Trace Element Content in Soils with Nitrogen Fertilisation and Humic Acids Addition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Methodology of the Experiment
2.2. Methods of Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Methods of Statistical Analysis
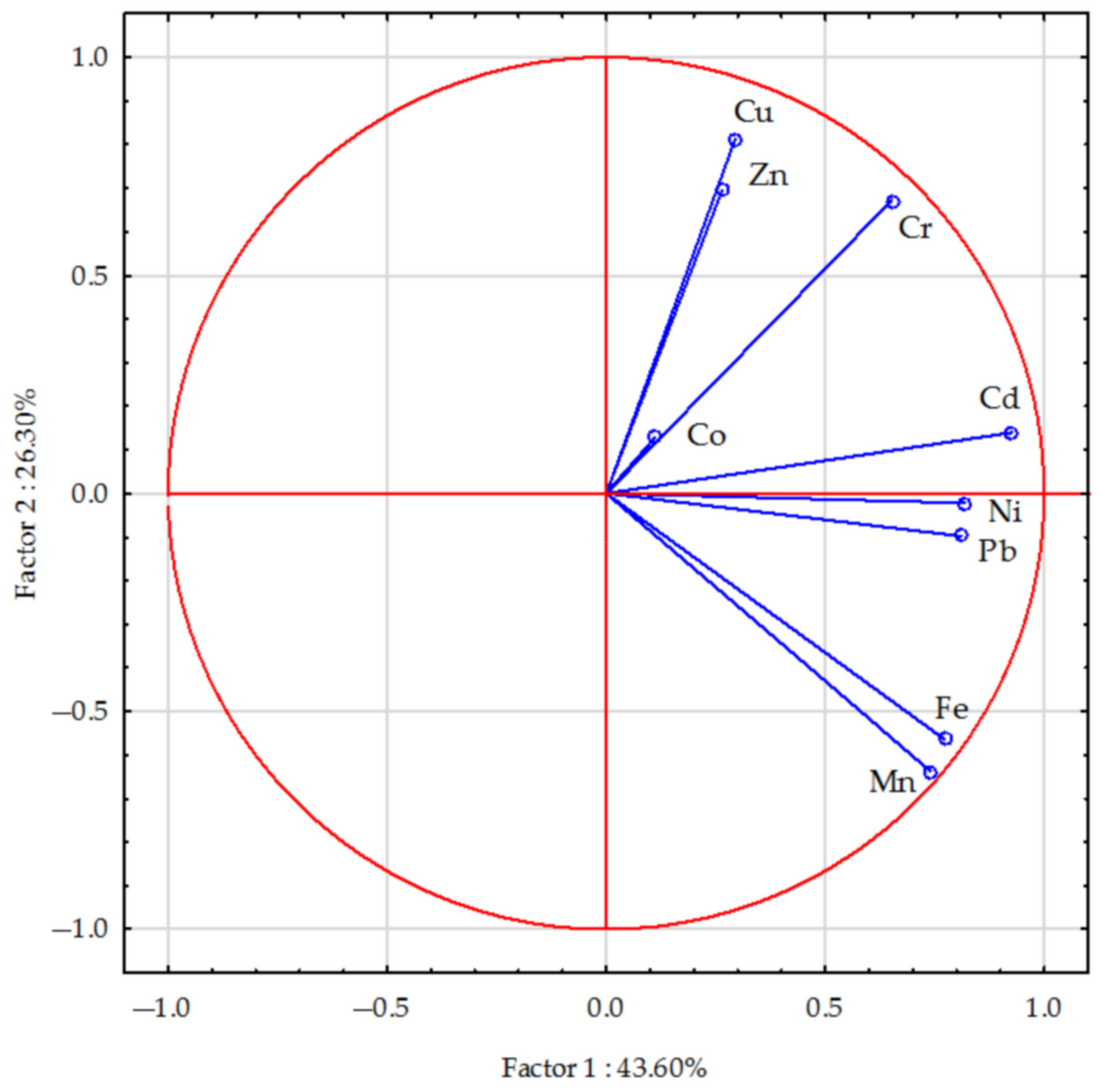
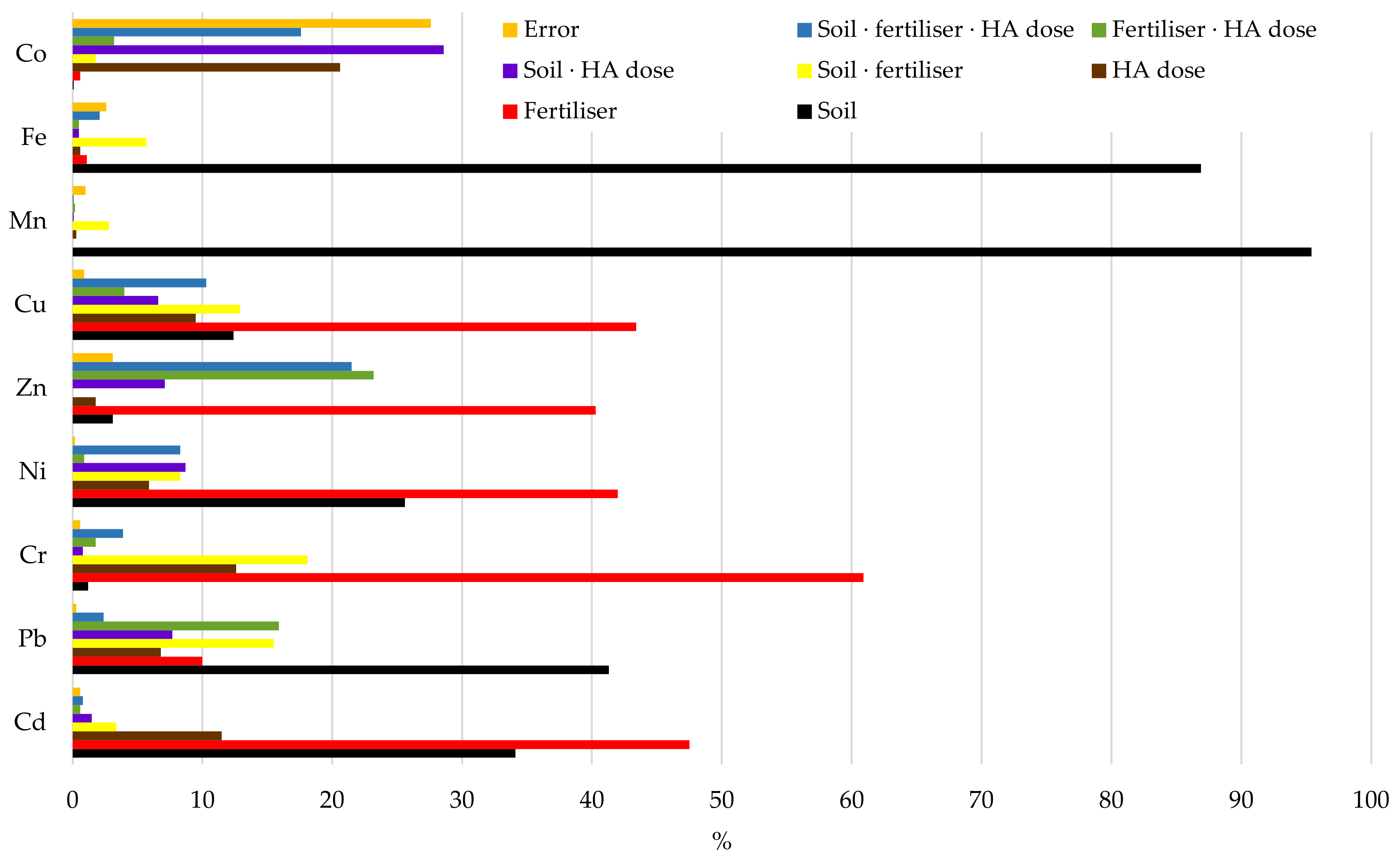
3. Results
3.1. Content of Trace Elements in Soil Depending on Type of Soil and Form of Nitrogen Fertilisers
3.2. Effect of Humus Acids on Content of Trace Elements in Soils
4. Discussion
4.1. Content of Trace Elements in Soil Depending on Type of Soil and Form of Nitrogen Fertilisers
4.2. Effect of Humus Acids on Content of Trace Elements in Soils
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bindraban, P.S.; Dimkpa, C.; Nagarajan, L.; Roy, A.; Rabbinge, R. Revisiting fertilisers and fertilisation strategies for improved nutrient uptake by plants. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowski, M.; Brodowska, M.S. Potassium and nitrogen fertilization vs. trace element content of maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture 2021, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timsina, J. Can organic sources of nutrients increase crop yields to meet global food demand? Agronomy 2018, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, J.P.; Sapkota, T.B.; Krupnik, T.J.; Rahut, D.B.; Jat, M.L.; Stirling, C.M. Factors affecting farmers’ use of organic and inorganic fertilizers in South Asia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 51480–51496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, Y.; Ronaghi, A.; Maftoun, M.; Karimian, N.A. Growth, nutrient status, and chlorophyll meter readings in wheat as affected by nitrogen and manganese. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowski, M.; Brodowska, M.S. Content of trace elements in soil fertilized with potassium and nitrogen. Agriculture 2020, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaie, M.; Tavakoly, A.R. Effects of municipal waste compost and nitrogen fertilizer on growth and mineral composition of tomato. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2016, 5, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, D.; Hejcman, M.; Száková, J.; Kunzová, E.; Tlustoš, P. Concentration of trace elements in arable soil after long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2009, 85, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soil and Plants, 4th ed.; CRS Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.G.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Denmead, O.T. Ammonia emission from mineral fertilizers and fertilized crops. Adv. Agron. 2004, 82, 557–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguta, P.; D’Orazio, V.; Senesi, N.; Sokołowska, Z.; Szewczuk-Karpisz, K. Insight into the interaction mechanism of iron ions with soil humic acids. The effect of the pH and chemical properties of humic acids. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J. Humic substances and their role in the environment. EC Agric. 2020, 3, 3–8. Available online: https://www.ecronicon.com/eco20/pdf/ECAG-03-ECO-0002.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Stevenson, F.J. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA; Chichester, UK, 1994; pp. 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Jarukas, L.; Ivanauskas, L.; Kasparaviciene, G.; Baranauskaite, J.; Marksa, M.; Bernatoniene, J. Determination of organic compounds, fulvic acid, humic acid, and humin in peat and sapropel alkaline extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi Khalaf Ansar, B.; Kavusi, E.; Dehghanian, Z.; Pandey, J.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Price, G.W.; Astatkie, T. Removal of organic and inorganic contaminants from the air, soil, and water by algae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fang, F.; Wei, J.; Wu, X.; Cui, R.; Li Zheng, F.; Tan, D. Humic acid fertilizer improved soil properties and soil microbial diversity of continuous cropping peanut: A three-year experiment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannino, F.; Spaccini, R.; Savy, D.; Piccolo, A. Remediation of highly contaminated soil from an industrial site by employing a combined treatment with exogeneous HS and oxidative biomimetric catalysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuráň, P.; Trögl, J.; Nováková, J.; Pilařová, V.; Dáňová, P.; Pavlorková, J.; Kozler, J.; Novák, F.; Popelka, J. Biodegradation of spilled diesel fuel in agricultural soil: Effect of humates, zeolite, and bioaugmentation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 642427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, A.; Alikhani, H.A.; Ajdanian, L.; Babaei, M.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Effect of Different Enriched Vermicomposts, Humic Acid Extract and Indole-3-Acetic Acid Amendments on the Growth of Brassica napus. Plants 2022, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türkmen, Ö.; Dursun, A.; Turan, M.; Erdinç, Ç. Calcium and humic acid affect seed germination, growth, and nutrient content of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) seedlings under saline soil conditions. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Plant Soil Sci. 2004, 54, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçsoy, M.; Sönmez, F. The effect of potassium and humic acid applications on yield and nutrient contents of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. var. Delfii) with same soil properties. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2757–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandonadi, D.B.; Santos, M.P.; Dobbss, L.B.; Olivares, F.L.; Canellas, L.P.; Binzel, M.L.; Okorokova-Façanha, A.L.; Façanha, A.R. Nitric oxide mediates humic acids-induced root development and plasma membrane H+-ATPase activation. Planta 2010, 231, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L. Physiological responses to humic substances as plant growth promoter. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2014, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, S.; Schiavon, M.; Francioso, O. Chemical structure and biological activity of humic substances define their role as plant growth promoters. Molecules 2021, 26, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondareva, L.; Kudryasheva, N. Direct and Indirect Detoxification Effects of Humic Substances. Agronomy 2021, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, C.; Cozzolino, V.; Verrillo, M.; Vinci, G.; De Martino, A.; Scopa, A.; Piccolo, A. Combination of humic biostimulants with a microbial inoculum improves lettuce productivity, nutrient uptake, and primary and secondary metabolism. Plant Soil 2022, 481, 285–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, J.M.; Pitumpe Arachchige, P.S.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Maurmann, L.; Trivelin, P.C.O.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Sunoj, S.V.J. Co-addition of humic substances and humic acids with urea enhances foliar nitrogen use efficiency in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). Heliyon 2020, 6, e05100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Guo, M.J.; Wang, Y.G.; Yuan, X.Y.; Wen, Y.Y.; Song, X.E.; Dong, S.Q.; Guo, P.Y. Humic acid improves the physiological and photosynthetic characteristics of millet seedlings under drought stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1774212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Tang, C.; Antonietti, M. Natural and artificial humic substances to manage minerals, ions, water, and soil microorganisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6221–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nortcliff, S.; Tan, K.H. (Eds.) Principles of Soil Chemistry, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; p. 362. [Google Scholar]
- Pertusatti, J.; Prado, A.G.S. Buffer capacity of humic acid: Thermodynamic approach. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlakovs, J.; Kļaviņš, M.; Osinska, L.; Purmalis, O. The impact of humic substances as remediation agents to the speciation forms of metals in soil. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, M.; Cai, W.; Zeng, H. The effect of humic acid and fulvic acid on adsorption-desorption behavior of copper and zinc in the yellow soil. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1820, 040027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Antonietti, M. The sleeping giant: A polymer view on humic matter in synthesis and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 100, 101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Takei, T.; Yazawa, Y.; Wong, M.T.F.; Gilkes, R.J.; Swift, R.S. Effect of humic acid, sodium, and calcium additions on the formation of water-stable aggregates in Western Australian wheatbelt soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2004, 42, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlová, J.; Badalíková, B.; Pospíšilová, L.; Pokorný, E.; Šarapatka, B. Water stability of soil aggregates in different systems of tillage. Soil Water Res. 2015, 10, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampong, K.; Thilakaranthna, M.S.; Gorim, L.Y. Understanding the role of humic acids on crop performance and soil health. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 848621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Khan, M.Z.; Khan, A.; Saba, S.; Hussain, F.; Jan, I.U. Effect of humic acid on growth and crop nutrient status of wheat on two different soils. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ren, B.; Zhao, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J. Effects of humic acid added to controlled-release fertilizer on summer maize yield, nitrogen use efficiency and greenhouse gas emission. Agriculture 2022, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, D.; Misra, P.; Singh, S.; Kalra, A. Humic acid rich vermicompost promotes plant growth by improving microbial community structure of soil as well as root nodulation and mycorrhizal colonization in the roots of Pisum sativum. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 110, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, F.L.; Busato, J.G.; de Paula, A.M.; da Silva Lima, L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Canellas, L.P. Plant growth promoting bacteria and humic substances: Crop promotion and mechanisms of action. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborowska, M.; Woźny, G.; Wyszkowska, A.; Kucharski, J. Biostimulation of the activity of microorganisms and soil enzymes through fertilisation with composts. Soil Res. 2018, 56, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; Huo, L.; Li, Y.C.; Li, X.; Xia, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, B. Humic acids derived from Leonardite to improve enzymatic activities and bioavailability of nutrients in a calcareous soil. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelcov, M.; Mizera, J.; Skorov, I.; Pekař, M. Sorption of metal ions on lignite and the derived humic substances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Kong, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, L.; Shen, D. Patterns of heavy metal immobilization by MSW during the landfill process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Mina, J.M.; Antolin, M.C.; Sanchez-Diaz, M. Metal-humic complexes and plant micronutrient uptake: A study based on different plant species cultivated in diverse soil. Plant Soil 2004, 258, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Temminghoff, E.J.; Lofts, S.; Tipping, E.; Van Riemsdijk, W.H. Complexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4804–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhilin, D.M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Perminova, I.V. Reduction of Cr(VI) by peat and coal humic substances. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2004, 2, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Chen, J. Enhanced microbial reduction of Cr(VI) and U(VI) by different natural organic matter fractions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barłóg, P.; Grzebisz, W.; Łukowiak, R. Fertilizers and fertilization strategies mitigating soil factors constraining efficiency of nitrogen in plant production. Plants 2022, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T. Soil Degradation, land scarcity and food security: Reviewing a complex challenge. Sustainability 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014. World Soil Resources Report; International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps. Update 2015; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; p. 182. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i3794en/I3794en.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Brodowska, M.S.; Wyszkowski, M.; Kordala, N. Use of organic materials to limit the potential negative effect of nitrogen on maize in different soils. Materials 2022, 15, 5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. US-EPA Method 3051A: Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediment, Sludges, Soils, and Oils; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 1–30.
- Ostrowska, A.; Gawliński, S.; Szczubiałka, Z. Methods for Analysis and Evaluation of Soil and Plant Properties; Institute of Environmental Protection: Warsaw, Poland, 1991; pp. 1–334. [Google Scholar]
- TIBCO Software Inc. Statistica Version 13; Data Analysis Software System; Tibco Software Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2021; Available online: http://statistica.io (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, H. Trace elements in soils and selected agricultural plants in the Tongling Mining Area of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrelja, I.; Šestak, I.; Delač, D.; Pereira, P.; Bogunović, I. soil chemical properties and trace elements after wildfire in Mediterranean Croatia: Effect of severity, vegetation type and time-since-fire. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowska, M.S.; Wyszkowski, M.; Bujanowicz-Haraś, B. Mineral fertilization and maize cultivation as factors which determine the content of trace elements in soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Yoon, Y.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.B. Long-term inorganic fertilization effect on the micronutrient density in soil and rice grain cultivated in a South Korean paddy field. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1603–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Łabętowicz, J. Influence of soil fertilization on concentration of microelements in soil solution of sandy soil. J. Elem. 2009, 14, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symanowicz, B.; Kalembasa, S.; Jaremko, D.; Niedbała, M. Effect of nitrogen application and year on concentration of Cu, Zn, Ni, Cr, Pb and Cd in herbage of Galega orientalis Lam. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atafar, Z.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Nouri, J.; Homaee, M.; Yunesian, M.; Ahmadimoghaddam, M.; Mahvi, A.H. Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowska, J.; Kovačik, P.; Sienkiewicz, S.; Krzebietke, S.; Bowszys, T. Determination of heavy metals and their availability to plants in soil fertilized with different waste substances. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; Cang, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Fan, X.H.; Qin, S.W. Soil micronutrient availability to crops as affected by long-term inorganic and organic fertilizer applications. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 96, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Sosulski, T.; Stępień, W. Soil micronutrient availability to crops affected by long-term inorganic and organic fertilizer applications. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ding, W.; Chen, Z.; Ziadi, N. Thirty-year amendment of horse manure and chemical fertilizer on the availability of micronutrients at the aggregate scale in black soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyszkowski, M.; Brodowska, M.S.; Kordala, N. Trace element contents in maize following the application of organic materials to reduce the potential adverse effects of nitrogen. Materials 2023, 16, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, S.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, Q. Influence of humic acid complexation with metal ions on extracellular electron transfer activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, K.M.; Khan, K.S.; Rukh, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, S.; Billah, M.; Bashir, S.; Danish, S.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Elshikh, M.S.; et al. Immobilization of Cd, Pb and Zn through organic amendments in wastewater irrigated soils. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska-Malina, J. Functions of organic matter in polluted soils: The effect of organic amendments on phytoavailability of heavy metals. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 123, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, F.; Alp, S. The Effects of applications humic acids on macronutrient, micronutrient, heavy metal and soil properties. YYU J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 29, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendana, M.; Idris, W.M.R.; Rahim, S.A.; Rahman, Z.A.; Lihan, T. Effects of organic amendment on heavy metal and macronutrient contents in paddy soil. Sains Malays. 2022, 51, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, R.; Peng, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X. Effect of humic acid on transformation of soil heavy metals. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 207, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Spaccini, R.; De Martino, A.; Scognamiglio, F.; Di Meo, V. Soil washing with solutions of humic substances from manure compost removes heavy metal contaminants as a function of humic molecular composition. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, M.; Hu, W.; Chen, L.; Ai, S. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and their immobilization at micro-scale interfaces among diverse soil components. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Mohamed, E.; Li, Q.; Lu, T.; Yu, H.; Jiang, W. Effect of humic acid addition on buffering capacity and nutrient storage capacity of soilless substrates. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 644229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydinalp, C.; Marinova, S. Distribution and forms of heavy metals in some agricultural soils. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Maillard, É.; Angers, D.A. Animal manure application and soil organic carbon stocks: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeplau, C.; Kätterer, T.; Bolinder, M.A.; Börjesson, G.; Berti, A.; Lugato, E. Low stabilization of aboveground crop residue carbon in sandy soils of Swedish long-term experiments. Geoderma 2015, 237–238, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.L.; Schjønning, P.; Watts, C.W.; Christensen, B.T.; Obour, P.B.; Munkholm, L.J. Soil degradation and recovery—Changes in organic matter fractions and structural stability. Geoderma 2020, 364, 114181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Sand | Loamy Sand |
|---|---|---|
| % or Value Per kg−1 Soil | ||
| Grain size | ||
| <0.002 | 0.68% | 2.50% |
| 0.002–0.050 | 7.44% | 19.95% |
| >0.050 | 91.88% | 77.55% |
| Cation exchange capacity (CEC) | 76.11 mM (+) | 82.41 mM (+) |
| pH in KCl | 6.47 | 6.33 |
| Total nitrogen | 0.579 g | 0.620 g |
| Available forms: | ||
| P | 125.35 mg | 105.48 mg |
| K | 65.02 mg | 91.07 mg |
| Mg | 62.36 mg | 40.99 mg |
| Total: | ||
| Cd | 0.602 mg | 0.850 mg |
| Pb | 10.26 mg | 11.97 mg |
| Cr | 22.68 mg | 22.47 mg |
| Ni | 22.60 mg | 26.78 mg |
| Zn | 21.16 mg | 21.09 mg |
| Cu | 4.685 mg | 4.236 mg |
| Mn | 223.6 mg | 284.3 mg |
| Fe | 8754 mg | 9998 mg |
| Co | 3.205 mg | 3.626 mg |
| HA Dose g kg−1 of Soil | Sand | Loamy Sand | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium Nitrate | Urea | UAN | Mean | Ammonium Nitrate | Urea | UAN | Mean | |
| Cadmium | ||||||||
| 0 | 0.661 j–k | 0.472 ef | 0.304 bc | 0.479 D | 0.914 m | 0.858 m | 0.626 h–j | 0.799 H |
| 0.05 | 0.651 i–k | 0.444 e | 0.237 b | 0.444 C | 0.721 kl | 0.784 l | 0.533 hg | 0.679 G |
| 0.10 | 0.623 h–i | 0.440 e | 0.153 a | 0.405 B | 0.737 l | 0.647 ij | 0.423 de | 0.602 F |
| 0.15 | 0.567 jk | 0.363 cd | 0.128 a | 0.353 A | 0.658 i–k | 0.588 g–i | 0.416 de | 0.554 E |
| Mean | 0.626 D | 0.430 B | 0.206 A | 0.420 A | 0.758 F | 0.719 E | 0.500 C | 0.659 B |
| r | −0.949 | −0.915 | −0.981 | −0.995 | −0.884 | −0.988 | −0.956 | −0.981 |
| Lead | ||||||||
| 0 | 11.58 fg | 14.21 kl | 8.09 cd | 11.29 B | 12.22 gh | 15.16 m | 12.46 h | 13.28 A |
| 0.05 | 12.23 gh | 14.09 j–l | 7.39 b | 11.24 B | 13.43 ij | 13.67 j–l | 12.50 h | 13.20 A |
| 0.10 | 11.44 f | 8.43 d | 7.62 bc | 9.16 D | 12.91 hi | 13.51 i–k | 15.49 m | 13.97 E |
| 0.15 | 10.20 e | 7.96 b–d | 5.75 a | 7.97 C | 13.93 j–l | 11.10 f | 14.27 l | 13.10 A |
| Mean | 11.36 A | 11.17 A | 7.21 C | 9.92 A | 13.12 B | 13.36 B | 13.68 D | 13.39 B |
| r | −0.751 | −0.915 | −0.861 | −0.952 | 0.813 | −0.948 | 0.738 | 0.075 |
| Chromium | ||||||||
| 0 | 23.05 ij | 17.05 ef | 6.81 b | 15.64 D | 22.85 ij | 11.53 d | 19.37 gh | 17.92 E |
| 0.05 | 23.28 j | 15.45 e | 4.29 b | 14.34 A | 19.58 gh | 10.64 cd | 11.57 d | 13.93 A |
| 0.10 | 21.00 hj | 11.11 d | 3.37 a | 11.83 B | 17.05 ef | 10.24 cd | 15.50 e | 14.26 A |
| 0.15 | 18.60 fg | 7.78 b | 3.26 a | 9.88 C | 17.92 fg | 8.46 bc | 7.18 b | 11.19 B |
| Mean | 21.48 E | 12.85 A | 4.43 B | 12.92 A | 19.35 D | 10.22 C | 13.41 A | 14.32 B |
| r | −0.927 | −0.986 | −0.905 | −0.993 | −0.874 | −0.962 | −0.806 | −0.928 |
| Nickel | ||||||||
| 0 | 25.53 hi | 27.59 k | 20.40 e | 24.51 A | 31.57 m | 26.36 ij | 20.30 e | 26.08 D |
| 0.05 | 24.88 h | 27.10 jk | 23.01 g | 25.00 A | 32.31 mn | 30.15 l | 21.68 f | 28.05 F |
| 0.10 | 22.88 g | 18.67 cd | 17.70 c | 19.75 C | 32.85 no | 33.93 o | 19.71 de | 28.83 G |
| 0.15 | 22.50 fg | 18.38 c | 16.47 a | 19.12 B | 27.80 k | 32.80 no | 20.16 e | 26.92 E |
| Mean | 23.95 E | 22.94 B | 19.40 D | 22.09 A | 31.13 A | 30.81 A | 20.46 C | 27.47 B |
| r | −0.965 | −0.913 | −0.757 | −0.895 | −0.609 | 0.887 | −0.363 | 0.352 |
| Zinc | ||||||||
| 0 | 22.83 ef | 19.81 bc | 21.20 c–e | 21.28 AB | 22.72 ef | 17.69 a | 23.80 fg | 21.40 A |
| 0.05 | 26.06 h | 21.02 c–e | 21.05 c–e | 22.71 C | 20.54 cd | 22.17 d–f | 18.41 ab | 20.37 BD |
| 0.10 | 23.53 fg | 19.85 bc | 20.56 cd | 21.31 AB | 25.10 gh | 22.61 ef | 18.45 ab | 22.05 AC |
| 0.15 | 23.60 fg | 23.83 fg | 18.02 ab | 21.82 AC | 23.80 fg | 18.45 ab | 17.15 a | 19.80 D |
| Mean | 24.01 D | 21.13 B | 20.21 A | 21.78 B | 23.04 C | 20.23 A | 19.45 A | 20.91 A |
| r | -0.020 | 0.745 | −0.873 | 0.041 | 0.522 | 0.139 | −0.868 | −0.399 |
| Copper | ||||||||
| 0 | 5.834 j | 5.147 h | 3.688 bc | 4.890 F | 4.841 g | 4.047 d–f | 4.124 d–f | 4.337 BC |
| 0.05 | 5.674 j | 5.246 h | 4.276 f | 5.065 F | 4.651 g | 3.887 cd | 4.032 d–f | 4.190 B |
| 0.10 | 5.590 ij | 4.101 d–f | 4.208 ef | 4.633 D | 4.253 f | 3.933 c–e | 3.917 cd | 4.034 A |
| 0.15 | 5.338 hi | 3.291 a | 3.589 b | 4.073 AB | 4.208 ef | 4.238 f | 4.040 d–f | 4.162 AB |
| Mean | 5.609 C | 4.446 B | 3.940 A | 4.665 B | 4.488 B | 4.026 A | 4.028 A | 4.181 A |
| r | −0.980 | −0.934 | −0.134 | −0.860 | −0.962 | 0.511 | −0.557 | −0.708 |
| Manganese | ||||||||
| 0 | 244.3 a–c | 242.2 a–c | 245.5 bc | 244.0 A | 320.8 de | 338.0 ef | 319.7 de | 326.2 B |
| 0.05 | 245.5 bc | 233.0 a–c | 249.9 c | 242.8 A | 322.5 d–f | 340.2 f | 320.6 de | 327.8 B |
| 0.10 | 247.2 bc | 228.7 ab | 249.4 c | 241.8 A | 316.6 d | 330.3 d–f | 317.9 d | 321.6 B |
| 0.15 | 246.2 bc | 226.6 a | 245.0 a–c | 239.3 A | 312.7 d | 329.2 d–f | 317.7 d | 319.9 B |
| Mean | 245.8 A | 232.6 C | 247.5 A | 242.0 A | 318.2 B | 334.4 D | 319.0 B | 323.9 B |
| r | 0.784 | −0.954 | −0.101 | −0.977 | −0.886 | −0.853 | −0.798 | −0.869 |
| Iron | ||||||||
| 0 | 9097 b–d | 8842 a–d | 8858 a–d | 8932 A | 10,447 ef | 10,371 ef | 10,113 e | 10310 B |
| 0.05 | 9202 cd | 8774 a–c | 9090 b–d | 9022 A | 10,490 ef | 10,403 ef | 10,264 e | 10386 B |
| 0.10 | 9102 b–d | 8615 ab | 9335 d | 9017 A | 10,538 ef | 10,917 f | 10,160 e | 10538 B |
| 0.15 | 9067 b–d | 8472 a | 8945 a–d | 8828 A | 10,416 ef | 10,928 f | 10,001 e | 10448 B |
| Mean | 9117 A | 8676 C | 9057 A | 8950 A | 10,473 B | 10,655 B | 10,135 D | 10421 B |
| r | −0.418 | −0.988 | 0.313 | −0.450 | −0.110 | 0.911 | −0.521 | 0.757 |
| Cobalt | ||||||||
| 0 | 3.345 a–d | 2.776 a–c | 3.263 a–d | 3.128 BC | 3.895 a–d | 4.422 b–d | 3.768 b–d | 4.028 A |
| 0.05 | 3.428 a–d | 3.018 a–d | 3.766 a–d | 3.404 AB | 4.113 cd | 4.647 d | 3.428 a–d | 4.063 A |
| 0.10 | 4.647 d | 3.180 a–d | 4.290 cd | 4.039 A | 3.596 a–d | 4.156 a–d | 3.263 a–d | 3.672 AB |
| 0.15 | 3.098 a–d | 3.428 a–d | 3.263 a–d | 3.263 A–C | 3.387 a–d | 3.262 a | 2.697 ab | 3.115 C |
| Mean | 3.630 A | 3.101 A | 3.646 A | 3.459 A | 3.748 A | 4.122 A | 3.289 A | 3.720 A |
| r | 0.089 | 0.997 | 0.138 | 0.333 | −0.822 | −0.844 | −0.975 | −0.919 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wyszkowski, M.; Kordala, N.; Brodowska, M.S. Trace Element Content in Soils with Nitrogen Fertilisation and Humic Acids Addition. Agriculture 2023, 13, 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13050968
Wyszkowski M, Kordala N, Brodowska MS. Trace Element Content in Soils with Nitrogen Fertilisation and Humic Acids Addition. Agriculture. 2023; 13(5):968. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13050968
Chicago/Turabian StyleWyszkowski, Mirosław, Natalia Kordala, and Marzena S. Brodowska. 2023. "Trace Element Content in Soils with Nitrogen Fertilisation and Humic Acids Addition" Agriculture 13, no. 5: 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13050968
APA StyleWyszkowski, M., Kordala, N., & Brodowska, M. S. (2023). Trace Element Content in Soils with Nitrogen Fertilisation and Humic Acids Addition. Agriculture, 13(5), 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13050968






