Analysis of Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activity, Microbial Diversity in Rhizosphere Soil of Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) Under Organic and Chemical Fertilizers, Irrigation Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Field Experiment Design
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Soil Enzymes Assay
2.5. Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing of Soil Microbial DNA
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Rhizosphere Soil in Coconut
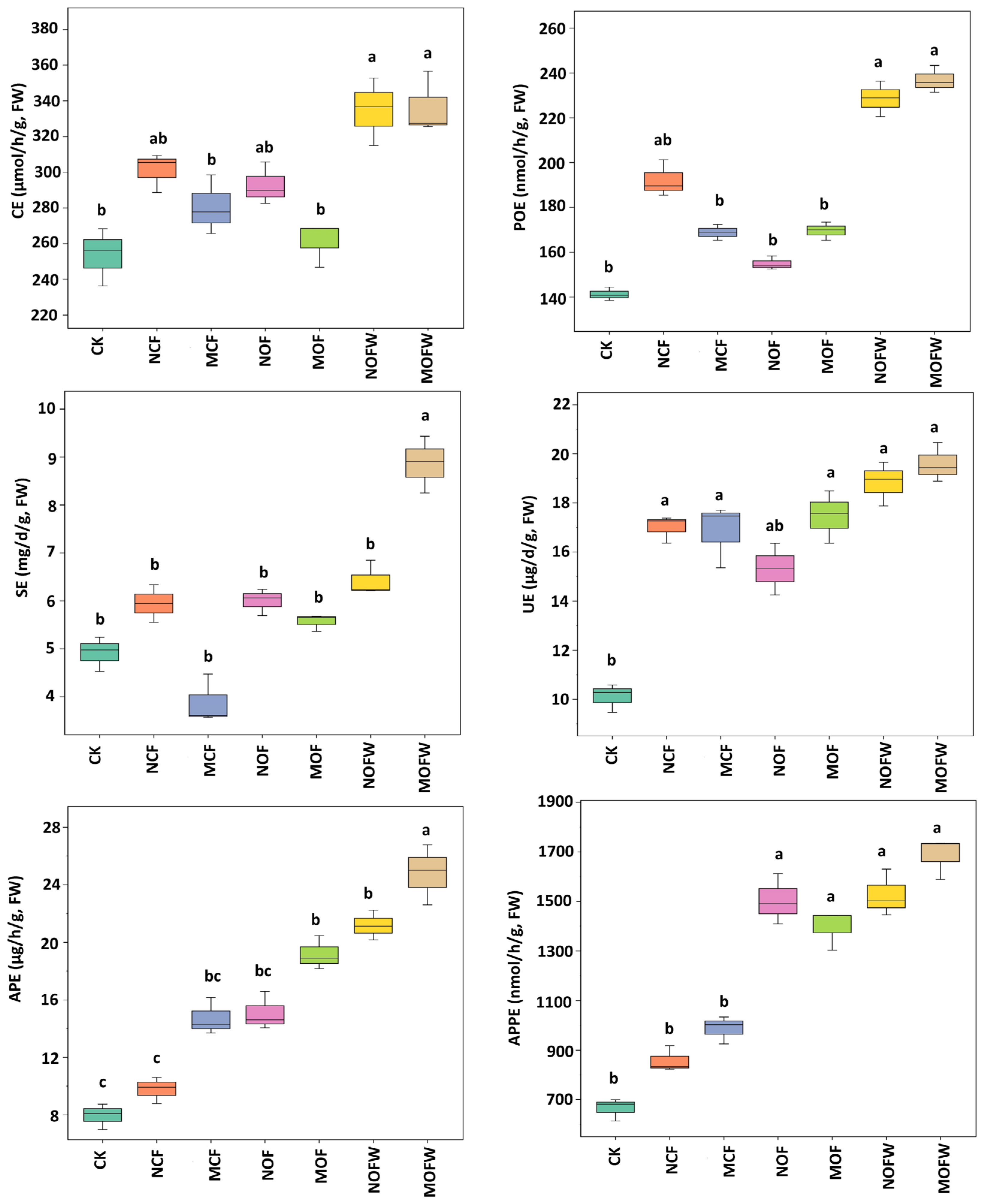
3.2. Enzyme Activity of Rhizosphere Soil in Coconut
3.3. Diversity and Community Structure of Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms
3.3.1. Sequencing Data Preprocessing Results
3.3.2. Diversity of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities
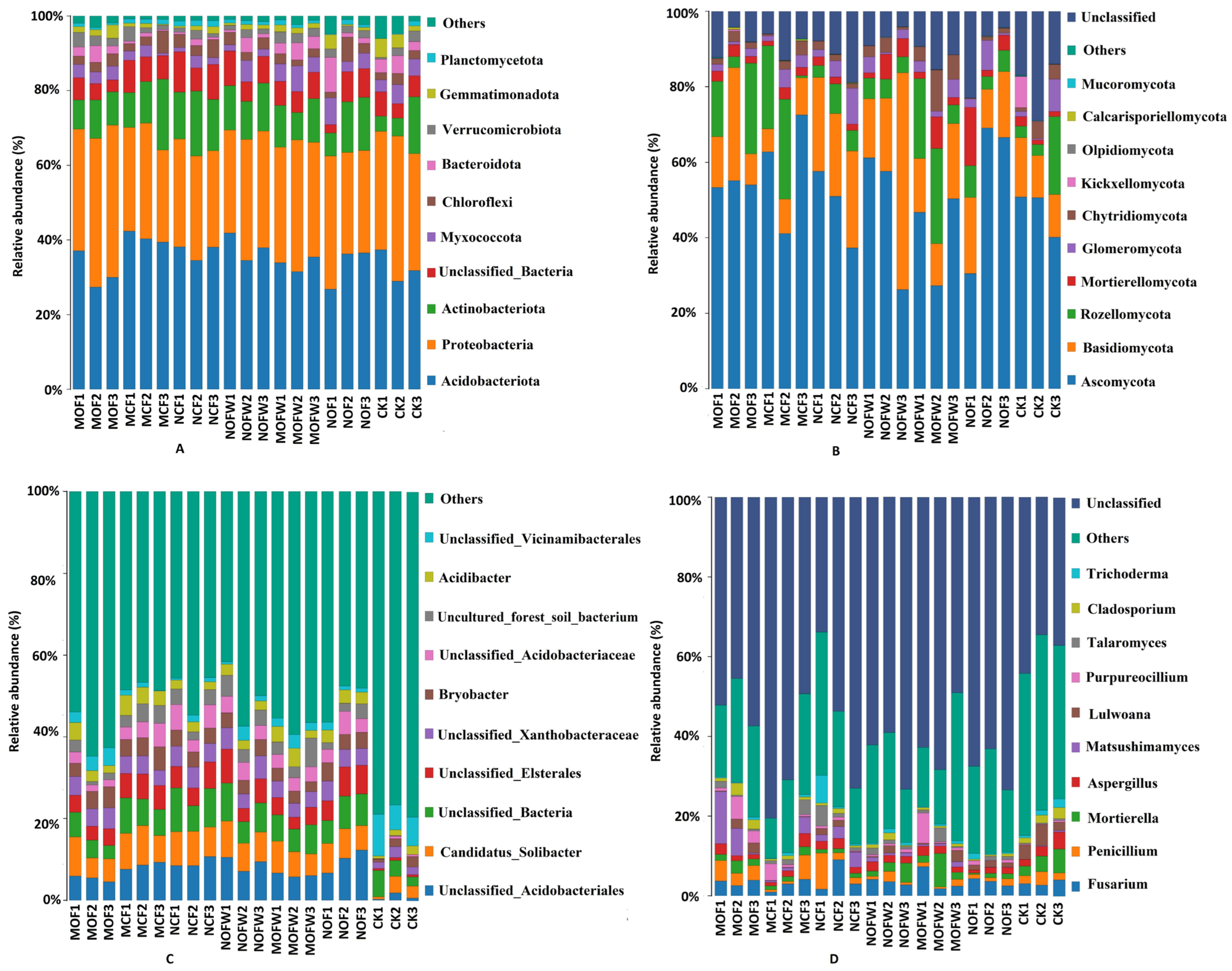
3.3.3. Microbial Community Composition of Rhizosphere Soil
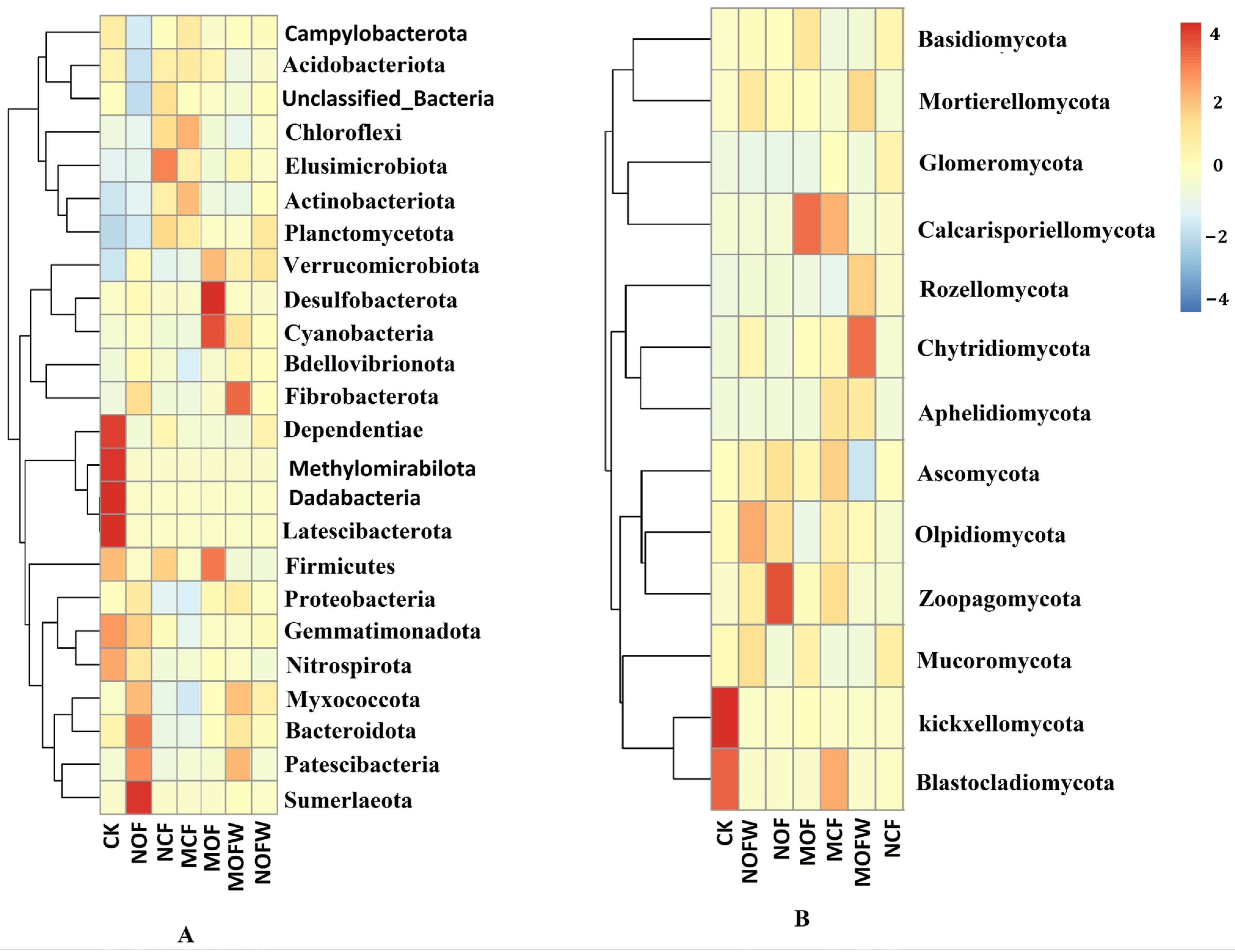
3.4. Differential Analysis of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities
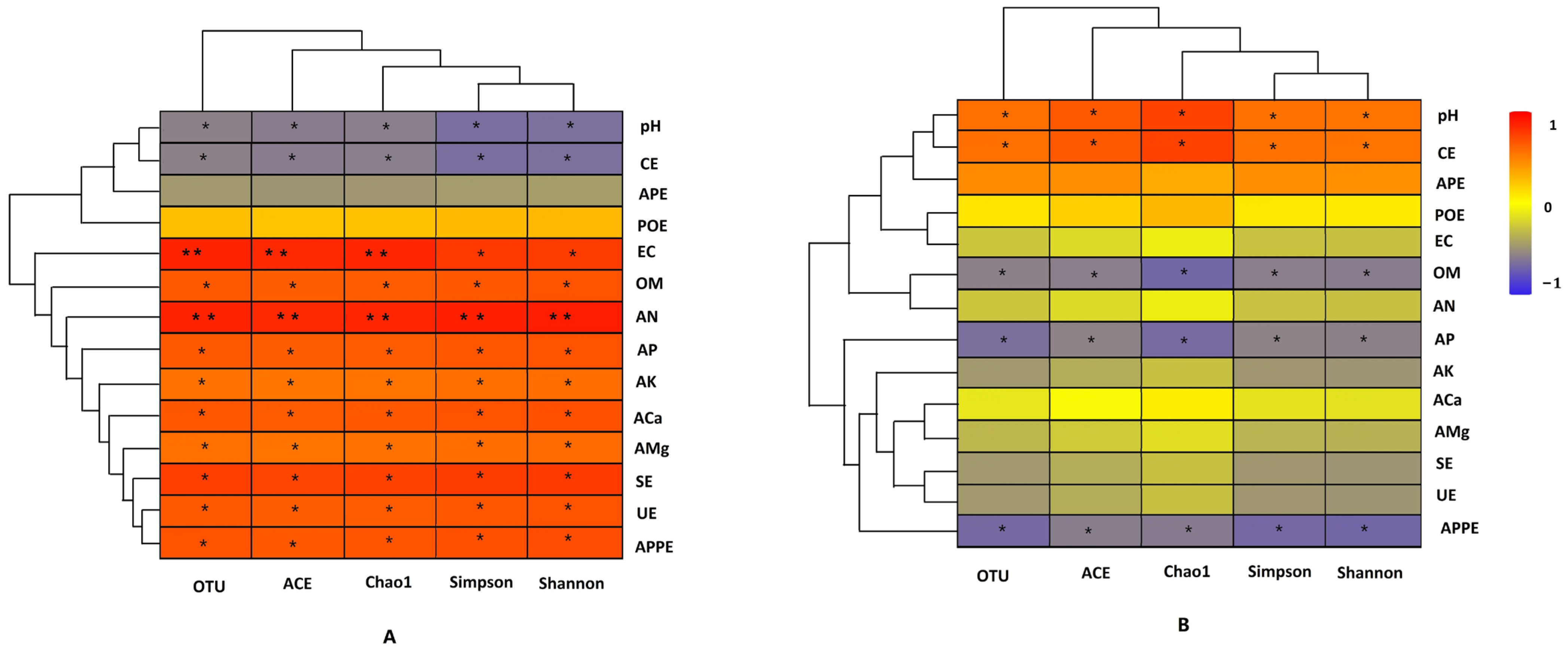
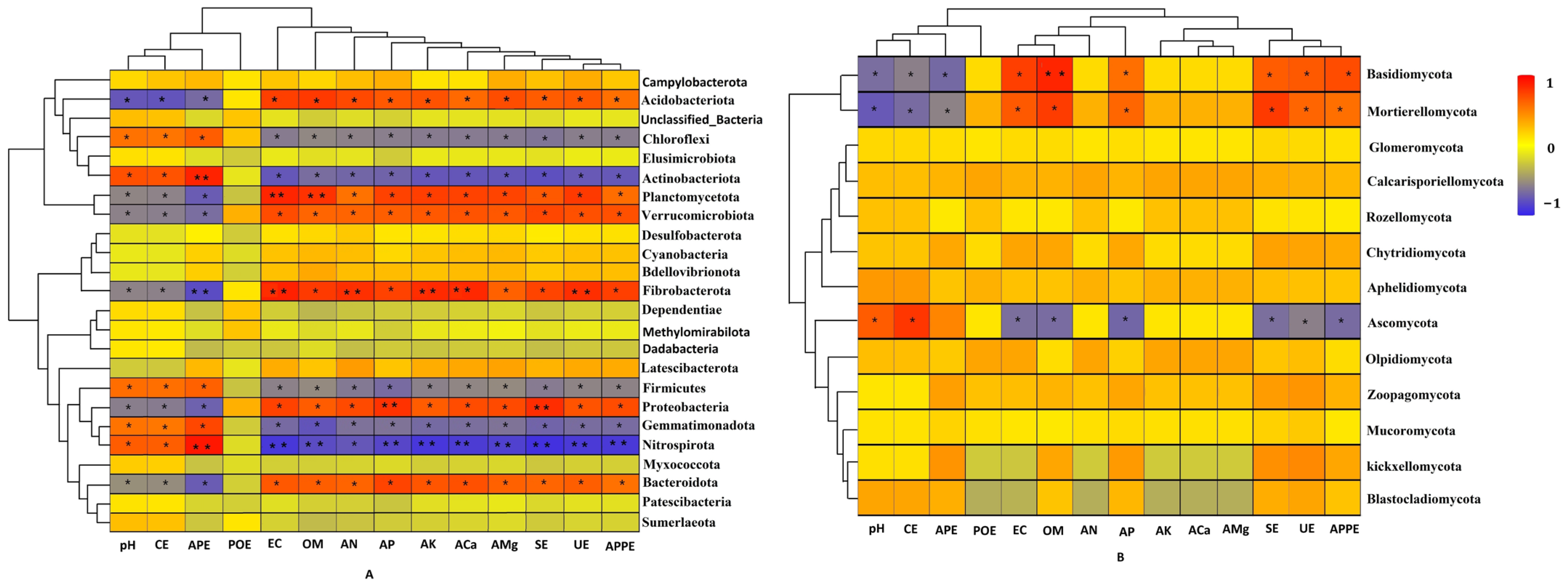
3.5. Relationship Between Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community and Physicochemical Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Organic Fertilizer Treatment on Basic Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activities of Rhizosphere Soil in Coconut
4.2. Effect of Different Fertilizer Treatments on Microbial Community Abundance, Diversity, and Composition of Rhizosphere Soil in Coconut
4.3. The Relationship Between Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activity, and Microorganisms of Rhizosphere Soil in Coconut Under Different Fertilization Treatments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, L.L.; Liu, R.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Shen, X.; Li, H.; Fan, H. Research Progress on Coconut Germplasm Resources, Cultivation and Utilization. J. Trop. Crop. 2021, 42, 1795–1803. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.L.; Huang, Y.K.; Yang, Y.D. Research Methods and Fertilization of Coconut Nutrition-Diagnosis and Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 1–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Liu, L.; Zeng, P.; Sun, C.; Wei, Q. The content and variation patterns of N, P, and K in coconut leaves at different maturity levels. J. Jiangxi Agri. 2009, 21, 64–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.Z.; Tang, H.Y.; Nie, Y.C.; Zhang, X. Responses of cotton growth, yield, and biomass to nitrogen split application ratio. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 35, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.J.; He, M.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Lv, Q.; Xie, R.J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Deng, L.; Yi, S.L.; Li, J. Effects of partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer on Ponkan growth and yield and soil biological properties. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Xiao, H.J.; Zhao, H.; Qin, S.; Gou, J.L.; Zhao, T.F.; Hu, G.; Zhao, L.X.; He, C.X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Effects of commercial organic fertilizer as substitution of chemical fertilizer on growth, yield of spring maize and soil fertility. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 35, 148–152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheteiwy, M.S.; Ali, D.F.S.; Xiong, Y.C.; Brestic, M.; Skalicky, M.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Ulhassan, Z.; Shaghaleh, H.; AbdElgawad, H.; Farooq, M.; et al. Physiological and biochemical responses of soybean plants inoculated with Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Bradyrhizobium under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheteiwy, M.S.; Elgawad, H.A.; Xiong, Y.C.; Macovei, A.; Brestic, M.; Skalicky, M.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; El-Sawah, A.M. Inoculation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and mycorrhiza confers tolerance to drought stress and improve seed yield and quality of soybean plant. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 2153–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, K.; Hana, K.; Ondrej, U.; Strejcek, M.; Jirina, S.; Jindrich, P.T.; Jiri, B.; Katerina, D.; Hana, S. Response of Soil Microbes and Soil Enzymatic Activity to 20 Years of Fertilization. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jin, F.R.; Guan, T.W.; Xu, H.X.; Hu, X.P.; Xie, Q. Short-term effect of partial substitution of inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer on soil fertility and fungal communities in greenhouse. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2021, 30, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, X.; Guan, D.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Zhou, B. Influence of inorganic fertilizer and organic manure application on fungal communities in a long-term field experiment of Chinese Mollisols. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 111, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommermann, L.; Geistlinger, J.; Wibberg, D.; Deubel, A.; Zwanzig, J.; Babin, D.; Schlüter, A.; Schellenberg, I. Fungal community profiles in agricultural soils of a long-term field trial under different tillage, fertilization and crop rotation conditions analyzed by high-throughput ITS-amplicon sequencing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L. Change of soil microbial community under long-term fertilization in a reclaimed sandy agricultural ecosystem. Peer. J. 2019, 7, e6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, A.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liang, G.; Hou, E. Manure acts as a better fertilizer for increasing crop yields than synthetic fertilizer does by improving soil fertility. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okore, C.; Ogechukwu, M.; Bright, O.; Assumpta, U.; Agaptus, O.; Uloma, N.; Chimahhalam, A. Effects of NPK fertilizer on soil enzymes and micro biota. GRF Davos. Planet@Risk 2014, 2, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yi, M.; Yi, H.; Guo, E.; Zhang, A. Manure and mineral fertilization change enzyme activity and bacterial community in millet rhizosphere soils. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holík, L.; Hlisnikovský, L.; Honzík, R.; Trögl, J.; Burdová, H.; Popelka, J. Soil microbial communities and enzyme activities after long-term application of inorganic and organic fertilizers at different depths of the soil profile. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Chung, R.; Tsai, Y. Effect of different application rates of organic fertilizer on soil enzyme activity and microbial population. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 53, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, M.; Jiang, X.; Guan, D.; Wei, D.; Zhao, B. Impact of 36 years of nitrogen fertilization on microbial community composition and soil carbon cycling-related enzyme activities in rhizospheres and bulk soils in northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 136, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bom, F.; Nunes, I.; Sophie, N.; Hansen, V.; Bonnichsen, L.; Magid, J.; Nybroe, O.; Stoumann, L. Long-term fertilisation form, level and duration affect the diversity, structure and functioning of soil microbial communities in the field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.; Lin, H.X.; Li, K.M.; Chen, S.B.; Ou, W.J. Effects of fertilization methods on bacterial diversity and community structure characteristics of cassava rhizosphere soil. J. Fujian Univ. Agric. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 51, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.X.; Liu, J.J.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Yao, Q.; Wang, G.H. Effects of different continuous cropping years of soybeans on the structure of the bacterial community of black soil. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4337–4346. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, T.; Lin, R.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Lin, W.X. Effects of contiInuous cropping on bacterial community diversity in rhizosphere soil of Rehmanniaglutinosa. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, D.S.; Lebeis, S.L.; Paredes, S.H.; Yourstone, S.; Gehring, J.; Malfatti, S.; Tremblay, J.; Engelbrektson, A.; Kunin, V.; Rio, T.G.D.; et al. Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 2012, 488, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Kong, L.; Yang, Q.; Nian, H.; Liang, J. Analysis of Microbial Diversity in Rhizosphere Soil of Panax notoginseng under Different Water and Microbial Fertilizer Conditions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Park, J.; Laurence, J.S.; Parthasarathy, R.; Misra, A.; Spencer, P. Ternary phase diagram of model dentin adhesive exposed to over-wet environments. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-von-Wobeser, E.; Rocha-Estrada, J.; Shapiro, L.R.; de la Torre, M. Enrichment of Verrucomicrobia, Actinobacteria and Burkholderiales drives selection of bacterial community from soil by maize roots in a traditional milpa agroecosystem. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yuan, G.; Jeppesen, E.; Ge, D.; Li, W.; Zou, D.; Huang, Z.; Wu, A.; Liu, Q. Local and regional drivers of turnover and nestedness components of species and functional beta diversity in lake macrophyte communities in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, E.; Ferreras, L.; Toresani, S. Soil bacterial functional diversity as influenced by organic amendment application. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.A.; Zhou, L.M. Soil organic carbon sequestration and fertility response to newly-built terraces with organic manure and mineral fertilizer in a semi-arid environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 172, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of farmland scale on farmers’ application behavior with organic fertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, S.; Fu, X.; Feng, S.; Zhuang, Z. A sustainable agricultural supply chain considering substituting organic manure for chemical fertilizer. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Liang, Y.; Wakelin, S.A.; Chu, G. Supplementing chemical fertilizer with an organic component increases soil biological function and quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wu, Z.; You, Z.; Yi, X.; Ni, K.; Guo, S.; Ruan, J. Effects of organic substitution for synthetic N fertilizer on soil bacterial diversity and community composition: A 10-year field trial in a tea plantation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 268, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Fei, J.; Luo, G. Biochar amendments combined with organic fertilizer improve maize productivity and mitigate nutrient loss by regulating the C–N–P stoichiometry of soil, microbiome, and enzymes. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Swenson, N.G.; Ji, N.; Mi, X.; Ren, H.; Guo, L.; Ma, K. Differential soil fungus accumulation and density dependence of trees in a subtropical forest. Science 2019, 366, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.D. Rarefaction, Alpha Diversity, and Statistics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z. The effect of fertilization on the characteristics of rhizosphere microbial community in oil soybean. Arid. Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, X.; Li, M. Effects of different fertilization treatments on inter-root soil nutrients and fungal communities of ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ grapes. Microbiol. Bull. 2023, 50, 4876–4893. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, K.; Kapoor, K.K.; Gupta, A.P. Impact of organic manures with and without mineral fertilizers on soil chemical and biological properties under tropical conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, C.; Fangueiro, D.; Mota, M.; Martins, M.; Braga, R.P.; Ribeiro, H. Partial replacement of chemical fertilizers with animal manures in an apple orchard: Effects on crop performance and soil fertility. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Barrow, N. Soil pH-nutrient relationships: The diagram. Plant Soil. 2023, 486, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. Crop yield, plant nutrient uptake and soil physicochemical properties under organic soil amendments and nitrogen fertilization on Nitisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.; Saha, S.; Mina, B.; Pande, H.; Kundu, S.; Gupta, H.S. Influence of organic amendments on growth, yield and quality of wheat and on soil properties during transition to organic production. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2008, 82, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.K.; Labanya, R.; Joshi, H.C. Influence of long-term chemical fertilizers and organic manures on soil fertility—A review. Univers. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Chetani, R. A review on the effect of organic and chemical fertilizers on plants. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M. Chemical fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer effectively improve soil fertility and microbial community from newly cultivated land in the Loess Plateau of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165, 103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Káš, M.; Mühlbachová, G.; Kusá, H.; Pechová, M. Soil phosphorus and potassium availability in long-term field experiments with organic and mineral fertilization. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The biological activities of β-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Song, M. The role of plants and soil microorganisms in regulating nutrient cycling in ecosystems. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 34, 979–988. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, X. Changes in the microbial community and enzyme activity in the root zone of cucumber under continuous cropping in a solar greenhouse. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 15, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.G.; Jin, K.; Li, Z.M.; Rong, X.N. Research progress on soil microbial diversity under different fertilization and farming systems. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2010, 16, 744–751. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Z.G.; Yang, S.Y.; Tang, H.Z.; Zhang, X.B.; Wang, B.B.; Lv, L.W. Effects of bioorganic fertilizer on the fungal community of the pineapple rhizosphere and incidence of heart rot. J. Fruit. Sci. 2022, 39, 1678–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Ran, W. Effects of long-term no-tillage and application of organic fertilizer on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2002, 39, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, Z.S.; Jacobs, K.; Hawkins, H.J. The impact of crop rotation on soil microbial diversity: A meta-analysis. Pedobiologia 2016, 59, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Sun, H.F.; Li, C.Y.; Jing, L.Q.; Yang, X.G.; Liu, K. Response of soil microbial community structure to different degradation in alpine swamp wetland in the source region of the Yellow River. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 42, 3971–3984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.J.; Sun, J.P.; Dai, X.L.; Liu, Y.H. Effects of straw returning combined with reduced fertilization on rice yield and soil nutrients. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, J.N.; Lu, M.; Qin, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Yang, L.; Shen, Q.R. Microbial communities of an arable soil treated for 8 years with organic and inorganic fertilizers. Biol. Fertil. Soil. 2016, 52, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Yang, Z. Studies on diversity of higher fungi in Yunnan, southwestern China: A review. Plant Divers. 2018, 40, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.F.; Yi, W.H.; Wang, W.B.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, H.T. Study of soil bacterial diversity in continuous poplar plantation based on high-throughput sequencing technology. Shandong Univ. J. (Sci. Ed.) 2014, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, S.; LI, S.; Jin, B.H.; Quan, Y.J.; Wang, W.P.; Yang, K.; He, H.X. Effects of Panax notoginseng bionic planting on rhizosphere soil microbial diversity in Shilin County. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, Y.X.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Zhao, P. Effects of biological inoculants on the structure and function of soil microbial communities. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.J.; Huang, Y.L.; Jin, R.Y.; Ma, F.Y.; An, R.; Tian, Q.; Chen, B.J. Study on the structure and diversity of soil bacteria in four plantations in the Yellow River Delta based on high-throughput sequencing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Letuma, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, W.; Chen, H.; Lin, W. A positive response of rice rhizosphere to alternate moderate wetting and drying irrigation at grain filling stage. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 207, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.L.; Bastida, F.; Ondoño, S.; García, C.; Manuela, A.A.; Francisco, R.L. Agro-forestry management of Paulownia plantations and their impact on soil biological quality: The effects of fertilization and irrigation treatments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 117, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, G.; Chen, S.; Lan, S.; Wang, D. Effects of different organic fertilizer treatments on the soil microbial community structure in the purple-soil Camellia oleifera forest. Chinese J. Appl. Env. Biol. 2020, 26, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Different Proportions of Organic Fertilizer in Place of Chemical Fertilizer on Microbial Diversity and Community Structure of Pineapple Rhizosphere Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, M.; Krasnov, G.; Semenov, V.; Ksenofontova, N.; Zinyakova, N.B.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Does fresh farmyard manure introduce surviving microbes into soil or activate soil-borne microbiota? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Calderón, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Noll, L.; Böckle, T.; Dietrich, M.; Wanek, W. Soil multifunctionality is affected by the soil environment and by microbial community composition and diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 107521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, H.; Jiang, N.; et al. Organic Fertilizer with High Nutrient Levels Affected Peanut-Growing Soil Bacteria More Than Fungi at Low Doses. Agronomy 2024, 14, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Liang, G.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community in both the rhizosphere and bulk soil to long-term fertilization practices in a fluvo-aquic soil. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Burger, M.; Yang, L.; Gong, P.; Wu, Z. Changes in Soil Carbon and Enzyme Activity as a Result of Different Long-Term Fertilization Regimes in a Greenhouse Field. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akça, M.O.; Namlı, A. Effects of poultry litter biochar on soil enzyme activities and tomato, pepper and lettuce plants growth. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2015, 4, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]





| Microbial Community | Treatments | OTU | ACE | Chao1 | Simpson | Shannon | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | CK | 1118 ± 1.34 b | 1266 ± 1.01 b | 1295 ± 1.22 b | 0.9889 ± 0.004 b | 7.9140 ± 0.02 a | 0.9964 ± 0.003 a |
| NCF | 1176 ± 1.02 ab | 1264 ± 0.97 ab | 1283 ± 1.01 b | 0.9884 ± 0.002 b | 7.8952 ± 0.03 a | 0.9977 ± 0.006 a | |
| MCF | 1161 ± 1.11 ab | 1255 ± 1.18 ab | 1280 ± 1.15 b | 0.9936 ± 0.001 a | 8.3356 ± 0.06 a | 0.9976 ± 0.008 a | |
| NOF | 1260 ± 1.34 ab | 1276 ± 1.02 ab | 1313 ± 1.34 ab | 0.9909 ± 0.002 a | 8.0785 ± 0.03 a | 0.9972 ± 0.006 a | |
| MOF | 1262 ± 1.32 a | 1368 ± 1.05 a | 1391 ± 1.20 a | 0.9918 ± 0.006 a | 8.2896 ± 0.08 a | 0.9971 ± 0.008 a | |
| NOFW | 1322 ± 1.42 a | 1387 ± 1.03 a | 1395 ± 1.24 a | 0.9908 ± 0.001 a | 8.2612 ± 0.05 a | 0.9980 ± 0.004 a | |
| MOFW | 1402 ± 1.41 a | 1481 ± 1.11 a | 1517 ± 1.02 a | 0.9938 ± 0.006 a | 8.4901 ± 0.08 a | 0.9976 ± 0.006 a | |
| Fungi | CK | 750 ± 1.02 a | 903 ± 1.08 a | 927 ± 1.02 a | 0.9739 ± 0.004 a | 7.0966 ± 0.05 a | 0.9985 ± 0.005 a |
| NCF | 672 ± 0.98 ab | 706 ± 0.87 ab | 756 ± 1.04 ab | 0.9724 ± 0.006 a | 6.9655 ± 0.08 a | 0.9993 ± 0.009 a | |
| MCF | 556 ± 0.88 b | 582 ± 0.97 b | 598 ± 1.03 b | 0.9598 ± 0.007 a | 6.5597 ± 0.09 a | 0.9997 ± 0.005 a | |
| NOF | 639 ± 1.23 ab | 718 ± 1.02 ab | 769 ± 1.15 ab | 0.9659 ± 0.007 a | 6.7788 ± 0.07 a | 0.9988 ± 0.009 a | |
| MOF | 729 ± 0.87 a | 898 ± 0.93 a | 906 ± 1.23 a | 0.9641 ± 0.008 a | 6.8733 ± 0.05 a | 0.9986 ± 0.006 a | |
| NOFW | 685 ± 0.88 ab | 739 ± 0.76 ab | 742 ± 1.01 ab | 0.9052 ± 0.008 a | 6.7092 ± 0.08 a | 0.9992 ± 0.009 a | |
| MOFW | 670 ± 1.03 ab | 715 ± 0.84 ab | 744 ± 1.05 ab | 0.9596 ± 0.008 a | 6.6961 ± 0.05 a | 0.9992 ± 0.006 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, L.; Tong, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W. Analysis of Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activity, Microbial Diversity in Rhizosphere Soil of Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) Under Organic and Chemical Fertilizers, Irrigation Conditions. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111937
Lu L, Tong C, Liu Y, Yang W. Analysis of Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activity, Microbial Diversity in Rhizosphere Soil of Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) Under Organic and Chemical Fertilizers, Irrigation Conditions. Agriculture. 2024; 14(11):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111937
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Lilan, Chaoqun Tong, Yingying Liu, and Weibo Yang. 2024. "Analysis of Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activity, Microbial Diversity in Rhizosphere Soil of Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) Under Organic and Chemical Fertilizers, Irrigation Conditions" Agriculture 14, no. 11: 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111937
APA StyleLu, L., Tong, C., Liu, Y., & Yang, W. (2024). Analysis of Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activity, Microbial Diversity in Rhizosphere Soil of Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) Under Organic and Chemical Fertilizers, Irrigation Conditions. Agriculture, 14(11), 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111937





