Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Field of Agriculture: A Review
Abstract
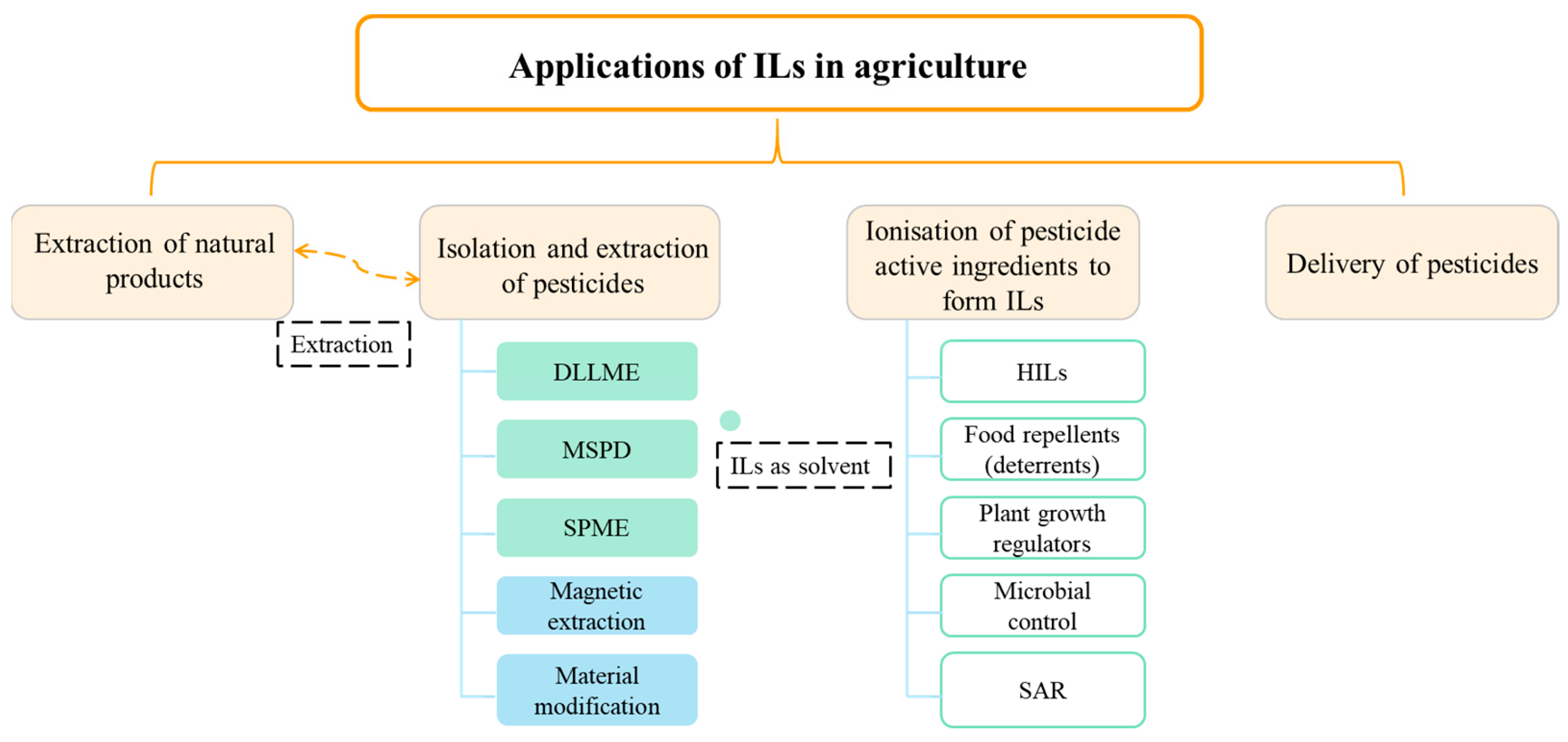
:1. Introduction
2. Extraction of Natural Products
3. Isolation and Extraction of Pesticides
3.1. ILs as Solvent
3.1.1. DLLME
3.1.2. Solid-Phase Dispersion (MSPD)
3.1.3. Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME)
3.2. Magnetic Extraction
3.3. Material Modification
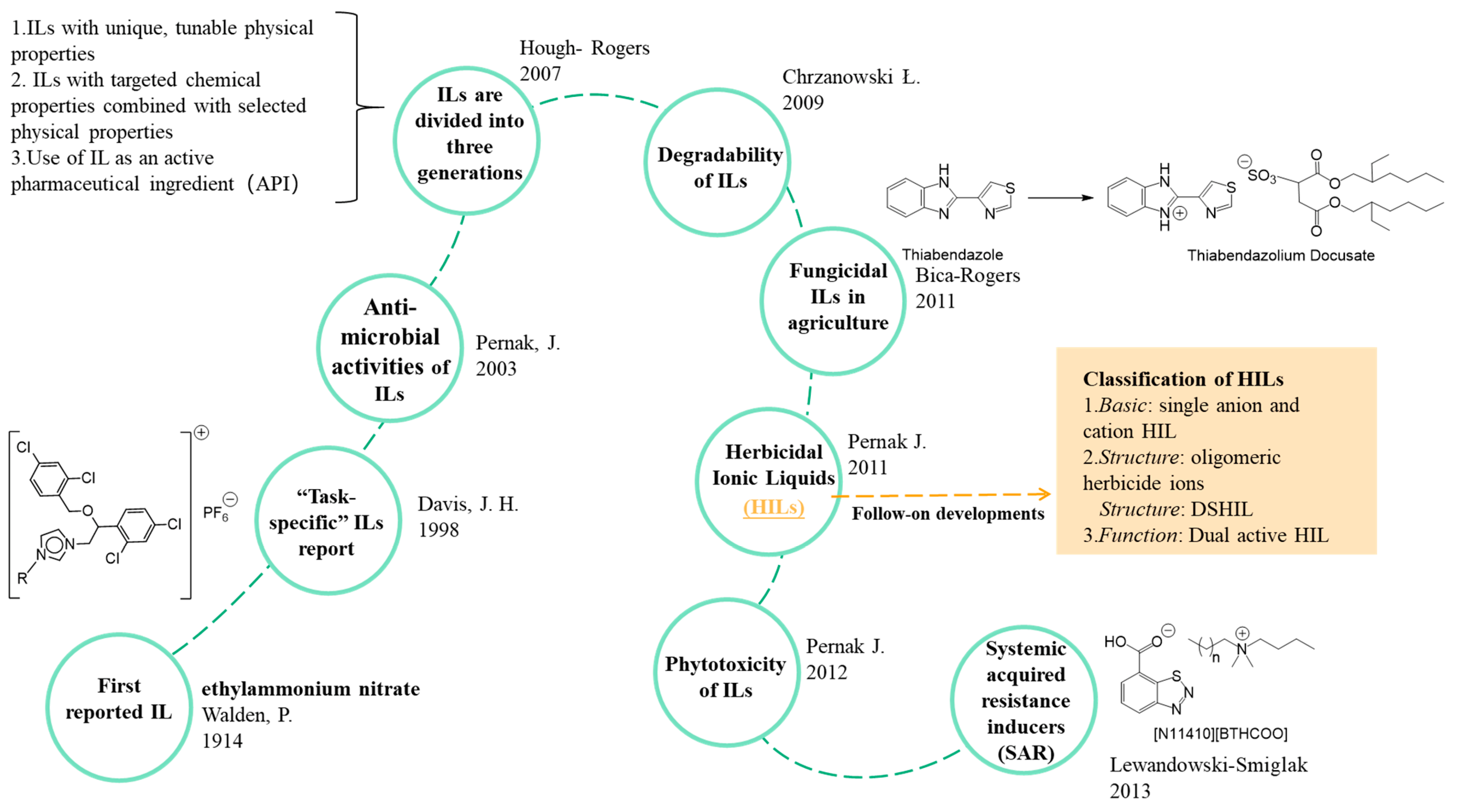
4. Types of ILs Based Pesticides
4.1. Herbicidal ILs (HILs)
4.1.1. Single Anion and Cation HILs
4.1.2. Double-Salt HILs
4.1.3. Dual-Activity HILs
4.2. Food Repellents (Deterrents)
4.3. Plant Growth Regulators
4.4. ILs for Microbial Control
4.4.1. Antibacterial Activity
4.4.2. Antifungal Activity
4.4.3. IL with Inherently Antifungal and Bacterial Properties
4.5. Plant Immunity Inducers (SAR)
5. Applications in Pesticide Delivery
6. Biodegradability and Toxicity
6.1. Toxicity
6.2. Biodegradation
7. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ILFF-SPE | Ionic-liquid-based foamflotation solid-phase extraction |
| SB-μ-SPE | Stir-bar supported membrane protected micro-solid-phase extraction |
| D-μSPE | Dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction |
| HS-SPME | Headspace solid-phase microextraction |
| DI-SPME | Direct immersion solid-phase microextraction |
| ILMB-ME | Ionic liquid magnetic bar microextraction |
| MEPS | Microextraction by packed sorbent |
| PT-SPE | Pipette-tip solid-phase extraction |
| ILE-MSPE | Ionic-liquid-based effervescence-enhanced magnetic solid-phase extraction |
| 2,4-DB | Butyl 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate |
| Bet | Betaine |
| [N8881][PF6] | Methyltrioctylammonium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [C6MIM][BF4] | 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C6MIM][PF6] | 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [C4MIM][PF6] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [N4444][PF6] | Tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate |
| [MCOOC2MIM][NTf2] | 3-Methyl-1-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl) imidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-imide |
| [C4C4MIM][Br] | 1,3-Dibutylimidazolium bromide |
| [C4C5MIM][Br] | 1-Pentyl-3-butylimidazolium bromide |
| [C4C6MIM][Br] | 1-Hexyl-3-butylimidazolium bromide |
| [C4(C4MIM)2][Br2] | 1,1’-(Butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-butylimidazolium) bromide |
| [C4(MIM)2][Br2] | 1,1’-(Butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-methylimidazolium) bromide |
| [C4MMIM][FeCl4] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate |
| [C4MIM][BF4] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [1-NA][FeCl4] | 4-Methylbenzenaminium tetrachloroferrate (III) |
| [4-MA][FeCl4] | 1-Naphthylammonium tetrachloroferrate (III) |
| SiO2@MIM–PF6 | Methylimidazolium-hexafluorophosphate functionalized silica |
| [C8MIM][Br] | 1-Methyl-3-octyl-imidazolium bromide |
| [C12MIM][Br] | 1-Methyl-3-undecyl-imidazolium bromide |
| [C18MIM][Br] | 1-Methyl-3-octadecyl-imidazolium bromide |
| [C16MIM][NTf2] | 1-Hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifuluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [VBIMC16][NTf2] | 1-Vinylbenzyl-3-hexadecylimidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [VBIMC10OH][NTf2] | 1-Vinyl-3-(10-hydroxydecyl)imidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [(VBIM)2C12]2[NTf2] | 1,12-Di(3-vinylbenzylimidazolium)dodecane bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [(VB(BIM))2C12]2[NTf2] | 1,12-Di(3-vinylbenzyl(benzimidazolium))dodecane bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [VIMC12][NTf2] | 1-Vinyl-4-dodecylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| [(VIM)2C12]2[NTf2] | 1,12-Di(3-vinylbenzylimidazolium)dodecane dibis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [VBIMC8][NTf2] | 1-Vinylbenzyl-3-octylimidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-MIM | Magnetite nanoparticles modified with 1-carboxymethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-MMIM | Magnetite nanoparticles modified with 1,3-dimethylimidazolium-2-carboxylate |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-C4MIM | Magnetite nanoparticles modified with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium-2-carboxylate |
| [C8MIM][BF4] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C8MIM][PF6] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [P66614][Gd(III)(hfacac)4] | Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tetrakis(hexafluoroacetylaceto)gadolinate(iii) |
| [P66614][Dy(III)(hfacac)4] | Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tetrakis(hexafluoroacetylaceto)dysprosate(iii) |
| [P66614][Co(II)(hfacac)3] | Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tris(hexafluoroacetylaceto)cobaltate(ii) |
| [P66614][Mn(II)(hfacac)3] | Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tris(hexafluoroacetylaceto)manganate(ii) |
| [P66614][Ni(II)(hfacac)3] | Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tris(hexafluoroacetylaceto)nickelate(ii) |
| zIL@T@SiO2 | 1-Vinyl-3-(butyl-4-sulfonate) imidazolium-thiol-SiO2 |
| IL@T@GO | 1-Allyl-3-(perfluorobenzyl)-imidazolium bromide-thiol-graphene oxide |
| Fe3O4@Na2CO3@[C6MIM][PF6] effervescent tablet | Ionic-liquid-based magnetic effervescent tablet composed of magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) as an alkaline source, and an ionic liquid ([C6MIM][PF6]) |
References
- Gavrilescu, M. Fate of pesticides in the environment and its bioremediation. Eng. Life Sci. 2005, 5, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.; Parween, M.; Raju, N.J. Pesticides in the hydrogeo-environment: A review of contaminant prevalence, source and mobilisation in India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 5481–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzini, S.; Teggi, S.; Bigi, A.; Ghermandi, G.; Filippini, T.; Malagoli, C.; Nannini, R.; Vinceti, M. Atmospheric dispersion modelling and spatial analysis to evaluate population exposure to pesticides from farming processes. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hong, X. Application of ionic liquids in organic pollutants control. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 99, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, R.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Structure and nanostructure in lonic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6357–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, H.; Singla, M. Diverse applications of ionic liquids: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirpour, N.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Zeinali Heris, S. Ionic liquids: Promising compounds for sustainable chemical processes and applications. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 264–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, D.; Siciliano, C.; Trombino, S.; Dumitrescu, D.E.; Suciu, F.; Di Gioia, M.L. Green solvents for the formation of amide linkages. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qu, P.; Zhou, M.; Qian, L.; Bai, T.; Jin, J.; Xin, B. Ionic liquids as promisingly multi-functional participants for electrocatalyst of water splitting: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Koo, Y.-M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Introduction: Ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6633–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Rao, S.S.; Filippov, A.; Johansson, P.; Shah, F.U. Aromatic heterocyclic anion based ionic liquids and electrolytes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 3502–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.K.; Tiwari, H.; Verma, R.; Dong, W.-L.; Azizov, S.; Kumar, B.; Pandey, S.; Kumar, D. Role and recent advancements of ionic liquids in drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veríssimo, N.V.; Vicente, F.A.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Likozar, B.; Oliveira, R.P.d.S.; Pereira, J.F.B. Ionic liquids as protein stabilizers for biological and biomedical applications: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 61, 108055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Rodríguez, H.; Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Daly, D.T.; Pernak, J.; Grisel, J.E.; Carliss, R.D.; Soutullo, M.D.; et al. The third evolution of ionic liquids: Active pharmaceutical ingredients. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-W.; Pham, T.P.T.; Zhao, Y.; Stolte, S.; Yun, Y.-S. Review of the toxic effects of ionic liquids. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten, A.; Zazybin, A.; Zolotareva, D.; Dauletbakov, A.; Rafikova, K.; Yu, V.; Giner, B. Ionic liquids in agrochemistry. Curr. Org. Chem. 2020, 24, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murador, D.C.; de Souza Mesquita, L.M.; Vannuchi, N.; Braga, A.R.C.; de Rosso, V.V. Bioavailability and biological effects of bioactive compounds extracted with natural deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids: Advantages over conventional organic solvents. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 26, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, H.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic liquid solutions as extractive solvents for value-added compounds from biomass. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4786–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Bi, W.; Tian, M.; Row, K.H. Application of ionic liquid for extraction and separation of bioactive compounds from plants. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 904, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Enhanced extraction of caffeine from guaraná seeds using aqueous solutions of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciochi, R.A.; Dieu, V.; Vauchel, P.; Pradal, D.; Dimitrov, K. Reduction of environmental impacts of caffeine extraction from guarana by using ultrasound assistance. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 127, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.; Gad, S.F.; Abdu-Allah, H.H.M.; Qayed, W.S.; AbouElmagd, S.A.; Ibrahim, E.A. Ionic liquid of ketoprofen-piperine modulates the pharmaceutical and therapeutic characters of ketoprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 620, 121724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ye, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Mo, W. Ionic liquid-based ultrasonic-assisted extraction of piperine from white pepper. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 640, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Zu, Y.-g.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of the three terpenoid indole alkaloids vindoline, catharanthine and vinblastine from Catharanthus roseus using ionic liquid aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.-C.; Shi, M.-Z.; Yu, Y.-L.; Cao, J. Simultaneous extraction and enrichment of alkaloids from lotus leaf by in-situ cloud point-reinforced ionic liquid assisted mechanochemical extraction technology. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yu, G. Structural effects on thermodynamic behavior and hydrogen bond interactions of water–ionic liquid systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 230, 116186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Marrucho, I.M.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Coutinho, J.A.P. High-performance extraction of alkaloids using aqueous two-phase systems with ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1715–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B. Ionic liquid-aqueous solution ultrasonic-assisted extraction of three kinds of alkaloids from Phellodendron amurense Rupr and optimize conditions use response surface. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 24, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Sui, X.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Yang, L. Development of a novel functionality for a highly efficient imidazole-based ionic liquid non-aqueous solvent system for the complete extraction of target alkaloids from Phellodendron amurense Rupr. under ultrasound-assisted conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 168, 113596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Lu, Y.; Hu, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y. Application of ionic liquids based microwave-assisted extraction of three alkaloids N-nornuciferine, O-nornuciferine, and nuciferine from lotus leaf. Talanta 2010, 80, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Tan, Z. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of sinomenine from Sinomenium acutum using magnetic ionic liquids coupled with further purification by reversed micellar extraction. Process Biochem. 2017, 58, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Luo, H.; Li, C.; Li, H. Efficient reaction systems for lignocellulosic biomass conversion to furan derivatives: A minireview. Ploymers 2022, 14, 3671. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Dong, S.-J.; Ma, H.-H.; Zhang, B.-X.; Wang, Y.-F.; Hu, X.-M. Fractionation of corn stover into cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin using a series of ionic liquids. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyafuji, H. Application of ionic liquids for effective use of woody biomass. J. Wood Sci. 2015, 61, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngs, T.G.A.; Holbrey, J.D.; Mullan, C.L.; Norman, S.E.; Lagunas, M.C.; D’Agostino, C.; Mantle, M.D.; Gladden, L.F.; Bowron, D.T.; Hardacre, C. Neutron diffraction, NMR and molecular dynamics study of glucose dissolved in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1594–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngs, T.G.A.; Hardacre, C.; Holbrey, J.D. Glucose solvation by the ionic liquid 1, 3-dimethylimidazolium chloride: A simulation study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13765–13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Understanding cellulose dissolution: Effect of the cation and anion structure of ionic liquids on the solubility of cellulose. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Xu, A.; Wang, J. Cation does matter: How cationic structure affects the dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A.; Song, Z.; Olubajo, O.; Crittle, T.; Peters, D. Designing enzyme-compatible ionic liquids that can dissolve carbohydrates. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Han, B. Catalytic transformation of lignocellulose into chemicals and fuel products in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6834–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, G. Comparative metabolomics of flavonoids in twenty vegetables reveal their nutritional diversity and potential health benefits. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, P.; Kumar, H.; Jain, R.; Jain, A.; Jain, V. Flavonoids as omnipotent candidates for cancer management. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 158, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Shao, X.; Cui, W.; Du, Y.; Guo, M.; Tang, D. Highly efficient and selective extraction of minor bioactive natural products using pure ionic liquids: Application to prenylated flavonoids in licorice. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 80, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Li, F. A novel combined process for extracting, separating and recovering flavonoids from flos sophorae immaturus. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.-Y.; Xiao, X.-H.; Luo, X.-J.; Li, G.-K. Application of ionic liquids in the microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from medicinal plants. Talanta 2009, 78, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Ao, X.; Guo, Y. Study on the synthesis of dual-chain ionic liquids and their application in the extraction of flavonoids. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1628, 461446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chu, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, R.; Chen, L. Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Bauhinia championii (Benth.) Benth. Molecules 2012, 17, 14323–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Nie, C.; Yuan, Y. Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction of rutin from Chinese medicinal plants. Talanta 2010, 83, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakkori, P.; Tağaç, A.A.; Merdivan, M. Fabrication of montmorillonite/ionic liquid composite coated solid-phase microextraction fibers for determination of phenolic compounds in fruit juices by gas chromatography and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1635, 461741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, S.; Rodríguez, H.; Arce, A.; Soto, A. Improved concentration of citrus essential oil by solvent extraction with acetate ionic liquids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2014, 361, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wilfred, C.D.; Shaharun, M.S. Comparative assessment of various extraction approaches for the isolation of essential oil from polygonum minus using ionic liquids. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. Extraction of rosmarinic acid from Perilla seeds using green protic ionic liquids. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sui, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, T. Application of cellulase treatment in ionic liquid based enzyme-assisted extraction in combine with in-situ hydrolysis process for obtaining genipin from Eucommia ulmoides Olive barks. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1569, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Tang, F.; Long, Y.; Yao, S. Ionic liquid surfactant-mediated ultrasonic-assisted extraction coupled to HPLC: Application to analysis of tanshinones in Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 4220–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, C.J.; Tu, W.-C.; Levers, O.; Bröhl, A.; Hallett, J.P. Green and sustainable solvents in chemical processes. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 747–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musarurwa, H.; Tavengwa, N.T. Emerging green solvents and their applications during pesticide analysis in food and environmental samples. Talanta 2021, 223, 121507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep eutectic solvents: A review of fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Row, K.H. Recent applications of ionic liquids in separation technology. Molecules 2010, 15, 2405–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarurwa, H.; Chimuka, L.; Tavengwa, N.T. Green pre-concentration techniques during pesticide analysis in food samples. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2019, 54, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Huynh, T.T.T.; Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, P.H. Recent advances in the application of ionic liquid-modified silica gel in solid-phase extraction. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Gao, H.; Li, J. In-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of ionic liquids for the determination of benzoylurea insecticides in water and tea beverage samples. Talanta 2017, 162, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. Ionic liquid–based dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction of five organophosphorus pesticides in coarse cereals. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gure, A.; Lara, F.J.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Megersa, N.; del Olmo-Iruela, M. Vortex-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in wine samples by capillary high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Li, W.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Gao, H. A rapid and simple pretreatment method for benzoylurea insecticides in honey samples using in-syringe dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the direct solidification of ionic liquids. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1471, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Zhou, X.; Shi, G.; Zhou, T. Rational design of an ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction method for the detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Analyst 2019, 144, 2166–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Fan, C.; Kong, D.; Tang, G.; Zhang, W.; Dong, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, D.; Cao, Y. Synthesis and application of imidazolium-based ionic liquids as extraction solvent for pretreatment of triazole fungicides in water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Matrix solid-phase dispersion coupled with magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in oilseeds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, B.; Yao, D.; Yu, R.; Yu, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, A. Separation and concentration of sulfonylurea herbicides in milk by ionic-liquid-based foam flotation solid-phase extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi Hassan, A.; Sajid, M.; Al Ghafly, H.; Alhooshani, K. Ionic liquid-based membrane-protected micro-solid-phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides in environmental water samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Cano, F.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction with ionic liquid-modified silica for the determination of organophosphate pesticides in water by ultra performance liquid chromatography. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelit, F.O.; Pelit, L.; Dizdaş, T.N.; Aftafa, C.; Ertaş, H.; Yalçınkaya, E.E.; Türkmen, H.; Ertaş, F.N. A novel polythiophene—Ionic liquid modified clay composite solid phase microextraction fiber: Preparation, characterization and application to pesticide analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 859, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Yang, P.; Pang, R.; Lu, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Ionogel-based ionic liquid coating for solid-phase microextraction of organophosphorus pesticides from wine and juice samples. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazbayeva, D.; Koziel, J.A.; Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Anderson, J.L.; Kenessov, B. Polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings in headspace solid-phase microextraction: A green sample preparation technique for the determination of pesticides in soil. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeger, V.R.; Bell, D.S.; Herrington, J.S.; Anderson, J.L. Selective isolation of pesticides and cannabinoids using polymeric ionic liquid-based sorbent coatings in solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1680, 463416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubin, A.; Sukhanov, P.; Kushnir, A.; Shikhaliev, K.; Potapov, M.; Kovaleva, E. Ionic-liquid-modified magnetite nanoparticles for MSPE-GC-MS determination of 2,4-D butyl ester and its metabolites in water, soil, and bottom sediments. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Xiao, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Cheng, M. Ionic liquid magnetic bar microextraction and HPLC determination of carbamate pesticides in real water samples. Microchim. Acta 2012, 179, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, R.; Zhang, D. Extraction of acetanilide herbicides in naked oat (Avena nuda L.) by using ionic-liquid-based matrix solid-phase dispersion-foam flotation solid-phase extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Anderson, J.L.; Stalikas, C.D. Matrix solid-phase dispersion based on magnetic ionic liquids: An alternative sample preparation approach for the extraction of pesticides from vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1581–1582, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan-Sinisterra, M.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Lanças, F.M. Microextraction by packed sorbent of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in brewed coffee samples with a new zwitterionic ionic liquid-modified silica sorbent. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, C.; Yan, H.; Han, Y.; Han, D. An integrated solid phase extraction with ionic liquid-thiol-graphene oxide as adsorbent for rapid isolation of fipronil residual in chicken eggs. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1631, 461568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Mammah, M.; Du, L.; Wang, X. Ionic-liquid-based effervescence-enhanced magnetic solid-phase extraction for organophosphorus pesticide detection in water samples. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, R.; Hu, J. Frequently used pesticides and their metabolites residues in apple and apple juice from markets across China: Occurrence and health risk assessment. LWT 2023, 178, 114610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Daniel Ruan, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C.; Phung, D.T. Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani, M.F. Pesticides toxicity in fish: Histopathological and hemato-biochemical aspects—A review. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, F.; Yan, T.; Tian, F.; Ren, L.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S. Research progress in the sample pretreatment techniques and advanced quick detection methods of pesticide residues. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejabri Kandeh, S.; Amini, S.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Development of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan/aloe vera gel electrospun composite nanofibers as a novel sorbent for thin-film micro-extraction of pesticides in water and food samples followed by HPLC-UV analysis. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykowska, I.; Ziemblińska, J.; Nowak, I. Modern approaches in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) based on ionic liquids: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 259, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primel, E.G.; Caldas, S.S.; Marube, L.C.; Escarrone, A.L.V. An overview of advances in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the extraction of pesticides and emerging contaminants from environmental samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, S.L.I.; McFarlane, J.; Tsouris, C.; DePaoli, D.W.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. Room-temperature ionic liquids in liquid–liquid extraction: Effects of solubility in aqueous solutions on surface properties. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2006, 24, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himani; Pratap Singh Raman, A.; Babu Singh, M.; Jain, P.; Chaudhary, P.; Bahadur, I.; Lal, K.; Kumar, V.; Singh, P. An update on synthesis, properties, applications and toxicity of the ILs. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 119989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fan, C.; Tang, G.; Zhang, W.; Dong, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, M.; Cao, Y. Relationship between the structure of ionic liquid and its enrichment ability to trace fungicides from an environmental water sample. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9418–9425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyckens, D.J.; Henderson, L.C. A Review of Solvate Ionic Liquids: Physical Parameters and Synthetic Applications. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Begum, A.; Xue, J. Analytical methods to analyze pesticides and herbicides. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1770–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.D.; Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Anderson, J.L. Advances in the analysis of biological samples using ionic liquids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4567–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wen, Y.; Fan, S.; Liu, C. Determination of pyrethroid residues in herbal tea using temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by high performance liquid chromatography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ötles, S.; Aliment, C.K.J.A.S.P.T. Solid-phase extraction (SPE): Principles and applications in food samples. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2016, 15, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, B.; Zohrabi, P.; Shamsipur, M. Recent developments and applications of different sorbents for SPE and SPME from biological samples. Talanta 2018, 187, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, L.; Riekkola, M.-L.; Canals, A. Ionic liquid-modified materials for solid-phase extraction and separation: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 715, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.-Z.; Yu, Y.-L.; Zhu, S.-C.; Yang, J.; Cao, J. Latest development of matrix solid phase dispersion extraction and microextraction for natural products from 2015–2021. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2023, 52, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M. Recent analytical applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Nanochem. Res. 2016, 1, 264–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varona, M.; Eor, P.; Ferreira Neto, L.C.; Merib, J.; Anderson, J.L. Metal-containing and magnetic ionic liquids in analytical extractions and gas separations. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 140, 116275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Pierson, S.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Stalikas, C.D. Enhanced magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of triazines and sulfonamides through a one-pot, pH-modulated approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; e Silva, F.A.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic-liquid-mediated extraction and separation processes for bioactive compounds: Past, present, and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzimitakos, T.; Anagnostou, P.; Constantinou, I.; Dakidi, K.; Stalikas, C. Magnetic ionic liquids in sample preparation: Recent advances and future trends. Separations 2021, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, S.; Rafique, U.; Javed Akhtar, M. Removal of pirimicarb from agricultural waste water using cellulose acetate–modified ionic liquid membrane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 15795–15802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Wang, S. N-Methylimidazolium ionic liquid-functionalized silica as a sorbent for selective solid-phase extraction of 12 sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water and soil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.D.; Nacham, O.; Purslow, J.A.; Pierson, S.A.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical chemistry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 934, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Niemczak, M.; Rzemieniecki, T.; Marcinkowska, K.; Praczyk, T. Dicationic herbicidal ionic liquids comprising two active ingredients exhibiting different modes of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.H.; Forrester, K.J.; Merrigan, T. Novel organic ionic liquids (OILs) incorporating cations derived from the antifungal drug miconazole. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 8955–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, P.J.B.A.I.S. Molecular weights and electrical conductivity of several fused salts. Bull. Acad. Imper. Sci. 1914, 8, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Pernak, J.; Sobaszkiewicz, K.; Mirska, I. Anti-microbial activities of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowski, Ł.; Stasiewicz, M.; Owsianiak, M.; Szulc, A.; Piotrowska-Cyplik, A.; Olejnik-Schmidt, A.K.; Wyrwas, B. Biodegradation of diesel fuel by a microbial consortium in the presence of 1-alkoxymethyl-2-methyl-5-hydroxypyridinium chloride homologues. Biodegradation 2009, 20, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bica, K.; Cooke, L.R.; Nugent, P.; Rijksen, C.; Rogers, R.D. Toxic on purpose: Ionic liquid fungicides as combinatorial crop protecting agents. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2344–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Syguda, A.; Janiszewska, D.; Materna, K.; Praczyk, T. Ionic liquids with herbicidal anions. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 4838–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Wasiński, K.; Praczyk, T.; Nawrot, J.; Cieniecka-Rosłonkiewicz, A.; Walkiewicz, F.; Materna, K. Sweet ionic liquids-cyclamates: Synthesis, properties, and application as feeding deterrents. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, P.; Kukawka, R.; Pospieszny, H.; Smiglak, M. Bifunctional quaternary ammonium salts based on benzo[1,2,3]thiadiazole-7-carboxylate as plant systemic acquired resistance inducers. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1372–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilms, W.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Niemczak, M.; Parus, A.; Frankowski, R.; Wolko, Ł.; Czarny, J.; Piotrowska-Cyplik, A.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Heipieper, H.J.; et al. 2,4-D versus 2,4-D based ionic liquids: Effect of cation on herbicide biodegradation, tfdA genes abundance and microbiome changes during soil bioaugmentation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ławniczak, Ł.; Syguda, A.; Borkowski, A.; Cyplik, P.; Marcinkowska, K.; Wolko, Ł.; Praczyk, T.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Pernak, J. Influence of oligomeric herbicidal ionic liquids with MCPA and Dicamba anions on the community structure of autochthonic bacteria present in agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parus, A.; Zdebelak, O.; Ciesielski, T.; Szumski, R.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Framski, G.; Baranowski, D.; Niemczak, M.; Zembrzuska, J.; Cajthaml, T.; et al. Can ionic liquids exist in the soil environment? Effect of quaternary ammonium cations on glyphosate sorption, mobility and toxicity in the selected herbicidal ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parus, A.; Homa, J.; Radoński, D.; Framski, G.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Syguda, A.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Novel esterquat-based herbicidal ionic liquids incorporating MCPA and MCPP for simultaneous stimulation of maize growth and fighting cornflower. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Ding, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Guo, M.; Geng, Q.; Cao, Y. Ionic liquid forms of clopyralid with increased efficacy against weeds and reduced leaching from soils. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Kaczmarek, D.K.; Rzemieniecki, T.; Niemczak, M.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Praczyk, T. Dicamba-based herbicides: Herbicidal ionic liquids versus commercial forms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4588–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parus, A.; Lisiecka, N.; Zembrzuska, J.; Framski, G.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Niemczak, M. Evaluation of the influence of different cations on the mobility and performance of dicamba-based ionic liquids. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, K.; Praczyk, T.; Niemczak, M.; Rzemieniecki, T.; Kaczmarek, D.K.; Łacka, A.; Pernak, J. Herbicidal ionic liquids containing double or triple anions as a new potential tool for weed control including herbicide-resistant biotypes. Crop Prot. 2023, 169, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, J.; Tang, G.; Huo, H.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y. Novel herbicide ionic liquids based on nicosulfuron with increased efficacy. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilms, W.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Syguda, A.; Niemczak, M.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Pernak, J.; Rogers, R.D.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Herbicidal ionic liquids: A promising future for old herbicides? Review on synthesis, toxicity, biodegradation, and efficacy studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10456–10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Giszter, R.; Biedziak, A.; Niemczak, M.; Olszewski, R.; Marcinkowska, K.; Praczyk, T. Alkyl(C16, C18, C22)trimethylammonium-based herbicidal ionic liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, O.A.; Shamshina, J.L.; Gurau, G.; Syguda, A.; Praczyk, T.; Pernak, J.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquid forms of the herbicide dicamba with increased efficacy and reduced volatility. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Niemczak, M.; Shamshina, J.L.; Gurau, G.; Głowacki, G.; Praczyk, T.; Marcinkowska, K.; Rogers, R.D. Metsulfuron-methyl-based herbicidal ionic liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3357–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczak, M.; Rzemieniecki, T.; Biedziak, A.; Marcinkowska, K.; Pernak, J. Synthesis and structure–property relationships in herbicidal ionic liquids and their double salts. ChemPlusChem 2018, 83, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, H.; Pernak, J.; Shamshina, J.L.; Niemczak, M.; Giszter, R.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Praczyk, T.; Marcinkowska, K.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Rogers, R.D. Two herbicides in a single compound: Double salt herbicidal ionic liquids exemplified with glyphosate, dicamba, and MCPA. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6261–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymaniak, D.; Maćkowiak, A.; Ciarka, K.; Praczyk, T.; Marcinkowska, K.; Pernak, J. Synthesis and characterization of double-salt herbicidal ionic liquids comprising both 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetate and trans-cinnamate Anions. ChemPlusChem 2020, 85, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Barik, S.; Preeyanka, N.; Sarkar, M. Interaction of lysozyme with monocationic and dicationic ionic liquids: Toward finding a suitable medium for biomacromolecules. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; Tang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Huo, H.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.; Cao, Y. Dicationic ionic liquids of herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid with reduced negative effects on environment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10362–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatel, G.; Pereira, J.F.B.; Debbeti, V.; Wang, H.; Rogers, R.D. Mixing ionic liquids—“simple mixtures” or “double salts”? Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2051–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Kelley, S.P.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Chemistry: Develop ionic liquid drugs. Nature 2015, 528, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzemieniecki, T.; Wojcieszak, M.; Materna, K.; Praczyk, T.; Pernak, J. Synthetic auxin-based double salt ionic liquids as herbicides with improved physicochemical properties and biological activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagator, M.; Vogwill, T.; Mead, A.; Colegrave, N.; Neve, P. Herbicide mixtures at high doses slow the evolution of resistance in experimentally evolving populations of chlamydomonas reinhardtii. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, S.B.; Yu, Q. Evolution in action: Plants resistant to herbicides. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 317–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, K.; Praczyk, T.; Gawlak, M.; Niemczak, M.; Pernak, J. Efficacy of herbicidal ionic liquids and choline salt based on 2,4-D. Crop Prot. 2017, 98, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Markiewicz, B.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Gwiazdowski, R.; Marcinkowska, K.; Praczyk, T. Ionic liquids with dual pesticidal function. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 39751–39754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Niemczak, M.; Materna, K.; Marcinkowska, K.; Praczyk, T. Ionic liquids as herbicides and plant growth regulators. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 4665–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukawka, R.; Spychalski, M.; Stróżyk, E.; Byzia, E.; Zajac, A.; Kaczyński, P.; Łozowicka, B.; Pospieszny, H.; Smiglak, M. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of bifunctional ionic liquids based on dodine ion. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciarka, K.; Olszewski, R.; Praczyk, T.; Pernak, J. Synthesis and characterization of herbicidal ionic liquids based on (4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)acetate and phenoxyethylammonium. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3607–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syguda, A.; Wojcieszak, M.; Materna, K.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Parus, A.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Double-action herbicidal ionic liquids based on dicamba esterquats with 4-CPA, 2,4-D, MCPA, MCPP, and clopyralid anions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14584–14594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Nawrot, J.; Kot, M.; Markiewicz, B.; Niemczak, M. Ionic liquids based stored product insect antifeedants. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25019–25029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, B.; Sznajdrowska, A.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Kubiak, K.; Nawrot, J.; Pernak, J. Ionic liquids with a theophyllinate anion. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 3146–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Łęgosz, B.; Walkiewicz, F.; Klejdysz, T.; Borkowski, A.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Ammonium ionic liquids with anions of natural origin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65471–65480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klejdysz, T.; Łęgosz, B.; Czuryszkiewicz, D.; Czerniak, K.; Pernak, J. Biobased ionic liquids with abietate anion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6543–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Gao, H. Preparation and properties of multifunctional phenoxyacetate-based ionic liquids and their application in citrus bacteriostatic preservation. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 22621–22632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, D.K.; Pacholak, A.; Burlaga, N.; Wojcieszak, M.; Materna, K.; Kruszka, D.; Dąbrowski, P.; Sobańska, K.; Kaczorek, E. Dicationic ionic liquids with an indole-3-butyrate anion—Plant growth stimulation and ecotoxicological evaluations. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 13282–13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Niu, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, R.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Development of poly(ionic liquids) based on mepiquat chloride with improved rainfastness and long-lasting activity on growth regulation of cotton plant. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14996–15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigt, D.; Siatkowski, I.; Magaj, M.; Tomkowiak, A.; Nawracała, J. Impact of ionic liquids on induction of wheat microspore embryogenesis and plant regeneration. Agronomy 2020, 10, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Feder-Kubis, J. Synthesis and properties of chiral ammonium-based ionic liquids. Chemistry 2005, 11, 4441–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.; Pereira, A.R.; Simões, L.C.; Cagide, F.; Borges, F. Biofilm control by ionic liquids. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkata Nancharaiah, Y.; Reddy, G.K.K.; Lalithamanasa, P.; Venugopalan, V.P. The ionic liquid 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium demonstrates comparable antimicrobial and antibiofilm behavior to a cationic surfactant. Biofouling 2012, 28, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulski, J.; Wiśniewska, A.; Kulig-Adamiak, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Praczyk, T.; Michalczyk, A.; Walkiewicz, F.; Materna, K.; Pernak, J. Mandelate and prolinate ionic liquids: Synthesis, characterization, catalytic and biological activity. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 1325–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Gao, T.; Wan, F.; Yu, B.; Pei, X.; Zhou, F.; Xue, Q. Grafting poly(ionic liquid) brushes for anti-bacterial and anti-biofouling applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13123–13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Qi, J.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y. Ionic liquids: Emerging antimicrobial agents. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, D.K.; Gwiazdowska, D.; Juś, K.; Klejdysz, T.; Wojcieszak, M.; Materna, K.; Pernak, J. Glycine betaine-based ionic liquids and their influence on bacteria, fungi, insects and plants. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 6344–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, J.; Wiśniewska, A.; Kulig-Adamiak, A.; Lewicka, L.; Cieniecka-Rosłonkiewicz, A.; Kita, K.; Fojutowski, A.; Nawrot, J.; Materna, K.; Pernak, J. Long-alkyl-chain ouaternary ammonium lactate based ionic liquids. Chemistry 2008, 14, 9305–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, A.; Syguda, A.; Wyrwas, B.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Heipieper, H.J. Toxicity evaluation of selected ammonium-based ionic liquid forms with MCPP and dicamba moieties on Pseudomonas putida. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz, M.; Lewandowski, P.; Spychalski, M.; Kukawka, R.; Feder-Kubis, J.; Beil, S.; Smiglak, M.; Stolte, S. New bifunctional ionic liquid-based plant systemic acquired resistance (SAR) inducers with an improved environmental hazard profile. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5138–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiewicz, M.; Fojutowski, A.; Kropacz, A.; Pernak, J. 1-Alkoxymethyl-X-dimethylaminopyridinium-base ionic liquids in wood preservation. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabielska-Matejuk, J.; Stangierska, A.; Kot, M. New ammonium- and 1,2,4-triazolium-based ionic liquids for wood preservation. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2015, 35, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeier, J. Metabolic regulation of systemic acquired resistance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 62, 102050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzai, Y.; Noutoshi, Y.; Inoue, K.; Shimizu, M.; Onda, Y.; Mochida, K. Benzothiadiazole, a plant defense inducer, negatively regulates sheath blight resistance in Brachypodium distachyon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiglak, M.; Hines, C.C.; Wilson, T.B.; Singh, S.; Vincek, A.S.; Kirichenko, K.; Katritzky, A.R.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids Based on Azolate Anions. Chem.-Eur. J. 2010, 16, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukawka, R.; Czerwoniec, P.; Lewandowski, P.; Pospieszny, H.; Smiglak, M. New ionic liquids based on systemic acquired resistance inducers combined with the phytotoxicity reducing cholinium cation. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 11984–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Moshikur, R.; Chowdhury, M.R.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Goto, M. Biocompatible ionic liquids and their applications in pharmaceutics. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8116–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curreri, A.M.; Mitragotri, S.; Tanner, E.E.L. Recent advances in ionic liquids in biomedicine. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Y.; Tang, J.; Gao, Y.; Niu, J.; Dong, H.; Tang, R.; Tang, G.; Cao, Y. Sustainable preparation of microcapsules with desirable stability and bioactivity using phosphonium ionic liquid as a functional additive. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13440–13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Yang, J.; Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y. Prodrug based on ionic liquids for dual-triggered release of thiabendazole. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 3484–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steudte, S.; Bemowsky, S.; Mahrova, M.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Tojo-Suarez, E.; Stepnowski, P.; Stolte, S. Toxicity and biodegradability of dicationic ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5198–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.E.S.J.; Prydderch, H.; Spulak, M.; Shimizu, S.; Walker, A.J.; Gathergood, N. Green profiling of aprotic versus protic ionic liquids: Synthesis and microbial toxicity of analogous structures. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 7, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butucel, E.; Balta, I.; Ahmadi, M.; Dumitrescu, G.; Morariu, F.; Pet, I.; Stef, L.; Corcionivoschi, N. Biocides as biomedicines against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajac, A.; Kukawka, R.; Pawlowska-Zygarowicz, A.; Stolarska, O.; Smiglak, M. Ionic liquids as bioactive chemical tools for use in agriculture and the preservation of agricultural products. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4764–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.F.; Gil, F.; Lacasaña, M. Toxicological interactions of pesticide mixtures: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiewicz, M.; Mulkiewicz, E.; Tomczak-Wandzel, R.; Kumirska, J.; Siedlecka, E.M.; Gołebiowski, M.; Gajdus, J.; Czerwicka, M.; Stepnowski, P. Assessing toxicity and biodegradation of novel, environmentally benign ionic liquids (1-alkoxymethyl-3-hydroxypyridinium chloride, saccharinate and acesulfamates) on cellular and molecular level. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Niemczak, M.; Giszter, R.; Shamshina, J.L.; Gurau, G.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Praczyk, T.; Marcinkowska, K.; Rogers, R.D. Glyphosate-based herbicidal ionic liquids with increased efficacy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2845–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Parus, A.; Ciesielski, T.; Trzebny, A.; Szumski, R.; Wilms, W.; Homa, J.; Framski, G.; Baranowski, D.; Frankowski, R.; et al. Effect of cation sorption on 2, 4-D mobility of herbicidal ionic liquids in agricultural soil combined with diversity of the bacterial community. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12559–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Types of Separation Technology | Sample Type | Analyte(s) | Evaluated IL(s) | Limits of Detection (μg/kg) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLLME | Water; Tea beverage | Benzoylurea insecticides | [N8881][PF6] | 0.29–0.59 | [62] |
| DLLME | Coarse cereals | Organophosphorus pesticide | [C6MIM][BF4] | 2.5–5.5 | [63] |
| DLLME | Wine | Sulfonylurea herbicides | [C6MIM][PF6], | 3.2–6.6 | [64] |
| [C4MIM][PF6] | |||||
| DLLME | Honey | Benzoylurea insecticides | [N4444][PF6] | 0.21–0.42 | [65] |
| DLLME | River water | Organophosphorus pesticides | [MCOOC2MIM][NTf2] | 0.7–2.7 | [66] |
| DLLME | Water | Triazole fungicides | [C4C4MIM][Br], | 0.74–1.44 | [67] |
| [C4C5MIM][Br], | |||||
| [C4C6MIM][Br], | |||||
| [C4(C4MIM)2][Br2], | |||||
| [C4(MIM)2][Br2], | |||||
| DLLME | Oilseeds | Triazine herbicides | [C4MMIM][FeCl4] | 1.20–2.72 | [68] |
| ILFF-SPE | Milk | Sulfonylurea herbicides | [C4MIM][BF4] | 0.6–1.3 | [69] |
| SB-µ-SPE | Agricultural wastewater | Organochlorine pesticides | [1-NA][FeCl4] [4-MA][FeCl4] | 0.25–3.4 | [70] |
| D-μSPE | Water | Organophosphate pesticides | SiO2@MIM–PF6 | 0.3–0.6 | [71] |
| SPME | Grape juice | Volatile endocrine-disruptor pesticides | [C8MIM][Br], | 0.002–0.667 | [72] |
| [C12MIM][Br], | |||||
| [C18MIM][Br] | |||||
| SPME | Wine; Juice | Organophosphorus pesticides | [C16MIM][NTf2] | 0.57–4.13 | [73] |
| HS-SPME | Soil | Epoxiconazole, fluroxypyr, metribuzin, and oxyfluorfen | [VBIMC16][NTf2], | 0.2–2 | [74] |
| [VIMC10OH][NTf2], | |||||
| [(VBIM)2C12]2[NTf2], | |||||
| [(VB(BIM))2C12]2[NTf2] | |||||
| DI-SPME | Water | 20 pesticides | [VIMC8][NTf2], | 1–200 | [75] |
| [VIMC12][NTf2], | |||||
| [(VIM)2C12]2[NTf2], | |||||
| [VBIMC8][NTf2], | |||||
| [(VBIM)2C12]2[NTf2] | |||||
| SPME | Soils, ground and river waters, and bottom sediments | 2,4-D, 2,4-D ester, and metabolites | Fe3O4@SiO2-MIM, | 1 × 10−4–3 × 10−2 | [76] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-MMIM, | |||||
| Fe3O4@SiO2-C4MIM | |||||
| ILMB-ME | Tap, lake and rain water | Carbamate pesticides | [C4MIM][PF6], | 1.4–3.4 | [77] |
| [C6MIM][PF6] | |||||
| MSPD | Naked oat | Acetanilide herbicides | [C4MIM][BF4], | 0.29–0.59 | [78] |
| [C6MIM][BF4], | |||||
| [C8MIM][BF4], | |||||
| [C4MIM][PF6], | |||||
| [C6MIM][PF6], | |||||
| [C8MIM][PF6] | |||||
| MSPD | Vegetables | Organophosphate, organochloride and triazine pesticides | [P66614][Gd(III)(hfacac)4], | 0.002–0.009 | [79] |
| [P66614][Dy(III)(hfacac)4], | |||||
| [P66614][Co(II)(hfacac)3], | |||||
| [P66614][Mn(II)(hfacac)3], | |||||
| [P66614][Ni(II)(hfacac)3] | |||||
| MEPS | Brewed coffee | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | zIL@T@SiO2 | 4.5–6.7 | [80] |
| PT-SPE | Egg | Fipronil | IL@T@GO | 4.76 | [81] |
| ILE-MSPE | Water | Organophosphorus pesticides | Fe3O4@Na2CO3@[C6MIM][PF6] effervescent tablet | 0.14–0.22 | [82] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Qin, X.; Dong, H.; Liang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Qian, K.; Yang, F. Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Field of Agriculture: A Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122279
Wang Z, Qin X, Dong H, Liang Y, Huo Z, Qian K, Yang F. Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Field of Agriculture: A Review. Agriculture. 2023; 13(12):2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122279
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zijun, Xin Qin, Hongqiang Dong, You Liang, Zhongyang Huo, Kun Qian, and Fengping Yang. 2023. "Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Field of Agriculture: A Review" Agriculture 13, no. 12: 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122279
APA StyleWang, Z., Qin, X., Dong, H., Liang, Y., Huo, Z., Qian, K., & Yang, F. (2023). Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Field of Agriculture: A Review. Agriculture, 13(12), 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122279








