Abstract
Opium poppy is one of the most important medicinal plant species cultivated in several regions of the world for pharmaceutical and food purposes. Although it has been bred and used in many countries for centuries, taxonomical studies on the intraspecific variability are still not numerous. In the course of this study, the genetic diversity of 58 opium poppy accessions were assessed with SSR markers. Out of the 25 tested SSR markers, only 19 showed successful amplification and seven were found to reveal polymorphism. These seven markers produced 2–11 alleles within the size range of 144–280 bp. PIC value varied between 0.284 and 0.767, expected heterozygosity was between 0.136 and 1, and observed heterozygosity was between 0.344 and 0.794. Altogether, a low genetic diversity was found, and several accessions have been characterized with the same SSR allele profile. The clustering in the PCoA co-ordinate system indicates four groups, which is confirmed by the STRUCTURE analysis as well and reflects the known relationships of hybrid cultivars in several cases. The landrace taxa clearly deviate from the majority of cultivars selected for industrial purposes. The applied SSR markers were not able to distinguish the genotypes according to their geographic origin or seed color. However, in several cases, the grouping in the PCoA system reflected a diversification connected to alkaloid content and petal color of the accessions. Our results demonstrate the importance of further molecular marker studies focusing on genotypes with different alkaloid content and useful agronomical traits in order to establish more effective breeding.
1. Introduction
Opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) is an annual medicinal herb, belonging to the family Papaveraceae, cultivated in very diverse areas of the world from temperate to tropical regions. Although being cultivated from prehistoric times, the gene-center of the species is not fully clarified. Supposedly, it lies in Central-Asia [1], however recent studies suggest the Mediterranean as the center of its origin and domestication [2,3]. Its main economic significance is due to the production of more than 80 alkaloids, primarily morphine, codeine, thebaine, and noscapine, which have analgesics and antitussive effects. The cultivation of opium poppy is under international drug control conventions and national legislations [4,5]. However, a large extent of illicit cultivation is also obvious [6]. Poppy is cultivated not only as a pharmaceutical raw material (capsules or opium) but also as food (seed and seed oil), and sometimes as an ornamental plant (flowers, dried capsules). During the long period of poppy cultivation, selection has been going on with different intensity, methods, and goals. For the pharmaceutical industry, high alkaloid content and specific alkaloid profile is targeted, and for the food industry there is minimal alkaloid, but high oil content is required [7]. In several Asian and European areas, even today, the cultivated materials are landraces, populations without any consequent breeding. On the other side, in some countries, very intensive and high potential cultivars and patented strains have been developed. Therefore, poppy populations differ in their numerous morpho-phenological characteristics (e.g., height, flower and seed color, capsule shape, vegetation length, etc.), yields of seeds, capsules and opium, chemical constituents, and resistance. In the CPVO (Community Plant Variety Office) Variety finder [8], 255 items are listed as registered cultivars.
The taxonomical classification of P. somniferum is not fully resolved even today. Hanelt and Hammer [9] divided the species into three subspecies: the cultivated taxa as subsp. somniferum and subsp. songaricum and subsp. setigerum, which may represent the wild relative of poppy. They differ primarily in their geographical areas and the form of stigmatic lobes. Within the subspecies, the cultivars are distinguished by morphological traits like seed color and dehiscence of capsules. However, these characteristics may be influenced by growing site and are highly variable. An intraspecific classification system, based on the diversity of alkaloid synthesis and accumulation, was elaborated by Tétényi in 1963, distinguishing ‘morphinan’ and ‘isoquinoline’ chemoconvarieties. Later, this system was elaborated in more detail [10]. Nevertheless, even though there are already highly sensitive techniques for chemical analysis, these methods are not sufficiently valid at the fine scale necessary for the discrimination of individual cultivars, as the chemical composition is dependent on environmental factors and may show a great intracultivar variability [11,12]. DNA markers developed in the last decades are not influenced by external factors, and therefore may be more robust and helpful. The initial attempts to evaluate genetic variability and diversity among plant cultivars were carried out by random molecular markers like random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR), or amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) due to the fact that these methods do not require any sequence information about the genome to be studied. Using AFLP method, Dubey et al. [13] successfully identified downy mildew resistant and sensitive poppy genotypes. Besides, AFLP proved to show good selection power in discriminating high- and low ‘morphinan’ genotypes, while RAPD method was useless for that purpose [14]. Using RAPD and ISSR, Acharya and Sharma [15] found a low genetic diversity among 24 accessions. However, in the last two studies the investigated genotypes originated—with some exceptions—from India. Later, the use of SSR markers provided good results especially in the field of plant genetics compared to other markers. Opium poppy-specific SSR markers have been developed using the publicly available expressed sequence tag (EST) database at NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) [16,17]. Due to the detected low polymorphism and lessened availability of the poppy specific genic SSR markers, Celik et al. [18] used pyrosequencing technology to develop opium poppy-specific genomic SSR markers. They tested a subset of the SSR markers for transferability and polymorphism in opium poppy and related species, which showed the importance of these markers for fingerprinting, diversity, mapping, and breeding studies. Later, a complex study using AFLP, genomic and EST-SSR markers was performed by Celik et al. [19] to reveal diversity and association mapping in poppy, using 118, mostly Turkish landraces and cultivars. In Europe, Mičianová et al. [20] evaluated 23 mostly Slovakian and Czech poppy genotypes by EST-SSR method and established that the potential of these markers is appropriate for PCR-based forensic analyses. Recently, 200 trinucleotide genic and genomic SSR markers have been tested in 29 varieties of poppy, bred for pharmaceutical, food, and ornamental purposes beside four other Papaver species, but only 17 of them proved to be high quality markers [12].
Even though more and more results of molecular taxonomic studies are accumulating about P. somniferum, based on the above, further investigations are necessary to clarify intraspecific relationships on a more diverse pool of accessions. Therefore, our study presented here aimed to gain an extended series of data, which allows the evaluation of the variation among available poppy germplasm collections. Based on the relationships of the different accessions, the appropriate parent strains might be determined for further testing in order for accelerated, goal-oriented hybrid breeding. Besides, we wanted to check the potential of the method for variety and forensic control activities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and DNA Extraction
Seeds of 58 Papaver somniferum L. accessions from diverse geographical origins and of different domestication level were chosen from our own genestock, from commercial items, and from international genebanks (Table 1). DNA was isolated directly from seed samples (approx. 15–20 pieces) by NucleoSpin Plant II DNA kit (Macherey-Nagel, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. DNA concentration and quality was assessed using NanoDrop ND-1000 (BioScience, Hungary) and visually checked on 1% agarose gel. Isolated DNA was stored at −20 °C until used. Some cultivars were duplicated in the experiment as control.

Table 1.
Origin of the studied plant material.
2.2. SSR Marker Amplification
Twenty-five SSR markers were randomly chosen from the studies of Vašek et al. [12], Lee et al. [16], Selale et al. [17], and Celik et al. [18,19] from the most polymorphic loci (Table 2).

Table 2.
The studied SSR loci with amplification success and polymorphism.
PCR amplifications were performed in a final reaction volume of 15 μL, including 20–80 ng DNA, 10X PCR reaction buffer, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.02 mM dNTP mix, 0.3 μmol of each 5′ and 3′ end primers with 0.5 unit of DreamTaq DNA polymerase (Fermentas, Szeged, Hungary), 2% BSA, and 1% DMSO and sterile distilled water. PCRs were performed in a Swift MaxPro thermocycler (Esco Healthcare Pte, Singapore) using the following cycling parameters: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 4 min; followed by 30 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 50 °C for 40 s, 72 °C for 60 s; and a final synthesis at 72 °C for 5 min. Successful amplification was verified on a 1% (w/v) ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel in 1×TBE buffer with xylencyanol loading buffer. Fragment sizes were estimated by comparison with the 100 bp DNA ladder (Fermentas, Waltham, MA, USA). The exact size of the amplified fragments was determined by fragment length analysis performed by capillary electrophoresis on an automated sequencer ABI PRISM 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Budapest, Hungary) at Biomi Ltd. (Gödöllő, Hungary). Fragment length determination was done by Peak Scanner software 1.0 (Applied Biosystems) manually. Results were collected in MS Excel.
Characterization of the accessions regarding the alkaloid production capacity (low/high) was done based on data obtained from the CPVO database [8], websites and personal communication of the genebanks mentioned in Table 1, as well as from our own investigations and data collection during breeding. Information on other traits discussed in the following chapters like petal color, seed color, and frost tolerance was taken from the same sources, as well as from additional literatures [11,20]. In some cases, no information was available, and this fact is indicated in the text.
The statistical analysis was performed with an MS Excel Marko GenAlEx 6.5 [21]. This software was used to perform AMOVA, examine principal coordinate analysis (PCoA), allelic frequency (Pi), expected heterozygosity (He), observed heterozygosity (Ho), and Shannon Index (I). Polymorphic Information Content (PIC) was calculated with an online tool at gene-calc.pl/pic. Cluster analysis showing dendrogram figures was performed by PAST software version 4.03 [22]. STRUCTURE 2.3.4 [23] was used to infer the most likely number of groups in the SSR data. The analysis was run with an admixture model with correlated allele frequencies. The value of K was set to 1–10 with a burn-in period of 100,000 steps followed by 500,000 repetitions of Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC). Testing 20 independent repetitions were set for each run. Then, the ‘pophelper’ package in R [24] was used to apply the Evanno method [25] to detect the value of K that best fit the data. The 20 simulations were averaged using CLUMPP v1.1.2 [26].
3. Results
Amplification was successful with 19 SSR primer pairs out of the selected 25 markers (Table 2). Two markers (psSSRg853 and psSSR073) amplified four fragments, being multiloci, and were excluded from the final evaluation. A further ten markers produced a monomorphic allele pattern so in the final evaluation only seven markers were included, which are highlighted in Table 2.
The number of alleles per locus ranged from 2–11. The seven primer pairs produced a total of 37 alleles. The amplified alleles’ sizes were around the expected size based on previous studies. Genetic indices are given in Table 3. In case of psSSRg484 marker only two alleles were identified, and most samples were homozygous either for one or the other allele. This is also manifested in the genetic indices (Table 3), showing the lowest heterozygosity and PIC values for this marker. PIC value varied between 0.284 and 0.767, expected heterozygosity was between 0.136 and 1, while observed heterozygosity was between 0.344 and 0.794. Locus psSSRg47 possessed only three alleles, but almost all accessions were heterozygous, resulting in rather high values for all genetic indices. The most polymorphic locus was OPEST053c [12], producing eleven alleles and having the highest PIC value. All of the PIC values were higher than indicated in the corresponding previous literatures [12,16,17,18,19]. One of the reasons might be the much more diverse genepool used by us compared to the former studies.

Table 3.
The number of the amplified alleles and genetic indices at the studied SSR loci.
The Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) widely scattered the 58 accessions (Figure 1). Four groups (A–D) could be identified. Group A contains 13 accessions, mostly registered varieties, or former, expired varieties of Hungarian breeding, or from neighboring countries. According to personal information from breeders, some of them have French or Australian origin as one parent side. ‘Medea’ and ‘Minoan’ originate from the same cross and are very close to each other. ‘Botond’ and ‘Slovakian 2′ may also be related through breeding. Australian accessions (2 and 4) originate from different pools, but a common origin cannot be excluded. Indeed, they share exactly the same SSR profile in the selected loci. ‘Tebona’ is an old industrial variety selected from a genotype originated from an international seed exchange without any further known details. In case of the remaining two accessions, it is difficult to explain their position in this group. According to genebank passport information, the origin of ‘Berkut’ is the Ukraine. The accession ‘PSTG Mures’ was received from VÚRV genebank, with the information about Belgian origin. However, its name refers to Romanian origin.
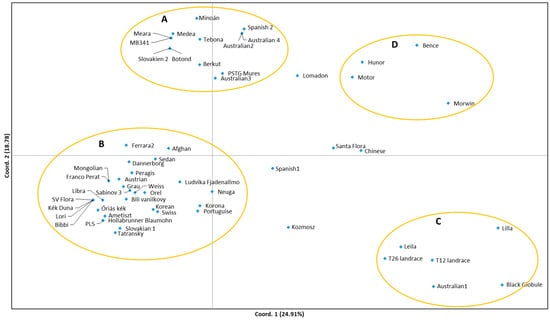
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional plot of the principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of SSR data showing the clustering of 58 opium poppy accessions. The 1st axis explains 24.91%, while the 2nd axis explains 18.78% of the variability.
Group B is the largest one in the PCoA, containing 31 accessions (Figure 1). The majority are of Western-European origin in close connection, interestingly, with some Far-Eastern accessions. These latter ones, the Mongolian and Korean accessions, have been described as landraces—meaning cultivated populations without official variety registration—while the status of the Afghan accession is not known. Among the Western European accessions there are French, English, Belgian, Dutch, Swiss, Swedish, Austrian, Danish, and German origins. These might have undergone serial seed exchanges during the decades through genebank and/or breeding activity, and thus, their relationship is likely. Using the seven SSR markers, some accessions were characterized with exactly the same genetic fingerprint shown at the same spot in the PCoA (Figure 1). The coincidence in profiles of ‘Bibbi’, ‘SV Flora’, and ‘Lori’ supports the fact that they are related taxa. Indeed, based on NordGen genebank information, ‘Flora’ should be one of the parents of both ‘Lori’ and ‘Bibbi’. The situation of the fourth taxon in this common fingerprint, ‘Kék Duna’, seems to be somewhat different, as it is an old Hungarian cultivar. Another overlap in this group includes the accessions ‘Hollabrunner’ and ‘PLS’, where the first one is a landrace from Austria, and the real origin of the second one is not known: we obtained it from Slovakia, but the passport data mentioned its origin from a Polish genebank, through Belgium. Thus, even a real relationship between these two accessions cannot be excluded.
The PCoA diagram (Figure 1) indicates further genetic relationships as well, which, according to our knowledge, should be adequate. One parent of the variety ‘Korona’ was of French origin and one of the variety ‘Sedan’ of English origin. ‘Óriás kék’ is one of the parent varieties of ‘Ametiszt’, while the other is ‘Libra’. All of these three are very closely situated to each other (Figure 1). Some further accessions, presumably landraces or old selections from Slovakia, Czech Republic, and Austria, are also closely situated in Group B, and although there is no direct evidence, they might share a common origin in this Central-European region. The situation of the Portuguese accession is special, as it is a P. somniferum subsp. setigerum taxon (as denominated in the genebank item) but seems to be also well included in this group.
Groups C and D are more scattered and include less taxa than the former groups (Figure 1). A common feature is that many of them are Hungarian landraces (‘T12’, ‘T26’) or have such a relationship (‘Leila’, ‘Lilla’, ‘Kozmosz’, ‘Hunor’, ‘Motor’). ‘Morwin’ is also an old Hungarian selection, although further information is not available to us. The inclusion of some foreign accessions like ‘Black Globule’, a Moroccan variety and especially the ‘Australian 1’, is interesting and currently not clear, although they are somewhat at the edge of these groups. ‘Bence’ is a cross of varieties placed in Group A, therefore its appearance in group D can not be explained either. The origin of the remaining accessions (‘Santa Flora’, ‘Lomadon’) is not known to us.
AMOVA was performed by classifying the samples into the groups identified in the PCoA diagram. Beside the four groups, a fifth group was created for the samples in the middle of the PCoA, which did not fit into any of the groups. AMOVA (Table 4), using 999 permutations and suppressing individual-level analysis, showed that 96% of the variance was identified within the groups and only 4% among the groups (and 0% among the individuals). Significant differentiation, based on the FST value of 0.042 (p = 0.018), was detected among the groups, which confirms the grouping of the accessions on the PCoA plot (Figure 1).

Table 4.
The number of the amplified alleles and genetic indices at the studied SSR loci.
Bayesian STRUCTURE analysis (Figure 2) confirmed the groups identified in the PCoA plot (Figure 1). The Evanno method (ΔK and Mean K) indicated that a K = 4 model best fits the data, meaning that the accessions represent four main genetic clusters. Accessions from group A were the least admixed (mainly blue in Figure 2). Additionally, group C harboring the landraces was less admixed compared to the remaining accessions (mostly orange in Figure 2). Accessions belonging to group B are mostly composed of three genetic clusters (In the middle of the barplot, Figure 2). Accessions of group A and accessions from the middle of the PCoA plot are composed of all four genetic clusters and are hard to distinguish in the barplot. Accessions from group A have a higher proportion from the blue cluster, which is dominant in group C, while the accessions, which are located in the middle of the PCoA plot, share the four genetic clusters in varying ratios. Genetic indices, in the case of these four groups, are shown in Table 5.
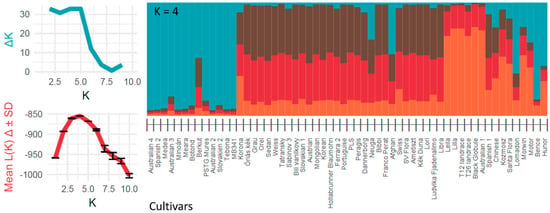
Figure 2.
STRUCTURE analysis bar plot of the 58 opium poppy accessions for the runs with highest likelihood out of 20 runs for cluster K = 4. 58 bars represent the 58 accessions broken into different colored genetic clusters. The height of each color within a bar corresponds to the probability of assignment to one of the genetic clusters. Accessions that share the same colors are more similar.

Table 5.
Genetic indices for the four groups obtained by STRUCTURE analysis.
4. Discussion
Using seven SSR primers, a good resolution of the 58 studied opium poppy accessions could be achieved. Their distribution in the PCoA co-ordinate system and the STRUCTURE barplot reflects, in several cases, the connections of hybrid cultivars and their parent or sister accessions. The findings indicate a close relationship among the poppy accessions. The narrow genetic diversity of P. somniferum has also been emphasized by former studies [12,13,14,15,17]. Poppy is a crop cultivated in several areas of the world, but it seems that these areas have not been in strict isolation from each other. Transfer of genetic materials thorough the centuries might be likely. On the other side, it is known that consequent breeding of poppy is still a relatively young activity [1], which still could not establish a very broad genetic background.
We established that clustering (Figure 1 and Figure 2) of the studied accessions did not reflect their geographic origin. The different genebank accessions showed a sometimes surprisingly close relationship to each other, e.g., Mongolian-French, Korean-Swiss, Danish-Afghan, etc. As data about the exact origins of many of the studied accessions is missing, even the identity or a close relationship through introduction from other country cannot be excluded, not to mention eventual mixing or exchange of items. In parallel, the four Australian accessions were placed into different groups together with European and other cultivars. Saunders et al. [27] also described the distribution of different Australian cultivars in separate groups, clustering together with several Western-European ones. The authors concluded the transfer of these accessions to Australia at different times from different areas. Concerning the fact, that both Australia and some European countries (Czech Republik, Spain, France, Hungary, etc.) are among the biggest producers and breeders of poppy, transfer of genetic materials and use of them for further breeding seems to be likely. This also means that, for hybrid development, using these genepools as parents might not promise a large vigor.
The clustering of the Portuguese accession has a special significance, as this represents a P. setigerum taxon. Until the 1930’s of the last century, the species P. setigerum D.C. was described as the ancestor of opium poppy. Later, based on traditional genetic investigations, considerable differences between P. setigerum and the cultivated poppy had been described. The gene centers of both species were distinguished by the results of botanical expeditions [1]. In the last decades, even molecular marker-based investigations resulted in contradictory findings. According to Hosokawa et al. [28], five Papaver species were clearly distinguishable from each other, but P. somniferum and P. setigerum proved to be identical based on their three plastid sequences. Similarly, Saunders et al. [27] established that in the AFLP dendrogram, P. setigerum is situated among P. somniferum accessions. Lohwasser et al. [29], however, determined P. setigerum as a tetraploid subspecies of P. somniferum, which can be clearly distinguished from other taxa both by bud hairiness as morphological factor and also by AFLP analysis. Our findings now support the close relationship between this taxon and other opium poppy genotypes, especially to those in Group B (Figure 1).
Regarding the alkaloid content of the studied accessions, a characteristic pattern can be observed (Figure 1). In this context, instead of the exact concentration values, a classification as high (industrial) or low (food) accumulation potential is considered. The landraces (Group C), usually possessing a lower alkaloid content, along with the cultivars directly selected from these, are separated from the majority of cultivars bred for industrial purposes, especially from Group A. This indicates, that for developing new variability within the breeding stock for alkaloid-oriented utilization, landrace genotypes might offer an excellent source. Obviously, as landraces are usually characterized with a lower alkaloid content, consequent screening is necessarily focusing on the breeding aim. Formerly, Celik et al. [19] emphasized that landraces were found to have higher average genetic diversity (0.10) than cultivars (0.07) and concluded that breeding might have caused a slight bottleneck in the genetic background of poppy, thus introduction of genetic material from other countries should be advantageous. His suggestion is confirmed based on the present findings.
In Group A, all genotypes are high alkaloid containing industrial cultivars, and therefore this group is uniform for this trait, except the ‘Berkut’ and ‘PSTG Mures’, about which we have no information concerning their alkaloid content. Group D also includes cultivars selected for high alkaloid content. Among the industrial cultivars, the only exception is ‘Korona’, which—despite its high alkaloid content—is located in Group B. However, the main alkaloid of this special cultivar is noscapine, while in the case of the other cultivars the main compound is morphine or thebain [11]. This altered alkaloid profile might explain the positioning of ‘Korona’. Several accessions in Group B represent cultivars with low alkaloid content like ‘Ametiszt’, ‘Kék Duna’, ‘Sedan’, and ‘Libra’. Unfortunately, the alkaloid content of many of the other genotypes in Group B is not known by us. However, based on the available information about alkaloid contents, the above results indicate a downward gradient from the high alkaloid containing accessions to the low alkaloid containing ones in Figure 1. Dubey et al. [13] demonstrated the successful screening of high and low alkaloid poppy strains based on 12 unique AFLP primer pair combinations. However, they tested only four selected genotypes from their own breeding materials in India. Later, in Turkey, Celik et al. [19] found only a single SSR (genomic) marker associated significantly (p = 0.002) with morphine content of capsules (r2 = 0.18) but explained it with the possible fact that multiple genes for morphine synthesis are dispersed in the poppy genome resulting in lower association of the examined QTL loci with the concentration of morphine. According to the presented results, it could be suggested that the establishment of a reliable molecular method focusing on markers connected to alkaloid concentration of the capsules might assure an effective pre-screening of the breeding material for development both of industrial and food cultivars.
As for the morphological and phenological traits, based on the available information, flower and seed colors are worthy of discussion. The seed color of opium poppy may vary from white-yellowish to dark blue [7] (Figure 3). Flowers have very frequently white petals with a purple spot at the bottom, however, clean white or violet, purple, pink colors at different intensity also occur (Figure 4). The studied SSR markers did not show any diversification based on seed color: genotypes with light colored seeds were found, for example, both in Group B (‘Weiss’) and in Group C (‘T12’). The flower color shows a somewhat different pattern: the majority of the genotypes in Groups C and D develop pink or purple petals (except the ‘Moroccan’ and ‘Australian 1’ accessions about which there is no information). However, petal color might be a secondary trait linked to the winter hardiness of these accessions. Among Central-European conditions, the frost-resistance of poppy is an important agronomic trait, as the tolerant varieties can be sown as winter poppy and assure more stable yields. The colored petals are more abundant in these winter poppy ecotypes [30] and according to our knowledge, in parallel; the majority of accessions in Groups C and D show a good overwintering character. This finding might also be traced back to some functional role of the studied genic EST-SSR markers but should be ascertained by further studies.

Figure 3.
Color of opium poppy seeds may vary from white-yellowish to dark blue. An example is shown for white seeds (A) from cultivar ‘Weiss’ and for grey seeds (B) from cultivar ‘Minoan’ (Photo: Zámboriné Németh, É.).

Figure 4.
Color of opium poppy flowers may vary from white to purple. An example is shown for light violet flower (A) of cultivar ‘Korona’ and for dark purple flower (B) of cultivar ‘Leila’ (Photo: Zámboriné Németh, É.).
5. Conclusions
Based on the results of the study on 58 poppy accessions, we concluded that geographical origin itself is not necessarily the best point of view when choosing far away partners for heterosis breeding. However, landraces might be a good source to increase genetic variability.
The present data confirm the close relationship of P. somniferum and P. setigerum.
Our results, together with previous data, suggest the necessity and importance of further molecular marker studies, focusing not only on the origin but also on the alkaloid content of the accessions in order to clarify the potential of the method in separating low and high alkaloid containing taxa.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, É.Z.N. and Z.G.; methodology, Z.G.; investigation, S.A. and P.P.; data curation, Z.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.G.; writing—review and editing, É.Z.N.; visualization, Z.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the genebanks mentioned in this manuscript (Table 1) providing us the poppy accessions and the available information about them and to Endre Gy. Tóth for his help in the STRUCTURE analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bernáth, J.; Németh, É. Breeding of poppy. In Oil Crops; Vollmann, J., Rajcan, I., Eds.; Springer Sciences & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 449–468. [Google Scholar]
- Jesus, A.; Bonhomme, V.; Evin, A.; Ivorra, S.; Soteras, R.; Salavert, A.; Antolín, F.; Bouby, L. A morphometric approach to track opium poppy domestication. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salavert, A.; Zazzo, A.; Martin, L.; Antolín, F.; Gauthier, C.; Thil, F.; Tombret, O.; Bouby, L.; Manen, C.; Mineo, M.; et al. Direct dating reveals the early history of opium poppy in western Europe. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labanca, F.; Ovesnà, J.; Milella, L. Papaver somniferum L. taxonomy, uses and new insight in poppy alkaloid pathways. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Lal, R.K.; Singh, V.R.; Shanker, K. Estimation of Components of Genetic Variation and Graphical Analysis in Opium Poppy (Papaver somniferum L.). Adv. Crop. Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.K.; Rastog, A.; Siddiqui, A. Opium Poppy: Genetic Upgradation Through Intervention of Plant Breeding Techniques. IntechOpen 2013, 524, 209–238. [Google Scholar]
- Bernáth, J.; Németh, É. Poppy—Utilization and genetic resources. In Genetic Resources, Chromosome Engineering and Crop Improvement; Singh, R.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; Volume 6, Medicinal Plants; pp. 353–392. [Google Scholar]
- Community Plant Variety Office: Variety Finder. Available online: https://cpvo.europa.eu/en/applications-and-examinations/cpvo-variety-finder (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Hanelt, P.; Hammer, K. Einige infraspezifische Umkombinationen und Neubeschreibungen bei Kultursippen von Brassica L. und Papaver L. Feddes Rep. 1987, 98, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tétényi, P. Morphinoides du genere Papaver. Acte Colloq. Montréal Chicoutimi 1989, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Németh-Zámbori, É.; Jászberényi, C.; Rajhárt, P.; Bernáth, J. Evaluation of alkaloid profiles in hybrid generations of different poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) genotypes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašek, J.; Čílová, D.; Melounová, M.; Svoboda, P.; Vejl, P.; Štikarová, R.; Vostrý, L.; Kuchtová, P.; Ovesná, J. New EST-SSR Markers for Individual Genotyping of Opium Poppy Cultivars (Papaver somniferum L.). Plants 2019, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, M.K.; Shasany, A.K.; Dhawan, O.P.; Shukla, A.K.; Khanuja, S.P.S. AFLP studies on downy-mildew-resistant and downy-mildew-susceptible genotypes of opium poppy. J. Genet. 2010, 89, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, M.K.; Shasany, A.K.; Dhawan, O.P.; Shukla, A.K.; Shanker, K.; Khanuja, S.P.S. Detection of DNA polymorphism in Papaver somniferum genotypes differing in straw morphinan alkaloid content. Plant Biosyst. 2010, 114, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, H.S.; Sharma, V. Molecular characterisation of opium poppy (Papaver somniferum) germplasm. Am. J. Infec. Dis. 2009, 5, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Jin, G.N.; Lee, K.L.; Han, M.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Yang, M.S. Exploiting expressed sequence tag databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived simple sequence repeat markers in the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) for forensic applications. J. Forensic. Sci. 2011, 56, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şelale, H.; Çelik, I.; Gültekin, V.; Allmer, J.; Doǧanlar, S.; Frary, A. Development of EST-SSR markers for diversity and breeding studies in opium poppy. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Gultekin, V.; Allmer, J.; Doganlar, S.; Frary, A. Development of genomic simple sequence repeat markers in opium poppy by next-generation sequencing. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Camci, H.; Kose, A.; Kosar, F.C.; Doganlar, S.; Frary, A. Molecular genetic diversity and association mapping of morphine content and agronomic traits in Turkish opium poppy (Papaver somniferum) germplasm. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mičianová, V.; Ondreičková, K.; Muchová, D.; Klčová, L.; Hudcovicová, M.; Havrlentová, M.; Mihálik, D.; Kraic, J. Forensic applicaton of EST-derived STR markers in opium poppy. Biologia 2017, 72, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. J. Bioinform. 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron. 2001, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.M. Pophelper: An R package and web app to analyse and visualize population structure. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, J.A.; Pedroni, M.J.; Penrose, L.D.J.; Fist, A.J. AFLP analysis of opium poppy. Crop Sci. 2001, 41, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosokawa, K.; Shibata, T.; Nakamura, I.; Hishida, A. Discrimination among species of Papaver based on the plastid rp116 gene and rp116-rp114 spacer sequences. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2004, 139, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohwasser, U.; Ditbrenner, A.; Budahn, H.; Marthe, F.; Börner, A. Taxonomy of plant genetic resourches- use of morphological, molecular and phytochemical data in order to verify existing classifications. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2010, 75, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Dobos, G.; Kurch, R.; Börner, A.; Lohwasser, U. Studies of winter hardiness of opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) of the genebank in Gatersleben. Z. Arznei Gewürzpfla 2011, 16, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).