Research on a Low-Cost High-Precision Positioning System for Orchard Mowers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
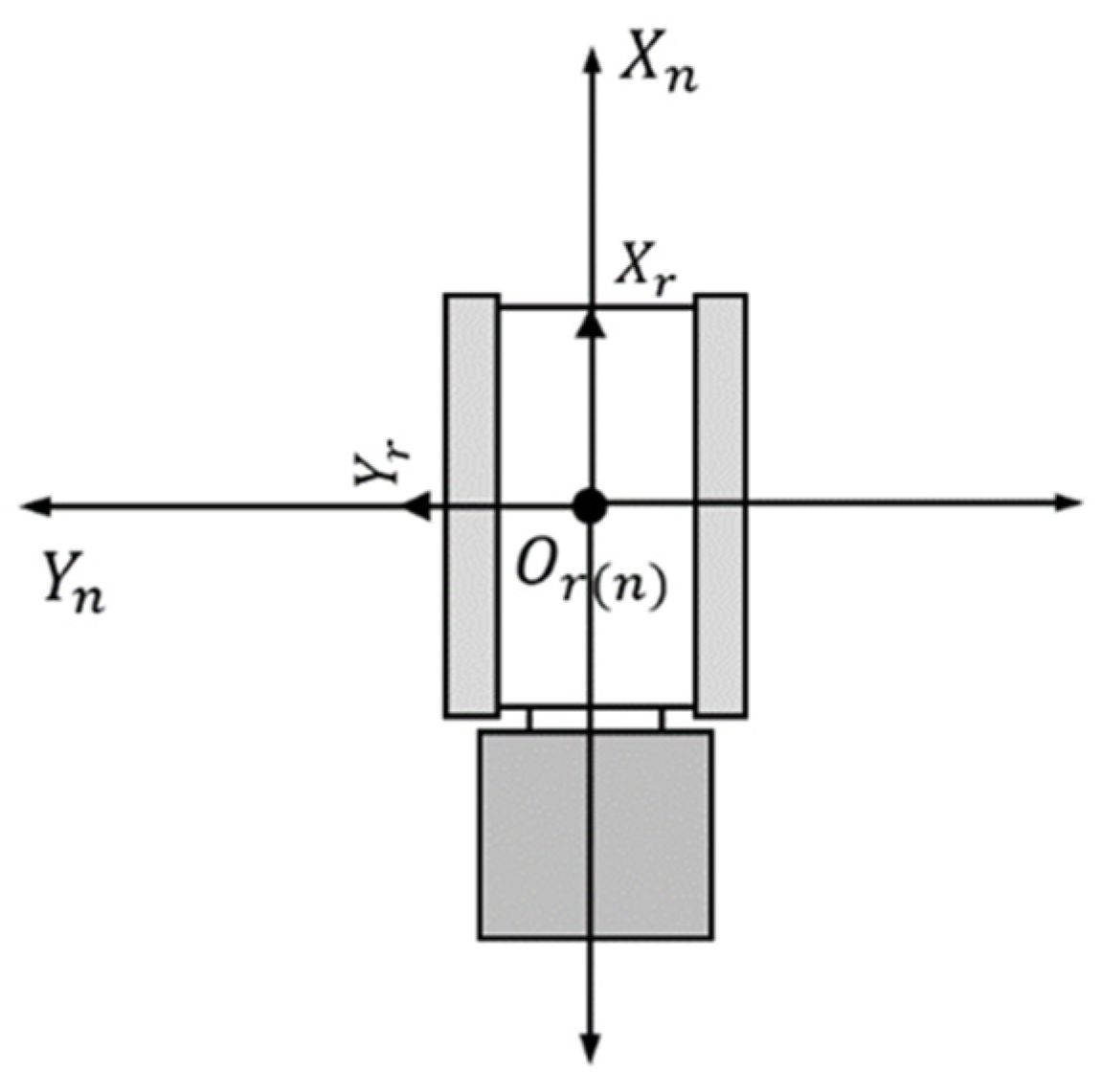
2.2.1. Definition of the Co-Ordinate System
2.2.2. Experimental Methods and Procedures
2.3. Orchard Mower Positioning System Design
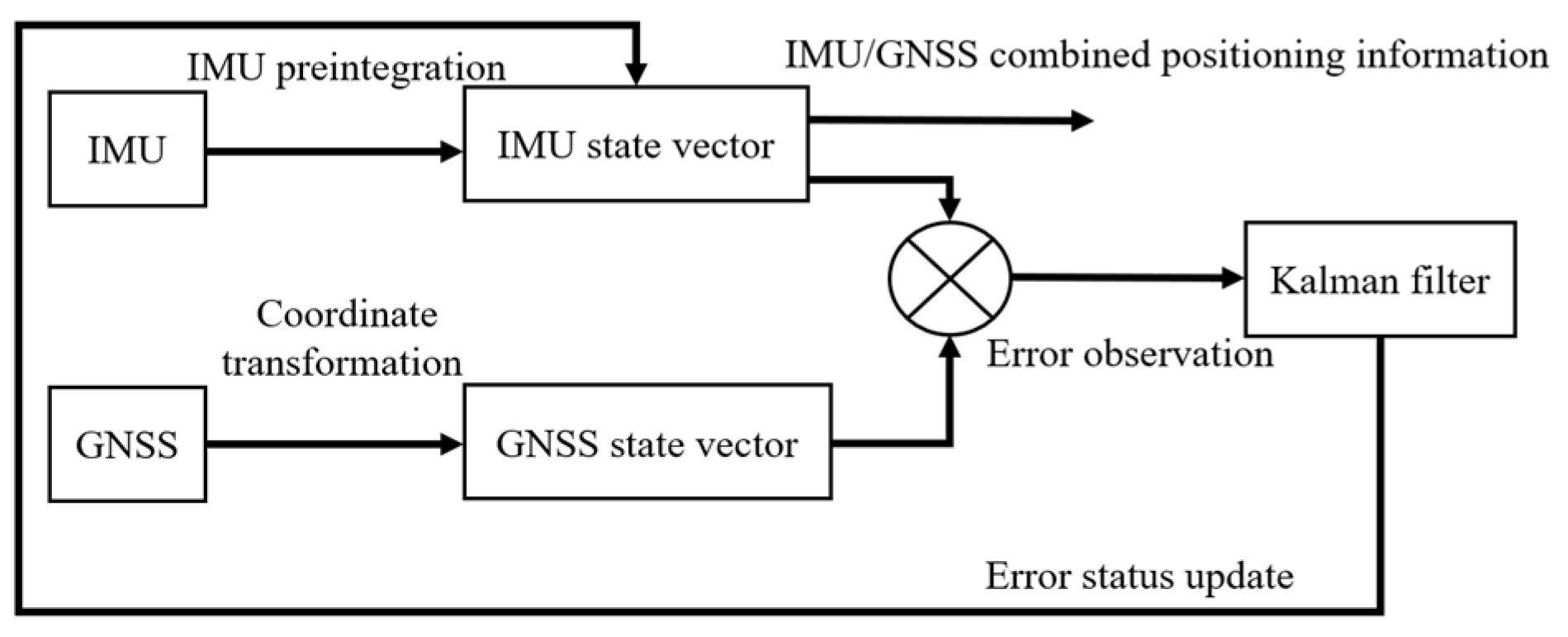
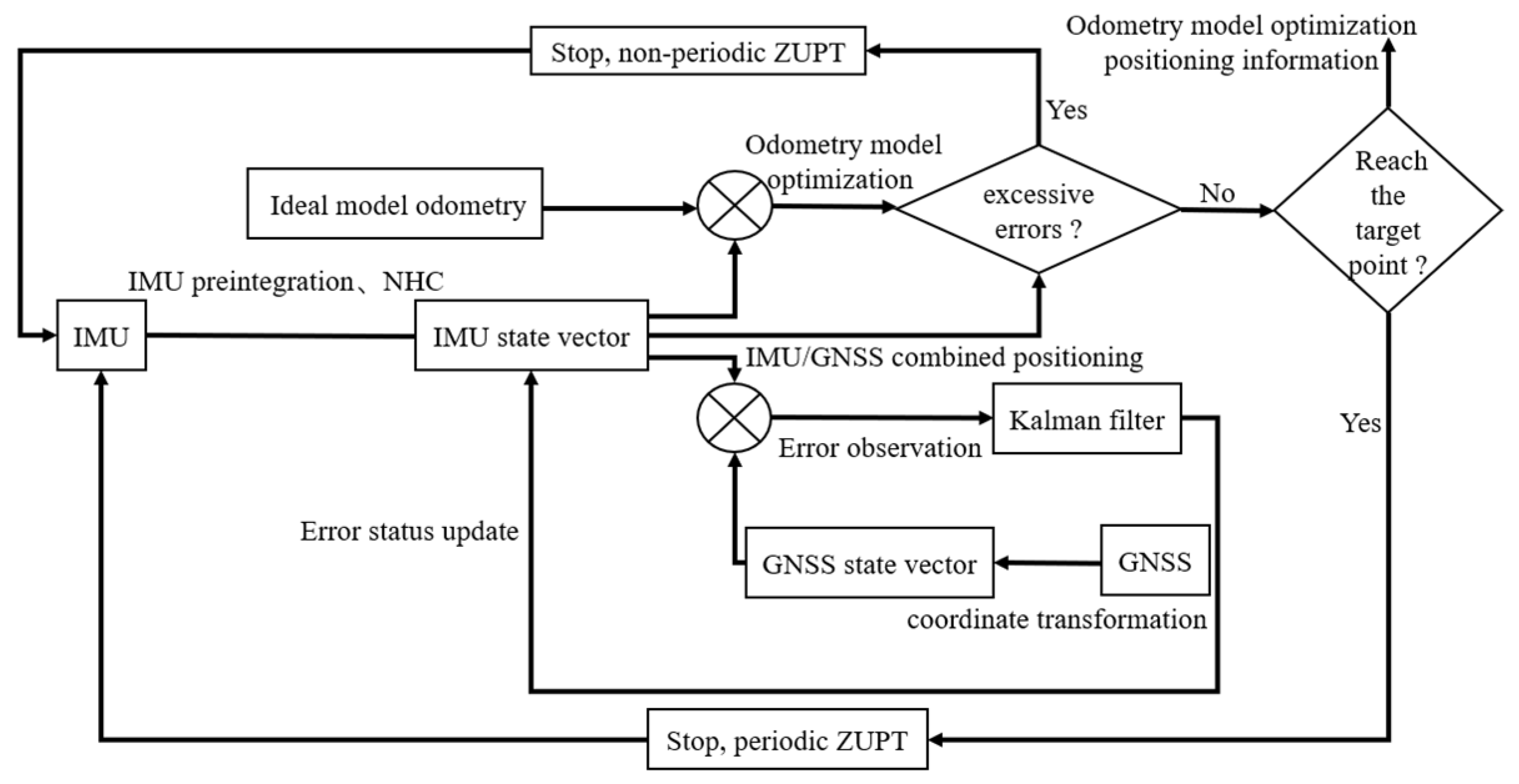
2.3.1. IMU/GNSS Combined Positioning Design
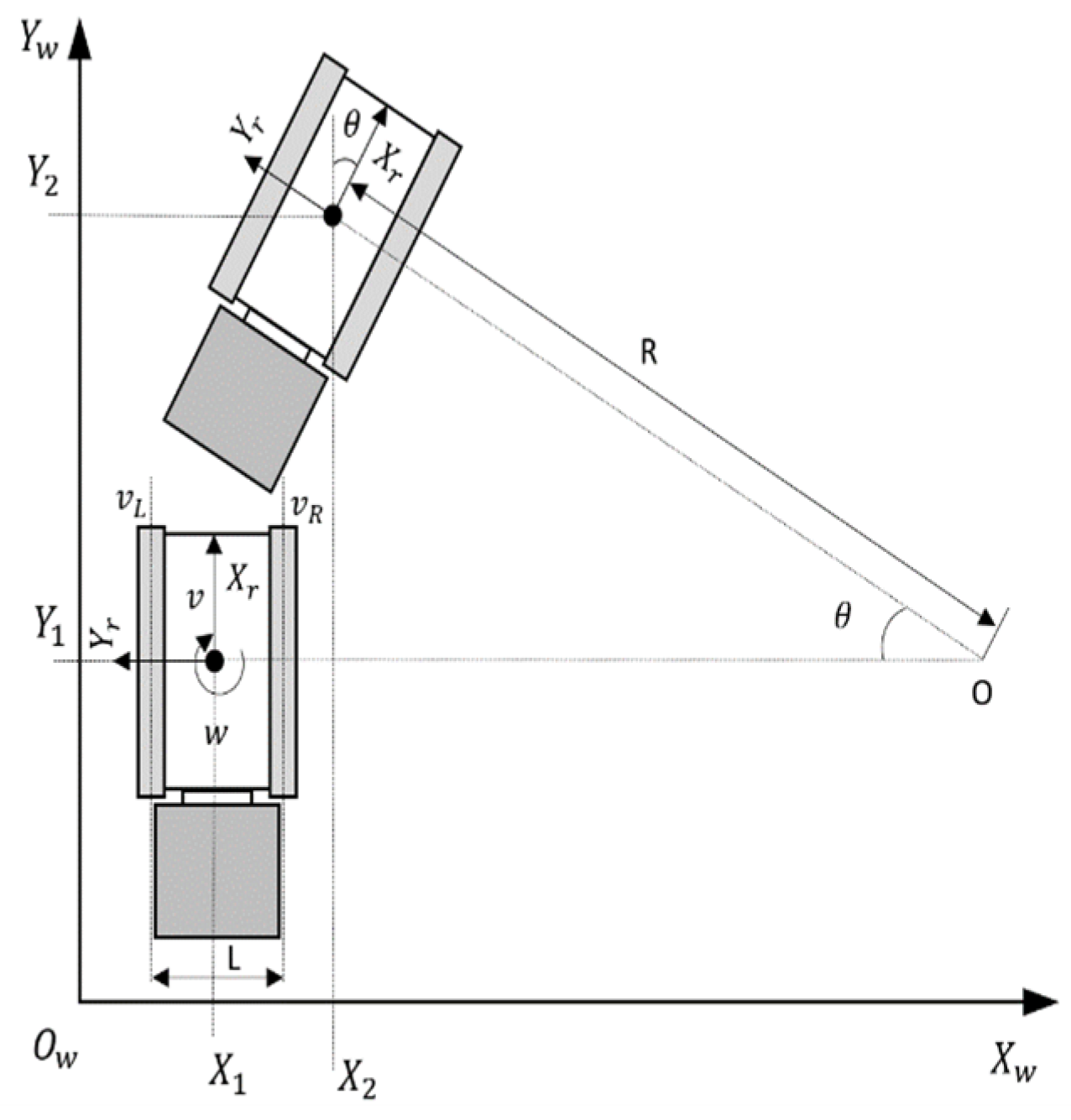
2.3.2. Optimization of the Odometry Model for Tractor Mowers
- (1)
- The center of mass of the mower coincides with the center of geometric velocity, and no side-slip with the ground occurs during motion;
- (2)
- Since there is only one drive motor on each side, the kinematic model is simplified to a two-wheel differential model;
- (3)
- The deformation of the track, the change in the contact surface between the track and the ground, and the effect of transmission resistance are neglected.
2.3.3. Design of the ZUPT-Based Mower Positioning System
3. Results
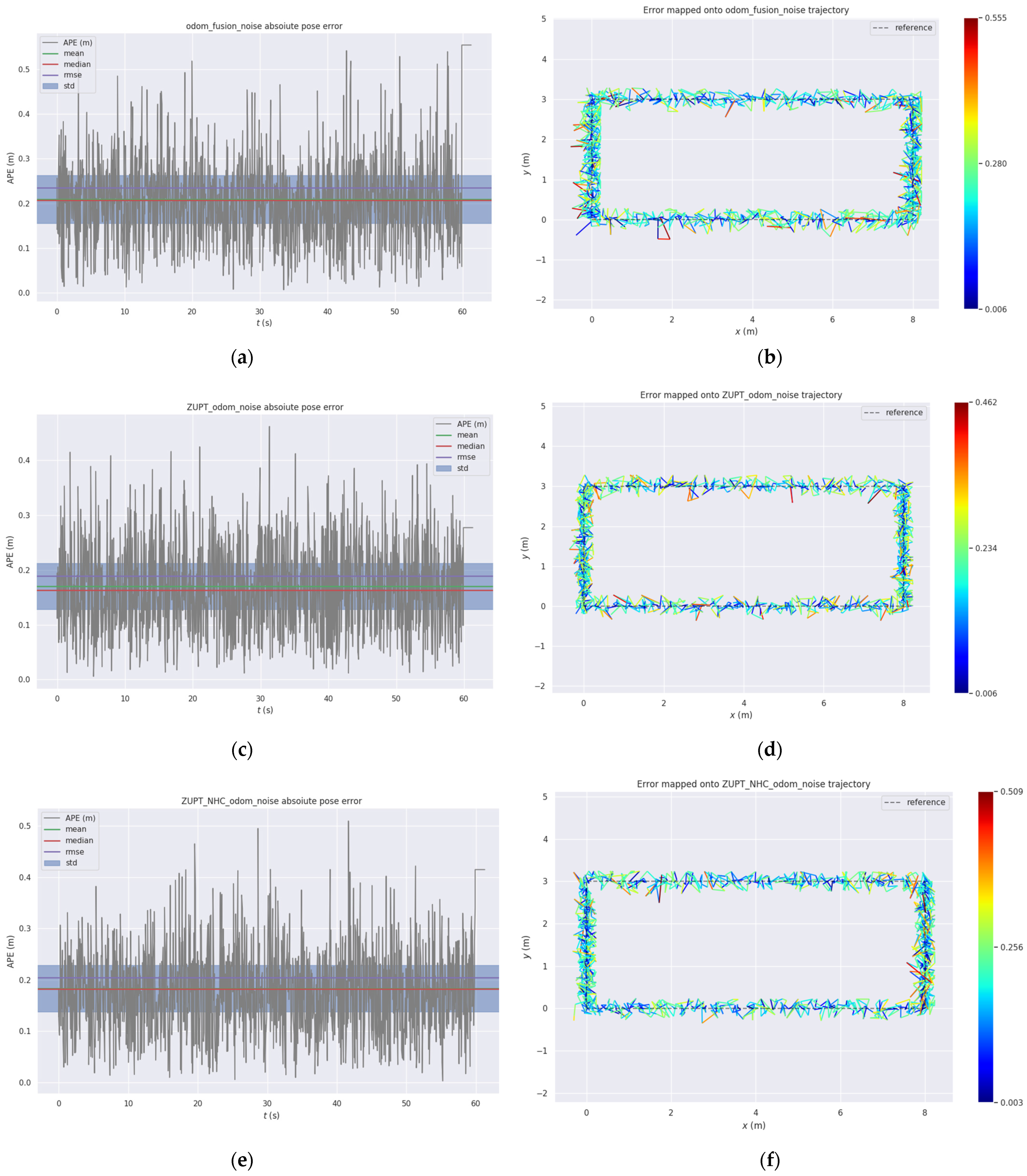
3.1. Experiment 1: Positioning Error Comparison Experiment without IMU Data Updating Methods
3.2. Experiment 2: Positioning Accuracy Experiment with the IMU Data Update
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Averill, K.M.; Westbrook, A.S.; Pineda-Bermudez, L.; O’Briant, R.P.; DiTommaso, A.; Ryan, M.R. Effects of Tertill® Weeding Robot on Weed Abundance and Diversity. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingsheim, M.L.; Döring, T.F. What weeding robots need to know about ecology. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, J.C.; Liu, J.J. Research on GNSS INS & GNSS/INS Integrated Navigation Method for Autonomous Vehicles: A Survey. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 79033–79055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Jiang, J.G.; Yan, P.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Xie, D.P. A lightweight odometry network for GNSS/INS integration during GNSS outages. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 151, 111143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bai, S.; Niu, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, B.; Wei, L.; Xiong, S.; Liu, L. Research progress on mechanized harvesting technology and equipment for forest fruit. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2022, 38, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Xue, M.; Yuan, H. Design of the GNSS/INS integrated navigation system for intelligent agricultural machinery. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2021, 37, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.U.; Zhimin, W.; Pei, W.; Jie, H.E.; Jinkang, J.; Chenyang, W.; Mingjin, L.I. Agricultural robot positioning system based on laser sensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2023, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Gao, F.; Qin, T.; Gao, W.; Liu, T.; Wu, W.; Yang, Z.; Shen, S. Autonomous aerial navigation using monocular visual-inertial fusion. J. Field Robot. 2018, 35, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.J.; Wu, Y.B.; Kuang, J. Wheel-INS: A Wheel-Mounted MEMS IMU-Based Dead Reckoning System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 9814–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.I.; Yuhao, W. Inter-line Pose Estimation and Fruit Tree Location Method for Orchard Robot. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 16–26+39. [Google Scholar]
- Saidani, M.; Kim, H. Quantification of the environmental and economic benefits of the electrification of lawn mowers on the US residential market. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, B.; Han, X.S.; Hao, Y.P. Attitude Determination Method by Fusing Single Antenna GPS and Low Cost MEMS Sensors Using Intelligent Kalman Filter Algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 4517673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsman, D.; Klein, I. Information-Aided Inertial Navigation: A Review. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, K.; Liang, W.J.M.S. A zero-velocity update method based on neural network and Kalman filter for vehicle-mounted inertial navigation system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 045110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, J.H.; Cheng, Q.; Mao, Y.; Ochieng, W.Y. A new IMU-aided multiple GNSS fault detection and exclusion algorithm for integrated navigation in urban environments. Gps Solut. 2021, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Niu, X.; Zhang, T.; Tang, H.; Chen, Q.J.M. Accuracy and Robustness of ODO/NHC Measurement Models for Wheeled Robot Positioning. Measurement 2022, 201, 111720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, X. Estimate the pitch and heading mounting angles of the IMU for land vehicular GNSS/INS integrated system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 6503–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongliang, Y.; Junyu, Y.; Rui, T.; Jianwei, D.U. High-precision Localization of Autonomous Agricultural Machinery Using Low-cost IMU and Motion Constraints. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Takanose, A.; Kondo, K.; Hoda, Y.; Meguro, J.-i.; Takeda, K.J.J.R.M. Localization System for Vehicle Navigation Based on GNSS/IMU Using Time-Series Optimization with Road Gradient Constrain. Robot. Mechatron. 2023, 35, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhawaja, F.; Jaradat, M.A.; Romdhane, L. Low-cost depth/IMU intelligent sensor fusion for indoor robot navigation. Robotica 2023, 41, 1689–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzione, F.; Ferraro, R.; Renga, A.; Grassi, M. Multipurpose Earth Orbit Navigation System for autonomous orbit determination during satellite low thrust LEO-MEO transfer. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Metrology for Aerospace (MetroAeroSpace), Florence, Italy, 22–23 June 2016; pp. 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, C.; Ohi, N.; Gu, Y.; Gross, J. Slip-Based Autonomous ZUPT Through Gaussian Process to Improve Planetary Rover Localization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 4782–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Amin, M.G. Tracking performance and average error analysis of GPS discriminators in multipath. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1224–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.C.; Shen, W.B.; Ning, J.S. Development of Lee’s exact method for Gauss-Kruger projection. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Mu, S.; Wu, C.; Chen, K.; Liao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liao, Q. Steering kinematic analysis and experiment of tracked combine harvester working in paddy field. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2020, 36, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, C.; Das, S.; Gutierrez, E.; Watson, R.; Gross, J. ZUPT aided GNSS factor graph with inertial navigation integration for wheeled robots. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021), St. Louis, MO, USA, 20–24 September 2021; pp. 3285–3293. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Tang, F.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, B. Implementation of ZUPT Aided GNSS/MEMS-IMU Deeply Coupled Navigation System. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT), Qingdao, China, 14–17 May 2023; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, M.; Ning, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J. Sensor Fusion of GNSS and IMU Data for Robust Localization via Smoothed Error State Kalman Filter. Sensors 2023, 23, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
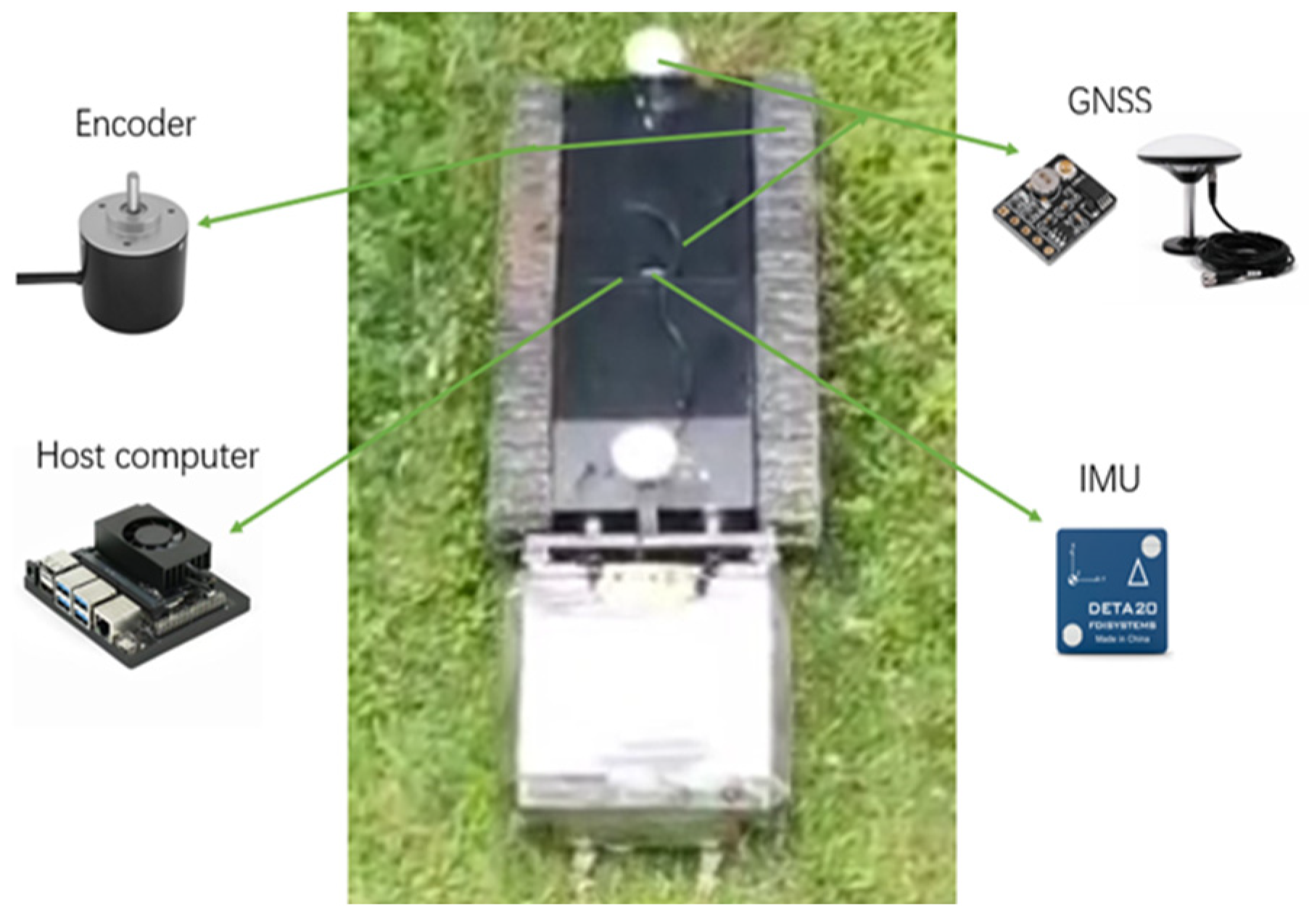







| Project | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Tracking sensitivity | −162 dBm |
| Velocimetry accuracy | <2.5 m |
| Position accuracy | <0.1 m/s |
| Frequency | ≤10 Hz |
| Project | Accelerometer | Gyro | Magnetometer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | ±8 g | ±2000/s | ±4900 uT |
| Linearity | 0.1% FS | 0.1% FS | 0.1% |
| Orthogonality error | ±0.05° | ±0.05° | ±0.05° |
| Frequency | 500 Hz | 300 Hz | 250 Hz |
| Methods | Average Error (m) | Maximum Error (m) | Standard Deviation (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | X | Y | X | Y | |
| GNSS positioning IMU pre-integrated positioning | 1.186 | 1.068 | 2.682 | 2.324 | 0.541 | 0.489 |
| 1.625 | 1.604 | 3.013 | 3.021 | 0.773 | 0.736 | |
| IMU/GNSS combined positioning | 0.642 | 0.535 | 3.013 | 1.125 | 0.316 | 0.309 |
| Ideal odometry positioning | 0.553 | 0.614 | 1.235 | 0.942 | 0.303 | 0.326 |
| Odometry optimized positioning | 0.343 | 0.362 | 0.524 | 0.539 | 0.176 | 0.183 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fei, K.; Mai, C.; Jiang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, J. Research on a Low-Cost High-Precision Positioning System for Orchard Mowers. Agriculture 2024, 14, 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060813
Fei K, Mai C, Jiang R, Zeng Y, Ma Z, Cai J, Li J. Research on a Low-Cost High-Precision Positioning System for Orchard Mowers. Agriculture. 2024; 14(6):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060813
Chicago/Turabian StyleFei, Ke, Chaodong Mai, Runpeng Jiang, Ye Zeng, Zhe Ma, Jiamin Cai, and Jun Li. 2024. "Research on a Low-Cost High-Precision Positioning System for Orchard Mowers" Agriculture 14, no. 6: 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060813
APA StyleFei, K., Mai, C., Jiang, R., Zeng, Y., Ma, Z., Cai, J., & Li, J. (2024). Research on a Low-Cost High-Precision Positioning System for Orchard Mowers. Agriculture, 14(6), 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060813







