Abstract
Several attempts have been made to evaluate the abundance and distribution of the bacterial community in the rhizosphere of medicinal plants. Many describe information based on an estimation of the community structure and the effects of plant cover in determining microbial community composition. The ability of plants to specifically shape their microbial community in general and medicinal plants in particular is largely unknown. With the arrival of molecular biology, understanding the microbial community’s composition, diversity, and function became possible. We hypothesized that microbial communities associated with medicinal shrubs would differ from each other. To test this hypothesis, we characterized the soil microbial composition under each of five Mediterranean medicinal plants, differentiated by their medicinal use and ecophysiological adaptation, namely, Salvia fruticosa, Pistacia lentiscus, Myrtus communis, Origanum syriacum, and Teucrium capitatum, and an open-space bare soil between the plants, inhabiting natural ecosystems characterized by similar climatic conditions typical of a Mediterranean environment. The results demonstrated the importance of plant ecophysiological adaptations, which play an important role in determining microbial community composition and functional diversity. The intensity of a plant’s response to its surroundings can have either positive or negative effects that will determine the microbial community composition and interactions among the belowground parts. A total of 11 phyla, 21 orders, and 409 genera were found in the soil rhizosphere in the vicinity of the four plants and open space samples. The distinguishing attributes of each shrub trigger and stimulate the microbial community’s rhizosphere. This results in distinct patterns of bacterial diversity and functionality between the different shrubs and the control. The rhizosphere bacterial community composition differed between the plants in a PERMANOVA test, but there was little difference in terms of phyla and order relative abundances. This study shows how five medicinal plants, coexisting in a common habitat, impact the bacterial community. The noticeable shift in bacterial composition further supports our discovery that root exudates effectively govern the makeup of soil bacterial communities.
1. Introduction
The plant rhizosphere is defined as the interaction zone between the root system and the soil environment. According to Philippot et al. [1], the root zone region has an impact and comprises a diverse community of microorganisms and invertebrates that affect the plant through direct and indirect interactions. Such root zone patches facilitate differences in the soil biota community that promote ecosystem heterogeneity and have significant effects on the belowground soil biota [2]. Microorganisms that surround the root zone create hotspots of microbial activity with beneficial effects on the plant’s health [3]. The unique ecological niche that forms the root rhizosphere shapes the microbial community and the level of interaction between the individual plant and the soil abiotic and biotic factors by releasing root exudates into the soil and producing root litter [4,5,6]. The composition and diversity of biota rhizosphere communities are shaped by a multitude of factors extending beyond plant species alone. These encompass soil characteristics such as soil type and pedoclimate, as well as the health and developmental stage of the plant, fluctuations in climate and seasons, the presence of grazing animals, and an array of other biological triggers and environmental influences. These symbiotic associations, widely prevalent across the plant kingdom, are renowned for their profound impact on the plant’s surroundings through phenomena like allelopathy, ensuring the plant’s survival and fostering its growth [7].
Bacteria are one of the most important and abundant microbial communities in the rhizosphere. This community includes some plant pathogenic bacteria [8], while others benefit plant growth in various ways. Some of these plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) contribute to the suppression of plant diseases [9], while others fix atmospheric nitrogen [10] or increase Fe solubility and acquisition [11,12]. Moreover, PGPRs can help plants overcome abiotic stresses, such as water stress [13], by promoting beneficial populations in their surrounding microbiome. A comprehensive review of the rhizosphere microbiome by Mendes et al. [3] emphasized the importance of the rhizosphere microbiome in spurring beneficial microorganisms for plant growth. Microorganisms present in the soil are closely associated with soil particles and are found in microcolonies, where the size, density, and diversity are controlled by a matrix of organic compounds. Elements such as resource availability, for example, in the plant rhizosphere, influence the size, composition, diversity, and distribution of microbial communities, similarly to other biotic communities [14,15].
According to Petrovska [16], medicinal plants have been used for thousands of years due to their therapeutic effects and are still in use today as in ancient times. The uses and significance of medicinal plants are recognized globally by the WHO (2013) and are important in the pharmaceutical industry [17,18]. Secondary metabolites produced by medicinal plants were reported in the major parts of the plant [19] and are known to affect vertebrates, invertebrates, aboveground, and belowground microorganisms [20].
Studies on agroecosystems have suggested that the composition of the microbial community depends on plant cover and is differentiated by cultivar, phylogentic stage, and genotype [21,22,23].
In the present study, we sampled the soil rhizosphere of five medicinal plants, namely, Myrtus communis, Origanum syriacum, Pistacia lentiscus, Salvia fruticose, and Teucrium capitatum, inhabiting natural systems with the same climatic conditions in a Mediterranean environment. In a previous study, we analyzed the fungal rhizosphere of these plants [24]. The rhizosphere bacteria of some of these plants have been researched in several studies, where some PGPRs have been isolated from S. syriacum [25,26]. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of five medicinal plants’ soil rhizosphere on bacterial community composition. We hypothesized that the effect of each plant on the soil rhizosphere would be expressed by significantly different relative abundances, compositions, and functionality of bacterial taxa.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The study site is located in Neot-Kedumim, a nature reserve and park in Israel located near the city of Modi’in. The site is located at N 34°58′23″ E 46′31°56 at 198 m a.s.l. The basic climate for the study site is characterized by rainy winters (October–April) and long, dry summers (June–August). The plant-growing season commences soon after the first rains, between October and December. The average multiannual rainfall is 350 mm, and the mean multiannual temperature is 20 °C. Vegetation is dominated by shrubs, such as Pistacia lentiscus, Calicotome villosa, Rhamnus lycioides, and Origanum syriacum, and large numbers of herbaceous (mostly annual) plant species. The soil at the study site is terra rosa (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Study site.
2.2. Researched Plants—Ecophysiology and Medicinal Use
Origanum syriacum belongs to the family Lamiaceae. It is an eastern Mediterranean perennial evergreen subshrub, with a well-defined seasonally related phenology [27,28]. The plant has a woody base, is 30–50 cm tall, and has soft-wooly, glandular hairs. O. syriacum possesses antioxidant, antibacterial, fungicidal, and nematocidal activities [28].
Salvia fruticosa is a Mediterranean perennial evergreen shrub from the family Lamiaceae. It is 1–1.5 m tall [27,28] and is used for a variety of medicinal purposes, where the most common use is based on its hypoglycemic effect, probably due to reducing intestinal absorption of glucose [29].
Teucrium capitatum is a subshrub of the Mediterranean phytogeographic region [27] and is used by the local inhabitants for treating gastrointestinal ailments, general pain, wounds, and diabetes. It is known to have antimicrobial properties [30,31,32].
Myrtus communis is a perennial evergreen shrub of Mediterranean origin belonging to the family Myrtacea. It is known to have a variety of medicinal uses, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiproliferative, antigenotoxic, neuroprotective, antimutagenic, antidiabetic, and antiviral effects [33].
Pistacia lentiscus, from the family Anacardiaceae, is a Mediterranean perennial evergreen shrub [27,28]. Its oil is used for human and animal purposes and is intended to help in relieving/facilitating recovery from bronchitis and digestive problems [28].
2.3. Soil Sample Collection
On the 12th of May 2020, toward the end of the spring season, five plants from each of the species O. syriacum, S. fruticosa, T. capitatum, M. communis, and P. lentiscus were randomly marked at the study site, and soil samples (0–10 cm) were collected from the rhizosphere zone beneath three representatives of each species (n = 3) or beneath the plant canopy. Control soil samples (n = 3) were collected (0–10 cm) from the open inter-plant space at a minimal distance of 3 m from the researched plants. The soil samples were placed in individual plastic bags and stored in cool, insulated boxes until their arrival at the laboratory. Bulk soil samples were kept at 4 °C after sieving (2-mm mesh) to remove other organic debris, stones, and root particles, and 1.5 mL of each sieved sample was placed in a sterile plastic vial at −20 °C for DNA extraction.
2.4. Soil Analysis
Soil moisture (%), organic matter, pH, and electrical conductivity (as µS cm−1) were determined as described by Applebaum et al. [24].
2.5. Molecular—Taxonomy Determination
Soil DNA was extracted from 0.5 g of soil using the Exgene soil DNA mini kit from GeneAll (Seoul, Korea), according to the producer’s protocol, using 50 µL of elution buffer in the elution stage and storing the eluted DNA at −20 °C until DNA amplification. The eluted DNA was amplified twice using PCR.
PCR1 was conducted by mixing 12.5 µL PCRBIO HS Taq Mix Red, 9.5 µL ultrapure water, 1 µL of primer CS1_515F (ACACTGACGACATGGTTCTACAGTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGT), 1 µL of primer CS2_806R (TACGGTAGCAGAGACTTGGTCTGGACTACHVGGGTWTCT), and 1 µL of the eluted DNA. The thermal cycling program was 95 °C for 3 min, 24 cycles of 98 °C for 10 s, 55 °C for 10 s, and 72 °C for 20 s, followed by 72 °C for 1 min.
For this, 2 µL sample from PCR1 amplified sample containing CS1/CS2 adaptors was amplified for 10 cycles in 10 µL using Fluidigm Access Array Barcode library according to manufacturer’s protocol (2 µL barcode per reaction). DNA was purified using Kapa Pure Beads at a ratio of 0.65× and quantified with qubit using the Denovix DsDNA high-sensitivity assay. DNA size and integrity were quantified by Tapestation using Agilent DNA screen tape and reagents.
2.6. Data Analysis
All analyses were conducted in the R software environment v4.1.0 (R Core Team, 2016). The alpha and beta diversity analyses, including the PERMANOVA and CoA, were performed using functions available in the R “vegan” v2.5-7 package [34,35].
PICRUSt (phylogenetic investigation of communities by reconstruction of unobserved states [36]). Functional profiling of microbial communities was predicted using the 16S rRNA marker [37], which relies on operational taxonomic units (OTUs) for each sample. The OTU table was converted to biome format using the ‘biome convert’ command to produce a file compatible with the PICRUSt2 program. First, OTUs were phylogenetically placed using the ‘place_seqs.py’ script within PICRUSt2. Then, gene family content was predicted using the hsp.py script. Finally, MetaCyc pathway abundance was predicted using the pathway_pipeline.py script. The scripting functions within PICRUSt2 are dependent on the following tools: EPA-NG and gappa (place_seqs.py), Caster (hsp.py), and MinPath (pathway_pipeline.py) [34,38,39,40]. The output files from the PICRUSt2 analysis were then uploaded to the Statistical Analysis of Metagenomic Profiles (STAMP) [41] software package. This program performs further statistical analyses of all predicted functional datasets and can be used to produce graphical depictions of key functional pathway data.
The raw sequence data were submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive database under accession number PRJNA913697.
A permutational multivariate analysis of the variance of the whole bacterial community was undertaken using distance matrices in Microsoft Excel 2021 Professional. The dependent variable is: Workbook = Bacteria OTU contained 18 rows and 3789 columns R Function [42]. To identify specific OTUs that characterize each of the plant types, we ran an Indicator Species Analysis in R v4.2.2 using the package indic-v1.7.12 species. The indicator groups of each plant were determined by a multilevel pattern analysis using the ‘multipatt’ function. Results with a significance level (alpha) of p < 0.05 between plant taxa were considered.
3. Results
Abiotic Variables
The mean values of different soil physical parameters of the five plants and the inter-shrub open sites (control) are presented in Table 1, as described by Applebaum et al. [24]. Applebaum et al. [24] have shown variability in soil moisture (SM) that ranged from 7.83% in the control to 21.73% in the M. communis soil samples, values that were significantly (p < 0.05) different. Moreover, the SM in the vicinity of the M. communis and P. lentiscus rhizospheres was significantly higher relative to the control and the T. capitatum soil samples. No significant differences in organic matter (OM%) were found between the soil samples collected beneath the plants and the control, although the values ranged between 6.37% in the control and 16.57% in the rhizosphere of P. lentiscus. The pH values showed higher alkaline levels, ranging from 7.8 in the samples collected under P. lentiscus to 8.10 in the samples collected under O. syriacum.

Table 1.
Mean values (±SD) of soil abiotic parameters in the rhizosphere of different plants. Different letters denote significantly different (p < 0.05) values [24]. SM—soil moisture; OM—organic matter; EC—electric conductivity as µS·cm−1.
Electric conductivity (EC) in the soil collected from the rhizosphere of T. capitatum was 78.57 µS·cm−1, and in the control soil, it was 86.30 µS·cm−1. The values of the other samples ranged between these two values.
4. Taxonomic Analysis
4.1. Phyla
Ten phyla were identified, as well as one unidentified phylum (Table 2), where an increase in relative cumulative abundance from Other (Unknown) phyla toward the Actinobacteria phylum was obtained. The figures display a relatively similar increase in the rhizosphere of each plant species, whereas the data obtained in Table 2 demonstrate the presence of each phylum relative to its presence in the control samples. The higher number of phyla in the plant rhizosphere with a positive ratio relative to the control phyla samples was obtained in the rhizosphere of T. capitatum, followed by O. syriacum, S. frutcosa, P. lentis, and M. communis.

Table 2.
Mean values (±SD) of soil bacterial phyla level taxa relative abundance of the five medicinal plants and control sample, followed by the H’ (Shannon Index) determined for each of the plants.
The phylum Actinobacteria was co-eudominant relative to the control researched soils, whereas the Chloroflexi and Bacteroidetes phyla were eudominant in the rhizospheres of O. syriacum, S. fruticosa, and T. capitatum and dominant in the rhizospheres of S. fruticose, T. capitatum, and P. lentiscu. The Acidobacteria, Planctomycetes, and Cyanobacteria phyla were the only phyla present in the rhizosphere of T. capitatum.
Only the phylum Chloroflexi significantly differed in relative abundance between samples, revealing a small impact of the plants on the bacterial community composition at the phyla level. Shannon index (H’) was significantly lower in the M. communis sample compared to the control, S. fruticosa, and T. capitatum samples.
4.2. Order
A total of 21 orders were identified, including an Other (unknown) order in which the order Actinomycetales was eudominant in the rhizopheres of M. communis and P. lentiscus, followed by a dominant order in all other rhizospheres, including the control soil (Table 3). Orders Solirubrobacterales, Acidimicrobiales, and Rhizobiales were dominant in all researched soils. Order Pseudomonadales was dominant in the rhizospheres of M. communis, O. syriacum, P. lentiscus, and S. fruticosa, while order RB41 was dominant in the control soil and the rhizosphere of T. capitatum. Order JG30-KF-CM45 was dominant in the rhizosphere of O. syriacum, while order Burkholderiales was dominant in the control soil.

Table 3.
Mean (±SD) (n = 3) values of order taxa of bacterial phyla relative abundance in the rhizosphere of the different plants and control, including the H’ (Shannon Index) determined for each of the plants.
Only the Myxococcales and WD2101 orders differed significantly in relative abundance between samples, and the Shannon index (H’) score did not significantly differ between samples either, indicating a low variation on the order taxonomic level.
4.3. Genus
We found 409 genera, of which 214 were identified and 195 were unknown, with 60 bacterial genera with above 10% OTUs of the total OTUs. The dominant bacterial genera in all samples were Acinetobacter, Kaistobacter, Janthinobacterium, Balneimonas, Mycobacterium, Rhodoplanes, Rubrobacter, Streptomyces, Candidatus, Bacillus, and Agromyces, without any significant differences observed.
4.4. Potential Bacterial Functions Captured by 16S rDNA
The taxonomic composition and functionality of the bacterial community in the soil samples collected in the rhizospheres of the five medicinal plants and control samples were determined using functional profiling. We obtained a group of 14 functions that contained 215 categories (Figure 2). Each function contained a different number of functions, and the metabolism function was compiled into 80 categories, of which only 10 represented 83% of the total functions above 1%. Membrane transport function was found to be represented by 7 out of a total of 13 categories, representing 98%. Replication and repair functions reached 100% and included all categories. The translation and transcription functions reached 99.5% by two functions. Signaling included 11 categories, whereas 99.5% of the function was fulfilled by only 6 categories. For enzyme families, six functions were active and fulfilled 100%. Folding, sorting, and degradation comprised 29 categories, of which 20 fulfilled 93.2% of the functions. Biosynthesis comprised 41 categories; 22 categories with 1% and above reached 93.21%, while 39 were represented by less than 1% presence. Moreover, 58.1% of the cellular processes were determined by the two-component system out of nine categories. In the cell motility categories, only one of the four bacterial motility proteins fulfilled 53.2% of the total OTUs. The unknown function, with two categories, determined 70.5% of the function. Secondary metabolism and cellular structure categories contributed less than 1% each.
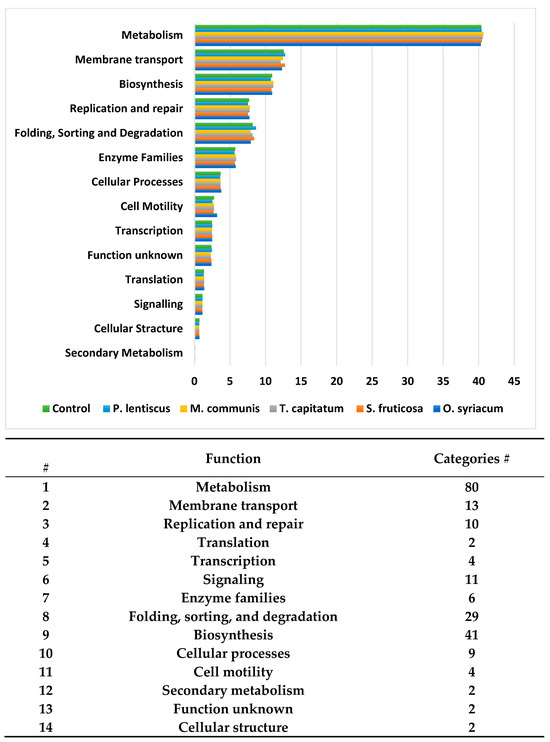
Figure 2.
Potential bacterial functions captured by 16S rDNA profiling of the bacterial community in the soil samples collected in the rhizosphere of the five medicinal plants and control samples by division into different bacterial functions.
By using the permutational multivariate analysis of variance using distance Mat-dependent variables (Table 4), we obtained a significance of p < 0.010, elucidating the existence of significant differences between the six sampling locations. Using RDA to elucidate the differences between the community compositions of the different samples (Figure 3), we found that M. communis and O. syriacum differed the most from the control sample.

Table 4.
Permutational multivariate analysis of variance using distance Mat-dependent variables (ANOVA).
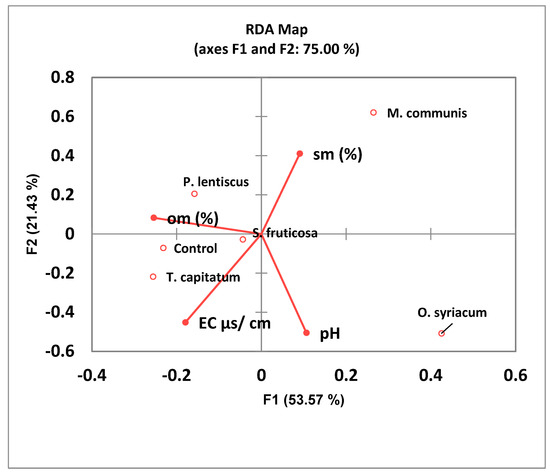
Figure 3.
The effect of the different plants and abiotic variables (sm—soil moisture; EC—electric conductivity) in relation to the bacterial community in the rhizosphere of the five plants and the control elucidated by the redundancy analysis (RDA) biplot of the plant habitats.
In order to identify OTUs that characterize each plant type, we ran an Indicator Species Analysis with a significance level (alpha) of p < 0.05 (Table 5). A total of 19 taxa were found to elucidate the difference between the 6 sampling locations, of which the control samples contained 10 taxa, representing 52% of the entire taxa found. M. communis was represented by seven taxa (40% of the total), where no shared taxa were found with the control. P. lentiscus contained 40% of the total taxa and shared five taxa with the control and one with M. communis. T. capitatum was represented by one unique taxon, while the other taxa (32% of its total) were shared with the control, M. communis, and P. capitatum. O. syriacum was represented by four taxa without sharing any taxa with the control samples. S. fruticosa was represented by only 2 unique taxa of the total 19 (11%), sharing these unique taxa with three plant representatives (M. communis, P. lentiscus, and O. syriacum). As can be seen from the data, there are great differences between representatives of the soil bacterial community taxa composition.

Table 5.
Significance values (p < 0.05) of species indicator analysis based on OTU values along the bacteria taxa for the soil collected under the five plant and control samples. Co. = control soil, M. = M. communis, P. = P. lentiscus, T. = T. capitatum, O. = O. syriacum, S. = S. fruticose.
5. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that the soil rhizosphere of each medicinal plant species will be represented by bacterial taxa with significantly different relative abundances and that the influence of the rhizosphere will alter the bacterial abundance and functionality. Our results indicate that while there are differences between the different rhizospheres’ bacterial community composition, these differences are at the OTU level and not at the higher taxa level, such as order or phyla. Additionally, based on our functional results, there did not seem to be a large difference in the functional profiles of the different rhizospheres.
The contribution of perennial plant soil to the belowground biota is largely based on interactions between the two, which are mainly based on rhizosphere processes. Microbial communities are known to be highly dependent on plants for carbon and play a major role in substrate supply [4]. Microbial activity and interaction with other microbial communities and additional organisms, as well as with soil particles, depend on the microhabitat, which may differ from microhabitats created by different nearby plants [43].
A study on the rhizobacteria of eleven medicinal plants [26] showed that the density of total microbial counts (cfu/g dry soil) beneath O. syracum was among the lowest. However, the relative abundance of the Solirubrobacterales order in the soil samples beneath O. syracum was high compared to other plant species.
The antibacterial potential of Salvia species was evaluated against different Staphylococcus bacterial strains and showed significant health effects on humans. However, the plant was also found to have a strong anti-inflammatory effect and to be cytotoxic to tumor cells [44]. The elevated presence of Chloroflexi in three plant rhizospheres, except for M. communis and P. lentiscus, shows that both bacterial phyla also play an important role in biochemical cycling and soil development in contaminated soils [45].
This evaluation helps determine the potential of these plants as sources of crude natural antimicrobial compounds. The similarity in bacterial community functions, regardless of the medicinal plant cover, elucidates the closeness between 14 functions necessary to fulfill their role and their function without being able to differentiate between the bacterial taxa-phyla and functional diversity [46,47], similar to the findings reported by Steinberger et al. [48].
In order to gain further insight into the differences between the sampling sites, a multilevel pattern (MP) analysis was performed. This analysis enables us to gain a better understanding of the microbial structure and functions of the community between the different sampling sites. Use of the above method, in which the metabolic pathways and their functionality provide a better understanding, helps differentiate between the effects of different medicinal plants on their rhizosphere.
6. Conclusions
The current study represents an initial and foundational stage. Further research is warranted to enhance our comprehension of the seasonal impact on medicinal plants, as this factor can significantly influence the composition, density, and diversity of microbial communities within the rhizosphere. It can be inferred that the ecophysiological adaptation of indigenous medicinal plants and its influence on soil biota communities hold promise as an eco-friendly approach, pending additional investigation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S.; Methodology, C.S. and M.J.; Software, T.D.; Validation, Y.S., C.S. and I.A.; Investigation, M.J. and I.A.; Data curation, Y.S., T.D., M.J. and I.A.; Writing—original draft, I.A.; Writing—review & editing, Y.S. and I.A.; Project administration, Y.S. and C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available by request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Philippot, L.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Lemanceau, P.; Van Der Putten, W.H. Going Back to the Roots: The Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortal, S.; Bastida, F.; Moreno, J.L.; Armas, C.; García, C.; Pugnaire, F.I. Benefactor and Allelopathic Shrub Species Have Different Effects on the Soil Microbial Community along an Environmental Severity Gradient. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Cross-Kingdom Similarities in Microbiome Functions. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1905–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckling, C.D.; Broz, A.K.; Bergelson, J.; Manter, D.K.; Vivanco, J.M. Root Exudates Regulate Soil Fungal Community Composition and Diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.; Maymon, M.; Agapakis, C.M.; Lee, A.; Wang, A.; Prigge, B.A.; Volkogon, M.; Hirsch, A.M. A Survey of the Microbial Community in the Rhizosphere of Two Dominant Shrubs of the Negev Desert Highlands, Zygophyllum dumosum (Zygophyllaceae) and Atriplex halimus (Amaranthaceae), Using Cultivation-Dependent and Cultivation-Independent Methods. Am. J. Bot. 2013, 100, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veen, G.F.; Fry, E.L.; ten Hooven, F.C.; Kardol, P.; Morriën, E.; De Long, J.R. The Role of Plant Litter in Driving Plant-Soil Feedbacks. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.; Singh, B.K. Plant–Microbiome Interactions: From Community Assembly to Plant Health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S.V.; Machado, M.A.; et al. Top 10 Plant Pathogenic Bacteria in Molecular Plant Pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expósito, R.G.; de Bruijn, I.; Postma, J.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Current Insights into the Role of Rhizosphere Bacteria in Disease Suppressive Soils. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.E.; Barea, J.M.; McNeill, A.M.; Prigent-Combaret, C. Acquisition of Phosphorus and Nitrogen in the Rhizosphere and Plant Growth Promotion by Microorganisms. Plant Soil. 2009, 321, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Xie, X.; Kim, M.S.; Dowd, S.E.; Paré, P.W. A Soil Bacterium Regulates Plant Acquisition of Iron via Deficiency-Inducible Mechanisms. Plant J. 2009, 58, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Palumbo, G.; He, J.Z.; Pinton, R.; Cesco, S. Review on Iron Availability in Soil: Interaction of Fe Minerals, Plants, and Microbes. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayak, S.; Tirosh, T.; Glick, B.R. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria That Confer Resistance to Water Stress in Tomatoes and Peppers. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, V. Soil Invertebrates—Effects on Nutrient Turnover and Soil Structure—A Review. Z. Für Pflanzenernährung Und Bodenkd. 1991, 154, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudoin, E.; Benizri, E.; Guckert, A. Impact of Growth Stage on the Bacterial Community Structure along Maize Roots, as Determined by Metabolic and Genetic Fingerprinting. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 19, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovska, B.B. Historical Review of Medicinal Plants’ Usage. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2012, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smet, P.A.G.M. The Role of Plant-Derived Drugs and Herbal. Medicines in Healthcare. Drugs 1997, 54, 801–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, V.; Tripathi, A.K.; Khanuja, S.P.S.; Kumar, S. Anti-Insect Screening of Medicinal Plants from Kukrail Forest, Lucknow, India. Pharm. Biol. 2003, 41, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilova, L.; Ridl, J.; Polivkova, M.; Macek, T.; Uhlik, O. Effects of Secondary Plant Metabolites on Microbial Populations: Changes in Community Structure and Metabolic Activity in Contaminated Environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohrmann, A.B.; Küting, M.; Jünemann, S.; Jaenicke, S.; Schlüter, A.; Tebbe, C.C. Importance of Rare Taxa for Bacterial Diversity in the Rhizosphere of Bt-and Conventional Maize Varieties. ISME J. 2013, 7, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalenberger, A.; Tebbe, C.C. Bacterial Community Composition in the Rhizosphere of a Transgenic, Herbicide-Resistant Maize (Zea Mays) and Comparison to Its Non-Transgenic Cultivar Bosphore. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 40, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Levi, M.; Applebaum, I.; Sherman, C.; Doniger, T.; Steinberger, Y. Soil Fungal Community of Wheat Triticum Aestivum Rhizosphere at Different Phenological Stages under a Rain-Fed Management. Rhizosphere 2022, 24, 100605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebaum, I.; Jeyaraman, M.; Sherman, C.; Doniger, T.; Steinberger, Y. Structure and Function of the Soil Rhizosphere Fungal Communities in Medicinal Plants—A Preliminary Study. Agriculture 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowafy, A.M.; Alraey, D.A.; Omar, M.N.; Elshobaky, A.; Haroun, S.A. Origanum Syriacum Ssp. Sinaicum Associated Growth Promoting Bacteria. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2016, 10, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.A.; Hassan, E.A.; Tobgy, K.M.K.E.; Ramadan, E.M. Evaluation of Rhizobacteria of Some Medicinal Plants for Plant Growth Promotion and Biological Control. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2014, 59, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinbrun-dothan, N.; Danin, A.; Plitmann, U. Analytical Flora of Eretz-Israel; Cana Publishing House: Toronto, ON, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv, Z.; Dudai, N. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of the World Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of the Middle-East; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Perfumia, M.; Arnoldb, N.; Tacconid, R. Hypoglycemic Activity of Salvia fruticosa Mill. from Cyprus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1991, 34, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawash, O.; Shudiefat, M.; Al-Tabini, R.; Al-Khalidi, K. Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Commonly Used by Local Bedouins in the Badia Region of Jordan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccioni, A.; Falconieri, D.; Porcedda, S.; Piras, A.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Alves-Silva, J.M.; Salgueiro, L.; Maxia, A. Antifungal Activity and Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil from the Aerial Parts of Two New Teucrium capitatum L. Chemotypes from Sardinia Island, Italy. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 6007–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabane, S.; Boudjelal, A.; Napoli, E.; Benkhaled, A.; Ruberto, G. Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant and Wound Healing Activities of Teucrium polium Subsp. Capitatum (L.) Briq. Essential Oil. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2021, 33, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, G.; Dashti, S.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Review of Pharmacological Effects of Myrtus communis L. and Its Active Constituents. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Doebeli, M. Efficient Comparative Phylogenetics on Large Trees. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/vegandevs/vegan/ (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2: An Improved and Customizable Approach for Metagenome Inference. BioRxiv 2019, 672295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive Functional Profiling of Microbial Communities Using 16S RRNA Marker Gene Sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, L.; Barbera, P.; Stamatakis, A. Supplementary Text: Software Comparison Genesis and Gappa: Processing, Analyzing and Visualizing Phylogenetic (Placement) Data. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3263–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbera, P.; Kozlov, A.M.; Czech, L.; Morel, B.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. EPA-Ng: Massively Parallel Evolutionary Placement of Genetic Sequences. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Doak, T.G. A Parsimony Approach to Biological Pathway Reconstruction/Inference for Genomes and Metagenomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical Analysis of Taxonomic and Functional Profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Package “vegan3d” Title Static and Dynamic 3D. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Buscot, F.; Varma, A. Microorganisms in Soils: Roles in Genesis and Functions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; ISBN 3540222200. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, A.F.; Pereira, O.R.; Fernandes, Â.S.F.; Calhelha, R.C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Cardoso, S.M. The Health-Benefits and Phytochemical Profile of Salvia apiana and Salvia farinacea var. Victoria Blue Decoctions. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, L.; Lanzén, A.; Blanco, F.; Urich, T.; Garbisu, C. Adaptation of Soil Microbial Community Structure and Function to Chronic Metal Contamination at an Abandoned Pb-Zn Mine. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedje, J.M.; Cho, J.C.; Murray, A.; Treves, D.; Xia, B.; Zhou, J. Soil teeming with life new frontiers for soil science. In Sustainable Management of Soil Organic Matter; CABi: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. 393–425. [Google Scholar]
- Torsvik, V.; Øvreås, L. Microbial diversity and function in soil: From genes to ecosystems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberger, Y.; Doniger, T.; Sherman, C.; Applebaum, I.; Eshel, G. Effect of Soil Aggregate Size on Vineyard Bacterial Communities under Organic and Conventional Agro-Managements. Land 2022, 11, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).