Urban Agriculture as an Alternative for the Sustainable Production of Maize and Peanut
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Seeds
2.3. Organic Composting
2.4. Analyzed Soil and Compost Samples
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Morphological Characteristics
2.6.1. Leaf Area (la)
2.6.2. Leaf Area Index (LAI)
2.7. Produce Obtained from Crops
2.8. Maize and Peanut Yield
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
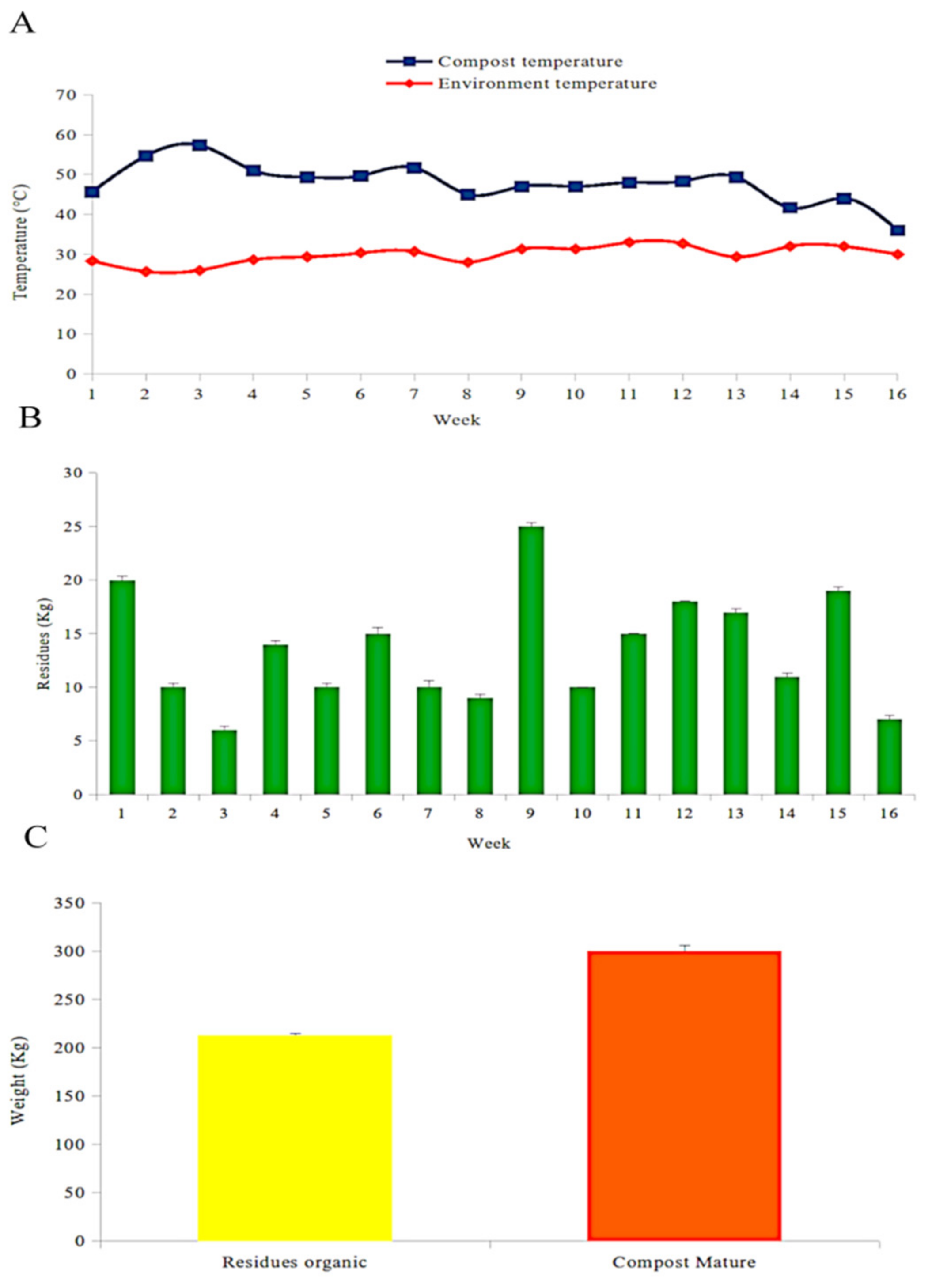
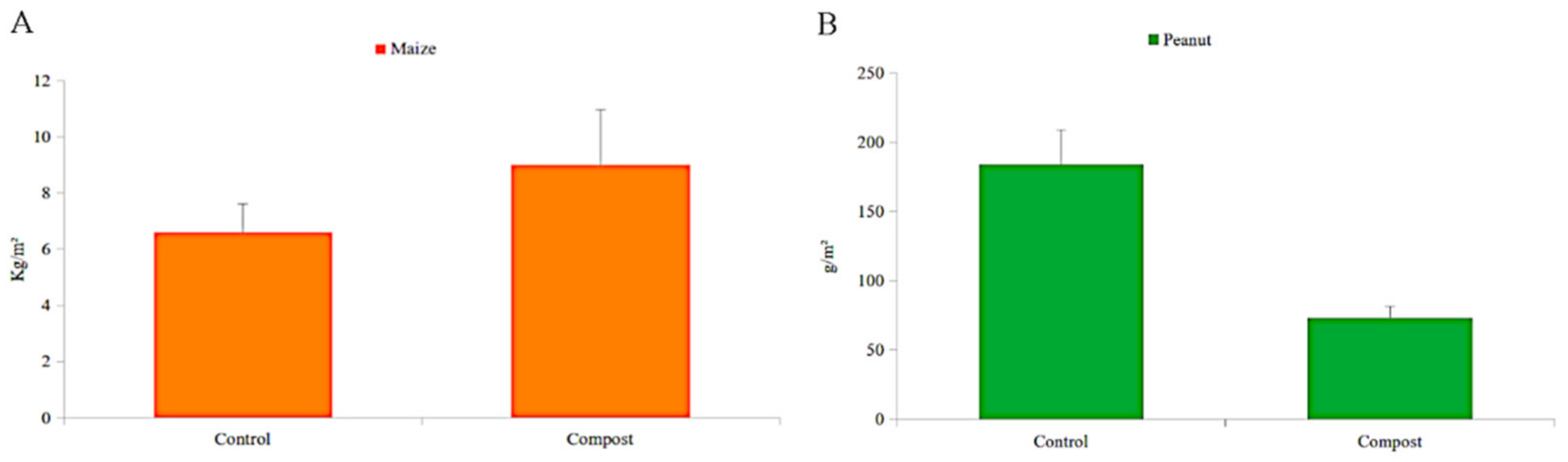
3.1. Compost Production and Yield
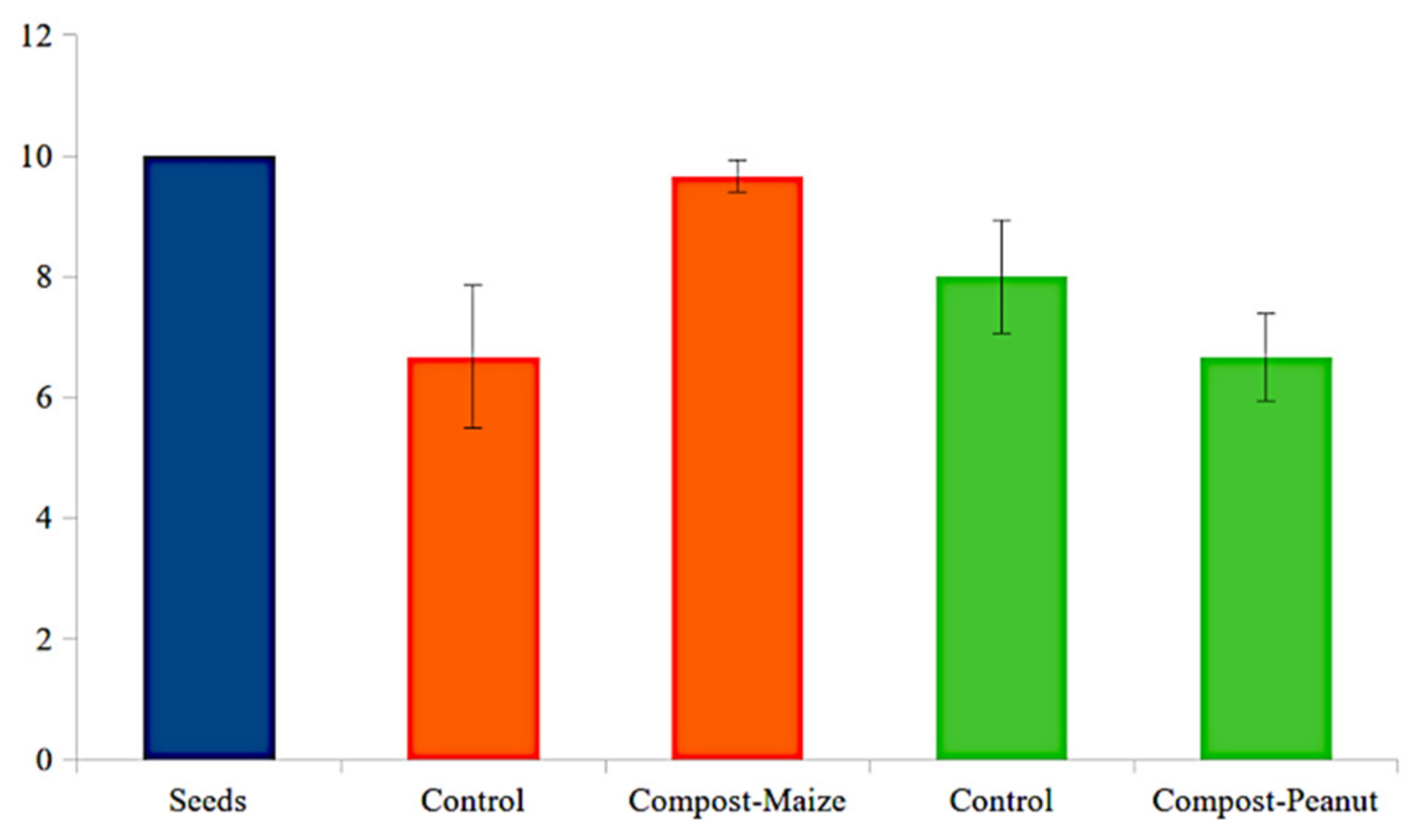
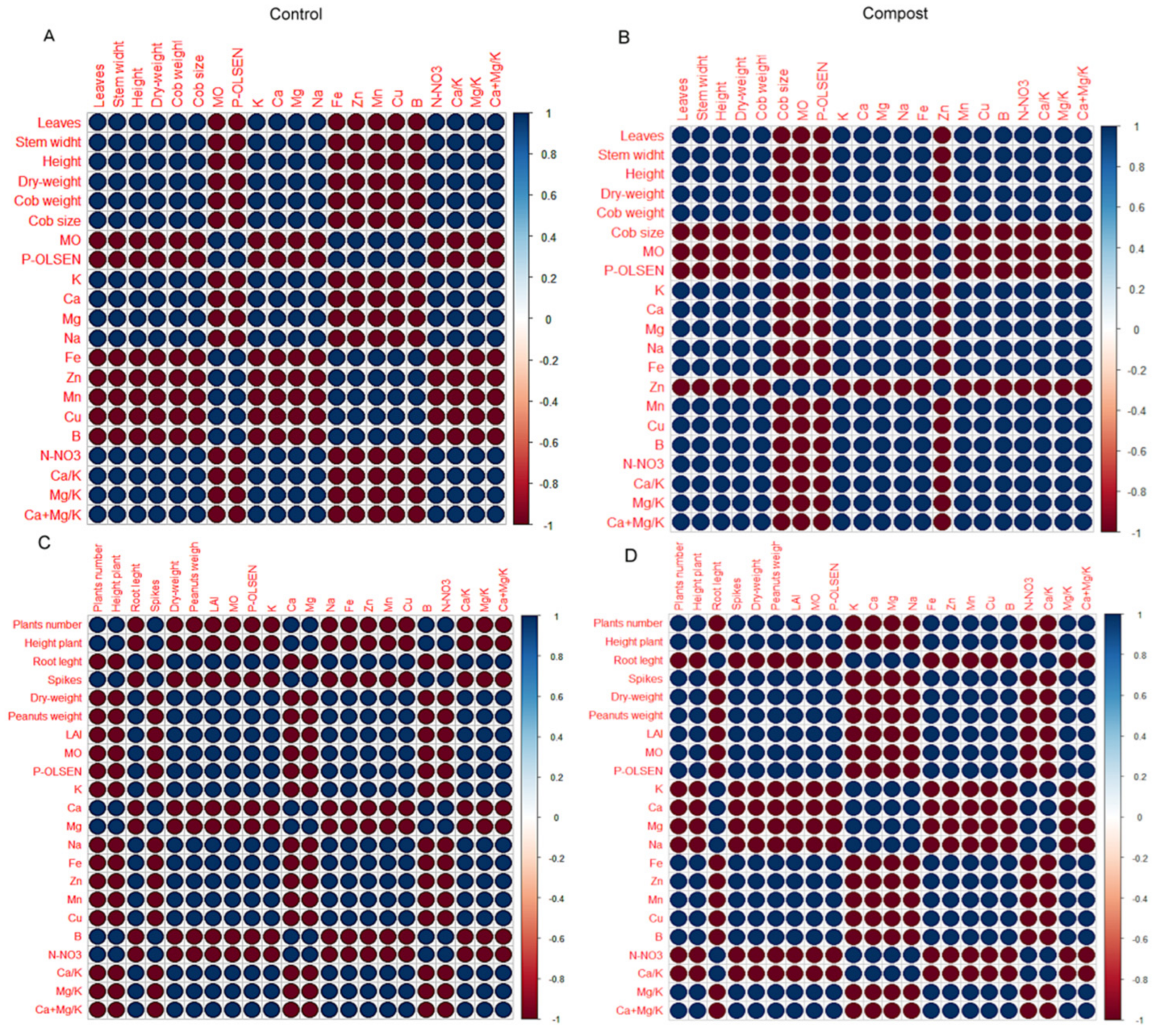
3.2. Experimental Crops
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haque, M.; Zaman, M.; Uz, R.; Rahman, M.; Hossain, M.; Shurid, T.I.; Rimi, T.A.; Arby, H.; Rabbany, M. A Review on Impacts of COVID-19 on Global Agricultural System and Scope for Bangladesh after Pandemic. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 54060–54071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Farooq, M.; Lee, D.-J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Sustainable Agricultural Practices for Food Security and Ecosystem Services. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 84076–84095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiertz, H. Challenges for Crop Production Research in Improving Land Use, Productivity and Sustainability. Sustainability 2013, 5, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Sonder, K.; Mottaleb, K.; Prasanna, B.M. Global Maize Production, Consumption and Trade: Trends and R&D Implications. Food Sec. 2022, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.C.K.; Stock, J.T. Life History Transitions at the Origins of Agriculture: A Model for Understanding How Niche Construction Impacts Human Growth, Demography and Health. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmann, G.; Azim, K.; Brányiková, I.; Chander, M.; David, W.; Erisman, J.W.; Grimm, D.; Hammermeister, A.; Ji, L.; Kuenz, A.; et al. Innovative, Sustainable, and Circular Agricultural Systems for the Future. Org. Agric. 2021, 11, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowysz, A.; Mazur, Ł.; Vaverková, M.D.; Koda, E.; Winkler, J. Urban Agriculture as an Alternative Source of Food and Water Security in Today’s Sustainable Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.; Fanzo, J.; Wiebe, K.; Huybers, P.; Smith, M. Current Guidance Underestimates Risk of Global Environmental Change to Food Security. BMJ 2022, 378, e071533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K. Can We Feed the World? BMJ 2008, 336, 1336–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giller, K.E.; Hijbeek, R.; Andersson, J.A.; Sumberg, J. Regenerative Agriculture: An Agronomic Perspective. Outlook Agric. 2021, 50, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Rochell, V.; Plat, K.; Jaworski, A. Circular Approaches in Small-Scale Food Production. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2021, 1, 1231–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, B.R.; Davies, J.A.C.; Falagán, N.; Kourmpetli, S.; Liu, L.; Hardman, C.A. Urban Agriculture in Times of Crisis: The Role of Home Food Growing in Perceived Food Insecurity and Well-Being during the Early COVID-19 Lockdown. Emerald. Open Res. 2021, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyuka, N.N.; Sibanda, M.; Bob, U. Perceptions of the Challenges and Opportunities of Utilising Organic Waste through Urban Agriculture in the Durban South Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, C.; Oltmanns, M.; Matthes, C.; Schmehe, B.; Schaaf, H.; Burghardt, D.; Horst, H.; Spieß, H. Compost as an Option for Sustainable Crop Production at Low Stocking Rates in Organic Farming. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Sommer, S.G.; Chadwick, D.; Qing, C.; Guoxue, L.; Michel, F.C. Current Approaches and Future Trends in Compost Quality Criteria for Agronomic, Environmental, and Human Health Benefits. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 144, pp. 143–233. ISBN 978-0-12-812419-2. [Google Scholar]
- Azim, K.; Soudi, B.; Boukhari, S.; Perissol, C.; Roussos, S.; Thami Alami, I. Composting Parameters and Compost Quality: A Literature Review. Org. Agric. 2018, 8, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, E.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, W. Impact of Composting Methods on Nitrogen Retention and Losses during Dairy Manure Composting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, H.; Mendoza, H.; Diánez, F.; Santos, M. Parameter Selection for the Evaluation of Compost Quality. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Small, G.E.; Kay, A. Quantifying Nutrient Recovery Efficiency and Loss from Compost-Based Urban Agriculture. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, K.; Wu, Q.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J. Effects of Narrow Plant Spacing on Root Distribution and Physiological Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Summer Maize. Crop J. 2013, 1, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shareef, R.; Mamat, A.; Al-Shaheen, M.R. The Effect of Soil PH, High-Calcium Compost and Cadmium on Some of Growth Characters in Corn (Zea Maysl.). J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 4, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandil, E.E.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Mansour, M.A.; Ali, H.M.; Siddiqui, M.H. Potentials of Organic Manure and Potassium Forms on Maize (Zea Mays L.) Growth and Production. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.K.; Bhatnagar-Mathur, P. Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). In Agrobacterium Protocols; Wang, K., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 347–358. ISBN 978-1-59745-130-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Davis, K.E.; Patterson, C.; Oo, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Fontana, J.E.; Thornburg, T.E.; et al. Response of Root Growth and Development to Nitrogen and Potassium Deficiency as Well as MicroRNA-Mediated Mechanism in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 695234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agegnehu, G.; Bass, A.M.; Nelson, P.N.; Muirhead, B.; Wright, G.; Bird, M.I. Biochar and Biochar-Compost as Soil Amendments: Effects on Peanut Yield, Soil Properties and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Tropical North Queensland, Australia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Ukita, M.; Imai, T.; Higuchi, T. Recycling Mineral Nutrients to Farmland via Compost Application. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondek, M.; Weindorf, D.C.; Thiel, C.; Kleinheinz, G. Soluble Salts in Compost and Their Effects on Soil and Plants: A Review. Compost. Sci. Util. 2020, 28, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, R.; Kristiansen, P.; Rader, R. Small-Scale Urban Agriculture Results in High Yields but Requires Judicious Management of Inputs to Achieve Sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Félix, G.K.; Peinado-Guevara, V.M.; Peinado-Guevara, H.J.; Cuadras-Berrelleza, A.A.; Herrera-Barrientos, J.; de López-López, J.J.; Zúñiga-Espinoza, N.G. Backyard Agricultural and Farm Activity as an Option of Socioeconomic and Food Improvement in the Rural Towns of the Municipality of Guasave, Sinaloa. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Determination | Results |
|---|---|
| pH | 8.49 ± 0.00 |
| Electric conductivity (d-S1 m) | 1.90 ± 0.04 |
| Total Nitrogen (%) | 1.06 ± 0.00 |
| Phosphorus (P) (%) | 0.49 ± 0.01 |
| Potassium (K) (%) | 0.66 ± 0.00 |
| Calcium (Ca) (%) | 17.16 ± 0.39 |
| Magnesium (Mg) (%) | 0.27 ± 0.00 |
| Sodium (Na) (%) | 0.08 ± 0.00 |
| Sulfur(S) (%) | 0.27 ± 0.00 |
| Iron (Fe) (%) | 5249.33 ± 37.26 |
| Cooper (Cu) (ppm) | 10.76 ± 0.37 |
| Manganese (Mn) (ppm) | 275.33 ± 2.59 |
| Zinc (Zn) (ppm) | 113.36 ± 26.13 |
| Boron (B) (ppm) | 29.40 ± 21.92 |
| Ashes (%) | 81.06 ± 1.73 |
| Maize | Leaves/Plant | Stem Width (cm) | Plant Height (cm) | Cob Size (cm) | Cob Weight (g) | Dry Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 13.94 ± 0.12 | 2.60 ± 0.08 | 2.18 ± 0.04 | 28.30 ± 0.04 | 142.60 ± 4.77 | 4.61 ± 0.10 |
| Compost | 14.15 ± 0.19 | 2.73 ± 0.09 | 2.98 ± 0.07 | 28.21 ± 0.63 | 127.35 ± 4.05 | 4.83 ± 0.03 |
| Significant * p < 0.05 | * | ns | * | ns | ns | ns |
| Peanut | Plant Height (cm) | Root Length (cm) | Spikes Number | Peanut Weight (g) | Dry Weight (kg) | Leaf Area Index |
| Control | 48.40 ± 2.15 | 8.96 ± 0.45 | 17.38 ± 1.78* | 48.87 ± 1.12 | 227.22 ± 48.18* | 2.27 ± 0.18 |
| Compost | 44.40 ± 1.57 | 8.01 ± 0.34 | 11.00 ± 0.81* | 47.65 ± 0.70 | 49.11 ± 2.14 | 1.86 ± 0.00 |
| Significant * p < 0.05 | ns | ns | * | ns | * | * |
| Properties | Determination | Control | Compost | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | * p < 0.05 | Peanut | * p < 0.05 | |||
| Soil properties | Class | Loamy | Loamy | ns | Loamy | ns |
| Saturation point (%) | 48.5 ± 1.76 | 55 ± 2.12 | ns | 55.1 ± 2.19 | ns | |
| Field capacity (%) | 25.85 ± 0.95 | 29.40 ± 1.13 | ns | 29.50 ± 1.20 | ns | |
| Permanent Wilting Point (%) | 15.40 ± 0.56 | 17.45 ± 0.67 | ns | 17.55 ± 0.74 | ns | |
| Electric conductivity (cm/hr) | 3.15 ± 0.17 | 2.05 ± 0.60 | ns | 2.05 ± 0.60 | ns | |
| Apparent density (g/cm3) | 1.19 ± 0.00 | 1.10 ± 0.02 | ns | 1.05 ± 0.01 | ns | |
| pH (1.2 water) | 8.08 ± 0.05 | 8.40 ± 0.00 | ns | 8.38 ± 0.17 | ns | |
| Total Carbonates (%) | 36.95 ± 4.00 | 41.45 ± 3.57 | ns | 33.8 ± 1.76 | ns | |
| Salinity (Extract CE) (dS/m) | 1.38 ± 0.02 | 0.65 ± 0.04 | * | 0.78 ± 0.01 | * | |
| Relation between Cations | Ca/K | 23.60 ± 0.07 | 14.55 ± 0.03 | ns | 13.85 ± 0.03 | * |
| Mg/K | 1.90 ± 0.01 | 1.41 ± 0.00 | ns | 1.53 ± 0.00 | * | |
| Ca/Mg/K | 25.50 ± 0.07 | 16.0 ± 0.07 | ns | 15.4 ± 0.07 | * | |
| Ca/Mg | 12.55 ± 0.03 | 10.4 ± 0.00 | * | 9.04 ± 0.01 | * | |
| Cation Exchange Capacity | Calcium (Ca) | 87.55 ± 0.03 | 84.40 ± 0.14 | * | 83.00 ± 0.14 | * |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 6.06 ± 0.01 | 8.09 ± 0.00 | * | 9.18 ± 0.00 | * | |
| Potassium (K) | 3.70 ± 0.01 | 5.81 ± 0.03 | * | 6.00 ± 0.14 | * | |
| Sodium (Na) | 1.75 ± 0.01 | 1.71 ± 0.14 | ns | 1.78 ± 0.42 | ns | |
| Soil fertilization | Organic material (MO) (%) | 3.95 ± 0.03 | 4.91 ± 0.17 | ns | 5.72 ± 0.17 | * |
| P-OLSEN (ppm) | 144.50 ± 0.03 | 182.50 ± 3.18 | * | 193.50 ± 0.17 | * | |
| K (ppm) | 388.50 ± 0.03 | 582.50 ± 3.88 | * | 600.50 ± 0.17 | * | |
| Ca (ppm) | 4710.50 ± 0.03 | 4339.00 ± 31.82 | * | 4259.50 ± 0.17 | ns | |
| Mg (ppm) | 228.00 ± 0.03 | 252.50 ± 2.47 | ns | 285.50 ± 0.17 | ns | |
| Na (ppm) | 107.00 ± 0.03 | 100.80 ± 10.04 | ns | 104.00 ± 0.17 | ns | |
| Fe (ppm) | 6.63 ± 0.03 | 8.76 ± 0.01 | * | 9.63 ± 0.17 | * | |
| Zn (ppm) | 7.75 ± 0.03 | 7.99 ± 0.14 | * | 8.05 ± 0.17 | ns | |
| Mn (ppm) | 2.62 ± 0.03 | 3.89 ± 0.02 | ns | 3.38 ± 0.17 | ns | |
| Cu (ppm) | 1.17 ± 0.03 | 1.13 ± 0.02 | ns | 0.99 ± 0.17 | ns | |
| B (ppm) | 0.79 ± 0.03 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | ns | 1.04 ± 0.17 | * | |
| S (ppm) | 16.10 ± 0.03 | 1.40 ± 0.00 | ns | 2.09 ± 0.17 | * | |
| N-NO3 (ppm) | 95.35 ± 0.03 | 14.35 ± 0.67 | * | 22.95 ± 0.17 | * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villalpando-Aguilar, J.L.; Chi-Maas, D.F.; López-Rosas, I.; Aquino-Luna, V.Á.; Arreola-Enríquez, J.; Alcudia-Pérez, J.C.; Matos-Pech, G.; Gómez-García, R.C.; Martínez-Puc, J.F.; Cetzal-Ix, W. Urban Agriculture as an Alternative for the Sustainable Production of Maize and Peanut. Agriculture 2023, 13, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010059
Villalpando-Aguilar JL, Chi-Maas DF, López-Rosas I, Aquino-Luna VÁ, Arreola-Enríquez J, Alcudia-Pérez JC, Matos-Pech G, Gómez-García RC, Martínez-Puc JF, Cetzal-Ix W. Urban Agriculture as an Alternative for the Sustainable Production of Maize and Peanut. Agriculture. 2023; 13(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillalpando-Aguilar, José Luis, Daniel Francisco Chi-Maas, Itzel López-Rosas, Victor Ángel Aquino-Luna, Jesús Arreola-Enríquez, Julia Cristel Alcudia-Pérez, Gilberto Matos-Pech, Roberto Carlos Gómez-García, Jesús Froylán Martínez-Puc, and William Cetzal-Ix. 2023. "Urban Agriculture as an Alternative for the Sustainable Production of Maize and Peanut" Agriculture 13, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010059
APA StyleVillalpando-Aguilar, J. L., Chi-Maas, D. F., López-Rosas, I., Aquino-Luna, V. Á., Arreola-Enríquez, J., Alcudia-Pérez, J. C., Matos-Pech, G., Gómez-García, R. C., Martínez-Puc, J. F., & Cetzal-Ix, W. (2023). Urban Agriculture as an Alternative for the Sustainable Production of Maize and Peanut. Agriculture, 13(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010059





