The Spatiotemporal Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Forces of Carbon Emissions from Major Livestock Farming in the Shaanxi–Gansu–Ningxia Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
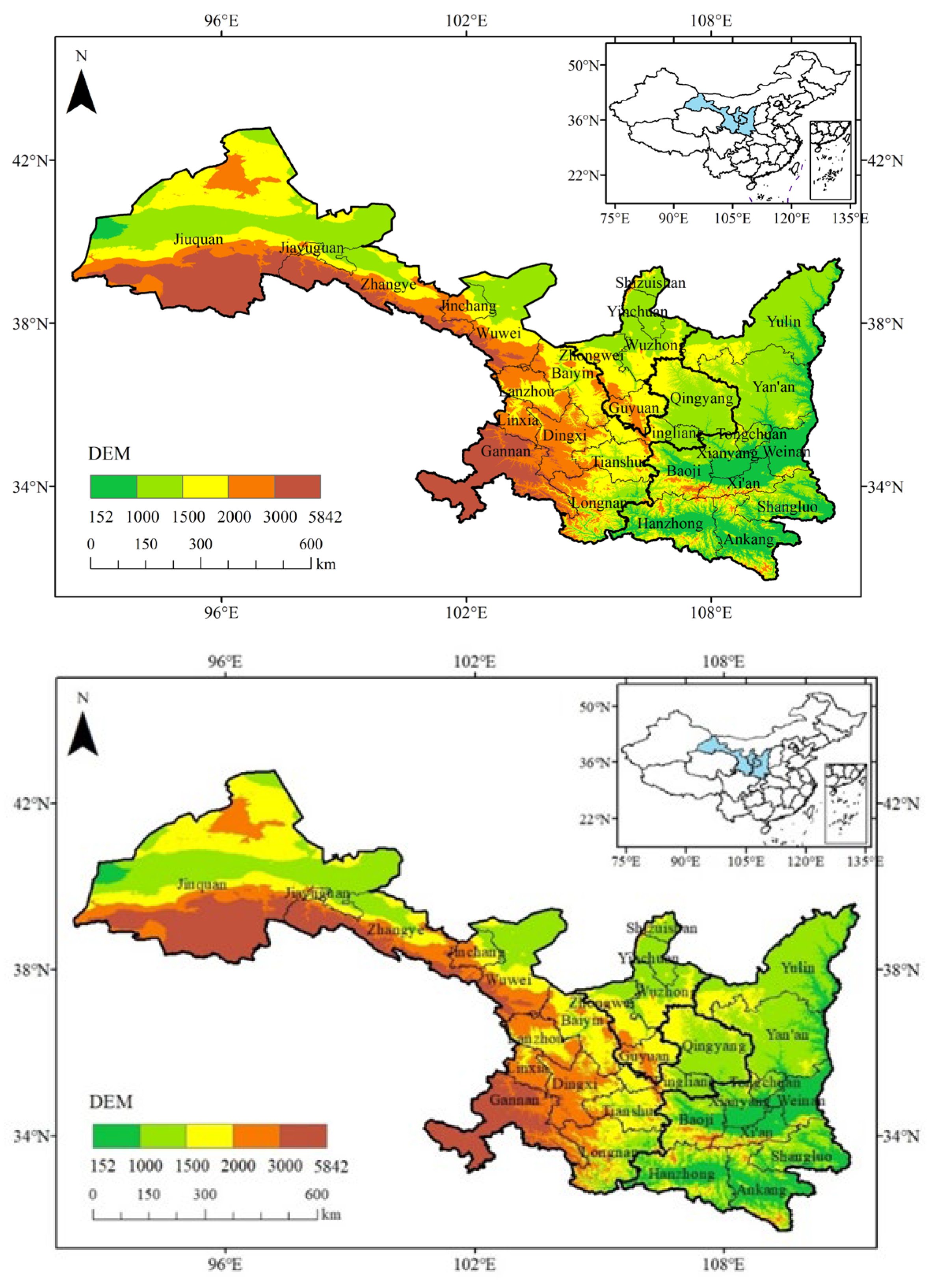
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. CEs and CEI Measurement Methods for Pig, Cattle, and Sheep Rearing
2.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
2.3.3. GeoDetector
3. Results
3.1. Spatial–Temporal Evolution of CEs from Pig, Cattle, and Sheep Rearing in the SGN Region
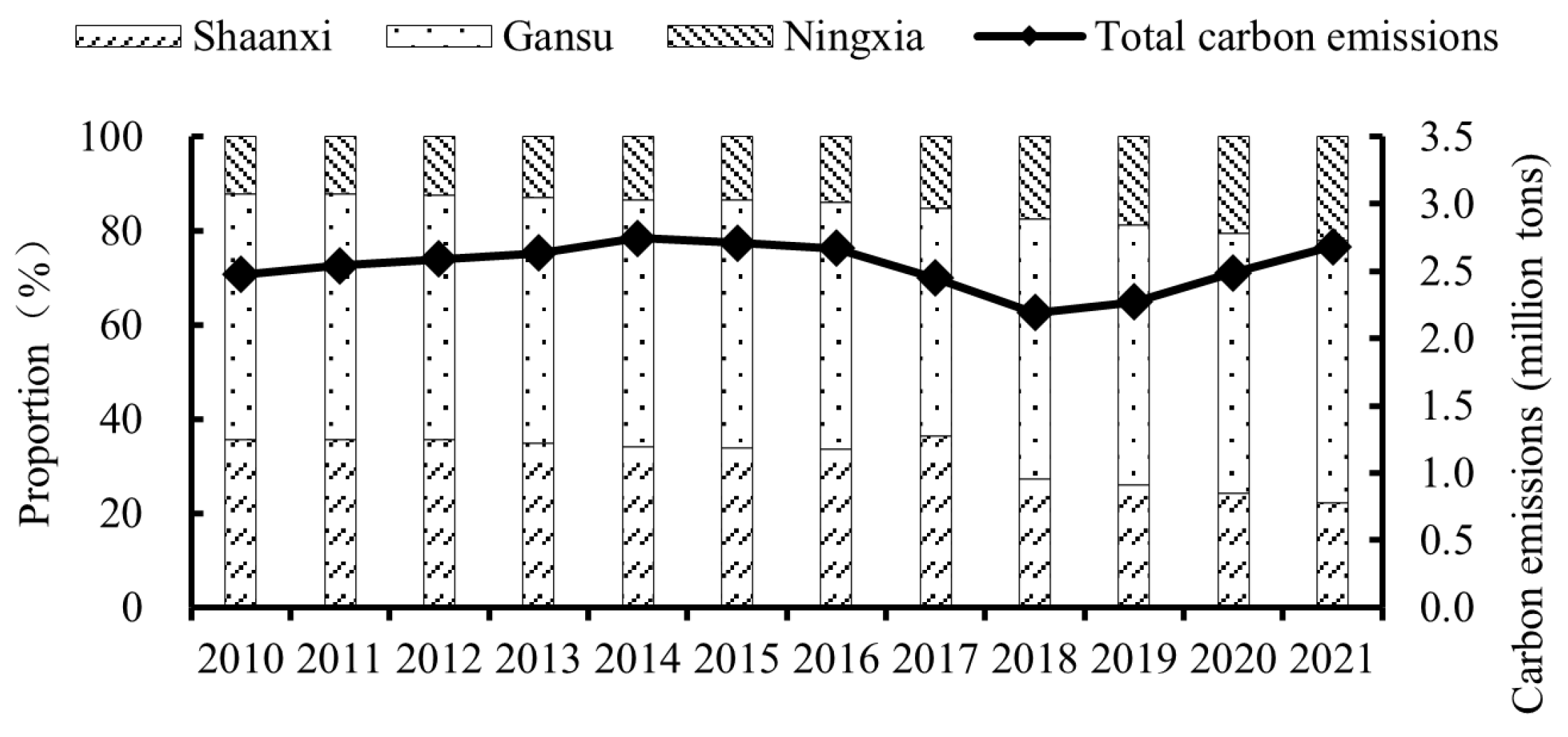
3.1.1. Temporal Evolution of CEs from Pig, Cattle, and Sheep Rearing in SGN Region
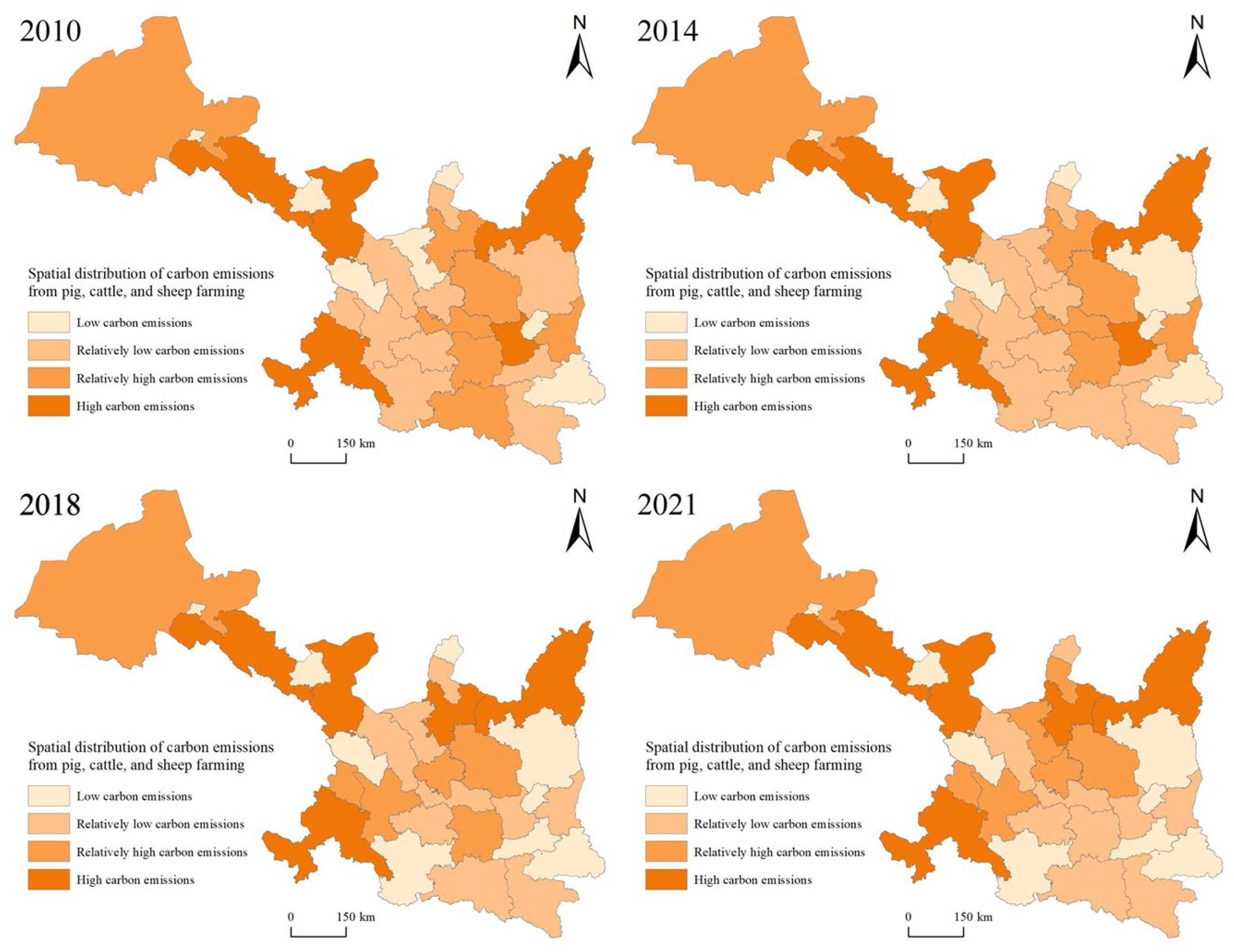
3.1.2. Trends in Spatial Evolution of CEs from Pig, Cattle, and Sheep Rearing in the SGN Region
3.2. Trends in the Spatial–Temporal Evolution of the CEI in the SGN Region
3.2.1. Temporal Evolution of the CEI in the SGN Region
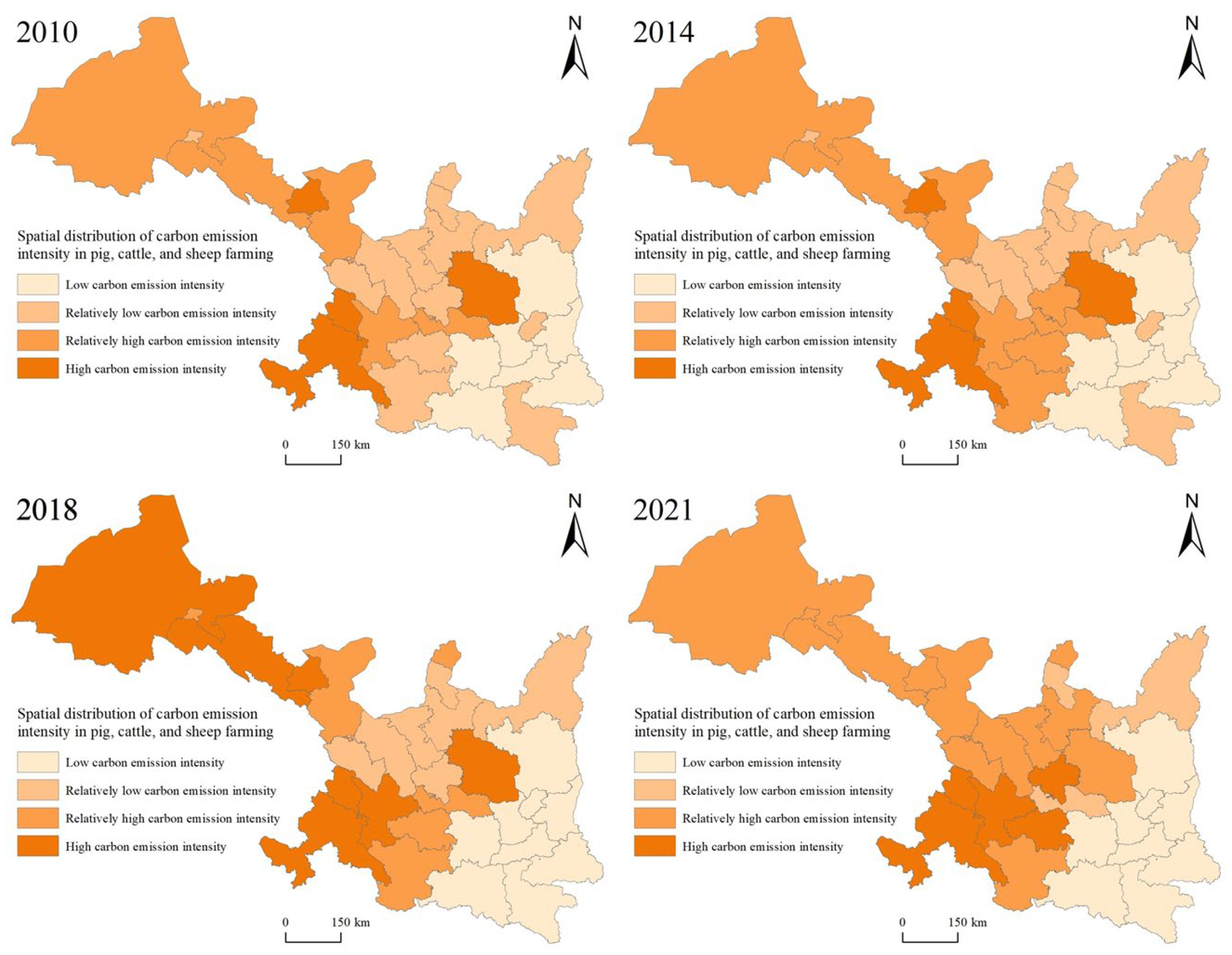
3.2.2. Spatial Evolution Trend of the CEI in the SGN Region
3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis Based on the Moran Index I
3.4. Analysis of the Driving Forces of the CEI in the SGN Region
3.4.1. Driving Force Indicators
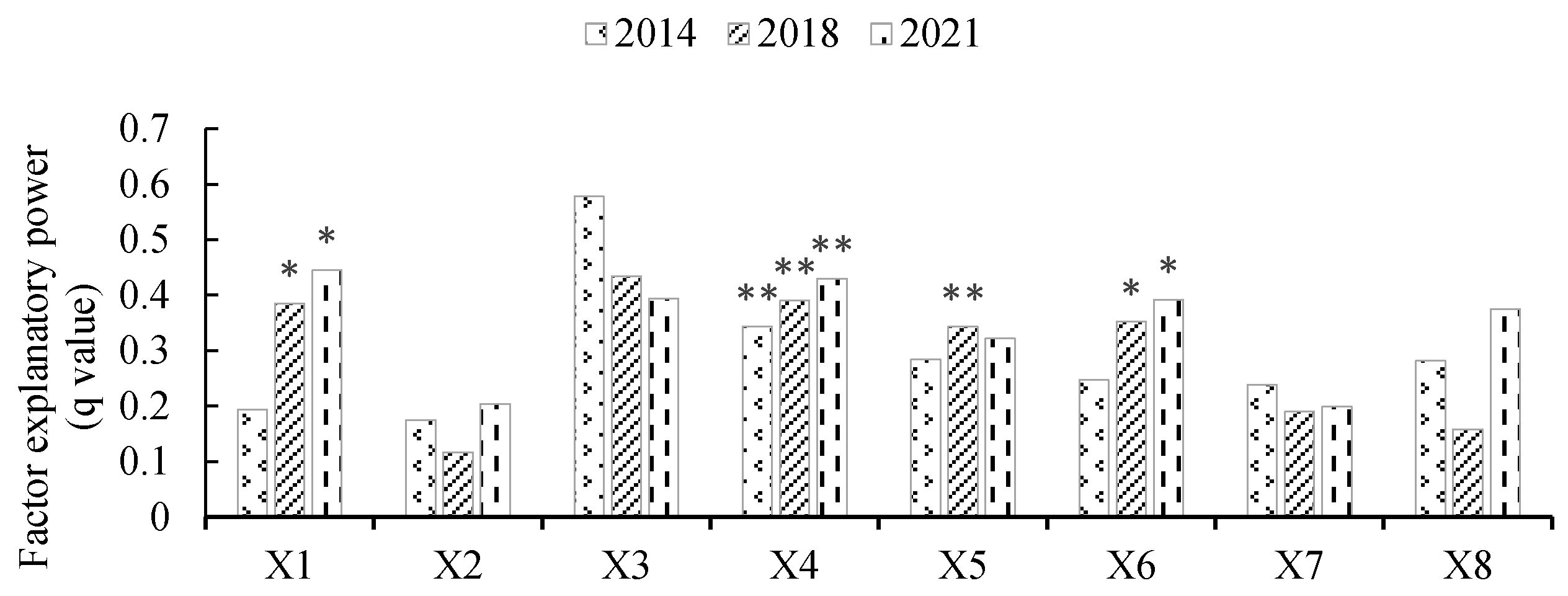
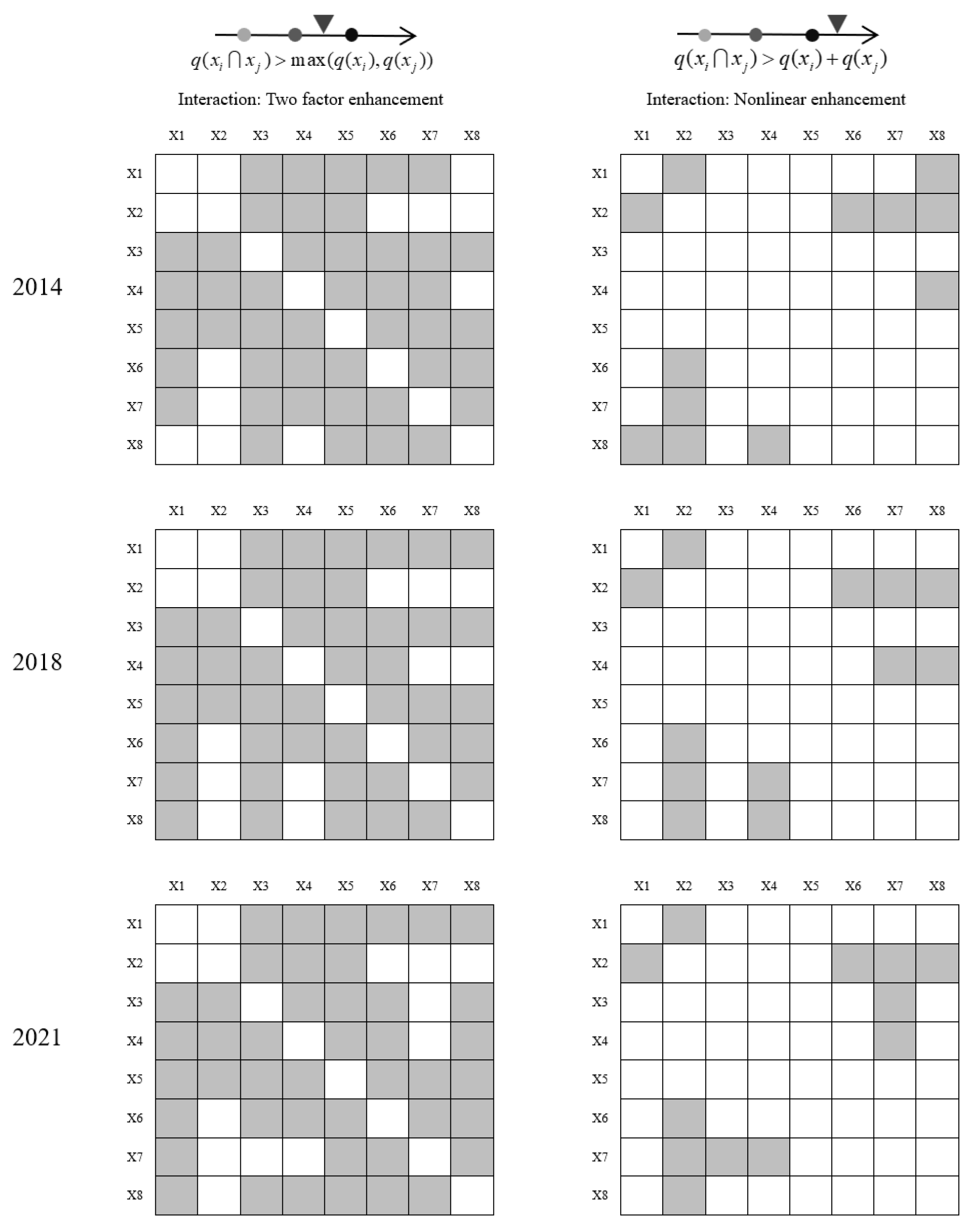
3.4.2. Analysis of the Results of the GeoDetector Measurements
4. Discussion
4.1. Research on CEs and Carbon Intensity
4.2. Focus of Future Policy
4.3. Research Deficiencies and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenzweig, C.; Mbow, C.; Barioni, L.G.; Benton, T.G.; Herrero, M.; Krishnapillai, M.; Liwenga, E.T.; Pradhan, P.; Rivera-Ferre, M.G.; Sapkota, T.; et al. Climate Change Responses Benefit from a Global Food System Approach. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, X. From Large to Powerful: International Comparison, Challenges and Strategic Choices for China’s Livestock Industry. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomislav, K. The Concept of Sustainable Development: From Its Beginning to the Contemporary Issues. Zagreb Int. Rev. Econ. Bus. 2018, 21, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Xie, B. Spatial distance-based integrated evaluation of environmentally sensitivity for ecological management in northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Guo, Z.; Shi, P.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Pang, S.; Xie, B. Spatiotemporal Changes of Land Desertification Sensitivity in Northwest China from 2000 to 2017. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J. “South to North Migration of Pigs” marks the beginning of the adjustment of pig farming layout. New Rural. Technol. 2018, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Coluccia, B.; Agnusdei, G.P.; de Leo, F.; Vecchio, Y.; La Fata, C.M.; Miglietta, P.P. Assessing the Carbon Footprint across the Supply Chain: Cow Milk vs Soy Drink. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laca, A.; Gómez, N.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Overview on GHG Emissions of Raw Milk Production and a Comparison of Milk and Cheese Carbon Footprints of Two Different Systems from Northern Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1650–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Yao, W. Trend Prediction of Carbon Peak in China’s Animal Husbandry Based on the Empirical Analysis of 31 Provinces in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 2017–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, Y. Quantitative Assessment, Spatial and Temporal Characteristics, and Dynamic Evolution of Carbon Emissions from Animal Husbandry in China: 2001–2020. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 116186–116201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Godde, C.; Medina-Hidalgo, D.; van Wijk, M.; Silvestri, S.; Douxchamps, S.; Stephenson, E.; Power, B.; Rigolot, C.; Cacho, O.; et al. Closing System-Wide Yield Gaps to Increase Food Production and Mitigate GHGs among Mixed Crop–Livestock Smallholders in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Syst. 2016, 143, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesschen, J.P.; van den Berg, M.; Westhoek, H.J.; Witzke, H.P.; Oenema, O. Greenhouse Gas Emission Profiles of European Livestock Sectors. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2011, 166–167, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirone, R.; Paulillo, A.; Salatino, P.; Salzano, A.; Cristofaro, B.; Cristiano, T.; Campanile, G.; Neglia, G. Life Cycle Assessment of Buffalo Milk: A Case Study of Three Farms in Southern Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.E.; Tricarico, J.M.; Kebreab, E. Impact of Nitrate and 3-Nitrooxypropanol on the Carbon Footprints of Milk from Cattle Produced in Confined-Feeding Systems across Regions in the United States: A Life Cycle Analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 5074–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, C. Impact of Industrial Agglomeration on Carbon Emissions from Dairy Farming—Empirical Analysis Based on Life Cycle Assessmsent Method and Spatial Durbin Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 137081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y. Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Increased Carbon Footprint on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during Past Three Decades. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Chen, K.; Ma, H.; He, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Huang, T.; et al. Carbon Footprints in Pork Production and Consumption in China from 2005 to 2020. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wei, K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. The Relationship between Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Economic Development and Carbon Emissions in Henan Province, the Analysis of Factors Affecting Carbon Emissions, and Carbon Emissions Prediction. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizga, J.; Feng, K.; Hubacek, K. Drivers of CO Emissions in the Former Soviet Union: A Country Level IPAT Analysis from 1990 to 20102. Energy 2013, 59, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, J.L.; Ma, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, Y. Development of an Extended STIRPAT Model to Assess the Driving Factors of Household Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Ma, W.; Li, C.; Yang, H.; Xue, B.; Gou, X. The Equity of Carbon Emissions in International Trade from the Perspective of Value Added. Geogr. J. 2023, 159, e12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Duan, F.; Wang, Y. Initial Provincial Allocation and Equity Evaluation of China’s Carbon Emission Rights—Based on the Improved TOPSIS Method. Sustainability 2018, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, X. Forecasting China’s Energy Consumption and Carbon Emission Based on Multiple Decomposition Strategy. Energy Strateg. Rev. 2023, 49, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zeng, B.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, X. Forecasting Chinese Carbon Emissions Using a Novel Grey Rolling Prediction Model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 147, 110968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Zhu, D.; Jia, Y. Research on the Policy Effect and Mechanism of Carbon Emission Trading on the Total Factor Productivity of Agricultural Enterprises. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, J.; Gao, X.; Chen, L. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Agriculture Green Total Factor Productivity in China, 1998-2016: Based on More Sophisticated Calculations of Carbon Emissions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Yang, W.; Jiang, X.; Lian, J.; Hu, D.; Yan, X.; Yan, L. A novel integrated urban flood risk assessment approach coupling GeoDetector-dematel and clustering method. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, M. Regional Difference Decomposition and Its Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evolution of Chinese Agricultural Carbon Emission: Considering Carbon Sink Effect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38909–38928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; He, T.; Khan, A.; Zhao, M. Carbon Emissions Changes of Animal Husbandry in China: Trends, Attributions, and Solutions: A Spatial Shift-Share Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Guo, Z. Influencing Mechanism of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Mitigation Strategies of Livestock Sector in Developed Regions of Eastern China: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39937–39947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Qian, S.; Li, Z.; Liang, L. Measurement and spatiotemporal evolution mechanism of carbon emissions from inter provincial animal husbandry in China. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 698–712. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Analysis of regional differences, dynamic evolution and convergence of carbon emissions in China’s livestock industry—Based on livestock industry data from 31 provinces (cities) in China, 1997–2017. Jianghan Trib. 2020, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Quantitative assessment, temporal and spatial characteristics and dynamic evolution of China’s animal husbandry carbon emissions: 2001–2020. J. Arid. Land. Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Shen, S.; Zhang, B. The spatial pattern and influencing factors of coupling coordination in five dimensions of rural revitalization in China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, 42, 218–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetectors: Principles and Prospects. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Driving Forces and Their Interactions of Built-up Land Expansion Based on the Geographical Detector—A Case Study of Beijing, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 2188–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, P.; Lo, K.; Li, J.; Liu, S. The Urban Transition Performance of Resource-Based Cities in Northeast China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Jing, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, J. A Cellular Automaton Model for Grasshopper Population Dynamics in Inner Mongolia Steppe Habitats. Ecol. Model. 2016, 329, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Yang, X. Landscape Spatial Patterns in the Maowusu (Mu Us) Sandy Land, Northern China and Their Impact Factors. Catena 2016, 145, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y. Real Drivers and Spatial Characteristics of CO2 Emissions from Animal Husbandry: A Regional Empirical Study of China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Wang, R.; Gao, C.; Song, X.; Liu, W.; Hu, G. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Influence Factors of Carbon Emission from Livestock Industry in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Y. Assessing Carbon Emissions from Animal Husbandry in China: Trends, Regional Variations and Mitigation Strategies. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Zhu, H.; Cui, Y. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emissions of China’s Livestock Husbandry in the Post-COVID-19 Era-Based on the Supply-Side Perspective. Sustainability 2023, 15, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, S.; Pan, C.; Xu, S.; Lei, Q. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Carbon Emission Efficiency of Pig Farming and the Influencing Factors in China. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1073902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Q.; Bao, Y.; Fu, E.; Chen, Y.; Ni, T. Research on the Measurement and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emissions in the Swine Industry from the Perspective of the Industry Chain. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manioudis, M.; Meramveliotakis, G. Broad Strokes towards a Grand Theory in the Analysis of Sustainable Development: A Return to the Classical Political Economy. New Polit. Econ. 2022, 27, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| City (State) | Drop % | Ranking | City (State) | Drop % | Ranking | City (State) | Drop % | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tongchuan | 87.38 | 1 | Yulin | 68.06 | 11 | Wuzhong | 48.17 | 21 |
| Xi’an | 81.48 | 2 | Jiuquan | 67.26 | 12 | Yinchuang | 47.99 | 22 |
| Pingliang | 78.89 | 3 | Shangluo | 66.47 | 13 | Lanzhou | 47.31 | 23 |
| Xianyang | 76.17 | 4 | Yan’an | 65.64 | 14 | Shizuishan | 41.44 | 24 |
| Weinan | 74.28 | 5 | Wuwei | 65.56 | 15 | Tianshui | 37.97 | 25 |
| Qingyang | 72.27 | 6 | Hanzhong | 62.28 | 16 | Guyuan | 34.57 | 26 |
| Gannan | 70.92 | 7 | Linxia | 61.47 | 17 | Jiayuguan | 33.43 | 27 |
| Ankang | 70.29 | 8 | Longnan | 59.88 | 18 | Zhongwei | 24.64 | 28 |
| Jinchang | 69.20 | 9 | Baoji | 56.63 | 19 | Dingxi | 22.10 | 29 |
| Zhangye | 68.31 | 10 | Baiyin | 50.15 | 20 |
| Year | Morans’I | E (I) | Sd (I) | Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.280 | −0.036 | 0.015 | 2.582 | 0.010 |
| 2011 | 0.310 | −0.036 | 0.017 | 2.670 | 0.008 |
| 2012 | 0.299 | −0.036 | 0.017 | 2.606 | 0.009 |
| 2013 | 0.343 | −0.036 | 0.018 | 2.800 | 0.005 |
| 2014 | 0.342 | −0.036 | 0.019 | 2.748 | 0.006 |
| 2015 | 0.368 | −0.036 | 0.019 | 2.907 | 0.004 |
| 2016 | 0.354 | −0.036 | 0.019 | 2.813 | 0.004 |
| 2017 | 0.391 | −0.036 | 0.019 | 3.055 | 0.002 |
| 2018 | 0.558 | −0.036 | 0.020 | 4.185 | 0.000 |
| 2019 | 0.523 | −0.036 | 0.019 | 4.044 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.559 | −0.036 | 0.020 | 4.245 | 0.000 |
| 2021 | 0.622 | −0.036 | 0.021 | 4.528 | 0.000 |
| Type | Probe Factor | Metric Factors | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population | X1 | Urban population proportion | % |
| X2 | Rural population number | Ten thousand people | |
| Industrial structure | X3 | Agricultural industry structure | % |
| X4 | Pig, cattle, and sheep rearing structure | % | |
| Economic development | X5 | Gross national product | A hundred million yuan |
| X6 | Per capita gross national product | CNY | |
| X7 | Disposable income of urban residents | CNY | |
| X8 | Disposable income of rural residents | CNY |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | X1 | ||||||||
| X2 | N | ||||||||
| X3 | Y | Y | |||||||
| X4 | N | N | N | ||||||
| X5 | N | N | N | N | |||||
| X6 | N | N | N | N | N | ||||
| X7 | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| X8 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | ||
| 2018 | X1 | ||||||||
| X2 | N | ||||||||
| X3 | N | N | |||||||
| X4 | N | N | N | ||||||
| X5 | N | N | N | N | |||||
| X6 | N | N | N | N | N | ||||
| X7 | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| X8 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | ||
| 2021 | X1 | ||||||||
| X2 | N | ||||||||
| X3 | N | N | |||||||
| X4 | N | N | N | ||||||
| X5 | N | N | N | N | |||||
| X6 | N | N | N | N | N | ||||
| X7 | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| X8 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Shan, T.; Khan, H.S.; Dong, L.; Li, H. The Spatiotemporal Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Forces of Carbon Emissions from Major Livestock Farming in the Shaanxi–Gansu–Ningxia Region. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101748
Wu H, Shan T, Khan HS, Dong L, Li H. The Spatiotemporal Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Forces of Carbon Emissions from Major Livestock Farming in the Shaanxi–Gansu–Ningxia Region. Agriculture. 2024; 14(10):1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101748
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hao, Tongtong Shan, Hassan Saif Khan, Lin Dong, and Hua Li. 2024. "The Spatiotemporal Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Forces of Carbon Emissions from Major Livestock Farming in the Shaanxi–Gansu–Ningxia Region" Agriculture 14, no. 10: 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101748
APA StyleWu, H., Shan, T., Khan, H. S., Dong, L., & Li, H. (2024). The Spatiotemporal Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Forces of Carbon Emissions from Major Livestock Farming in the Shaanxi–Gansu–Ningxia Region. Agriculture, 14(10), 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101748





