Research on Real-Time Detection of Maize Seedling Navigation Line Based on Improved YOLOv5s Lightweighting Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
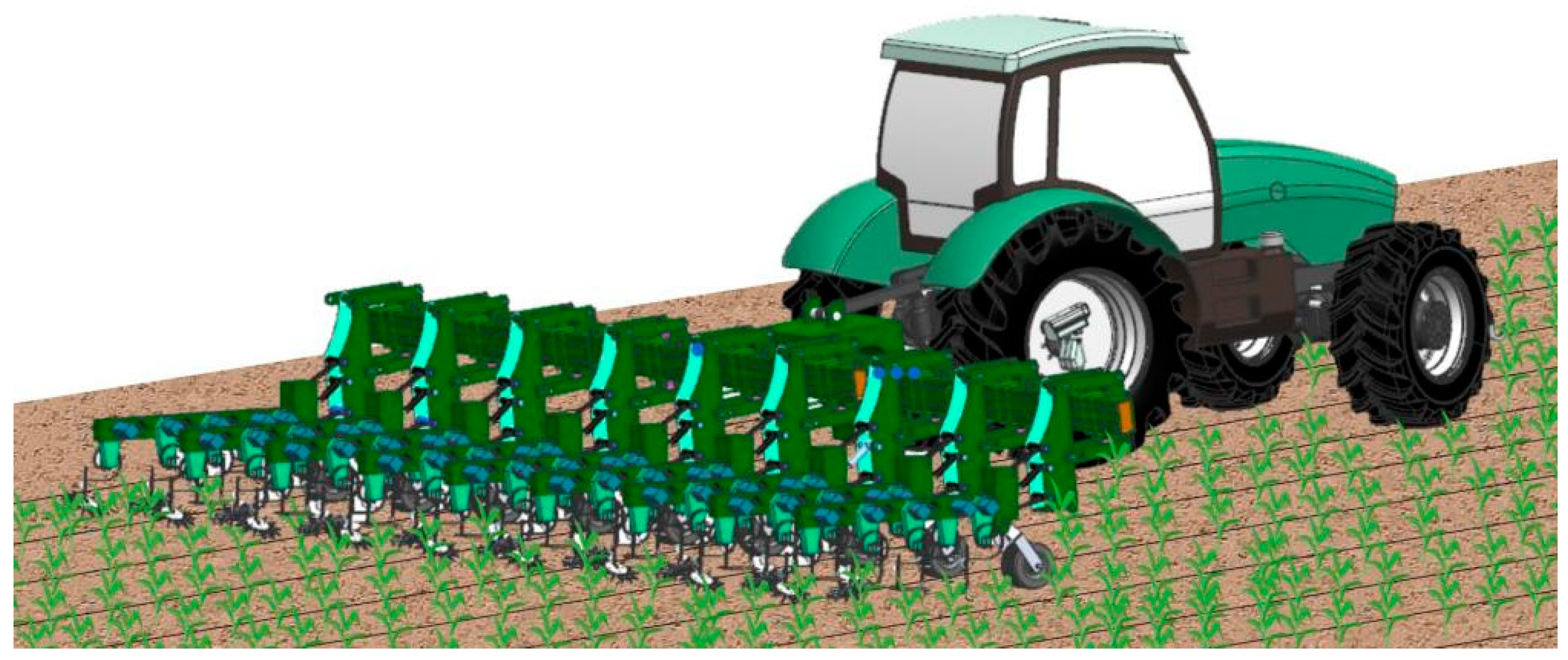
2.1. Structure and Operating Principle of Inter-Row Weeding Machine
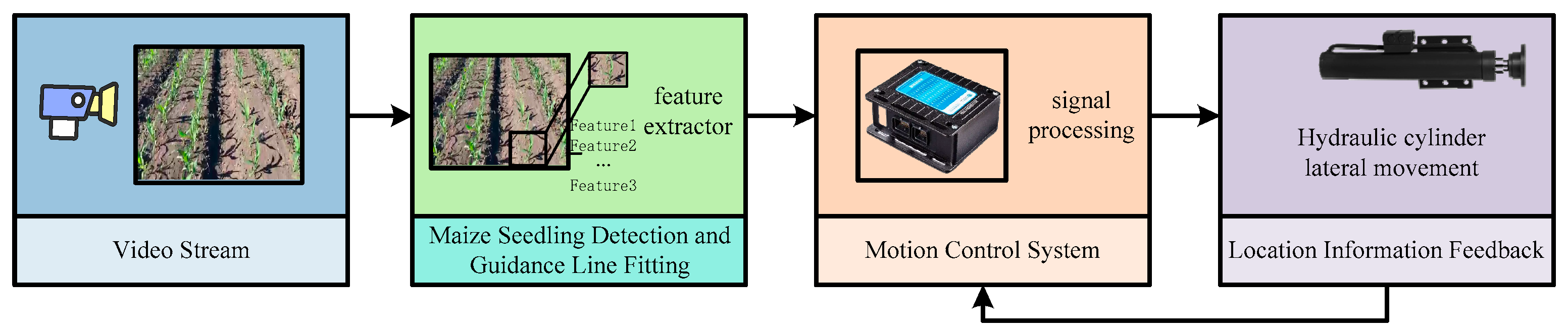
2.2. Method for Extracting Crop Row Navigation Line
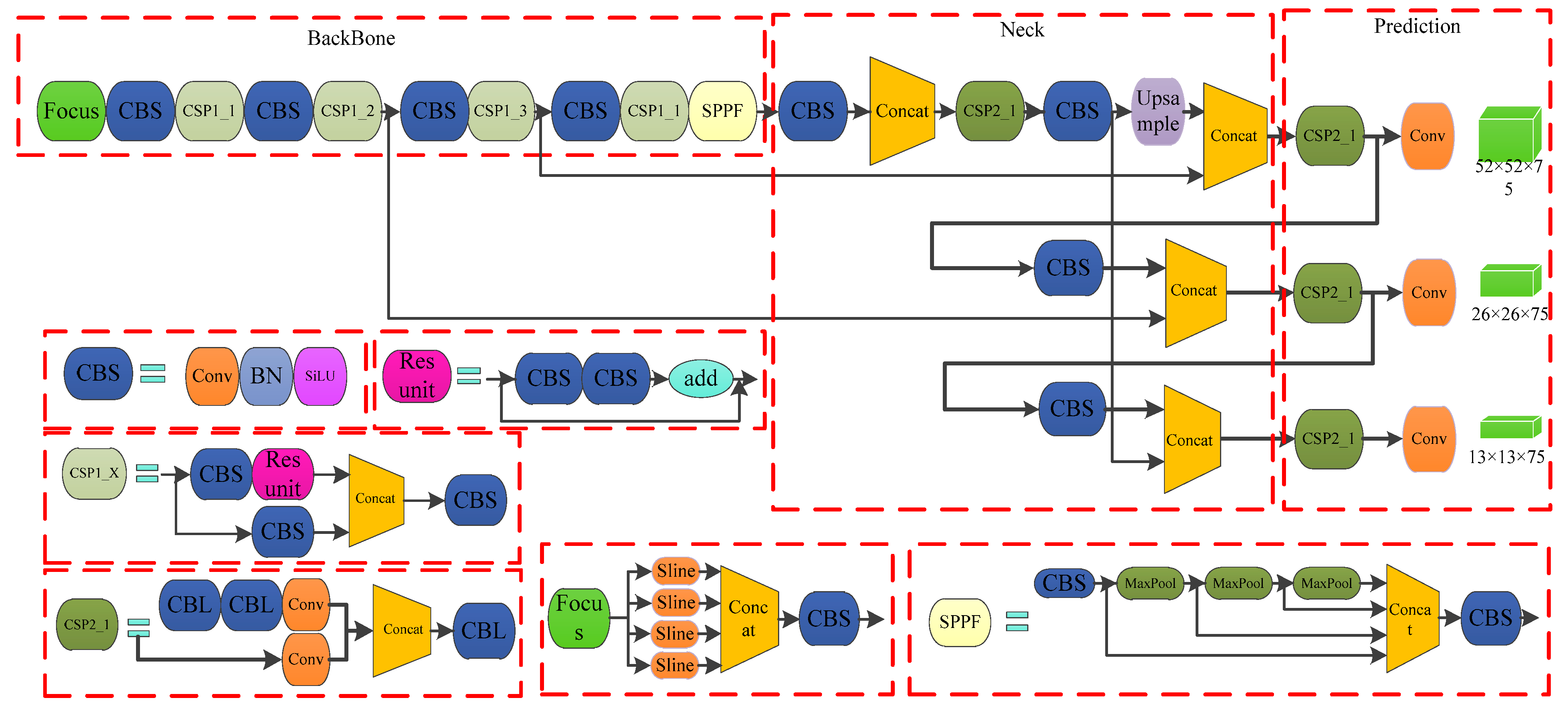
2.3. YOLOv5 Object Detection Model
2.4. Improvements to YOLOv5’s Object Detection Model
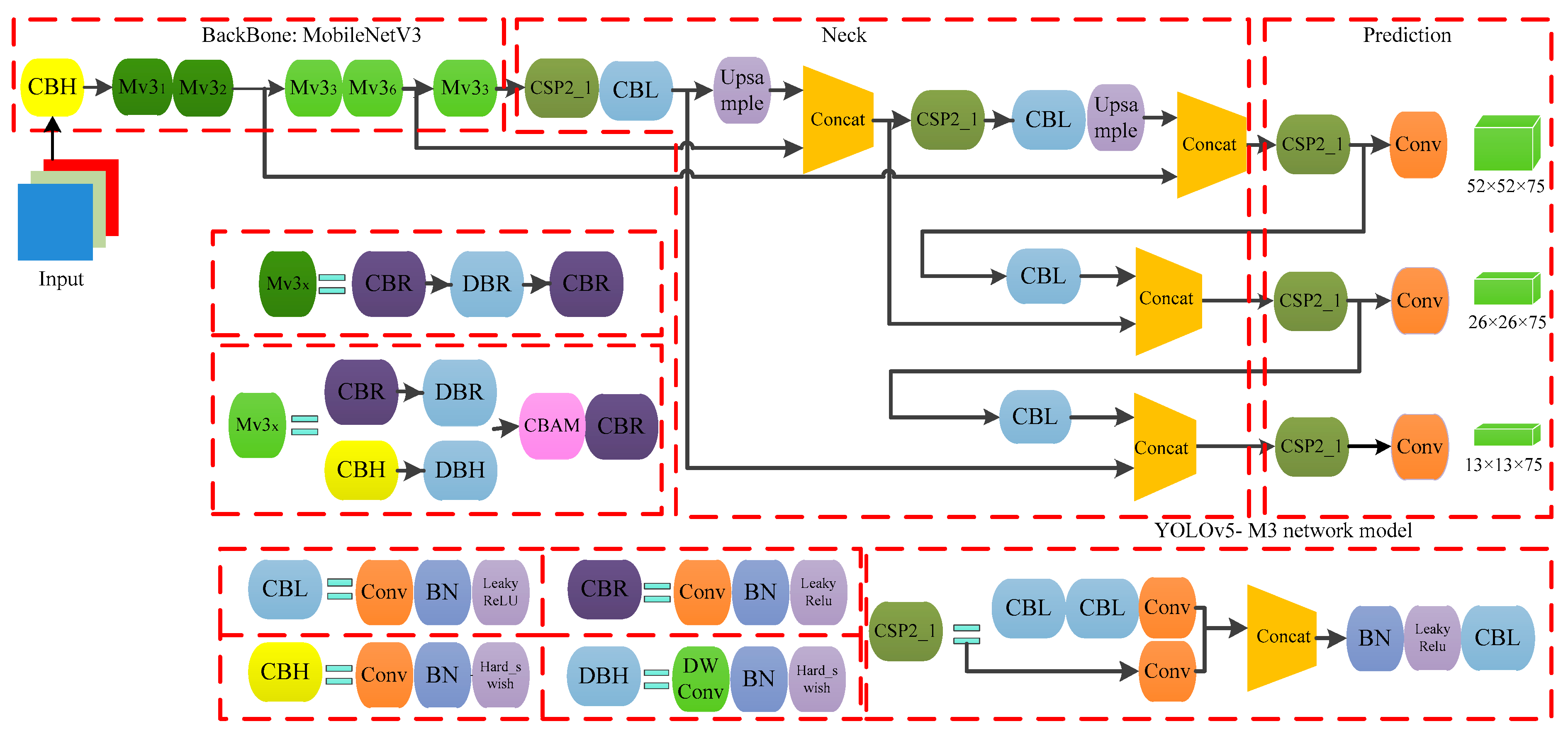
2.4.1. Design of YOLOv5-M3 Network Model
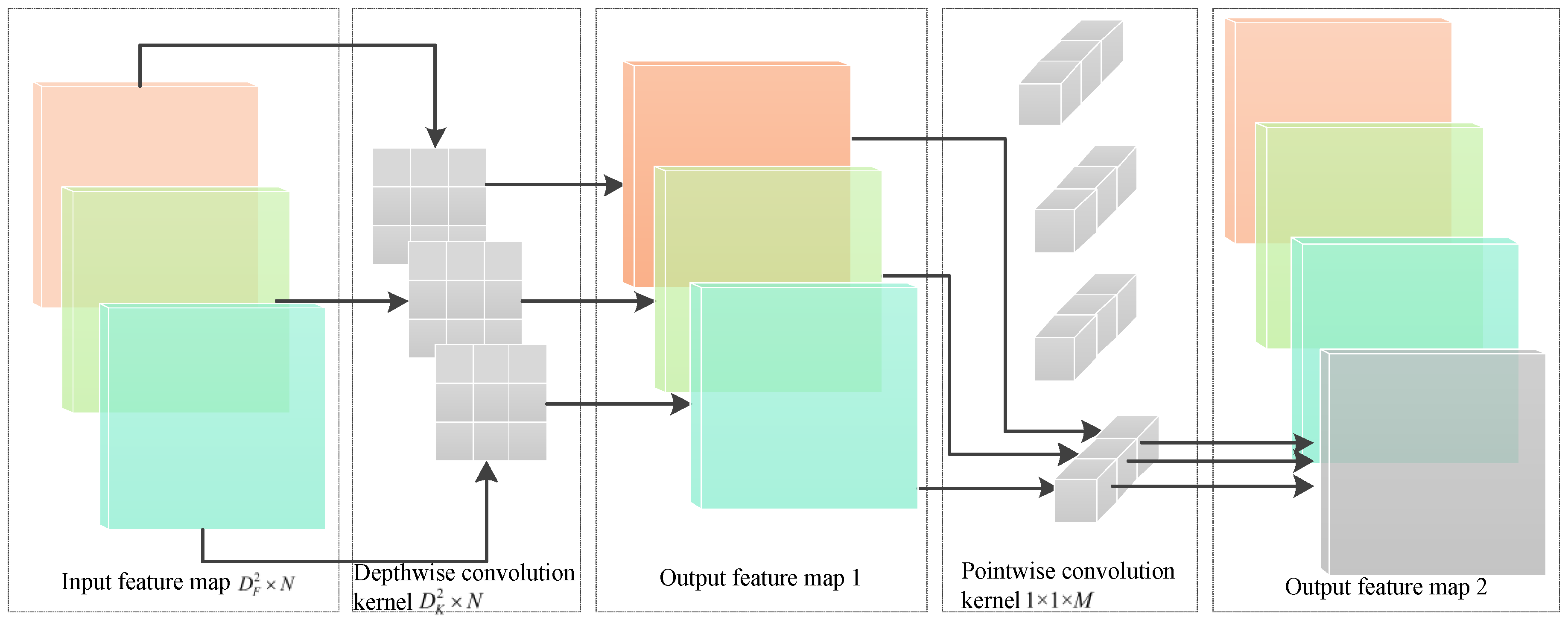
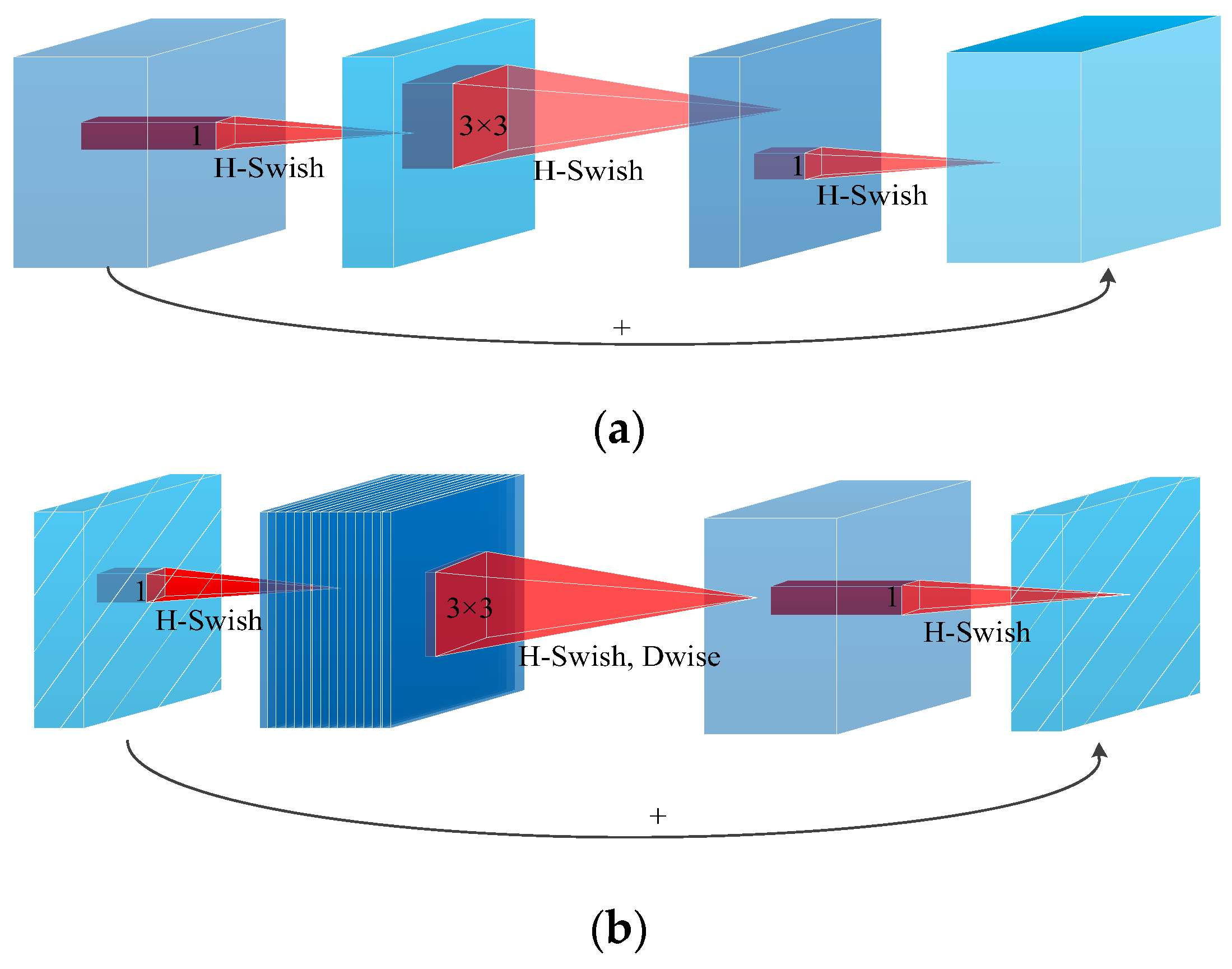
2.4.2. Optimization of Backbone Network in YOLOv5s
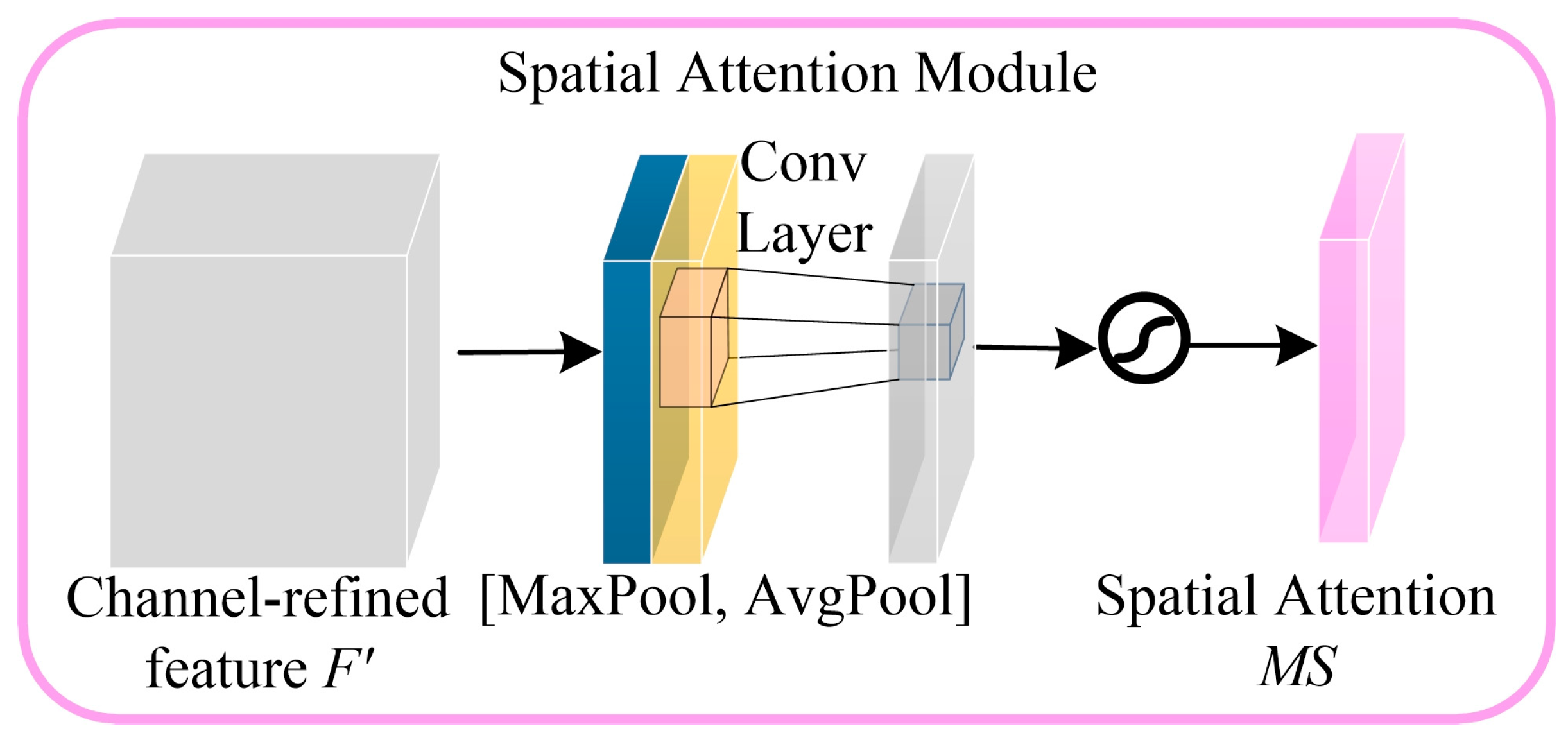
2.4.3. Convolutional Block Attention Module’s Attention Mechanism
2.4.4. Improved Non-Maximum Suppression
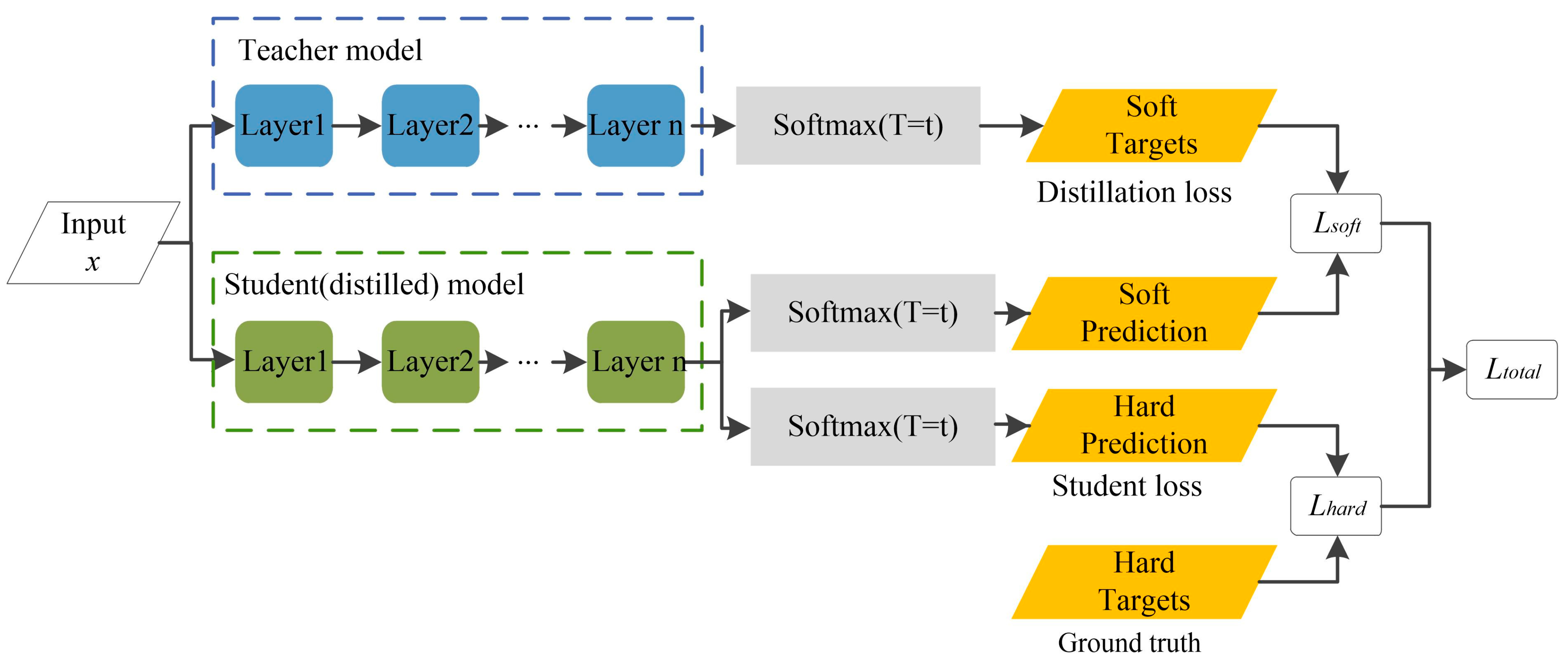
2.4.5. Knowledge Distillation
2.5. Crop Row Fitting Method
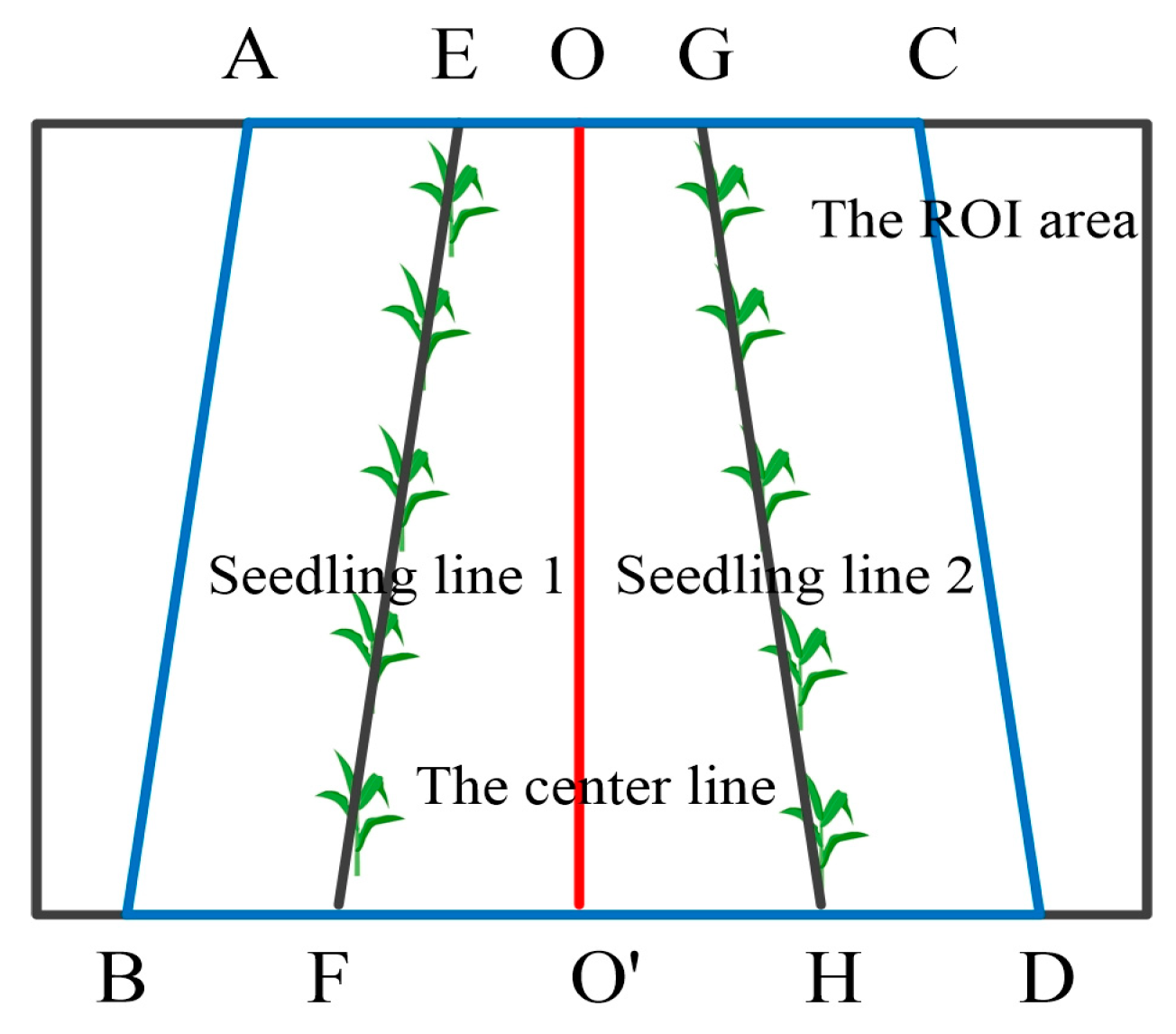
2.5.1. Extraction of Crop Image ROI Based on Perspective Projection
2.5.2. Calculation of Maize Seedling Positions
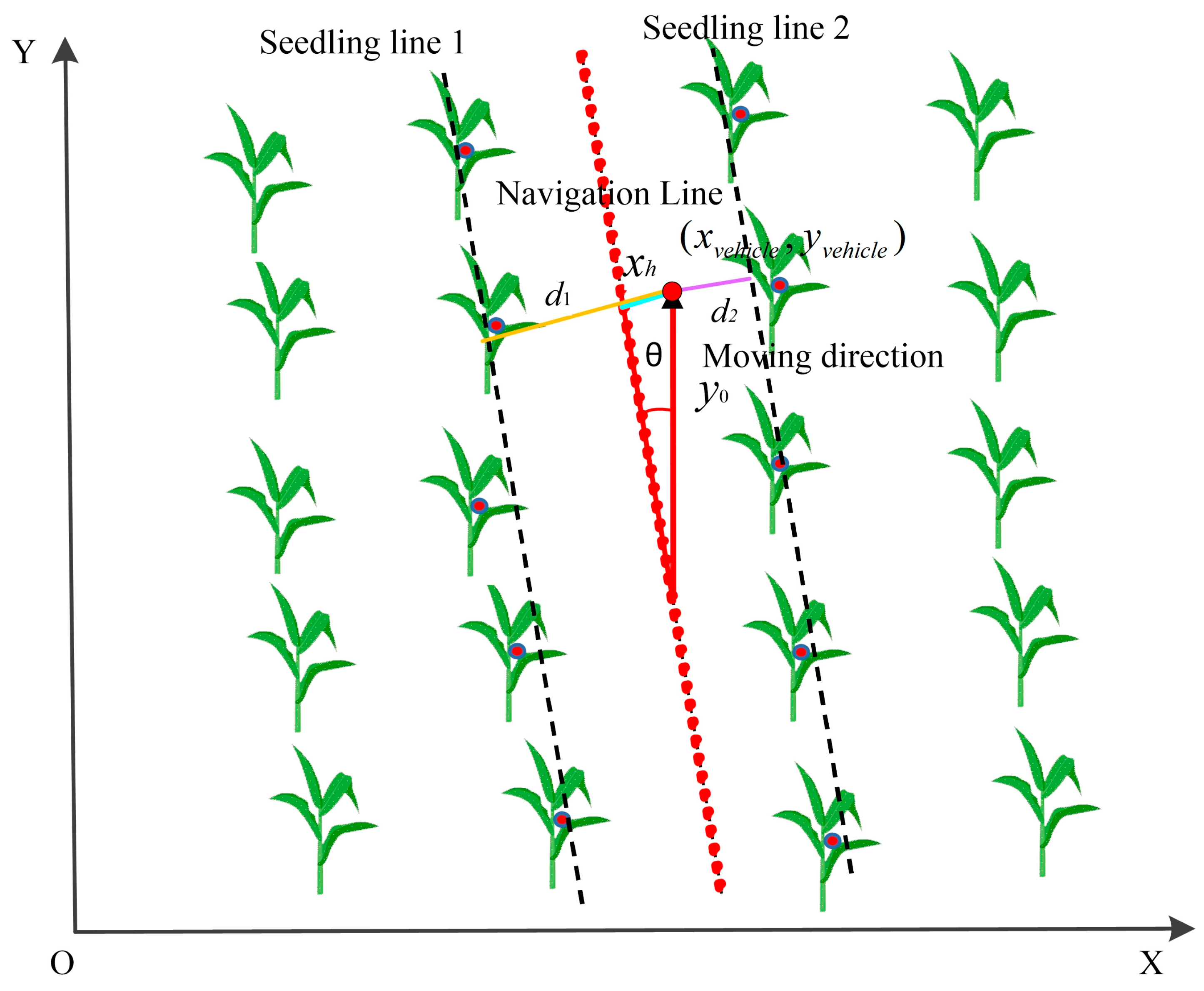
2.5.3. Fitting of Crop Seedlings
2.5.4. Calculation of Optimal Weed Removal Positions
2.6. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.7. Experimentation and Analysis
2.7.1. Experimental Platform and Parameter Settings
2.7.2. Model Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Test Results of Various Backbone Networks
3.2. Ablation Experiment
3.3. Test Results of Different Network Models
3.4. Improved Testing of YOLOv5s Network Model
3.5. Crop Row Fitting Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pannacci, E.; Tei, F. Effects of mechanical and chemical methods on weed control, weed seed rain and crop yield in maize, sunflower and soyabean. Crop Prot. 2014, 64, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Santos, S. Sustainable approach to weed management: The role of precision weed management. Agronomy 2022, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, W.; Wei, X. A review on weed detection using ground-based machine vision and image processing techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 158, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Guo, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J.; He, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J. Navigation line extraction algorithm for corn spraying robot based on improved YOLOv8s network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Potgieter, J.; Arif, K.M. Automation in Agriculture by Machine and Deep Learning Techniques: A Review of Recent Developments. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 2053–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Bao, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, N. Recognition method of maize crop rows at the seedling stage based on MS-ERFNet model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 211, 107964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Feng, H.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z. Maize seedling detection under different growth stages and complex field environments based on an improved Faster R–CNN. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 184, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Tao, Z.; Du, X.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C. Automatic detection of crop root rows in paddy fields based on straight-line clustering algorithm and supervised learning method. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 211, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Z.; Chang, P.; Cui, S.; Luo, J.; Gao, R.; Su, Z. A precise crop row detection algorithm in complex farmland for unmanned agricultural machines. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 232, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J. Deep learning-based weed detection in turf: A review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Elangovan, D.; Govindarajan, P.L.; Elnaggar, M.F.; Alrashed, M.M.; Kamel, S. A comprehensive review of path planning for agricultural ground robots. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Huang, D.; Zhou, D.; Liu, H.; Qu, M.; Ma, Z. Maize (Zea mays L.) seedling detection based on the fusion of a modified deep learning model and a novel Lidar points projecting strategy. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasingham, S.; Ekpanyapong, M.; Chaihan, R. Integrating machine vision-based row guidance with GPS and compass-based routing to achieve autonomous navigation for a rice field weeding robot. Precis. Agric. 2020, 21, 831–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Fu, H.; Yang, S.; Zhai, C. Cabbage and weed identification based on machine learning and target spraying system design. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 924973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranya, T.; Deisy, C.; Sridevi, S.; Anbananthen, K.S.M. A comparative study of deep learning and Internet of Things for precision agriculture. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhang, G.; Wen, X.; Ma, B.; Xu, L.; Chen, L. Real-time detection of crop rows in maize fields based on autonomous extraction of ROI. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Tian, G.; Xiong, Y.; Gu, B. Automated robust crop-row detection in maize fields based on position clustering algorithm and shortest path method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 154, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Wheat rows detection at the early growth stage based on Hough transform and vanishing point. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wen, X.; Yue, X.; Chen, L. Autonomous detection of crop rows based on adaptive multi-ROI in maize fields. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhyumna, P.; Shreya, G.P. Graph Neural Network (GNN) in Image and Video Understanding Using Deep Learning for Computer Vision Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 Second International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 4–6 August 2021; pp. 1183–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Jabir, B.; Falih, N. Deep learning-based decision support system for weeds detection in wheat fields. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 12, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.; Doshi, A.; Patel, P.; Shah, M. A comprehensive review on automation in agriculture using artificial intelligence. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostis, A.; Tagarakis, A.C.; Kateris, D.; Moysiadis, V.; Sørensen, C.G.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Orchard mapping with deep learning semantic segmentation. Sensors 2021, 21, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.M.; Harnal, S.; Mohiuddin, K.; Gautam, V.; Nasr, O.A.; Goyal, N.; Alwetaishi, M.; Singh, A. A Deep Learning-Based Novel Approach for Weed Growth Estimation. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 31, 1157–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razfar, N.; True, J.; Bassiouny, R.; Venkatesh, V.; Kashef, R. Weed detection in soybean crops using custom lightweight deep learning models. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; He, X.; Tan, W.; Wu, X.; Shen, J.; Lu, H. Recognition of crop seedling and weed recognition based on dilated convolution and global pooling in CNN. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, C.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Song, C. CNN feature based graph convolutional network for weed and crop recognition in smart farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Zhao, G.; Feng, H.; Quan, L. Row anchor selection classification method for early-stage crop row-following. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, H. Study on Lightweight Model of Maize Seedling Object Detection Based on YOLOv7. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Saha, I.; Sanghvi, R.M.; Save, S.A.; Patel, Y.J. A review: Object detection models. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Maharashtra, India, 2–4 April 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xiangpeng, F.; Jianping, Z.; Yan, X.U.; Kaijing, L.I.; Desheng, W. Identification and localization of weeds based on optimized faster R-CNN in cotton seedling stage. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L. Weed detection in images of carrot fields based on improved YOLO v4. Trait. Signal 2021, 38, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Song, H. Using lightweight deep learning algorithm for real-time detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 207, 107765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaur, B.; Mishra, K.K. Small-object detection based on YOLOv5 in autonomous driving systems. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 168, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabab, S.; Badenhorst, P.; Chen, Y.P.; Daetwyler, H.D. A template-free machine vision-based crop row detection algorithm. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 124–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjumea, A.; Teeti, I.; Cuzzolin, F.; Bradley, A. YOLO-Z: Improving small object detection in YOLOv5 for autonomous vehicles. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wang, S.; Xie, J. An Image Object Detection Model Based on Mixed Attention Mechanism Optimized YOLOv5. Electronics 2023, 12, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, K.; Ahirrao, S.; Kotecha, K.; Sahu, S. Detection and localization of multiple image splicing using MobileNet V1. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 162499–162519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ke, C.; Lin, H.; Xu, H.; Koundal, D. Research on Pedestrian Detection Algorithm Based on MobileNet-YoLo. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 8924027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z. Bending diagnosis of rice seedling lines and guidance line extraction of automatic weeding equipment in paddy field. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2020, 142, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenovic, M.; Karanovic, M.; Sladojevic, S.; Anderla, A.; Stefanovic, D. Solving Current Limitations of Deep Learning Based Approaches for Plant Disease Detection. Symmetry 2019, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kc, K.; Yin, Z.; Wu, M.; Wu, Z. Depthwise separable convolution architectures for plant disease classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 165, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Automatic detection of crop rows based on multi-ROIs. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 2429–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Han, S.; Han, S.; Park, K.; Kim, K.; Kim, S. Morphology-based guidance line extraction for an autonomous weeding robot in paddy fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 113, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zhao, B.; Jiao, Y.; Kong, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Z. Weed recognition for depthwise separable network based on transfer learning. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2021, 27, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Fan, P.; Lei, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F. A real-time apple targets detection method for picking robot based on improved YOLOv5. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, M.; İnci, B.; Musaoğlu, E.; Çobanoğlu, H.; Kocakır, N.; Karademir, Ö. An efficient deep learning framework for people detection in overhead images. In Artificial Intelligence in Industrial Applications: Approaches to Solve the Intrinsic Industrial Optimization Problems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Choi, W.; Yu, X.; Han, T.; Chandraker, M. Learning efficient object detection models with knowledge distillation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 742–751. [Google Scholar]







| Floor | Input | Output | Numbers | Activation Function | CBAM Attention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv2D_BN_ hard-swish | 4162 × 3 | 2082 × 16 | 1 | hard-swish | × |
| Bneck_block | 2082 × 16 | 2082 × 16 | 1 | relu | × |
| Bneck_block | 2082 × 16 | 1042 × 24 | 2 | relu | × |
| Bneck_block | 1042 × 24 | 522 × 40 | 3 | relu | √ |
| Bneck_block | 522 × 40 | 262 × 112 | 6 | hard-swish | √ |
| Bneck_block | 262 × 112 | 132 × 160 | 3 | hard-swish | √ |
| Name | Device-Related Configuration |
|---|---|
| CPU | 11th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM)i7-11700@2.50 GHz |
| Main memory | 16 GB |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti |
| GPU acceleration library | CUDA11.0.3, CUDNN8.2.1 |
| Operating system | Windows 10 (64 bit) |
| Software environment | Python 3.7, Pytorch 1.7.0 |
| Network Model | Backbone Network | F1-Score/% | Params/106 | FLOPs/109 | mAP/% | FPS/(frame·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | CSPDarkNet-53 | 90.2 | 7.21 | 7.5 | 89.4 | 31 |
| EfficientNet | 88.3 | 3.62 | 7.1 | 86.2 | 35 | |
| DensenNet-169 | 87.4 | 14.2 | 33.1 | 86.9 | 17 | |
| ResNet-50 | 88.9 | 25.6 | 10.3 | 87.3 | 27 | |
| ShuffleNetV2 | 86.1 | 3.12 | 5.9 | 85.2 | 30 | |
| MolieNetv3 | 91.2 | 5.42 | 6.2 | 91.8 | 33 |
| Model | MolieNetv3 | CBAM | DIoU-NMS | Lsoft | Params/M | FLOPs/109 | mAP | Model File/MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | - | - | - | - | 7.21 | 7.5 | 89.4 | 14.5 |
| √ | - | - | - | 5.42 | 6.2 | 91.8 | 11.2 | |
| √ | √ | - | - | 5.42 | 6.2 | 92.2 | 11.3 | |
| √ | √ | √ | - | 5.42 | 6.2 | 92.3 | 11.3 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 3.21 | 5.1 | 92.2 | 7.5 |
| Network Model | Precision/% | Recall/% | F1-Score/% | Params/106 | FLOPs/109 | mAP | Model File/MB | FPS/(frame·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-RCNN | 85.1 | 87.8 | 86.4 | 136 | 18.5 | 86.9 | 89.3 | 0.45 |
| YOLOv5s | 91.2 | 89.2 | 90.2 | 7.21 | 7.5 | 89.4 | 14.5 | 23 |
| SSD | 86.9 | 85.7 | 86.3 | 33.2 | 8.9 | 86.3 | 92.1 | 11 |
| YOLOX | 89.2 | 88.1 | 88.6 | 8.93 | 4.5 | 88.7 | 17.1 | 50 |
| YOLOv5-M3 | 93.2 | 91.1 | 92.1 | 3.21 | 5.1 | 92.2 | 7.5 | 39 |
| Four Situations | Average Angular Deviation (°) | Execution Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Maize seedling missing | 3.13 | 51 |
| Dense weed distribution | 3.91 | 65 |
| Sparse weed distribution | 2.43 | 62 |
| Weed-free | 2.32 | 53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, H.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, W. Research on Real-Time Detection of Maize Seedling Navigation Line Based on Improved YOLOv5s Lightweighting Technology. Agriculture 2024, 14, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010124
Gong H, Wang X, Zhuang W. Research on Real-Time Detection of Maize Seedling Navigation Line Based on Improved YOLOv5s Lightweighting Technology. Agriculture. 2024; 14(1):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010124
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Hailiang, Xi Wang, and Weidong Zhuang. 2024. "Research on Real-Time Detection of Maize Seedling Navigation Line Based on Improved YOLOv5s Lightweighting Technology" Agriculture 14, no. 1: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010124
APA StyleGong, H., Wang, X., & Zhuang, W. (2024). Research on Real-Time Detection of Maize Seedling Navigation Line Based on Improved YOLOv5s Lightweighting Technology. Agriculture, 14(1), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010124





