Response of Indian Dwarf Wheat and Persian Wheat to Sowing Density and Hydrothermal Conditions of the Growing Seasons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Crop Management
2.2. Measurements of Morphological and Agronomic Traits
2.3. Diseases Occurrence Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Yield and Biometric Features of Triticum sphaerococcum
3.2. Yield and Biometric Features of Triticum persicum
3.3. Occurrence of Diseases
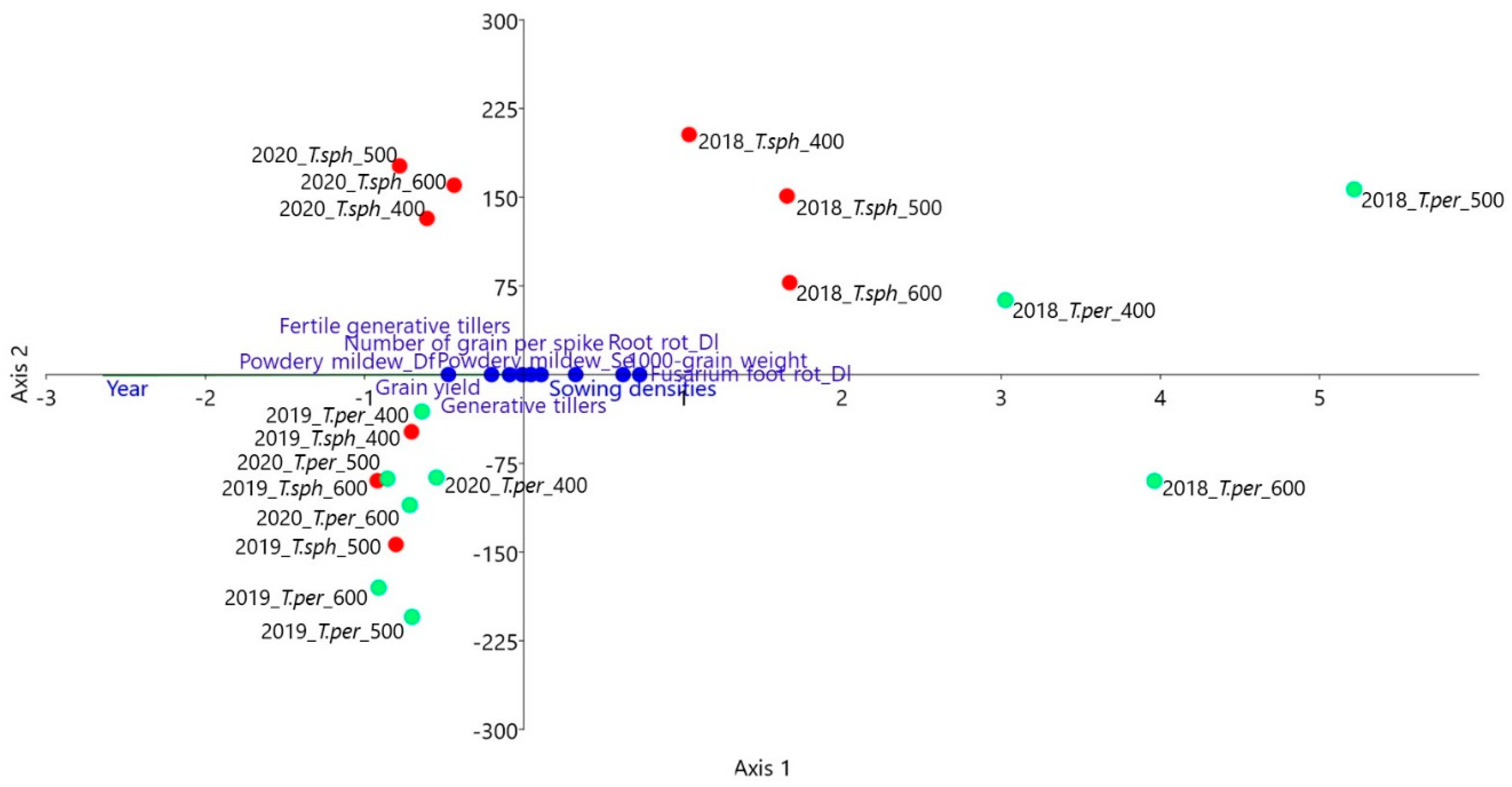
3.4. Variable Dependency Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphological and Agronomic Traits
4.2. Occurrence of Diseases
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Suchowilska, E.; Wiwart, M.; Kandler, W.; Krska, R.A. Comparison of macro- and microelement concentrations in the whole grain of four Triticum species. Plant Soil Environ. 2012, 58, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skrajda-Brdak, M.; Konopka, I.; Tańska, M.; Szczepanek, M.; Sadowski, S.; Rychcik, B. Low molecular phytochemicals of Indian dwarf (Triticum sphaerococcum Percival) and Persian wheat (T. carthlicum Nevski) grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 91, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josekutty, P.C. Defining the Genetic and Physiological Basis of Triticum sphaerococcum Perc. Master’s Thesis, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, N.; Ohta, S.; Chiba, H.; Takagi, T.; Niimi, Y.; Shinde, V.; Kajale, M.D.; Osada, T. Rediscovery of Indian dwarf wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ssp. sphaerococcum (Perc.) MK.) an ancient crop of the Indian subcontinent. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2013, 60, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, Y. Evolution of polyploid Triticum wheats under cultivation: The role of domestication, natural hybridization and allopolyploid speciation in their diversification. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosulishvili, M.; Bedoshvili, D.; Maisaia, I. A consolidated list of Triticum species and varieties of Georgia to promote repatriation of local diversity from foreign genebanks. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 5, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.A.; Khaliq, A.T.; Cheema, M.J.M. Evaluating the impact of seed rate and sowing dates on wheat productivity in semi-arid environment. Int. Agric. Biol. 2019, 22, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutala, R.; Korva, J.; Varis, E. Spring wheat cultivar performance in ecological and conventional cropping systems. J. Sustain. Agric. 1993, 3, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auškalnienė, O.; Auškalnis, A. The influence of spring wheat plant density on weed suppression and grain yield. Zemdirbyste 2008, 95, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, R.A.; Moreno-Ramos, O.H.; Monasterio-Ortiz, I.; Sayre, K.D. Yield response to plant density, row spacing and raised beds in low latitude spring wheat with ample soil resources. Field Crops Res. 2019, 22, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.L.; Carvalho, I.R.; Barbosa, M.H.; Conte, G.G.; Hutra, D.; Moura, N.B.; Souza, V.Q. Sowing density and clipping management: Effects on the architecture and yield of dual-purpose wheat. Biosci. J. 2020, 36, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Khan, E.A.; Hassan, G.; Gul, J.; Ozturk, M.; Alharby, H.; Hakeem, K.R.; Alamri, S. Integration of high seeding densities and criss cross row planting pattern suppresses weeds and increases grain yield of spring wheat. J. Environ. Biol. 2017, 38, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.; Kristensen, L.; Weiner, J. Influence of sowing density and spatial pattern of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum) on the suppression of different weed species. Weed Biol. Manag. 2006, 6, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.P.; Bazzo, J.H.; Marinho, J.L.; Zucareli, C. Effect of seed vigor and sowing densities on the yield and physiological potential of wheat seeds. J. Seed Sci. 2021, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavers, R.L.; Hammermeister, A.M.; Frick, B.; Astatkie, T.; Martin, R.C. Spring wheat yield response to variable seeding rates in organic farming systems at different fertility regimes. Can. J. Plant. Sci. 2008, 88, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Prasertsak, P.; Setter, T.L. Plant spacing, density, and yield of wheat subjected to postanthesis water deficits. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyasri, R.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Satish, L.; Pandian, S.K.; Chen, J.-T.; Ahmar, S.; Wang, X.; Mora-Poblete, F.; Ramesh, M. An overview of abiotic stress in cereal crops: Negative impacts, regulation, biotechnology and integrated omics. Plants 2021, 10, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, A.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, M.; Quan, M.; Irshad, S.; Xu, D.; Aleem, M.; Zhang, X.; Gull, S.; Li, F.; et al. Effects of environmental stresses (heat, salt, waterlogging) on grain yield and associated traits of wheat under application of sulfur-coated urea. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.; Pisipati, S.; Ristic, Z.; Bukovnik, U.; Fritz, A. Impact of nighttime temperature on physiology and growth of spring wheat. Crop. Sci. 2008, 48, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Sher, A.; Ijaz, M.; Ul-Allah, S.; Rizwan, M.S.; Hussain, M.; Jabran, K.; Cheem, M.A. Terminal drought and heat stress alter physiological and biochemical attributes in flag leaf of bread wheat. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhwar, N.A.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Baloch, G.M.; Soomro, Z.A.; Sial, M.A.; Demiraj, E.; Panhwar, S.A.; Afzal, A.; Lahori, A.H. Water stress affects the some morpho-physiological traits of twenty wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes under field condition. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Lu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jin, J. Effect of drought on agronomic traits of rice and wheat: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moosavi, S.S.; Abdi, F.; Abdollahi, M.R.; Enferadi, S.T.; Maleki, M. Phenological, morpho-physiological and proteomic responses of Triticum boeoticum to drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna-Chopra, R.; Viswanathan, C. Evaluation of heat stress tolerance in irrigated environment of T. aestivum and related species. I. Stability in yield and yield components. Euphytica 1999, 106, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsæter, L.O.; Mangerud, K.; Andersson, L.; Børresen, T.; Brodal, G.; Melander, B. Influence of mechanical weeding and fertilisation on perennial weeds, fungal diseases, soil structure and crop yield in organic spring cereals. Acta Agric Scand 2020, B, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, M.R.; Börner, A.; Struik, P.C. Editorial: Fungal wheat diseases: Etiology, breeding, and integrated management. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 671060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.A.; Chantry, T.; Taylor, M.C.; Kennedy, M.C. Changes in agronomic practices and incidence and severity of diseases in winter wheat in England and Wales between 1999 and 2019. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 1759–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, M.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Solomon, P.S. A review of wheat diseases—A field perspective. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ullah, M.; Ahmad, W.; Shah, S.U.A. The use of modern technologies to combat stripe rust in wheat. Rom. Biotech. Lett. 2020, 25, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanek, M.; Lemańczyk, G.; Lamparski, R.; Wilczewski, E.; Graczyk, R.; Nowak, R.; Prus, P. Ancient wheat species (Triticum sphaerococcum Perc. and T. persicum Vav.) in organic farming: Influence of sowing density on agronomic traits, pests and diseases occurrence, and weed infestation. Agriculture 2020, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccar, R.; Fournier, C.; Dornbusch, T.; Andrieu, B.; Gouache, D.; Robert, C. Modelling the effect of wheat canopy architecture as affected by sowing density on Septoria tritici epidemics using a coupled epidemic–virtual plant model. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, C.; Garin, G.; Abichou, M.; Houlès, V.; Pradal, C.; Fournier, C. Plant architecture and foliar senescence impact the race between wheat growth and Zymoseptoria tritici epidemics. Ann. Bot. 2018, 121, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beres, B.L.; Turkington, T.K.; Kutcher, H.R.; Irvine, B.; Johnson, E.N.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Harker, K.N.; Holzapfel, C.B.; Mohr, R.; Peng, G.; et al. Winter wheat cropping system response to seed treatments, seed size, and sowing density. J. Agron. 2016, 108, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walters, D. Disease Control in Crops: Biological and Environmentally Friendly Approaches; John Wiley & Sons: Edinburgh, UK, 2009; pp. 1–226. [Google Scholar]
- Pradawne Ziarno. Available online: http://www.pradawneziarno.pl/ (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- McDonald, J.H. Handbook of Biological Statistics, 2nd ed.; Sparky House Publishing: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2009; pp. 1–319. [Google Scholar]
- Tokatlidis, I.S. Addressing the yield by density interaction is prerequisite to bridge the yield gap of rain-fed wheat. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 65, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.G.; Souza, C.A.; Fioreze, S.L.; Sangoi, L.; Carneiro, J.F.; Bisato, M.M. Cultivar, sowing density, or time of emission: What influences mortality and performance of wheat tillers the most? Rev. Ciênc. Agrovet. 2021, 20, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, J.L.; Silva, S.R.; Nascimento-Souza, D.; Fonseca-Batista, I.C.; Bazzo-Bizzarri, J.H. Wheat yield and seed physiological quality affected by initial seed vigor, sowing density, and environmental conditions. Semin. Ciênc. Agrá. 2021, 42, 1595–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xi, N.; Weiner, J.; Zhang, D.Y. Differences in weed suppression between two modern and two old wheat cultivars at different sowing densities. Agronomy 2021, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, J.; Manent, J.; Viudas, J.; Lopez, A.; Santiveri, P. Seeding rate influence on yield and yield components of irrigated winter wheat in a Mediterranean climate. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Beest, D.E.; Paveley, N.D.; Shaw, M.W.; Van Den Bosch, F. Disease–weather relationships for powdery mildew and yellow rust on winter wheat. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semaškienė, R.; Tamošiūnas, K.; Dabkevičius, Z. Control of powdery mildew, Blumeria graminis (DC), in spring and winter wheat with decision support system based on assessments and weather data. Plant Prot. Sci. 2002, 38, 667–669. [Google Scholar]
- Lemańczyk, G.; Piekarczyk, M. Effect of fertilization, chemical crop protection and sowing density on health status of winter wheat grown in short-time monoculture on light soil. Prog. Plant Prot. 2013, 53, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Finckh, M.R.; Gacek, E.S.; Czembor, H.J.; Wolfe, M.S. Host frequency and density effects on powdery mildew and yield in mixtures of barley cultivars. Plant Pathol. 1999, 48, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbach, N.; Lucas, P.; Meynard, J.M. Influence of crop management on take-all development and disease cycles on winter wheat. Phytopathology 1997, 7, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemańczyk, G. Effects of farming system, chemical control, fertilizer and sowing density on sharp eyespot and Rhizoctonia spp. in winter wheat. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2012, 52, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eken, C.; Bulut, S.; Genc, T.; Öztürk, A. Effects of different fertilizer sources and sowing density on root and crown rot disease agents of organic wheat. Gaziosmanpașa Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Derg. 2014, 31, 12–19. [Google Scholar]


| N-NO3 | N-NH4 | pH (KCl) | P | K | Mg | C-org. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g kg−1 of Soil | g kg−1 of Soil | |||||
| 0.0042 | 0.0044 | 7.0 | 0.112 | 0.153 | 0.056 | 11.0 |
| Year | Days | March | April | May | June | July | March | April | May | June | July |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature °C | Precipitation mm | ||||||||||
| 2018 | 1–10 | 3.5 | 9.2 | 14.8 | 19.8 | 18.7 | 5.7 | 18.2 | 7.6 | 7.2 | 2.0 |
| 11–20 | 1.2 | 13.7 | 16.3 | 18.9 | 19.5 | 8.2 | 12.8 | 4.5 | 0.0 | 74.9 | |
| 20–30/31 | 1.7 | 13.2 | 19.5 | 16.6 | 23.0 | 2.7 | 9.4 | 2.1 | 19.2 | 9.1 | |
| Mean/Sum | 2.1 | 12.0 | 16.9 | 18.4 | 20.5 | 16.6 | 40.4 | 14.2 | 26.4 | 86.0 | |
| 2019 | 1–10 | 4.6 | 7.6 | 8.8 | 21.4 | 16.0 | 12.1 | 0.0 | 9.3 | 0.0 | 14.7 |
| 11–20 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 12.3 | 22.8 | 18.0 | 11.7 | 0.0 | 56.4 | 16.2 | 2.0 | |
| 21–30/31 | 6.8 | 13.7 | 15.0 | 21.6 | 21.6 | 5.0 | 1.5 | 23.5 | 1.5 | 5.7 | |
| Mean/Sum | 5.4 | 9.3 | 12.1 | 21.9 | 18.6 | 28.8 | 1.5 | 89.2 | 17.7 | 22.4 | |
| 2020 | 1–10 | 4.2 | 7.3 | 11.2 | 14.9 | 17.9 | 13.1 | 0.0 | 16.4 | 63.0 | 32.5 |
| 11–20 | 5.5 | 7.0 | 9.6 | 19.5 | 17.8 | 13.0 | 0.0 | 11.0 | 33.5 | 47.1 | |
| 21–30/31 | 2.1 | 10.4 | 12.0 | 19.4 | 18.3 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 7.2 | 57.4 | 5.5 | |
| Mean/Sum | 3.9 | 8.2 | 10.9 | 17.9 | 18.0 | 26.1 | 0.7 | 34.6 | 153.9 | 85.1 | |
| Year | Sowing Density (Grains m−2) | Grain Yield (Mg ha−1) | Number of Grain Per Spike | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Straw Yield (Mg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 400 | 1.67 ± 0.20 a 1 | 19.0 ±3.3 a | 32.1 ± 1.4 a | 1.40 ± 0.18 a |
| 500 | 1.68 ± 0.10 a | 19.7± 4.0 a | 32.6 ± 0.8 a | 1.64 ± 0.25 a | |
| 600 | 1.60 ± 0.11 a | 18.9 ± 2.3 a | 31.1 ± 0.7 a | 1.52 ± 0.11 a | |
| CV% | 8.14 | 15.46 | 3.57 | 13.27 | |
| 2019 | 400 | 2.37 ± 0.15 b | 25.2 ± 1.9 a | 28.3 ± 0.5 a | 4.39 ± 0.08 b |
| 500 | 2.42 ± 0.11 b | 23.6 ± 1.9 a | 26.7 ± 0.4 b | 4.26 ± 0.11 b | |
| 600 | 2.70 ± 0.03 a | 23.4 ± 3.1 a | 27.0 ± 1.0 ab | 4.74 ± 0.11 a | |
| CV% | 7.25 | 9.51 | 3.61 | 5.10 | |
| 2020 | 400 | 4.65 ± 0.10 a | 28.9 ± 1.6 a | 32.1 ± 0.3 a | 9.25 ± 0.32 a |
| 500 | 4.75 ± 0.15 a | 28.8 ± 1.2 a | 31.3 ± 0.9 a | 9.26 ± 0.95 a | |
| 600 | 4.79 ± 0.17 a | 29.8 ± 2.1 a | 32.2 ± 0.8 a | 9.52 ± 0.56 a | |
| CV% | 3.03 | 5.37 | 2.46 | 6.58 |
| Year | Sowing Density (Grains m−2) | Generative Tillers (No Plant−1) | Vegetative Tillers (No Plant−1) | Fertile Generative Tillers (No m−2) | Sterile Generative Tillers (No m−2) | Total Generative Tillers (No m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 400 | 0.96 ± 0.07 a 1 | 1.56 ± 0.24 a | 273 ± 20 a | 11.3 ± 0.9 a | 285 ± 19 a |
| 500 | 0.88 ± 0.08 a | 1.44 ± 0.16 a | 275 ± 20 a | 14.7 ± 9.6 a | 589 ± 21 a | |
| 600 | 0.72 ± 0.03 b | 1.56 ± 0.28 a | 280 ± 10 a | 20.0 ±11.8 a | 300 ± 4 a | |
| CV% | 13.96 | 14.39 | 5.76 | 57.20 | 5.63 | |
| 2019 | 400 | 1.04 ± 0.03 a | 1.43 ± 0.26 a | 313 ± 21 b | 18.5 ± 4.1 a | 331 ± 20 b |
| 500 | 1.05 ± 0.06 a | 1.06 ± 0.19 ab | 351 ± 12 ab | 23.0 ± 5.3 a | 374 ± 14 ab | |
| 600 | 1.05 ± 0.06 a | 0.69 ± 0.06 b | 378 ± 34 a | 38.0 ± 18.7 a | 416 ± 35 a | |
| CV% | 4.39 | 33.71 | 10.19 | 51.10 | 11.36 | |
| 2020 | 400 | 1.07 ± 0.17 a | 1.47 ± 0.38 a | 601 ± 67 a | 3.5 ± 1.9 a | 605 ± 68 a |
| 500 | 1.06 ± 0.07 a | 1.23 ± 0.28 a | 590 ± 82 a | 5.0 ± 4.8 a | 595 ± 84 a | |
| 600 | 1.09 ± 0.08 a | 1.27 ± 0.35 a | 596 ± 14 a | 3.3 ± 1.0 a | 599 ± 13 a | |
| CV% | 9.82 | 24.46 | 9.38 | 72.59 | 6.51 |
| Year | Sowing Density (Grains m−2) | Grain Yield (Mg ha−1) | Number of Grain per Spike | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Straw Yield (Mg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 400 | 0.46 ± 0.03 a 1 | 10.7 ± 2.8 a | 32.4 ± 0.3 a | 1.02 ± 0.12 a |
| 500 | 0.40 ± 0.06 ab | 9.3 ± 1.9 a | 33.3 ± 2.8 a | 1.05 ± 0.16 a | |
| 600 | 0.36 ± 0.01 b | 9.8 ± 2.0 a | 34.5 ± 4.1 a | 1.00 ± 0.08 a | |
| CV% | 13.97 | 21.58 | 8.31 | 10.91 | |
| 2019 | 400 | 1.32 ± 0.05 c | 17.9 ± 2.0 ab | 25.2 ± 0.8 a | 3.27 ± 0.66 a |
| 500 | 1.42 ± 0.07 b | 15.6 ± 1.5 b | 24.8 ± 1.7 a | 3.44 ± 0.07 a | |
| 600 | 1.62 ± 0.01 a | 19.1 ± 1.5 a | 26.6 ± 1.3 a | 3.55 ± 0.17 a | |
| CV% | 9.47 | 12.26 | 5.55 | 10.99 | |
| 2020 | 400 | 3.52 ± 0.23 a | 25.9 ± 2.6 a | 27.7 ± 1.8 a | 6.77 ± 1.35 a |
| 500 | 3.38 ± 0.24 a | 25.4 ± 2.3 a | 25.9 ± 2.1 a | 6.36 ± 1.17 a | |
| 600 | 3.45 ± 0.16 a | 29.7 ± 2.6 a | 26.7 ± 0.93 a | 6.56 ± 0.43 a | |
| CV% | 5.87 | 11.22 | 6.33 | 14.87 |
| Year | Sowing Density (Grains m−2) | Generative Tillers (No Plant−1) | Vegetative Tillers (No Plant−1) | Fertile Generative Tillers (No m−2) | Sterile Generative Tillers (No m−2) | Total Generative Tillers (No m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 400 | 0.42 ± 0.08 a 1 | 2.08 ± 0.24 a | 168 ± 36 a | 22.7 ± 4.1 b | 191 ± 37 a |
| 500 | 0.57 ± 0.16 a | 1.76 ± 0.09 a | 120 ± 12 a | 30.7 ± 5.0 ab | 151 ± 14 a | |
| 600 | 0.34 ± 0.11 a | 1.86 ± 0.14 a | 146 ± 29 a | 38.0 ± 10.2 a | 184 ± 22 a | |
| CV% | 33.82 | 10.94 | 22.19 | 29.84 | 17.02 | |
| 2019 | 400 | 1.09 ± 0.11 b | 1.40 ± 0.30 a | 273 ± 13 b | 20.0 ± 2.8 a | 293 ± 10 b |
| 500 | 1.19 ± 0.16 b | 1.37 ± 0.23 a | 298 ± 31 b | 21.5 ± 1.0 a | 319 ± 32 b | |
| 600 | 1.48 ± 0.11 a | 1.61 ± 0.28 a | 401± 54 a | 23.0 ± 5.3 a | 424 ± 54 a | |
| CV% | 16.46 | 18.50 | 20.63 | 15.93 | 19.65 | |
| 2020 | 400 | 1.14 ± 0.10 a | 1.48 ± 0.42 a | 551 ± 86 a | 14.0 ± 10.8 a | 565 ± 96 a |
| 500 | 1.15 ± 0.06 a | 1.43 ± 0.21 a | 667 ± 83 a | 12.5 ± 6.6 a | 679 ± 86 a | |
| 600 | 1.20 ± 0.14 a | 1.56 ± 0.37 a | 602 ± 68 a | 13.5 ± 4.7 a | 615 ± 71 a | |
| CV% | 10.17 | 21.17 | 14.39 | 53.26 | 14.74 |
| Year | Sowing Density (Grains m−2) | Powdery Mildew Se | Powdery Mildew Df | Root Rot | Fusarium Foot Rot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf or Spike Area with Disease Symptoms (%) | |||||
| 2018 | 400 | 1.00 ± 0.00 a 1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 34.25 ± 5.12 b | 10.25 ± 2.87 a |
| 500 | 1.50 ± 0.58 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 46.00 ± 3.5 ab | 16.25 ± 3.77 a | |
| 600 | 1.75 ± 0.96 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 51.75 ± 9.91 a | 12.25 ± 2.50 a | |
| CV% | 47.19 | 0.00 | 22.18 | 29.61 | |
| 2019 | 400 | 45.58 ± 6.23 a | 0.38 ± 0.47 a | 5.50 ± 2.08 a | 0.50 ± 0.58 a |
| 500 | 56.67 ± 0.20 a | 0.20 ± 0.15 a | 6.50 ± 1.75 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| 600 | 49.58 ± 5.99 a | 0.07 ± 0.06 a | 4.75 ± 2.22 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| CV% | 15.47 | 133.13 | 35.38 | 180.91 | |
| 2020 | 400 | 7.75 ± 1.59 a | 0.26 ± 0.09 a | 22.71 ± 1.72 a | 9.38 ± 1.58 b |
| 500 | 5.92 ± 1.66 a | 0.25 ± 0.14 a | 13.54 ± 2.67 b | 11.04 ± 1.85 b | |
| 600 | 5.25 ± 1.45 a | 0.14 ± 0.06 a | 22.92 ± 6.89 a | 17.29 ± 2.29 a | |
| CV% | 28.55 | 20.01 | 30.65 | 31.54 | |
| Year | Sowing Density (Grains m−2) | Powdery Mildew Se | Powdery Mildew Df | Root Rot | Fusarium Foot Rot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf or Spike Area with Disease Symptoms (%) | |||||
| 2018 | 400 | 2.75 ± 0.96 b 1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 50.25 ± 4.57 a | 10.25 ± 1.89 b |
| 500 | 4.50 ± 0.58 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 56.25 ± 9.03 a | 35.25 ± 5.12 a | |
| 600 | 7.50 ± 1.73 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 63.25 ± 6.45 a | 9.00 ± 1.83 b | |
| CV% | 47.07 | 0.00 | 14.80 | 71.46 | |
| 2019 | 400 | 34.92 ± 11.18 b | 0.11 ± 0.07 a | 6.25 ± 1.50 a | 0.50 ± 1.00 a |
| 500 | 52.67 ± 4.12 a | 0.07 ± 0.00 a | 7.00 ± 2.83 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| 600 | 58.75 ± 3.70 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 6.50 ± 0.58 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| CV% | 25.44 | 54.69 | 26.28 | 346.41 | |
| 2020 | 400 | 45.00 ± 3.04 ab | 0.18 ± 0.07 a | 23.96 ± 1.72 a | 7.50 ± 1.18 a |
| 500 | 41.26 ± 2.84 b | 0.13 ± 0.00 a | 23.33 ± 2.45 a | 2.92 ± 1.08 b | |
| 600 | 49.42 ± 2.77 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 24.38 ± 2.75 a | 2.92 ± 0.48 b | |
| CV% | 9.63 | 29.55 | 9.09 | 54.42 | |
| Biometric Features | Triticum sphaerococcum | Triticum persicum |
|---|---|---|
| Number of grains per spike | 0.86 | 0.94 |
| 1000-grain weight | n.s. | −0.58 |
| Straw yield | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Generative tillers (plants −1) | 0.59 | 0.62 |
| Vegetative tillers (plants−1) | n.s. | −0.44 |
| Fertile generative tillers (m−2) | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| Sterile generative tillers (m−2) | -0.47 | −0.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczepanek, M.; Lemańczyk, G.; Nowak, R.; Graczyk, R. Response of Indian Dwarf Wheat and Persian Wheat to Sowing Density and Hydrothermal Conditions of the Growing Seasons. Agriculture 2022, 12, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020205
Szczepanek M, Lemańczyk G, Nowak R, Graczyk R. Response of Indian Dwarf Wheat and Persian Wheat to Sowing Density and Hydrothermal Conditions of the Growing Seasons. Agriculture. 2022; 12(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczepanek, Małgorzata, Grzegorz Lemańczyk, Rafał Nowak, and Radomir Graczyk. 2022. "Response of Indian Dwarf Wheat and Persian Wheat to Sowing Density and Hydrothermal Conditions of the Growing Seasons" Agriculture 12, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020205
APA StyleSzczepanek, M., Lemańczyk, G., Nowak, R., & Graczyk, R. (2022). Response of Indian Dwarf Wheat and Persian Wheat to Sowing Density and Hydrothermal Conditions of the Growing Seasons. Agriculture, 12(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020205







