Effect of Surface and Subsurface Drip Irrigation with Treated Wastewater on Soil and Water Productivity of Okra (Abemoschus esculentus) Crop in Semi-Arid Region of Tunisia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Experimental Setup
2.2. Field Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Irrigation Water Quality Assessment
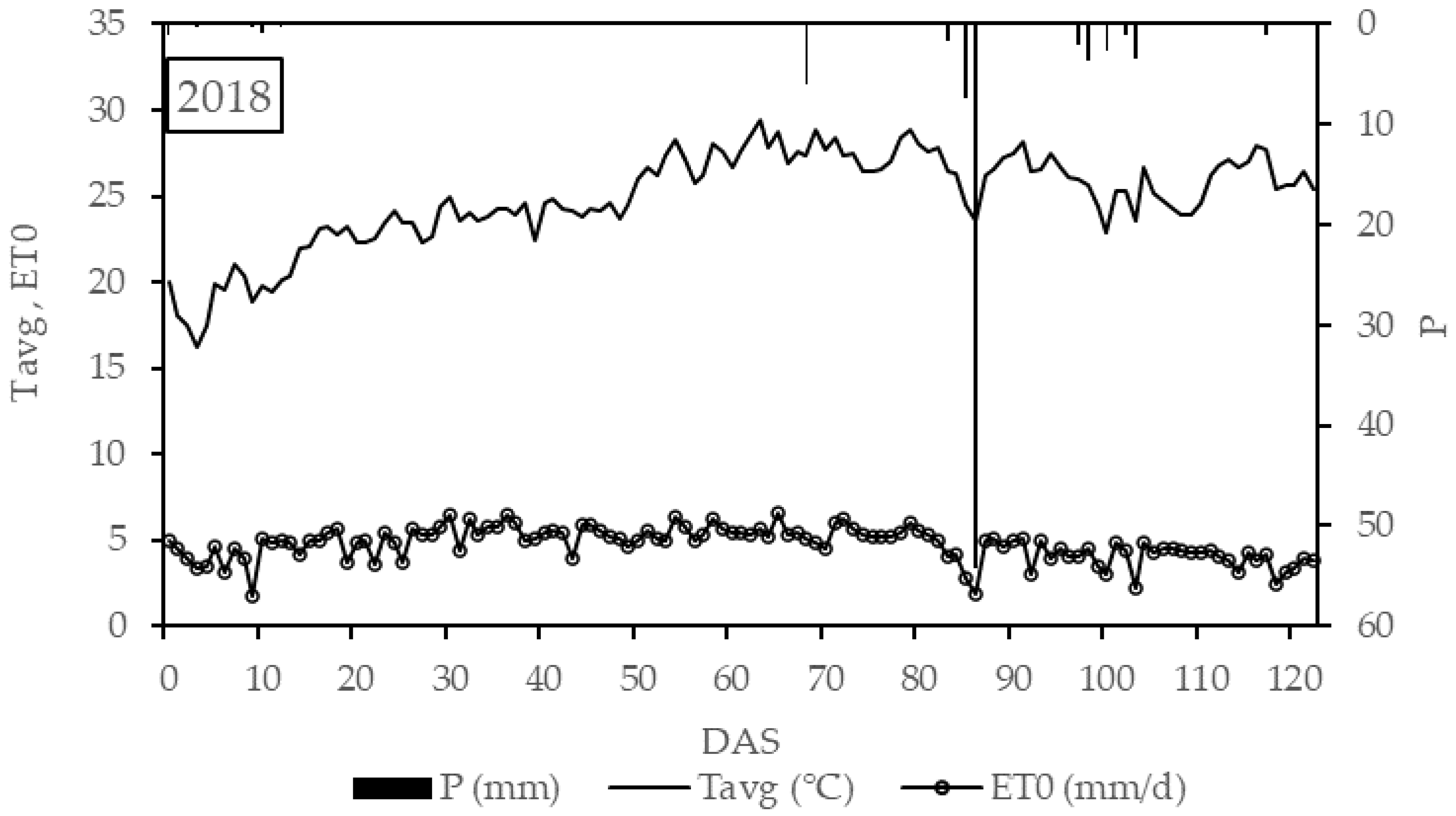
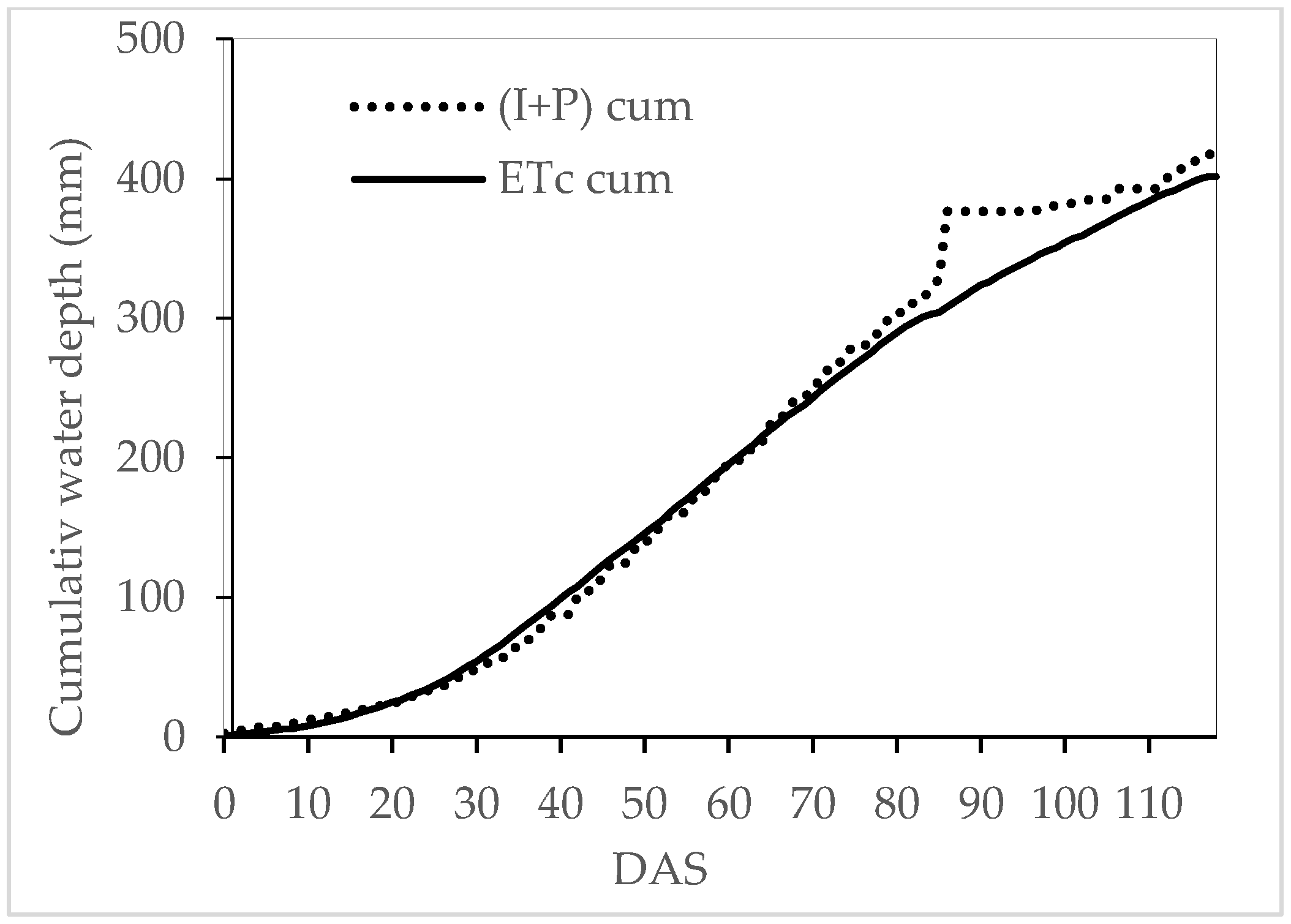
3.2. Agro-Meteorological Characterization of the Study Area
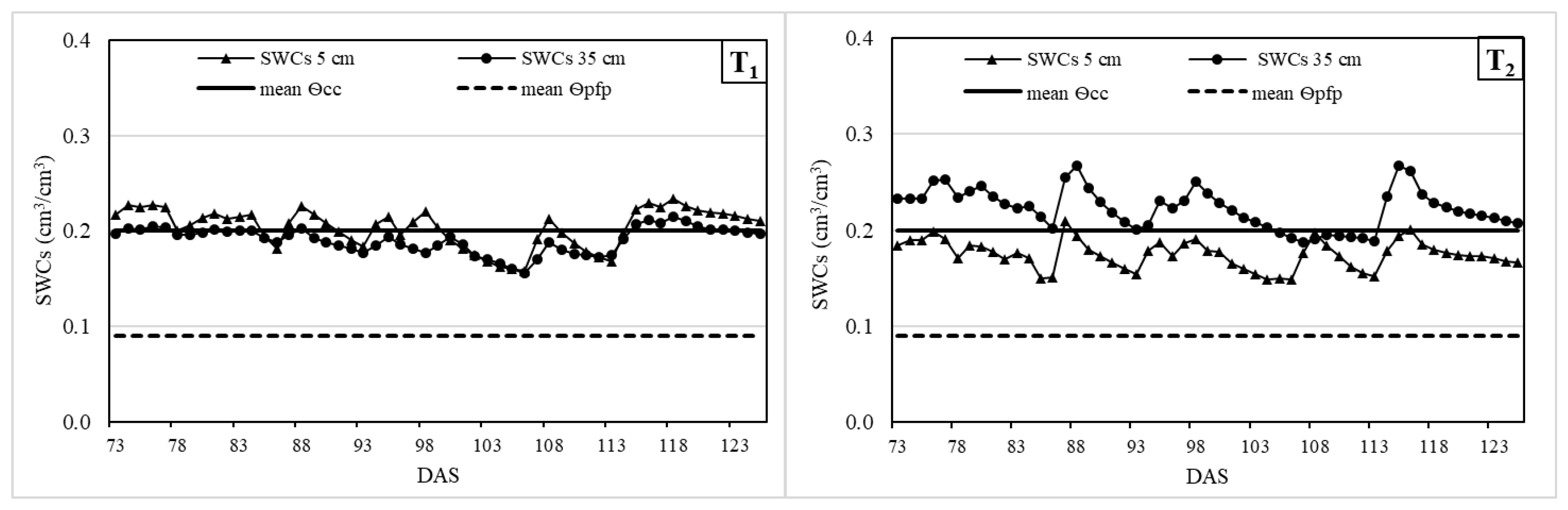
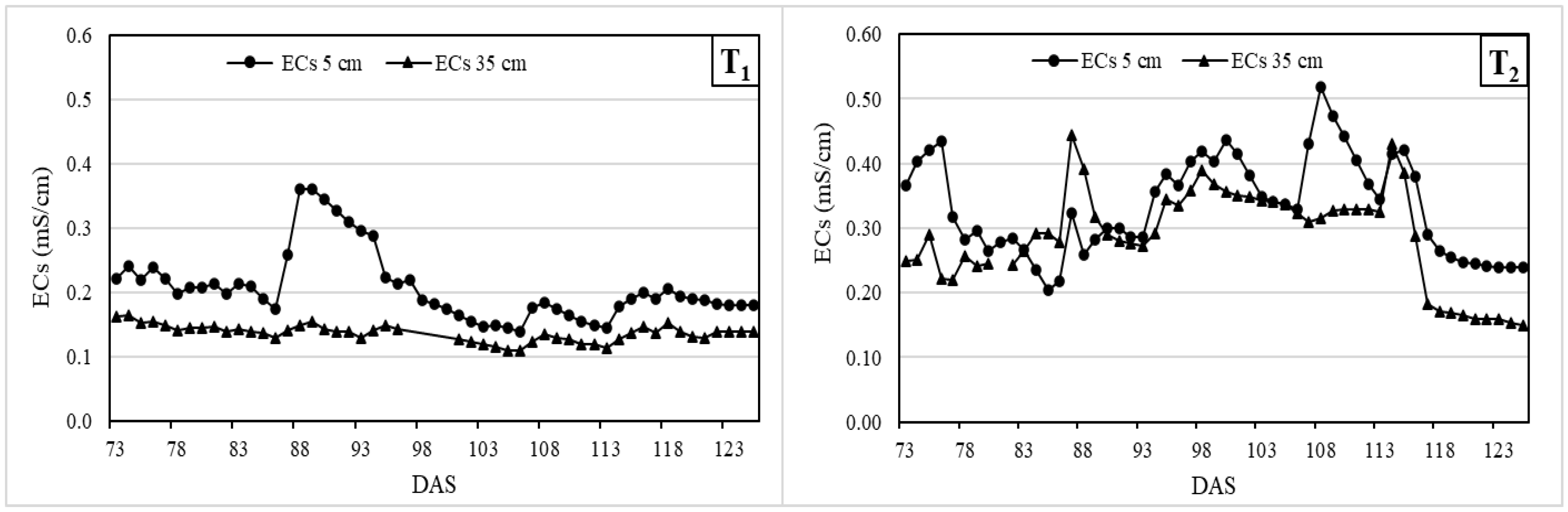
3.3. Soil Water and Electrical Conductivity Monitoring
3.4. Okra Response to Water
3.5. Sodium and Potassium Concentration in Okra Crop
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asgari, K.; Cornelis, W.M. Heavy metal accumulation in soils and grains, and health risks associated with use of treated municipal wastewater in subsurface drip irrigation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, M.F.; Restrepo, I. Wastewater reuse in agriculture: A review about its limitations and benefits. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassena, A.B.; Zouari, M.; Trabelsi, L.; Decou, R.; Amar, F.B.; Chaari, A.; Zouari, N. Potential effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mitigating the salinity of treated wastewater in young olive plants (Olea europaea L. cv. Chetoui). Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Datta, S.P. Impact of wastewater irrigation on the dynamics of metal concentrations in the vadose zone: Monitoring: Part I. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Do Monte, M.M.; Bontoux, L.; Asano, T. The status of wastewater reuse practice in the Mediterranean basin: Need for guidelines. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessira, M.; Hamdy, A. Gestion de l’irrigation avec les eaux non conventionnelles; Bari: CIHEAM/EU DG Research. In Proceedings of the International Workshop, Alger, Algeria, 12–14 June 2005; pp. 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- ONAS. Activity Report of the National Sanitation Utility. Tunisia. 2020. Available online: http://www.onas.nat.tn/Fr/page.php?code=19 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Ayars, J.; Fulton, A.; Taylor, B. Subsurface drip irrigation in California-here to stay? Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 157, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.H.; Fatahi Nafchi, R.; Najafi, P.; Karizan, M.M.; Nazem, Z. Comparison of traditional and modern deficit irrigation techniques in corn cultivation using treated municipal wastewater. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2017, 6, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gimeno, M.A.; Bonet, L.; Provenzano, G.; Badal, E.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Ballester, C. Assessment of yield and water productivity of clementine trees under surface and subsurface drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 206, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinsakir, K.; Buyuktas, D.; Dinç, N.; Erdurmus, C.; Bayram, E.; Yegin, A.B. Yield and bioethanol productivity of sorghum under surface and subsurface drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kooij, S.; Zwarteveen, M.; Boesveld, H.; Kuper, M. The efficiency of drip irrigation unpacked. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 123, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelous, M.M.; Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Malek, K. Soil water content distributions between two emitters of a subsurface drip irrigation system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Díaz, M.P.; Mendoza-Grimón, V.; Fernández-Vera, J.R.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, F.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Hernández-Moreno, J.M. Subsurface drip irrigation and reclaimed water quality effects on phosphorus and salinity distribution and forage production. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, C.R. Subsurface drip irrigation: A review. Trans. ASAE 1998, 41, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Rajput, T.B.S. Response of lateral placement depths of subsurface drip irrigation on okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Int. J. Plant Prod. 2007, 1, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harbi, A.R.; Al-Omran, A.M.; El-Adgham, F.L. Effect of drip irrigation levels and emitters depth on okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) growth. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 8, 2764–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, S.; Mansuroglu, G.S. Responses of unheated greenhouse grown green bean to buried drip tape placement depth and watering levels. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Amor, M.A.; Del Amor, F.M. Response of tomato plants to deficit irrigation under surface or subsurface drip irrigation. J. Appl. Hortic. 2007, 9, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omran, A.M.; Al-Harbi, A.R.; Wahb-Allah, M.A.; Nadeem, M.; Al-Eter, A. Impact of irrigation water quality, irrigation systems, irrigation rates and soil amendments on tomato production in sandy calcareous soil. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2010, 34, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, M.X.M.; Mei, Y.U.; Jin, W. Effects of irrigation water quality and drip tape arrangement on soil salinity, soil moisture distribution, and cotton yield (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under mulched drip irrigation in Xinjiang, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Mohammadi, P.; Sanikhani, H.; Salih, S.Q.; Yaseen, Z.M. Modeling wetted areas of moisture bulb for drip irrigation systems: An enhanced empirical model and artificial neural network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Ferré, T.P.; Liu, Y.; Xian, Y.; Shan, T.; Ping, X. Spatial distribution of soil moisture, soil salinity, and root density beneath a cotton field under mulched drip irrigation with brackish and fresh water. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, A.; Javed, Q.; Sun, J.; Nawaz, M.I.; Ullah, I.; Kama, R.; Du, D. Functional traits of okra cultivars (Chinese green and Chinese red) under salt stress. Folia Hortic. 2020, 32, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Kader, A.; Shaaban, S.; Abd El-Fattah, M. Effect of irrigation levels and organic compost on okra plants (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) grown in sandy calcareous soil. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2010, 1, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chopra, A.K.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, J.; Thakur, R.K. Irrigating okra with secondary treated municipal wastewater: Observations regarding plant growth and soil characteristics. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Owusu-Sekyere, J.D.; Annan, E. Effect of deficit irrigation on growth and yield of Okra (Abelmoscus esculentus). J. Sci. Technol. Ghana 2010, 30, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Willie, W.K.T.; Owusu-Sekyere, J.D.; Sam-Amoah, L.K. Interactions of deficit irrigation, chicken manure and NPK 15: 15: 15 on okra growth and yield and soil properties. Asian J. Agric. Res. 2016, 10, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, S.M.; Suarez, D.L. Technical note: A short note on calculating the adjusted SAR index. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2009, 52, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaz, K.; EL Mokh, F.; Alva, A.K.; Masmoudi, M.M.; Ben Mechlia, N. Potato response to different irrigation regimes using saline water. Irrig. Drain. 2016, 65, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline Alkali Soils; Handbook 60; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 78, p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Bucks, D.A.; Nakayama, F.S.; Gilbert, R.G. Trickle irrigation water quality and preventive maintenance. Agric. Water Manag. 1979, 2, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morvannou, A.; Forquet, N. Projet ROSEEV: Role du Sol Dans les Zones de Rejet Végétalisées. Etude de l’Application de Différentes Charges Hydrauliques sur la Plateforme Lysimétrique de Mionnay (69); Irstea: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Djedidi, N.; Hassen, A. Propriétés physiques des sols et pouvoir colmatant des eaux usées en fonction de leur degré de traitement. Cah. ORSTOM Pédologie 1991, 26, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, C.F.; McCarthy, D.T.; Deletic, A. Predicting physical clogging of porous and permeable pavements. J. Hydrol. 2013, 481, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, T.; Berndtsson, R.; Persson, M.; Somaida, M.; El-Kiki, M.; Hamed, Y.; Zhou, Q. Influence of geometric design of alternate partial root-zone subsurface drip irrigation (APRSDI) with brackish water on soil moisture and salinity distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.M.; Yang, P.L.; An, Q.X.; Xu, R.; Yao, B.L.; Li, F.Y.; Zhang, X.X. Investigation into surface and subsurface drip irrigation for jujube trees grown in saline soil under extremely arid climate. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 81, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.L.; White, S.A.; Warrick, A.W.; Thompson, T.L. Tape depth and germination method influence patterns of salt accumulation with subsurface drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelil, M.N.; Rejeb, S.; Henchi, B.; Destain, J.P. Effects of irrigation water quality and nitrogen rate on the recovery of 15N fertilizer by sorghum in field study. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, L.D.; Ichikawa, M.; Pham, D.V.; Sasaki, A.; Watanabe, T. High yield of protein-rich forage rice achieved by soil amendment with composted sewage sludge and topdressing with treated wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayapiratha, U.; Sivakumar, S. Performance evaluation of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Asian J. Agric. Res. 2010, 4, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Siyal, A.A.; Mashori, A.S.; Bristow, K.L.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Alternate furrow irrigation can radically improve water productivity of okra. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 173, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarchouna, L.G.; Merdy, P.; Raynaud, M.; Pfeifer, H.R.; Lucas, Y. Effects of long-term irrigation with treated wastewater. Part I: Evolution of soil physico-chemical properties. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z. Optimum combination of soil amendments under drip irrigation with different water sources in coastal areas of East China. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, J.B.; Cisse-camara, M.; Sess, D.E.; Tiahou, G.G.; Monde, A.A.; Djohan, F.Y. Détermination des teneurs en fer, en calcium, en cuivre et en zinc de deux variétés de gombo. Bull. Soc. R. Sci. Liége 2013, 82, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ahiakpa, J.K.; Quartey, E.K.; Amenorpe, G.; Klu, G.Y.P.; Agbemavor, W.S.K.; Amoatey, H.M. Essential mineral elements profile of 22 accessions of Okra (Abelmoscus spp L.) from eight regions of Ghana. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 6, 18–25. [Google Scholar]

| Soil Depth | Sand | Clay | Loam | Bd 1 | pH | OC 2 | Humus | ECs 3 | Mn | Ni | Zn | Fe | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | % | (g·cm−3) | % | mS·cm−1 | (mg·Kg−1) | ||||||||
| 0–10 | 79 | 7.1 | 13.9 | 1.40 | 8.1 | 0.70 | 1.4 | 1.46 | 106.3 | 5.5 | 69.1 | 14,007 | 15.8 |
| 10–20 | 76.7 | 7.5 | 15.8 | 1.45 | 8.0 | 0.60 | 1.3 | 1.24 | 108.3 | 7.9 | 69.1 | 15,483 | 7.8 |
| 20–30 | 79.3 | 7.0 | 13.7 | 1.4 | 8.2 | 0.60 | 1.1 | 1.12 | 115.9 | 7.8 | 78.7 | 15,900 | 13.7 |
| 30–40 | 75.1 | 8.2 | 16.7 | 1.57 | 8.3 | 0.60 | 1.1 | 1.21 | 126.2 | 4.9 | 64.4 | 17,373 | 10.8 |
| 40–50 | 73.4 | 8.5 | 18.1 | 1.52 | 8.4 | 0.53 | <1.1 | 1.15 | 95.5 | 8.1 | 51.3 | 13,512 | 15.9 |
| 50–60 | 77 | 7.4 | 15.6 | 1.50 | 8.4 | 0.53 | <1.1 | 1.39 | 70.4 | 3.4 | 19.8 | 12,555 | 8.3 |
| Permissible limit 4 | 2000 | 50 | 300 | - | 100 | ||||||||
| Crop Development Stages | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Development | Mid-Season | Final Season | |
| Period length (d) | 10 | 31 | 25 | 20 |
| Kc | 0.2 | 0.2–1 | 1 | 0.9 |
| Treated Wastewater | Fresh Water | NT 106.03 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.25 ± 0.21 | 7.4 | 6.5–8.5 | |
| CE (mS/cm) | 3.35 ± 0.22 | 2.77 | 7 | |
| SAR | 8.06 ± 0.20 | 5.09 | - | |
| Dry residue (g/L) | 2.17 ± 0.26 | mg/L | 1.94 | - |
| N-NO3− | <5 | - | - | |
| N-NH4+ | 38.70 ± 3.82 | - | - | |
| P | 5.05 ± 1.68 | - | - | |
| K+ | 42.71 ± 11.06 | 8.4 | - | |
| Na+ | 487.6 ± 54.53 | 325 | - | |
| Cl− | 666.2 ± 93.51 | 518.3 | 2000 | |
| Ca2+ | 126.3 ± 5.42 | 178 | - | |
| Mg2+ | 88.4 ± 7.09 | 78 | - | |
| HCO3− | 333.1 ± 34.39 | 579.5 | - | |
| SO42− | 490.6 ± 158.4 | 288 | - | |
| Cd | 0.0072 ± 0.0032 | - | 0.01 | |
| Co | 0.0114 ± 0.0099 | - | 0.1 | |
| Cr | 0.0312 ± 0.0302 | - | 0.10 | |
| Cu | 0.0084 ± 0.0054 | - | 0.50 | |
| Fe | 0.2348 ± 0.1370 | 0.03 | 5 | |
| Mn | 0.0120 ± 0.0140 | 0.08 | 0.50 | |
| Ni | 0.0137 ± 0.0121 | - | 0.20 | |
| Pb | 0.0349 ± 0.0142 | - | 1 | |
| Zn | 0.0144 ± 0.0090 | 0.03 | 5 |
| Treatment | ETc (mm) | P (mm) | I (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | |||
| T1-0 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| T1-5 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| T1-15 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| T1-25 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| T2 | |||
| T2-0 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| T2-5 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| T2-15 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| T2-25 | 401.4 | 87.6 | 365.4 |
| Treatment | P (mm) | I (mm) | Yield (t ha−1) | WPirrig (Kg m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | ||||
| T1-0 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 2.55 ± 0.93 a | 0.72 ± 0.33 |
| T1-5 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 2.7 ± 0.37 a | 0.75 ± 0.23 |
| T1-15 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 2.6 ± 0.46 a | 0.73 ± 0.30 |
| T1-25 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 2.8 ± 0.22 a | 0.78 ± 0.18 |
| T2 | ||||
| T2-0 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 3.9 ± 0.34 b | 1.10 ± 0.26 |
| T2-5 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 4.4 ± 0.22 b | 1.23 ± 0.18 |
| T2-15 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 4.1 ± 0.09 b | 1.16 ± 0.23 |
| T2-25 | 87.6 | 365.4 | 3.9 ± 0.6 b | 1.08 ± 0.26 |
| Emitter Depth (cm) | Na+ Contents | K+ Contents | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roots | Shoots | Fruits | Roots | Shoots | Fruits | |||||||
| T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | |
| 0 | 1.37 bc | 1.11 a | 0.22 a | 0.41 cd | 0.74 ab | 0.64 a | 1.79 cd | 1.72 c | 2.87 a | 3.09 b | 4.03 a | 4.13 bc |
| 5 | 1.19 ab | 1.41 c | 0.27 ab | 0.49 d | 0.62 a | 1.52 a | 1.40 b | 1.65 c | 2.99 ab | 3.21 c | 3.43 a | 4.17 bc |
| 15 | 1.19 ab | 1.89 e | 0.39 c | 0.44 cd | 0.63 a | 1.14 c | 1.06 a | 2.03 d | 3.06 ab | 3.03 ab | 3.93 ab | 4.13 bc |
| 25 | 1.44 c | 1.73 d | 0.31 bc | 0.56 e | 0.75 b | 0.84 a | 1.18 a | 2.51 e | 3.09 b | 3.02 ab | 4.10 a | 4.27 c |
| average | 1.30 | 1.54 | 0.30 | 0.48 | 0.69 | 1.04 | 1.36 | 1.98 | 3.00 | 3.09 | 3.87 | 3.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoudi, M.; Khelil, M.N.; Hechmi, S.; Latrech, B.; Ghrib, R.; Boujlben, A.; Yacoubi, S. Effect of Surface and Subsurface Drip Irrigation with Treated Wastewater on Soil and Water Productivity of Okra (Abemoschus esculentus) Crop in Semi-Arid Region of Tunisia. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122048
Mahmoudi M, Khelil MN, Hechmi S, Latrech B, Ghrib R, Boujlben A, Yacoubi S. Effect of Surface and Subsurface Drip Irrigation with Treated Wastewater on Soil and Water Productivity of Okra (Abemoschus esculentus) Crop in Semi-Arid Region of Tunisia. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122048
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoudi, Malika, Mohamed Naceur Khelil, Sarra Hechmi, Basma Latrech, Rim Ghrib, Abdelhamid Boujlben, and Samir Yacoubi. 2022. "Effect of Surface and Subsurface Drip Irrigation with Treated Wastewater on Soil and Water Productivity of Okra (Abemoschus esculentus) Crop in Semi-Arid Region of Tunisia" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122048
APA StyleMahmoudi, M., Khelil, M. N., Hechmi, S., Latrech, B., Ghrib, R., Boujlben, A., & Yacoubi, S. (2022). Effect of Surface and Subsurface Drip Irrigation with Treated Wastewater on Soil and Water Productivity of Okra (Abemoschus esculentus) Crop in Semi-Arid Region of Tunisia. Agriculture, 12(12), 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122048





