culture. Acta Hortic. 2009, 843, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Qin, X.; Li, F.-M.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Brandl, H.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Uptake and Distribution of Stable Strontium in 26 Cultivars of Three Crop Species: Oats, Wheat, and Barley for Their Potential Use in Phytoremediation. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2015, 17, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimešová, J.; Martínková, J.; Ottaviani, G. Belowground Plant Functional Ecology: Towards an Integrated Perspective. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.F.; McNickle, G.G. The Behavioral Ecology of Nutrient Foraging by Plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 42, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, M.A.; Hinton, T.G.; Webb, S.B. A Comparison of 90Sr and 137Cs Uptake in Plants via Three Pathways at Two Chernobyl-Contaminated Sites. J. Environ. Radioact. 2002, 58, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, R.K.; Narayanan, U.; Bhat, I.S. Investigations on Interception and Translocation of Airboren 85Sr, 131I, 137Cs in Beans, Spinach and Radish Plants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1998, 101, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnder, H.J.; Kopp, P.; Eikenberg, J.; Feller, U.; Oertli, J.J. Uptake and Transport of Radioactive Cesium and Strontium into Grapevines after Leaf Contamination. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1995, 46, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambler, J.E. Translocation of Strontium from Leaves of Bean and Corn Plants. Radiat. Bot. 1964, 4, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).