QTL-Seq Approach Identified Pi63 Conferring Blast Resistance at the Seedling and Tillering Stages of Thai Indigenous Rice Variety “Phaladum”
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of Mapping Population
2.2. Evaluation of Blast Resistance
2.3. Construction of Bulks, DNA Extraction, and Whole-Genome Resequencing
2.4. QTL-Seq Analysis
2.5. Candidate Gene Annotation
2.6. Development of KASP Markers and Marker-Trait Association Analysis
3. Results
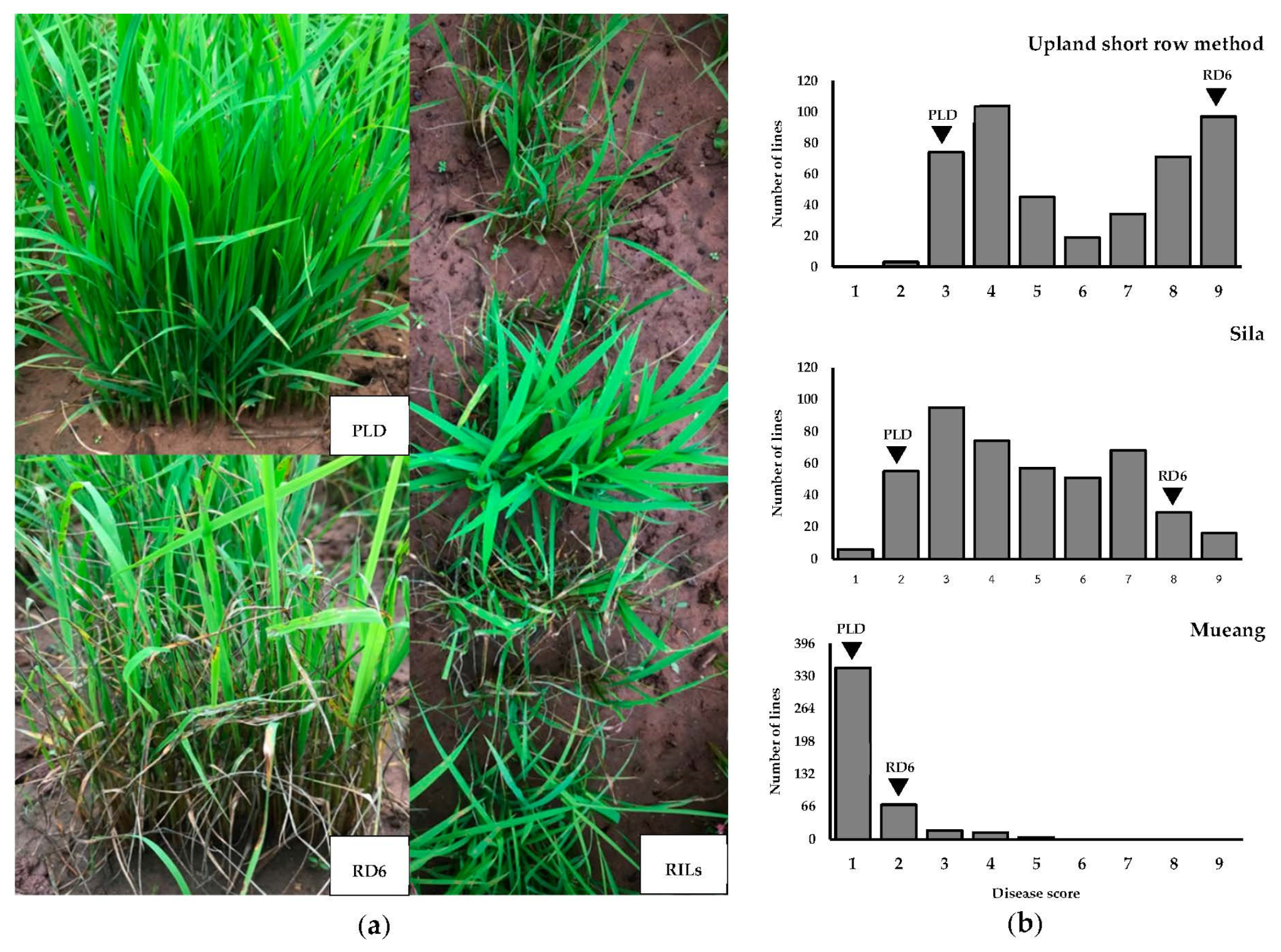
3.1. Evaluation of Blast Resistance and Plant Selection for Bulk Preparation
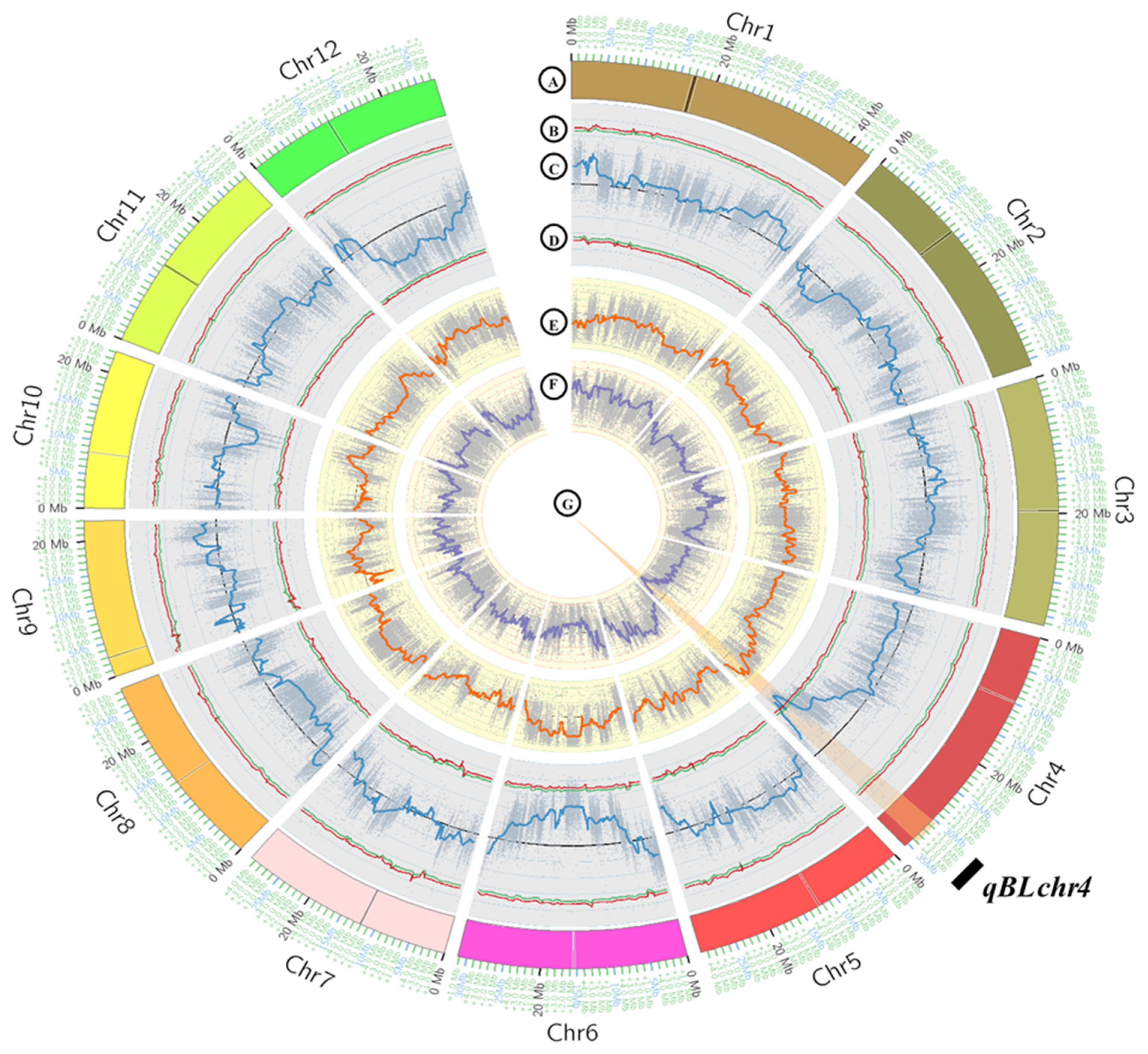
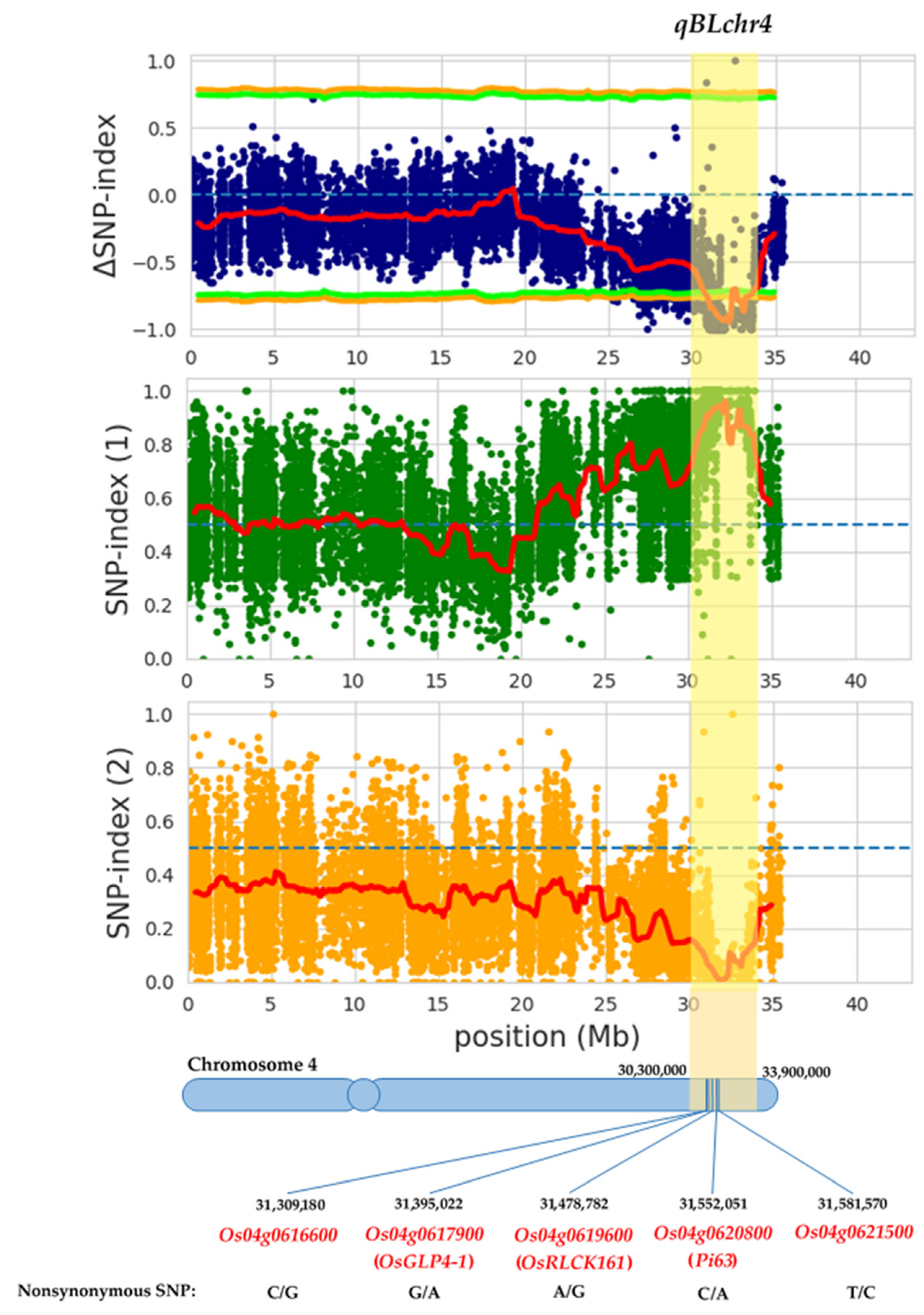
3.2. QTL-Seq Analysis Identified QTL for Blast Resistance in PLD
3.3. Validation and Confirmation of Identified QTL on Chromosome 4
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srivastava, D.; Shamim, M.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, P.; Kumar, D.; Yadav, P.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Singh, K.N. Current status of conventional and molecular interventions for blast resistance in rice. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Rasabandith, S.; Angeles, E.R.; Khush, G.S. Inheritance of resistance to bacterial blight in 21 cultivars of rice. Phytopathology 2003, 93, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Xiao, N.; Yu, L.; Pan, C.H.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Liu, G.Q.; Dai, Z.Y.; Pan, X.B.; Li, A.H. Combination patterns of major R genes determine the level of resistance to the M. oryzae in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Li, A. Strategy for use of rice blast resistance genes in rice molecular breeding. Rice Sci. 2020, 27, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, K.; Baisakh, N.; Maung Thet, K.; Tu, J.; Datta, S.K. Pyramiding transgenes for multiple resistance in rice against bacterial blight, yellow stem borer, and sheath blight. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 106, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthasalam, S.; Kalpana, K.; Kumar, K.K.; Loganathan, M.; Poovannan, K.; Raja, J.A.J.; Kokiladevi, E.; Samiyappan, R.; Sudhakar, D.; Balasubramanian, P. Pyramiding transgenic resistance in elite indica rice cultivars against the sheath blight and bacterial blight. Plant. Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, K.; Vera Cruz, M.C.; Gruissem, W.; Bhullar, N.K. Large-scale germplasm screening for identification of novel rice blast resistance sources. Front. Plant. Sci. 2014, 5, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Peng, J. Resistance genes and their interactions with bacterial blight/leaf streak pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 2020, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkani, S.; Yusop, M.R.; Shabanimofrad, M.; Azadi, A.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Azizi, P.; Latif, M.A. Allele mining strategies: Principles and utilisation for blast resistance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2015, 17, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkani, S.; Rafii, M.Y.; Shabanimofrad, M.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Ravanfar, S.A.; Latif, M.A. Molecular progress on the mapping and cloning of functional genes for blast disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Current status and future considerations. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 36, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaday, M.K.; Aravindan, S.; Ngangkham, U.; Raghu, S.; Praphukarthikeyan, S.R.; Keerthana, U.; Marndi, B.C.; Adak, T.; Munda, S.; Deshmukh, R.; et al. Blast resistance in Indian rice landraces: Genetic dissection by gene-specific markers. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Dhatwalia, S.; Kaachra, A.; Sharma, K.D.; Rathour, R. Genetic and physical mapping of a new rice blast resistance specificity Pi-67 from a broad spectrum resistant genotype Tetep. Euphytica 2019, 215, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.R.; Rai, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, N.K. Broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi-kh cloned from rice line Tetep designated as Pi54. J. Plant. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.W.; Zhai, K.R.; Xie, Z.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhu, X.D.; Liu, J.Z.; Wang, X.; Qin, P.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhang, G.M.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance. Science 2017, 355, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fang, N.; Guan, C.; He, W.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, H. Characterization and fine mapping of a blast-resistant gene Pi-jnw1 from the japonica rice landrace Jiangnanwan. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, X.W.; Li, S.G.; Xu, J.C.; Zhai, W.X.; Ling, Z.Z.; Ma, B.T.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, W.M.; Cao, G.; Ma, Y.Q.; et al. Identification of two blast resistance genes in a rice variety, Digsu. J. Phytopathol. 2004, 152, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khannetah, K.R.; Ramchander, S.; Leon, M.T.A.P.; Shoba, D.; Saravanan, S.; Kannan, R.; Yasin, J.K.; Pillai, M.A. Genetic diversity analysis in indigenous rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm for bacterial leaf blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. eryzae) (BB) using resistance genes-linked markers. Euphytica 2021, 217, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwanwah, M.R.; Wongsa, T.; Monkham, T.; Chankaew, S.; Falab, S.; Sanitchon, J. Thai indigenous lowland rice germplasms: Sources of bacterial blight disease resistance and agronomic attributes. AGRIVITA J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 42, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumpol, A.; Chankaew, S.; Saepaisan, S.; Monkham, T.; Sanitchon, J. New sources of rice blast resistance obtained from Thai indigenous upland rice germplasm. Euphytica 2018, 214, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kosugi, S.; Natsume, S.; Mitsuoka, C.; Uemura, A.; Utsushi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Takuno, S.; et al. QTL-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole-genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant. J. 2013, 74, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiso-Tanaka, E.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Nonoue, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Fushimi, E.; Koide, Y.; Okumoto, Y.; Yano, M.; Saito, H. Detection of novel QTLs QDTH4.5 and QDTH6.3, which confer late heading under short-day conditions, by SSR marker-based and QTL-seq analysis. Breed. Sci. 2017, 67, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Z.; Nong, B.; Zeng, Y.; Xiong, F.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Deng, G.; Li, D. QTL mapping by whole genome re-sequencing and analysis of candidate genes for nitrogen use efficiency in rice. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadambari, G.; Vemireddy, L.R.; Srividhya, A.; Nagireddy, R.; Jena, S.S.; Gandikota, M.; Patil, S.; Veeraghattapu, R.; Deborah, D.A.K.; Reddy, G.E.; et al. QTL-seq-based genetic analysis identifies a major genomic region governing dwarfness in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant. Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Cheng, P.; Cheng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Huang, D.; Huang, T.; Song, X.; Ying, J. QTL-seq identified a major QTL for grain length and weight in rice using near-isogenic F2 population. Rice Sci. 2018, 25, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikit, S.; Wanchana, S.; Khanthong, S.; Saensuk, C.; Thianthavon, T.; Vanavichit, A.; Toojinda, T. QTL-seq identifies cooked grain elongation QTLs near soluble starch synthase and starch branching enzymes in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommisetty, R.; Chakravartty, N.; Bodanapu, R.; Naik, J.B.; Panda, S.K.; Lekkala, S.P.; Lalam, K.; Thomas, G.; Mallikarjuna, S.J.; Eswar, G.R.; et al. Discovery of genomic regions and candidate genes for grain weight employing next-generation sequencing-based QTL-seq approach in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubankoh, P.; Wanchana, S.; Saensuk, C.; Ruanjaichon, V.; Cheabu, S.; Vanavichit, A.; Toojinda, T.; Malumpong, C.; Arikit, S. QTL-seq reveals genomic regions associated with spikelet fertility in response to a high temperature in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Plant. Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thianthavon, T.; Aesomnuk, W.; Pitaloka, M.K.; Sattayachiti, W.; Sonsom, Y.; Nubankoh, P.; Malichan, S.; Riangwong, K.; Ruanjaichon, V.; Toojinda, T.; et al. Identification, and validation of a QTL for bacterial leaf streak resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) against Thai Xoc strains. Genes 2021, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beredo, J.; Mendoza, R.; Reyes, E.; Hermosada, H.; Javier, M.A.; Islam, M.R.; Collard, B. Use of a rapid generation advance (RGA) system for IRRI’s irrigated breeding pipeline. In In Proceedings of the IRRI-BMGF’s Transforming Rice Breeding (TRB) Project Objective 3.0, Metro Manila, Philippines, 6 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- International Rice Research Institute. Standard Evaluation System (SES) for Rice, 5th ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 2013; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A.; Kosugi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Natsume, S.; Takagi, H.; Kanzaki, H.; Matsumura, H.; Yoshida, K.; Mitsuoka, C.; Tamiru, M.; et al. Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerema, G.; Mengistu, G.; Kebede, M.; Lule, D.; Desalegn, K.; Birahanu, C.; Debela, M. Seedling, and adult plant resistance to Pyricularia oryzae in Ethiopian rice cultivars. Acta Univ. Sapientiae Agric. Environ. 2020, 12, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lei, C.L.; Xu, X.T.; Hao, K.; Wang, J.L.; Cheng, Z.J.; Ma, X.D.; Ma, J.; Zhou, K.N.; Zhang, X.; et al. Pi64, encoding a novel CC-NBS-LRR protein, confers resistance to leaf and neck blast in rice. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Yu, L.; Pan, C.H.; Dai, Z.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Xiao, N.; Zhang, X.X.; Ji, H.J.; Huang, N.S.; Zhao, B.H.; et al. Development of near-isogenic lines with different alleles of Piz locus and analysis of their breeding effect under Yangdao 6 background. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Century, K.S.; Lagman, R.A.; Adkisson, M.; Morlan, J.; Tobias, R.; Schwartz, K.; Smith, A.; Love, J.; Ronald, P.C.; Whalen, M.C. Developmental control of Xa21-mediated disease resistance in rice. Plant. J. 1999, 20, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, K.; Hayano-Saito, Y. Genetics of durable resistance to rice panicle blast derived from an indica rice variety Modan. Jpn. J. Plant. Sci. 2017, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, N.; Inoue, H.; Kato, T.; Funao, T.; Shirota, M.; Shimizu, T.; Kanamori, H.; Yamane, H.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Durable panicle blast-resistance gene Pb1 encodes an atypical CC-NBS-LRR protein and was generated by acquiring a promoter through local genome duplication. Plant. J. 2010, 64, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, S.; Dai, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Pan, S.; Wang, D.; et al. Molecular mapping of the blast resistance gene Pi49 in the durably resistant rice cultivar Mowanggu. Euphytica 2013, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenbayashi-Sawata, K.; Ashizawa, T.; Koizumi, S. Pi34-AVRPi34: A new gene-for-gene interaction for partial resistance in rice to blast caused by Magnaporthe grisea. J. Gen. Plant. Pathol. 2005, 71, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumbar, S.D.; Kulwal, P.L.; Patil, J.V.; Gaikwad, A.P.; Jadhav, A.S. Inheritance of blast resistance and identification of SSR marker associated with it in rice cultivar RDN 98-2. J. Genet. 2013, 92, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.; Hao, K.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; et al. Identification and fine mapping of two blast resistance genes in rice cultivar 93-11. Crop. J. 2013, 1, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, M.; Yano, M.; Hirasawa, H. Mapping of quantitative trait loci conferring blast field resistance in the Japanese upland rice variety Kahei. Breed. Sci. 2001, 51, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Chern, M.S.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.W. Recent advances in broad-spectrum resistance to the rice blast disease. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2019, 50, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Qiu, D.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, S. Isolation and manipulation of quantitative trait loci for disease resistance in rice using a candidate gene approach. Mol. Plant. 2008, 1, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.L.; Chen, S.P.; Chen, L.K.; Sun, K.; Huang, C.H.; Zhou, D.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Wang, J.F.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Development of core SNP arrays based on the KASP method for molecular breeding of rice. Rice 2019, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hayashi, N.; Wang, C.; Fukuoka, S.; Kawasaki, S.; Takatsuji, H.; Jiang, C. Rice blast resistance gene Pikahei-1(t), a member of a resistance gene cluster on chromosome 4, encodes a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat protein. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raidan, G.J.; Collier, S.M.; Sacco, M.A.; Baldwin, T.T.; Boettrich, T.; Moffett, P. The coiled-coil and nucleotide-binding domains of the potato Rx disease resistance protein function in pathogen recognition and signaling. Plant. Cell 2008, 20, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tameling, W.I.; Elzinga, S.D.; Darmin, P.S.; Vossen, J.H.; Takken, F.L.; Haring, M.A.; Cornelissen, B.J. The tomato R gene products I-2 and MI-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity. Plant. Cell. 2002, 14, 2929–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takken, F.L.; Albrecht, M.; Tameling, W.I. Resistance proteins: Molecular switches of plant defence. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2006, 9, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooijen, G.; Mayr, G.; Kasiem, M.M.A.; Albrecht, M.; Cornelissen, B.J.C.; Takken, F.L.W. Structure-function analysis of the NB-ARC domain of plant disease resistance proteins. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukder, Z.I.; Tharreau, D.; Price, A.H. Quantitative trait loci analysis suggests that partial resistance to rice blast is mostly determined by race-specific interactions. N. Phytol. 2004, 162, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, G.; Rafii, Y.R.; Ismail, M.R.; Puteh, A.B.; Rahim, H.A.; Asfaliza, R.; Latif, M.A. Blast resistance in rice: A review of conventional breeding to molecular approaches. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2369–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Clean Reads | Clean Data (Gb) | Read Alignment (%) | Genome Coverage (%) | Average Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLR-Bulk | 108,940,496 | 16.30 | 76.12 | 94.53 | 33.20 |
| BLS-Bulk | 113,062,190 | 17.00 | 73.02 | 94.43 | 33.00 |
| PLD | 106,155,076 | 15.90 | 86.65 | 92.49 | 35.10 |
| RD6 | 109,607,418 | 16.40 | 85.52 | 92.83 | 34.80 |
| Chromosome | Length | Number of SNPs 1 | Selected SNPs 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43,270,923 | 174,528 | 88,590 |
| 2 | 35,937,250 | 154,536 | 78,724 |
| 3 | 36,413,819 | 144,210 | 75,668 |
| 4 | 35,502,694 | 116,622 | 59,979 |
| 5 | 29,958,434 | 108,057 | 56,814 |
| 6 | 31,248,787 | 121,894 | 59,695 |
| 7 | 29,697,621 | 110,016 | 50,525 |
| 8 | 28,443,022 | 119,664 | 61,922 |
| 9 | 23,012,720 | 90,455 | 42,175 |
| 10 | 23,207,287 | 95,062 | 43,039 |
| 11 | 29,021,106 | 118,196 | 52,202 |
| 12 | 27,531,856 | 103,970 | 50,387 |
| Total | 373,245,519 | 1,457,210 | 719,720 |
| QTL | Chromosome | Location | Interval (Mb) | Delta (SNP Index) | Confidence Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Min | Max | 95% | 99% | |||
| qBLchr4 | 4 | 30,300,000 | 33,900,000 | 3.6 | −0.60 | −0.96 | −0.73 | −0.76 |
| Markers | Chr | Upland Short Row Method | Sila | Mueang | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD | PVE (%) | Add | Dom | LOD | PVE (%) | Add | Dom | LOD | PVE (%) | Add | Dom | ||
| LOC_Os04g0616600 | 4 | 36.86 | 58.58 | −1.93 | −0.69 | 34.14 | 55.81 | −1.74 | −0.46 | 9.64 | 20.63 | −0.44 | −0.35 |
| LOC_Os04g0617900 | 4 | 51.78 | 70.94 | −2.12 | −0.61 | 45.81 | 66.52 | −1.90 | −0.56 | 8.59 | 18.63 | −0.43 | 0.00 |
| LOC_Os04g0619600 | 4 | 73.28 | 82.48 | −2.22 | −1.65 | 65.76 | 79.10 | −2.01 | −1.36 | 11.30 | 23.73 | −0.46 | −0.49 |
| LOC_Os04g0620800 | 4 | 77.65 | 84.18 | −2.23 | −1.72 | 68.35 | 80.34 | −2.03 | −1.37 | 11.14 | 23.43 | −0.46 | −0.34 |
| LOC_Os04g0621500 | 4 | 75.06 | 83.20 | −2.25 | −1.21 | 66.23 | 79.33 | −2.03 | −0.94 | 9.66 | 20.68 | −0.44 | −0.11 |
| Lines | Blast Score | DTF | TN | PH | SL | SW | PL | NFGP | 1000 GW | GYP (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USR | Sila | (cm) | (mm) | (mm) | (g) | ||||||
| 100 | 3.50 | 1.67 | 107 | 11 | 136 | 10.30 | 3.12 | 26.33 | 119 | 28.73 | 36.12 |
| 124 | 3.00 | 1.11 | 71 | 14 | 118 | 9.99 | 2.68 | 27.00 | 131 | 21.23 | 29.35 |
| 126-1 | 4.00 | 2.67 | 91 | 14 | 159 | 10.10 | 2.66 | 29.43 | 144 | 23.16 | 22.85 |
| 132 | 2.50 | 1.00 | 71 | 12 | 166 | 10.32 | 2.66 | 30.50 | 185 | 25.12 | 29.62 |
| 238 | 4.00 | 1.00 | 70 | 17 | 143 | 9.73 | 2.64 | 26.75 | 183 | 23.47 | 30.44 |
| 335 | 4.00 | 1.56 | 89 | 13 | 126 | 9.97 | 2.74 | 26.50 | 141 | 24.51 | 32.00 |
| 361 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 90 | 10 | 150 | 10.39 | 2.80 | 26.67 | 143 | 26.80 | 29.49 |
| PLD | 3.00 | 2.57 | 69 | 13 | 126 | 9.54 | 2.91 | 26.35 | 145 | 26.35 | 28.16 |
| RD6 | 9.00 | 5.72 | 102 | 11 | 175 | 10.17 | 2.78 | 27.38 | 196 | 25.14 | 32.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Netpakdee, C.; Mathasiripakorn, S.; Sribunrueang, A.; Chankaew, S.; Monkham, T.; Arikit, S.; Sanitchon, J. QTL-Seq Approach Identified Pi63 Conferring Blast Resistance at the Seedling and Tillering Stages of Thai Indigenous Rice Variety “Phaladum”. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081166
Netpakdee C, Mathasiripakorn S, Sribunrueang A, Chankaew S, Monkham T, Arikit S, Sanitchon J. QTL-Seq Approach Identified Pi63 Conferring Blast Resistance at the Seedling and Tillering Stages of Thai Indigenous Rice Variety “Phaladum”. Agriculture. 2022; 12(8):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081166
Chicago/Turabian StyleNetpakdee, Chaiwat, Sittiwut Mathasiripakorn, Arthit Sribunrueang, Sompong Chankaew, Tidarat Monkham, Siwaret Arikit, and Jirawat Sanitchon. 2022. "QTL-Seq Approach Identified Pi63 Conferring Blast Resistance at the Seedling and Tillering Stages of Thai Indigenous Rice Variety “Phaladum”" Agriculture 12, no. 8: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081166
APA StyleNetpakdee, C., Mathasiripakorn, S., Sribunrueang, A., Chankaew, S., Monkham, T., Arikit, S., & Sanitchon, J. (2022). QTL-Seq Approach Identified Pi63 Conferring Blast Resistance at the Seedling and Tillering Stages of Thai Indigenous Rice Variety “Phaladum”. Agriculture, 12(8), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081166






