Nano-Selenium Reduces Concentrations of Fecal Minerals by Altering Bacteria Composition in Feedlot Goats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Goats, Diets, and Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Procedures and Collection of Samples
2.3. Sample Analyses
2.4. Measurement of Fecal Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs)
2.5. DNA Extraction of Feces, 16S rRNA Gene Amplification, and Sequencing
2.6. Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dry Matter Intake, Average Daily Gain, and Rectal Temperature
3.2. Concentrations of Minerals in Rumen Fluid, Serum, and Feces
3.3. Concentrations of Fecal Volatile Fatty Acids
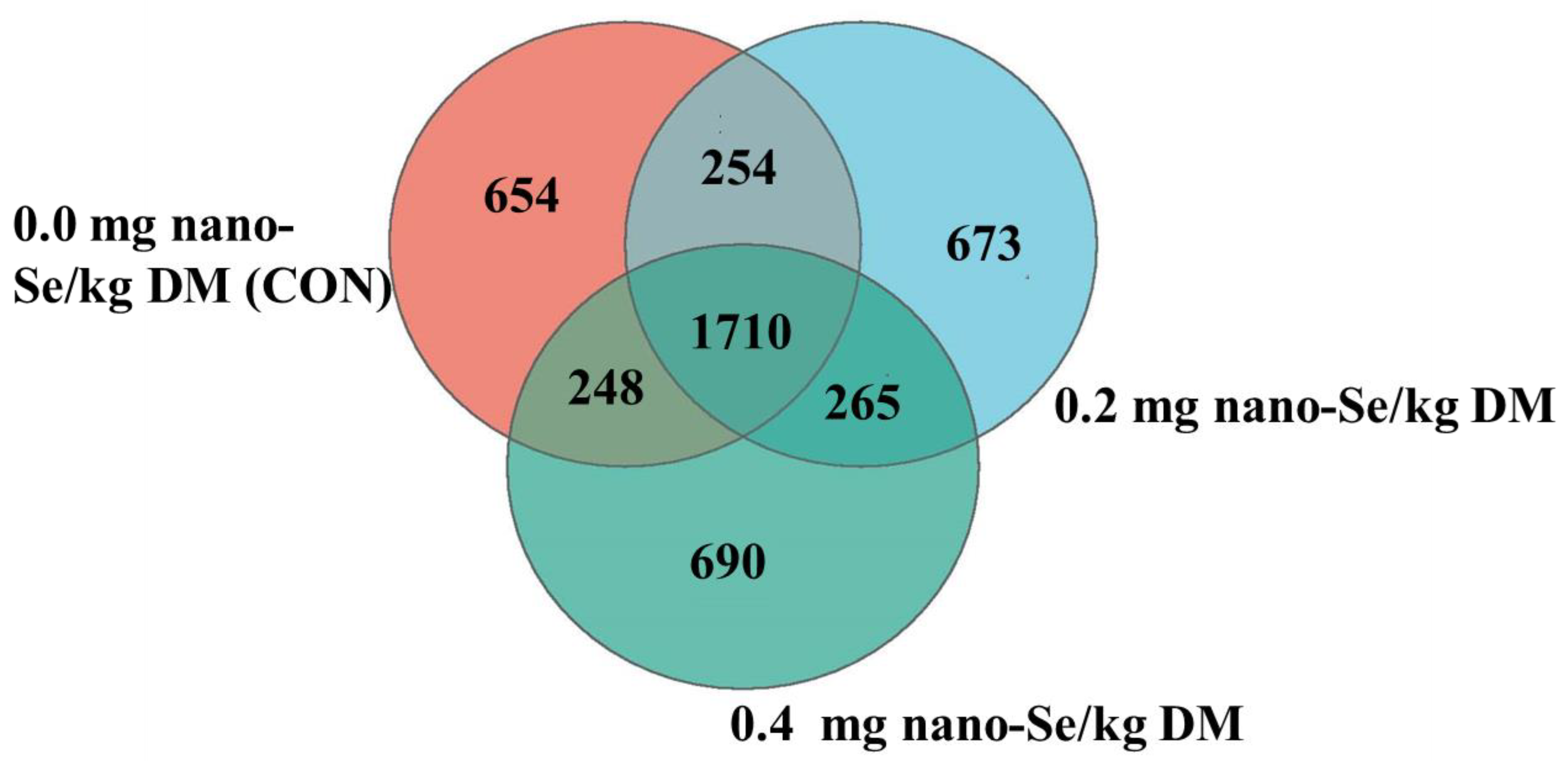
3.4. Summary of Collective Sequencing Data
3.5. Microbial Community Composition in Feces of Hainan Black Goats
3.6. Correlations Between Fecal Bacteria Abundances and Fecal Mineral Concentrations or Volatile Fatty Acids
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Dietary Nano-Selenium Levels on Dry Matter Intake, Average Daily Gain, and Rectal Temperature
4.2. Effect of Dietary Nano-Selenium Levels on Concentrations of Minerals in Rumen Fluid, Serum, and Feces
4.3. Effect of Dietary Nano-Selenium Levels on Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) Concentrations
4.4. Effect of Dietary Nano-Selenium Levels on Fecal Microbial Composition in the Feces
4.5. Effect of Dietary Nano-Selenium Levels on Correlations Between Fecal Bacteria and Concentrations of Fecal Minerals and Short-Chain Fatty Acids
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, X.; Ding, L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Degen, A.; Long, R. The adaptive strategies of yaks to live in the Asian highlands. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yu, Q.; Fang, C.; Chen, S.; Tang, X.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Fang, R.J. Effect of selenium source and level on performance, egg quality, egg selenium content, and serum biochemical parameters in laying hens. Foods 2020, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, R.R.; Cifelli, A.M.; Kostas, G.; Kim, I.Y. Optimizing Protein Intake in Adults: Interpretation and Application of the Recommended Dietary Allowance Compared with the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, R.A.; Belcher, S.E.; Hermanson, L.; Klein, T.A.; Lowe, J.A.; Jones, C.D.; Morice, C.P.; Rayner, N.A.; Scaife, A.A.; Stott, P.A. Approaching 1.5 °C: How will we know we’ve reached this crucial warming mark? Nature 2023, 624, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Zhong, J.; Hu, X. Impacts of climate change-induced heat stress on pig productivity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Javid, A.; Tian, G.; Zhang, K.; Bai, S.; Ding, X.; Wang, J.P.; Lv, L.; Xuan, Y.; Li, S.S.; et al. Metabolomics analysis to interpret changes in physiological and metabolic responses to chronic heat stress in Pekin ducks. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.F.; Zhou, L.L.; Zhou, H.L.; Hou, G.Y.; Li, M. Effects of nutrition level of concentrate-based diets on growth performance and carcass characteristics of Hainan black goats. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2014, 46, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.X.; Shi, L.G.; Hou, G.Y.; Zhou, H.L.; Xun, W.J. Genetic diversity and selection signatures in Hainan black goats revealed by whole-genome sequencing data. Animal 2024, 18, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.G.; Xun, W.J.; Yue, W.B.; Zhang, C.X.; Ren, Y.S.; Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, R.J.; Lei, F.L. Effect of sodium selenite, Se-yeast and nano-elemental selenium on growth performance, Se concentration and antioxidant status in growing male goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 96, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Yin, Y. Selenium in modern agriculture. Mod. Agric. 2023, 1, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xie, T.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, H. Effects of selenium as a dietary source on performance, inflammation, cell damage, and reproduction of livestock induced by heat stress: A review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, e820853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, M.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, C.J.; Zuo, G.; Yang, J.C.; Lei, X.G.; et al. Optimum doses and forms of selenium maintaining reproductive health via regulating homeostasis of gut microbiota and Testicular redox, inflammation, cell proliferation, and apoptosis in Roosters. J. Nutr. 2023, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.B.; Jin, X.W.; Song, W.X.; Zhang, R.; Tong, M.J.; Qi, Z.; Mi, L. Dietary selenium levels affect mineral absorbability, rumen fermentation, microbial composition and metabolites of the grazing sheep. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2024, 308, 115877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.B.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.K.; Li, X.L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, L.M.; Li, W.X.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Sheep fecal transplantation affects growth performance in mouse models by altering gut microbiota. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Z.L. Effect of different seasons (spring vs summer) on the microbiota diversity in the feces of dairy cows. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Pei, C.; Degen, A.; Hao, L.; Cao, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.W.; Long, R.J. A comparison between yaks and Qaidam cattle in in vitro rumen fermentation, methane emission, and bacterial community composition with poor quality substrate. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2022, 291, 115395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ran, T.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Wu, X.; Degen, A.; Long, R.J.; Shi, Z.J.; Zhou, J.W. Comparison of rumen bacterial communities between yaks (Bos grunniens) and Qaidam cattle (Bos taurus) fed a low protein diet with different energy levels. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 982338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, T.; Jiao, P.; Alzahal, O.; Xie, X.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Niu, D.; Yang, W. Fecal bacterial community of finishing beef steers fed ruminally protected and non-protected active dried yeast. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Feng, T.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.P.; Xuan, Z.Y.; et al. The multi-kingdom microbiome of the goat gastrointestinal tract. Microbiome 2023, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Peng, W.; Mao, K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, K.; Zeng, M.; Han, X.T.; Han, J.C.; Zhou, H.L. The changes in fecal bacterial communities in goats offered rumen-protected fat. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. China National Feeding Standard of Meat-Producing Sheep and Goats (NY/T 816-2021); China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese)
- Srivastava, A.; Yadav, P.; Mahajan, A.; Anand, M.; Yadav, S.; Madan, A.K.; Yadav, B. Appropriate THI model and its threshold for goats in semi-arid regions of India. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 96, 102845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, P.; Nelson, G.; Mayberry, D.; Herrero, M. Increases in extreme heat stress in domesticated livestock species during the twenty-first century. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 5762–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, J.M.; Kieran, T.J.; Seidel, D.S.; Glenn, T.C.; Da Silveira, M.F.; Callaway, T.R.; Stewart, R.L. Jr Comparison of the ruminal and fecal microbiotas in beef calves supplemented or not with concentrate. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Officiating Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Van-Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.B.; Van Soest, P.J. The detergent system of analysis and its application to human foods. In The Analysis of Dietary Fiber in Food; James, W.P., Theander, O., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 23–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Hu, S.; Mu, R.; Qing, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhou, L.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Fang, R. Effects of different patterns and sources of trace elements on laying performance, tissue mineral deposition, and fecal excretion in laying hens. Animals 2021, 11, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wong, Y. Generation of selenium-enriched rice with enhanced grain yield, selenium content and bioavailability through fertilisation with selenite. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, L.S.; Cao, Z.J. Heat stress on calves and heifers: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechno. 2020, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Fang, C.; Mu, R.; Zhuo, R.; Xiao, Y.; Qing, Y.; Tang, J.X.; Fang, R.J. Potential Mechanism and effects of different selenium sources and different effective microorganism supplementation levels on growth performance, meat quality, and muscle fiber characteristics of three-yellow chickens. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, e869540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortizmorales, O.; Efrenramirezbribiesca, J.; Hernandezbautista, J.; Hernandezsanchez, D.; Ricardobarcenagama, J.; Hernandeztrujillo, E.; Hernández-Trujillo, E.; Díaz-Sánchez, V.M.; Garrido-Fariña, G.; López-Ojeda, J.C.; et al. Effect of supranutritional dosage selenium in neonatal goat kids on productive performance, physicochemical profiles in meat, selenium levels in tissues, and histopathological findings. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 4374–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, A.J.F. Energy metabolism and requirements. In Digestive Physiology and Nutrition of Ruminants, 2nd ed.; Church, D.C., Ed.; O & B Books Inc.: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1979; pp. 210–229. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, F.N.; Ojea, L.T.; Sariol, R.O.G.; Serrano, A.F.; Serrano, J.O.; Grizelj, J. Indicators of the gas-energy fasting metabolism in Pelibuey sheep in Cuba. Pastos Forrajes 2022, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, R.; Arya, A.; Kumar, D.; Goel, A.; Rout, P.K. Genetic studies of heat stress regulation in goat during hot climatic condition. J. Therm. Biol. 2023, 113, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daramola, J.O.; Abioja, M.O.; Iyasere, O.S.; Oke, O.E.; Majekodunmi, B.C.; Logunleko, M.O.; Adekunle, E.O.; Nwosu, E.U.; Smith, O.F.; James, I.J.; et al. The resilience of Dwarf goats to environmental stress: A review. Small Rumin. Res. 2021, 205, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.J.; Shi, L.G.; Cao, T.; Zhao, C.P.; Yu, P.; Wang, D.F.; Hou, G.Y.; Zhou, H.L. Dual functions in response to heat stress and spermatogenesis: Characterization of expression profile of small heat shock proteins 9 and 10 in goat testis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 686239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, N.S.; Hashem, N.M.; Morsy, A.S.; Abo-Elezz, Z.R. Effects of organic selenium on the physiological response, blood metabolites, redox status, semen quality, and fertility of rabbit bucks kept under natural heat stress conditions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L. Ruminant Nutrition; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, R.; Ai, C.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, X. Effect of selenite on organic selenium speciation and selenium bioaccessibility in rice grains of two Se-enriched rice cultivars. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J. Selection of copper and zinc dosages in pig diets based on the mutual benefit of animal growth and environmental protection. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, K.; Tang, X.; Chen, S.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Degen, A.; Fang, R. Effect of the level and source of supplementary dietary zinc on egg production, quality, and zinc content and on serum antioxidant parameters and zinc concentration in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6233–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Meng, L.; Zhang, R.; Tong, M.; Qi, Z.; Mi, L. Effects of essential mineral elements deficiency and supplementation on serum mineral elements concentration and biochemical parameters in grazing Mongolian sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1214346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, J.; Mushi, D.E.; Kifaro, G.C.; Mtenga, L.A.; Eik, L.O. Seasonal variation in chemical composition of native forages, grazing behaviour and some blood metabolites of Small East African goats in a semi-arid area of Tanzania. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2011, 164, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Khan, A.; Badshah, M.; Degen, A.; Yang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.W.; Long, R.J. Yak rumen fluid inoculum increases biogas production from sheep manure substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Takaoka, M.; Pan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, A.; Li, X.; Yan, J. PCDD/Fs and heavy metals in the vicinity of landfill used for MSWI fly ash disposal: Pollutant distribution and environmental impact assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzeh, N.S.; Popoola, P.A.; Adeleke, A.; Adeosun, S. Physical concentration of heavy minerals: A brief review on low and high intensity magnetic separation process techniques. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2024, 76, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosnedlova, B.; Kepinska, M.; Skalickova, S.; Fernandez, C.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Malevu, T.D.; Sochor, J.; Baron, M.; Melcova, M.; Zidkova, J.; et al. A Summary of new findings on the biological effects of selenium in selected animal species—A critical review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Acosta, S.; Selma-Royo, M.; Collado, M.C.; Navarro-Roldán, F.; Abril, N.; García-Barrera, T. Selenium supplementation influences mice testicular selenoproteins driven by gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadoo, S.; Dinev, I.; Chapman, J.; Hughes, R.J.; van Hao, T.T.; Moore, R.J.; Stanley, D. Selenium nanoparticles in poultry feed modify gut microbiota and increase abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.L.; Gao, S.T.; Wang, K.; Xu, J.C.; Sanz-Fernandez, M.V.; Baumgard, L.H.; Bu, D.P. Effects of source on bioavailability of selenium, antioxidant status, and performance in lactating dairy cows during oxidative stress-inducing conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, H. Rumen and fecal microbiota profiles associated with immunity of young and adult goats. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 978402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Shahzad, K.; Han, M.; Guo, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; et al. Seasonal differences in fecal microbial community structure and metabolism of house-feeding Chinese merino fine-wool sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, e875729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransom-Jones, E.; Jones, D.L.; Mccarthy, A.J.; Mcdonald, J.E. The fibrobacteres: An important phylum of cellulose-degrading bacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Li, Y.X.; Tang, Z.R.; Sun, W.Z.; Wu, L.T.; An, R.; Chen, H.Y.; Wan, K.; Sun, Z.H. Reducing protein content in the diet of growing goats: Implications for nitrogen balance, intestinal nutrient digestion and absorption, and rumen microbiota. Animal 2020, 14, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.P. Distinct stage changes in early-life colonization and acquisition of the gut microbiota and its correlations with volatile fatty acids in goat kids. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 584742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahayri, T.M.; Fliegerova, K.O.; Mattiello, S.; Celozzi, S.; Mrazek, J.; Mekadim, C.; Sechovcová, H.; Kvasnová, S.; Atallah, E.; Moniello, G. Host species affects bacterial evenness, but not diversity: Comparison of fecal bacteria of cows and goats offered the same diet. Animals 2022, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.T.; Howell, K.; Suleria, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, S.; Ng, K. Flavones interact with fiber to affect fecal bacterial communities in vitro. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Ma, L.; Gao, S.; Bu, D.; Yu, Z. Heat stress impacts the multi-domain ruminal microbiota and some of the functional features independent of its effect on feed intake in lactating dairy cows. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, S.; Liu, S.J.; Duan, L.P. Beneficial effect of butyrate-producing Lachnospiraceae on stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liang, N.; Zhang, X.; Han, C.; Nan, X. Functional differentiation related to decomposing complex carbohydrates of intestinal microbes between two wild zokor species based on 16S rRNA sequences. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Sun, P. Effects of different selenium supplements on rumen fermentation and apparent nutrient and selenium digestibility of mid-lactation dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3131–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, M.; Böck, A.; Wyss, C. Selenium-dependent growth of Treponema denticola: Evidence for a clostridial-type glycine reductase. Arch. Microbiol. 2001, 177, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lordan, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Gut microbes from the phylogenetically diverse genus Eubacterium and their various contributions to gut health. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1802866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Mao, C.Q.; Ji, D.; Su, L.L.; Gao, B.; et al. Effects of wine processed Polygonatum polysaccharides on immunomodulatory effects and intestinal microecology in mice. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crop. 2023, 15, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Sun, X.; He, Q.; Luo, J.Y.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Effects of fermented herbal tea residues on the intestinal microbiota characteristics of holstein heifers under heat stress. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, e01014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shah, A.M.; Wang, L.; Jin, L.; Wang, Z.; Xue, B.; Peng, Q.H. Relationship between the true digestibility of dietary calcium and gastrointestinal microorganisms in goats. Animals 2020, 10, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shah, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, Z.; Xue, B.; Peng, Q.H. Relationship between true digestibility of dietary phosphorus and gastrointestinal bacteria of goats. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabee, A.E.; Khalil, M.M.; Khadiga, G.A.; Elmahdy, A.; Sabra, E.A.; Zommara, M.A.; Khattab, I.M. Response of rumen fermentation and microbiota to dietary supplementation of sodium selenite and bio-nanostructured selenium in lactating Barki sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items | Content |
|---|---|
| Ingredients, g/kg of DM | |
| Corn stalk | 500 |
| Corn grain, ground | 150 |
| Wheat bran | 50.0 |
| Soybean meal | 130 |
| DDGS | 41.5 |
| Barley grain | 80.0 |
| NaHCO3 | 10.0 |
| Limestone | 12.0 |
| CaHPO4 | 9.50 |
| NaCl | 5.00 |
| Urea | 2.00 |
| Premix 1 | 10.0 |
| Chemical composition | |
| Dry matter, g/kg | 920 |
| Crude protein, g/kg | 140 |
| Neutral detergent fiber, g/kg | 398 |
| Acid detergent fiber, g/kg | 202 |
| Ether extract, g/kg | 50.0 |
| Calcium, g/kg | 7.58 |
| Phosphorus, g/kg | 3.19 |
| Selenium, mg/kg | 0.37 |
| Zinc, mg/kg | 109 |
| Copper, mg/kg | 37.9 |
| Manganese, mg/kg | 349 |
| Iron, g/kg | 4.71 |
| ME, MJ/kg | 7.60 |
| Time | 08:00 | 10:00 | 12:00 | 14:00 | 16:00 | 18:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average THI | 70.22 | 71.74 | 72.60 | 72.70 | 72.11 | 71.28 |
| Items | Nano-Se, mg/kg DMI | SEM | p-Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | Nano-Se | L | ||
| Initial body weight, kg | 18.6 | 18.4 | 18.7 | 0.69 | 0.973 | 0.881 |
| Final body weight, kg | 22.3 a | 23.1 a,b | 24.3 b | 0.75 | 0.025 | 0.012 |
| Dry matter intake, kg/d | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 0.113 | 0.865 | 0.954 |
| Average daily gain, g/d | 88.1 a | 113 b | 132 c | 7.39 | 0.013 | <0.01 |
| DMI: ADG | 11.4 c | 9.26 b | 7.54 a | 0.752 | 0.012 | <0.01 |
| Rectal temperatures, °C | 39.0 | 39.1 | 38.9 | 0.011 | 0.444 | 0.464 |
| Items | Nano-Se, mg/kg | SEM | p-Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | Nano-Se | L | |||
| Rumen fluid | P, g/L | 1.80 | 1.94 | 1.75 | 0.122 | 0.462 | 0.830 |
| Se, μg/L | 9.31 a | 17.9 b | 41.6 c | 0.31 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Ca, mg/L | 1418 b | 1241 a | 1295 a | 33.9 | 0.012 | 0.028 | |
| Cu, mg/L | 2.74 a | 2.75 a | 3.39 b | 0.123 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Zn, mg/L | 11.6 | 11.7 | 11.4 | 0.51 | 0.918 | 0.766 | |
| Mn, mg/L | 24.0 | 22.4 | 22.8 | 0.72 | 0.314 | 0.252 | |
| Fe, mg/L | 256 | 233 | 244 | 11.5 | 0.398 | 0.469 | |
| Serum | P, mg/L | 125 | 118 | 126 | 3.6 | 0.284 | 0.840 |
| Se, μg/L | 69.6 a | 76.6 b | 77.7 b | 2.79 | 0.040 | 0.025 | |
| Ca, mg/L | 812 a | 968 b | 820 a | 38.9 | <0.01 | 0.083 | |
| Cu, mg/L | 2.68 | 2.99 | 3.05 | 0.122 | 0.077 | 0.074 | |
| Zn, mg/L | 7.38 a | 8.87 c | 7.95 b | 0.251 | <0.01 | 0.076 | |
| Mn, mg/L | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.015 | 0.075 | 0.210 | |
| Fe, mg/L | 32.2 a | 32.7 a | 37.8 b | 1.39 | 0.031 | 0.019 | |
| Feces | P, g/kg | 5.64 | 5.40 | 5.65 | 0.447 | 0.905 | 0.982 |
| Se, mg/kg | 0.42 a | 0.66 b | 0.89 c | 0.037 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Ca, g/kg | 33.5 | 32.9 | 31.7 | 0.780 | 0.190 | 0.079 | |
| Cu, mg/kg | 76.8 c | 70.0 a | 68.1 a | 1.66 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Zn, mg/kg | 241 b | 227 a | 220 a | 5.90 | 0.045 | 0.020 | |
| Mn, mg/kg | 731 | 743 | 715 | 19.7 | 0.619 | 0.572 | |
| Fe, g/kg | 11.4 b | 11.1 b | 10.9 a | 0.135 | 0.030 | 0.010 | |
| Items | Nano-Se, mg/kg | SEM | p-Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | Nano-Se | L | ||
| Total VFAs, mM | 21.0 b | 20.1 b | 18.4 a | 0.55 | 0.020 | 0.007 |
| Acetate, mM | 15.0 b | 14.8 b | 13.8 a | 0.27 | 0.021 | 0.011 |
| Propionate, mM | 2.96 b | 2.73 b | 2.41 a | 0.139 | 0.025 | 0.008 |
| Butyrate, mM | 2.32 c | 1.83 b | 1.44 a | 0.131 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| Iso-VFA, mM | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.046 | 0.411 | 0.797 |
| Acetate: propionate | 5.08 a | 5.42 b | 5.73 c | 0.137 | 0.033 | 0.011 |
| Items | Nano-Se, mg/kg DM | SEM | p-Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | Nano-Se | L | ||
| Ace | 1485 | 1546 | 1484 | 55.8 | 0.674 | 0.994 |
| Chao | 1434 | 1483 | 1438 | 52.5 | 0.768 | 0.954 |
| Shannon | 5.05 | 5.14 | 5.14 | 0.070 | 0.592 | 0.393 |
| Simpson | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.003 | 0.481 | 0.302 |
| Sobs | 1274 | 1305 | 1274 | 47.9 | 0.869 | 0.996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Mao, K.; Peng, W.; Degen, A.; Zuo, G.; Yang, Y.; Han, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, K.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Nano-Selenium Reduces Concentrations of Fecal Minerals by Altering Bacteria Composition in Feedlot Goats. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122233
Liu H, Mao K, Peng W, Degen A, Zuo G, Yang Y, Han J, Wu Q, Wang K, Jiang Q, et al. Nano-Selenium Reduces Concentrations of Fecal Minerals by Altering Bacteria Composition in Feedlot Goats. Agriculture. 2024; 14(12):2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122233
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hu, Kaiyu Mao, Weishi Peng, Allan Degen, Gang Zuo, Yuanting Yang, Jiancheng Han, Qun Wu, Ke Wang, Qinyang Jiang, and et al. 2024. "Nano-Selenium Reduces Concentrations of Fecal Minerals by Altering Bacteria Composition in Feedlot Goats" Agriculture 14, no. 12: 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122233
APA StyleLiu, H., Mao, K., Peng, W., Degen, A., Zuo, G., Yang, Y., Han, J., Wu, Q., Wang, K., Jiang, Q., & Zhou, H. (2024). Nano-Selenium Reduces Concentrations of Fecal Minerals by Altering Bacteria Composition in Feedlot Goats. Agriculture, 14(12), 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122233






