Abstract
Within the framework of sustainable agriculture, the integrated rice-snail-crayfish farming system has been recognized as a highly efficient agroecological approach that enhances crop production while minimizing the application of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Nonetheless, the mechanisms by which this system influences soil microbial community composition to achieve these benefits remain unknown. In this study, we focused on traditional rice farming (TR), the integrated rice-snail-crayfish (R-S-C) farming system, and mono-rice farming (CK), and systematically examined the impacts of these farming systems on soil chemical properties, microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and microbial community composition. Our results showed that the R-S-C significantly increased soil pH, microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and the MBC/microbial biomass phosphorus (MBP) ratio compared to TR, as well as the peroxidase activity. Moreover, the R-S-C significantly increased soil total phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA), bacterial PLFAs, Gram-negative bacterial (GN) PLFAs, anaerobic bacteria PLFAs, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) abundances, and the bacteria/fungi ratio compared to the other two systems. However, the soil microbial α-diversity indices, including Shannon–Wiener index (H), Simpson index (D), and Pielou evenness index (J), were significantly lower in the R-S-C system than in the other two systems. Further exploration suggested that soil pH, microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN), the MBN/total nitrogen (TN) ratio, and the MBC/MBP ratio were critical factors governing microbial community composition under the three farming practices. Notably, soil pH alone accounted for 64.5% of the observed variation in microbial community composition. Path analysis using partial least squares structural equation modeling further revealed the pathways by which the R-S-C system enhanced total PLFAs, AMF, and gram-positive bacteria by regulating the soil pH and MBN/TN ratio. This study provides insights into the regulatory mechanisms driving soil microbial communities in the R-S-C system and offers a theoretical foundation for developing sustainable agricultural management practices.
1. Introduction
Rice paddies are a crucial global food production system that plays an essential role in enhancing agricultural productivity while maintaining soil health [1,2,3]. However, the excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in modern agriculture frequently results in soil degradation and ecosystem imbalances, thereby threatening the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems [3,4,5,6]. In this context, ecological rice-aquaculture systems have garnered increasing attention due to their potential in reducing chemical inputs and have been widely promoted, especially in major rice-producing areas of Asia, particularly China [5,7]. Snail (Cipangopaludina chinensis) and crayfish (Procambarus clarkii), both economically valuable, are key aquaculture species in subtropical regions owing to the high demand by the food industry [8,9]. In China, the annual consumption of snail exceeds 1 million tons, whereas that of crayfish reaches 3.16 million tons [10,11]. Current research on rice-snail systems has primarily focused on the ecology and physiology of aquaculture species [12], differences in microbiota between the digestive tract and sediment [10], aquaculture techniques [13], nutritional and medicinal properties [14], and morphological and genetic traits [15]. In contrast, studies on rice-crayfish systems have focused on rice yield, changes in soil properties, microbial community succession, and shifts in carbon utilization capacity [16,17,18]. However, the actual impact of these aquaculture systems on soil health remains controversial, and the mechanisms involved are largely underexplored.
An integrated rice-snail-crayfish (R-C-S) farming system, which incorporates both snails and crayfish into rice paddies, is anticipated to have profound effects on soil microbial communities and overall soil health [19]. In these integrated systems, snails are commonly stocked in the shallow water zones of rice paddies or near the rice roots. They consume organic debris, algae, small aquatic organisms, and parts of rice roots, thereby aiding in the control of weeds and pests within paddies. Additionally, excretion enriches rice plants with nutrients [13]. Crayfish, on the other hand, are better adapted to slightly deeper water regions or canals within rice paddy fields. Their diet includes benthic fauna, organic debris, and plant-based foods found in the paddies. They also excavate burrows, which alter the ventilation conditions and soil structure of rice paddies [17,18]. The effects of this integrated farming system on soil health and the underlying mechanisms regulating microbial community dynamics are still in the early stages of investigation. In particular, research on the unique ecological context of the subtropical South Asian region remains scarce and lacks comprehensive and systematic scientific data to support an in-depth understanding of these mechanisms.
Soil microbial communities play central roles in soil fertility, nutrient cycling, and ecosystem functioning [20,21]. The structure and diversity of these communities are influenced by various factors, including soil pH [20], moisture [22], organic matter content [23], carbon cycling [24], and availability of multiple nutrients [25]. Previous studies have demonstrated that soil management practices exert complex effects on microbial communities, involving physicochemical alterations and interactions between microorganisms and their environment [25,26]. For example, different fertilization and tillage practices significantly alter microbial diversity and function, which consequently affects soil health and agricultural productivity [19,27,28]. Increasing evidence suggests that soil health threats and other environmental challenges can be effectively addressed through microbial regulation of soil properties [25]. Therefore, investigating changes in soil microbial communities and their driving factors in R-S-C farming systems is essential for advancing sustainable agricultural development.
Currently, research on the impact of co-introducing snails and crayfish into paddy fields on soil microbial communities is limited. Although rice-fish and rice-crayfish systems have been shown to enhance soil microbial diversity and biomass [16,18,29], some studies suggest that these changes may be short-lived, with limited effects on α-diversity indices [30]. The influences of various management practices on soil microbes are complex and varied, and the specific driving factors in different integrated systems require further investigation and validation. In microbial community assessments, phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) analysis remains a fundamental technique for evaluating microbial community composition and diversity [31,32]. As changes in soil physicochemical properties, enzyme activities, and microbial biomass are key indicators of soil health [33,34], they must be considered when exploring the factors influencing microbial communities.
In this study, we aimed to evaluate whether the integrated farming system exhibited a more stable soil microbial community composition and diversity than traditional farming systems and to explore the key factors and pathways that influence changes in soil microbial community composition. We hope that our findings provide support for optimizing soil management strategies for paddy field ecosystems. Our focus was to compare traditional rice farming (TR), the R-S-C system, and mono-rice farming (CK) in the tropical southern regions of China, based on the following hypotheses: (i) the R-S-C has a more complex soil microbial community structure than the other systems and (ii) the mechanisms underlying these differences could be influenced by soil chemical properties, microbial biomass, and enzymatic activities or a combination of these factors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Experimental Design
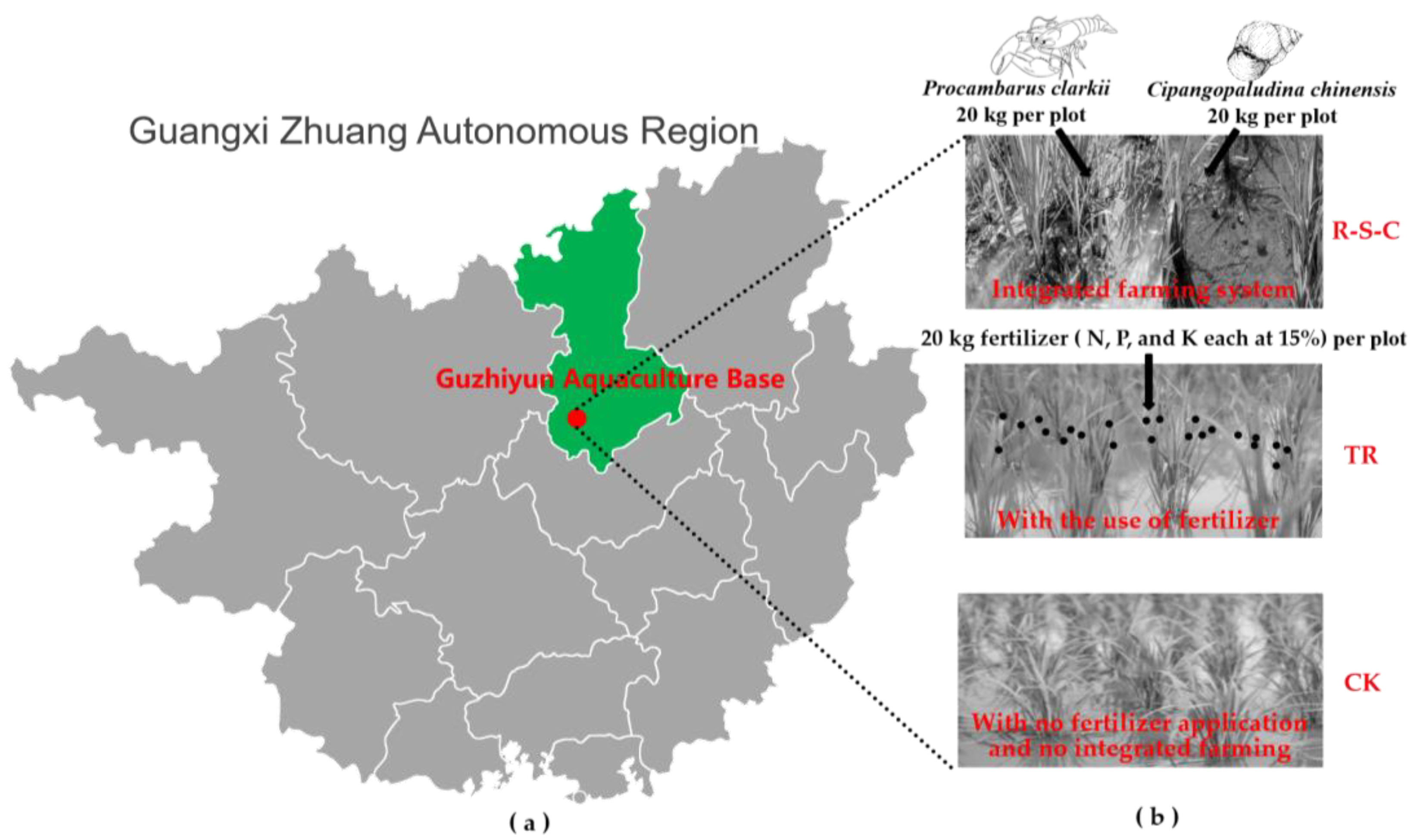
The research was conducted at the Guzhiyun Aquaculture Base (24°8′ N, 109°2′ E), located in Liuzhou, Guangxi, China (Figure 1a). The area lies in a subtropical monsoon climate zone, characterized by humid to semi-humid conditions, with an average annual precipitation of approximately 1400 mm, an average temperature of 21 °C, and an average annual sunshine of 1462.2 h (from 2018 to 2022). The soil in the study region is classified as waterlogged paddy soil in government reports, which is equivalent to hydragric anthrosols in the WRB Soil Taxonomy. The original patterns of soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, and total phosphorus are listed in Table 1.
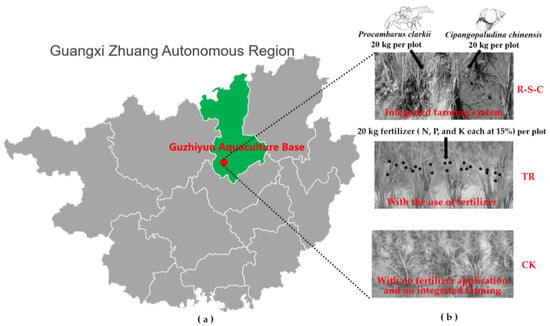
Figure 1.
The study was conducted in the Guzhiyun Aquaculture Base, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, southwestern China (a). Treatment methods for three farming systems (b).

Table 1.
Soil chemical properties of rice farming without fertilizer application at the base in 2020 [35] (mean ± standard error; n = 3).
In 2018, nine experimental plots (10 × 20 m2) were set up at the Guzhiyun Aquaculture Base for CK, TR, and R-S-C treatments (Figure 1b). Each treatment had three replicate plots. Each plot was enclosed by a 1-m high cement bund below the ground, with an additional 60 cm above ground. An 80 cm-wide, 50 cm-deep aquaculture ditch was maintained around each plot. Between 2018 and 2022, farmland management measures for nine plots were the same, except the treatment.
(1) In the R-S-C plots, rice planting began in June, with seedlings spaced approximately 25 × 25 cm2 apart. Two weeks later, after the completion of rice seedling tillering, the plots were evenly treated with 15 kg of quicklime, a practice considered effective for sterilization in this region. Subsequently, 20 kg of uniformly sized, intact-shelled, disease-free snails (each weighing approximately 20 g) and crayfish (each weighing approximately 20 g) were introduced, and the water depth in the paddy fields was maintained at approximately 15 cm. The rice was harvested between September and October based on its maturity, whereas the aquatic products were harvested after five months of cultivation. (2) For the TR plots, snails and crayfish were not introduced. Instead, the rice had been annually fertilized with 20 kg of compound fertilizer (with N, P, and K at 15% each), with all other management practices remaining identical to those in the R-S-C plots. (3) In the CK plots, neither fertilization nor the introduction of snails and crayfish were carried out. All other management practices were consistent with those used in the R-S-C plots.
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
In August 2022, five years after the implementation of CK, TR, and R-S-C, soil samples were collected using a five-point sampling method. Before soil samples collection, all water in the paddy fields had been drained out. After 10 days of drainage, the soil samples were collected when the soil was solid. One soil core was taken from the center of each plot using an 8.7 cm inner diameter stainless tube, and four additional cores were collected from points 8 m away in the four diagonal corners. All cores were collected at a depth of 0–20 cm below the soil surface [36]. After removing stones, plant residues, and other impurities, the five cores were combined to form a composite sample for each plot. Each composite soil sample was divided into three subsamples. One subsample was further air-dried to a constant weight, rolled and pressed with a clean wooden stick, and passed through a 2-mm sieve. This prepared subsample was used for soil property analysis, including soil pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), available phosphorus (AP), total potassium (TK), available potassium (AK), and alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen (AN). Another subsample, also sieved through a 2-mm sieve, was immediately stored at −4 °C to measure the soil water content (WC), microbial biomass carbon (MBC), microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN), microbial biomass phosphorus (MBP), and enzyme activity. The final subsample was stored at −20 °C for PLFA analysis [37].
The WC was determined by drying a sub-sample at 105 °C until constant weight. The soil pH was measured in a 1:2.5 soil-to-water suspension using a calibrated pH meter. SOC was analyzed using the K2Cr2O7 (0.8 M)-H2SO4 oxidation heating method. The TN, TP, and TK levels were assessed after digestion with 98% H2SO4. TN and TK were quantified in the supernatant with a continuous flow analytical system (AA3, SEAL Analytical, Norderstedt, Germany) and an atomic absorption spectrometer (ZEENIT 700P; Analytik, Jena, Germany) [31], respectively. TP and AP were determined through Mo-Sb-Vc colorimetry of the supernatant after digestion, with extraction in HCl (0.05 M)-H2SO4 (0.025 M). AK was quantified using atomic absorption spectrometry following extraction in 1 M NH4OAC. AN was extracted with NaOH (1.0 M), and ammonia was captured in an H3BO3 (20 g·L−1) solution and titrated with H2SO4 (0.005 M) for quantification [37].
MBC and MBN in the soil were determined via fumigation-extraction, with 0.5 M K2SO4 used as the extraction reagent, and analyzed using a total organic carbon analyzer (1020A, OI, College Station, TX, USA). MBP was extracted with 0.5 M NaHCO3 and quantified using the molybdenum blue colorimetric method [37,38].
PLFA analysis was performed on freeze-dried soil samples to examine the composition of the soil microbial community, according to the method established by Bossio et al. (1998) [37]. Phospholipids were extracted from soil (8 g) through soaking in a solution of CHCl3:CH3OH:C6H8O7 with a volume ratio of 1:2:0.8, followed by separation, purification, and esterification to form fatty acid methyl esters. Finally, the content of various fatty acids (i.e., their response, equivalent carbon chain length, peak name, percent, comment, peak area of total name, and total amount) in the microorganisms was determined by chromatography. PLFA markers corresponding to specific soil microbial groups are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Phospholipid fatty acid markers used to identify particular soil microbial groups.
To evaluate soil microbial function, the activities of oxidoreductases (phenol oxidase (POD) and peroxidase (PO)) and hydrolytic enzymes (β-1,4-glucosidase (βG), N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), urease (URE), and acid phosphatase (ASP)) were also measured. POD and PO activities were quantified using L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) as the substrate [37]. Fresh soil samples (1 g) were mixed with 2 mL of 5 mM L-DOPA and 1.5 mL of sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0) to assess the PO activity. Alternatively, a mixture of 2 mL of 5 mM DOPA, 0.2 mL of 0.3% H2O2, and 1.5 mL of the same buffer was used to determine POD activity. Both mixtures were incubated at 20 °C for 1 h and assayed colorimetrically at 460 nm. The activities of βG and NAG were determined with p-nitrophenyl-N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminide as the substrate. Fresh soil samples (4 g) were combined with 10 mL of 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0) (soil-to-liquid ratio of 1:2.5). After incubation at 20 °C for 0.5 h, the samples were centrifuged. Subsequently, 0.2 mL of 50 mM 4-nitrophenyl β-d-glucopyranoside and 0.2 mL of 10 mM 4-nitrophenyl N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminide were added, and the samples were incubated at 20 °C for 1 h to assess βG and NAG, respectively. The URE activity was measured using the sodium hypochlorite-phenol colorimetric method. The procedure involved mixing 5 g of soil with 1 mL of toluene, which was then oscillated for 15 min, then 10 mL 10% urea and 20 mL citrate buffer (pH 6.7) were added before incubation at 37 °C for 24 h. After filtration, 1 mL filtrate was mixed with 4 mL 1.35 M C6H5ONa and 3 mL 0.9% NaClO, color developed for 20 min, then volume adjusted. Colorimetric analysis was conducted at 578 nm. The ASP activity was determined using p-nitrophenyl phosphate disodium as the substrate [44]. The mixture (5 g soil: 2.5 mL toluene) was shaken for 15 min with 20 mL 0.2 M acetate buffer, and then was incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. This was then added to 100 mL 0.3% (w/v) aluminum sulfate, and then filtered. We then pipetted 3 mL filtrate into a 50-mL flask, and color development was performed according to the standard curve, measured at 660 nm.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The species richness index (Richness, S) referred to the number of PLFA markers identified in each soil sample. The Shannon–Wiener index (H) [31], Simpson’s index (D) [31,45], and Pielou’s evenness index (J) [46] were calculated using the following formulas, respectively:
In Equations (1)–(3), Pi indicates the relative abundance of the i-th PLFA marker and s refers to the total number of identified PLFA markers.
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to assess the differences in indicators across different farming systems. Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS software (version 25.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Differences between means were evaluated using the least significant difference (LSD) test at a significance level of p < 0.05. Correlation analyses were also conducted using the SPSS software.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) was performed to elucidate the relationships between biotic and abiotic factors and soil microbial composition using the CANOCO 5 software for Windows (Biometris-Plant Research International, Wageningen, The Netherlands). Data were log-transformed prior to analysis. The forward selection procedure in RDA, utilizing Monte Carlo permutation with 499 iterations, was used to ascertain the dominant variables affecting PLFA composition. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 for all analyses.
Venn diagrams were generated online using the VENNN DIAGRAMS tool (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/ (accessed on 11 August 2024)).
In recent studies of microbial driving factors, partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) has been increasingly used [47,48]. We used the SmartPLS 4.0 software (https://www.smartpls.com (accessed on 19 August 2024)) to construct a PLS-SEM model to evaluate the causal relationships between soil characteristics, soil microbial biomass, key enzyme activities, and microbial communities. To detect multicollinearity, we calculated variance inflation factor (VIF) values and ensured that these values for each factor in both the external and internal models remained below 3 [49]. The model fit was assessed using fit indices such as the standardized root mean square residual (SRMR < 0.08), the squared Euclidean distance (d_ULS < 0.95), and the geodesic distance (d_G < 0.95), which indicate the goodness of fit of the model to the dataset [50]. The coefficient of determination (R2) quantifies the proportion of variance explained by each endogenous variable, with R2 values > 0.19, 0.33, and 0.67 representing weak, moderate, and substantial explanatory power, respectively [47]. All visualizations were created using the Prism 10 software.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Soil Chemical Properties in Different Farming Systems
The R-S-C system had the highest pH and TN and SOC contents, while TR had the highest TK, AP, and AK contents. However, some soil chemical properties (i.e., WC, TP, TN, SOC, and AN) did not differ significantly among the three farming systems (Table 3).

Table 3.
Soil chemical properties (0–20 cm soil depth) in traditional rice farming (TR), integrated rice-snail-shrimp farming (R-S-C), and mono-rice farming (CK, control) systems (mean ± standard error; n = 3).
3.2. Changes in Soil Microbial Biomass in Different Farming Systems
Among the three farming systems, the R-S-C system showed the highest MBC and MBN contents and MBC/MBN, MBC/MBP, MBN/MBP, MBC/SOC, and MBN/TN ratios. By contrast, the TR system exhibited the highest MBP content and MBP/TP ratio. Among these indicators, except for the MBC content and the MBC/MBP ratio, none showed significant differences between the TR and R-S-C systems. There were no significant differences in the other indicators among the three systems (Table 4).

Table 4.
Soil microbial biomass in the three farming systems (mean ± standard error; n = 3).
3.3. Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity in Different Farming Systems
Among the three farming systems, the R-S-C system exhibited the highest NAG and URE activities (Table 5). However, significant differences were observed only in PO activity among the systems. Specifically, PO activity was significantly lower in the TR system than in the R-S-C and CK systems. In contrast, the activities of ASP, βG, NAG, URE, and POD did not show significant variation among the three systems.

Table 5.
Soil extracellular enzyme activities in the three farming systems (mean ± standard error; n = 3).
3.4. PLFAs in Different Farming Systems
3.4.1. Abundance of PLFAs
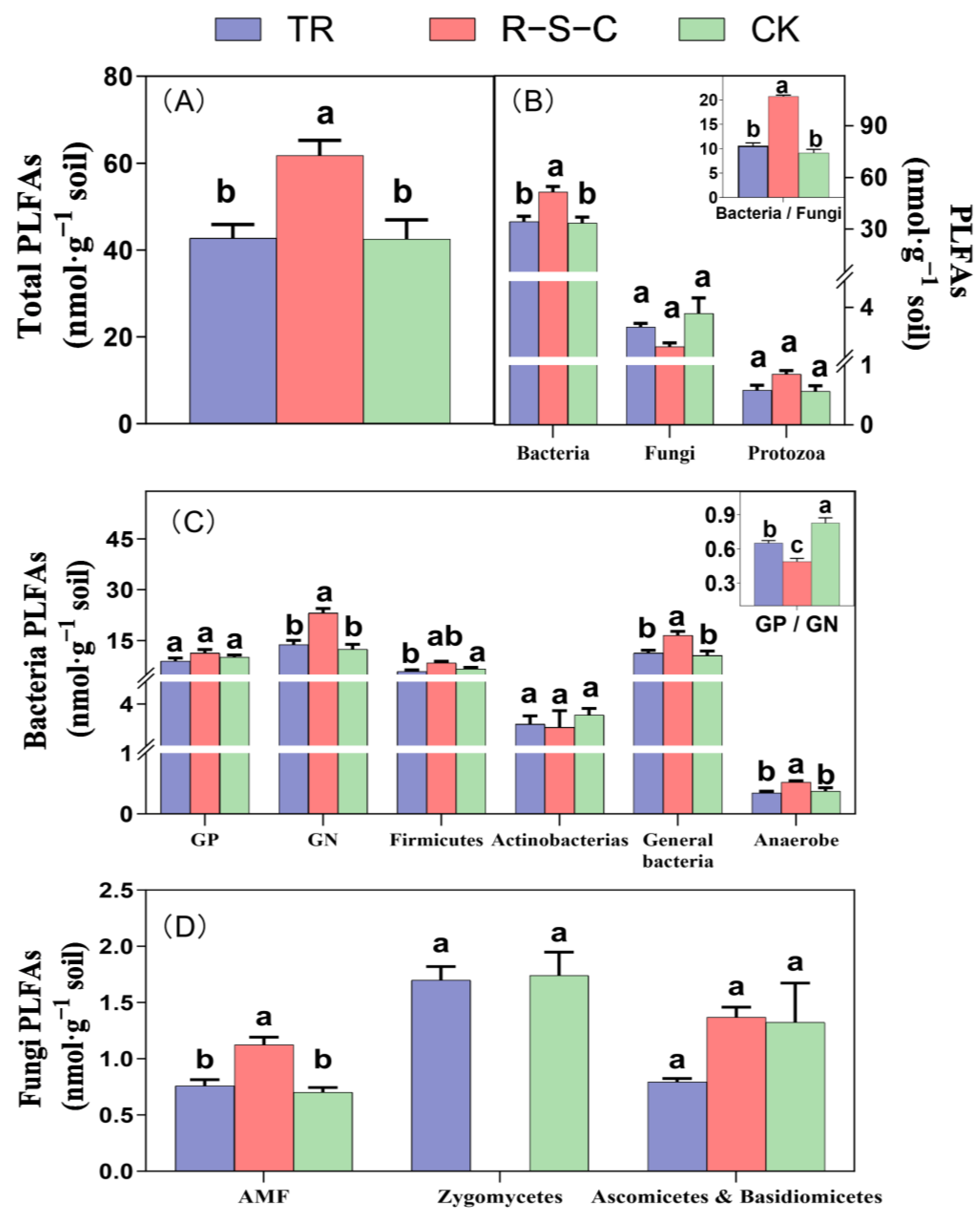
Total PLFAs, bacterial PLFAs, the bacteria/fungi ratio, GN (gram-negative) bacterial PLFAs, general bacterial PLFAs, anaerobic bacteria PLFAs, and PLFAs indicative of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) were significantly higher in the R-S-C system than in TR and CK (Figure 2). Conversely, the GP (gram-positive)/GN PLFA ratio was significantly lower in the R-S-C system than in TR or CK.
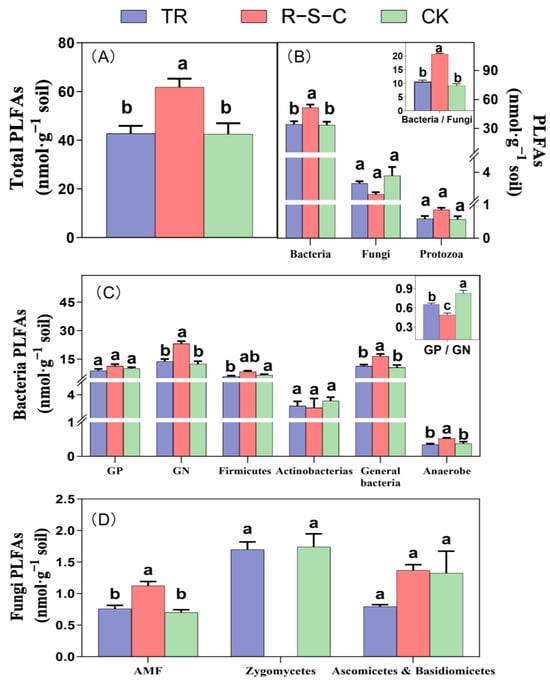
Figure 2.
Soil microbial community PLFA content and structure (0–20 cm soil depth) in three farming systems, including Total PLFAs (A), PLFA Types (B), Bacteria PLFAs (C), and Fungi PLFAs (D). Different letters above the bars denote significant differences at p < 0.05 by LSD multiple comparisons among farming systems (n = 3). GP, gram-positive bacteria PLFAs; GN, gram-negative bacteria PLFAs; AMF, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi PLFAs; GP/GN, GP-to-GN ratio.
Specifically, zygomycete PLFAs were not detected in the R-S-C system, but were consistently present in both TR and CK. Additionally, although not statistically significant, the abundance of other PLFAs (i.e., those indicative of protozoa, GP bacteria, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota) tended to be higher in the R-S-C system than in the other two farming systems.
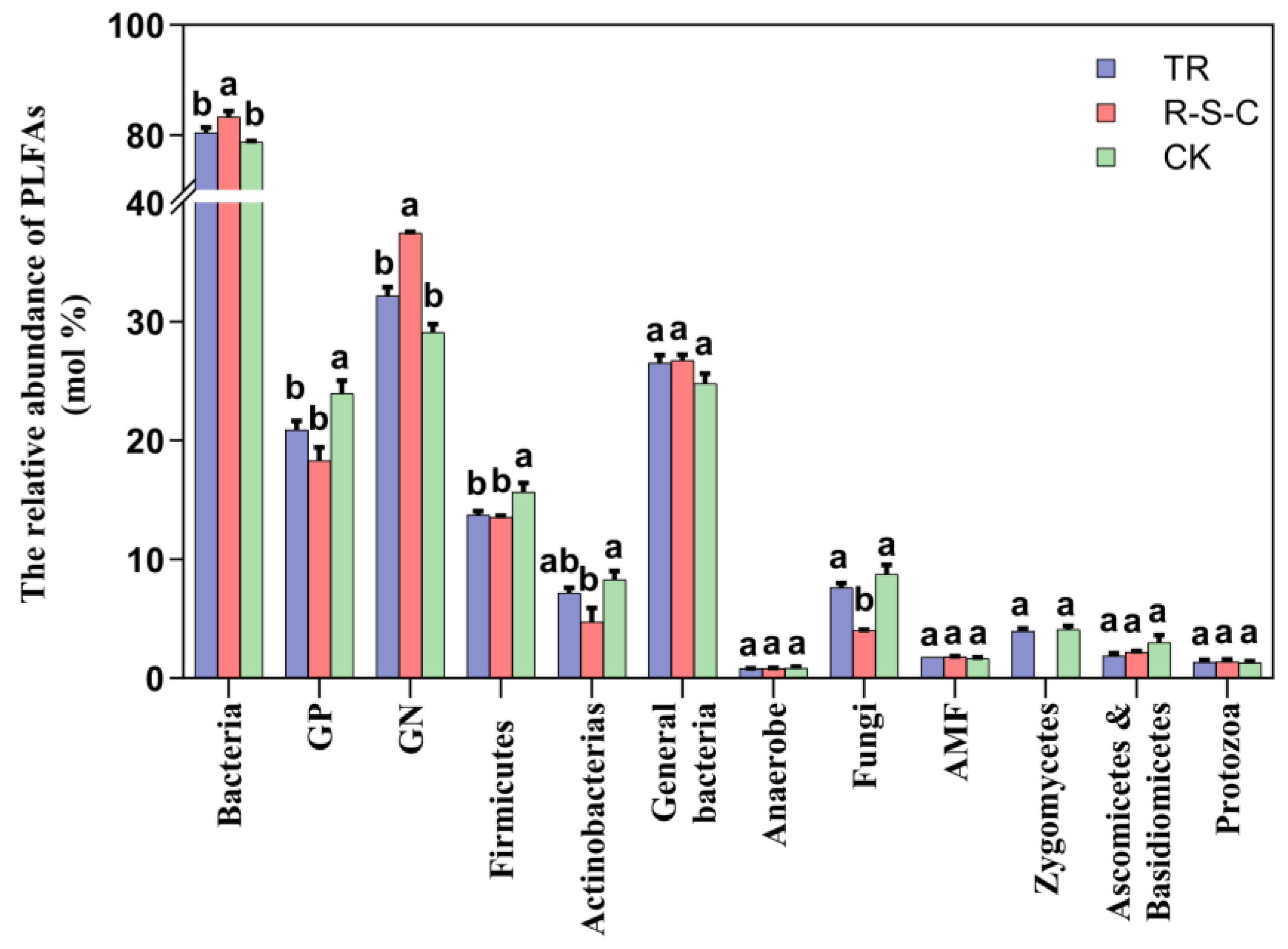
Bacterial PLFAs were the most abundant in all farming systems, followed by fungal and protozoan PLFAs (Figure 3). The different farming systems significantly altered the relative abundance of PLFAs. The R-S-C system exhibited a significantly higher relative abundance of bacterial PLFAs, particularly those derived from GN bacteria, and a notably lower relative abundance of fungal PLFAs. In contrast, CK had a significantly higher relative abundance of GP-bacterial PLFAs, particularly Firmicutes.
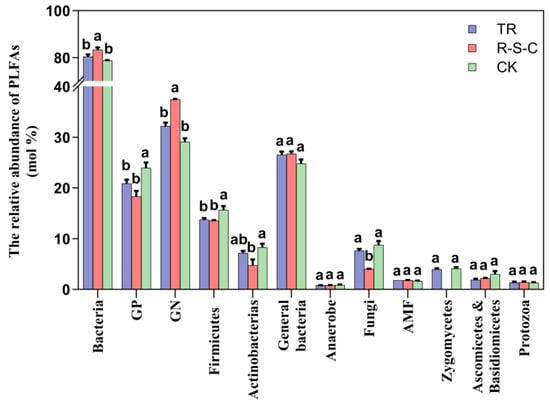
Figure 3.
Relative abundance of PLFAs (mol %) in three farming systems. Different letters above the bars denote significant differences at p < 0.05 by LSD multiple comparisons among the three farming systems (n = 3).
3.4.2. Soil Microbial Diversity Indices
Soil microbial diversity indices (Shannon–Wiener (H), Simpson (D), Pielon (J), and species richness (S)) were calculated based on the PLFA values (Table 6). Among these indices, significant differences were observed for H, D, and J across all three farming systems. Notably, the R-S-C system exhibited the highest S value, although this difference was not statistically significant compared to the other two farming systems. In contrast, the R-S-C system had significantly lower H, D, and J diversity indices.

Table 6.
Soil Microbial alpha diversity indices of the three farming systems, based on PLFA data.
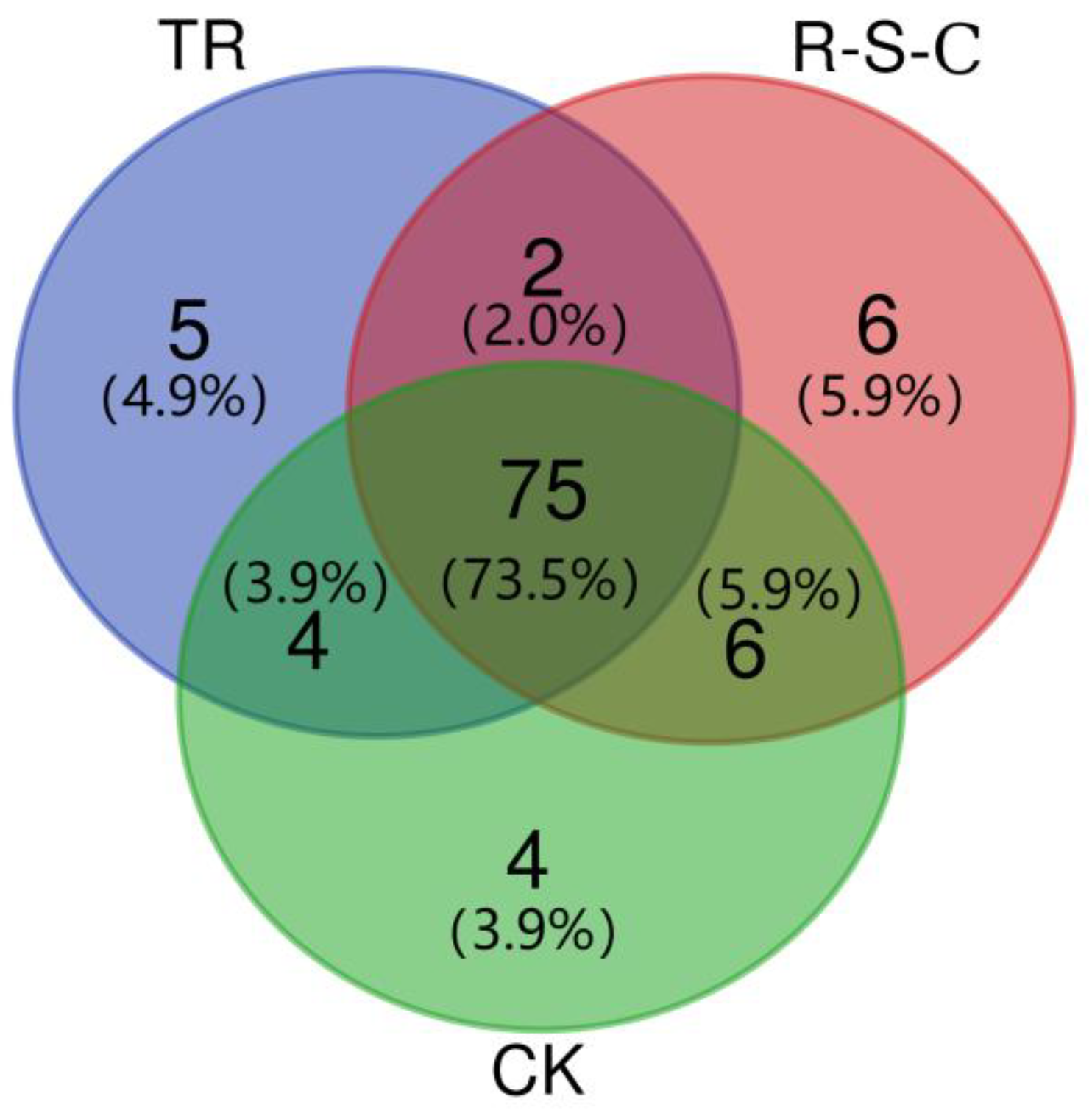
Venn diagrams were used to provide a clearer visualization of common and unique PLFAs across the different farming systems. As depicted in Figure 4, the numbers of core PLFAs (shared by all samples) and unique PLFAs (present exclusively in a particular farming system) among the 9 soil samples were 75 and 15, respectively. Specifically, TR encompassed 86 PLFAs, 5 of which were unique. The R-S-C system contained 89 PLFAs, including 6 unique PLFAs. Similarly, CK exhibited a total of 89 PLFAs, with 4 unique PLFAs.
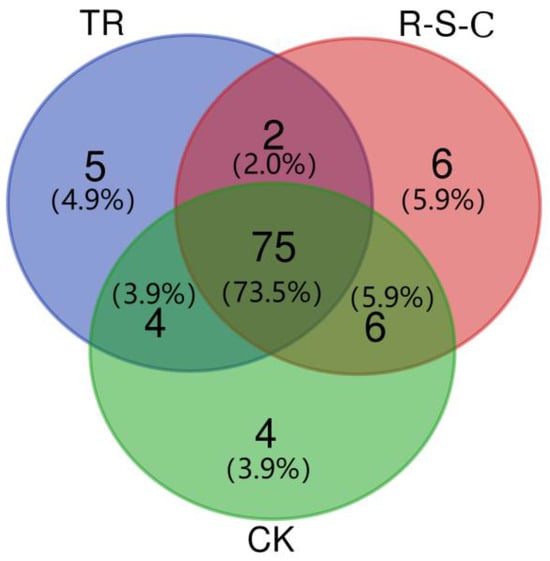
Figure 4.
Comparison of the number of PLFAs in different farming systems.
3.5. Relationship Between Biotic and Abiotic Factors and Soil Microbial Community Composition
3.5.1. Factors Driving Microbial Community Changes
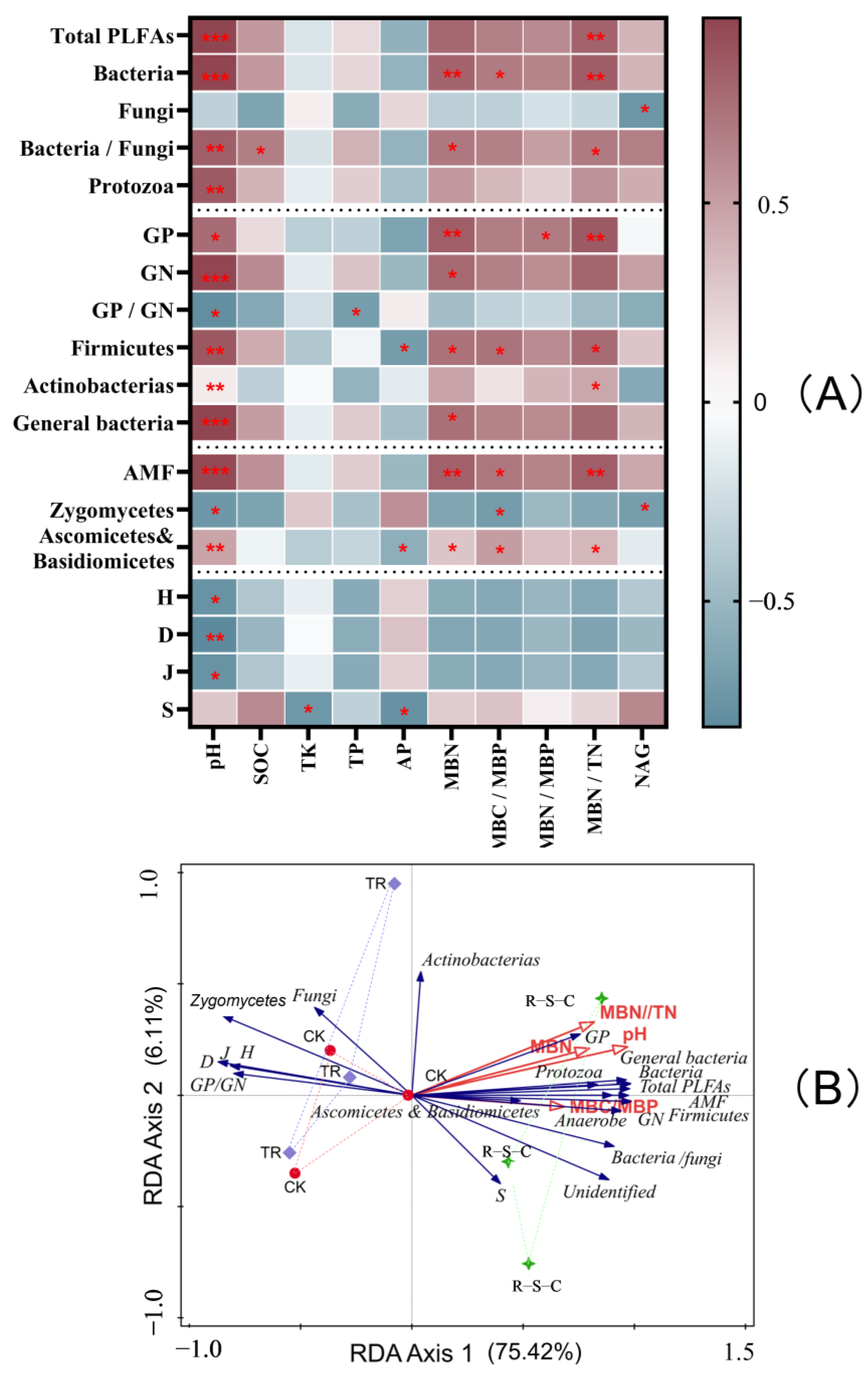
The results were visualized in a correlation heat map (Figure 5A), which highlights only significant correlations by excluding unrelated indicators. This heat map revealed that soil microorganisms exhibited varying correlations with soil chemical properties, microbial biomass, and enzyme activities. Notable trends included significant positive correlations of soil pH, MBN, and the MBN/TN ratio with PLFAs indicates of bacteria, GP bacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, AMF, Ascomycetes, and Basidiomycetes, and the bacteria/fungi ratio. In contrast, soil pH was significantly negatively correlated with the microbial diversity indices H, D, and J. Additionally, soil NAG enzyme activity was significantly negatively correlated with PLFAs indicative of fungi and Zygomycetes.
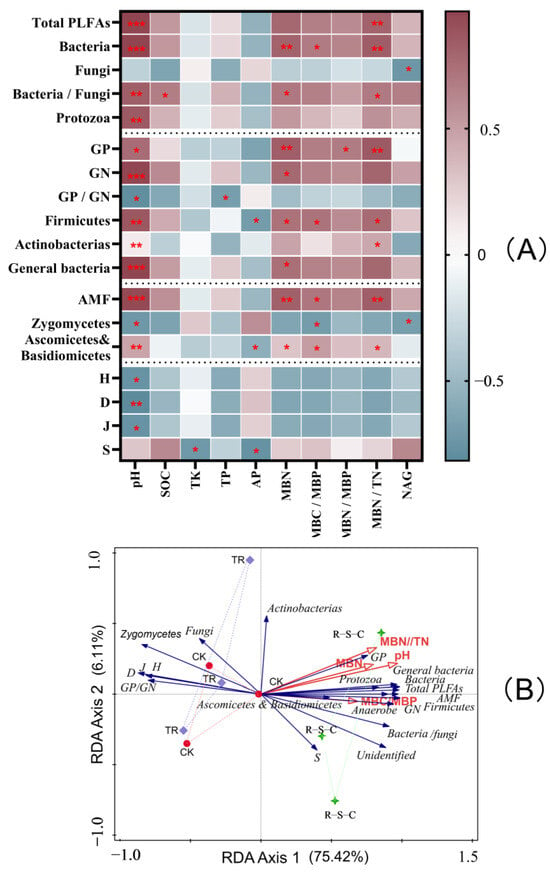
Figure 5.
Correlation heatmap of soil microbial PLFA markers with various biotic and abiotic factors (A) and redundancy analysis (B) across the three farming systems. SOC, soil organic carbon; TK, total potassium; TP, total phosphorus; AP, available phosphorus; MBC, microbial biomass carbon; MBN, microbial biomass nitrogen; MBP, microbial biomass phosphorus; NAG, N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase; GP, gram-positive bacteria PLFAs; GN, gram-negative bacteria PLFAs; AMF, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi PLFAs; S, species richness index; H, Shannon-Wiener index; D, Simpson index; J, Pielou’s evenness index. Statistical significance in the correlation heatmap is given as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
The RDA (Figure 5B), employed to investigate the impact of various biotic and abiotic factors on soil microbial community composition across different farming systems, revealed that the first two axes accounted for 81.53% of the variation in soil microbial community composition (F = 5.7, p = 0.004). The R-S-C system was projected in a notably distinct region compared to the other two systems in this analysis. Four biotic and abiotic factors, including pH (F = 12.7, p = 0.002), the MBN/TN ratio (F = 5.4, p = 0.004), MBN (F = 5.2, p = 0.01), and the MBC/MBP ratio (F = 4.0, p = 0.032), were significantly related to soil microbial community composition. These factors were particularly influential in the R-S-C system, in which they affected total PLFAs and PLFAs indicative of bacteria, GP bacteria, GN bacteria, AMF, Firmicutes, anaerobes, Protozoa, Ascomycetes, and Basidiomycetes. Among these factors, soil pH was the major factor correlated with changes in soil microbial community composition, explaining 64.5% of the variance in this parameter.
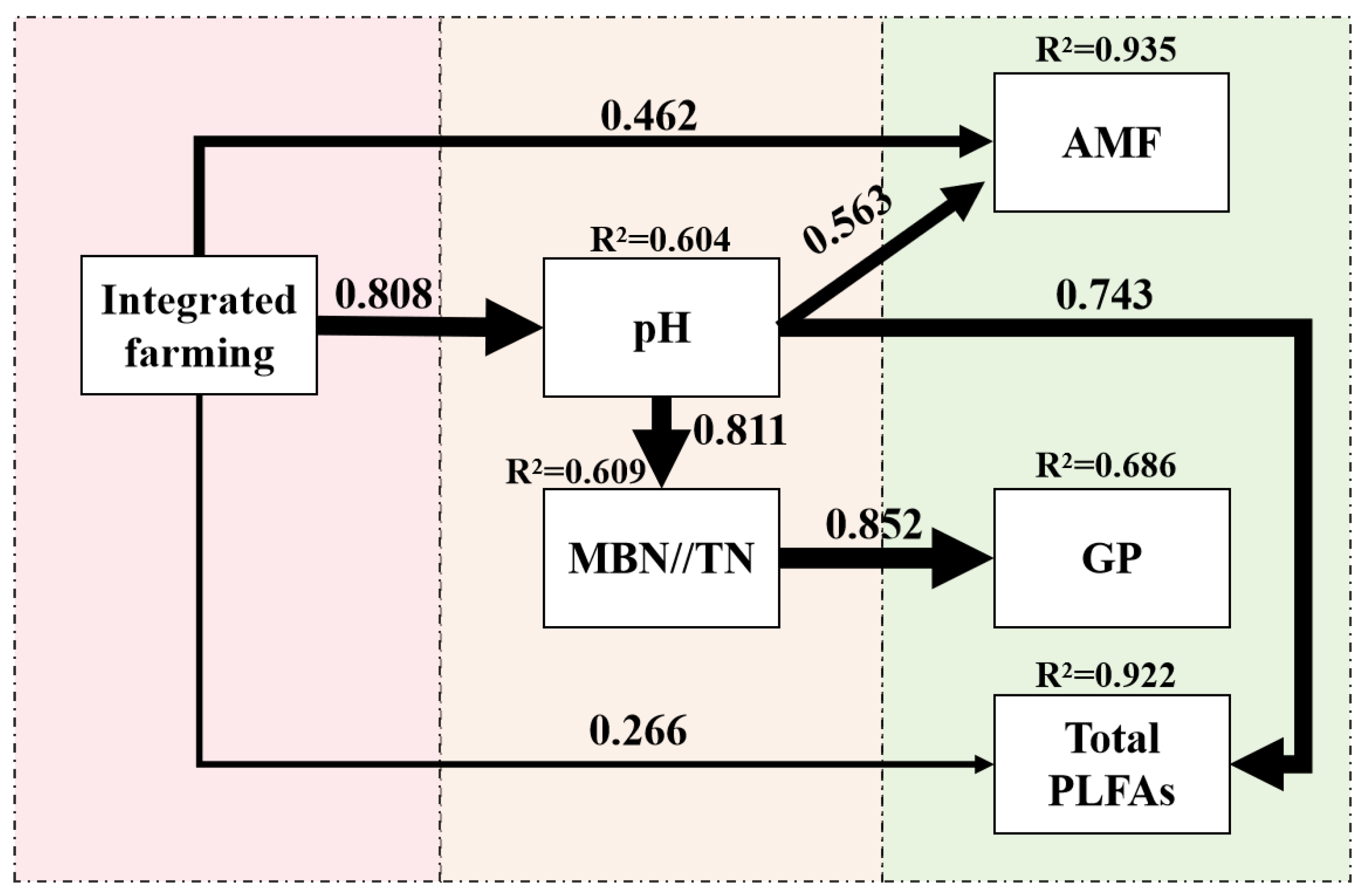
3.5.2. Regulatory Pathway of Soil Microbial Community Composition Induced by Integrated Farming
The path model for regulating soil microbial community structure (Figure 6) showed that integrated farming explained 92.2%, 93.5%, and 68.6% of the variance in total PLFAs, AMF PLFAs, and GP bacterial PLFAs, respectively. Integrated farming and soil pH had direct positive effects on soil AMF and total PLFA contents, whereas the soil MBN/TN ratio had a direct positive effect on GP bacterial PLFAs. Integrated farming significantly enhanced AMF and total PLFA contents through its effect on soil pH; integrated farming also increased the MBN/TN ratio via pH changes, subsequently boosting GP bacterial PLFAs.
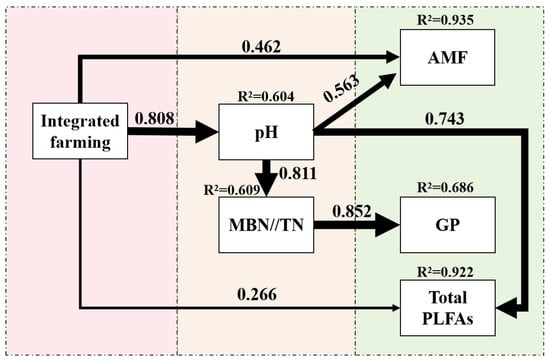
Figure 6.
Pathway analysis illustrating the effects of introducing snails and crayfish into rice farming on soil microbial communities, specifically arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and gram-positive bacteria (GP). Variables included in the model are represented by rectangles, with the numbers on the arrows indicating the standardized direct path coefficients (direct effects). The R2 values reflect the proportion of variance explained for each dependent variable. Arrow thickness and correlation values represent the strength of the effects. In the model, the “integrated farming” was coded as 1 for the R-S-C system, while the other two farming systems were coded as 0. This figure presents the PLS-SEM structural model with SRMR = 0.045, d_ULS = 0.042, and d_G = 0.466, all of which were consistent with the recommended thresholds (SRMR < 0.08, d_ULS < 0.95, and d_G < 0.95), indicating a satisfactory model fit. The VIF values, ranging from 1 to 2.88, were below the suggested threshold (VIF < 3), indicating acceptable multicollinearity among key variables and no collinearity issues. The normed fit index (NFI) score of 0.843 reflected good model fit.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects and Ecological Implications of R-S-C on Soil Properties and Microbial Biomass
In the three farming systems studied, the pH of the R-S-C system was the highest, while TR had the highest values of TK, AP, and AK (Table 3). TR, characterized by fertilization, exhibited significantly higher levels of TK, AP, and AK than the other systems, underscoring the role of fertilization in enhancing soil chemical fertility. Conversely, the higher pH in the R-S-C system indicates that the interaction between rice, Cipangopaludina chinensis, and Procambarus clarkii may mitigate soil acidification, thereby improving and stabilizing the soil pH. This finding aligns with previous research showing that animals, such as loach and shrimp, in rice ecosystems can effectively enhance soil aeration and reduce acidification [51]. Other studies have also revealed that the pH levels in integrated rice-fish systems are significantly higher than those in conventional rice farming systems [52]. In comparison, CK, which lacked both fertilization and ecological farming practices, displayed lower soil nutrient levels. This control reflected the physicochemical properties of the soil under conventional, non-intervening conditions. These results emphasize the distinction between traditional fertilization and integrated farming systems in enhancing soil physicochemical properties, with TR relying more on direct nutrient supplementation and the R-S-C system modulating soil conditions through biological interactions.
In this study, despite the fact that the highest SOC contents were observed in the R-S-C system, there were no significant differences in SOC contents between the traditional fertilization and CK systems (Table 3). In addition, the SOC pattern in TR systems exhibited similarity to the original pattern, while that in R-S-C systems showed a significantly higher level compared to the original pattern. Conversely, the SOC pattern in CK systems was lower than the original pattern. Integrated farming systems typically increase soil organic matter and carbon accumulation through the addition of aquatic animals that contribute organic material via their excretions and uneaten feed [18,53]. Furthermore, fertilizer application significantly enhanced SOC levels [54]. The application of no fertilizer, however, will lead to a decrease in soil organic carbon (SOC) levels in fields.
The total amount and quality of soil organic matter changes slowly, and soil spatial heterogeneity complicates the measurement of these changes. Thus, microbial biomass has been proposed as a more sensitive indicator of the soil organic matter status and its changes. In this respect, the ratios of MBC/SOC, MBN/TN, and MBP/TP have most often been used [55,56]. These ratios also serve as indicators of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus availability in soil [37,57]. Moreover, the ratios of C, N, and P in microbial biomass may be useful for evaluating nutrient limitation in terrestrial ecosystem processes [58,59]. Therefore, we calculated these ratios and their corresponding relationships with SOC, TN, and TP.
We found that MBC and the MBC/MBP ratio in the R-S-C system were significantly higher than those in TR (Table 4), suggesting that the integrated system provides more favorable conditions for soil microbial growth. This finding is consistent with previous findings on rice-crayfish and rice-duck farming systems, in which biological interactions have been shown to significantly enhance microbial activity by increasing organic matter and nutrient supply through animal activities [60,61]. Additionally, aquatic animal activities alter soil aeration, which in turn promotes microbial anabolism and SOM decomposition, leading to increased microbial biomass [62]. However, other studies reported contradictory results. For example, research has shown a 65.84% decrease in MBC in rice-crayfish farming systems [17]. Our study provides experimental evidence that traditional fertilization does not significantly enhance microbial biomass, although it can increase soil nutrient levels. This may indicate that over-reliance on external fertilizer inputs could result in adverse changes in soil properties, such as acidification, which could inhibit the growth of certain microbes and reduce the MBC content [63].
Globally, 30–40% of arable land suffers from phosphorus deficiency [64]. A higher MBC/MBP ratio indicates increased MBC and reduced MBP contents, reflecting a phosphorus-conserving strategy. In this study, the R-S-C system exhibited a higher MBC/MBP ratio than the traditional fertilization system (Table 4), suggesting an advantage in microbial phosphorus utilization strategies. Previous studies have shown that, under low-phosphorus conditions, soil microorganisms adopt phosphorus-conserving strategies, thus driving phosphorus mineralization by consuming organic carbon and improving phosphorus-use efficiency [62]. Ecological rice farming systems regulate the MBC/MBP ratio to maintain a stoichiometric balance between soil nutrients and microbial demands [65,66]. Moreover, the higher MBN content and MBN/TN ratios in the R-S-C system indicated enhanced nitrogen use efficiency (Table 4). These findings not only provide theoretical support for the practical application of integrated farming systems but also lay the foundation for further exploration of the complex relationships between microorganisms and the soil environment.
Additionally, the PO activity in the R-S-C system was significantly higher than that in TR (Table 5). This is in contrast to the findings from other integrated farming systems, such as rice-fish-duck, rice-fish, and rice-crayfish systems, in which animal activities were found to enhance enzymes activities, such as those of URE, catalase, and phosphatase [53,60,67,68]. PO participates in the oxidation of polyphenols, which are the key components of soil organic matter. However, accumulating evidence suggests that soil enzymatic activity is closely associated with microbial biomass and represents the combined effects of microorganisms and decomposed plant and animal residues, which vary significantly across regions [59,63]. Consequently, PO is strongly linked to SOC and MBC, and the results of this study support this relationship. Previous studies have indicated that the use of chemical fertilizers may reduce PO activity in paddy soils [69], potentially due to oxygen depletion from overfertilization, which inhibits PO activity [70].
4.2. R-S-C Increased the Abundance of Soil Bacteria and AMF but Reduced Microbial Diversity
PLFA analysis indicated that the R-S-C system significantly enhanced total, bacterial, and AMF PLFAs while reducing the GP/GN ratio (Figure 2). This shift suggests that the R-S-C system creates a microbial community that is more bacterially dominated and AMF-enriched, potentially benefiting nutrient cycling and plant health [71,72,73]. Previous studies have shown that, compared to monoculture systems, integrated farming practices tend to improve AMF abundance, which in turn promotes plant growth [71]. These findings imply that the R-S-C system fosters a more complex soil microbial community, which supports efficient nutrient cycling and plant development. Additionally, this result aligns with our first hypothesis that the integrated farming system creates a more complex microbial community than traditional fertilization or non-fertilized monoculture systems. Such advantages cannot be achieved by fertilization alone, as TR did not enhance the abundance of these specific microbial groups compared to CK.
Zygomycete PLFAs were not detected in the R-S-C system, but persisted in both TR and CK, suggesting that certain fungal groups may be suppressed in the integrated farming system, possibly due to competitive exclusion or changes in soil conditions [74,75]. Moreover, the Shannon–Wiener (H), Simpson (D), and Pielou’s evenness (J) indices were significantly lower in the R-S-C system (Table 6), indicating lower microbial diversity. This result is consistent with findings from other studies in which integrated farming systems, such as rice-fish co-farming, also had decreased microbial alpha diversity [76]. However, other studies have demonstrated that soil microbial diversity in rice-crayfish systems is significantly higher than that in conventional rice farming systems, suggesting a more stable microbial diversity in integrated systems [77,78].
Notably, lower microbial diversity does not necessarily imply reduced functional efficiency. Under specific environmental conditions, microbial communities may shift toward greater specialization, enhancing their efficiency in certain ecological functions such as nutrient cycling [79,80]. Increased microbial abundance but decreased diversity can be understood from the perspectives of resource competition and niche differentiation. In the R-S-C system, snails and crayfish may create a more favorable environment for certain microbial groups through their biological activities or metabolic byproducts, leading to a rapid increase in the abundance of specific microorganisms. However, this increase might be accompanied by enhanced resource use, which could suppress the growth of other microbial populations, ultimately reducing overall diversity. The observed decrease in the GP/GN ratio in the R-S-C system supports this hypothesis. Previous studies have shown that GN bacteria are sensitive to easily available carbon sources [81], whereas GP bacteria, actinomycetes, and fungi are adept at decomposing complex substrates [82,83]. Combined with our results, this suggests that the introduction of snails and crayfish significantly increases the availability of labile carbon in the soil, thereby promoting the expansion of bacterial communities, particularly those capable of rapidly utilizing simple substrates. This not only facilitates efficient carbon turnover in the soil but also creates a more stable resource supply for other microbial communities. At the bacterial level, this finding reinforces our first hypothesis that integrated farming systems harbor more stable soil microbial communities than traditional cropping systems. The significant increase in the relative bacterial abundance, especially the notable increase in the proportion of GN bacteria (Figure 3), further supports this conclusion.
4.3. Key Factors and Pathways Affecting Soil Microbial Community Structure in the R-S-C System
Correlation and RDA identified soil pH, MBN, and the MBC/MBP ratio as pivotal factors affecting the microbial community composition (Figure 5A,B). Unlike in other integrated rice systems, such as those involving Macrobrachium nipponense, soil organic matter, total organic carbon, AP, and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) were the main factors that influenced microbial communities [77]. Among these factors, soil pH was the most significant, accounting for up to 64.5% of the variation in microbial community composition (Figure 5B). This underscores its critical role in influencing soil microbial communities. Soil pH governs nutrient availability and microbial enzyme activity, thus exerting a profound effect on microbial communities [84,85]. This result aligns with those of previous studies, which highlight the strong impact of pH on the global distribution of bacteria and fungi [20,86]. Notably, AMF, which are essential functional microorganisms, are particularly sensitive to changes in soil pH, which regulates AMF-mediated organic carbon turnover [87,88,89]. The PLS-SEM model further substantiated that even subtle variations in soil pH could modify the microbial habitat and influence the overall composition of microbial communities.
Global studies have highlighted the substantial regulatory flexibility of the MBC/MBP ratio across various ecosystems, emphasizing its crucial role in ecosystem regulation [90]. In our study, both the MBC/MBP and MBN/TN ratios were key factors influencing changes in the soil microbial community (Figure 5B). The PLS-SEM model revealed that integrated farming practices directly increased the abundance of AMF and total PLFAs and indirectly enhanced the abundance of AMF, GP, and total PLFAs through their effects on soil pH and the MBN/TN ratio (Figure 6). The results of the structural model confirmed our second hypothesis. This suggests that the R-S-C system not only alters the composition of the microbial community but also modulates biotic and abiotic factors that influence microbial dynamics. These findings offer new insights into the mechanisms of biological interactions that shape soil microbial community composition and provide a theoretical foundation for future agricultural management strategies. Future research should include a broader range of samples and conduct long-term dynamic monitoring to further validate the generalizability of our findings.
4.4. Whether the R-S-C System Boosts Economic Benefits
In South Subtropical China, the R-S-C system has increased economic benefits. According to data provided by the Guangxi Aquatic Products Scientific Research Institute, between 2021 and 2023, Guangxi Province extensively promoted the R-S-C system. At the Guzhiyun Aquaculture Base, covering an area of 20 ha, the yields of rice, snails, and crayfish over three years were 5664.95 ± 1042.47, 8845.15 ± 2395.38, and 1222.35 ± 371.53 kg/ha, respectively. The corresponding output values reached 1.70 ± 0.31 × 104, 6.84 ± 2.11 × 104, and 7.33 ± 2.23 × 104 CNY/ha, respectively, totaling 15.88 ± 2.03 × 104 CNY/ha. Across Liuzhou, Luzhai, Sanjiang, and Wuzhou, the demonstration bases for the R-S-C system covered a combined area of 234.67 ha, with rice, snail, and crayfish yields of 6829.84 ± 1446.84, 7094.90 ± 2892.87, and 1164.95 ± 511.44 kg/ha, respectively. The output values were 2.05 ± 0.48 × 104, 6.05 ± 2.56 × 104, and 6.56 ± 2.20 × 104 CNY/ha, respectively, totaling 14.66 ± 3.24 × 104 CNY/ha. In parallel, our survey of traditional rice farming among 20 local residents revealed an average yield of 6746.25 ± 225.59 kg/ha and an average output value of 2.02 ± 0.07 × 104 CNY/ha. Although the R-S-C system did not demonstrate a significant advantage in rice yield compared to traditional farming, with some bases even yielding less, the R-S-C system significantly increased overall output value by efficiently utilizing environmental resources, approximately six times more than traditional rice farming.
Notably, China’s rice yield per unit area in 2023 was 5987.0 kg/ha [91]. Based on this, we can infer that the R-S-C system brings particularly significant economic benefits in aquatic products. Furthermore, compared to the average values of the integrated rice-fish farming industry, the R-S-C system also exhibits clear advantages in aquatic product yields. Rice yields in China’s integrated rice-fish farming industry were 8104.67, 7824.07, 7485.01, and 7950.82 kg/ha in 2023 [92], 2022 [93], 2021 [94], and 2019 [95], respectively, while aquatic product yields were 1500.91, 1402.04, 1294.43, and 1327.27 kg/ha, respectively.
However, due to the variability in soil environments and integrated farming practices across different regions, a more comprehensive understanding of the specific circumstances in which the R-S-C system and other integrated rice-aquaculture systems enhance economic benefits while maintaining soil health is required. To achieve this, further data collection from a broader range of regions is necessary, encompassing the yields and output values of rice and aquatic products from these integrated systems. Additionally, the analysis of biotic and abiotic soil indicators should be conducted. This will aid in deepening our understanding of the operational mechanisms of these systems and provide a scientific basis for their future promotion and application.
5. Conclusions
The R-S-C system significantly enhanced the abundance of total PLFAs and PLFAs indicative for bacteria, GN bacteria, anaerobic bacteria, and AMF. Furthermore, the R-S-C system also improved the microbial community composition, particularly by increasing the bacterial/fungal ratio and decreasing the GP/GN ratio. These changes were driven by the combined effects of soil chemical properties, microbial biomass, and their interactions, with soil pH playing a pivotal role alongside the MBN, MBN/TN ratio, and MBC/MBP ratio. The PLS-SEM model further demonstrated that integrated farming increased AMF and total PLFA abundances by elevating soil pH and promoted GP bacterial abundance through its effect on the MBN/TN ratio. In extensive demonstration fields across the region, the R-S-C system demonstrated remarkable economic benefits, particularly through the introduction of aquatic products. Overall, this study provides novel insights into the mechanisms by which biotic interactions regulate soil microbial community composition, while offering a theoretical foundation for enhancing soil health and productivity through optimized integrated farming systems in future agricultural practices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.W.; methodology, W.W., X.D., Z.Q. and Q.L.; software, W.W.; formal analysis, W.W.; investigation, Z.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, W.W.; writing—review and editing, W.W and F.P.; supervision, F.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Capacity Building Program for Young and Middle-aged Faculty in Basic Research at Guangxi Universities (2021KY0344), Doctoral Scientific Research Project of Guangxi University of Science and Technology (XKB21Z09), Guangxi Science and Technology Base and Talent Project (GUIKE AD20159063), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2023GXNSFBA026053), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32460318, 32001208), Guangxi Institute of Indus-trial Technology Research (CYY-HT2023-JSJJ-0038), and supported by Guangxi College Key Laboratory of Innovation Research on Medical and Engineering Integration.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support provided by the Guziyun Experimental Base for offering the experimental fields used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, D.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Tian, J.; Xie, J. Ecosystem services analysis for sustainable agriculture expansion: Rice-fish co-culture system breaking through the Hu line. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Peng, H.; Xia, Y.; Gong, W.; Li, Z.; Yu, E.; Tian, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, J. Evaluating ecological mechanisms and optimization strategy of rice-fish co-culture system by ecosystem approach. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Hu, L.; Tang, J.; Wu, X.; Li, N.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Luo, S.; Chen, X. Ecological mechanisms underlying the sustainability of the agricultural heritage rice-fish coculture system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1381–E1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Tang, R.; Xie, J.; Tian, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, K. Valuation of ecosystem services of rice-fish coculture systems in Ruyuan County, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 41, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Sun, M.; Du, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Nie, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, H. Ecological rice-cropping systems mitigate global warming—A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Z.; Wong, M. Integrated wetlands for food production. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xu, G.; Shen, N.; Nie, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Valuation of ecosystem services for the sustainable development of Hani terraces: A rice-fish-duck integrated farming model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Qin, J.; Pang, H.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Du, X.; Wen, L.; Pan, X.; Lin, Y. Comparison of the composition and function of gut microbes between adult and juvenile cipangopaludina chinensis in the rice snail system. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, L.; Jin, T.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Zhou, M.; Qin, J.; Du, X.; Wen, L.; Pan, X.; et al. Muscle main nutrients of four species of snails in Viviparidae. J. Fish. China 2021, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Qin, J.; Pang, H.; Liang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Du, X.; Zhou, K. Microbiota comparison of cipangopaludina chinensis intestine and sediment under a rice-snail system. Freshw. Fish. 2024, 54, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- National Fisheries Technology Extension Center; China Society of Fisheries. Report on the development of china’s crayfish industry. China Fish. 2024, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Horgan, F.G. The ecophysiology of apple snails in rice: Implications for crop management and policy. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2018, 172, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Huang, B.; Yin, X.; Wang, H.; Xia, Q.; Jin, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Research on integrated rice-snail farming technology. Sci. Fish Farming 2022, 3, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Yan, W.; Yu, B.; Xiong, Q. Preliminary characterization and potential hepatoprotective effect of polysaccharides from cipangopaludina chinensis. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, K.; Zou, X.; Lin, Y.; Ye, H.; Luo, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Du, X.; et al. Analysis of feature and marker development of microsatellites for cipangopaludina chinensis based on full-length transcriptome data. J. Hydroecology 2023, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Song, Q.; Wang, H.; Yi, J.; Bi, Y.; Mi, W.; Song, G. Integrated rice-crayfish farming on soil fertility and microbial community. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Cheng, W.; Shen, Y. Effects of long-term rice-crayfish coculture systems on soil nutrients, carbon pools, and rice yields in northern Zhejiang province, China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Pan, R.; Hu, H.W.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Tan, W.; Liu, Y.R.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Effects of integrated rice-crayfish farming on soil biodiversity and functions. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 2311–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Takakura, K.I.; Kanai, R.; Tawa, K.; Murakami, D.; Sawada, H. Impacts of environmental factors in rice paddy fields on abundance of the mud snail (cipangopaludina chinensis laeta). J. Molluscan Stud. 2014, 80, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Response of soil properties and microbial communities to agriculture: Implications for primary productivity and soil health indicators. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockett, B.F.T.; Prescott, C.E.; Grayston, S.J. Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, M.; Chen, J.; Tie, L.; Zhou, S.; Buckeridge, K.M.; Cornelissen, J.; Huang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Microbial necromass under global change and implications for soil organic matter. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3503–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimel, J.P.; Schaeffer, S.M. Microbial control over carbon cycling in soil. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, P.K.; Nayak, A.K.; Panda, B.B.; Senapati, A.; Panneerselvam, P.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, R.; Poonam, A.; Shahid, M.; Mohapatra, S.D.; et al. Rice-based integrated farming system improves the soil quality, bacterial community structure and system productivity under sub-humid tropical condition. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Ma, B.; Sun, L.; Cai, Y.; Chang, S.X. Long-term nitrogen fertilization, but not short-term tillage reversal, affects bacterial community structure and function in a no-till soil. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Girvan, M.S.; Verchot, L.; Bullimore, J.; Borelli, T.; Albrecht, A.; Scow, K.M.; Ball, A.S.; Pretty, J.N.; Osborn, A.M. Soil microbial community response to land use change in an agricultural landscape of western Kenya. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, D.; Geisen, S.; Zhu, H. Soil microbial biomass and bacterial diversity enhanced through fallow cover cropping in rice-fish coculture. Agronomy 2024, 14, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sansupa, C.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Soil microbial diversity and community composition in rice-fish co-culture and rice monoculture farming system. Biology 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, W.; Miao, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Sui, X.; Li, M. The diversity and composition of soil microbial communities differ in three land use types of the Sanjiang plain, northeastern China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szejgis, J.; Carrillo, Y.; Jeffries, T.C.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Chieppa, J.; Horn, S.; Bristol, D.; Maisnam, P.; Eldridge, D.; Nielsen, U.N. Altered rainfall greatly affects enzyme activity but has limited effect on microbial biomass in Australian dryland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 189, 109277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Shukla, M.K.; Mao, X. Long-term plastic film mulching altered soil physicochemical properties and microbial community composition in Shiyang River Basin, Northwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. A Sect. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 193, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Zheng, B.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Luo, F.G.; Jiang, M.; Li, Y.H. Effects of bio-fertilizer on the yield of freshwater snails in rice-field aquaculture, water quality, and soil fertility. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2022, 61, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q. Effects of organic-inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. A Sect. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, H.; You, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Yan, L.; Li, H.; et al. Coniferous-broadleaf mixture increases soil microbial biomass and functions accompanied by improved stand biomass and litter production in subtropical China. Forests 2019, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, D.S.; Miguel, V.S.; Calviño, D.F. Study of microbial communities in Lusitanian organic and conventional agricultural soils by phospholipid fatty acid analysis. J. Agrar. Sci. 2022, 45, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Joergensen, R.G. Phospholipid fatty acids in soil—Drawbacks and future prospects. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2022, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Fan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, C.; Filimonenko, E.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, X.; et al. Nitrogen fertilizer builds soil organic carbon under straw return mainly via microbial necromass formation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 188, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, R.; Gujre, N.; Mitra, S.; Sharma, M.P. Decoding the PLFA profiling of microbial community structure in soils contaminated with municipal solid wastes. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 114993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Yang, L.; Harbo, L.S.; Yan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Miao, Y.; et al. Effects of land use on soil microbial community structure and diversity in the yellow river floodplain. J. Plant Ecol. 2023, 16, rtac075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S.; Sun, O.J. Relating microbial community structure to functioning in forest soil organic carbon transformation and turnover. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1967, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Tang, F.; Wang, Y. Microbial mechanisms for improved soil phosphorus mobilization in monoculture conifer plantations by mixing with broadleaved trees. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 359, 120955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, S.; Ma, J.; Qu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Cai, Y. New insights into assembly processes and driving factors of urban soil microbial community under environmental stress in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Hubona, G.; Ray, P.A. Using PLS path modeling in new technology research: Updated guidelines. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.; Lan, X.; Ye, S. Soil-microbial interactions in rice-loach-shrimp integrated farming: Multivariate analysis of ecological intensification. Water 2024, 16, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.K.; Nayak, A.K.; Panda, B.B.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Poonam, A.; Shahid, M.; Tripathi, R.; Kumar, U.; Mohapatra, S.D.; et al. Ecological mechanism and diversity in rice based integrated farming system. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, K. Rice-fish-duck system regulation of soil phosphorus fraction conversion and availability through organic carbon and phosphatase activity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 979234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Ray, S.; Deka, J.; Das, A.; Devi, H. Assessment of rice farming management practices based on soil organic carbon pool analysis. Trop. Ecol. 2016, 57, 607–611. [Google Scholar]
- Bosatta, E.; Ågren, G.I. Theoretical analysis of microbial biomass dynamics in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.; Domsch, K.H. Ratios of microbial biomass carbon to total organic carbon in arable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1989, 21, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insam, H.; Domsch, K.H. Relationship between soil organic carbon and microbial biomass on chronosequences of reclamation sites. Microb. Ecol. 1988, 15, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad, S.J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.-H.; Yuan, J.-F.; Peng, C.-L.; Zhao, S.-J.; Xu, D.-B.; Yu, Y.-B.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Zhou, J.-X. Mechanism of long-term integrated rice-crayfish farming increasing soil biological fertility of paddy fields. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, M.; Cao, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, M.; Yue, L.; Shahrear, A. Dynamics of methane emission, active soil organic carbon and their relationships in wetland integrated rice-duck systems in southern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ren, T.; Yan, J.; Zhu, D.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cong, R.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Straw returning mediates soil microbial biomass carbon and phosphorus turnover to enhance soil phosphorus availability in a rice-oilseed rape rotation with different soil phosphorus levels. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 335, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Sheoran, S.; Prakash, D.; Yadav, D.B.; Yadav, P.K.; Jat, M.K.; Apurva, A. Long-term application of organic manures and chemical fertilizers improve the organic carbon and microbiological properties of soil under pearl millet-wheat cropping system in North-Western India. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atere, C.T.; Ge, T.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Shibsitova, O.; Guggenberger, G.; Wu, J. Assimilate allocation by rice and carbon stabilisation in soil: Effect of water management and phosphorus fertilisation. Plant Soil 2019, 445, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooshammer, M.; Wanek, W.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Richter, A. Stoichiometric imbalances between terrestrial decomposer communities and their resources: Mechanisms and implications of microbial adaptations to their resources. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, T.; Chen, Y.; Westby, A.P.; Ren, W. Soil physicochemical and biological properties of paddy-upland rotation: A review. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 856352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Peng, C.; Si, G.; Sha, A.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, S.; Xu, D.; Liu, W. Effects of straw returning on soil chemical properties and microbial community diversity under the rice-crayfish integrated system. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, P.; Nayak, A.K.; Gautam, P.; Lal, B.; Shahid, M.; Raja, R.; Tripathi, R.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Panda, B.B.; Mohanty, S.; et al. Long-term effect of rice-based farming systems on soil health. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, T.; Li, W.; Liu, K. Soil enzymatic activities response to long-term fertilization during key growth stages of early rice. Arch. Für Acker Und Pflanzenbau Und Bodenkd. 2022, 68, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefroy, R.D.B.; Blair, G.J.; Strong, W.M. Changes in soil organic matter with cropping as measured by organic carbon fractions and 13C natural isotope abundance. Plant Soil 1993, 155–156, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.; Said, E.K.; Miloud, S.; Abdellatif, H.; El Hassan, A.; Rachid, B. Effect of agricultural management practices on diversity, abundance, and infectivity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: A review. Symbiosis 2023, 91, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujvari, G.; Turrini, A.; Avio, L.; Agnolucci, M. Possible role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated bacteria in the recruitment of endophytic bacterial communities by plant roots. Mycorrhiza 2021, 31, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Feng, G.; Limpens, E.; Bonfante, P.; Xie, X.; Zhang, L. Cross-kingdom nutrient exchange in the plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus-bacterium continuum. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, M.L.; Murrell, E.; Barbercheck, M.; Kaye, J.; Finney, D.; Garcia-Gonzalez, I.; Bruns, M.A. Fungal community shifts in soils with varied cover crop treatments and edaphic properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Mechanisms and implications of bacterial-fungal competition for soil resources. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Diao, W.; Jia, R.; Sun, W.; Feng, W.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Variations in antibiotic resistomes associated with archaeal, bacterial, and viral communities affected by integrated rice-fish farming in the paddy field ecosystem. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Gu, H.; Gu, Z.; Xv, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of rice-prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense) co-culture on the microbial community of soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 7361–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Ge, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Bai, N.; et al. Long-term rice-crayfish-turtle co-culture maintains high crop yields by improving soil health and increasing soil microbial community stability. Geoderma 2022, 413, 115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, P.; Pun, B.; Joshi, S. Microbial diversity for agricultural productivity. In Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology; Verma, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 519–547. [Google Scholar]
- Lazcano, C.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Revilla, P.; Domínguez, J. Short-term effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial community structure and function. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Microbial community variation and its relationship with soil carbon accumulation during long-term oasis formation. Appl. Soil Ecol. A Sect. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 168, 104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mooshammer, M.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sardans, J.; Wanek, W. The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant-microbial-soil organic matter transformations. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Kirk, M.F. pH as a primary control in environmental microbiology: 1. Thermodynamic perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Zhao, J.; Yan, L.; Feng, G.; Gao, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L. Soil ph is the primary factor driving the distribution and function of microorganisms in farmland soils in northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Netherway, T.; Hildebrand, F.; Pritsch, K.; Drenkhan, R.; Loit, K.; Anslan, S.; Bork, P.; Tedersoo, L. Plant nutrient-acquisition strategies drive topsoil microbiome structure and function. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liu, X. Does arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation influence soil carbon sequestration? Biol. Fertil. Soils 2024, 60, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, W.; Song, F.; Li, X. Diversity and composition of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in the cropland black soils of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X. Stochastic processes contribute to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community assembly in paddy soils along middle and lower Yangtze River. Appl. Soil Ecol. A Sect. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 183, 104759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Bai, E.; Wang, S.; Zong, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, C.; Hagedorn, F. Three-dimensional mapping of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil microbial biomass and their stoichiometry at the global scale. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6728–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Announcement on Early Rice Production Data for 2023 by the National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202308/content_6899676.htm (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- China National Aquatic Products Technical Extension Service Center and Chinese Society of Fisheries. Full Release of the Report on the Development of Integrated Rice-Fish Farming Industry in China (2024). China Fish. 2024, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.J.; Hao, X.J.; Dang, Z.Q.; Yang, L.K. Report on the Development of Integrated Rice-Fish Farming Industry in China (2023). China Fish. 2023, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.J.; Hao, X.J.; Dang, Z.Q.; Yang, L.K. Report on the Development of Integrated Rice-Fish Farming Industry in China (2022). China Fish. 2023, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- China National Aquatic Products Technical Extension Service Center and Chinese Society of Fisheries. Report on the Development of Integrated Rice-Fish Farming Industry in China (2020). China Fish. 2020, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).