Application of Blended Controlled-Release and Normal Urea with Suitable Maize Varieties to Achieve Integrated Agronomic and Environmental Impact in a High-Yielding Summer Maize System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
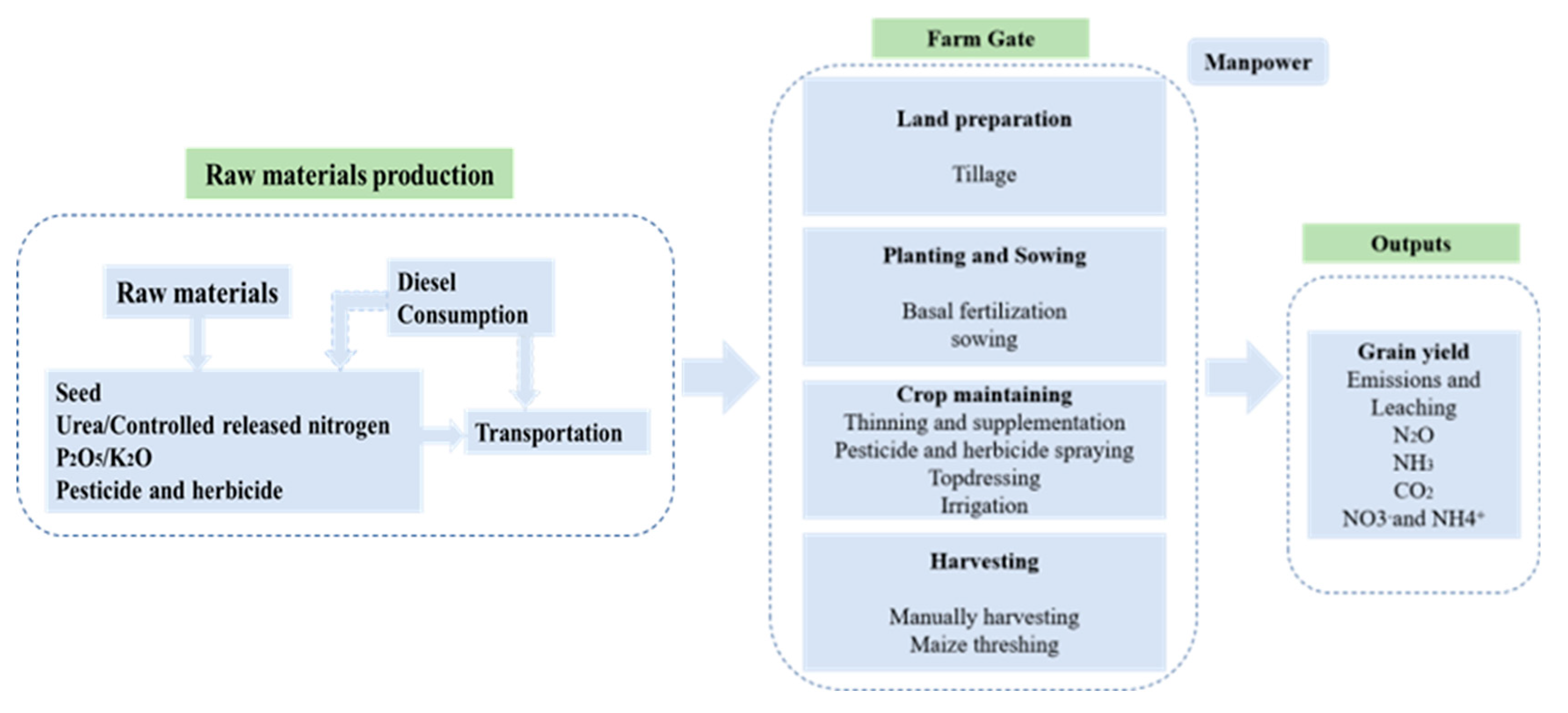
2.2. Experimental Materials and Design
2.3. Analysis of Aboveground Biomass Samples and Evaluation Index
2.3.1. Aboveground Biomass Sampling and Nitrogen Analysis
2.3.2. Reactive N Losses and GHG Emissions
2.3.3. Nitrogen-Derived Ecosystem Economic Benefits
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yield and Aboveground N Uptake
3.2. Nr Losses and N Footprint
3.3. GHG Emission and C Footprint
3.4. Ecosystem Economic Benefits
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Combinations of CRU and Urea on the Yield and Aboveground N Uptake of Two Maize Varieties
4.2. Effects of the Combination of CRU and Urea on Nr Losses and N Footprint of Two Maize Varieties
4.3. Effects of the Combination of CRU and Urea on GHG Emissions and the C Footprint of Two Maize Varieties
4.4. Effect of the Combination of CRU and Urea on Socioeconomic and Ecosystem Economic Benefits
4.5. Comprehensive Analysis and Potential Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhuang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ying, H.; Yin, Y.; Cui, Z. The sustainability of staple crops in China can be substantially improved through localized strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, F.S.; Chen, X.P.; Dou, Z.X.; Li, J.L. In-season nitrogen management strategy for winter wheat: Maximizing yields, minimizing environmental impact in an over-fertilization context. Field Crop Res. 2010, 116, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Mu, Y.; Pei, S.; Lun, X. Emissions of nitrous oxide, nitrogen oxides and ammonia from a maize field in the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2956–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Suddick, E.C.; Rice, C.W.; Prokopy, L.S. More food, low pollution (mo fo lo Po): A grand challenge for the 21st century. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flis, S. The 4Rs in Crop Nitrogen Research. Crops Soils 2017, 50, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Venterea, R.T. Enhanced efficiency fertilizers: A multi-site comparison of the effects on nitrous oxide emissions and agronomic performance. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.S.; Liang, Z.Y.; He, X.M.; Wang, X.Z.; Shi, X.J.; Zou, C.Q.; Chen, X.P. The effects of controlled release urea on maize productivity and reactive nitrogen losses: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Fugice, J.; Singh, U.; Lewis, T.D. Development of fertilizers for enhanced nitrogen use efficiency e trends and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.Y.; Yagi, K. Evaluation of effectiveness of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers as mitigation options for N2O and NO emissions from agricultural soils: Meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Blaylock, A.D.; Chen, X.P. Mixture of controlled release and normal urea to optimize nitrogen management for high-yielding (&15 Mg ha−1) maize. Field Crop Res. 2017, 204, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Noellsch, A.J.; Motavalli, P.P.; Nelson, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R. Corn response to conventional and slow-release nitrogen fertilizers across a Claypan Landscape. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Du, C.; Zhou, J.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Y. Economic and soil environmental benefits of using controlled-release bulk blending urea in the North China Plain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 2370–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Tiller development affected by nitrogen fertilization in a high-yielding wheat production system. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.L.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S. Development of regional nitrogen rate guidelines for intensive cropping systems in China. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, H.S.; Alharby, H.F.; Fahad, S. Antioxidative defense system, hormones, and metabolite accumulation in different plant parts of two contrasting rice cultivars as influenced by plant growth regulators under heat stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 911846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sadras, V.O.; Xu, J.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. Chapter Five—Genetic Improvement of Crop Yield, Grain Protein and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Wheat, Rice and Maize in China. Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Massachusetts, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 203–252. [Google Scholar]
- Worku, M.; Bänziger, M.; Erley, G.S.; Friesen, D.; Diallo, A.O.; Horst, W.J. Nitrogen uptake and utilization in contrasting nitrogen efficient tropical maize hybrids. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Daud, M.; Ullah, N.; Ali, S.; Khan, M.; Malik, Z.; Zhu, S. Pretreatment with salicylic acid and ascorbic acid significantly mitigate oxidative stress induced by copper in cotton genotypes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9922–9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, W.S.; Wang, X.B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, D.Y.; Chen, X.P. Agronomic, environmental, and ecosystem economic benefits of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizers for maize production in Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistic of China (NBSC). Chinese Statistical Bulletin of National Economy and Social Development in China in 2017; National Bureau of Statistic of China: Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/jsj/zxfb/201802/t20180228_1585631.html (accessed on 1 September 2018). (In Chinese)
- Yang, X.; Geng, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Tian, X. Cumulative release characteristic of controlled-release nitrogen and potassium fertilizers and their effects on soil fertility, and cotton growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T.; Yang, H.S. Meeting cereal demand while protecting natural resources and improving environmental quality. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 315–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO-14040; Environmental Management Life Cycle Assessment Principles and Framework. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2006.
- ISO-14044; Environmental Management Life Cycle Assessment Requirements and Guidelines. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2006.
- Yin, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Comparative effects of nitrogen application on growth and nitrogen use in a winter wheat/summer maize rotation system. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Ye, Y.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X. Managing nitrogen for sustainable wheat production. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yan, X. Ecologically optimal nitrogen application rates for rice cropping in the Taihu Lake region of China. Sustain. Sci. 2012, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiermeier, Q. Atmospheric science: Fixing the sky. Nature 2009, 460, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, H.; Yamn, H.M.; Huang, H. Studies on the external costs of and the optimum use of nitrogen fertilizer based on the balance of economic and ecological benefits in the paddy field system of the Dongting Lake area. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2006, 39, 2531–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Yan, X. Life-cycle evaluation of nitrogen-use in rice-farming systems: Implications for economically-optimal nitrogen rates. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 3159–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Ge, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xu, B.; Luo, W.; Jiang, H.; Gu, B.; Chang, J. Atmospheric reactive nitrogen in China: Sources, recent trends, and damage costs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9420–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, W.F.; Zhang, F.S. Establishing a regional nitrogen management approach to mitigate greenhouse gas emission intensity from intensive smallholder maize production. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.R.; Walters, D.T. Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. AMBIO 2002, 31, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.A.; Nippert, J.B.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Messina, C.D.; Ciampitti, I.A. Post-silking 15N labelling reveals an enhanced nitrogen allocation to leaves in modern maize (Zea mays) genotypes. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 268, 153577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhen, S.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y. Grain yields and nitrogen use efficiencies in different types of stay-green maize in response to nitrogen fertilizer. Plants 2020, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U.; Zhang, W.; Ruan, S.; Chen, X. Integrated assessment of agronomic, environmental and ecosystem economic benefits of blending use of controlled-release and common urea in wheat production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.N.; Liu, T.Q.; Hu, Q.Y.; Liu, M.; Cai, M.L.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, C.G. Effect of microbial community structures and metabolite profile on greenhouse gas emissions in rice varieties. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassini, P.; Cassman, K.G. High-yield maize with large net energy yield and small global warming intensity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasundara, S.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Dias, G.; Kariyapperuma, K.A. Energy and greenhouse gas intensity of corn (Zea mays L.) production in Ontario: A regional assessment. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 94, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, K. Information provision, policy support, and farmers’ adaptive responses against drought: An empirical study in the North China Plain. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, e275–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowder, S.K.; Skoet, J.; Raney, T. The number, size, and distribution of farms, smallholder farms, and family farms worldwide. World Dev. 2016, 87, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Griffiths, S.M. From economic development to public health improvement: China faces equity challenges. Public Health 2011, 125, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J. Genotype × environment interaction for plant density in maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci. 2016, 56, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Varieties | N Treatment | Total N Rate | Basal N Rate | Topdressing N Rate (V6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea-N | CRU-N | Urea-N | |||
| (kg N ha−1) | |||||
| ZD958 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N180U | 180 | 72 | 0 | 108 | |
| N180C1 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| N180C2 | 180 | 60 | 120 | 0 | |
| N180C | 180 | 0 | 180 | 0 | |
| YH988 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N180U | 180 | 72 | 0 | 108 | |
| N180C1 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| N180C2 | 180 | 60 | 120 | 0 | |
| N180C | 180 | 0 | 180 | 0 | |
| Varieties | N Rate | 2019 | 2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N Uptake (kg N ha−1) | NUE (%) | N Uptake (kg N ha−1) | NUE (%) | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 147.6 c | —— | 131.6 d | —— |
| N180U | 221.6 b | 43.1 b | 219.9 bc | 49.1 bc | |
| N180C1 | 219.8 b | 47.2 b | 228.3 b | 53.7 b | |
| N180C2 | 244.9 a | 62.2 a | 249.1 a | 65.3 a | |
| N180C | 228.1 b | 51.7 b | 214.3 c | 45.9 c | |
| YH988 | N0 | 136.1 c | —— | 131.2 d | —— |
| N180U | 213.6 b | 43.1 b | 214.1 c | 46.1 b | |
| N180C1 | 239.7 a | 57.6 a | 239.8 a | 60.3 a | |
| N180C2 | 223.1 b | 48.4 bc | 229.6 ab | 54.7 ab | |
| N180C | 223.4 b | 48.5 b | 222.9 bc | 51.0 b | |
| Varieties | N Rate | N-Derived Grain Benefits | N Costs | Labor Costs | Ecological Costs | Health Costs | Private Profitability | Ecosystem Economic Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (USD ha−1) | ||||||||
| ZD598 | N180U | 985 ab | 57 | 231 | 126 | 87 | 697 ab | 484 b |
| N180C1 | 975 b | 112 | 115 | 120 | 82 | 748 ab | 546 ab | |
| N180C2 | 1282 a | 167 | 115 | 103 | 66 | 1000 a | 831 a | |
| N180C | 875 b | 222 | 115 | 73 | 38 | 538 b | 427 b | |
| YH988 | N180U | 1188 ab | 57 | 231 | 126 | 87 | 900 ab | 686 ab |
| N180C1 | 1531 a | 112 | 115 | 120 | 82 | 1304 a | 1101 a | |
| N180C2 | 1330 ab | 167 | 115 | 103 | 66 | 1048 ab | 879 ab | |
| N180C | 1013 b | 222 | 115 | 73 | 38 | 676 b | 565 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Li, H.; Yan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shao, R.; Guo, J.; Yang, Q. Application of Blended Controlled-Release and Normal Urea with Suitable Maize Varieties to Achieve Integrated Agronomic and Environmental Impact in a High-Yielding Summer Maize System. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081247
Ma M, Li H, Yan D, Zhang Y, Song M, Wang Y, Wang H, Shao R, Guo J, Yang Q. Application of Blended Controlled-Release and Normal Urea with Suitable Maize Varieties to Achieve Integrated Agronomic and Environmental Impact in a High-Yielding Summer Maize System. Agriculture. 2022; 12(8):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081247
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Mengjin, Huan Li, Dongliang Yan, Yihan Zhang, Miaomiao Song, Yongchao Wang, Hao Wang, Ruixin Shao, Jiameng Guo, and Qinghua Yang. 2022. "Application of Blended Controlled-Release and Normal Urea with Suitable Maize Varieties to Achieve Integrated Agronomic and Environmental Impact in a High-Yielding Summer Maize System" Agriculture 12, no. 8: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081247
APA StyleMa, M., Li, H., Yan, D., Zhang, Y., Song, M., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Shao, R., Guo, J., & Yang, Q. (2022). Application of Blended Controlled-Release and Normal Urea with Suitable Maize Varieties to Achieve Integrated Agronomic and Environmental Impact in a High-Yielding Summer Maize System. Agriculture, 12(8), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081247





