Abstract
Pesticide foliage treatment is used in agricultural production to protect plants from diseases, pests, or weeds. Tank-mix adjuvants added to the barrel can improve the effective utilization rate of pesticides. Herein, a comparative study was conducted to investigate the effect of three kinds of tank-mix adjuvant on the deposition, absorption, and permeation behavior of epoxiconazole and chlorantraniliprole solutions. Surface tension and contact angle results indicate that polyether-modified trisiloxane may be the best surface-active agent for pesticides, whereas methyl oleate and green-peel orange essential oil were found to be more suitable for improving pesticide deposition, absorption, and permeation in some cases. These findings indicate that various tank-mix adjuvants had different effects on pesticide application on plants. Appropriate tank-mix adjuvants need to be selected for comprehensive practical application.
1. Introduction
Disease, pest, and weed control is key to improving agricultural yield and quality [1]. The development of chemistry provides farm workers with a wide variety of pesticides, including insecticides, fungicides, herbicides, etc. Foliage treatment is used widely in the process of pesticide application. The efficacy of pesticides is directly related to the wetting and retention ability of the pesticide solution on the target plant [2,3]. Wetting and retention capacity is linked to the surface tension and the contact angle of the pesticide solution on the leaf surface [4]. However, due to the complexity of the crop-growing environment, traditional pesticide formulations, such as suspension concentrate (SC), emulsifiable concentrate (EC), and wettable powder (WP), cannot effectively moisten the crop leaf surface. The phenomena interface loss, such as spray drift, splash, shatter, bounce off, etc., result in a severe loss of pesticide solutions. Many studies have shown that tank-mix adjuvants added to the barrel can improve spray performance, reduce the surface tension of the spray solution, and promote the deposition and absorption of pesticide solutions on the target crop surface [5,6,7,8,9]. However, if used incorrectly, tank-mix adjuvants cannot improve or even reduce the deposition of pesticides.
Tank-mix adjuvants developed into a branch of science long ago. Many studies have been conducted on tank-mix adjuvants to increase the biological effects of pesticides. It was reported that tank-mix adjuvants could increase the deposition of pesticides, improve their control efficacy on wheat aphids and rust, and prolong their effective duration [10]. Even when the dosage was reduced by one-third, the spray solution showed excellent disease control and effective deposition of the active ingredient on wheat leaves [11]. Tank-mixing adjuvants were also found to enhance the efficacy of fludioxonil on cucumber anthracnose [12]. The most frequently used pesticide tank-mix adjuvants are surfactants, organosilicon, mineral oil, plant oil, and plant essential oil [13,14]. Plant oil is obtained from plant fruits, seeds, and germs. It is mainly composed of unsaturated higher fatty acid glycerides and their derivatives [15,16], such as methylated sunflower oil, cottonseed oil, sodium sulfate, and methyl oleate. Plant essential oils differ considerably from plant oil. They are volatile natural mixtures extracted from different plant parts, including many terpenoid structures, and are obtained by hydro or steam distillation [17,18]. In a previous study, we found that the essential oil extracted from orange and orange peel is the most commonly used tank-mix adjuvant due to its good adhesion properties [19]. Organosilicon is a kind of siloxane surfactant modified by polyether. It can significantly reduce the surface tension of pesticides; reduce the contact angle between pesticide droplets and the leaf surface or insect body; and enhance the wettability, adhesion, or spreading ability of the solution on the plant surface [20,21].
The absorption process of pesticides by plants is very complex. The cuticle coating on the surface of plant leaves is a lipid substance synthesized by epidermal cells and deposited outside the cell wall. Pesticides pass through the cuticle by a diffusion process and then desorb from the cuticle into the cell wall [22]. Systemic pesticides can be absorbed by plants, penetrate the plant from the treated site, and move to other parts to inhibit diseases or pests [23,24]. However, only a small amount pesticides enter the plant body, and most remain on the surface of the leaves [25]. In order to enhance the deposition of pesticides on target plants, pesticide adjuvants are widely added to pesticide solution to reduce the surface tension, improve the wetting ability, and increase the spreading area of the liquid on the leaf surface, as well as improving the ability to resist rainwater erosion. It is important to increase the permeability of pesticide solution when tank-mix adjuvants are selected.
In this work, we focused on two systemic pesticides: epoxiconazole (EPX) and chlorantraniliprole (CLR), the chemical structures of which are shown in Figure 1. Both EPX and CLR are widely used in rice production. Therefore, EPX and CLR were chosen as representatives to study the deposition, absorption, and permeation behavior of pesticide solutions on rice leaves. EPX is a triazole fungicide that inhibits the synthesis of ergosterol and hinders the formation of the cell wall and has a good control effect on cereal crop diseases [26,27]. EPX can increase the activity of chitinase in crops, cause the contraction of fungal haustoria, and inhibit the invasion of pathogens [28]. CLR is an ultra-high-effect and broad-spectrum insecticide with strong permeability. It can pass through the epidermal cell layer of the stem, enter the xylem, and transmit along the xylem to other parts of the plant [29]. CLR can activate the ryanodine receptor, release calcium from insect muscle cells, and cause their paralysis and death [30].
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of epoxiconazole (EPX) and chlorantraniliprole (CLR).
The purpose of this work was to regulate the deposition, absorption, and permeation behavior of pesticide solutions on rice plants using different tank-mix adjuvants. Polyether-modified trisiloxane (PT), methyl oleate (MO), and green-peel orange essential oil (GOEO) were used as representatives of organosilicon, plant oil, and plant essential oil, respectively. A comparative study of EPX and CLR SC sprayed with the three adjuvants was conducted to determine the effect of tank-mix adjuvants on pesticide solution deposition, absorption, and permeation. The study showed that tank-mix adjuvants have a considerable effect on surface tension, contact angle, and absorption of pesticide solution. During the spray process, the selection of tank-mix adjuvant for pesticide application is of critical importance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
The technical material of EPX (95%) and CLR (95%) was provided by the Central Research Institute of China Chemical Science and Technology. GOEO was obtained from Axeb Biotech SI (Lleida, Spain). PT and MO were obtained from the Central Research Institute of China Chemical Science and Technology. Agrilan 788 and 500 LQ were purchased from AkzoNobel Agrochemicals (Amsterdam, The Netherlands). Sag 1522 was purchased from Momentive Performance Materials Inc. (Waterford, NY, USA). Xanthan gum and propylene glycol were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Primary secondary amine (PSA) and MWCNTs (multi-walled carbon nanotubes) were purchased from Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.2. Preparation of EPX and CLR Suspension Concentrates
EPX and CLR SC were prepared in a bead milling process. The formulations are shown in Table 1. The active ingredient of EPX and CLR accounted for 125 and 200 g/L, respectively. A BT-9300ST laser particle size distribution meter (Dandong Baxter Instrument Co., Ltd., Dandong, China) was used to measure the particle size of SC. The D50 of EPX and CLR SC was 2.287 and 0.897 μm, respectively.

Table 1.
EPX and CLR SC formulation.
2.3. Surface Tension Measurements
To measure the surface activity of pesticide solution with different tank-mix adjuvants, the surface tension was measured by the Wilhelmy plate method. Measurements were carried out at 298 ± 0.1 K using a DCAT 21 tensiometer (Data Physics, Filderstadt, Germany) at room temperature. The tensiometer was calibrated using the surface tension of water. Before measurement, the samples were equilibrated until surface tension values remained constant. Three repeated measurements were conducted for each sample, and the standard deviations were no more than 0.20 mN/m.
2.4. Contact Angle Measurements
An OCA 20 contact angle meter (Data Physics, Filderstadt, Germany) was used to measure the contact angles of the pesticide solution droplets on the rice leaf surfaces at room temperature. Doubly distilled water with a surface tension of 72 mN/m was used in all experiments. The contact angles of the pesticide solution droplets were recorded with a Dataphysics OCA 20 contact angle system, with which 8 μL water droplets were dropped carefully onto the sample-deposited glass substrates. Solution droplets of 3 μL were dropped and deposited on the rice leaf surfaces within 60 s. Each measurement was repeated 3 times in this step.
2.5. Rice Plant Treatment
Rice seedlings were grown in plastic pots in a greenhouse. The temperature was kept at 25 °C. When the height of the seedlings was about 30 cm, foliar applications of EPX and CLR SC were conducted, respectively. According to the references on the pesticide product labels, the concentrations of EPX were set at 125 and 187 mg/L, and the concentrations of CLR were set at 66.7, and 100 mg/L. 0.03% of PT, 0.3% of MO, and 0.2% of GOEO was added to the pesticide solution, respectively, according to the recommendations on their labels. Six pots of rice seedlings with uniform growth were selected for each treatment. Before the formal experiment, we used water instead of pesticide solution for a pre-experiment to determine the amount of spray required to wet the leaves and avoid droplet slippage. In the pretest, water was sprayed in different volumes to determine the best spray volume, avoiding droplet slippage and wetting of the blades. As a result, 500 mL of pesticide solution was sprayed on the rice plant to wet the leaves. Treatments with 500 mL of water were also conducted in the control group.
During the collection process, a cluster of intact rice seedling was collected, and the roots and plants were separated. Plant parts and roots were collected into sealed bags 4 h, 3 d, and 5 d after treatment. Each treatment was repeated 3 times. The pesticide on the surface of the plant parts was absorbed by an ultrasonic wave with 200 mL of deionized water. The pesticide concentrations of water, plant, and roots were determined.
2.6. Sample Preparation
A quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe (QuEChERS) method is widely used to determine pesticide concentration in plants. In this work, a modified QuEChERS method was established to analyze EPX and CLR in rice. Briefly, 2.00 g (±0.01 g) of rice plant or roots was weighed into a 50 mL plastic centrifuge tube with a plug. A volume of 10 mL of acetonitrile was added and vortexed for 5 min. Then, 3.0 g of sodium chloride was added and vortexed again for 5 minutes. After centrifugation for 5.0 min at 3500 rpm, acetonitrile extract was obtained as the supernatant.
A cleanup process was performed using 1 mL of the acetonitrile extract. Some loose sorbents were added to the acetonitrile extract and vortexed for 3 minutes. For rice plant samples, the sorbents were chosen as 15 mg of MWCNTs and 150 mg of anhydrous magnesium sulfate. For rice root samples, the sorbents were selected as 25 mg of PSA and 150 mg of anhydrous magnesium sulfate. After centrifugation for 5.0 min at 10,000 rpm, the acetonitrile extract was filtered through a 0.22 m filter membrane for HPLC-MS/MS analysis. The acetonitrile extracts were diluted before analysis due to their high concentration levels.
2.7. Analytical Method
The precision and reliability of the proposed method were evaluated in this work. Five replicates at three fortification levels (0.05, 0.1, and 0.5 mg/kg) for EPX and CLR were set in the recovery and reproducibility experiments. Ultimate 3000 HPLC with a reverse-phase column (Hypersil Gold C18, 50 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.9 μm, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used. The mobile phase was set as acetonitrile/0.1% formic acid water (80/20, v/v) with a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. The column temperature was kept at 30 °C, and the injection volume was set at 5 μL. A Thermo Fisher Scientific HPLC/MS system with an HESI source was employed to conduct mass spectrometric analysis. The precursor–product ion transition was detected in e selective reaction monitoring (SRM) mode. The parameters of the operation were as follows: capillary temperature, 300 °C; vaporizer temperature, 300 °C; sheath gas pressure, 35 Arb; aux gas pressure, 15 Arb; spray voltage: positive polarity, 3500 V. The precursor–product ion transition, tube lens, and collision energy for EPX and CLR are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
HPLC-MS/MS parameters for EPX and CLR.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All data were analyzed as means with standard deviation. One-way analysis of variance and Duncan’s multiple range test were performed to analyze the differences between treatments using SPSS 17.0 software. Significant differences were considered at the level of p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Surface Tension
The surface tension of pesticide solution with different tank-mix adjuvants was measured, as shown in Table 3. The concentrations of tank-mix adjuvants were consistent with the rice plant treatment. The surface tension of EPX and CLR SC diluted by water was 44.45~47.76 mN/m. After tank-mix adjuvants were added, the value decreased considerably. The surface tension of EPX and CLR SC with PT was the lowest, at 21.14–21.36 mN/m. When MO and GOEO were added, the surface tension was 26.66~26.69 and 29.29~29.45 mN/m, respectively. No significant difference was observed among pesticide concentrations or types. The surface tension mainly depended on the tank-mix adjuvants in this work.

Table 3.
Surface tension (mN/m) of EPX and CLR SC with spray adjuvants in different treatment concentrations.
3.2. Contact Angle
The contact angle of pesticide solution with different tank-mix adjuvants was measured, as shown in Figure 2. The contact angle was maintained at 115.6–120.1° for EPX and CLR solution without any tank-mix adjuvants for 60 s. The changing trend of contact angle did not change when a different tank-mix adjuvants were added. MO, GOEO, and PT significantly decreased the contact angle for both low and high concentrations of pesticide solutions. In particular, the contact angle was the lowest (10.3–37.3°) when PT was added as a tank-mix adjuvant. On the other hand, the contact angle varied according to the pesticide solutions. For example, the contact angle was 38.4° and 24.1° for EPX solutions at low and high concentrations, respectively, with GOEO as the tank-mix adjuvant. In CLR solutions, it was 40.2° and 28.0° at low and high concentrations, respectively. The concentration and composition of pesticide solution should be considered when tank-mix adjuvants are used.
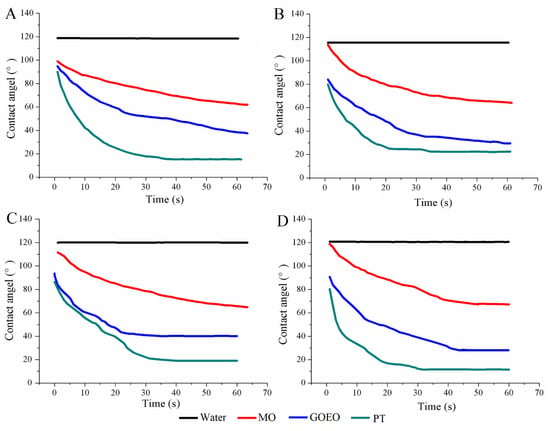
Figure 2.
Contact angles of pesticide solutions with different spray adjuvants: (A) EPX at 125 mg/L, (B) EPX at 187 mg/L, (C) CLR at 66.7 mg/L, and (D) CLR at 100 mg/L.
3.3. Validation of Analytical Method
Considering the matrix effect, a matrix-matched calibration curve was used in this study. The results are summarized in Table 4. The linear range was set at 0.05–0.5 mg/L for both EPX and CLR in cucumber plant, root, and water. A good linear relationship was obtained with a correlation coefficient (R2) better than 0.999. Limit of quantification (LOQ) and limit of detection (LOD) was calculated, as the rate of signal/noise was 10 and 3, respectively. LOQs for EPX and CLR were 0.26–0.33 and 0.33–0.64 μg/kg, respectively. LODs for EPX and CLR were 0.93–1.03 and 1.01–1.96 μg/kg, respectively.

Table 4.
Recoveries, RSDs, linear equation, coefficients of determination (R2), LODs, and LOQs of EPX and CLR in different matrices.
A recovery test was employed to evaluate the analytical method. Recovery and reproducibility experiments were carried out for the cucumber plant and root samples. As shown in Table 4, the recoveries of EPX in plant and root samples were in the range of 96.8–117.1% and 91.1–101.0%, respectively. The recoveries of CLR in plant and root samples were in the range of 98.0–101.9% and 96.4–101.4%, respectively. The relative standard deviations were lower than 9.0 for all cases. The results showed that the analytical method met the requirements for pesticide analysis.
3.4. Deposition of EPX and CLR on the Leaf Surface
Deionized water was used to wash the pesticide deposited on the leaf surface under ultrasonic waves 4 h, 3 d, and 5 d after treatment. The deposition concentrations of EPX and CLR on the leaf surface are shown in Figure 3. It was obvious that PT increased the deposition of EPX from 3.7 to 7.2 mg/kg on the leaf surface in a low concentration of treatment at 4 h. There was no significant difference between EPX solution with or without tank-mix adjuvant at 3 d and 5 d. For high-concentration treatment of EPX, the pesticide deposition in the GOEO group reached 7.7 mg/kg, which increased significantly compared with the PT, MO, and water groups. Similar to low-concentration treatment, the pesticide deposition showed no significant difference between tank-mix adjuvants and water groups at 3 d and 5 d. On the other hand, MO increased the CLR deposition on the leaf surface significantly, as it was 6.5, 4.2, and 2.5 mg/kg at 4 h, 3 d, and 5 d, respectively. However, PT decreased the deposition of CLR compared with the water group at low concentrations, and GOEO showed no significant difference compared to the water group. For high-concentration CLR treatment, there was no significant difference between treatments. At 5 d, the deposition of CLR on the leaf surface was in the range of 3.6–3.9 mg/kg with PT, MO, and GOEO, which increased significantly compared to the water group.
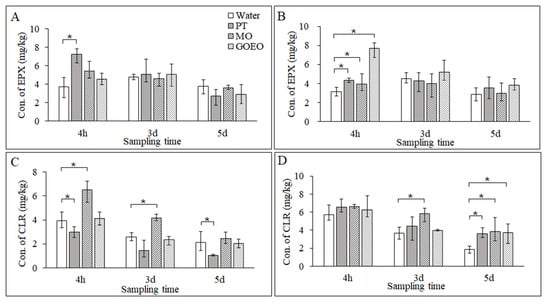
Figure 3.
The deposition concentrations of EPX and CLR on the leaf surface: (A) EPX at 125 mg/L, (B) EPX at 187 mg/L, (C) CLR at 66.7 mg/L, and (D) CLR at 100 mg/L. * p < 0.05.
3.5. Permeation of EPX and CLR in the Leaves
To evaluate the permeation performance of pesticide solution with different tank-mix adjuvants, the concentrations of EPX and CLR in rice plants were analyzed after the rice leaves were washed with deionized water. As shown in Figure 4, PT, MO, and GOEO had different effects on the permeation of pesticides in rice plants. In two different concentrations of pesticide treatment, all the tank-mix adjuvants increased EPX and CLR permeation 4 h after treatment. In the EPX treatment, it was obvious that MO resulted in the highest EPX permeation relative to MO and GOEO. Compared with the water group, the concentration of EPX increased significantly after 4 h and 3 d of low-concentration treatment. EPX permeation in the MO and GOEO groups showed an increasing trend, but there was no significant difference compared with the water group. On the other hand, in a low concentration of CLR treatment, GOEO improved CLR permeation by 55.3 % in rice plants 4 h after treatment compared with the water group. With high-concentration CLR treatment, the GOEO group also exhibited the highest CLR permeation performance in rice plants, at 1.0–1.1 mg/kg. However, PT could decrease CLR permeation sometimes in rice plants. For example, the permeation of CLR in the high-concentration PT group was only 44.4% of that in the water group 5 d after treatment.
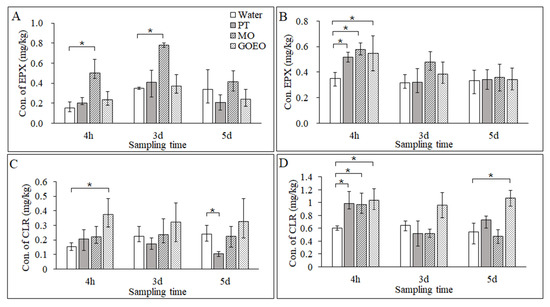
Figure 4.
The concentrations of EPX and CLR in rice shoots: (A) EPX at 125 mg/L, (B) EPX at 187 mg/L, (C) CLR at 66.7 mg/L, and (D) CLR at 100 mg/L. * p < 0.05.
3.6. Translocation of EPX and CLR to the Roots
The concentrations of EPX and CLR in rice roots were also detected to evaluate the pesticide translocation performance, as shown in Figure 5. Both EPX and CLR were translocated from wheat shoots to roots. The concentrations of EPX and CLR in roots were lowest at 4 h and increased slowly at 3 d and 5 d. For the treatment of EPX in low concentration with PT, the concentrations of EPX in roots were significantly higher than those in the water group at 4 h and 5 d. MO and GOEO showed no significant improvement effect on the translocation of EPX to the roots. For the treatment of EPX in high concentration, the concentrations of roots in the PT, MO, GOEO, and water groups were similar at 4 h and 3 d. PT and MO showed an improvement effect on the translocation of EPX to the roots compared with the water group at 5 d, but no significant difference was observed. On the other hand, the improvement effect of tank-mix adjuvants on the translocation of CLR to the roots was obvious. For the treatment of CLR in low concentration, CLR in the water group was not detected in roots at 4 h, and the concentrations in PT, MO, and GOEO were in the range of 0.0064 to 0.012 mg/kg. After 5 d, the concentrations in the MO and GOEO groups were significantly higher than those in the water group. For high-concentration CLR treatment, the concentrations of CLR in roots increased significantly at 4 h and 5 d when GOEO was added as a tank-mix adjuvant.
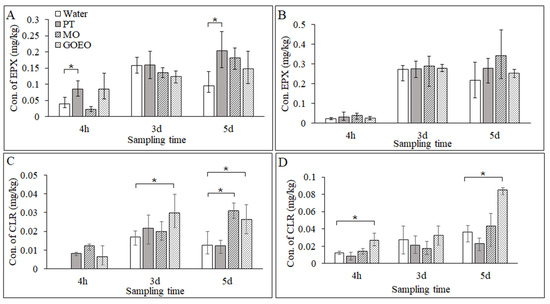
Figure 5.
The concentrations of EPX and CLR in rice roots: (A) EPX at 125 mg/L, (B) EPX at 187 mg/L, (C) CLR at 66.7 mg/L, and (D) CLR at 100 mg/L. * p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
Tank-mix adjuvants have different effects on pesticide performance. Many other factors, such as formula composition, water consumption of spray, pesticide application method, weather, crop species, etc., also affect pesticide performance. In this work, we focused on the effect of tank-mix adjuvants on the deposition, absorption, and permeation behavior of pesticide solutions on rice plants. To keep other conditions the same, we prepared EPX and CLR SC using a common recipe. References about commercial formulations with different adjuvant applications are provided in Table S1 (Supporting information). Those results indicate that different adjuvants have effects on pesticide performance.
The most commonly used pesticide tank-mix adjuvants are surface-active agents based on surface tension reduction [20]. Adding several surfactant-based adjuvants to pesticide spray can slightly reduce the volume of the average droplet, thus improving the utilization rate of pesticides [31], in addition to changing spray dynamics [32]. This study showed that PT, MO, and GOEO decreased the surface tension of EPX and CLR solution to varying degrees. Among them, the surface tension decreased the most with the addition of PT as a tank-mix adjuvant. It was previously reported that organosilicone adjuvant could significantly reduce surface tension and increase the spreading coefficient of pesticide solutions, regardless of solution concentrations [33].
Wettability was detected by measuring the contact angle of each water droplet on the top leaf surface. It was obvious that PT, GOEO, and MO could wet the rice leaf surfaces when the contact angles of pesticide solutions with different tank-mix adjuvants were less than 80° and those without tank-mix adjuvants were about 120°. PT exhibited the best wettability behavior, followed by GOEO and MO. However, it was previously reported that smaller contact angles of the pesticide solution might lead to a higher rate of plant poisoning [34]. Organosilicone surfactants may not be safe, as they are toxic to bees [35]. Therefore, when choosing to use tank-mix adjuvants, their safety and effectiveness should be comprehensively considered rather than only pursuing a reduction in contact angle.
Generally, tank-mix adjuvants can improve the deposition spread, penetration, and uptake of pesticides on leaf surfaces. Organosilicon and mineral oil improve pesticide deposition on banana leaves [14], and oil adjuvants increase the deposition of pesticides on greenhouse strawberries [36]. In a previous study, we found that plant essential oil enhanced the deposition absorption and permeation of pesticides on cucumbers [19]. According to the results in this work, different tank-mix adjuvants should be selected when EPX or CLR is sprayed. When EPX was used, PT, MO, and GOEO increased the deposition of pesticides on the leaf surface, but MO showed the best effect in terms of promoting absorption of EPX in rice plant, and PT significantly enhanced the translocation of pesticides from shoots to roots (treatments of 125 mg/L at 4 h and 5 d). For CLR application, MO showed the best effect in terms of increasing deposition, followed by GOEO, and PT was found to reduce the deposition performance under treatment with 66.7 mg/L. GOEO usually exhibited the best CLR absorption and translocation in rice shoots. PT was also found to reduce the absorption and translocation performance of CLR in some cases.
Although surface tension and contact angle results indicated that PT is the best surface-active agent for pesticide spray, it did not show the best effect in practical application in all cases. For EPX spray, PT improved deposition, absorption, and translocation performance, and MO showed the best effect on EPX absorption in rice shoots. PT had a negative effect on the deposition of CLR. MO was the most suitable for improving CLR deposition on the plant surface, whereas GOEO was the most suitable for improving CLR absorption and translocation inside rice plants. Therefore, tank-mix adjuvants cannot be selected only on the basis of laboratory data, such as surface tension and contact angles. Data of actual plant applications are more important in terms of choosing a suitable tank-mix adjuvant. Selecting an appropriate tank-mix adjuvant can improve the activity of pesticides.
5. Conclusions
Tank-mix adjuvant application in pesticide solution is an effective method to improve their effective utilization rate. The purpose of this work was to regulate the deposition, absorption, and permeation behavior of pesticide solutions on rice plants using tank-mix adjuvants. A comparative study was conducted on EPX and CLR SC sprayed with PT, MO, and GOEO on rice plants. Surface tension and contact angle results indicated that PT might be the best surface-active agent for pesticide spray, but it did not always show the best effect in practical applications. MO showed the best effect on EPX absorption in rice shoots and CLR deposition on the plant surface. GOEO was the most suitable for improving CLR absorption and translocation inside rice plants. Various kinds of tank-mix adjuvants had different effects on pesticide application on plants. The results may differ with various commercial formulations in the field because of different commercial pesticide recipes on the market. The selection of tank-mix adjuvant according to the practical application effect is essential to enhance the effective utilization rate of pesticides.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture12081119/s1, Table S1: References about commercial formulations with different adjuvants application [5,37,38,39,40,41].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.H. and P.Z.; methodology, L.Z. and Y.L.; validation, C.W. and C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.Z.; funding acquisition, L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research Development Program of China (2019YFD1002103) and the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (No. Y2020XK14).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, X.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Cui, B.; Zeng, Z. Development strategies and prospects of nano-based smart pesticide formulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6504–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Cao, C.; Chen, Z.; Cao, L.; Huang, Q.; Song, B. Efficient pesticide formulation and regulation mechanism for improving the deposition of droplets on the leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3198–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, T.; Bao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Du, F. Catechol functionalized hat-shape carriers for prolonging pesticide retention and flush resistance on foliage. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, P.J.; Butler Ellis, M.C.; Webb, D.A.; Western, N.M.; Tuck, C.R.; Hayes, A.L.; HMiller, P.C. Effects of some agricultural tank-mix adjuvants on the deposition efficiency of aqueous sprays on foliage. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.A.; Usano-Alemany, J.; Guedes, J.V.C.; Hunsche, M. Impact of tank-mix adjuvants on deposit formation, cuticular penetration and rain-induced removal of chlorantraniliprole. Crop Prot. 2015, 78, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsche, M.; Alexeenko, A.; Damerow, L.; Noga, G. Rain-induced removal of copper from apple leaves: Influence of rain properties and tank-mix adjuvants on deposit characteristics at the micro scale. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, B.; Spanoghe, P.; Heremans, B.; Haesaert, G.; Steurbaut, W. Possibilities to use tank-mix adjuvants for better fungicide spreading on triticale ears. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8041–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliverdi, A.; Ahmadvand, G. Tank-mix adjuvants to reduce the adverse effect of muddy rain on the activity of paraquat against winter wild oat. Crop Prot. 2020, 28, 105013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.B.; Yadav, A.; Punia, S.S.; Chauhand, B.S. Management of herbicide-resistant Phalaris minor in wheat by sequential or tank-mix applications of pre- and post-emergence herbicides in north-western Indo-Gangetic Plains. Crop Prot. 2016, 89, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zeng, A.; Song, J.; Xu, T.; Lv, X.; He, X. Effects of adjuvants on spraying characteristics and control efficacy in unmanned aerial application. Agriculture 2022, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yu, M.; Sun, Z.; Li, L.; Shang, H.; Xi, W.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X. Using tank-mix adjuvant improves the physicochemical properties and dosage delivery to reduce the use of pesticides in unmanned aerial vehicles for plant protection in wheat. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wei, G.; Mu, W.; Li, B.; Liu, F. Tank-mixing adjuvants enhanced the efficacy of fludioxonil on cucumber anthracnose by ameliorating the penetration ability of active ingredients on target interface. Colloid Surface B 2021, 204, 111804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, W.; Lord, J.C.; Nechols, J.R.; Loughin, T.M. Efficacy of Beauveria bassiana for red flour beetle when applied with plant essential oils or in mineral oil and organosilicone carriers. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Long, X.; Ge, S.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Y. Deposition amount and dissipation kinetics of difenoconazole and propiconazole applied on banana with two commercial spray adjuvants. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19780–19790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelatti, Z.A.S.; Hartbauer, M. Plant oil mixtures as a novel botanical pesticide to control gregarious locusts. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.A.R.; Metzger, J.O.; Schubert, U.S. Plant oil renewable resources as green alternatives in polymer science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1788–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Commercial development of plant essential oils and their constituents as active ingredients in bioinsecticides. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, Y.X.; Yeo, C.R.; Chung, H.L.; Yuk, H.-G. Plant essential oils as active antimicrobial agents. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2014, 54, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhao, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Cao, L.; Huang, Q. Natural green-peel orange essential oil enhanced the deposition, absorption and permeation of prochloraz in cucumber. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 20395–20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazen, J.L. Adjuvants—terminology, classification, and chemistry. Weed Technol. 2000, 14, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.G.; Sieverding, E.G.; Viljoen, D.J.; Fourie, P.H. Evaluation of two organosilicone adjuvants at reduced foliar spray volumes in South African citrus orchards of different canopy densities. Crop Prot. 2014, 64, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, S.; Yang, T.; Clark, J.M.; He, L. Alteration of the nonsystemic behavior of the pesticide ferbam on tea leaves by engineered gold nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6216–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łozowicka, B.; Kaczyński, P.; Mojsak, P.; Rusiłowska, J.; Beknazarova, Z.; Ilyasova, G.; Absatarova, D. Systemic and non-systemic pesticides in apples from Kazakhstan and their impact on human health. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 90, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z. The plant as metaorganism and research on next-generation systemic pesticides—Prospects and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keikotlhaile, B.M.; Spanoghe, P.; Steurbaut, W. Effects of food processing on pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables: A meta-analysis approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, S.; Moore, T.; Padgett, W.T.; Murphy, L.; Wood, C.E.; Nesnow, S. The hepatocarcinogenic conazoles: Cyproconazole, epoxiconazole, and propiconazole induce a common set of toxicological and transcriptional responses. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 127, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konwick, B.K.; Garrison, A.W.; Avants, J.K.; Fisk, A.T. Bioaccumulation and biotransformation of chiral triazole fungicides in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honorato Júnior, J.; Zambolim, L.; Aucique-Pérez, C.E.; Resende, R.S.; Rodrigues, F.A. Photosynthetic and antioxidative alterations in coffee leaves caused by epoxiconazole and pyraclostrobin sprays and Hemileia vastatrix infection. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2015, 123, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cui, H.; Fan, S.; Wang, M.; Lu, C.; Yang, Y. Systemicity of chlorantraniliprole in velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti). J. AOAC Int. 2013, 96, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Liang, P.; Zhou, X.; Gao, X. Novel mutations and mutation combinations of ryanodine receptor in a chlorantraniliprole resistant population of Plutella xylostella (L.). Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijs, R.; Bonn, D. The effect of adjuvants on spray droplet size from hydraulic nozzles. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3487–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilz, E.; Vermeer, A.W. Spray drift review: The extent to which a formulation can contribute to spray drift reduction. Crop Prot. 2013, 44, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Hu, H.; Ma, Y. Surface tension and spreading coefficient of single-and mix-pesticide solutions with aerial spraying organosilicone adjuvant. Int. J. Precis. Agric. Aviat. 2021, 4, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Santos, R.T.; Vechia, J.F.D.; dos Santos, C.A.M.; Almeida, D.P.; Ferreira, M.D.C. Relationship of contact angle of spray solution on leaf surfaces with weed control. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullin, C.A.; Fine, J.D.; Reynolds, R.D.; Frazier, M.T. Toxicological risks of agrochemical spray adjuvants: Organosilicone surfactants may not be safe. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cang, T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Qi, P.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q. Positive effects of an oil adjuvant on efficacy, dissipation and safety of pyrimethanil and boscalid on greenhouse strawberry. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2018, 160, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, W.A.; Kimberley, M.O. The contribution of spray formulation component variables to foliar uptake of agrichemicals. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichiheb, N.; Bedos, C.; Personne, E.; Benoit, P.; Bergheaud, V.; Fanucci, O.; Bouhlel, J.; Barriuso, E. Measuring leaf penetration and volatilization of chlorothalonil and epoxiconazole applied on wheat leaves in a laboratory-scale experiment. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Sun, Z.; Bird, N.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X. Effects of tank-mix adjuvants on physicochemical properties and dosage delivery at low dilution ratios for unmanned aerial vehicle application in paddy fields. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1582–15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landim, T.N.; da Cunha, J.P.A.R.; Alves, G.S.; Marques, M.G.; Silva, S.M. Interactions between adjuvants and the fungicide azoxystrobin+benzovindiflupyr in hydraulic spraying. Engenharia Agrícola 2019, 39, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedobová, J.; Skalský, M.; Ouředníčková, J.; Michalko, R.; Bartošková, A. Synergistic effects of glyphosate formulation herbicide and tank-mixing adjuvants on Pardosa spiders. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).