Abstract
Machine learning is used widely in near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for fruit qualification. However, the directly split training set used contains redundant samples, and errors may be introduced into the model. Euclidean distance-based and K-nearest neighbor-based instance selection (IS) methods are widely used to remove useless samples because of their accessibility. However, they either have high accuracy and low compression or vice versa. To compress the sample size while improving the accuracy, the least-angle regression (LAR) method was proposed for classification instance selection, and a discrimination experiment was conducted on a total of four origins of 952 apples. The sample sets were split into the raw training set and testing set; the optimal training samples were selected using the LAR-based instance selection (LARIS) method, and the four other selection methods were compared. The results showed that 26.9% of the raw training samples were selected using LARIS, and the model based on these training samples had the highest accuracy. Thus, the apple origin classification model based on LARIS can achieve the goal of high accuracy and compression and provide experimental support for the least-angle regression algorithm in classification instance selection.
1. Introduction
Near-infrared has the ability to detect adulteration [1]. Apples are one of the most economically important crops in China but it is difficult for people to distinguish their origins only from their appearance. Having apples from various origins means that there are different internal and external qualities, such as color, size, taste, and texture [2]. Trade in shoddy goods is widespread in the market [3]. It is necessary to discriminate apple origin via technology. The chemometrics method combined with NIRS is a convenient technique [4].
The training set is critical for the classifiers. In order to establish a model with high accuracy, a large number of samples are introduced [5]. This can lead to an excessive number of samples and introduce redundant samples to the raw training set. The redundant samples are involved in the training of classifiers. The results of the parameters of models have larger errors than the true parameters, causing increasing generalization errors for classifiers [6,7]. Thus, it is essential to eliminate the redundant samples to mitigate their effects on large datasets [8,9,10]. Instance selection (IS) is one of the most useful methods [11] used to pick up the effective sample sub-set to improve the performance of models. The effective dataset is also significant for storage and transmission [12,13].
For classification, the commonly used IS methods are Euclidean distance and K-nearest neighbor algorithms [14]. These methods are very popular for NIR detection to cluster and remove samples from high-dimensional and strong overlapping spectra sets. Although the sample size is compressed in these methods, it tends to be changed for the distribution and the balance degree of the set. Either the accuracy is higher, and the compression rate is lower, or vice versa [11]. The more common the large dataset becomes, the more obviously this problem is exposed.
According to the selection strategies, IS algorithms can be summarized into condensation [11], edition [9], hybrid [15], clustering [16], boosting [17,18], ranking [19,20], adaptive [21], active learning [22], etc. [23]. The condensation strategy aims to eliminate internal samples which do not affect the classification. Edition methods are used to remove the noisy samples at the boundary. The hybrid strategy is used to select the smallest subset with the best generalization performance. The clustering strategy has the advantage of preserving the classification boundary and region. The boosting strategy constructs an ensemble of classifiers by modifying the sample distribution according to the model effect. The ranking strategy tries to weigh accuracy and compression. The adaptive strategy has the advantage of a varying sampling ratio.
It is necessary to use an IS method to select effective training samples and compress the sample size while improving the accuracy. In 2004, Bradley Efron proposed the least-angle regression (LAR) algorithm for performing both regression and subset selection [24,25]. LAR is a superb method, and it is widely used in the field of variable selection. There have been several derivative methods proposed based on the LAR models for regression and variable selection. However, the public has overlooked that LAR is also a sorting method [26].
In this paper, the sorting property of LAR is mentioned, and it was used to select training samples optimally and improve the accuracy [27]. The least-angle regression-based instance selection (LARIS) method was proposed. The LARIS method has the advantages of clustering strategy, ranking strategy and the least-angle regression method for instance selection [25]. Experiments on the apple origin classification were conducted to study the effects of LARIS on the samples and the model prediction in this paper. The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the experimental materials which are needed to develop modeling. Section 3 presents the fundamentals of least-angle regression and other data processing methods. Section 4 discusses their roles in the measurement based on both statistics and prediction results. Finally, the main conclusions are presented in Section 5.
2. Samples and Spectra
A total of 952 Fuji apples with a consistent appearance and intact epidermises were prepared. Before collection, all samples were placed in a storage cabinet at 5 °C for 24 h. Overall, 280 apples from Aksu were Class 1, and they were numbered from 1 to 280. In total, 244 apples from Panzhihua were Class 2, and they were numbered from 281 to 524. A total of 228 apples from Luochuan were Class 3, and they were numbered from 525 to 752. Finally, 200 Yantai apples were Class 4, and they were numbered from 753 to 952. Four points were evenly marked at the equatorial part. Spectra acquisitions were carried out at 25 °C under laboratory ambient conditions [2].
Spectra were collected using the Felix F750 portable NIR spectrometer. This spectrometer could automatically scan seven times in a single measurement, and an average spectrum was the output. The four spectra at the equatorial points of each sample were collected, and then the average spectrum was calculated to represent the sample [2]. There was a total of 83 wavelength points in one sample spectrum, and they ranged from 729 to 975 nm with a resolution of 3 nm.
3. Theory and Algorithm
The steps of the experiments are shown in Figure 1. First, the best preprocessing method and outliers are determined [19]. The raw spectra are preprocessed by six methods such as Savitzky–Golay (S-G) smooth filter, S-G filter with 1-derivative, S-G filter with 2-derivative, PLS decomposition, PCA decomposition, multiple scattering correction (MSC), and their combinations. The outliers are determined by two statistics. Second, the raw training set is split into raw training set and testing set by sample set partitioning joint x–y distance (SPXY). Third, the raw training set and five optimal training sets are built and evaluated. The five optimal training sets are selected by LARIS, random sampling (RS), Kennard–Stone (KS), SPXY, and K-nearest neighbor-based segmental sample data selection method (SSK) algorithms, respectively.
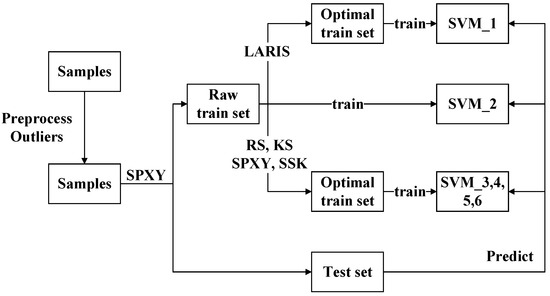
Figure 1.
The flow.
3.1. LARIS
LAR is an approximating method in the direction of least angle. During approximation, the variable is eliminated and sorted. LAR works for sorting as follows. The algorithm starts with the variable xi and begins at = 0 (xi is the most correlated variable with the target variable y, is the initial estimate of y). The estimation path approaches from along xi until the next variable xj has as much correlation with the current residual y − . The current estimate is updated to . Next, instead of continuing along xi, the estimation path steers along in the direction of equiangular u2 between xi and xj, until the next variable xk earns its way into the “most correlated” set, etc. [25]. The estimation path ends when there are no unselected samples or the residual value is less than ε. In this process, the correlation value of the unselected variables is assigned to 0 because of their fewer contributions. The variables with non-zero correlation are sorted from large to small as a sequence according to the correlation. The formula for LAR is as follows:
where, X is the training variables. is the estimate value of y. β describes how much the correlation is for the variable xi to the current residual y − . ui represents the unit vector of the direction forward. Formally, the formula is similar to the regression model. This approximation way has the advantage of ensuring high accuracy and selecting the most correlated variables from a group of closely distributed variables. Samples of the same class are very similar in chemical composition, structure and properties, and their spectra are also very similar. LAR is suitable for compressing redundant NIR spectra with very close distribution.
The LAR is modified to enable spectral classification instance selection as follows. The key is that the target variable y is substituted by the standard spectrum of the Class i samples. The raw training set is supposed to contain k class samples.
(a) The first step is to calculate the standard spectrum of each class (i = 1, 2, …, k). is usually approximated by the mean spectrum of Class i.
(b) The second step is to select the optimal samples of Class i from the entire raw training set by LAR. The approximation is supervised with . The k classes of the optimal samples sets X1′, X2′, …, Xk′ are obtained in turn. In the optimization process of the Class i sample, the approximation is ended when there are no unselected samples in the raw training set or the residual value is less than ε. is the estimated value of . The correlations of the unselected samples are 0.
(c) The third step is to obtain the union X′ of k optimal samples sets and calculate the mean spectrum of X′, where, X′ = X1′∪X2′∪…∪Xk′.
(d) The final step is to obtain an ordered optimal training sample sequence from X′ by LAR supervised with . The first model is trained by the top 10k samples, the second model is trained by the top 10k + 1 samples, the third model is trained by the top 10k + 2 samples, until all samples are introduced to establish models, etc. Finally, the optimal training set is determined by the highest accurate model. To avoid overfitting, 10-fold cross-validation is used during modeling.
The algorithm of LARIS is depicted in Figure 2.
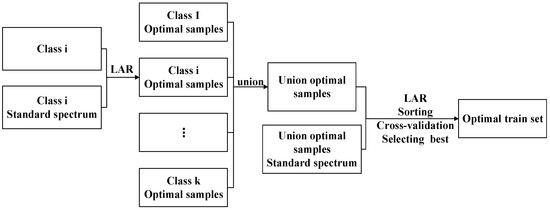
Figure 2.
Algorithm of LARIS description.
3.2. Selection Methods
In this paper, four other methods, namely RS, KS, SPXY, and SSK were used to build the optimal training set. KS and SPXY are typical Euclidean distance-based algorithms for spectral sample selection. SSK is a commonly used K-nearest neighbor-based IS algorithm. RS, used to verify the optimal samples, is more effective than randomly selected samples with the same size as LARIS. These four methods are mature and commonly used in near-infrared spectroscopy, which makes the comparison more convincing.
KS and SPXY methods both directly sort the samples based on Euclidean distance, SPXY is needed to refer the labels, and KS is not needed. These two methods are often used in spectroscopy. KS and SPXY work as follows [13]. First, the two samples with the largest Euclidean distance are selected as the set. Then, in subsequent iterations, the sample with the maximum and minimum distances to the set is added to the set. When the set size is equal to the product of the sample number and split ratio, the iteration is ended. The split ratio is the parameter that controls the samples size in two methods. In this paper, the ratio is set from 10% to 100%.
The SSK method is an instance selection method based on KNN technology. It has the advantages of compressing the sample size and ensuring model performance [14]. SSK works as follows. First, samples are clustered by KNN. Second, whether the clustering result is correct or incorrect is determined by referring to the class labels. Third, the correct samples are sorted and divided into five segments according to the distance between the sample and clustering center. Finally, the samples of odd segments and the incorrect samples are selected to form the optimal training set. In SSK, the nearest neighbors’ number needs to be determined. In this paper, the nearest neighbors’ number is set from 4 to 24, respectively. The nearest neighbors’ number with the highest accuracy is determined as the best parameter of SSK.
3.3. Preprocessing, Decomposition and Outliers Methods
Spectrometers are sensitive to environmental conditions, so the acquired signals are susceptible to baseline, drift scattering, and high collinearity of the spectra. In this paper, the multivariate statistics and signal processing methods such as correction, filter, decomposition, and their combinations were applied before modelling [28,29].
In this paper, the multiplicative scatter correction (MSC) and Savitzky–Golay filter (S-G filter) are used for signal processing. MSC is used to reduce the scattering effect, and there is no need to set parameters. The S-G filter is used to improve the spectral signal-to-noise ratio and baseline correction. The S-G filter combined with smoothing, 1-derivative, and 2-derivative is used to suit the data points within the window. S-G smoothing and S-G derivation can be achieved by the savgol_filter function. When the parameter “deriv” is set as 0, the function runs the smoothing operation. When deriv = 1, the function performs first-order derivation, and when deriv = 2, the function performs second-order derivation. Since the two parameters, window_length and polyorder, have no effect on the result, they are set as window_length = 9 and polyorder = 3 for preprocessing.
Partial least squares decomposition (PLS decomposition) and principal component analysis decomposition (PCA decomposition) are two statistical techniques for decomposition. In NIR, a large number of measured spectral variables can be projected to a low-dimensional space by these techniques [30]. A number of latent variables (Lvs) are used to describe the dimensional space size. The input matrix X and y are used by PLS decomposition. Simply, X is used by PCA decomposition without y [31]. In this paper, the effect of PLS and PCA decomposition is both analyzed and compared [32]. Since the paper does not focus on the size of the low-dimensional space, to ensure consistency of information for each IS method, the value of Lvs is set as 83, which is the same as the wavelength point number of the spectrometer.
The outliers are far away from the average of the entire training set and they have a strong mutual masking property. The principal components and model robustness are interfered with by the spectra of outliers. In order to avoid outliers affecting the sample selection, outlier elimination is performed after preprocessing. Hotelling’s T2 and Q-residuals are two statistics often combined with a 5% confidence interval F-test for eliminating outliers on MSPC. Hotelling’s T2 is used to test if all samples are from the same population, and the smaller it is, the better it is. The variables that cannot be interpreted by the error matrix are excluded by Q-residuals.
3.4. The Classifier
In this paper, support vector machine (SVM) was implemented to classify the SVC function. The kernel, C, gamma, and decision_function_shape are the parameters of SVM. The kernel impacts the shape of the classification boundary, C and gamma impact the position of the classification boundary, and decision_function_shape determines the unbalanced strategy [11]. There are two values for decision_function_shape: OVR and OVO [33]. They are all set as the default values: kernel = rbf, C = 1.0, gamma = scale, and decision_function_shape = OVR.
The imbalance rate IR [34] is introduced to check the set:
Nmax, Nmin are the numbers of the majority and minority class samples, respectively. The value of the unbalanced dataset is more than 1.5. The value of the balanced dataset is less than 1.5.
3.5. Evaluation Metrics
To evaluate the model performance and sample distribution, some specific evaluation metrics are introduced. These metrics are ACC (Equation (4)), F-Measure (Equation (5)). F-Measure is calculated from the precision (Equation (6)) and recall (Equation (7)). The equations of Accuracy, F-Measure, precision, and recall are expressed as follows:
where, TP, TN, FP, and FN represent the number of true positives, true negatives, false positives, respectively, and the false negatives samples are predicted by the SVM classifier. Accuracy is used to calculate the percent of all true labels in the entire set. The ACC_CV is denoted as the cross-validation of Accuracy of the training set. The ACC_P is denoted as the Accuracy of the testing set. F-Measure is calculated from the precision and recall, and it is employed to measure the accuracy of samples of each class. The precision is interested in the correctness of the total positive labels. The recall is significant for the true rate of predicted positive labels [35].
The Calinski–Harabas index (CH) can be used to evaluate the relationship between- and within-class, where the score is higher when the clusters are dense and well separated [36]. The equation is as follows:
where, Bk is the between-class covariance matrix and Wk is the within-class covariance matrix, with nE the number of samples in the set.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Spectral Analysis and Processing
Figure 3a shows the average of the raw spectra of four origins. In Figure 3a, the spectral shapes of the four classes are very similar. This makes classification difficult. The significant differences in average spectra occur at the 735–755 nm, 915–945 nm, and 955–970 nm wave peaks and troughs. These positions have some consistent spectral absorption peaks. It is difficult to classify the origin because the spectra have too many overlapping bands and slight differences in absorbance.
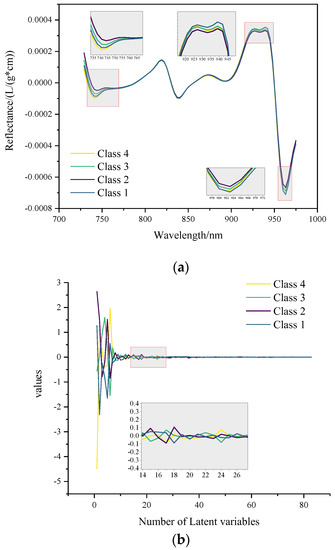
Figure 3.
The average of spectra of the four origins. (a) Raw spectra and (b) decomposed and corrected spectra.
Table 1 shows the prediction results of various preprocessing methods after ten-fold cross-validation on the entire sample set. The most effective method is PLS decomposition. F-measure results of all classes are 100%, obtained through PLS decomposition with MSC. The ACC_CV also exceeds 95% using only the PLS decomposition method. Figure 3b shows the average of the decomposed and corrected spectra of the four origins. In terms of trend, the primary spectral information is included in the first 20 latent variables. The ACC_CV of the raw spectra without preprocessing is only 55.57%. The performances of S-G smoothing and numerical derivatives are as bad as the raw, but their ACC_CV is improved by about 15% after preprocessing of MSC. The spectra of the four origins are very similar and are difficult to distinguish. Without the supervision of the response vector, the PCA decomposition is not effective. PCA decomposition added with MSC makes the four classes of spectra even more indistinguishable, resulting in Class 2, Class 3, Class 4 samples all being misclassified as Class 1.

Table 1.
The results of various preprocessing methods after ten-fold cross-validation of the sample set.
4.2. Outliers
Figure 4 shows the sample distribution of the Hotelling’s T2 and Q-residuals. According to the 5% confidence interval F-test, the critical values of Hotelling’s T-square and Q-residuals were calculated to be 115.29 and 349.94. The outside samples can be regarded as abnormal samples for removal, which are marked with orange in Figure 4. A total of 19 samples were eliminated as the following: 2 samples from Class 1, 10 from Class 2, 6 from Class 3, and 1 from Class 4. Currently, the sample set contains 933 samples: 278 samples from Class 1, 234 from Class 2, 222 from Class 3, and 199 from Class 4.
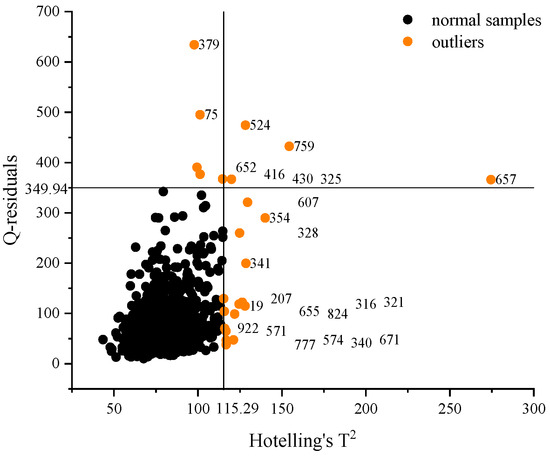
Figure 4.
The sample distribution of Hotelling’s T2 and Q-residuals.
4.3. Set Split and Optimization
The sample set was split into the 699 samples raw train set and 234 samples testing set by the SPXY method at the ratio of 3:1. The raw training set was optimized by LARIS, RS, KS, SPXY, and SSK, respectively.
The results of all train and testing sets are shown in Table 2. Among the six training sets, only the optimal training set established by the LARIS and SSK methods achieve sample compression while improving the ACC_CV. Compared with the raw training set, LARIS selects 73.1% of the samples and the accuracy is improved by 0.19%. To illustrate the effectiveness of the LARIS-training set compared with random training samples, the training set with the same compression ratio, is established by RS. The result of the RS-training set is an average of 42 random seeds of python code functions. From the average ACC_CV, CH, and IR of the RS-training set, it can be seen that the samples selected by RS reduce the model prediction effect, increase the distribution gap with the raw training set, and improve the imbalance. The least number of samples selected by the KS method is used to build a training set with only 20% of the raw training set. However, this training set is the most unbalanced and it has poor classification accuracy. The SPXY is better than KS in terms of balance and accuracy due to the added supervision of the labels. But, SPXY selects 90% of the 699 training samples and the model accuracy is improved by 0.01%; the value is higher than the raw training set. It does not achieve sample compression while improving the classification accuracy. SSK selects 64.8% of the 699 training samples with an accuracy improvement of 1.48%. In terms of sample distribution and imbalance comparison, the CH and IR values of the LARIS optimal training set are the closest to the testing set. Therefore, comprehensively considering several evaluation indexes such as ACC_CV, CH, and IR, the training set selected by LARIS is the most optimal.

Table 2.
Training set details.
The parameter training processes of KS, SPXY, and SSK are shown in Figure 5. The ACC_CV of the KS method is highest, when the samples are picked from the raw training set at 20%. The ACC_CV of the SPXY method is highest, when the samples are picked from the raw training set at 90%. The ACC_CV of the SSK is highest, when the neighbors of SSK are set as 22. The ACC_CV of the KS and SSK training sets are unstable; it can be seen that the sort way is volatile from the parameter training processes of the three methods.
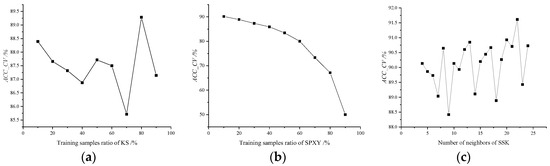
Figure 5.
The parameter training process of (a) KS, (b) SPXY, and (c) SSK.
Figure 6 shows the optimization process of the LARIS. Figure 6a,c,e,g shows the correlation values of all samples when each class is selected apart. The average correlation value and the number of optimal training samples are counted in Figure 6b,d,f,h. The correlation coefficient of the unselected training and testing samples are all assigned to 0. Statistically, 392, 391, 390, and 392 samples are optimally selected for each class by LARIS, and 688 samples are obtained after taking the union.
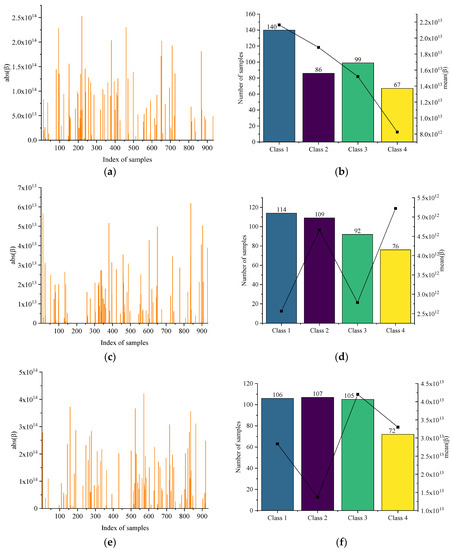
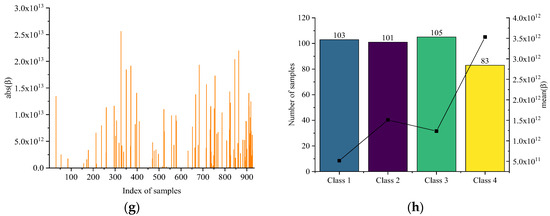
Figure 6.
(a) The absolute of β of each sample in raw training set and (b) the number of each class of optimal samples corresponding to . (c) The absolute of β of each sample in raw training set and (d) the number of each class of optimal samples corresponding to . (e) The absolute of β of each sample in raw training set and (f) the number of each class of optimal samples corresponding to . (g) The absolute of β of each sample in raw training set and (h) the number of each class of optimal samples corresponding to .
In terms of the size and correlation, the most significant effect is served on the Class i samples when the mean spectrum of Class i is used. In Figure 6a,b, when using , 392 samples are selected from the raw training set. There are 140 samples from Class 1 with other classes less than 100, and the sample of Class 1 has the largest number both in terms of size and correlation means. In Figure 6c,d, 391 samples are selected from the raw training set when using . Although Class 2 is ranked second on the size and correlation mean, the sum of the correlations and standard spectrum is the largest on all Class 2 samples. In Figure 6e,f, the first three class sizes are the same when using . The correlation sum of Class 3 is the largest. This is consistent with the optimization characteristics. In Figure 6g,h, the Class 4 samples size is the lowest, but the correlation means of Class 4 are much larger than the other classes. In addition, it is found that the Class 4 samples are always the least regardless of any class standard spectrum, which indicates that the Class 4 samples are more different from the rest of the raw training set.
A total of 688 samples is sorted by the absolute value of correlation from largest to smallest. The first 40 samples are regarded as the first train subset to gain the prediction result. Starting from the 41st sample, subsequent samples are added into the train subsets one by one. The variation of Accuracy with the index of 668 samples is shown in Figure 7a. The black line represents the accuracy variation of the optimal train subsets. The orange line represents the accuracy variation of the testing set. The maximum points of the two lines are marked with circles.
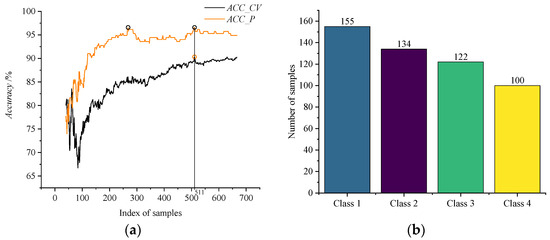
Figure 7.
The results of models established by 688 sorted samples. (a) The variation of Accuracy with the index of samples. (b) The detail of optimal training set selected by LARIS.
It can be seen from Figure 7a that the value of ACC_CV is maximum when the size of train subset is 511, and the value of ACC_P is also simultaneously the maximum. Figure 7b shows the 511 samples. The value of ACC_CV changes in a sawtooth pattern continually, and it decreases and then slowly rises back to a value close to maximum. But it is still less than the maximum. The value of ACC_P slowly decreases in a stepwise pattern. The value of ACC_P is already maximum at the first 268 training samples, but the value of ACC_CV is not at a maximum at this time. The value of ACC_CV still rises, and it indicates that the model is underfitted and not reliable.
In Table 3, the model established by the optimal training set is best whether the whole or each class. The 73.1% of the samples of the raw training samples are selected by LARIS; the accuracy is improved from 91.9% to 96.6%; the prediction performance of the raw and the random training sets are followed by the optimal training set. The overlapped and misclassified samples in the first three classes are reduced. Their average precision and recall are improved by about 6% on the optimal. Among them, the misclassified size of Class 1 samples is reduced, and the precision of Class 1 is improved by 7.1%. The recall of Class 2 is improved by 10.2%, and its precision increases the most. Since the Class 4 samples are well segmented by hyperplane, the precision of Class 4 is 100%. The performance of the model established by the random training set is as quiet as the raw training set. The standard for evaluating a model quality is the prediction ability for new samples. The prediction results of classifiers trained by all six training sets for the testing set are shown in Table 3. According to the results in Table 3, the best prediction result is obtained by the LARIS, whether the ACC_P for the entire testing set or the F-Measure for each class. Compared with the raw training set, the ACC_P is improved from 91.88% to 96.58%, and the F-Measure for each class is improved by 4.7% on average in the LARIS method. The model with the second highest ACC_P is the one built by the SPXY training set, but its compression is poor. The ACC_P is improved but the F-Measure is decreased for the Class 2 and Class 3 in the KS method. The predictive abilities of the model built by the RS and SSK training sets are decreased. Therefore, through a comprehensive comparison, LARIS can be used to improve the prediction accuracy while selecting representative samples and sample compression. So far, the effect of the LARIS has been verified by distribution and prediction performance.

Table 3.
The results of the three models.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, an instance selection method based on least angle regression was proposed and an apple origin discrimination experiment was conducted for verification. In the LARIS the advantages of clustering, ranking method, and classification boundaries were retained, the sample size was compressed, and high accuracy was achieved. The standard spectrum in LARIS had a great influence on the selected samples. In order to ensure the reliability and balance of the optimal sample set, the standard spectrum of each class was preferably only used once and then merged. The results showed that LARIS was better than the RS, KS, SPXY, and SSK in terms of sample distribution and model performance. A 26.9% compression ratio of the LARIS method was achieved, and the model accuracy was improved by about 5%. In terms of sample distribution and imbalance comparison, the LARIS optimal training set was the closest to the testing set. Therefore, the goals of high accuracy and compression of LARIS were verified on the apple origin classification experiment. This experiment provided theoretical support and experimental conduction to improve the model performance on larger spectral datasets.
Author Contributions
B.L.: Reviewing. Y.W.: Writing. L.L.: Data collection. Y.L.: Funding and equipment acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, funding number [31760344].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the request of the funding of the scientific research projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that have occurred to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- da Silva Medeiros, M.L.; Brasil, Y.L.; Cruz-Tirado, L.J.P.; Lima, A.F.; Godoy, H.T.; Barbin, D.F. Portable NIR spectrometer and chemometric tools for predicting quality attributes and adulteration levels in butteroil. Food Control 2023, 144, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstecken, D.; Stürz, B.; Robatscher, P.; Lozano, L.; Zanella, A.; Oberhuber, M. The potential of near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to trace apple origin: Study on different cultivars and orchard elevations. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 147, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y. A Standard-Free Calibration Transfer Strategy for a Discrimination Model of Apple Origins Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Agriculture 2022, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska, J.; Beć, K.B.; Ueno, N.; Huck, C.W. Analyzing the Quality Parameters of Apples by Spectroscopy from Vis/NIR to NIR Region: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2023, 12, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Mouazen, A. Optimal sample selection for measurement of soil organic carbon using on-line vis-NIR spectroscopy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 151, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-W.; Tsai, C.-F.; Lin, W.-C. Instance selection in medical datasets: A divide-and-conquer framework. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 90, 106957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodinová, Š.; Filzmoser, P.; Ortner, T.; Breiteneder, C.; Rohm, M. Robust and sparse k-means clustering for high-dimensional data. Adv. Data Anal. Classif. 2019, 13, 905–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucà, F.; Conforti, M.; Castrignanò, A.; Matteucci, G.; Buttafuoco, G.J.G. Effect of calibration set size on prediction at local scale of soil carbon by Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2017, 288, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhao, X.J.N. An efficient instance selection algorithm for k nearest neighbor regression. Neurocomputing 2017, 251, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáiz-Abajo, M.J.; Mevik, B.-H.; Segtnan, V.H.; Næs, T.J.A.C.A. Ensemble methods and data augmentation by noise addition applied to the analysis of spectroscopic data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 533, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Lv, F.; Konan, M.J.K.B.S. An efficient instance selection algorithm to reconstruct training set for support vector machine. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 116, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, C. Near-Infrared Spectra Combining with CARS and SPA Algorithms to Screen the Variables and Samples for Quantitatively Determining the Soluble Solids Content in Strawberry. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2015, 35, 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Galvao, R.K.; Araujo, M.C.; José, G.E.; Pontes, M.J.; Silva, E.C.; Saldanha, T.C. A method for calibration and validation subset partitioning. Talanta Int. J. Pure Appl. Anal. Chem. 2005, 67, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhu, W.; Ren, Q. Segmentation training data selection method based on K-means clustering. Appl. Res. Comput. 2021, 38, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Oommen, B.J. A brief taxonomy and ranking of creative prototype reduction schemes. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2003, 6, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.-j.; Mu, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Gou, J.; Chen, X.J.N. Large-scale support vector machine classification with redundant data reduction. Neurocomputing 2016, 172, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haro-García, A.; Cerruela-García, G.; García-Pedrajas, N. Instance selection based on boosting for instance-based learners. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 96, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pedrajas, N.; de Haro-García, A. Boosting instance selection algorithms. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 67, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, G.D.C.; Soares, R.J.O. Ranking-based instance selection for pattern classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 150, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.d.S.; Cavalcanti, G.D.C. Instance selection algorithm based on a Ranking Procedure. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, San Jose, CA, USA, 31 July–5 August 2011; pp. 2409–2416. [Google Scholar]
- Djouzi, K.; Beghdad-Bey, K.; Amamra, A. A new adaptive sampling algorithm for big data classification. J. Comput. Sci. 2022, 61, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, M. A Model Construction Method of Spectral Nondestructive Detection for Apple Quality Based on Unsupervised Active Learning. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2022, 42, 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Sarker, P.S.; Saud, A.A.; Shatabda, S.; Hakim Newton, M.A. Cluster-oriented instance selection for classification problems. Inf. Sci. 2022, 602, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Hastie, T.J.; Johnstone, I.M.; Tibshirani, R. Least angle regression. Ann. Stat. 2004, 32, 407–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Li, L.; Xiong, Y.; Kang, Q.; Du, Y. Ridge regression combined with model complexity analysis for near infrared (NIR) spectroscopic model updating. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 195, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmerhnia, L.; Djermoune, E.-H.; Carteret, C.; Brie, D. Simultaneous variable selection for the classification of near infrared spectra. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 211, 104268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaigre, S.; Adam, G.; Goux, X.; Noo, A.; De Vos, B.; Gerin, P.A.; Delfosse, P. Transfer of a static PCA-MSPC model from a steady-state anaerobic reactor to an independent anaerobic reactor exposed to organic overload. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 159, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, F. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy combined with multivariate analysis in monitoring of crude heparin purification process. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 109, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, J.L.; Vega, J.R.; Marchetti, J.L. A fault detection and diagnosis technique for multivariate processes using a PLS-decomposition of the measurement space. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2013, 128, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qin, S.J.; Zhou, D. Geometric properties of partial least squares for process monitoring. Automatica 2010, 46, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bais, A. A novel PCA-based calibration algorithm for classification of challenging laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy soil sample data. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2022, 193, 106451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarekegn, A.N.; Giacobini, M.; Michalak, K. A review of methods for imbalanced multi-label classification. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 118, 107965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramentol, E.; Vluymans, S.; Verbiest, N.; Caballero, Y.; Bello, R.; Cornelis, C.; Herrera, F. IFROWANN: Imbalanced Fuzzy-Rough Ordered Weighted Average Nearest Neighbor Classification. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 23, 1622–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskes, N.; Fakhfakh, S.; Kanoun, O.; Derbel, N. Representativeness consideration in the selection of classification algorithms for the ECG signal quality assessment. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 76, 103686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliński, T.; Ja, H. A Dendrite Method for Cluster Analysis. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1974, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).