The Effects of the Combined Application of Biochar and Phosphogypsum on the Physicochemical Properties of Cd-Contaminated Soil and the Yield Quality of Chinese Cabbage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Biochar
2.2. Harmless Disposal of Phosphogypsum
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Biochar and Phosphogypsum
2.4. Test Material
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Analysis of Results
3.1. Effect of Biochar with Phosphogypsum Application on pH of Cd-Contaminated Soil
3.2. The Effects of Biochar Combined with Phosphogypsum on the Contents of Alkali-Hydrolyzable Nitrogen, Available Phosphorus, and Available Potassium in Cd-Contaminated Soil
3.3. Effect of Biochar Combined with Phosphogypsum on Available Cd Content in Cd-Contaminated Soil
3.4. The Effect of the Application of Biochar with Phosphogypsum on the Cd Content in the Edible Part of Chinese Cabbage
3.5. The Effect of the Application of Biochar with Phosphogypsum on the Yield and Quality of Chinese Cabbage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakshi; Singh, S.K.; Haritash, A.K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Soil pollution and remediation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6489–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.R.; Van der Heijden, M.G.; Riedo, J.; Sanz-Lazaro, C.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bastida, F.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Soil contamination in nearby natural areas mirrors that in urban greenspaces worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, S. Legal system of soil pollution remediation in China and its regulation and guidance to soil pollution remediation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y. Technologies for removing heavy metal from contaminated soils on farmland: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Su, H. Employing gene chip technology for monitoring and assessing soil heavy metal pollution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Li, Q.; Peng, H.; Zhang, J.X.; Chen, W.J.; Zhou, B.C.; Chen, M. Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils with soil washing: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaramella, B.R.; Corinzia, S.A.; Cosentino, S.L.; Testa, G. Phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils using safflower. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lin, H.; Du, D.; Li, G.; Alam, O.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J. Remediation of heavy metals polluted soil environment: A critical review on biological approaches. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Dumat, C. A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 182, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Rinklebe, J.; Tack, F.M.; Hou, D. A review of green remediation strategies for heavy metal contaminated soil. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 37, 936–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, U.; Ahmad, H.; Shafqat, H.; Babar, M.; Munir, H.M.S.; Sagir, M.; Khoo, K.S. Remediation techniques for elimination of heavy metal pollutants from soil: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Castro, I.; Molina, L.; Prieto-Fernández, M.Á.; Segura, A. Past, present and future trends in the remediation of heavy-metal contaminated soil-Remediation techniques applied in real soil-contamination events. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, F.; You, X.; Hou, X. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of BcHHP3 under abiotic stress in Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. Chinensis). J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, Y.K.; Barkat, A.; CUI, X.Q.; Ying, F.E.N.G.; PAN, F.S.; Lin, T.A.N.G.; YANG, X.E. Cow manure and cow manure-derived biochar application as a soil amendment for reducing cadmium availability and accumulation by Brassica chinensis L. in acidic red soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Liu, S.; Ye, S.; Yang, H.; Song, B.; Qin, F.; Tan, X. Potential hazards of biochar: The negative environmental impacts of biochar applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcińczyk, M.; Oleszczuk, P. Biochar and engineered biochar as slow-and controlled-release fertilizers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ge, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Shen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, R. Rice straw biochar and lime regulate the availability of heavy metals by managing colloid-associated-but dissolved-heavy metals. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.J.; Zhang, N.M. Research progress on harmless modification of phosphogypsum and its application in farmland soil improvement. Soil 2023, 55, 699–707. [Google Scholar]
- Samet, M.; Charfeddine, M.; Kamoun, L.; Nouri-Ellouze, O.; Gargouri-Bouzid, R. Effect of compost tea containing phosphogypsum on potato plant growth and protection against Fusarium solani infection. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18921–18937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Deng, Y.; Liu, L.; Tian, X.; Gang, S.; Wei, Z.; Yue, K. The addition of biochar as a fertilizer supplement for the attenuation of potentially toxic elements in phosphogypsum-amended soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Mustafa, S.K.; Ditta, A.; Hessini, K. Diminishing heavy metal hazards of contaminated soil via biochar supplementation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, H.; Dinakaran, J.; Notup, T.; Vikram, K.; Rao, K.S. Comparison of adsorption performance of biochar derived from urban biowaste materials for removal of heavy metals. Environ. Manag. 2024, 73, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalovicz, L.; Müller, M.M.L.; Tormena, C.A.; Dick, W.A.; Vicensi, M.; Meert, L. Soil chemical attributes, nutrient uptake and yield of no-till crops as affected by phosphogypsum doses and parceling in southern Brazil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Nan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D.; Qin, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, W. Stress resistance enhancing with biochar application and promotion on crop growth. Biochar 2024, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, B. Application of phosphogypsum in soilization: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 10449–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Y. Preparation and characterization of MgO-modified rice straw biochars. Molecules 2022, 25, 5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Cheng, D.Y.; Shi, J.Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.L.; Wang, L. Study on the adsorption of Cd2+ by potassium permanganate modified wheat straw. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2019, 35, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Li, J.Q.; Bao, L.; Xia, Y.S.; Wang, S.; Wu, L.H.; Zhang, N.M. Effects of different control measures on the accumulation of Cd and lead in lettuce and its quality. Environ. Sci. 2023, 9, 5196–5203. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 17141-1997; Determination of Soil Quality Lead and Cadmium. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- GB/T 3739-2009; Determination of Heavy Metals in Soil. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB 5009.15-2014; Determination of Heavy Metals in Food. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, W.; Bao, L.; Zhang, N.M. Study on the difference of Cd and Pb accumulation and transport in maize by different foliar inhibitors. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.Y.; Yang, K.P.; Zhang, J.; Dai, J.C.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.P. Study on passivation remediation of lead and Cd contaminated soil by manganese dioxide/amino modified biochar. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2023, 39, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.B.; Ruan, S.L.; Zhu, X.L.; Qian, L.H.; Tong, C.M.; Yan, J.L. Effects of passivators on soil available Cd, Pb and their accumulation in the roots of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2024, 40, 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z. Effect of biochars on the immobilization and form of Cd (Cd) in simulated Cd deposition of iron rich soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.Q.; Ge, S.J.; Zheng, W.X.; Liu, J.H.; Chen, M.; Kong, Y.K.; Wang, Y.Y. Passivation remediation of Cd-contaminated soil by thiol-modified biochar and soil microbial response. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 5570–5577. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C.X.; Hu, Y.; Ma, L.P.; Yang, J.; Guo, Z.Y.; Ao, R.; Xie, L.G. The influence mechanism of modified phosphogypsum on the migration and change of heavy metals in sludge. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 9, 5063–5076. [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa, J.M.; Rosado, M.; Paneque, M.; Miller, A.Z.; Knicker, H. Effects of aging under field conditions on biochar structure and composition: Implications for biochar stability in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wei, Y.W.; Ji, X.M.; Yun, F.; Zou, K.; Long, Z. Effects of combined application of biochar-based fertilizer and Trichoderma harzianum agent on the quality of flue-cured tobacco and tobacco-planting soil. J. Crops 2021, 3, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.J.; Xia, H.J.; Liu, F.D.; Kong, W.J.; Lu, S.Y. Biochar characteristics and their effects on soil properties and mechanisms. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Feng, M.Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.J. Effects of straw biochar on the growth and development of Chinese cabbage and soil properties. South. Agric. 2019, 13, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.G.; Bai, L.H.; Yue, X.R.; Xia, Y.S.; Hong, C.Q.; Zhu, J. Analysis of chemical characteristics of main phosphogypsum in Yunnan Province. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2012, 5, 756–762. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, F.; Luo, X.; Ren, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J. Influence of EMR–Phosphogypsum–Biochar Mixtures on Sudan Grass: Growth Dynamics and Heavy Metal Immobilization. Agronomy 2024, 14, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Q.; Fan, S.; Wang, J.; Mu, S.; Zhu, C. Combined Application of Desulfurization Gypsum and Biochar for Improving Saline-Alkali Soils: A Strategy to Improve Newly Reclaimed Cropland in Coastal Mudflats. Land 2023, 12, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, H.S.; Gao, Z.Q.; Shang, X.S.; Zheng, P.H.; Yin, J.; Ma, S.J. The effects of phosphogypsum on CO2 emission and wheat yield in wheat field and its economic and environmental benefits were analyzed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.H.; Han, Y.Q.; Liu, M.M.; Du, J.D. Effects of different improvement measures on the growth and yield of kidney bean in saline-alkali land. J. Heilongjiang Bayi Agric. Univ. 2018, 30, 1–7+16. [Google Scholar]

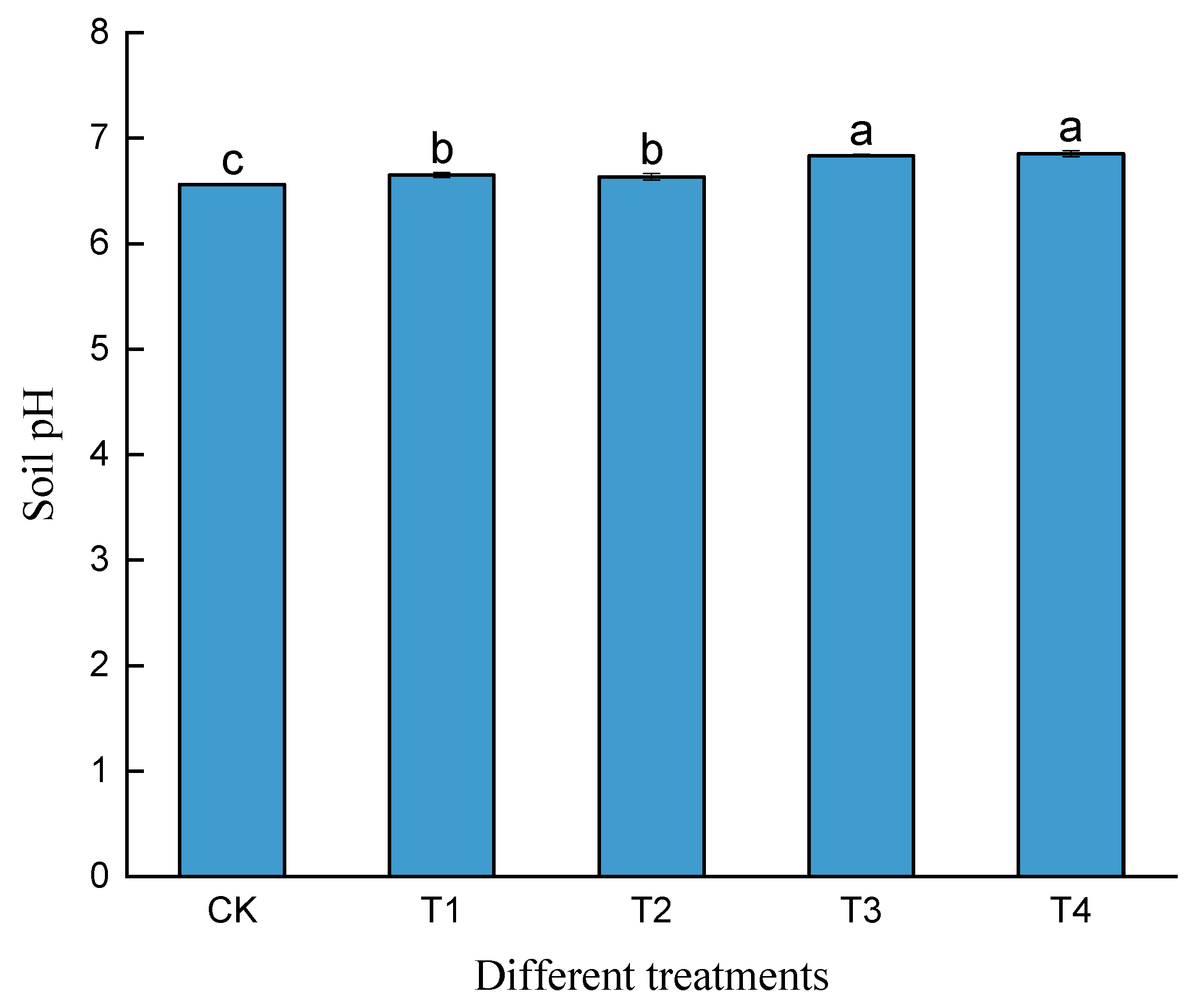
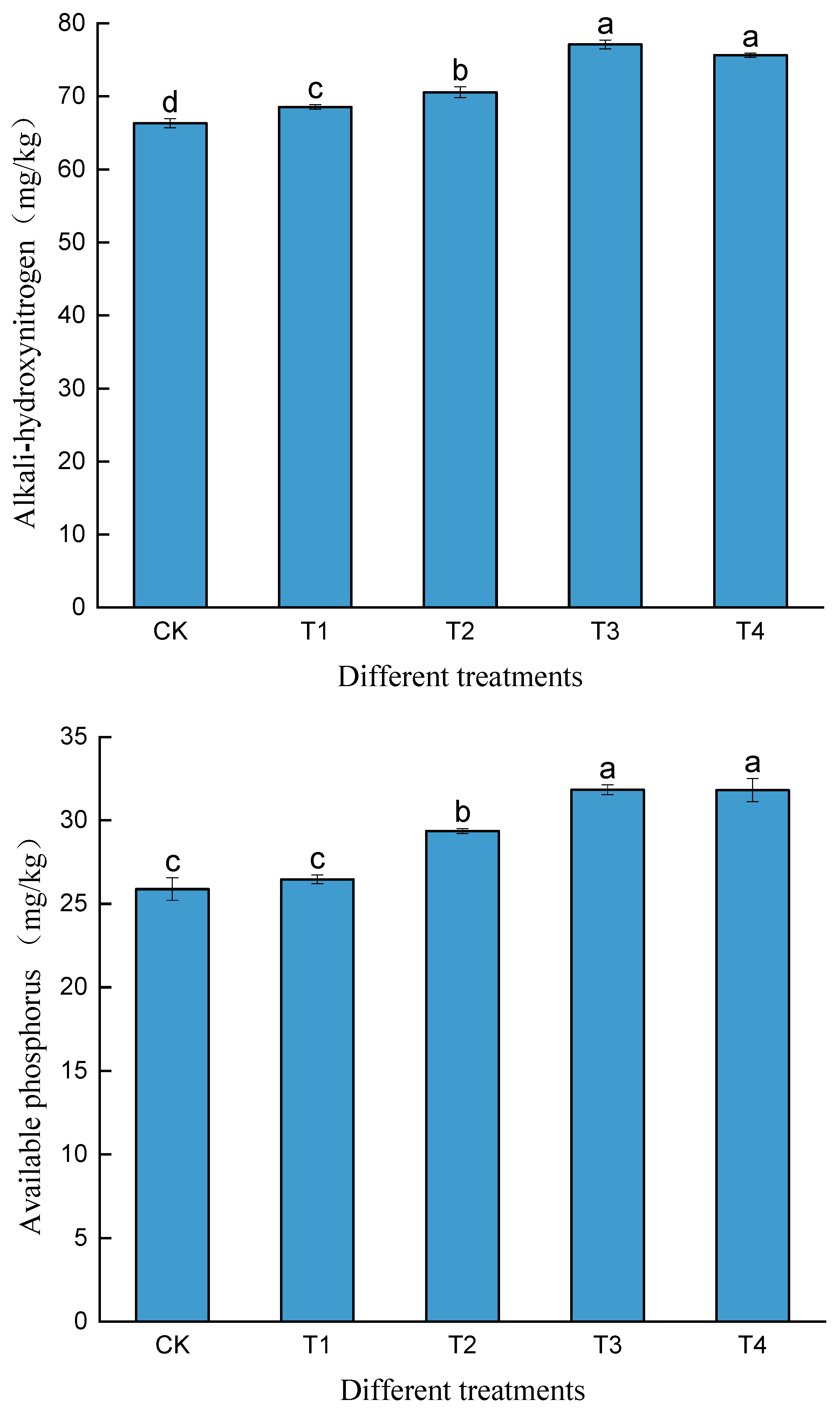
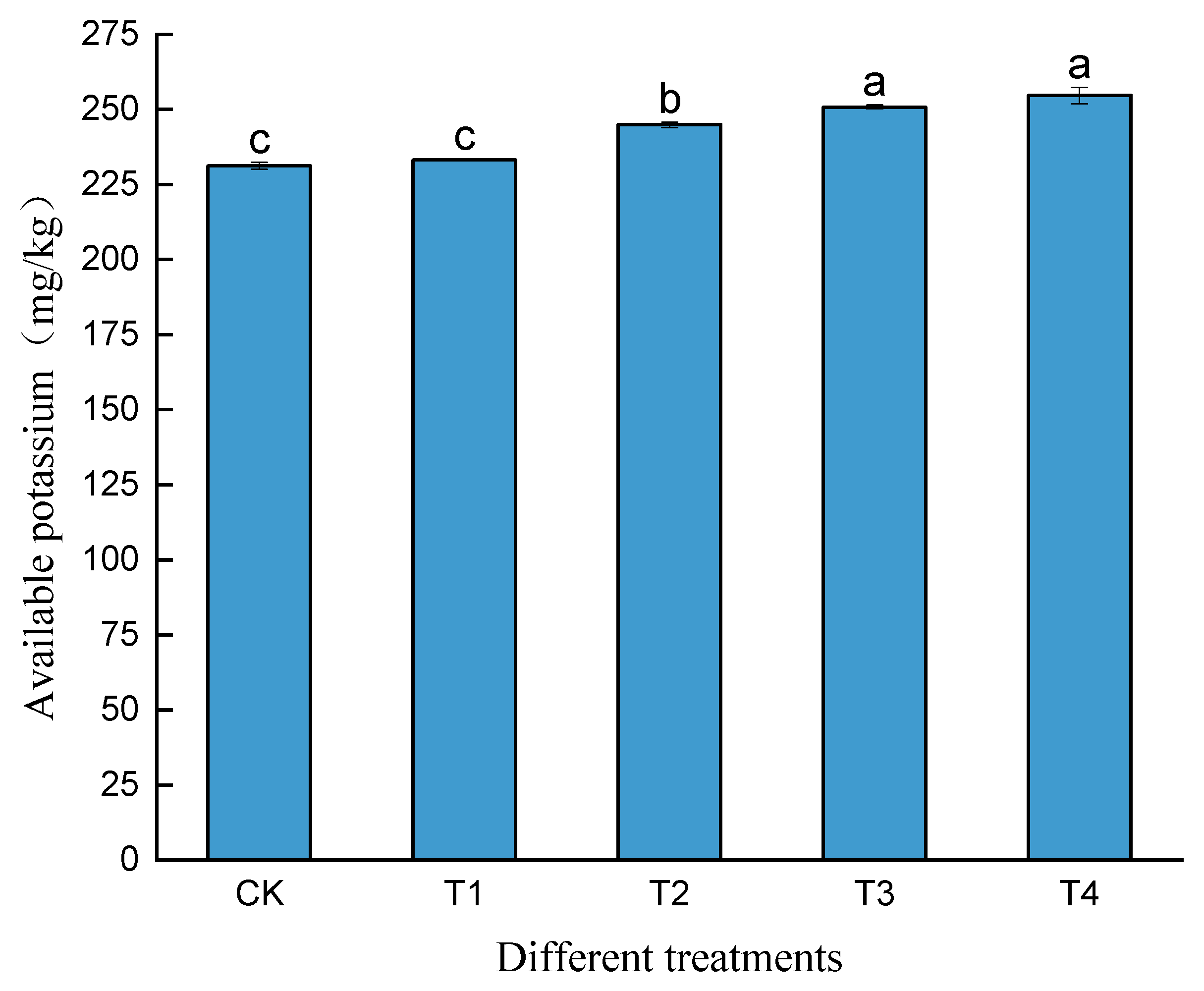
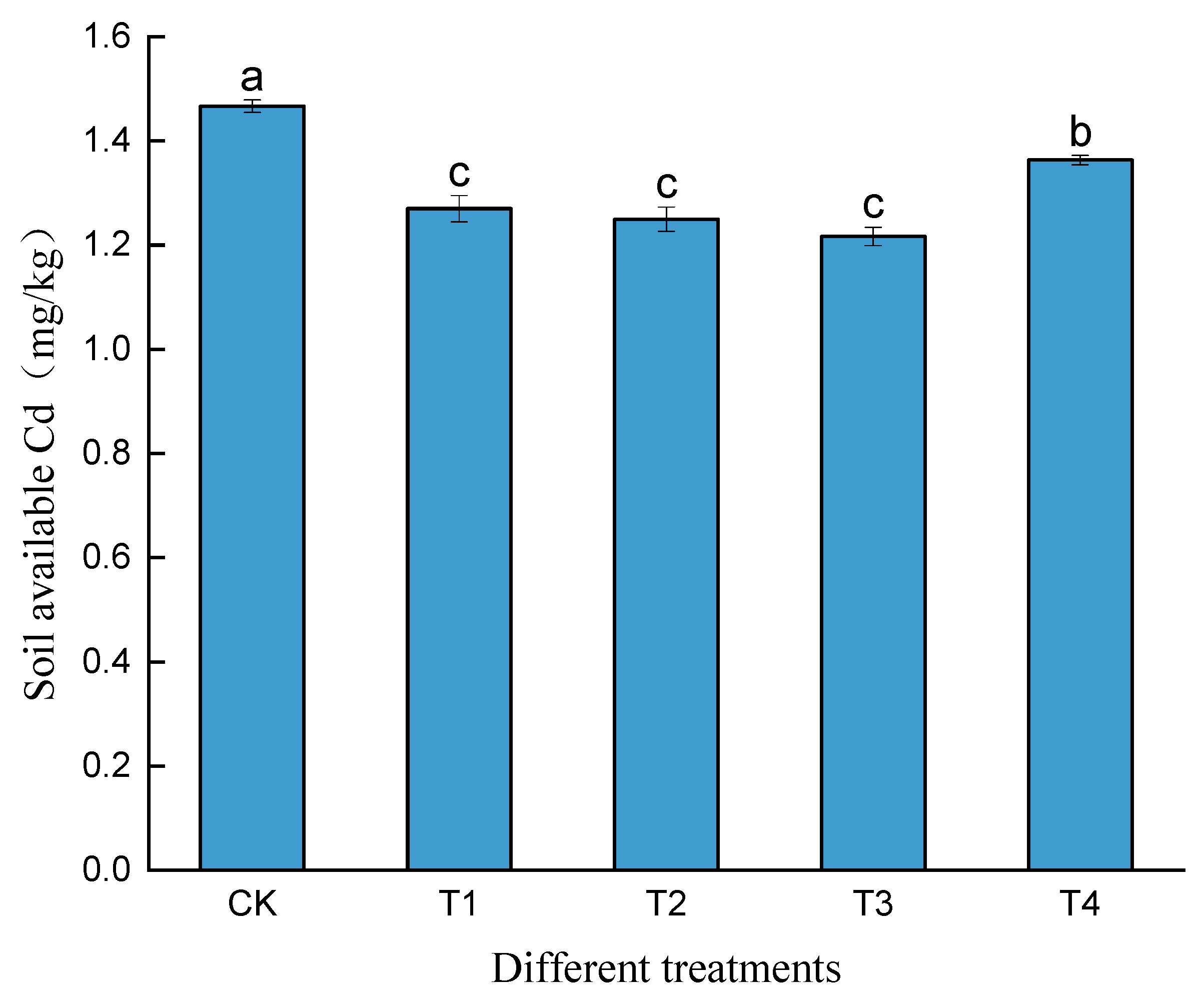

| pH | OM (g/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | Total Cd (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 6.34 | 21.6 | 68.87 | 25.4 | 233.67 | 2.32 |
| Phosphogypsum | 7.53 | 211.5 | 24.26 | 84.41 | 67.12 | 0.11 |
| Biochar | 8.56 | 617.3 | 73.62 | 36.81 | 51.74 | 0.09 |
| Yield (g) | Soluble Sugar (%) | Vitamin C (mg/100 g) | Chlorophyll (mg/100 g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 18.83 ± 0.24 d | 2.83 ± 0.04 c | 2.60 ± 0.04 c | 2.86 ± 0.01 c |
| T1 | 20.54 ± 0.27 c | 2.90 ± 0.06 bc | 2.83 ± 0.02 b | 3.09 ± 0.01 b |
| T2 | 19.20 ± 0.17 d | 2.95 ± 0.06 abc | 2.76 ± 0.03 b | 3.07 ± 0.02 b |
| T3 | 24.83 ± 0.68 a | 3.10 ± 0.02 a | 3.00 ± 0.02 a | 3.24 ± 0.02 a |
| T4 | 22.20 ± 0.34 b | 3.07 ± 0.06 ab | 3.03 ± 0.05 a | 3.12 ± 0.01 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, A.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Zhang, N.; Bao, L. The Effects of the Combined Application of Biochar and Phosphogypsum on the Physicochemical Properties of Cd-Contaminated Soil and the Yield Quality of Chinese Cabbage. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111865
Mu L, Zhou H, Li A, Wang L, Wang J, Sun S, Zhang N, Bao L. The Effects of the Combined Application of Biochar and Phosphogypsum on the Physicochemical Properties of Cd-Contaminated Soil and the Yield Quality of Chinese Cabbage. Agriculture. 2024; 14(11):1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111865
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Liyuan, Hongyin Zhou, Ao Li, Lijuan Wang, Junlei Wang, Sijing Sun, Naiming Zhang, and Li Bao. 2024. "The Effects of the Combined Application of Biochar and Phosphogypsum on the Physicochemical Properties of Cd-Contaminated Soil and the Yield Quality of Chinese Cabbage" Agriculture 14, no. 11: 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111865
APA StyleMu, L., Zhou, H., Li, A., Wang, L., Wang, J., Sun, S., Zhang, N., & Bao, L. (2024). The Effects of the Combined Application of Biochar and Phosphogypsum on the Physicochemical Properties of Cd-Contaminated Soil and the Yield Quality of Chinese Cabbage. Agriculture, 14(11), 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111865





