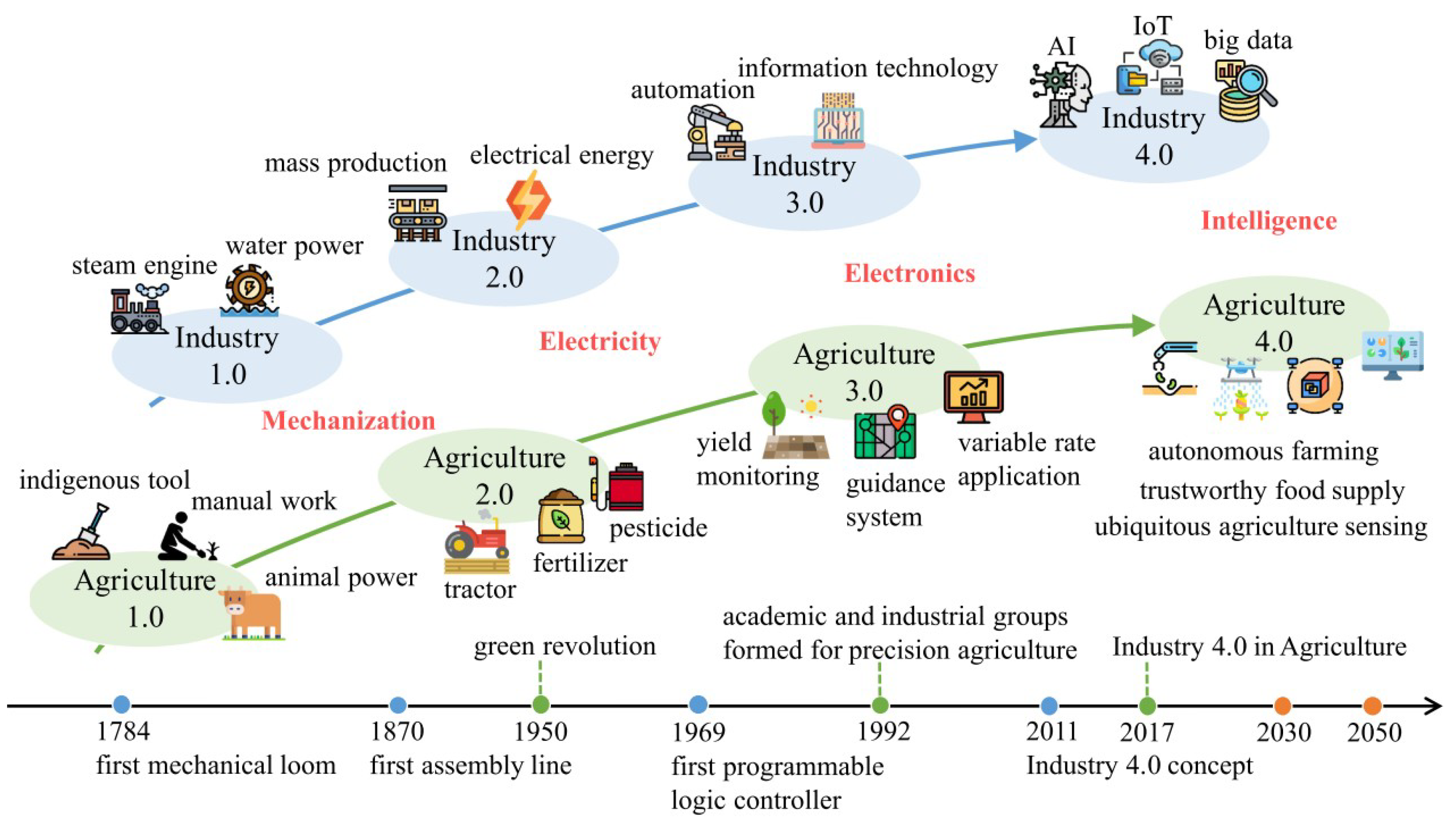
A Survey on Digital Agriculture in Five West African Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bibliometric Survey on Digital Agriculture
2.2. Survey on Technologies Used in Digital Agriculture
2.3. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bibliometric Study
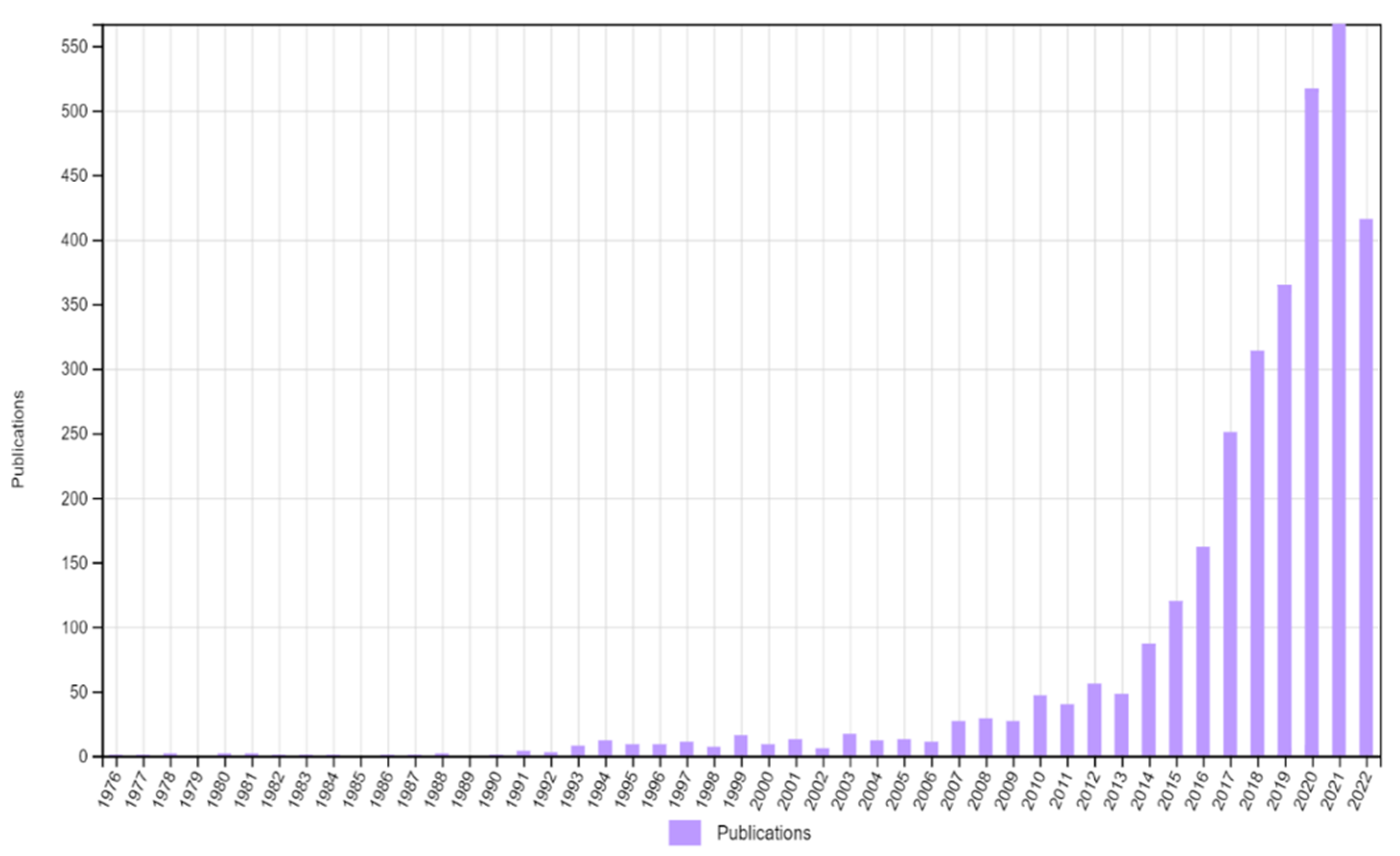
3.1.1. Annual Scientific Production
3.1.2. Relevant Source
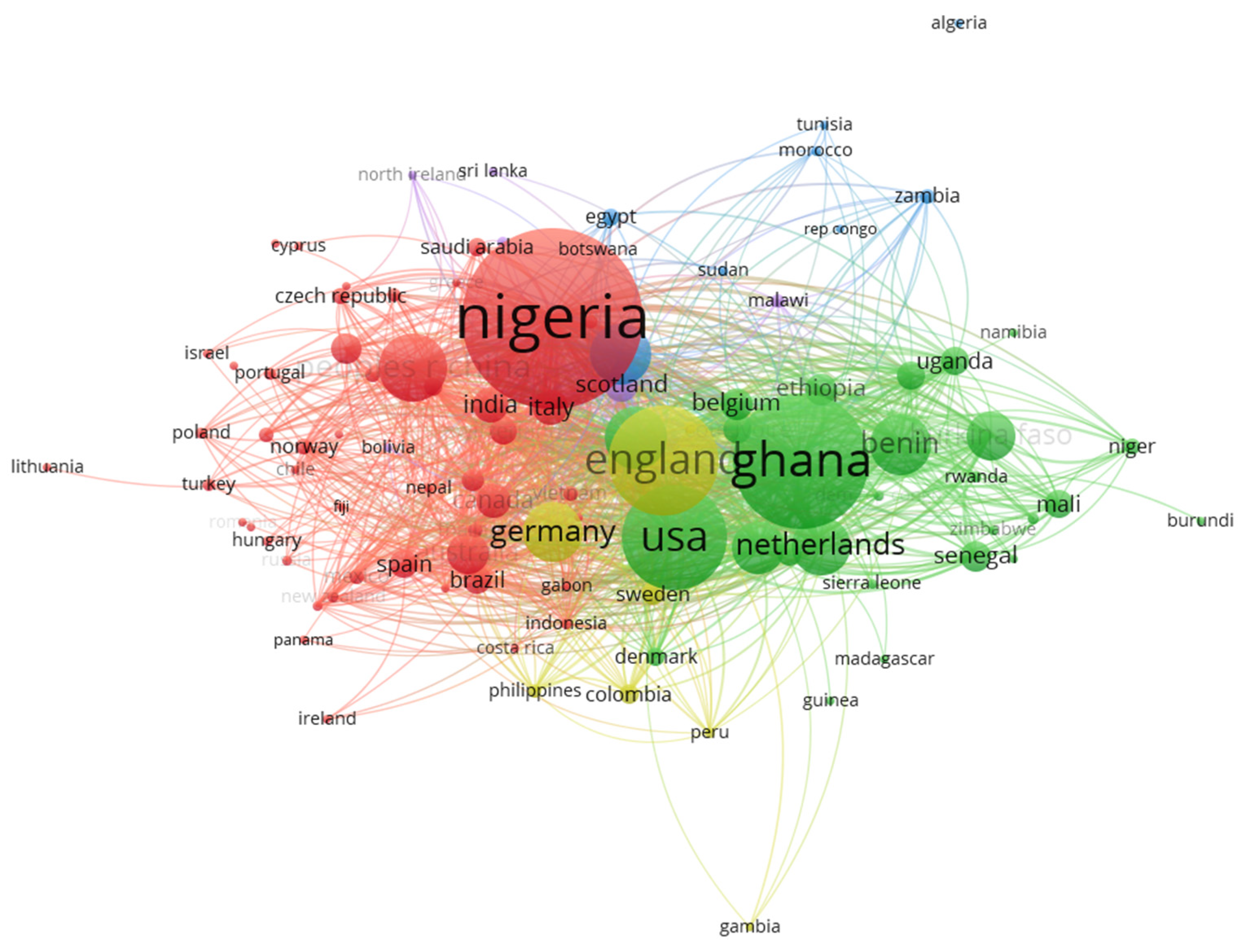
3.1.3. Author Countries
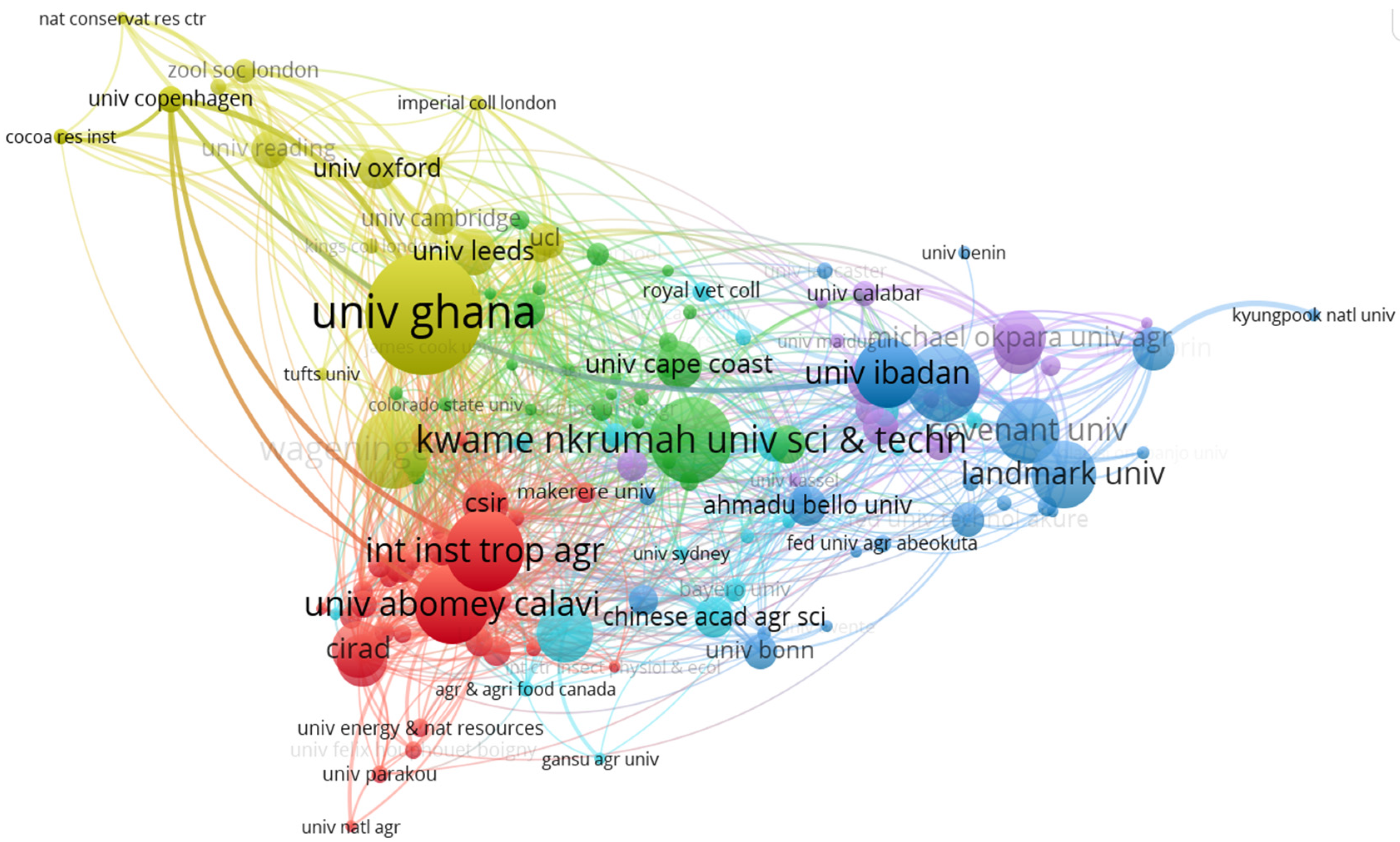
3.1.4. Author Organizations
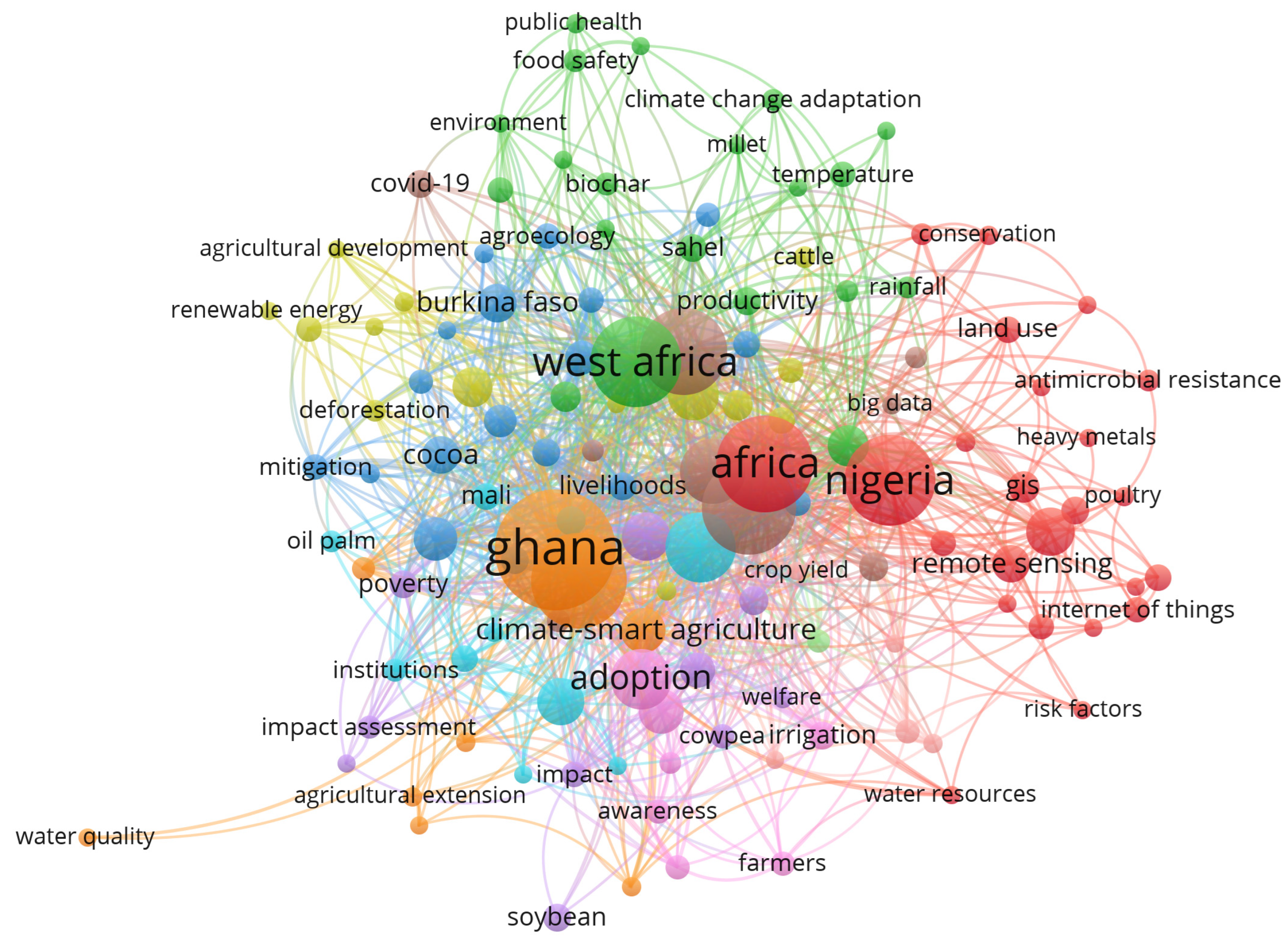
3.1.5. Co-Occurrence Network
3.2. Digital Technologies Survey in the Five West African Countries
3.3. Lessons Learned
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu, N.S.; Bukhari, W.M.; Ong, C.H.; Kassim, A.M.; Izzuddin, T.A.; Sukhaimie, M.N.; Norasikin, M.A.; Rasid, A.F.A. Internet of Things Applications in Precision Agriculture: A Review. J. Robot. Control (JRC) 2022, 3, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, U.C.; Agubor, C.K.; Ezema, L.S. Development of a Long-Range WAN Weather and Soil Monitoring System for Rural Farmers. Eximia 2022, 4, 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Sott, M.K.; da Silva Nascimento, L.; Foguesatto, C.R.; Furstenau, L.B.; Faccin, K.; Zawislak, P.A.; Mellado, B.; Kong, J.D.; Bragazzi, N.L. A Bibliometric Network Analysis of Recent Publications on Evolution Structure. Sensors 2021, 21, 7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Haneef, F.; Kumar, S.; Ongsakul, V. Internet of things and agriculture relationship: A bibliometric analysis. J. Glob. Bus. Adv. 2020, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzembrak, Y.; Klu¨che, M.; Gavai, A.; Marvin, H.J.P. Internet of Things in food safety: Literature review and a bibliometric analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 94, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.M.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Espitia, H.E. Bibliometric analysis of publications discussing the use of the artificial intelligence technique agent-based models in sustainable agriculture. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piot-lepetit, I.; Florez, M.; Gauche, K. Understanding the determinants of IT adoption in agriculture using an integrated TAM-TOE model: A bibliometric analysis. 170. EAAE Seminar: Governance of food chains and consumption dynamics: What are the impacts on food security and sustainability? In Proceedings of the 170th EAE Seminar, Montpellier, France, 15–17 May 2019; Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/hal/journl/hal-02789959.html (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Iftikhar, A.; Ali, I.; Arslan, A.; Tarba, S. Digital Innovation, Data Analytics, and Supply Chain Resiliency: A Bibliometric-based Systematic Literature Review. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Rejeb, K.; Rejeb, A.; Mostafa, M.M.; Zailani, S. Wireless Sensor Networks in Agriculture: Insights from Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Yerudkar, A.; Mariani, V.; Iannelli, L.; Glielmo, L. A Bibliometric Review of the Use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Precision Agriculture and Precision Viticulture for Sensing Applications. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmer, J.; Bugert, N.; Lasch, R. Analysis of resilience strategies and ripple effect in blockchain coordinated supply chains: An agent- based simulation study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Dixon, J.; Guin, U.; Dimase, D. A Blockchain-Based Framework for Supply Chain Provenance. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 157113–157125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Motamarri, S.; Hani, U.; Shams, R.; Fernando, M.; Babu, M.M.; Shen, K.N. Building dynamic service analytics capabilities for the digital marketplace. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 118, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, J.; Wamba, S.F.; Roubaud, D.; Foropon, C.R.H. Empirical investigation of data analytics capability and organizational flexibility as complements to supply chain resilience. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 59, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, U.; Mumtaz, R.; García-Nieto, J.; Hassan, S.A.; Zaidi, S.A.R.; Iqbal, N. Precision Agriculture Techniques and Practices: From Considerations to Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Society of Precision Agriculture (ISPA), ”Precision Agriculture”. 2019. Available online: https://www.springer.com/journal/11119/updates/17240272 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Jaiswal, S.P.; Bhadoria, V.S.; Agrawal, A.; Ahuja, H. Internet of Things (IoT) for Smart Agriculture and Farming in Developing Nations. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 8, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Mekonnen, Y.; Namuduri, S.; Burton, L.; Sarwat, A.; Bhansali, S. Review—Machine Learning Techniques in Wireless Sensor Network Based Precision Agriculture. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 167, 037522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Shu, L.; Hancke, G.P.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. From Industry 4.0 to Agriculture 4.0: Current Status, Enabling Technologies, and Research Challenges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 4322–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, G.; Persico, V.; Pescape, A. A survey on information and communication technologies for industry 4.0: State-of-the-art, tax- onomies, perspectives, and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2019, 21, 3467–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheni, E.; Machii, J.; Murumba, J. Internet of Things, Big Data Analytics, and Deep Learning for Sustainable Precision Agriculture. In Proceedings of the ST-Africa 2022 Conference Proceedings Miriam Cunningham and Paul Cunningham (Eds) IST-Africa Institute and IIMC, Dublin, Ireland, 16–20 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mushi, G.E.; Serugendo, G.D.M.; Burgi, P.-Y. Digital Technology and Services for Sustainable Agriculture in Tanzania: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayih, A.Z.; Morales, J.; Assabie, Y.; de By, R.A. Utilization of Internet of Things and Wireless Sensor Networks for Sustainable Smallholder Agriculture. Sensors 2022, 22, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderahman, R.; Steve, S.; Karim, R.; Horst, T.; Suhaiza, Z. Internet of Things research in supply chain management and logistics: A bibliometric analysis. Internet Things 2020, 12, 100318. [Google Scholar]
- Aoga, J.; Bae, J.; Veljanoska, S.; Nijssen, S.; Schaus, P. Impact of weather factors on migration intention using machine learning algorithms. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.02794. [Google Scholar]
- Gouly, Y.E.; Gusov, A. Digital technologies as the factor of development of agro-industrial clusters in the countries of Africa. In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference (ISPC), Yekaterinburg, Russia, 7–9 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piegnède, E.; Roudier, P.; Diedhiou, A.; Hermann, V.; N’Guessan, B.; Kobea, A.T.; Konate, D.; Bi Pene, C. Sugarcane yield forecast in Ivory Coast (West Africa) based on weather and vegetation index data Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, G.C.; Annor, T.; Odai, S.N.; Larbi, I. Land Use Landcover Change Monitoring and Projection in the Dano Catchment, Southwest Burkina Faso. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2019, 9, 3185–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkuor, G.; Hounkpatin, O.K.L.; Welp, G.; Thiel, M. High Resolution Mapping of Soil Properties Using Remote Sensing Variables in South-Western Burkina Faso: A Comparison of Machine Learning and Multiple Linear Regression Models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougmore, T.W.; Sadouanouan, M.A.L.O.; Kagembega, F.; Togueyini, A. Low cost IoT solutions for agricultures fish farmers in Afirca: A case study from Burkina Faso. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Smart Cities and Communities (SCCIC), Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 24–26 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Soro, M.-P.; Marcellin Yao, K.; Kouassi, G.L.B.; Ouattara, A.A.; Diaco, T. Modeling the Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Chlorophyll-a in Three Tropical Rivers Comoe, Bandama, and Bia Rivers (Cote d’Ivoire) by Artificial Neural Network. Appl. Wetl. Sci. 2020, 40, 939–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, S.; Medeni, T.D.; Soylu, D. Assessment of role of innovative technology through blockchain technology in Ghana’s Cocoa beans food supply chains. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 11–13 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.; Shabaz, M.; Pandit, P.; Parvathy, L.R.; Ofori, I. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain Technology in Healthcare and Agriculture. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 4228448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wally, D. Exploring the Application of ICTs and Big Data Analytics on Climate Data in Climate-Smart Agriculture to Increase Productivity for Small-Scale Farmers: The Case of Ghana. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Appiah-Badu, N.K.A.; Missah, Y.M.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Ussiph, N.; Frimpong, T.; Ahene, E. Rainfall Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms for the Various Ecological Zones of Ghana. IEEE Access 2021, 10, 5069–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nketia, K.; Asabere, S.; Ramcharan, A.; Herbold, S.; Erasmi, S.; Sauer, D. Spatio-temporal mapping of soil water storage in a semi-arid landscape of northern Ghana—A multi-tasked ensemble machine-learning approach. Geoderma 2022, 410, 115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedric, L.S.; Adoni, W.Y.H.; Aworka, R.; Zoueu, J.T.; Mutombo, F.K.; Krichen, M.; Kimpolo, C.L.M. Crops yield prediction based on machine learning models: Case of West African countries. Smart Agric. Technol. 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamekye, C.; Kwofie, S.; Ghansah, B.; Agyapong, E.; Boamah, L.A. Assessing urban growth in Ghana using machine learning and intensity analysis: A case study of the New Juaben Municipality. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, U.S.; Nyabam, M.; Orisekeh, K.; Umar, S.; Sani, B.; David, E.; Umoru, A.A. Exploiting IoT and LoRaWAN technologies for effective livestock monitoring in Nigeria. Arid. Zone J. Eng. Technol. Environ. 2019, 15, 146–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ajao, L.A.; Agajo, J.; Muazu, M.B.; Schuell, J.K. A scheduling- based algorithm for low energy consumption in smart agriculture precision monitoring system. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2020, 22, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Borgwardt, H. Conception of Smart Farming Solutions in the Context of Botswana’s Digital Development: Identifying and Evaluating Potential Innovations That Enable Smallholder Farmers in Botswana to Access Data, Connecting Them to New Resources, Knowledge, and Markets, Based on A Federated Digital Framework to Advance Africa’s Transition to a Digital Economy. Ph.D. Thesis, HTWG Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Elijah, O.; Orikumhi, I.; Rahman, T.A.; Babale, S.A.; Orakwue, S.I. Enabling smart agriculture in Nigeria: Application of IoT and data analytics. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electro-Technology for National Development (NIGERCON), Owerri, Nigeria, 7–10 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manoharan, A.M.; Rathinasabapathy, V. Smart water quality monitoring and metering using Lora for smart villages. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Smart Grid and Smart Cities, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–14 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bore, N.; Kinai, A.; Waweru, P.; Wambugu, I.; Mutahi, J.; Kemunto, E.; Weldemariam, K. AGWS: Blockchain-enabled Small-scale Farm Digitization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–6 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omo-Ojugo, E. Relevance of Big Data Analytics in Agriculture: Focus on Nigeria Agricultural Sector. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, M.A.; Sani, B.M.; Suleiman, U. An Overview of Machine and Deep Learning Technologies Application in Agriculture: Opportunities and Challenges in Nigeria. SLU J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, R.W.; Ikeremo, E.S.; Olubummo, D.A. Application of Machine Learning Identification and Classification of Muturu and Keteku Cattle Species for a Smart Agricultural Practice in Developing Countries such as Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2022, 26, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwabueze, C.A.; Akaneme, S.A.; Nwabueze, I.R. Enhancing agricultural production using wireless sensor network. Iconic Res. Eng. J. 2019, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Oyedeji, A. A review of wireless sensor network potential in Nigeria as a tool for sustainable development. J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 28, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asogwa, T.C.; Obiokafor, I.N. Wireless Sensor Network(WSN): Applications in Oil and Gas and Agriculture Industries in Nigeria. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2018, 6. ISSN 2278-1021 (Online). [Google Scholar]
- Bolaji, A.A. e-Cattle: Opportunity in the application of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) to cattle health/behavioral monitoring and tracking for farmers in Nigeria. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Science, Technology, Education, Arts, Management and Social Sciences, Nanjing, China, 26–27 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkadi, S.B.; Aminu, A.; Muhammad, F.; Kassim, A.; Muhammad, U.; Muhammad, B.; Yusuf, I. Forest Fires: Challenges and Impact Review. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Engineering and Natural Sciences, Konya, Turkey, 20–23 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaga, T.D.; Dube, T.; Shekede, M.D.; Shoko, C. Impacts of Climate Variability and Drought on Surface Water Resources in Sub-Saharan Africa Using Remote Sensing: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghmeh, N.; Waidah, I.; Mahadi, R.; Ahmad, Z. Mapping the research trends on blockchain technology in food and agriculture industry: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101272. [Google Scholar]

| Papers | Digital Technology | Details | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benin | |||
| J. Aoga et al. [26] | AI, machine learning | random forest (RF) and extreme gradient boosting (XGB) | Crops, production (forecasting of soil properties) |
| Burkina Faso | |||
| Y. E. Gouly and A. Gusov [27] | digital platforms, artificial intelligence, and robotics | Agro-industrial platform | Crops yield production (cereal and rice production), livestock and fisheries production |
| E. Pignede et al. [28] | AI, machine learning, automatic learning | rainfall data, temperature data, and sugarcane yield analysis | Sugarcane yield forecasting using the random forest method |
| Gloria C. Okafor et al. [29] | Satellite images | Rain-fed agriculture prediction | cassava, yam, groundnut, maize, and sorghum crops production |
| G. Forkuor et al. [30] | IoT, WSN, and IA | Satellite spectral data, terrain and climatic variables analyzed based on multiple linear regression (MLR), random forest regression (RFR), support vector machines for regression (SVM), and stochastic gradient boosting (SGB) | prediction of soil properties |
| T. W. Zoug- more et al. [31] | IoT | Sensor measure parameters, such as pH, dissolved oxygen, water temperature, soil moisture, and meteorological parameters (wind speed, air humidity, rainfall, sunshine) | soil moisture properties for papaya and banana crop production |
| Cote d’Ivoire | |||
| M-P. Soro et al. [32] | AI, machine learning | Artificial neural network | Riverine water monitoring |
| E. Pignede et al. [28] | AI, machine learning, automatic learning | Rainfall data, temperature data, and sugarcane yield analysis | Sugarcane yield forecasting using the random forest method |
| Ghana | |||
| S. Musah et al. [33] | Blockchain | Transparency and traceability enhancement, unethical activities mitigation | Cocoa bean food supply chains |
| S. Vyas et al. [34] | AI and blockchain | Food supply chains and drug supply chains management, quality maintenance, and intelligent prediction | Drug supply chain |
| D. Wally et al. [35] | Big data and ICT | Satellites and remote sensors, mobile phone and remote sensors, accounting software, and GPS | farmers income increasing, data quality, ownership, and accessibility |
| N. K. A. Appiah-Badu et al. [36] | AI, machine learning | Random forest and extreme gradient boosting method for rainfall prediction, temperature (minimum and maximum), relative humidity, sunshine hours, and wind speed data prediction | ecological zone |
| K. A. Nketia [37] | AI, machine learning | Random forest, extreme gradient boosting algorithms | soil water storage in landscape |
| L. S. Cedric et al. [38] | AI and big data | Crops yield prediction weather data and chemical data | predict bananas, dry beans, cassava, rice, maize, and seed cotton |
| C. Nyamekye et al. [39] | AI, machine learning | Evaluation of the transitions among the major land use/land cover categories in machine learning algorithms (random forest) and intensity analysis | Environment |
| Nigeria | |||
| U. S. Abdul- lahi et al. [40] | IoT-LoRaWAN | Precision agriculture that uses analytic measurements to optimize farming decisions | Livestock farming: IoT helps farmers in making lists, preparing reports, sorting cows by category, and tracking each animal’s overall lifetime |
| U. C. Njoku et al. [41] | Wireless sensor networks (WSNs)- LoRaWAN | Remote monitoring system of the environmental weather and soil conditions of the farmland to trigger irrigation automatically | field monitoring for rural farmers and automatic irrigation system |
| L. A. Ajao et al. [2] | IoT: WSN-Wi-Fi | Agro-climatic field parameters sensing using soil pH meter, soil moisture, and environmental temperature and humidity sensors. Energy consumption system managing using algorithmic state machine technique | Regular farm crops monitoring using the low energy consumption system |
| H. Borg- wardt [42] | Digital platforms, GPS tracking solution with LoRaWAN | Survey on smart farming and adoption | digital applications for market access and crowd farming, digital applications adoption |
| O. Elijah et al. [43] | IoT and data analysis | The application of IoT technologies and data analysis in agriculture: Sensing monitoring, use of RFID, etc. | Plant farms, animal farms, automated machinery, aquaponics |
| A. M. Manoha-ran, and V. Rathinasabapthy [44] | IoT-LoRaWAN | The LoRa mote along with sensors are placed in water tanks at villages and within corporation limits | smart village: Water quality monitoring and distribution, chemical leakage detection in rivers |
| N. Bore et al. [45] | blockchain | Agribusiness digital wallet (ADW) system development, which leverages blockchain to formalize the interactions and enable seamless data flow in small-scale farming ecosystem | Small-scale farming formalization digital trust establishment among the agriculture stakeholders |
| E. Omo Ojugo [46] | Big data | Big data analytics adoption for farming practices enhancement | Yield improvement |
| M. A. Umar et al. [47] | AI, machine learning, and deep learning | Models, such as ANN, SVM, EL/RF, ANN-XY, CNN, MLR, hybrid ANN, LSTM, LR/Bagging tree, FFNN, DT, BP, GWR, and XGBoost are used | Crop management, livestock management, water, and soil management |
| R. W. Bello et al. [48] | AI, machine learning and deep learning | Enhanced mask region-based convolutional neural networks (mask RCNN) | breeding improvement |
| Nwabueze, C. A. et al. [49] | WSN and GSM communication technology | Design of smart irrigation system to improve agricultural yield | Monitoring and control of various environmental factors, such as soil moisture and temperature |
| Ajibola O. [50] | WSN applications | Review on WSN: Measure of parameters, such as pH level, electrical conductivity, oxidation-reduction Potential (ORP), turbidity | Monitoring of the water quality distributed in the country |
| Asogwa, T. C. et al. [51] | Sensor nodes deployed in farm field to measure air temperature, relative humidity, and soil moisture. They are also used to keep livestock healthier with a minimum use of resources | Use of sensor nodes to monitor micro-climates in a potato, millet, or cassava field. Determination of the pH level and temperature inside the cow‘s rumen | |
| Bolaji A. A. et al. [52] | Electronic-cattle health monitoring using WSN | Cattle parameters monitoring, such as farming environment, cattle movement, cattle health, reproduction management, lactation and rumination monitoring | |
| Abdulkadir S. B. et al. [53] | Design of forest fire monitoring system using sensors. Arduino microcontroller is used as the brain of the research to regulate input from the AMG8833 sensor and GPS Ubox 6 M | hotspots detection from 19.25 to 122.5 °C by sensor nodes, which present the capcacity to detect fire in the distance range of 2.5 to 10 m | |
| Trisha D. B. et al. [54] | Remote sensing techniques of draft monitoring, traditional drought, and surface water body monitoring | Techniques tracking droughts using remote sensing, including its relevance in monitoring climate variability and hydrological drought impacts on surface water resource | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Degila, J.; Tognisse, I.S.; Honfoga, A.-C.; Houetohossou, S.C.A.; Sodedji, F.A.K.; Avakoudjo, H.G.G.; Tahi, S.P.G.; Assogbadjo, A.E. A Survey on Digital Agriculture in Five West African Countries. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051067
Degila J, Tognisse IS, Honfoga A-C, Houetohossou SCA, Sodedji FAK, Avakoudjo HGG, Tahi SPG, Assogbadjo AE. A Survey on Digital Agriculture in Five West African Countries. Agriculture. 2023; 13(5):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051067
Chicago/Turabian StyleDegila, Jules, Ida Sèmévo Tognisse, Anne-Carole Honfoga, Sèton Calmette Ariane Houetohossou, Fréjus Ariel Kpedetin Sodedji, Hospice Gérard Gracias Avakoudjo, Souand Peace Gloria Tahi, and Achille Ephrem Assogbadjo. 2023. "A Survey on Digital Agriculture in Five West African Countries" Agriculture 13, no. 5: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051067
APA StyleDegila, J., Tognisse, I. S., Honfoga, A.-C., Houetohossou, S. C. A., Sodedji, F. A. K., Avakoudjo, H. G. G., Tahi, S. P. G., & Assogbadjo, A. E. (2023). A Survey on Digital Agriculture in Five West African Countries. Agriculture, 13(5), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051067