Evaluation of the Impact of Changing from Rainfed to Irrigated Agriculture in a Mediterranean Watershed in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.3. The SWAT Model Description
2.4. The SWAT Model Set-Up, Calibration, and Validation
2.5. Irrigation Impact Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Evaluation
3.1.1. Sensitivity Analysis
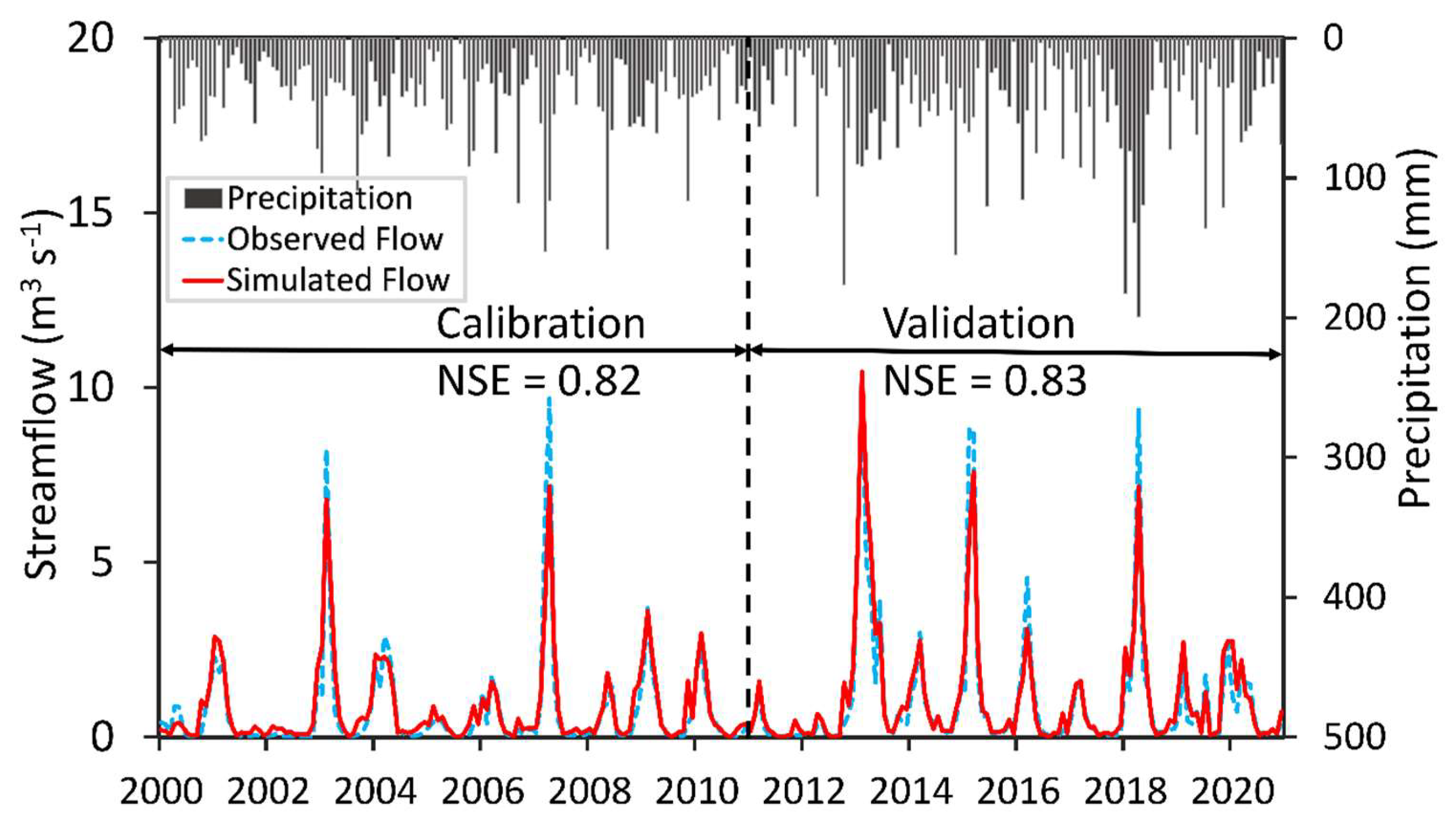
3.1.2. Calibration and Validation
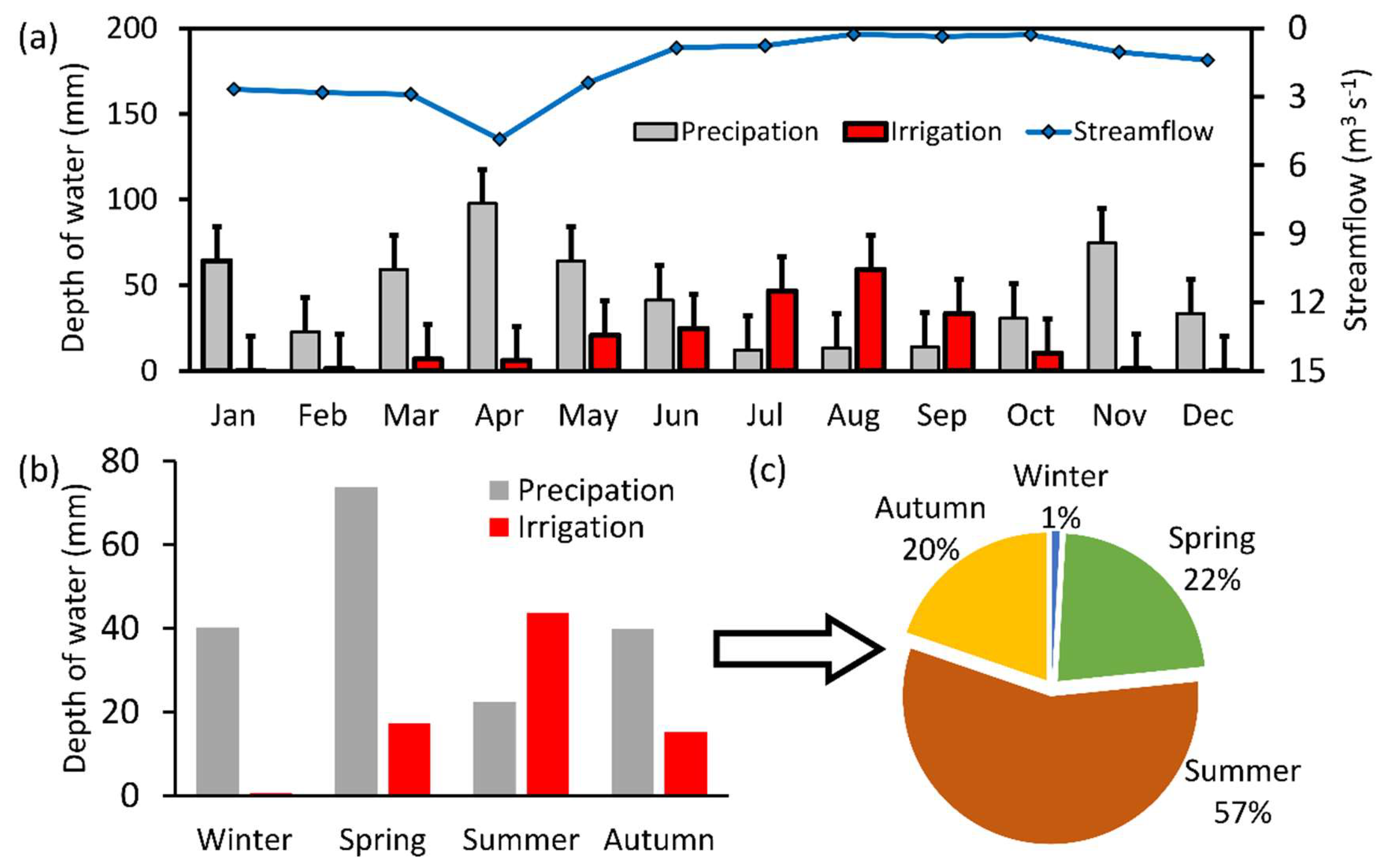
3.2. Irrigation Dynamics in the Watershed
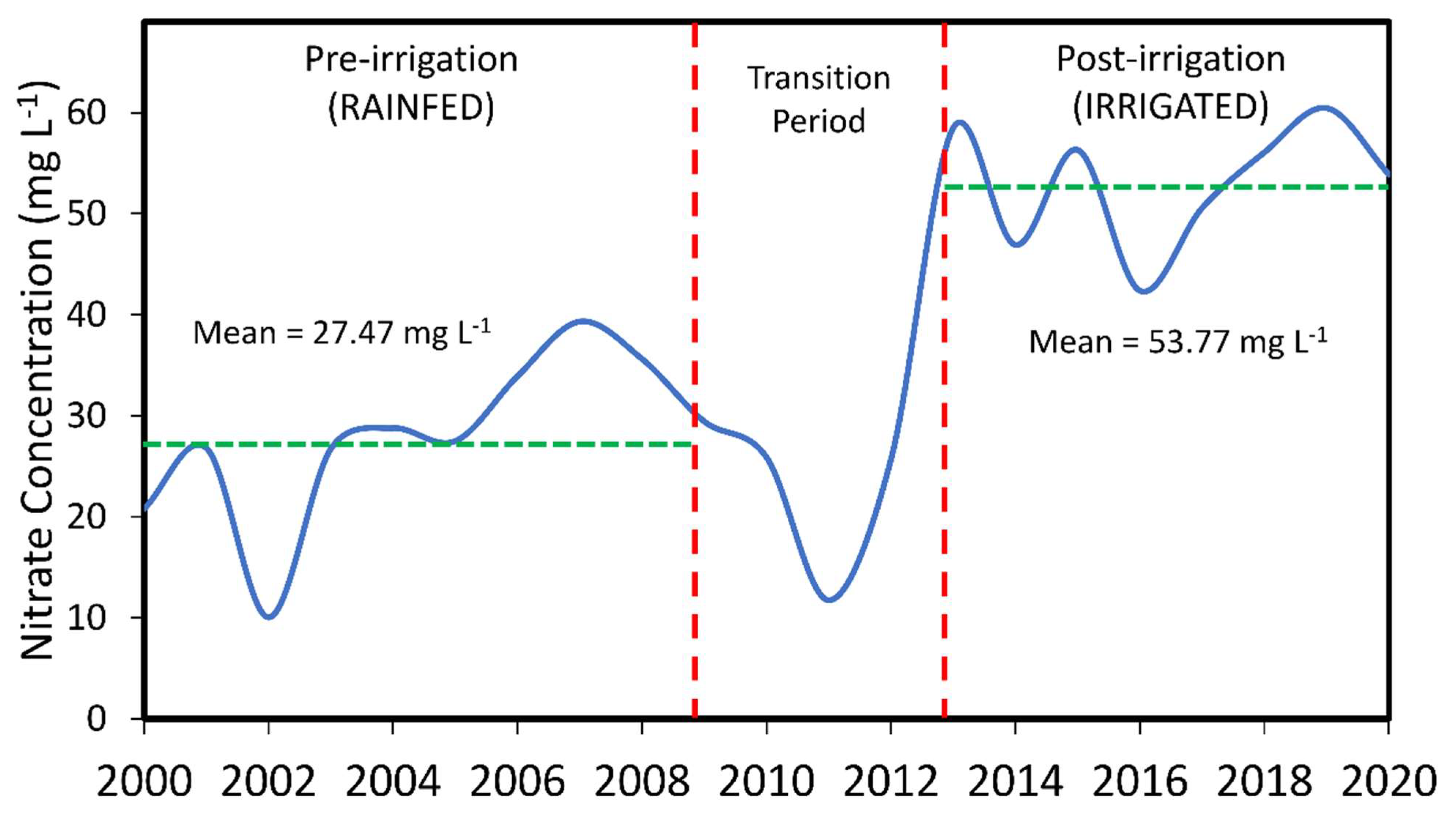
3.3. Observed Nitrate Concentration Dynamics
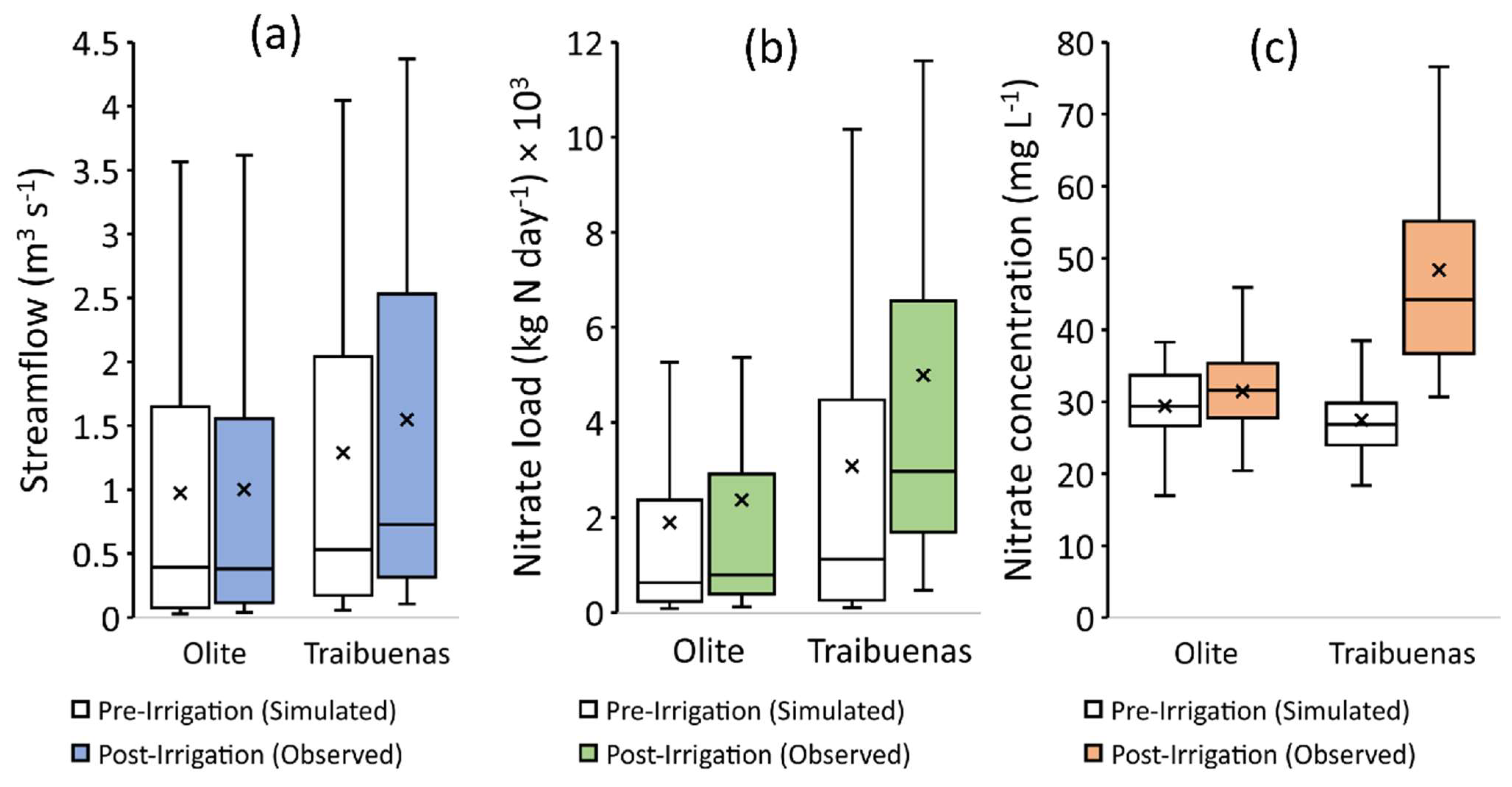
3.4. Variations in Streamflow and Nitrate (Load and Concentration) due to Irrigation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Bank Water in Agriculture. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/water-in-agriculture#1 (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- FAO. Water for Sustainable Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater Use for Irrigation—A Global Inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Cai, X. Analyzing Streamflow Changes: Irrigation-Enhanced Interaction between Aquifer and Streamflow in the Republican River Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; IWMI. More People, More Food, Worse Water? A Global Review on Water Pollution from Agriculture; Mateo-Sagasta, J., Zadeh, S.M., Turral, H., Eds.; FAO; Rome, Italy, IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2018; ISBN 9789251307298. [Google Scholar]
- MAPA Gestión Sostenible de Regadíos. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/desarrollo-rural/temas/gestion-sostenible-regadios/ (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- European Parliamentary Research Service (EPRS). Irrigation in EU Agriculture; EPRS: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich Böll Foundation. Agriculture Atlas: Facts and Figures on EU Farming Policy, 1st ed.; The European Commission’s LIFE Programme: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- DDRMAAL Estadísticas Agrícolas. Negociado de Estadística. Available online: http://www.navarra.es/home_es/Temas/Ambito+rural/Indicadores/agricultura.htm (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Government of Navarre Description of the Navarre Canal. Available online: https://www.canasa.es/proyecto/descripcion-canal-de-navarra (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Duncan, R.A.; Bethune, M.G.; Thayalakumaran, T.; Christen, E.W.; McMahon, T.A. Management of Salt Mobilisation in the Irrigated Landscape—A Review of Selected Irrigation Regions. J. Hydrol. 2008, 351, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Bosch, A.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P.; Vallejos, A.; Andreu, J.M.; Ceron, J.C.; Molina-Sanchez, L.; Sola, F. Impacts of Agricultural Irrigation on Groundwater Salinity. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Ritter, A.; Socorro, A.R.; Pérez, N. Nitrogen Evolution and Fate in a Canary Islands (Spain) Sprinkler Fertigated Banana Plot. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 52, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán, D.; Sanz, L.; Alfaro, A.; Pérez, I.; Goñi, M.; Solsona, F.; Hernández-García, I.; Pérez, C.; Casalí, J. Irrigation Implementation Promotes Increases in Salinity and Nitrate Concentration in the Lower Reaches of the Cidacos River (Navarre, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatis, G.; Parpodis, K.; Filintas, A.; Zagana, E. Groundwater Quality, Nitrate Pollution and Irrigation Environmental Management in the Neogene Sediments of an Agricultural Region in Central Thessaly (Greece). Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1081–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9789241549950. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, M.A.; Howard, C.M.; Erisman, J.W. The European Nitrogen Assessment—Sources, Effects and Policy Perspectives; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Casalí, J.; Gastesi, R.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; De Santisteban, L.M.; de Lersundi, J.D.V.; Giménez, R.; Larrañaga, A.; Goñi, M.; Agirre, U.; Campo, M.A.; et al. Runoff, Erosion, and Water Quality of Agricultural Watersheds in Central Navarre (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1111–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menció, A.; Mas-Pla, J.; Otero, N.; Regàs, O.; Boy-Roura, M.; Puig, R.; Bach, J.; Domènech, C.; Zamorano, M.; Brusi, D.; et al. Nitrate Pollution of Groundwater; All Right..., but Nothing Else? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.; Isidoro, D.; Aragüés, R. Irrigation Management, Nitrogen Fertilization, and Nitrogen Losses in the Return Flows of La Violada Irrigation District (Spain). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 155, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Garizábal, I.; Causapé, J.; Abrahao, R. Nitrate Contamination and Its Relationship with Flood Irrigation Management. J. Hydrol. 2012, 442–443, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, R.; Cuchí, J.A. Salt and Nitrate Exports from the Sprinkler-Irrigated Malfarás Creek Watershed (Ebro River Valley, Spain) during 2010. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2667–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavero, J.; Beltrán, A.; Aragüés, R. Nitrate Exported in Drainage Waters of Two Sprinkler-Irrigated Watersheds. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchán, D.; Causapé, J.; Abrahão, R.; García-Garizábal, I. Assessment of a Newly Implemented Irrigated Area (Lerma Basin, Spain) over a 10-Year Period. II: Salts and Nitrate Exported. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 158, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán, D.; Casalí, J.; Del Valle de Lersundi, J.; Campo-Bescós, M.A.; Giménez, R.; Preciado, B.; Lafarga, A. Runoff, Nutrients, Sediment and Salt Yields in an Irrigated Watershed in Southern Navarre (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iital, A.; Klõga, M.; Pihlak, M.; Pachel, K.; Zahharov, A.; Loigu, E. Nitrogen Content and Trends in Agricultural Catchments in Estonia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 198, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyllmar, K.; Forsberg, L.S.; Andersson, S.; Mårtensson, K. Small Agricultural Monitoring Catchments in Sweden Representing Environmental Impact. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 198, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Communities. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- European Communities. Council Directive of 12 December 1991 Concerning the Protection of Waters against Pollution Caused by Nitrate from Agricultural Sources (91/676/EEC); European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- INTIA. Informe Del Seguimiento de La Zona Regable Del Canal de Navarra Durante La Campaña 2020: Balance Hídrico, Calidad Del Riego y Contaminación Por Sales y Nitratos; INTIA: Pamplona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil & Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas A&M University System: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Haney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. Input/Output Documentation Soil & Water Assessment Tool, Version 2012; Texas Water Resources Insitute, TR-439: College Station, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- USDA Soil Conservation Service (SCS). National Engineering Handbook, Section 4: Hydrology; USDA Soil Conservation Service (SCS): Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Cunge, J.A. On the Subject of a Flood Propagation Computation Method (Muskingum Method). J. Hydraul. Res. 1969, 7, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.H.; van Griensven, A. Autocalibration in Hydrologic Modeling: Using SWAT2005 in Small-Scale Watersheds. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Frankenberger, J.R.; Engel, B.A.; Arnold, J.G. Representation of Agricultural Conservation Practices with SWAT. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3042–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-CUP: SWAT-Calibration and Uncertainty Programs (CUP)—A User Manual; EAWAG Aquatic Research: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 9780975840047. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Srinivasan, R. A Guideline for Successful Calibration and Uncertainty Analysis for Soil and Water Assessment: A Review of Papers from the 2016 International SWAT Conference. Water 2018, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Rouholahnejad, E.; Vaghefi, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H.; Kløve, B. A Continental-Scale Hydrology and Water Quality Model for Europe: Calibration and Uncertainty of a High-Resolution Large-Scale SWAT Model. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, C.; Muttiah, R.S.; Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R. A GIS-Based Regional Planning Tool for Irrigation Demand Assessment and Savings Using SWAT. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2005, 48, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M.; Ryberg, K.R.; Archfield, S.A.; Gilroy, E.J. Statistical Methods in Water Resources: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods, Book 4, Chapter A3. In Book 4, Hydrologic Analysis and Interpretation; U.S Department of the Interior, Ed.; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; p. 458. [Google Scholar]
- Niraula, R.; Meixner, T.; Norman, L.M. Determining the Importance of Model Calibration for Forecasting Absolute/Relative Changes in Streamflow from LULC and Climate Changes. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Navarro, E.; Hallack-Alegría, M.; Martínez-Pérez, S.; Ramírez-Hernández, J.; Mungaray-Moctezuma, A.; Sastre-Merlín, A. Hydrological Modeling and Climate Change Impacts in an Agricultural Semiarid Region. Case Study: Guadalupe River Basin, Mexico. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 175, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Navarro, E.; Trolle, D.; Martínez-Pérez, S.; Sastre-Merlín, A.; Jeppesen, E. Hydrological and Water Quality Impact Assessment of a Mediterranean Limno-Reservoir Under Climate Change and Land Use Management Scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficklin, D.L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, M. Watershed Modelling of Hydrology and Water Quality in the Sacramento River Watershed, California. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 27, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, A.M.; Cerro, I.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M.; Sauvage, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Antigüedad, I. Application of the SWAT Model to Assess the Impact of Changes in Agricultural Management Practices on Water Quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaurio, M.; Zabaleta, A.; Uriarte, J.A.; Srinivasan, R.; Antigüedad, I. Evaluation of SWAT Model’s Performance to Simulate Streamflow Spatial Origin. The Case of a Small Forested Watershed. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamian, R.; Jaleh, A.; Afyuni, M.; Mousavi, S.F.; Heidarpour, M.; Jalalian, A.; Abbaspour, K.C. Application of a SWAT Model for Estimating Runoff and Sediment in Two Mountainous Basins in Central Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolson, B.A.; Shoemaker, C.A. Cannonsville Reservoir Watershed SWAT2000 Model Development, Calibration and Validation. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettam, A.; Taleb, A.; Sauvage, S.; Boithias, L.; Belaidi, N.; Sanchez-Perez, J.M. Applications of a SWAT Model to Evaluate the Contribution of the Tafna Catchment (North-West Africa) to the Nitrate Load Entering the Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boithias, L.; Srinivasan, R.; Sauvage, S.; Macary, F.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M. Daily Nitrate Losses: Implication on Long-Term River Quality in an Intensive Agricultural Catchment of Southwestern France. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, R.; Cuchí, J.A. Analysis of Sprinkler Irrigation Management in the LASESA District, Monegros (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Garizábal, I.; Causapé, J.; Merchán, D. Evaluation of Alternatives for Flood Irrigation and Water Usage in Spain Under Mediterranean Climate. CATENA 2017, 155, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Garizábal, I.; Causapé, J.; Abrahao, R. Application of the Irrigation Land Environmental Evaluation Tool for Flood Irrigation Management and Evaluation of Water Use. CATENA 2011, 87, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Rosen, M.R.; Saito, L.; Decker, D.L. The Influence of Irrigation Water on the Hydrology and Lake Water Budgets of Two Small Arid-Climate Lakes in Khorezm, Uzbekistan. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INTIA. Informe Corregido Del Seguimiento de La Zona Regable Del Canal de Navarra Durante La Campaña 2018: Balance Hídrico, Calidad Del Riego y Contaminación Por Sales y Nitratos; INTIA: Pamplona, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- INTIA. Informe Del Seguimiento de La Zona Regable Del Canal de Navarra Durante La Campaña 2019: Balance Hídrico, Calidad Del Riego y Contaminación Por Sales y Nitratos; INTIA: Pamplona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Skhiri, A.; Dechmi, F. Impact of Sprinkler Irrigation Management on the Del Reguero River (Spain). I: Water Balance and Irrigation Performance. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Macías, J.M.; Merchán, D.; Causapé, J. Evolution and Assessment of a Nitrate Vulnerable Zone over 20 Years: Gallocanta Groundwater Body (Spain). Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-García, I.; Merchán, D.; Aranguren, I.; Casalí, J.; Giménez, R.; Campo-Bescós, M.A.; Del Valle de Lersundi, J. Assessment of the Main Factors Affecting the Dynamics of Nutrients in Two Rainfed Cereal Watersheds. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, L.; García-Gómez, H.; Gimeno, B.S.; Rovira, J.V. Headwater Streams: Neglected Ecosystems in the EU Water Framework Directive. Implications for Nitrogen Pollution Control. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán, D.; Causapé, J.; Abrahão, R. Impact of Irrigation Implementation on Hydrology and Water Quality in a Small Agricultural Basin in Spain. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causapé, J.; Quílez, D.; Aragüés, R. Assessment of Irrigation and Environmental Quality at the Hydrological Basin Level II. Salt and Nitrate Loads in Irrigation Return Flows. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 70, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHE (Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro) Control de Los Retornos de Las Actividades Agrarias de La Cuenca Del Ebro: Evaluación de Tendencias En La Calidad Del Agua, Control Experimental de Los Retornos y Propuesta de Red de Control (in Spanish). Available online: www.chebro.es (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Arauzo, M.; Valladolid, M.; Martínez-Bastida, J.J. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Nitrogen in River-Alluvial Aquifer Systems Affected by Diffuse Pollution from Agricultural Sources: Implications for the Implementation of the Nitrate Directive. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Crop | Cropping Cycle | Tillage Date | Fertilization Dates | Annual Fertilization (N kg yr−1 ha−1) | Type of Fertilizer Applied * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 1 Nov–1 Jul | 01 Oct | 1 Oct | 40 | 9-23-30 |
| 01 Jan | 60 | Urea + Ammonium sulfate | |||
| 01 Mar | 100 | Urea | |||
| Winter barley | 1 Nov–1 Jul | 01 Oct | 01 Oct | 40 | 9-23-30 |
| 01 Jan | 60 | Urea + Ammonium sulfate | |||
| 01 Mar | 100 | Urea | |||
| Corn | 1 May–1 Nov | 01 Apr | 15 Apr | 40 | 9-23-30 |
| 15 Jun | 260 | Urea | |||
| Tomato | 10 May–15 Sept | 01 Apr | 15 Apr | 60 | 9-23-30 |
| 15 Jun | 120 | 8-4-10 | |||
| Potato | 1 May–15 Sept | 01 Apr | 15 Apr | 60 | 9-23-30 |
| 15 Jun | 120 | NAC 27% |
| Dataset | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | 25 m, ETRS89 UTM Zone 30N projection | Government of Navarre, Spatial Data Infrastructure of Navarre (IDENA), Digital Elevation Model data (https://sitna.navarra.es/geoportal/geop_sitna/geoportal.aspx) |
| Land Use Map | 25 m, 2019 LULC map | Government of Navarre, Spatial Data Infrastructure of Navarre (IDENA), Land Use/Cover data (https://sitna.navarra.es/geoportal/geop_sitna/geoportal.aspx) |
| Soil Type Map | 1:25,000 | Government of Navarre, Navarre Spatial Data Infrastructure (IDENA), Soil type data (https://sitna.navarra.es/geoportal/geop_sitna/geoportal.aspx) |
| Meteorological Data | Daily (1990–2020) | Government of Navarre, Meteorology, and climatology of Navarre website (http://meteo.navarra.es/estaciones/mapadeestaciones.cfm) |
| Streamflow | Daily (2000–2020) | Government of Navarre, Water in Navarre website (http://www.navarra.es/home_es/Temas/Medio+Ambiente/Agua/Documentacion/DatosHistoricos/) and INTIA (https://www.intiasa.es/) |
| Water Quality (Nitrate) | Monthly (2000–2020) | Government of Navarre through, Environmental Management of Navarre GAN-NIK (https://gan-nik.es/) and INTIA (https://www.intiasa.es/) |
| Agricultural Management | Annual | Consultation with the farmers and key stakeholders (INTIA) |
| Irrigation Data | Monthly (2017–2020) | INTIA reports (https://www.intiasa.es/) and Aguacanal (https://www.aguacanal.es/en/) |
| Parameter | Description | Change Method * | Parameter Adjustment Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. Value | Max. Value | Fitted Value | |||
| CN2.mgt | Initial SCS runoff CN number for moisture condition II | R | −0.2 | 0.20 | −0.12 |
| ESCO.hru | Soil Evaporation compensation factor | R | −0.40 | −0.28 | −0.31 |
| GW_DELAY.gw | Groundwater delays (days) | V | 20 | 80 | 53.54 |
| CDN.bsn | Denitrification exponential rate coefficient | V | 0 | 1.62 | 0.04 |
| NPERCO | Nitrate Percolation coefficient | V | 0.01 | 1 | 0.17 |
| Performance Indicator | Streamflow | Nitrate Load | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | |
| p-factor | 0.56 | 0.65 | 0.72 | 0.63 |
| r-factor | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 0.98 |
| NSE | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.68 |
| R2 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.79 |
| PBIAS | −8.7% | −5.6% | −9.2% | −7% |
| RSR | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oduor, B.O.; Campo-Bescós, M.Á.; Lana-Renault, N.; Echarri, A.A.; Casalí, J. Evaluation of the Impact of Changing from Rainfed to Irrigated Agriculture in a Mediterranean Watershed in Spain. Agriculture 2023, 13, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010106
Oduor BO, Campo-Bescós MÁ, Lana-Renault N, Echarri AA, Casalí J. Evaluation of the Impact of Changing from Rainfed to Irrigated Agriculture in a Mediterranean Watershed in Spain. Agriculture. 2023; 13(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010106
Chicago/Turabian StyleOduor, Brian Omondi, Miguel Ángel Campo-Bescós, Noemí Lana-Renault, Alberto Alfaro Echarri, and Javier Casalí. 2023. "Evaluation of the Impact of Changing from Rainfed to Irrigated Agriculture in a Mediterranean Watershed in Spain" Agriculture 13, no. 1: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010106
APA StyleOduor, B. O., Campo-Bescós, M. Á., Lana-Renault, N., Echarri, A. A., & Casalí, J. (2023). Evaluation of the Impact of Changing from Rainfed to Irrigated Agriculture in a Mediterranean Watershed in Spain. Agriculture, 13(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010106










