The Effect of Dietary Humic Substances on Cellular Immunity and Blood Characteristics in Piglets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.2.1. Haematological and Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.2.2. Biomarker of the Lipid Peroxidation
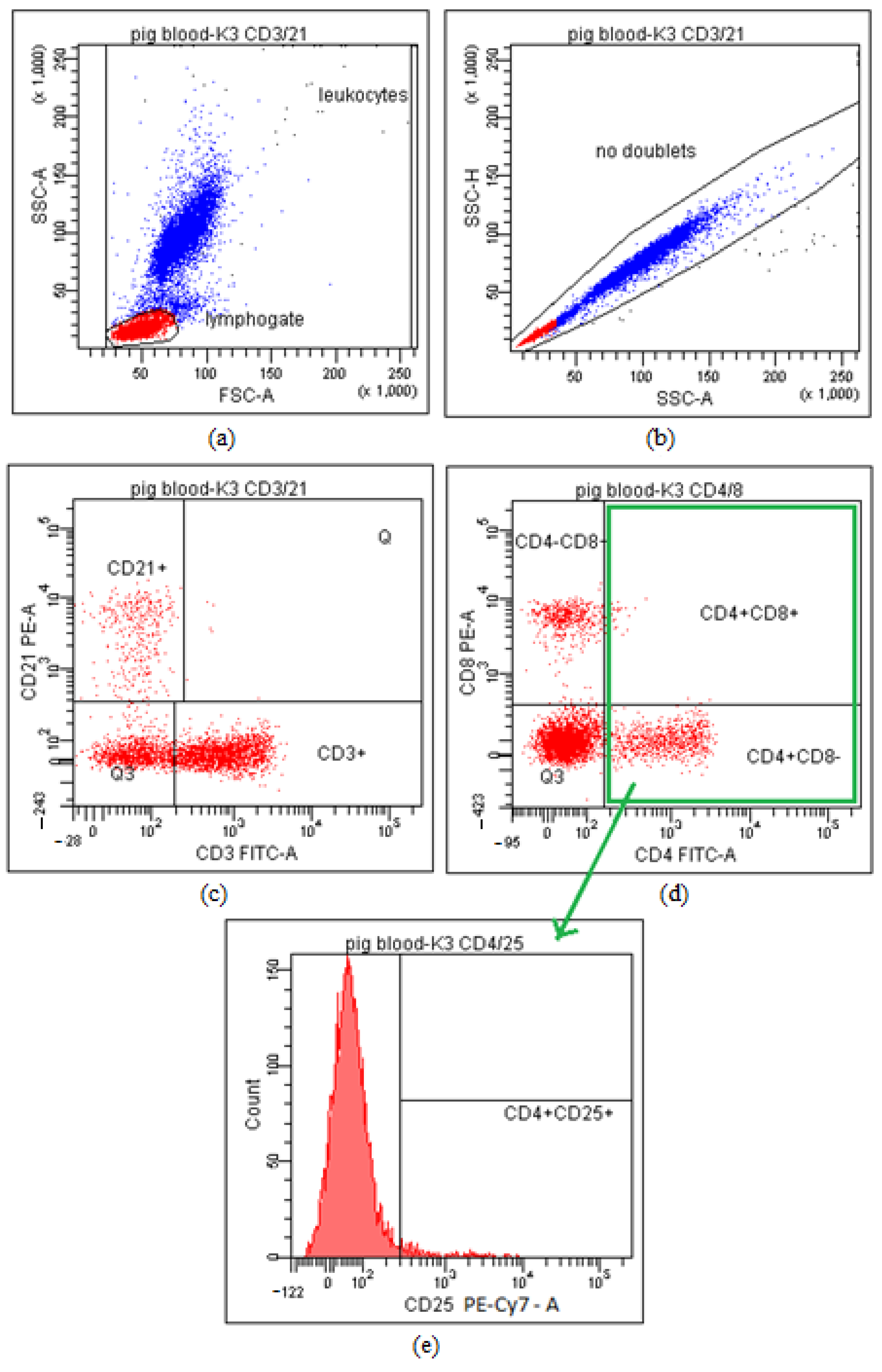
2.2.3. Phagocyte Activity Testing and Identification of Lymphocyte Subpopulations
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Haematological and Serum Biochemical Parameters
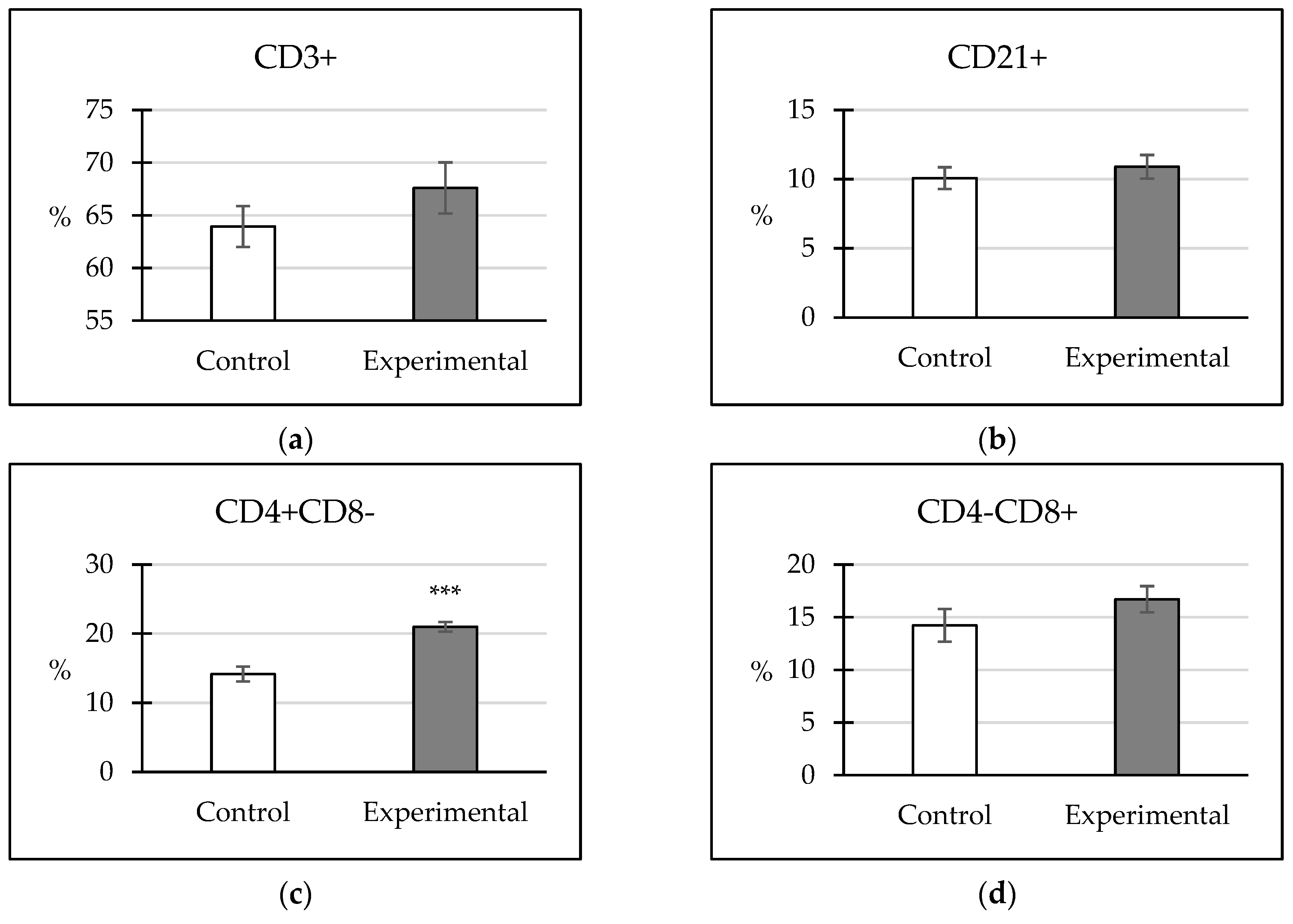
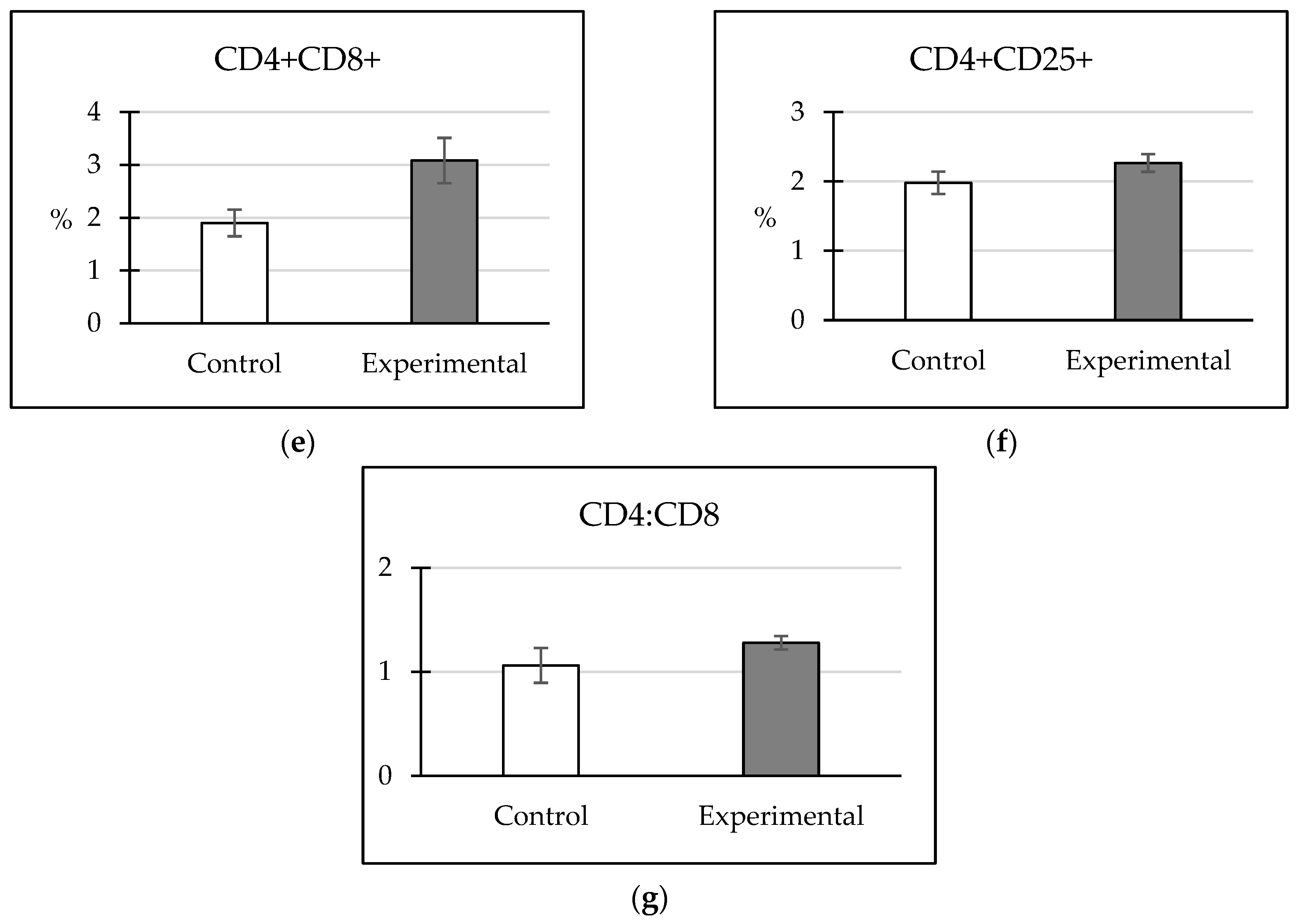
3.2. Cellular Immune Response
4. Discussion
4.1. Cellular Immune Response
4.2. Haematological and Serum Biochemical Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peña-Méndez, E.M.; Havel, J.; Patočka, J. Humic substances-compounds of still unknown structure: Applications in agriculture, industry, environment, and biomedicine. J. Appl. Biomed. 2005, 3, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.J.; Yoo, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Effects of supplemental humic substances on growth performance, blood characteristics and meat quality in finishing pigs. Livest. Sci. 2008, 117, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, S.A. Effect of humic substances on higher animals and man, the possible use of humic compounds in medical treatments. In Proceedings of the International Humic Acid Society Meeting, Sevilla, Spain, 1988; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, F.J. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions; Wiley-Inter-Science: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H.M.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Youssef, A.W.; Hassan, E.R. Effect of using organic acids to substitute antibiotic growth promoters on performance and intestinal microflora of broilers. Asian-Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálik, B.; Hrnčár, C.; Gašparovič, M.; Rolinec, M.; Hanušovský, O.; Juráček, M.; Šimko, M.; Zábranský, L.; Kovacik, A. The Effect of Humic Substances on the Meat Quality in the Fattening of Farm Pheasants (Phasianus colchicus). Agriculture 2023, 13, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoglu, M.; Macit, M.; Esenbuga, N.; Durdag, H.; Turgut, L.; Bilgin, O.C. Effect of supplemental humate at different levels on the growth performance, slaughter and carcass traits of broilers. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2004, 3, 406–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F.; McGlone, J.J.; Kim, S.W. Effects of dietary humic substances on pig growth performance, carcass characteristics, and ammonia emission. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 2482–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacková, Z.; Zigo, F.; Farkašová, Z.; Ondrašovičová, S. The Effect of Humic Substances as an Organic Supplement on the Fattening Performance, Quality of Meat, and Selected Biochemical Parameters of Rabbits. Life 2022, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaevska, M.; Lorencova, A.; Videnska, P.; Sedlar, K.; Provaznik, I.; Trckova, M. Effect of sodium humate and zinc oxide used in prophylaxis of post-weaning diarrhoea on faecal microbiota composition in weaned piglets. Vet. Med. 2016, 61, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trckova, M.; Matlova, L.; Hudcova, H.; Martin, F.; Zraly, Z.; Dvorska, L.; Beran, V.; Pavlik, I. Peat as a feed supplement for animals: A review. Vet. Med. -Czech. 2005, 50, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.E.; van Sambeek, D.M.; Gabler, N.K.; Kerr, B.J.; Moreland, S.; Johal, S.; Edmonds, M.S. Effects of dietary humic and butyric acid on growth performance and response to lipopolysaccharide in young pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 4172–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y. Modulation of the growth performance, meat composition, oxidative status, and immunity of broilers by dietary fulvic acids. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 4509–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepchenko, L.M. The role of humic preparations in the management of metabolic processes in the formation of biological products of agricultural animals. In Achievements and Prospects for the Use of Humic Substances in Agriculture; Publishing House of the Agricultural Institute: Dnepropetrovsk, Ukraine, 2008; pp. 70–74. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ying, J.; Zou, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.; Yu, D.; Li, W.; Zhan, X. Effects of dietary supplementation of humic acid sodium and zinc oxide on growth performance, immune status and antioxidant capacity of weaned piglets. Animals 2020, 10, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudroňová, D.; Karaffová, V.; Pešulová, T.; Koščová, J.; Maruščáková, I.C.; Bartkovský, M.; Marcinčáková, D.; Ševčíková, Z.; Marcinčák, S. The effect of humic substances on gut microbiota and immune response of broilers. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudroňová, D.; Karaffová, V.; Semjon, B.; Naď, P.; Koščová, J.; Bartkovský, M.; Makiš, A.; Bujňák, L.; Nagy, J.; Mojžišová, J.; et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of humic substances on production parameters, immune status and gut microbiota of laying hens. Agriculture 2021, 11, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 276, 33–79. [Google Scholar]
- Šimeček, K.; Zeman, L.; Heger, J. Nutrient requirement and tables of nutritional values of pig feeds, 3rd ed.; Czech Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Brno, Czech Republic, 2000; 125p. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 152/2009 of 27 January 2009 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of feed. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2009, 54, 2–54. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.M.; Santos, R.C.C.; Lima, E.S. A simple automated procedure for thiol measurement in human serum samples. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2006, 42, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELnaggar, A.S.; El-Kelawy, M.I. Effect of humic acid supplementation on productive performance, blood constituents, immune response and carcass characteristics of sasso chicken. Egypt. J. Anim. Prod. 2018, 55, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sanmiguel, P.R.; Rondón, B.I. Supplementation with humic substances affects the innate immunity in layer hens in posfasting phase. Rev. MVZ Córdoba 2016, 21, 5198–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, E.; Guclu, B.K.; Cetin, N. Effect of dietary humate and organic acid supplementation on social stress induced by high stocking density in laying hens. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, H.; Mansour, E.; Reham, R.R.; Abd El Hamid, E.S. Study on the effect of humic acid on growth performance, immunological, some blood parameters and control intestinal Closterdium in broiler chickens. Zag. Vet. J. 2015, 43, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Bae, I.; Cho, J.; Choi, Y.; Ha, J.; Choi, J. Effects of humic acid and blueberry leaf powder supplementation in feeds on the productivity, blood and meat quality of finishing pigs. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2019, 39, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, A.O.; Okwelum, N.; Irekhore, O.T.; Ogunlade, B.A.; Adigun, A.A.; Elegbede, L.A.; Oyedeji, M.M. Haematological and biochemical parameters of broiler chicken supplemented with humic acid in the drinking water. Appl. Trop. Agric. 2016, 21, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Terratol, L.L.C. Effects of Humic Acid on Animals and Humans. Available online: https://fulvic.info/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/M-Terratrol_Article-1.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Doubek, J.; Šlosárková, S.; Řeháková, K.; Bouda, J.; Scheer, P.; Piperisová, I.; Tomenendálová, J.; Matalová, E. Interpretation of Basic Biochemical and Hematological Findings in Animals, 2nd ed.; Noviko: Brno, Czech Republic, 2010; p. 102. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Kraft, W.; Dürr, U.M. Klinická Laboratórna Diagnostika vo Veterinárnej Medicíne, 1st ed.; Hajko & Hajková: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2001; pp. 1–380. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
- Herzig, I.; Navrátilová, M.; Totušek, J.; Suchý, P.; Večerek, V.; Blahová, J.; Zralý, Z. The effect of humic acid on zinc accumulation in chicken broiler tissues. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 54, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamudovská, A.; Demeterová, M. Effect of diet supplemented with natural humic compounds and sodium humate on performance and selected metabolic variables in broiler chickens. Acta Vet. Brno 2010, 79, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaďuttová, I.; Marcinčáková, D.; Bartkovský, M.; Semjon, B.; Harčárová, M.; Nagyová, A.; Váczi, P.; Marcinčák, S. The effect of dietary humic substances on the fattening performance, carcass yield, blood biochemistry parameters and bone mineral profile of broiler chickens. Acta Vet. Brno 2019, 88, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, N.C.; Huff, W.E.; Huff, G.R. Effects of humic acid on broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, S.; Tanaka, K.; Kitao, H.; Nakadomo, F. Exercise-induced lipid peroxidation and leakage of enzymes before and after vitamin E supplementation. Int. J. Biochem. 1989, 21, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.R.; Pirzado, S.A.; Liu, G.H.; Chen, Z.M.; Chang, W.H.; Cai, H.Y.; Bryden, W.L.; Zheng, A.J. Dietary supplementation with sodium humate improves egg quality and immune function of laying hens. J. Appl. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control Diet | Experimental Diet | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Components | |||
| Corn | [%] | 25.00 | 25.00 |
| Wheat | [%] | 22.50 | 22.50 |
| Barley | [%] | 28.00 | 27.50 |
| Soybean meal | [%] | 21.00 | 21.00 |
| Vitamin-mineral premix with 3-phytase 1 | [%] | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Sodium chloride | [%] | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| L-Lysine | [%] | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| DL-Methionine | [%] | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| L-Threonine | [%] | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| HS supplement 2 | [%] | - | 0.50 |
| Composition by analysis | |||
| Dry matter | [g·kg−1] | 885.2 | 884.3 |
| Crude protein | [g·kg−1] | 178.2 | 177.4 |
| Crude fibre | [g·kg−1] | 35.4 | 38.9 |
| Ash | [g·kg−1] | 54.1 | 57.6 |
| Starch | [g·kg−1] | 445.0 | 438.0 |
| Calcium | [g·kg−1] | 6.4 | 7.0 |
| Phosphorus | [g·kg−1] | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| Sodium | [g·kg−1] | 2.7 | 2.8 |
| Metabolisable energy | [MJ·kg−1] | 13.07 | 13.02 |
| Type | Fluorochrome | Clone | Amount/50 µL Blood | Producer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-CD3e | FITC | BB23-8E6 | 4 µL | BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA |
| anti-CD4 | FITC | MIL 17 | 4 µL | AbD Serotec, Kidlington, UK |
| anti-CD8a | R-PE | MIL 12 | 2 µL | AbD Serotec, Kidlington, UK |
| anti-CD25 | PE-Cy7 | PC 61.5 | 1 µL | eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA |
| anti-CD21 | R-PE | BB6-11C9.6 | 2 µL | SuthernBiotech, Homewood, AL, USA |
| Control | Experimental | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haematological indices | ||||
| Red blood cells | [T·L−1] | 6.82 ± 0.10 | 6.81 ± 0.10 | 0.954 |
| Mean corpuscular volume | [fL] | 51.00 ± 0.26 | 52.00 ± 0.89 | 0.308 |
| Haematocrit | [L·L−1] | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.739 |
| Haemoglobin | [g·dL−1] | 11.68 ± 0.25 | 11.58 ± 0.19 | 0.755 |
| White blood cells | [G·L−1] | 10.87 ± 0.20 | 12.28 ± 1.24 | 0.287 |
| Serum metabolites | ||||
| Total protein | [g·L−1] | 60.03 ± 0.55 | 60.41 ± 0.68 | 0.675 |
| Albumin | [g·L−1] | 28.78 ± 1.76 | 32.80 ± 0.87 | 0.067 |
| Glucose | [mmol·L−1] | 5.05 ± 0.05 | 5.19 ± 0.10 | 0.217 |
| Urea | [mmol·L−1] | 3.89 ± 0.20 | 3.73 ± 0.25 | 0.621 |
| Triglycerides | [mmol·L−1] | 0.78 ± 0.09 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 0.375 |
| Cholesterol | [mmol·L−1] | 2.45 ± 0.17 | 2.47 ± 0.19 | 0.934 |
| Creatinine | [μmol·L−1] | 79.90 ± 3.55 | 81.10 ± 3.72 | 0.820 |
| ALP | [μkat·L−1] | 4.24 ± 0.12 | 4.60 ± 0.10 * | 0.041 |
| AST | [μkat·L−1] | 0.84 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.06 | 0.546 |
| Ca | [mmol·L−1] | 2.68 ± 0.04 | 2.82 ± 0.05 | 0.052 |
| P | [mmol·L−1] | 2.09 ± 0.02 | 2.11 ± 0.04 | 0.692 |
| TBARs | [nmol MDA·mL−1] | 0.72 ± 0.03 | 0.69 ± 0.03 | 0.562 |
| PAtotal [%] | PANeu [%] | PAMo [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 83.08 ± 0.62 | 85.68 ± 0.60 | 77.18 ± 1.76 |
| Experimental | 84.90 ± 1.33 | 88.04 ± 0.94 | 78.08 ± 2.10 |
| p-Value | 0.251 | 0.067 | 0.751 |
| MFItotal | MFINeu | MFIMo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 31,775 ± 3010 | 34,783 ± 3223 | 18,744 ± 1858 |
| Experimental | 36,057 ± 1097 | 39,560 ± 1220 | 19,041 ± 929 |
| p-Value | 0.218 | 0.203 | 0.889 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bujňák, L.; Hreško Šamudovská, A.; Mudroňová, D.; Naď, P.; Marcinčák, S.; Maskaľová, I.; Harčárová, M.; Karaffová, V.; Bartkovský, M. The Effect of Dietary Humic Substances on Cellular Immunity and Blood Characteristics in Piglets. Agriculture 2023, 13, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030636
Bujňák L, Hreško Šamudovská A, Mudroňová D, Naď P, Marcinčák S, Maskaľová I, Harčárová M, Karaffová V, Bartkovský M. The Effect of Dietary Humic Substances on Cellular Immunity and Blood Characteristics in Piglets. Agriculture. 2023; 13(3):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030636
Chicago/Turabian StyleBujňák, Lukáš, Alena Hreško Šamudovská, Dagmar Mudroňová, Pavel Naď, Slavomír Marcinčák, Iveta Maskaľová, Michaela Harčárová, Viera Karaffová, and Martin Bartkovský. 2023. "The Effect of Dietary Humic Substances on Cellular Immunity and Blood Characteristics in Piglets" Agriculture 13, no. 3: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030636
APA StyleBujňák, L., Hreško Šamudovská, A., Mudroňová, D., Naď, P., Marcinčák, S., Maskaľová, I., Harčárová, M., Karaffová, V., & Bartkovský, M. (2023). The Effect of Dietary Humic Substances on Cellular Immunity and Blood Characteristics in Piglets. Agriculture, 13(3), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030636









