Influence of Effective Microorganisms and Clinoptilolite on Gut Barrier Function, Intestinal Health and Performance of Broiler Chickens during Induced Eimeria tenella Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Parasites and Inoculum Preparation
2.3. Clinical Signs and Growth Performance in Chickens
2.4. Faecal Collection and Counting of Oocysts
2.5. Lesion Scoring
2.6. Gastrointestinal Permeability
2.7. Intestinal Sample Collection
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR for Tight Junction Proteins, Mucin and Antioxidant Gene Expression
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Signs and Growth Performance in Chickens
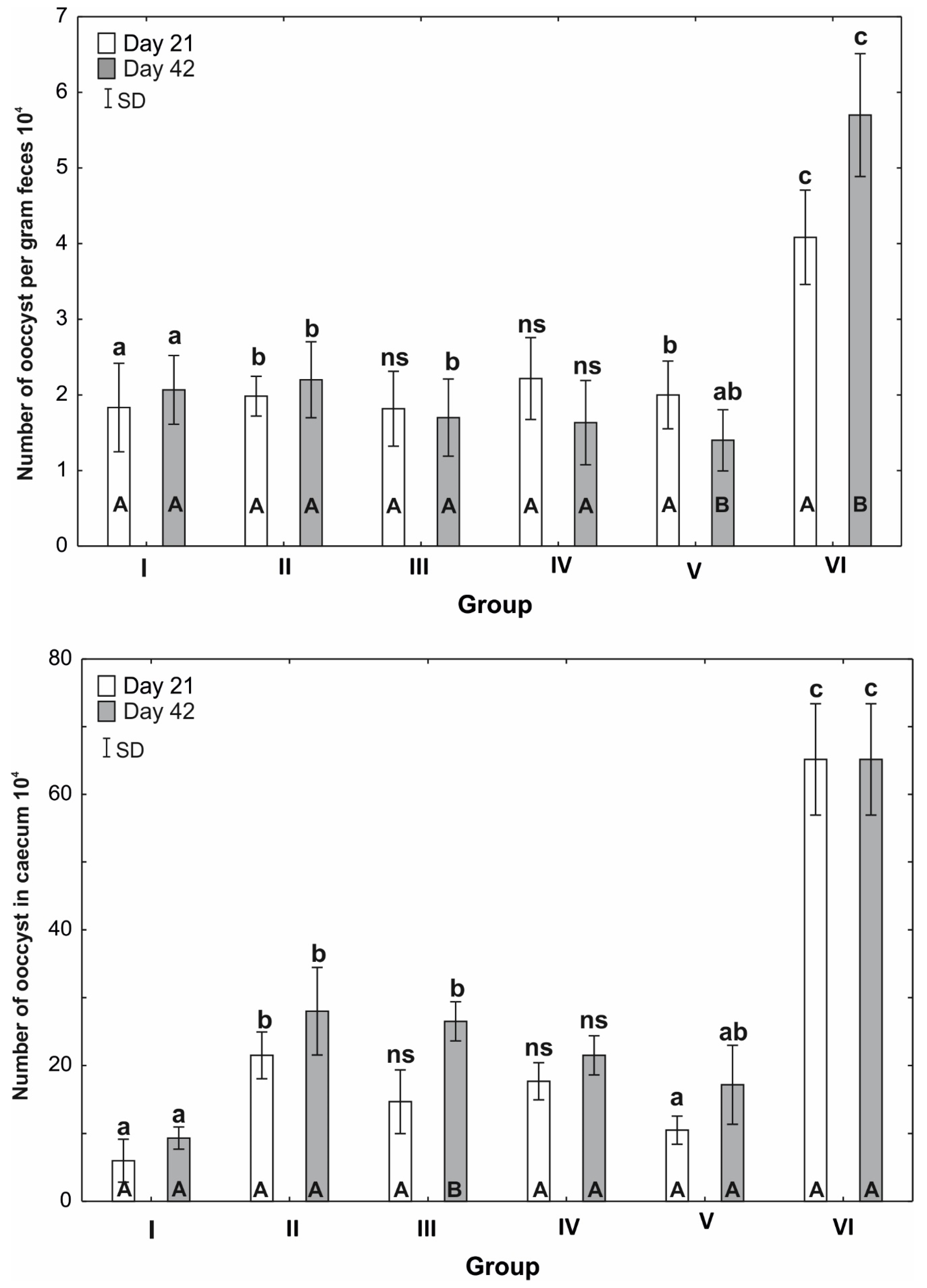
3.2. Numbers of Oocysts per Gram of Faeces
3.3. Numbers of oocysts in the Caecum
3.4. Scoring of Coccidial Intestinal Lesions
3.5. Evaluation of Gastrointestinal Permeability
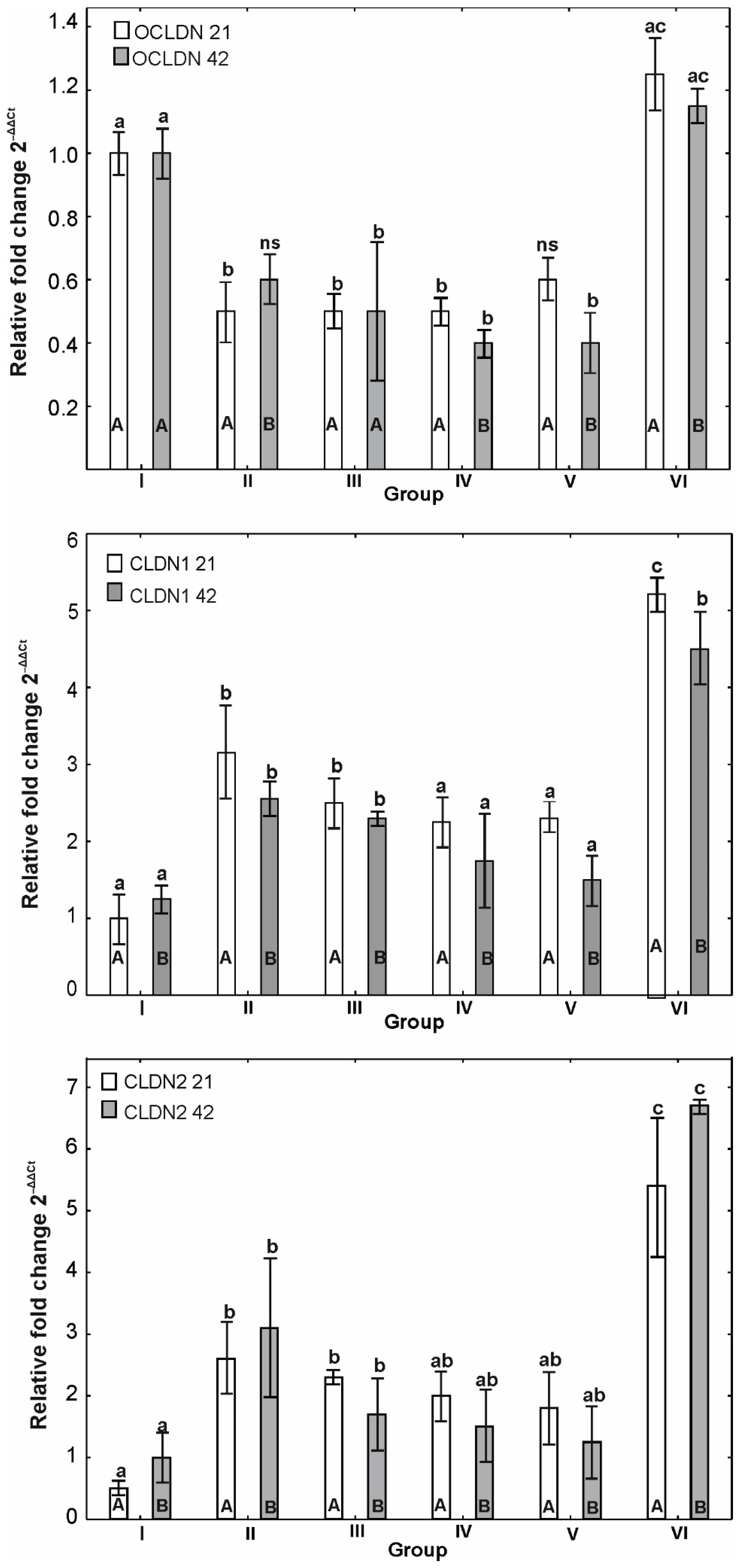
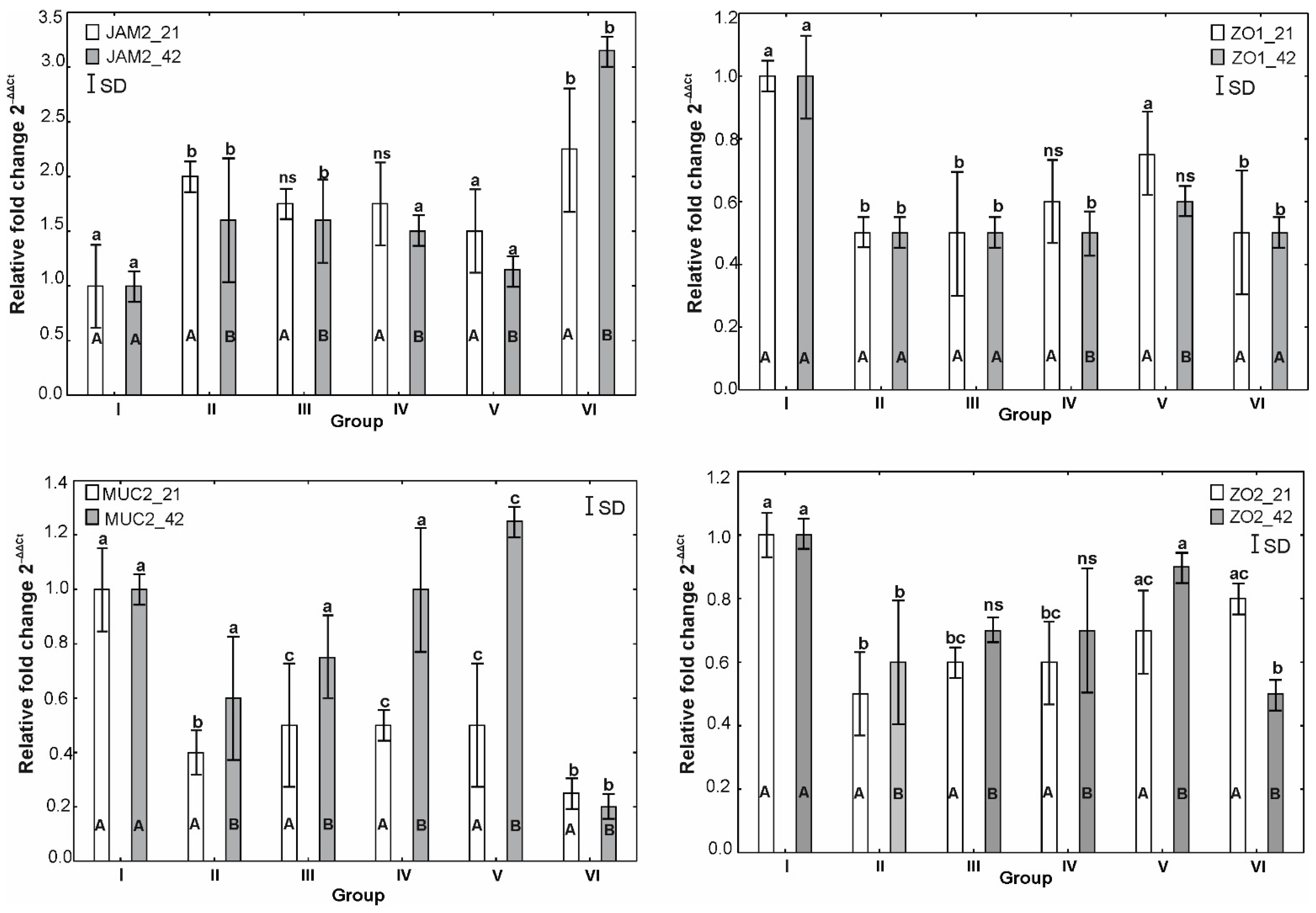
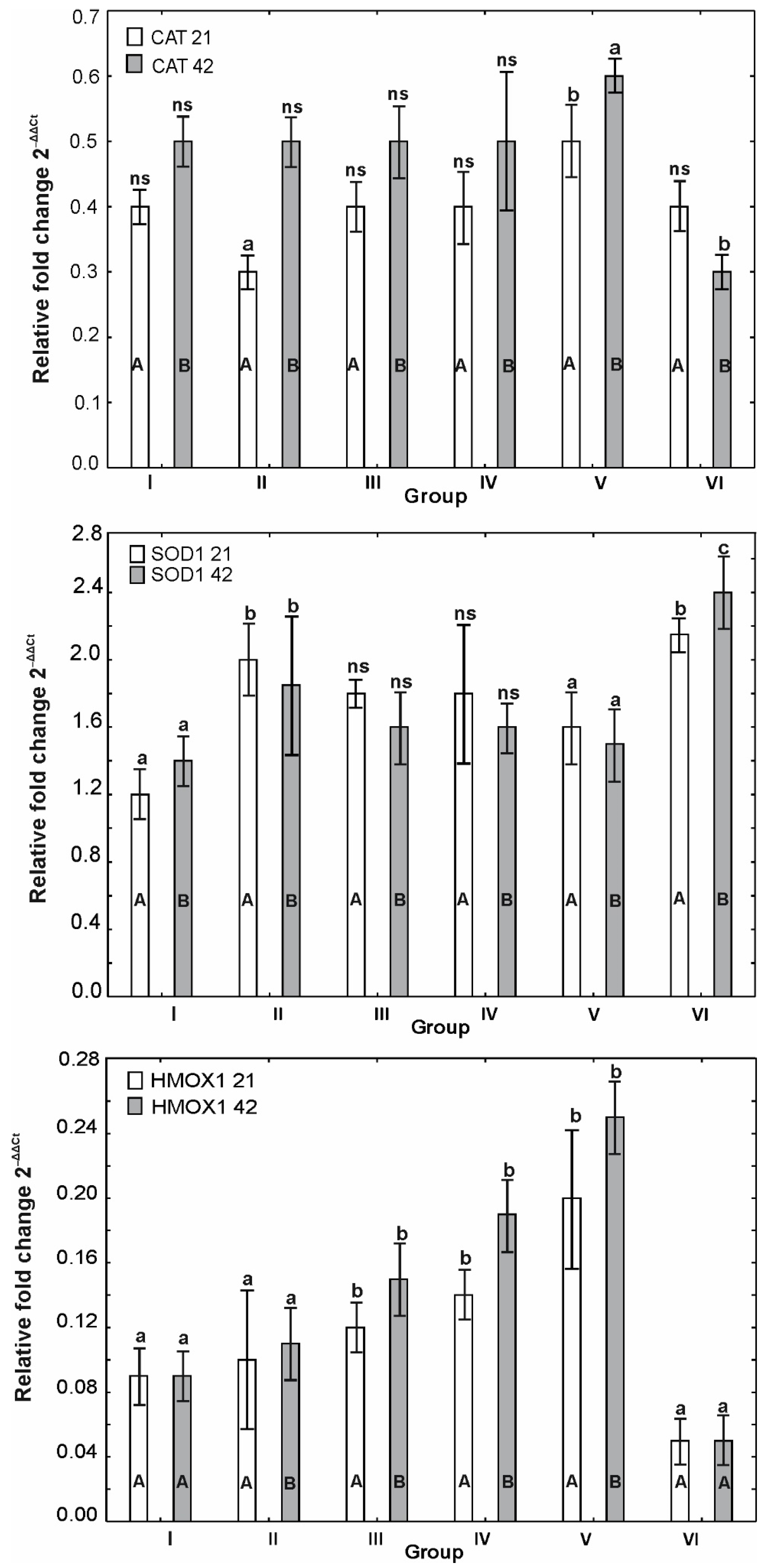
3.6. mRNA Expression of OCLDN, CLDN1, CLDN2, MUC2, ZO1, ZO2, JAM2, CAT, SOD1 and HMOX1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Quraishy, S.; Abdel-Baki, A.S.; Dkhil, M.A. Eimeria tenella infection among broiler chicks Gallus domesticus in Riyadh city, Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2009, 21, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attree, E.; Sanchez-Arsuaga, G.; Jones, M.; Xia, D.; Marugan-Hernandez, V.; Blake, D.; Tomley, F. Controlling the causative agents of coccidiosis in domestic chickens; an eye on the past and considerations for the future. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2021, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeurissen, S.H.; Janse, E.M.; Vermeulen, A.N.; Vervelde, L. Eimeria tenella infections in chickens: Aspects of host-parasite: Interaction. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 54, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, S.E.; Nolan, M.J.; Harman, K.; Boulton, K.; Hume, D.A.; Tomley, F.M.; Stabler, R.A.; Blake, D.P. Effects of Eimeria tenella infection on chicken caecal microbiome diversity, exploring variation associated with severity of pathology. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madlala, T.; Okpeku, M.; Adeleke, M.A. Understanding the interactions between Eimeria infection and gut microbiota, towards the control of chicken coccidiosis: A review. Parasite 2021, 28, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.H.S.; Hatabu, T. Eimeria tenella infection modulates the expression levels of intestinal epithelial barrier-related genes in chicken. J. Environ. Sci. Sustain. Soc. 2021, 10, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.H.S.; Matsubayashi, M.; Tsuji, N.; Hatabu, T. Relationship between Eimeria tenella associated-early clinical signs and molecular changes in the intestinal barrier function. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2021, 240, 110321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, P.Y.; Choi, J.; Tompkins, Y.; Lillehoj, H.; Kim, W. Impacts of increasing challenge with Eimeria maxima on the growth performance and gene expression of biomarkers associated with intestinal integrity and nutrient transporters. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Miska, K.B.; Fetterer, R.H.; Jenkins, M.C.; Wong, E.A. Expression of digestive enzymes and nutrient transporters in Eimeria-challenged broilers. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 150, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiss, M.M.; Harris, N.L. Interactions Between the Intestinal Microbiome and Helminth Parasites. Parasite. Immunol. 2016, 38, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, P.Y.; Yadav, S.; Castro, F.; Tompkins, Y.H.; Fuller, A.L.; Kim, W.K. Graded Eimeria challenge linearly regulated growth performance, dynamic change of gastrointestinal permeability, apparent ileal digestibility, intestinal morphology, and tight junctions of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4203–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Horng, Y.B.; Chen, W.J.; Hua, K.F.; Dybus, A.; Yu, Y.H. Effect of fermented products produced by Bacillus licheniformis on the growth performance and cecal microbial community of broilers under coccidial challenge. Animals 2021, 11, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatoba, A.J.; Adeleke, M.A. Diagnosis and control of chicken coccidiosis: A recent update. J. Parasit. Dis. 2018, 42, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannenas, I.; Florou-Paneri, P.; Papazahariadou, M.; Christaki, E.; Botsoglou, N.A.; Spais, A.B. Effect of dietary supplementation with oregano essential oil on performance of broilers after experimental infection with Eimeria tenella. Arch. Tierernahr. 2003, 57, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Dantán-González, E. Control of avian coccidiosis: Future and present natural alternatives. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 430610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthamilselvan, T.; Kuo, T.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Yang, W.C. Herbal remedies for coccidiosis control: A review of plants, compounds, and anticoccidial actions. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 2657981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohsin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, G. Effect of probiotics on the performance and intestinal health of broiler chickens infected with Eimeria tenella. Vaccines 2022, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsbeha, A.T.; Hailu, T.G. The impact of Effective Microorganisms (EM) on egg quality and laying performance of chickens. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 8895717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esatu, W.; Adey, S.; Dessie, T. Effect of effective microorganisms on growth parameters and serum cholesterol levels in broilers. Afr. J. Agric. Res 2011, 6, 3841–3846. [Google Scholar]
- Jwher, D.M.T.; Abd, S.K.; Mohammad, A.G. The study of using effective microorganisms (EM) on health and performance of broiler chicks. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 27, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Das, R.; Oak, S.; Mishra, P. Probiotics (Direct-Fed Microbials) in poultry nutrition and their effects on nutrient utilization, growth and laying performance, and gut health: A ystematic review. Animals 2020, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, A.M.; Ibrahim, N.S.; Shehata, A.M.; Mohamed, N.G.; Abdel-Moneim, A.M.E. Impact of multistrain probiotic, citric acid, garlic powder or their combinations on performance, ileal histomorphometry, microbial enumeration and humoral immunity of broiler chickens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronikashvili, T.G.; Urushadze, T.F.; Eprikashvili, L.G.; Kordzakhia, T.N.; Zautashvili, M.G.; Pirtzkhalava, N.V.; Dzagania, M.A. Natural zeolites in poultry farming. Ann Agra Sci. 2014, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shariatmadari, F. The application of zeolite in poultry production. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2008, 64, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlazło, Ł.; Nowakowicz-Dębek, B.; Kapica, J.; Kwiecień, M.; Pawlak, H. Removal of ammonia from poultry manure by aluminosilicates. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzyniak, A.; Kapica, M.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Szewerniak, R.; Olejarska, A.; Jarosz, Ł. Effect of feeding Transcarpathian Zeolite on gastrointestinal morphology and function in broiler chickens. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2017, 19, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olver, M.D. The effect of feeding clinoptilolite (zeolite) to laying hens. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 1983, 13, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.J.; Wang, L.C.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, T. Effects of clinoptilolite and modified clinoptilolite on the growth performance, intestinal microflora, and gut parameters of broilers. Poult Sci. 2013, 92, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.J.; Zhou, Y.M.; Wu, Y.N.; Wang, T. Intestinal development and function of broiler chickens on diets supplemented with clinoptilolite. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mumpton, F.A.; Fishman, P.H. The Application of Natural Zeolites in Animal Science and Aquaculture. J. Anim. Sci. 1977, 45, 1188–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, D.S.; Kyriakis, C.S.; Alexopoulos, C.; Tzika, E.D.; Polizopoulou, Z.S.; Kyriakis, S.C. A field study on the effect of the dietary use of a clinoptilolite-rich tuff, alone or in combination with certain antimicrobials, on the health status and performance of weaned, growing and finishing pigs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2004, 76, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khambualai, O.; Ruttanavut, J.; Kitabatake, M.; Goto, H.; Erikawa, T.; Yamauchi, K. Effects of dietary natural zeolite including plant extract on growth performance and intestinal histology in Aigamo ducks. Br. Poult. Sci. 2009, 50, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serek, P.; Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M. The effect of bacterial infections, probiotics and zonulin on intestinal barrier integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z. Effects of the dietary probiotic, Enterococcus faecium NCIMB11181, on the intestinal barrier and system immune status in Escherichia coli O78-challenged broiler chickens. Probiotics Antimicro. Prot. 2019, 11, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.H.; Teng, P.Y.; Lee, T.T.; Yu, B. Effects of multi-strain probiotic supplementation on intestinal microbiota, tight junctions, and inflammation in young broiler chickens challenged with Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcala-Canto, Y.; Gutierrez-Olvera, L.; Gutierrez-Olvera, C.; Sumano-Lopez, H. Effects of clinoptilolite on Eimeria spp. infection in sheep. Small Rum. Res. 2011, 100, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviagen. Ross Broiler Management Handbook; Aviagen: Newbridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hauck, R.; Pacheco, W.J. Detection of coccidia oocysts in litter and feces of broilers in a floor pen trial. J Parasitol. 2021, 107, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raether, W.; Hofmann, J.; Uphoff, M.; Eckert, H.S. In vitro cultivation of avian Eimeria species: Eimeria tenella. In Biotechnology. Guidelines on Techniques in Coccidiosis Research; Eckert, J., Braun, R., Shirley, M.W., Coudert, P., Eds.; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1995; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.A.; Hong, S.; Chung, Y.; Kim, O. Sensitive and specific identification by polymerase chain reaction of Eimeria tenella and Eimeria maxima, important protozoan pathogens in laboratory avian facilities. Lab. Anim. 2011, 27, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirley, M.W. Eimeria and Isospora. In Biotechnology, Guidelines on Techniques in Coccidiosis Research; Eckert, J., Braun, R., Shirley, M.W., Coudert, P., Eds.; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1995; pp. 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, J.N. Coccidiosis: Oocyst-counting technique for coccidiostat evaluation. Exp. Parasitol. 1970, 28, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Reid, W.M. Anticoccidial drugs: Lesion scoring techniques in battery and floor-pen experiments with chickens. Exp. Parasitol. 1970, 28, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttappan, V.A.; Berghman, L.R.; Vicuña, E.A.; Latorre, J.D.; Menconi, A.; Wolchok, J.D.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Faulkner, O.B.; Tellez, G.I.; Hargis, B.M.; et al. Poultry enteric inflammation model with dextran sodium sulfate mediated chemical induction and feed restriction in broilers. Poult Sci. 2015, 94, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammers, A.; Wieland, W.H.; Kruijt, L.; Jansma, A.; Straetemans, T.; Schots, A.; den Hartog, G.; Parmentier, H.K. Successive immunoglobulin and cytokine expression in the small intestine of juvenile chicken. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, E.S.; Cotoner, C.A.; Camacho, C.P.; Bedmar, M.C.; Vicario, M. The intestinal barrier function and its involvement in digestive disease. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2015, 107, 686–696. [Google Scholar]
- Takiishi, T.; Fenero, C.; Câmara, N. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: Shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers 2017, 5, e1373208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umeda, K.; Matsui, T.; Nakayama, M.; Furuse, K.; Sasaki, H.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Establishment and characterization of cultured epithelial cells lacking expression of ZO-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44785–44794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: Implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macelline, S.P.; Wickramasuriya, S.S.; Cho, H.M.; Kim, E.; Shin, T.K.; Hong, J.S.; Kim, J.C.; Pluske, J.R.; Choi, H.J.; Hong, Y.G.; et al. Broilers fed a low protein diet supplemented with synthetic amino acids maintained growth performance and retained intestinal integrity while reducing nitrogen excretion when raised under poor sanitary conditions. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakphaichit, M.; Thanomwongwattana, S.; Phraephaisarn, C.; Sakamoto, N.; Keawsompong, S.; Nakayama, J.; Nitisinprasert, S. The effect of including Lactobacillus reuteri KUB-AC5 during post-hatch feeding on the growth and ileummicrobiota of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhong, H.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y. Effect of probiotics on the meat flavour and gut microbiota of chicken. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamprecht, M.; Bogner, S.; Steinbauer, K.; Schuetz, B.; Greilberger, J.F.; Leber, B.; Wagner, B.; Zinser, E.; Petek, T.; Wallner-Liebmann, S.; et al. Effects of zeolite supplementation on parameters of intestinal barrier integrity, inflammation, redoxbiology and performance in aerobically trained subjects. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavelić, K.; Hadzija, M.; Bedrica, L.; Pavelić, J.; Dikić, I.; Katić, M.; Kralj, M.; Bosnar, M.H.; Kapitanović, S.; Poljak-Blazi, M.; et al. Natural zeolite clinoptilolite: New adjuvant in anticancer therapy. J. Mol. Med. 2001, 78, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavelic, K.; Katic, M.; Sverko, V.; Marotti, T.; Bosnjak, B.; Balog, T.; Stojkovic, R.; Radacic, M.; Colic, M.; Poljak-Blazi, M. Immunostimulatory effect of natural clinoptilolite as a possible mechanism of its antimetastatic ability. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 128, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, A.; Turner, J.R. Cell biology of tight junction barrier regulation and mucosal disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.; Stenson, W.F.; Kunz-Jenkins, C.; Swanson, P.E.; Duncan, R.; Stanley, S.L., Jr. Entamoeba histolytica interactions with polarized human intestinal Caco-2 epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5112–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utech, M.; Ivanov, A.I.; Samarin, S.N.; Bruewer, M.; Turner, J.R.; Mrsny, R.J.; Parkos, C.A.; Nusrat, A. Mechanism of IFN-gamma-induced endocytosis of tight junction proteins: Myosin II-dependent vacuolarization of the apical plasma membrane. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5040–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mankertz, J.; Tavalali, S.; Schmitz, H.; Mankertz, A.; Riecken, E.O.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Expression from the human occludin promoter is affected by tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 2085–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasuriya, S.S.; Park, I.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.H.; Przybyszewski, C.; Gay, C.G.; van Oosterwijk, J.G.; Lillehoj, H.S. Oral delivery of Bacillus subtilis expressing chicken NK-2 peptide protects against Eimeria acervulina infection in broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 684818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, U.; Schuetz, A. Structural features of Tight-Junction proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, C.H.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Lillehoj, E.P. Intestinal immune responses to coccidiosis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.C.; Fetterer, R.H. Recent advances in biology and immunobiology of Eimeria species and in diagnosis and control of infection with these coccidian parasites of poultry. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poritz, L.S.; Harris, L.R., 3rd; Kelly, A.A.; Koltun, W.A. Increase in the tight junction protein claudin-1 in intestinal inflammation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahner, C.; Mitic, L.L.; Anderson, J.M. Heterogeneity in expression and subcellular localization of claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the rat liver, pancreas, and gut. Gastroenterol. 2001, 120, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Inatomi, S.; Maeda, T.; Osanai, M.; Uchiyama, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Wada, T.; Kojima, T.; Yokozaki, H.; et al. Tight junction proteins claudin-2 and -12 are critical for vitamin D-dependent Ca2+ absorption between enterocytes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin and its regulation of intestinal barrier function: The biological door to inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasano, A. Regulation of intercellular tight junctions by zonula occludens toxin and its eukaryotic analogue zonulin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 915, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarpour, H.R.; Chamani, M.; Rahimi, G.; Sadeghi, A.A.; Qujeq, D. The Bacillus subtilis and lactic acid bacteria probiotics influences intestinal mucin gene expression, histomorphology and growth performance in broilers. Asian. Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Tellez, G.; Richards, J.D.; Escobar, J. Identification of potential biomarkers for gut barrier failure in broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Li, H.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y. Effects of antibacterial peptide combinations on growth performance, intestinal health, and immune function of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6481–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, D.R.; Michail, S.; Wei, S.; McDougall, L.; Hollingsworth, M.A. Probiotics inhibit enteropathogenic E. coli adherence in vitro by inducing intestinal mucin gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, 941–950. [Google Scholar]
- Mattar, A.F.; Teitelbaum, D.H.; Drongowski, R.A.; Yongy, F.; Harmon, C.M.; Coran, A.G. Probiotics up-regulate MUC-2 mucin gene expression in a Caco-2 cell-culture model. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2002, 18, 586–590. [Google Scholar]
- Surai, P.F.; Kochish, I.I.; Fisinin, V.I.; Kidd, M.T. Antioxidant defence systems and oxidative stress in poultry biology: An update. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Çam, Y.; Atasever, A.; Eraslan, G.; Kibar, M.; Atalay, Ö.; Beyaz, L.; Inci, A.; Liman, B.C. Eimeria stiedae: Experimental infection in rabbits and the effect of treatment with toltrazuril and ivermectin. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzales, S.; Perez, M.J.; Perazzo, J.C.; Tomaro, M.L. Antioxidant role of heme oxygenase-1 in prehepatic portal hypertensive rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 4149–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minatel, L.; Carfagnini, J.C. Copper deficiency and immune response in ruminants. Nutr. Res. 2000, 20, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahallawy, E.K.; Fehaid, A.; El-Shewehy, D.M.M.; Ramez, A.M.; Alkhaldi, A.A.M.; Mady, R.; Nasr, N.E.; Arafat, N.; Hassanen, E.A.A.; Alsharif, K.F.; et al. S-methylcysteine ameliorates the intestinal damage induced by Eimeria tenella infection via targeting oxidative stress and inflammatory modulators. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 754991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K. Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2007, 2, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, J.G.; del Carmen, S.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V.; Sesma, F.; Langella, P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Watterlot, L.; Perdigon, G.; de Moreno de LeBlanc, A. Use of superoxide dismutase and catalase producing lactic acid bacteria in TNBS induced Crohn’s disease in mice. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 151, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Lin, W.C.; Lee, T.T. Potential crosstalk of oxidative stress and immune response in poultry through phytochemicals—A review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalloul, R.A.; Lillehoj, H.S. Poultry coccidiosis: Recent advancements in control measures and vaccine development. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2006, 5, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, R.C.; Luns, F.D.; Beletti, M.E.; Assis, R.L.; Nasser, N.M.; Faria, E.S.; Cury, M.C. Histomorphometry and macroscopic intestinal lesions in broilers infected with Eimeria acervulina. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalloul, R.A.; Lillehoj, H.S. Recent advances in immunomodulation and vaccination strategies against coccidiosis. Avian Dis. 2005, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Sredkova, V.; Marasheva, V. Effect of dietary inclusion of probiotic on chickens performance and some blood indices. Biotech. Anim. Husb. 2009, 25, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Ingale, S.L.; Kim, Y.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, K.H.; Lohakare, J.D.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, H.S.; Ryu, M.H.; Kwon, I.K.; et al. Effect of supplementation of Bacillus subtilis LS 1-2 to broiler diets on growth performance, nutrient retention, caecal microbiology and small intestinal morphology. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, S.; Kathariou, S.; Grimes, J.L. Siletzky, R.M. Effect of direct-fed microbials on performance and Clostridium perfringens colonization of turkey poults. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2656–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfenden, R.E.; Pumford, N.R.; Morgan, M.J.; Shivaramaiah, S.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Pixley, C.M.; Green, J.; Tellez, G.; Hargis, B.M. Evaluation of selected direct-fed microbial candidates on live performance and Salmonella reduction in commercial turkey brooding houses. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Tan, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.M.; Gao, F.; Zhou, G.H. Effects of dietary supplementation with the combination of zeolite and attapulgite on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, secretion of digestive enzymes and intestinal health in broiler chickens. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannenas, I.; Papadopoulos, E.; Tsalie, E.; Triantafillou, E.; Henikl, S.; Teichmann, K.; Tontis, D. Assesment of dietary supplementation with probiotics on performance, intestinal morphology and microflora of chickens infected with Eimeria tenella. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 188, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannenas, I.; Tsalie, E.; Triantafillou, E.; Hessenberger, S.; Teichmann, K.; Mohnl, M.; Tontis, D. Assessment of probiotics supplementation via feed or water on the growth performance, intestinal morphology and microflora of chickens after experimental infection with Eimeria acervulina, Eimeria maxima and Eimeria tenella. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmerman, H.M.; Veldman, A.; van den Elsen, E.; Rombouts, F.M.; Beynen, A.C. Mortality and growth performance of broilers given drinking water supplemented with chicken-specific probiotics. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Wong, M.H.; Thelin, A.; Hansson, L.; Falk, P.G.; Gordon, J.I. Molecular analysis of commensal host-microbial relationships in the intestine. Science 2001, 291, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slamova, R.; Trckova, M.; Vondruskova, H.; Zraly, Z.; Pavlik, I. Clay minerals in animal nutrition. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, X. Effects of dietary supplementation with palygorskite on intestinal integrity in weaned piglets. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 86, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Dalloul, R.A.; Park, D.W.; Hong, Y.H.; Lin, J.J. Influence of Pediococcus-based probiotic on coccidiosis in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, T.L.; Watkins, K.L.; Southern, L.L. Interactive effects of sodium zeolite A (Ethacal) and monensin in uninfected and Eimeria acervulina-infected chicks. Poult. Sci. 1990, 69, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesic, V.; Aleksic, Z.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Knezevic, M.; Ilic, T.; Resanovic, R. The influence of a diet of mixed feed containing zeolite on the course of cecal coccidiosis in broilers. Acta Vet. 2003, 53, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Trckova, M.; Matlova, L.; Dvorska, L.; Pavlik, I. Kaolin, bentonite and zeolites as feed supplements for animals: Health advantages and risks. Vet. Med. 2004, 49, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.P.; Sasai, K.; Gaafar, S.M.; Smothers, C.D. Effects of different levels of oocyst inocula of Eimeria acervulina, E. tenella, and E maxima on plasma constituents, packed cell volume, lesion scores, and performance in chickens. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutter, F.; Werling, D.; Kim, S.; Pastor-Fernández, I.; Marugán-Hernández, V.; Tomley, F.M.; Blake, D.P. Impact of Eimeria tenella oocyst dose on parasite replication, lesion score and cytokine transcription in the caeca in three breeds of commercial layer chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 640041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apajalahti, J.; Kettunen, A.; Graham, H. Characteristics of the gastrointestinal microbial communities, with special reference to the chicken. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2004, 60, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, F.; Hinton, M.; Van Gils, B. Dietary mannan-oligosaccharides and their effect on chicken caecal microflora in relation to Salmonella enteritidis colonization. Avian Pathol. 2002, 31, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mountzouris, K.C.; Paraskevas, V.; Tsirtsikos, P.; Palamidi, I.; Steiner, T.; Schatzmayr, G.; Fegeros, K. Assessment of a phytogenic feed addtive effect on broiler growth performance, nutrient digestibility and caecal microflora composition. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2011, 168, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, M.R. Exogenous enzymes in monogastric nutrition—Their current value and future benefits. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2000, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
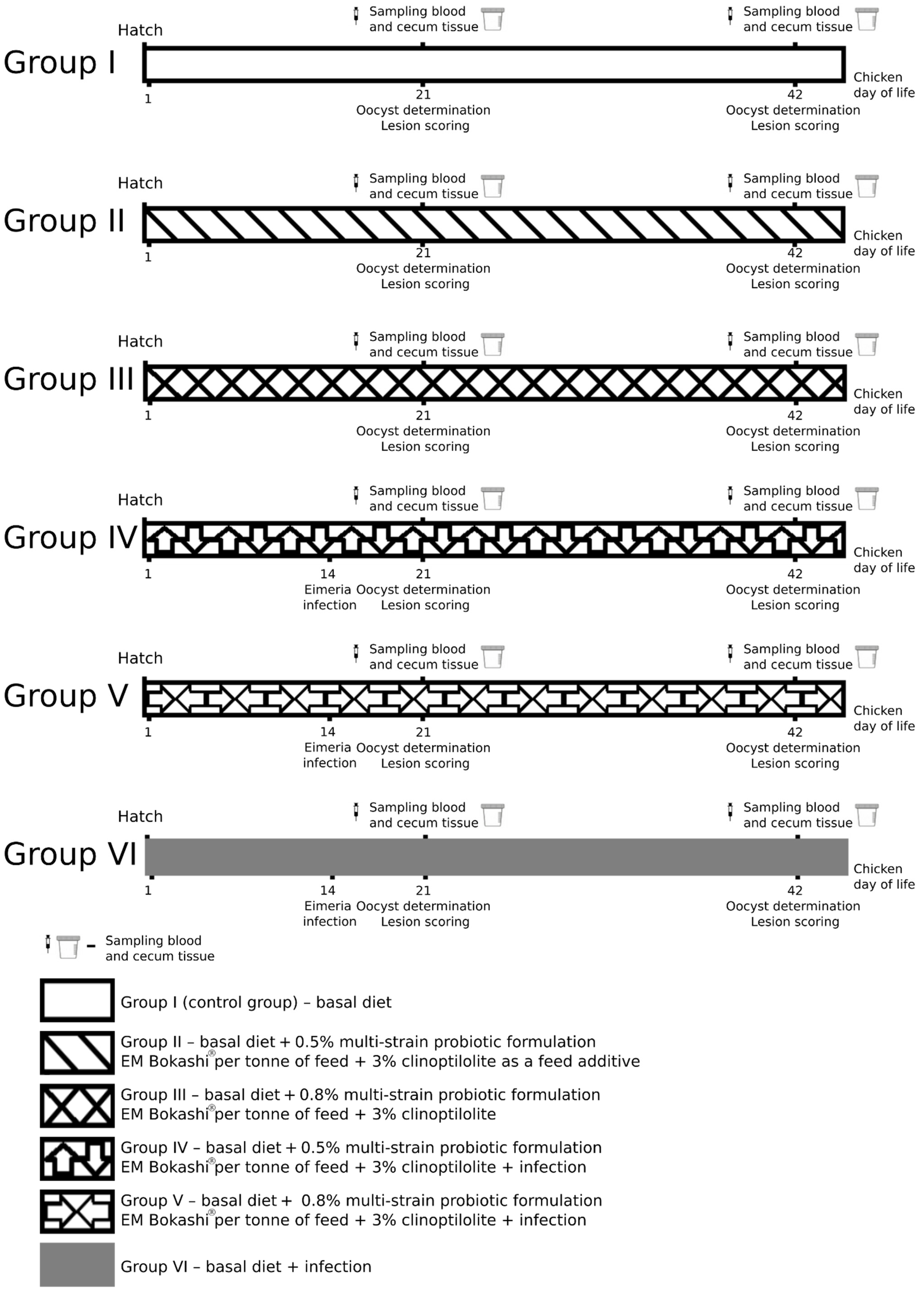


| Group | Basal Diet | Addition to Basal Diet | Infection 14 Days of Age | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Strain Probiotic Formulation EM Bokashi® | Clinoptilolite | |||
| I | + | - | - | - |
| II | + | 0.5% | 3% | - |
| III | + | 0.8% | 3% | - |
| IV | + | 0.5% | 3% | 1.7 × 104 E. tenella * |
| V | + | 0.8% | 3% | 1.7 × 104 E. tenella * |
| VI | + | - | - | 1.7 × 104 E. tenella * |
| Percentage % | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Starter (Days 1–21) | Grower (Days 22–35) | Finisher (Days 36–42) |
| Wheat (group I, VI) | 35.02 | 40.00 | 49.73 |
| Wheat (group II, IV) | 31.52 | 36.50 | 46.23 |
| Wheat (group III, V) | 31.22 | 36.20 | 45.93 |
| Soybean meal | 34.02 | 29.40 | 22.88 |
| Maize | 22.54 | 17.21 | 10.03 |
| Rapeseed oil | 2.01 | 2.50 | 4.11 |
| Lard | 2.00 | 2.97 | 3.50 |
| Rapeseed meal | 1.00 | 5.00 | 7.00 |
| Premix without coccidiostat 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Monocalcium phosphate | 0.72 | 0.55 | 0.41 |
| Calcium carbonate | 0.62 | 0.44 | 0.26 |
| L-Methionine | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.18 |
| L-Lysine | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.20 |
| Sodium chloride | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| NaHCO3 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
| Threonine | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| L-valine | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| Optiphos (0.01%) 2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| AMEN | 12.47 | 12.77 | 13.39 |
| Crude protein | 22.7 | 21.94 | 20.14 |
| Crude fat | 6.02 | 7.36 | 9.33 |
| P available | 0.48 | 0.43 | 0.4 |
| Ca | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.79 |
| Na | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| Cl | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| Lys dig. | 1.25 | 1.15 | 1.05 |
| Met dig. | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.46 |
| Thr dig. | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.7 |
| Val dig | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.79 |
| Microbial Composition | Strain Number | Content per Gram of Product | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Y200007 | 5 × 104 CFU/g |
| 2. | Lactobacillus casei | ATCC 7469 | 5 × 108 CFU/g |
| 3. | Lactobacillus plantarum | ATCC 8014 | 5 × 108 CFU/g |
| 4. | Enterococcus faecalis | UC-100 (CGMCC No.1.0130) | 2.5 × 106 CFU/g |
| 5. | Enterococcus faecium | NCIMB SF68 | 5 × 109 CFU/g |
| Item | Group I | Group II | Group III | Group IV | Group V | Group VI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality rate (%) | 8.00% (8 birds) | 6.00% (6 birds) | 5.00% (5 birds) | 5.00% (5 birds) | 4.00% (4 birds) | 11.00% (11 birds) |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | Diarrhoea lasting 5–6 days and remitting spontaneously (n = 16). | Diarrhoea lasting 2 days and remitting spontaneously (n = 22). | None | Diarrhoea with mucus and blood lasting 6 days and remitting spontaneously (n = 45). | Diarrhoea with mucus and blood lasting 4 days and remitting spontaneously (n = 52). | Diarrhoea with mucus and blood lasting 7 days (n = 18) andbloody diarrhoea (n = 39). |
| Respiratory symptoms | Cough n = 15 | - | Cough n = 15 | Cough n = 8 | - | - |
| Sneezing n = 23 | Sneezing n = 25 | Sneezing n = 26 | Sneezing n = 16 | Sneezing n = 8 | Sneezing n = 26 | |
| Conjunctivitis n = 36 | Conjunctivitis n = 28 | Conjunctivitis n = 42 | Conjunctivitis n = 31 | Conjunctivitis n = 11 | Conjunctivitis n = 38 | |
| Anatomopathological changes in dead birds | Intestinal hyperaemia, petechiae in the mucosa of the small intestine, and catarrhal enteritis. | Intestinal hyperaemia petechiae in the mucosa of the small intestine. | Intestinal hyperaemia petechiae in the mucosa of the small intestine. | Intestinal hyperaemia, isolated pinpoint petechiae in the mucosa of the small intestine, and catarrhal enteritis. | Intestinal hyperaemia, isolated pinpoint petechiae in the mucosa of the small intestine, and catarrhal enteritis. | Intestinal hyperaemia, isolated pinpoint petechiae in the mucosa of the small intestine, andhaemorrhagic enteritis. |
| Starter (0–10) | Grower (11–24) | Finisher (25–42) | Total (0–42) | |||||||||||
| Group | Addition | Infection | BWG | FI | FCR | BWG | FI | FCR | BWG | FI | FCR | BWG | FI | FCR |
| I | - | - | 206 | 222 | 1.08 | 1170 | 1546 | 1.31 | 1666 | 2593 | 1.53 | 3060 bc | 4384 | 1.43 |
| II | 0.5%X1 + 3%X2 | - | 214 | 222 | 1.04 | 1198 | 1621 | 1.33 | 1764 | 2689 | 1.56 | 3077 bc | 4518 | 1.45 |
| III | 0.8%X1 + 3%X2 | - | 213 | 229 | 1.06 | 1226 | 1627 | 1.35 | 1807 | 2873 | 1.50 | 3291a | 4794 | 1.44 |
| IV | 0.5%X1 + 3%X2 | + | 215 | 229 | 1.05 | 1235 | 1647 | 1.34 | 1787 | 2808 | 1.57 | 3237 a | 4684 | 1.45 |
| V | 0.8%X1 + 3%X2 | + | 211 | 230 | 1.09 | 1192 | 1606 | 1.38 | 1787 | 2814 | 1.54 | 3143 ab | 4650 | 1.45 |
| VI | - | + | 202 | 208 | 1.03 | 1163 | 1502 | 1.33 | 1596 | 2631 | 1.62 | 2965 c | 4235 | 1.47 |
| SEM | 1.720 | 2.079 | 0.006 | 10.610 | 13.594 | 0.006 | 20.031 | 24.778 | 0.010 | 24.873 | 0.006 | 0.222 | ||
| p value | 0.1931 | 0.014 | 0.0568 | 0.2954 | 0.0119 | 0.0711 | 0.0093 | 0.002 | 0.0157 | 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.6452 | ||
| Starter (0–10) | Grower (11–24) | Finisher (25–42) | Total (0–42) | |||||||||||
| Addition | Infection | BWG | FI | FCR | BWG | FI | FCR | BWG | FI | FCR | BWG | FI | FCR | |
| Main effects | ||||||||||||||
| - | 204 b | 215 b | 1.06 | 1167 | 1524 b | 1.32 b | 1631 b | 2612 b | 1.57 a | 3013 | 4309 b | 1.45 | ||
| 0.5%X1 + 3%X2 | 215 a | 226 a | 1.04 | 1216 | 1634 a | 1.34 ab | 1776 a | 2749 a | 1.57 a | 3157 | 4601a | 1.45 | ||
| 0.8%X1 + 3%X2 | 212 ab | 229 a | 1.07 | 1209 | 1617 a | 1.36 a | 1797 a | 2843 a | 1.52 b | 3217 | 4722 a | 1.45 | ||
| - | 211 | 224 | 1.06 | 1198 | 1598 | 1.33 | 1746 | 2718 | 1.53b | 3143 | 4566 | 1.44 | ||
| + | 210 | 222 | 1.06 | 1197 | 1585 | 1.35 | 1723 | 2751 | 1.57 a | 3115 | 4523 | 1.46 | ||
| p value | ||||||||||||||
| Addition | 0.039 | 0.0105 | 0.1721 | 0.1337 | 0.0017 | 0.0153 | 0.001 | 0.0004 | 0.0397 | 0.0009 | <0.0001 | 0.9778 | ||
| Infection | 0.6695 | 0.5561 | 0.9414 | 0.9457 | 0.6029 | 0.2876 | 0.5356 | 0.452 | 0.0197 | 0.5137 | 0.5359 | 0.2244 | ||
| Addition × Infection | 0.7893 | 0.0663 | 0.1374 | 0.3738 | 0.509 | 0.666 | 0.5786 | 0.242 | 0.1795 | 0.0085 | 0.106 | 0.3972 | ||
| RNA Target | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | Source of Reference | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLDN1 | For Rev | 5′- TGGAGGATGACCAGGTGAAGA -3′ 5′- CGAGCCACTCTGTTGCCATA -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | NM_001013611.2 |
| CLDN2 | For Rev | 5′- CCTGCTCACCCTCATTGGAG -3′ 5′- GCTGAACTCACTCTTGGGCT -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | NM_001277622.1 |
| OCLDN | For Rev | 5′- ACGGCAGCACCTACCTCAA -3′ 5′- GGCGAAGAAGCAGATGAG -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | NM_205128.1 |
| ZO1 | For Rev | 5′- CAACTGGTGTGGGTTTCTGAA -3′ 5′- TCACTACCAGGAGCTGAGAGGTAA -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | XM_015278981.2 |
| ZO2 | For Rev | 5′- ATCCAAGAAGGCACCTCAGC -3′ 5′- CATCCTCCCGAACAATGC -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | NM_204918.1 |
| JAM2 | For Rev | 5′- AGCCTCAAATGGGATTGGATT -3′ 5′- CATCAACTTGCATTCGCTTCA -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | NM_001006257.1 |
| MUC2 | For Rev | 5′- ATGCGATGTTAACACAGGACTC -3′ 5′- GTGGAGCACAGCAGACTTTG -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | JX284122.1 |
| SOD1 | For Rev | 5′- ATTACCGGCTTGTCTGATGG -3′ 5′- CCTCCCTTTGCAGTCACATT -3′ | Wickramasuriya et al., 2021 | NM205064.1 |
| CAT | For Rev | 5′- ACTGCAAGGCGAAAGTGTTT -3′ 5′- GGCTATGGATGAAGGATGGA -3′ | Wickramasuriya et al., 2021 | NM001031215.1 |
| HMOX1 | For Rev | 5′- CTGGAGAAGGGTTGGCTTTCT -3′ 5′- GAAGCTCTGCCTTTGGCTGTA -3′ | Wickramasuriya et al., 2021 | NM205344 |
| GAPDH a | For Rev | 5′- CCTCTCTGGCAAAGTCCAAG -3′ 5′- GGTCACGCTCCTGGAAGATA -3′ | Teng et al., 2021 | NM_204305.1 |
| Part of Intestine | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duodenum (I) | Jejunum (II) | Ileum (III) | Ceca and Rectum (IV) | |||||
| Day of Life | ||||||||
| Group | 21 | 42 | 21 | 42 | 21 | 42 | 21 | 42 |
| I | 0.17 ±0.41 A | 0.33 ±0.52 | 0.50 ±0.55 | 0.67 ±0.52 | 0.33 ±0.52 | 1.83 ±0.75 | 1.00 ±0.63 B | 2.17 ±0.75 |
| II | 0.33 ±0.52 | 0.33 ±0.52 A | 0.50 ±0.84 | 0.50 ±0.84 | 1.17 ±0.75 | 1.17 ±0.75 | 1.67 ±0.52 | 1.67 ±0.52 B |
| III | 0.17 ±0.41 | 0.17 ±0.41 A | 0.33 ±0.52 | 0.33 ±0.52 | 0.83 ±0.41 | 0.83 ±0.41 | 1.00 ±0.63 | 1.00 ±0.63 Ba |
| IV | 0.33 ±0.52 | 0.33±0.52 a | 0.17 ±0.41 A | 0.17 ±0.41 | 1.17 ±0.75 | 1.17 ±0.75 | 1.50 ±0.55 B | 1.50 ±0.55 Ba |
| V | 0.17 ±0.41 | 0.17 ±0.41 | 0.17 ±0.41 | 0.17 ±0.41 | 0.83 ±0.75 | 0.83 ±0.75 | 0.83 ±0.75 a | 0.83 ±0.75 b |
| VI | 0.33 ±0.52 A | 0.17 ±0.41 A | 0.67 ±0.82 A | 0.33 ±0.52 A | 1.50 ±0.55 | 2.00 ±0.63 | 2.67 ±0.82 Bb | 3.00 ±0.63 B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciszewski, A.; Jarosz, Ł.S.; Kalinowski, M.; Marek, A.; Grądzki, Z.; Grabowski, S.; Hejdysz, M.; Nowaczewski, S.; Rysiak, A. Influence of Effective Microorganisms and Clinoptilolite on Gut Barrier Function, Intestinal Health and Performance of Broiler Chickens during Induced Eimeria tenella Infection. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122176
Ciszewski A, Jarosz ŁS, Kalinowski M, Marek A, Grądzki Z, Grabowski S, Hejdysz M, Nowaczewski S, Rysiak A. Influence of Effective Microorganisms and Clinoptilolite on Gut Barrier Function, Intestinal Health and Performance of Broiler Chickens during Induced Eimeria tenella Infection. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122176
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiszewski, Artur, Łukasz S. Jarosz, Marcin Kalinowski, Agnieszka Marek, Zbigniew Grądzki, Sebastian Grabowski, Marcin Hejdysz, Sebastian Nowaczewski, and Anna Rysiak. 2022. "Influence of Effective Microorganisms and Clinoptilolite on Gut Barrier Function, Intestinal Health and Performance of Broiler Chickens during Induced Eimeria tenella Infection" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122176
APA StyleCiszewski, A., Jarosz, Ł. S., Kalinowski, M., Marek, A., Grądzki, Z., Grabowski, S., Hejdysz, M., Nowaczewski, S., & Rysiak, A. (2022). Influence of Effective Microorganisms and Clinoptilolite on Gut Barrier Function, Intestinal Health and Performance of Broiler Chickens during Induced Eimeria tenella Infection. Agriculture, 12(12), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122176






