Coupling Sewage Sludge Amendment with Cyanobacterial Inoculation to Enhance Stability and Carbon Gain in Dryland Degraded Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sewage Sludge Collection
2.2. Soil Collection
2.3. Culture of Cyanobacterial Inoculants
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Assessing Inoculum Growth
2.5.1. Chlorophyll a Content
2.5.2. Soil Spectral Response Measurements
2.6. Influence on Soil Properties
2.6.1. Soil Stability Measurements
2.6.2. Exopolysaccharide and Soil Organic Carbon Content
2.7. Inoculation of Saline Soils with Native Cyanobacteria
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Cyanobacterial Inoculum Viability Assessment
3.2. Effects on Soil Physico-Chemical Properties
3.2.1. Soil Stability
3.2.2. Total Organic Carbon and EPS Content
3.3. Cyanobacterial Effects in Saline Soils
4. Discussion
4.1. Inoculum Viability in Soils Amended with different SS Doses
4.2. Effects of the Inoculum and the SS Dose on Soil Properties
4.3. Effect of Cyanobacteria Inoculum on Salt Immobilization in SS-Amended Soils
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farooq, M.; Rehman, A.; Pisante, M. Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security. In Innovations in Sustainable Agriculture; Farooq, M., Pisante, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R. Soil Erosion and Agricultural Sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13268–13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Soils and Sustainable Agriculture. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Arrúe, J.L.; Cantero-Martínez, C.; Fanlo, R.; Iglesias, A.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J. Carbon Management in Dryland Agricultural Systems. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerson, M.; Morales, M.; Oñate, J.; Batáry, P.; Berendse, F.; Liira, J.; Aavik, T.; Guerrero, I.; Bommarco, R.; Eggers, S.; et al. How Agricultural Intensification Affects Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2016, 55, 43–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and Human Security in the 21st Century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.W.; Ericksen, P.J.; Chesterman, S.; Worden, J.S. Sustainable Intensification in Drylands: What Resilience and Vulnerability Can Tell Us. Agric. Syst. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Averyt, K.; Marquis, M. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis: Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY 10013-2473, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Prăvălie, R. Drylands Extent and Environmental Issues. A Global Approach. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 161, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, A.; Penman, T.D.; Gorissen, L.; Winslow, M.D.; Lehmann, J.; Tyrrell, T.D.; Twomlow, S.; Wilkes, A.; Lal, R.; Jones, J.W.; et al. Towards Sustainable Land Management in the Drylands: Scientific Connections in Monitoring and Assessing Dryland Degradation, Climate Change and Biodiversity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, F.T.; Eldridge, D.J.; Soliveres, S.; Kéfi, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Bowker, M.A.; García-Palacios, P.; Gaitán, J.; Gallardo, A.; Lázaro, R.; et al. Structure and Functioning of Dryland Ecosystems in a Changing World. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2016, 47, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-X.; Xu, B.-C.; Yin, L.-N.; Wang, S.-W.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Shan, L.; Kwak, S.-S.; Ke, Q.; Deng, X.-P. Dryland Agricultural Environment and Sustainable Productivity. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 14, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, D.; Lensky, I.M.; Mussery, A.; Leu, S. Rehabilitating Degraded Drylands by Creating Woodland Islets: Assessing Long-Term Effects on Aboveground Productivity and Soil Fertility. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 195–196, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Lan, M.; Liu, J.; Gao, M. Soil Aggregate and Organic Carbon Distribution at Dry Land Soil and Paddy Soil: The Role of Different Straws Returning. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27942–27952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smol, M.; Kulczycka, J.; Henclik, A.; Gorazda, K.; Wzorek, Z. The Possible Use of Sewage Sludge Ash (SSA) in the Construction Industry as a Way towards a Circular Economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovi, P.; Baldoni, G.; Toderi, G. Reuse of Liquid, Dewatered, and Composted Sewage Sludge on Agricultural Land: Effects of Long-Term Application on Soil and Crop. Water Res. 2005, 39, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavakala, B.K.; Le Faucheur, S.; Mulaji, C.K.; Laffite, A.; Devarajan, N.; Biey, E.M.; Giuliani, G.; Otamonga, J.-P.; Kabatusuila, P.; Mpiana, P.T.; et al. Leachates Draining from Controlled Municipal Solid Waste Landfill: Detailed Geochemical Characterization and Toxicity Tests. Waste Manag. 2016, 55, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chopra, A.; Kumar, A. A Review on Sewage Sludge (Biosolids) a Resource for Sustainable Agriculture. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2017, 2, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breda, C.C.; Soares, M.B.; Tavanti, R.F.R.; Viana, D.G.; Freddi, O.; da, S.; Piedade, A.R.; Mahl, D.; Traballi, R.C.; Guerrini, I.A. Successive Sewage Sludge Fertilization: Recycling for Sustainable Agriculture. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, G.; Pro, J.; Gómez, N.; Babín, M.M.; Fernández, C.; Alonso, E.; Tarazona, J.V. Sewage Sludge Applied to Agricultural Soil: Ecotoxicological Effects on Representative Soil Organisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Le Villio-Poitrenaud, M.; Houot, S. Improvement of Soil Aggregate Stability by Repeated Applications of Organic Amendments to a Cultivated Silty Loam Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, B.; Mounia, K.; Aziz, A.; Ahmed, H.; Rachid, B.; Lotfi, A. Sewage Sludge Used as Organic Manure in Moroccan Sunflower Culture: Effects on Certain Soil Properties, Growth and Yield Components. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burducea, M.; Zheljazkov, V.D.; Lobiuc, A.; Pintilie, C.A.; Virgolici, M.; Silion, M.; Asandulesa, M.; Burducea, I.; Zamfirache, M.-M. Biosolids Application Improves Mineral Composition and Phenolic Profile of Basil Cultivated on Eroded Soil. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 249, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Mourinha, C.; Farto, M.; Santos, T.; Palma, P.; Sengo, J.; Morais, M.-C.; Cunha-Queda, C. Sewage Sludge, Compost and Other Representative Organic Wastes as Agricultural Soil Amendments: Benefits versus Limiting Factors. Waste Manag. 2015, 40, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarick, K.A.; Ippolito, J.A.; McDaniel, J.; Hansen, N.C.; Peterson, G.A. Biosolids Application to No-till Dryland Agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 150, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.M.; Plaza, C.; García-Gil, J.C.; Polo, A. Biochemical Properties and Barley Yield in a Semiarid Mediterranean Soil Amended with Two Kinds of Sewage Sludge. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sort, X.; Alcañiz, J.M. Effects of Sewage Sludge Amendment on Soil Aggregation. Land Degrad. Dev. 1999, 10, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głąb, T.; Żabiński, A.; Sadowska, U.; Gondek, K.; Kopeć, M.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Sylwester, T.; Stanek-Tarkowska, J. Fertilization Effects of Compost Produced from Maize, Sewage Sludge and Biochar on Soil Water Retention and Chemical Properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, M.G.; Ryan, P.C.; Fenton, O.; Peyton, D.P.; Wall, D.P.; Morrison, L. Bioaccumulation of Metals in Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) Following the Application of Lime Stabilised, Thermally Dried and Anaerobically Digested Sewage Sludge. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari Lajayer, B.; Najafi, N.; Moghiseh, E.; Mosaferi, M.; Hadian, J. Micronutrient and Heavy Metal Concentrations in Basil Plant Cultivated on Irradiated and Non-Irradiated Sewage Sludge-Treated Soil and Evaluation of Human Health Risk. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 104, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, N.; Ragonezi, C.; Gouveia, C.S.S.; Pinheiro de Carvalho, M.Â.A. Review of Sewage Sludge as a Soil Amendment in Relation to Current International Guidelines: A Heavy Metal Perspective. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, H.; Benzarti, S.; Manusadžianas, L.; Aoyama, I.; Jedidi, N. Solid-Phase Bioassays and Soil Microbial Activities to Evaluate PAH-Spiked Soil Ecotoxicity after a Long-Term Bioremediation Process Simulating Landfarming. Chemosphere 2007, 70, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tella, M.; Bravin, M.N.; Thuriès, L.; Cazevieille, P.; Chevassus-Rosset, C.; Collin, B.; Chaurand, P.; Legros, S.; Doelsch, E. Increased Zinc and Copper Availability in Organic Waste Amended Soil Potentially Involving Distinct Release Mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Crohn, D.M. Compost Induced Soil Salinity: A New Prediction Method and Its Effect on Plant Growth. Compos. Sci. Util. 2012, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-González, J.C.; López-Chuken, U.J.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Flores-Banda, F.; Hernández-Ramírez, A.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L. Saline Irrigation and Zn Amendment Effect on Cd Phytoavailability to Swiss Chard (Beta vulgaris L.) Grown on a Long-Term Amended Agricultural Soil: A Human Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5909–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagae, H.J.; Langemeier, M.; Lybecker, D.; Barbarick, K. Economic Value of Biosolids in a Semiarid Agroecosystem. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, G.; Alcañiz, J.M.; Ortiz, O. Runoff and Losses by Erosion in Soils Amended with Sewage Sludge. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rajkumar, M.; Oliveira, R.S.; Zhang, C.; Freitas, H. Potential of Plant Beneficial Bacteria and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Phytoremediation of Metal-Contaminated Saline Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raklami, A.; Tahiri, A.; Bechtaoui, N.; Abdelhay, E.G.; Pajuelo, E.; Baslam, M.; Meddich, A.; Oufdou, K. Restoring the Plant Productivity of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil Using Phosphate Sludge, Marble Waste, and Beneficial Microorganisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, D.; Hu, C. Effects of Light and Temperature on Open Cultivation of Desert Cyanobacterium Microcoleus Vaginatus. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pichel, F.; Castenholz, R.W. Characterization and Biological Implications of Scytonemin, a Cyanobacterial Sheath Pigment1. J. Phycol. 1991, 27, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, L.; da Rocha, U.N.; Klitgord, N.; Luning, E.G.; Fortney, J.; Axen, S.D.; Shih, P.M.; Bouskill, N.J.; Bowen, B.P.; Kerfeld, C.A.; et al. Dynamic Cyanobacterial Response to Hydration and Dehydration in a Desert Biological Soil Crust. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2178–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirfam, H. Increasing Soil Potential for Carbon Sequestration Using Microbes from Biological Soil Crusts. J. Arid Environ. 2020, 172, 104022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo, S.; Cantón, Y.; Miralles, I.; Domingo, F. Biological Soil Crust Development Affects Physicochemical Characteristics of Soil Surface in Semiarid Ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 49, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, Y.; Chamizo, S.; Rodriguez-Caballero, E.; Lázaro, R.; Roncero-Ramos, B.; Román, J.R.; Solé-Benet, A. Water Regulation in Cyanobacterial Biocrusts from Drylands: Negative Impacts of Anthropogenic Disturbance. Water 2020, 12, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo, S.; Mugnai, G.; Rossi, F.; Certini, G.; De Philippis, R. Cyanobacteria Inoculation Improves Soil Stability and Fertility on Different Textured Soils: Gaining Insights for Applicability in Soil Restoration. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo, S.; Rodríguez-Caballero, E.; Román, J.R.; Cantón, Y. Effects of Biocrust on Soil Erosion and Organic Carbon Losses under Natural Rainfall. CATENA 2017, 148, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kant, C.; Yadav, R.K.; Reddy, Y.P.; Abraham, G. Cyanobacterial Exopolysaccharides: Composition, Biosynthesis, and Biotechnological Applications. In Cyanobacteria; Mishra, A.K., Tiwari, D.N., Rai, A.N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Chapter 17; pp. 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, F.; Esteban Lucas-Borja, M.; Pereira, P.; Muñoz-Rojas, M. Cyanobacteria as a Nature-Based Biotechnological Tool for Restoring Salt-Affected Soils. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, H. Current States and Challenges of Salt-Affected Soil Remediation by Cyanobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; De Philippis, R. Cyanobacterial Inoculation (Cyanobacterisation): Perspectives for the Development of a Standardized Multifunctional Technology for Soil Fertilization and Desertification Reversal. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero-Ramos, B.; Román, J.R.; Gómez-Serrano, C.; Cantón, Y.; Acién, F.G. Production of a Biocrust-Cyanobacteria Strain (Nostoc Commune) for Large-Scale Restoration of Dryland Soils. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 2217–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero-Ramos, B.; Román, J.R.; Acién, G.; Cantón, Y. Towards Large Scale Biocrust Restoration: Producing an Efficient and Low-Cost Inoculum of N-Fixing Cyanobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero-Ramos, B.; Muñoz-Martín, M.A.; Cantón, Y.; Chamizo, S.; Rodríguez-Caballero, E.; Mateo, P. Land Degradation Effects on Composition of Pioneering Soil Communities: An Alternative Successional Sequence for Dryland Cyanobacterial Biocrusts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 107824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero-Ramos, B.; Muñoz-Martín, M.Á.; Chamizo, S.; Fernández-Valbuena, L.; Mendoza, D.; Perona, E.; Cantón, Y.; Mateo, P. Polyphasic Evaluation of Key Cyanobacteria in Biocrusts from the Most Arid Region in Europe. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, J.R.; Roncero-Ramos, B.; Chamizo, S.; Rodríguez-Caballero, E.; Cantón, Y. Restoring Soil Functions by Means of Cyanobacteria Inoculation: Importance of Soil Conditions and Species Selection. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3184–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, J.R.; Roncero-Ramos, B.; Rodríguez-Caballero, E.; Chamizo, S.; Cantón, Y. Effect of Water Availability on Induced Cyanobacterial Biocrust Development. CATENA 2021, 197, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, J.R.; Chamizo, S.; Roncero-Ramos, B.; Adessi, A.; De Philippis, R.; Cantón, Y. Overcoming Field Barriers to Restore Dryland Soils by Cyanobacteria Inoculation. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 207, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belnap, J.; Phillips, S.L.; Witwicki, D.L.; Miller, M.E. Visually Assessing the Level of Development and Soil Surface Stability of Cyanobacterially Dominated Biological Soil Crusts. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.C.; Morrison, C.D.; Barger, N.N. Extraction of Chlorophyll a from Biological Soil Crusts: A Comparison of Solvents for Spectrophotometric Determination. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, R.J. Consistent Sets of Spectrophotometric Chlorophyll Equations for Acetone, Methanol and Ethanol Solvents. Photosynth. Res. 2006, 89, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Roush, T.L. Reflectance Spectroscopy: Quantitative Analysis Techniques for Remote Sensing Applications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1984, 89, 6329–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, J.R.; Rodríguez-Caballero, E.; Rodríguez-Lozano, B.; Roncero-Ramos, B.; Chamizo, S.; Águila-Carricondo, P.; Cantón, Y. Spectral Response Analysis: An Indirect and Non-Destructive Methodology for the Chlorophyll Quantification of Biocrusts. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cockell, C.S.; Wang, G.; Hu, C.; Chen, L.; De Philippis, R. Control of Lunar and Martian Dust--Experimental Insights from Artificial and Natural Cyanobacterial and Algal Crusts in the Desert of Inner Mongolia, China. Astrobiology 2008, 8, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrick, J.E.; Whitford, W.G.; de Soyza, A.G.; Van Zee, J.W.; Havstad, K.M.; Seybold, C.A.; Walton, M. Field Soil Aggregate Stability Kit for Soil Quality and Rangeland Health Evaluations. CATENA 2001, 44, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo, S.; Adessi, A.; Mugnai, G.; Simiani, A.; De Philippis, R. Soil Type and Cyanobacteria Species Influence the Macromolecular and Chemical Characteristics of the Polysaccharidic Matrix in Induced Biocrusts. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingorance, M.D.; Barahona, E.; Fernández-Gálvez, J. Guidelines for Improving Organic Carbon Recovery by the Wet Oxidation Method. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Larson, S.L.; Ballard, J.H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Arslan, Z.; Han, F.X. Laboratory Spiking Process of Soil with Various Uranium and Other Heavy Metals. MethodsX 2019, 6, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, K.; Khan, S.; Ghulam, S.; Khan, M.U.; Khan, N.; Khan, M.A.; Khalil, S.K. Sewage Sludge: An Important Biological Resource for Sustainable Agriculture and Its Environmental Implications. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 1708–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Selevsek, N.; Torres, I.F.; Hernández, T.; García, C. Soil Restoration with Organic Amendments: Linking Cellular Functionality and Ecosystem Processes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.; Pandey, V.C.; Singh, D.P. Efficient Soil Microorganisms: A New Dimension for Sustainable Agriculture and Environmental Development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Ansari, M.W.; Sahoo, R.K.; Tuteja, N. Biofertilizers Function as Key Player in Sustainable Agriculture by Improving Soil Fertility, Plant Tolerance and Crop Productivity. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, F.T.; Martín, N.; Díez, B.; López-Poma, R.; Santos, F.; Luque, I.; Cortina, J. Watering, Fertilization, and Slurry Inoculation Promote Recovery of Biological Crust Function in Degraded Soils. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Pérez, L.; Martínez, C.; Marcilla, P.; Boluda, R. Composting Rice Straw with Sewage Sludge and Compost Effects on the Soil–Plant System. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Ge, Y.; Jia, Y. Studies on Land Application of Sewage Sludge and Its Limiting Factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamastra, L.; Suciu, N.A.; Trevisan, M. Sewage Sludge for Sustainable Agriculture: Contaminants’ Contents and Potential Use as Fertilizer. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, N.; Schierstaedt, J.; Jechalke, S.; Nesme, J.; Ban, S.G.; Černe, M.; Sørensen, S.J.; Ban, D.; Schikora, A. Composted Sewage Sludge Influences the Microbiome and Persistence of Human Pathogens in Soil. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethany, J.; Johnson, S.L.; Garcia-Pichel, F. High Impact of Bacterial Predation on Cyanobacteria in Soil Biocrusts. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delïbacak, S.; Voroniïna, L.; Morachevskaya, E. Use of Sewage Sludge in Agricultural Soils: Useful or Harmful. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2020, 9, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Junior, C.H.; De Oliveira, M.G.; Cardoso, P.H.S.; Mandu, T.D.S.; Florentino, A.L.; Oliveira, F.C.; dos Reis, J.V.; Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Nogueira, T.A.R.; et al. Sewage Sludge Application in Eucalyptus Urograndis Plantation: Availability of Phosphorus in Soil and Wood Production. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Sun, X.; Xu, C.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Cao, X. Effects of Sewage Sludge Application on Plant Growth and Soil Characteristics at a Pinus Sylvestris Var. Mongolica Plantation in Horqin Sandy Land. Forests 2022, 13, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muter, O.; Dubova, L.; Kassien, O.; Čakāne, J.; Alsina, I. Application of the Sewage Sludge in Agriculture: Soil Fertility, Technoeconomic, and Life-Cycle Assessment. In Hazardous Waste Management; Jeyakumar R., B., Sankarapandian, K., Ravi Y., K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Gu, C.; Zhang, W.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Shan, Y.; Dai, Q. Sewage Sludge Amendment Improved Soil Properties and Sweet Sorghum Yield and Quality in a Newly Reclaimed Mudflat Land. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q.; Li, X.-Y. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) of Microbial Aggregates in Biological Wastewater Treatment Systems: A Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.; Quintelas, C.; Ferreira, E.C.; Mesquita, D.P. The Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Micropollutant Removal. Front. Chem. Eng. 2022, 4, 778469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Rossi, F.; Deng, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Adessi, A.; De Philippis, R. Macromolecular and Chemical Features of the Excreted Extracellular Polysaccharides in Induced Biological Soil Crusts of Different Ages. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Sadeghi Satri, M.; Kheirfam, H.; Zarei Darki, B. Runoff and Soil Loss from Small Plots of Erosion-Prone Marl Soil Inoculated with Bacteria and Cyanobacteria under Real Conditions. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 101, 103214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarpoor, A.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Zarei Darki, B.; Homaee, M. Changes in Morphologic, Hydraulic, and Hydrodynamic Properties of Rill Erosion Due to Surface Inoculation of Endemic Soil Cyanobacteria. CATENA 2022, 208, 105782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, S.M.; Soroush, A.; Huang, N. Wind Erosion Control Using Inoculation of Aeolian Sand with Cyanobacteria. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2104–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, J.; Strong, C.; Aubault, H. Cyanobacterial Soil Crust Responses to Rainfall and Effects on Wind Erosion in a Semiarid Environment, Australia: Implications for Landscape Stability. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2022, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Vela, J.; Sellés, S.; Navarro, J.; Bustamante, M.A.; Mataix, J.; Guerrero, C.; Gomez, I. Evaluation of Composted Sewage Sludge as Nutritional Source for Horticultural Soils. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Fawy, H.; Abdel-Hady, E.S. Study of Sewage Sludge Use in Agriculture and Its Effect on Plant and Soil. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. 2010, 1, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libutti, A.; Cammerino, A.R.B.; Monteleone, M. Risk Assessment of Soil Salinization Due to Tomato Cultivation in Mediterranean Climate Conditions. Water 2018, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysargyris, A.; Papakyriakou, E.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Tzortzakis, N. The Combined and Single Effect of Salinity and Copper Stress on Growth and Quality of Mentha Spicata Plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo, S.; Adessi, A.; Torzillo, G.; De Philippis, R. Exopolysaccharide Features Influence Growth Success in Biocrust-Forming Cyanobacteria, Moving From Liquid Culture to Sand Microcosms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 568224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Kapur, S.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y. Electrostatic Charges on Microalgae Surface: Mechanism and Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, S.; Bharti, A.; Gupta, H.; Gupta, K.; Gulia, U.; Prasanna, R. Cyanobacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS): Biosynthesis and Their Potential Applications. In Microbial and Natural Macromolecules; Das, S., Dash, H.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Chapter 14; pp. 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, J.; Luan, Y.; Dai, W. Application of Algae for Heavy Metal Adsorption: A 20-Year Meta-Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmen, J.; Strieth, D. The Beneficial Effects of Cyanobacterial Co-Culture on Plant Growth. Life 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Yadav, P.; Kujur, R.; Pandey, K.D.; Gupta, R.K. Cyanobacteria and Salinity Stress Tolerance. In Cyanobacterial Lifestyle and Its Applications in Biotechnology; Singh, P., Fillat, M., Kumar, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; Chapter 10; pp. 253–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Pandey, K.D.; Mesapogu, S.; Singh, D.V. Influence of NaCl on Photosynthesis and Nitrogen Metabolism of Cyanobacterium Nostoc Calcicola. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2015, 51, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. NaCl-Induced Physiological and Biochemical Changes in Two Cyanobacteria Nostoc Muscorum and Phormidium Foveolarum Acclimatized to Different Photosynthetically Active Radiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 151, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, D.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y. Effects of Drought and Salt Stresses on Man-Made Cyanobacterial Crusts. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


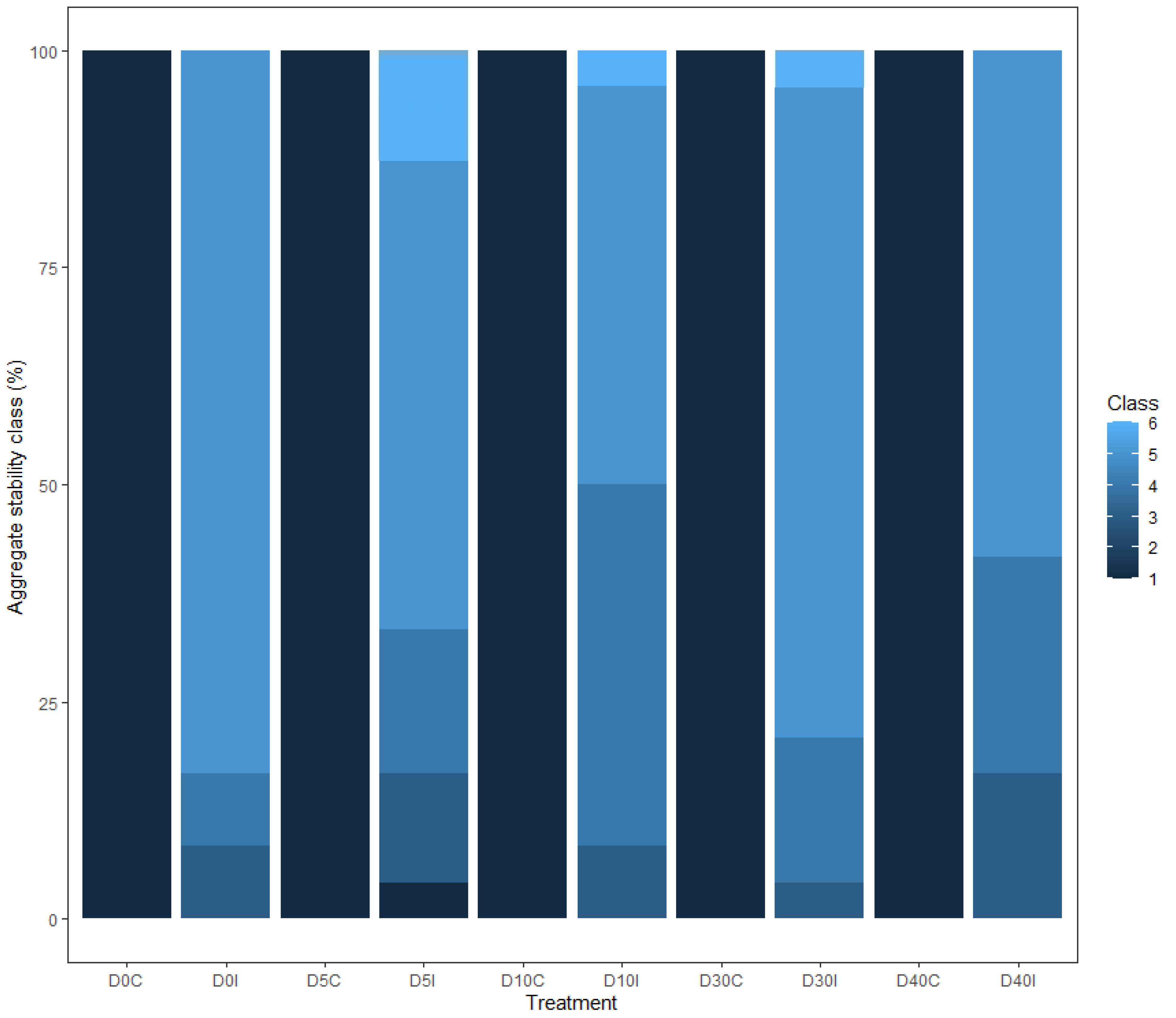

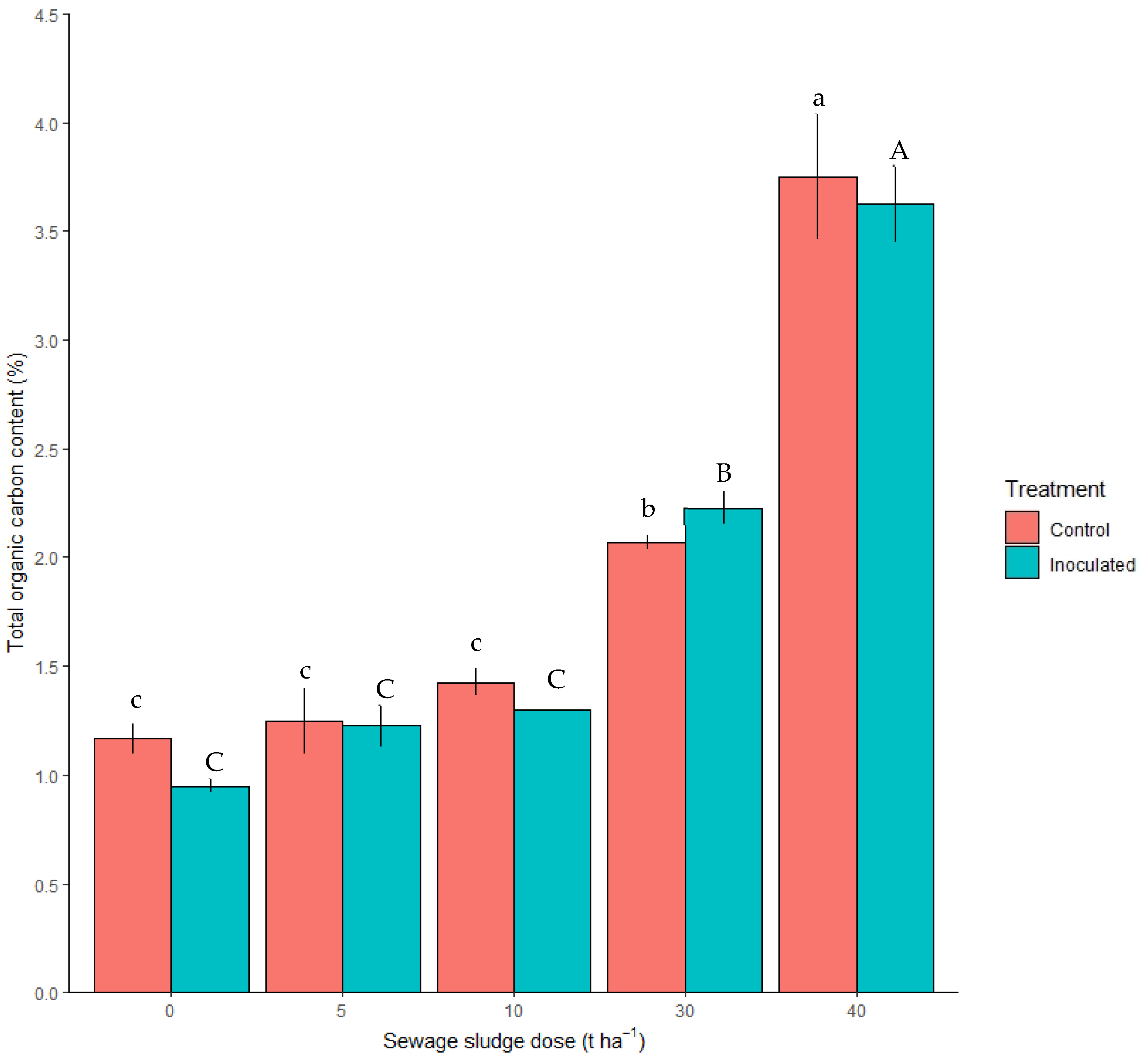
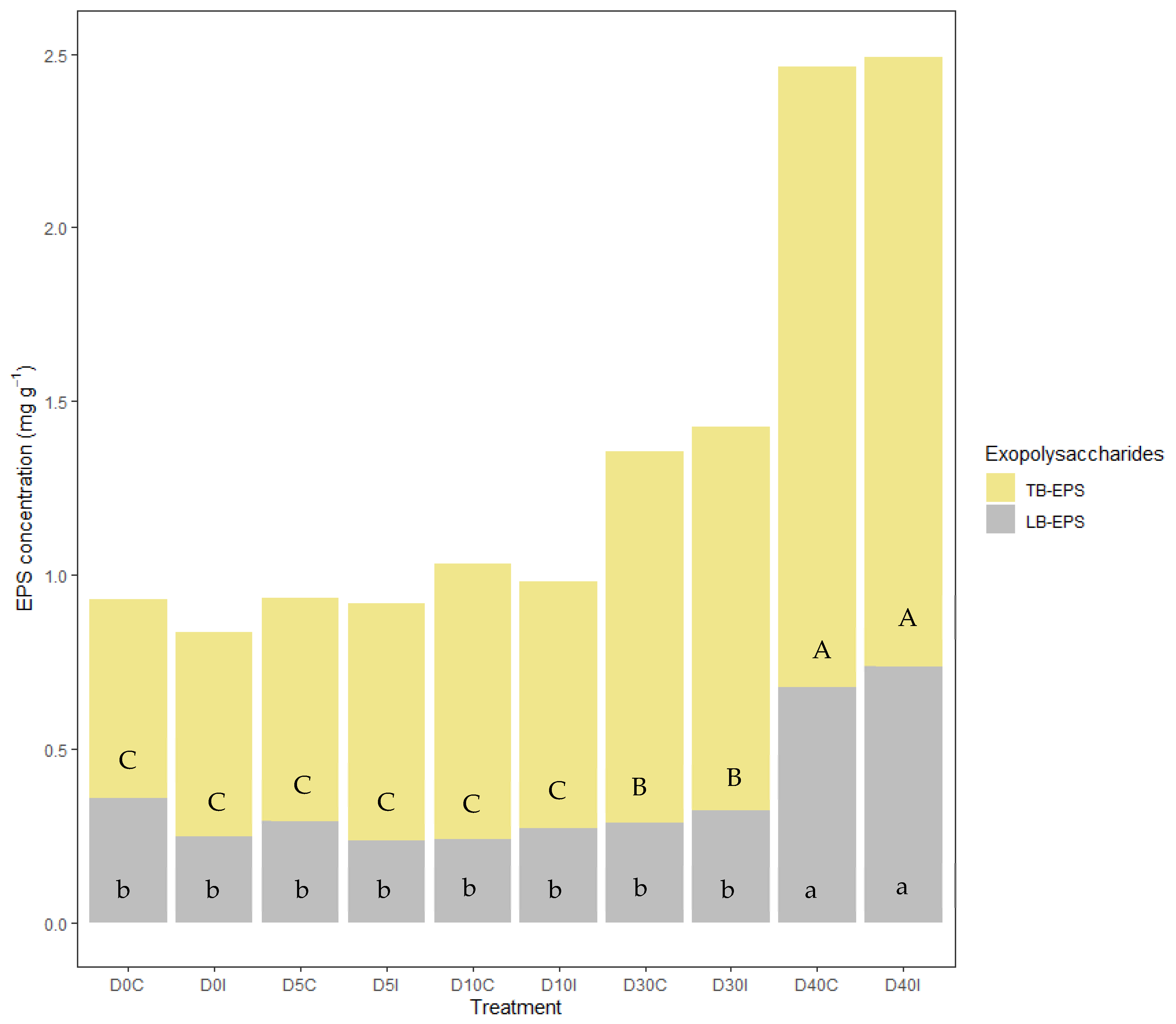


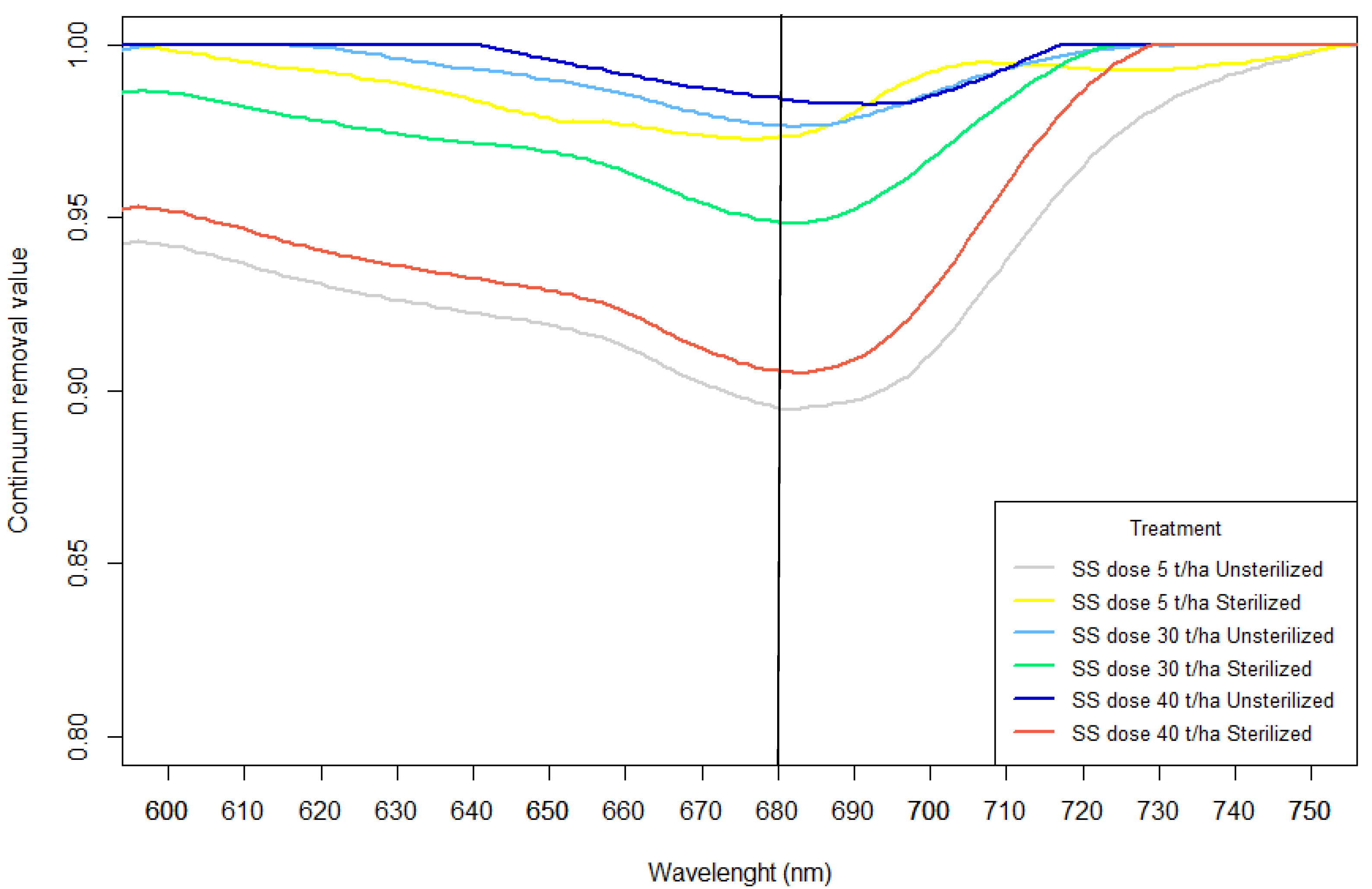
| Heavy Metals | Physicochemical Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromium (ppm) | 25.1 (1500) | Total organic carbon (%) | 19.19 |
| Nickel (ppm) | 16.8 (400) | Labile organic carbon (%) | 0.23 |
| Copper (ppm) | 106.36 (1750) | Total carbon (%) | 19.28 |
| Zinc (ppm) | 264.84 (4000) | Total nitrogen (%) | 2.88 |
| Lead (ppm) | 31.28 (1200) | pH | 6.17 |
| Cadmium (ppb) | 754.74 (40,000) | Electrical conductivity (ms cm−1) | 7.52 |
| Mercury (ppb) | 32.5 (25,000) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maggioli, L.; Chamizo, S.; Román, R.; Asensio-Grima, C.; Cantón, Y. Coupling Sewage Sludge Amendment with Cyanobacterial Inoculation to Enhance Stability and Carbon Gain in Dryland Degraded Soils. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121993
Maggioli L, Chamizo S, Román R, Asensio-Grima C, Cantón Y. Coupling Sewage Sludge Amendment with Cyanobacterial Inoculation to Enhance Stability and Carbon Gain in Dryland Degraded Soils. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121993
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaggioli, Lisa, Sonia Chamizo, Raúl Román, Carlos Asensio-Grima, and Yolanda Cantón. 2022. "Coupling Sewage Sludge Amendment with Cyanobacterial Inoculation to Enhance Stability and Carbon Gain in Dryland Degraded Soils" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121993
APA StyleMaggioli, L., Chamizo, S., Román, R., Asensio-Grima, C., & Cantón, Y. (2022). Coupling Sewage Sludge Amendment with Cyanobacterial Inoculation to Enhance Stability and Carbon Gain in Dryland Degraded Soils. Agriculture, 12(12), 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121993








