Effects of Chloropicrin, Dimethyl Disulfide and Metham Sodium Applied Simultaneously on Soil-Born Bacteria and Fungi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fumigants
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Triple Fumigation Method
2.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Changes to Species Diversity and Species Richness
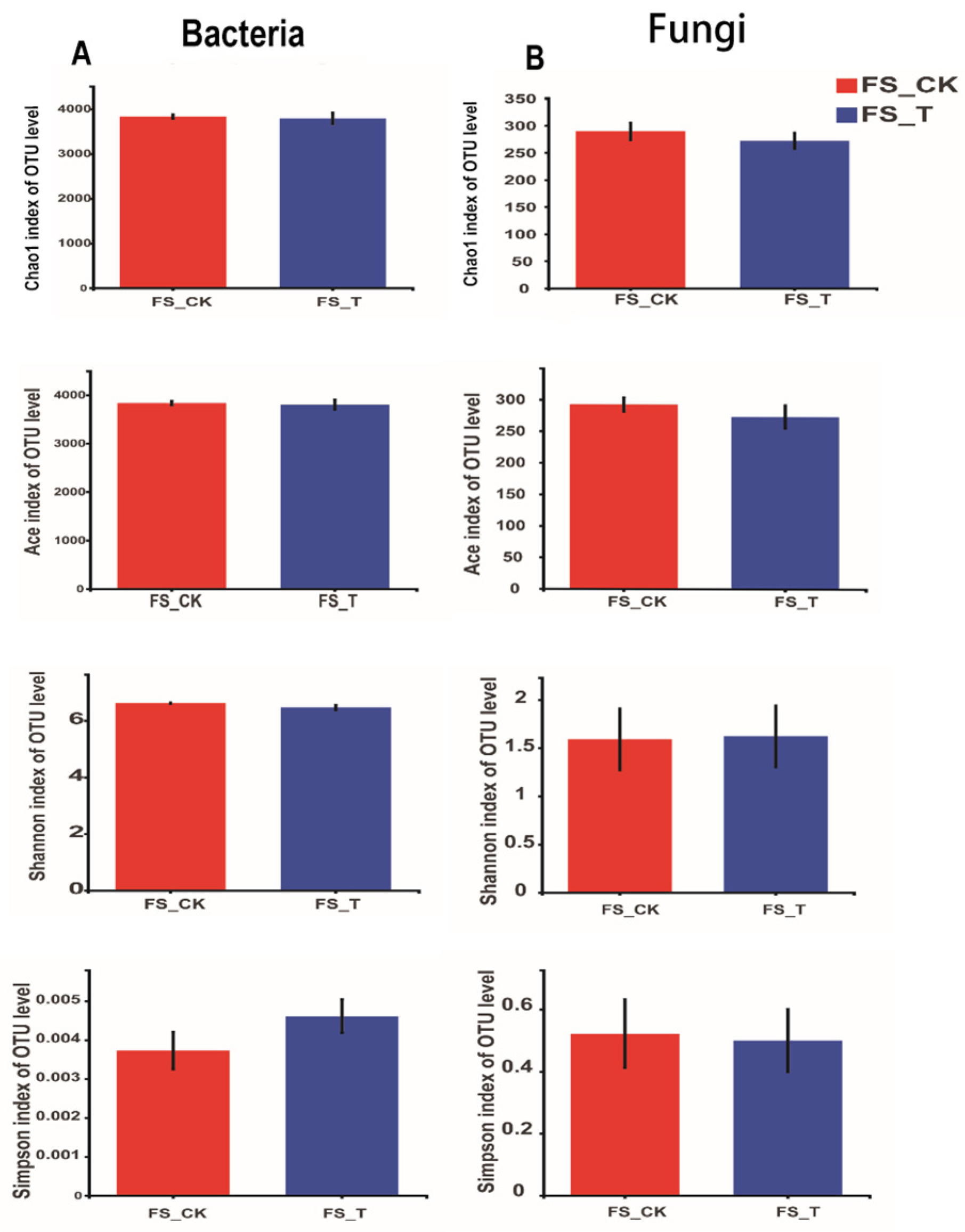
3.1.1. Bacterial and Fungal Taxonomic Changes in Triple-Fumigated Tomato Soil
3.1.2. Bacterial and Fungal Taxonomic Changes in Triple-Fumigated Watermelon Soil
3.1.3. Bacterial and Fungal Taxonomic Changes in Triple-Fumigated Cucumber Soil
3.1.4. Bacterial and Fungal Taxonomic Changes in Two Triple-Fumigated Soil Types Used to Produce Ginseng
3.1.5. Bacterial and Fungal Taxonomic Changes in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Ginger
3.2. Bacterial Community Taxonomic Analysis
3.2.1. Bacterial Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Tomatoes
3.2.2. Bacterial Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Watermelon
3.2.3. Bacterial Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Cucumber
3.2.4. Bacterial Taxonomic Change in Two Types of Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Ginseng
3.2.5. Bacterial Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Ginger
3.3. Fungal Community Taxonomic Analysis
3.3.1. Fungal Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Tomatoes
3.3.2. Fungal Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Watermelon
3.3.3. Fungal Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Cucumber
3.3.4. Fungal Taxonomic Change in Two Types of Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Ginseng
3.3.5. Fungal Taxonomic Change in Triple-Fumigated Soil Used to Produce Ginger
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Bacterial and Fungal Species Richness and Diversity
4.2. Changes in Bacterial Taxonomic Composition in the Soil
4.3. Changes in Fungal Taxonomic Composition in the Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, F.; Wang, J.H.; Cai, Y.X.; Cheng, J.Y.; Tang, Y.L.; Chen, H.L.; Ma, K.; Mi, G.Q.; Shi, X.J. Research Progress on catastrophe mechanism of continuous cropping obstacle in protected cucumber and application of enzymes. China Cucurbits Veg. 2022, 35, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Dinesh, K.; Varshney, R.; Dutta, P. The hunt for beneficial fungi for tomato crop improvement–advantages and perspectives. Plant Stress 2022, 6, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Li, L.; Shang, H.G. Present situation and Countermeasures of watermelon and melon industry in China. China Cucurbits Veg. 2020, 33, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.L.; Hu, H.Z.; Zhang, W.S.; Xin, W.F. Present situation and development suggestions of Panax notoginseng industry in Yunnan. Mod. Chin. Med. 2017, 19, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Huang, D.C.; Chen, G.T. Analysis of nutritional components of ginger from different habitats and Study on the properties of ginger polysaccharides. Food Nutr. China 2022, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, C.H. Summary of the research progress of the pharmacological action of Panax notoginseng. Guide China Med. 2011, 9, 209–210. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.B.; Pan, X.F.; Sun, Z.L. Research Progress on pharmacological action of Panax notoginseng. China Pharm. 2008, 10, 1185–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, A.C.; Fang, W.S.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.D.; Wang, Q.X.; Guo, M.X.; Huang, B.; Song, Z.X.; Jin, Q. Review of 60 years of soil fumigation in China. J. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.F. Analysis on the main harm and causation of soil borne diseases. Nong Min Zhi Fu Zhi You 2018, 22, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Zhang, D.Q.; Huang, B.; Ren, L.R.; Hao, B.Q.; Jin, Q.; Yan, D.D.; Wang, Q.X.; Cao, A.C. Research progress of microbial fertilizer on soil micro ecology after fumigant treatment. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 22, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.L.; Xia, Y.C. Common soil fumigants and their new development. Shandong Keji Bao 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.J.; Fang, W.S.; Yan, D.D.; Wang, Q.X.; Cao, A.C. Research Progress on the effect of fumigants on soil microorganisms. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2019, 21, 780–786. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.X.; Yan, D.D.; Wang, X.L.; Lü, P.X.; Li, X.Y.; Cao, A.C. Research advances in soil fumigants. J. Plant Prot. 2017, 44, 529–543. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Cai, B.Y. Research Progress on the influence of continuous cropping on soil microbial flora and its remediation. Crops 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Chen, X.; Mi, T.; Tan, F.Z. Research progress of soil fumigant chloropicrin. Liaoning Chem. Ind. 2018, 47, 425–426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.Y.; Yan, P.M.; Zhao, X.D.; Bai, X. Reconstruction and functional recovery of soil microbial community after fumigation of metam-sodium. Plant Prot. 2021, 47, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Fang, W.; Han, D.; Yan, D.; Guo, M.; Cao, A. Effects of fumigation with metam-sodium on soil microbial biomass, respiration, nitrogen transformation, bacterial community diversity and genes encoding key enzymes involved in nitrogen cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Wang, Q.X.; Yan, D.D.; Mao, L.G.; Guo, M.X.; Yan, P.M.; Cao, A.C. Effect of dimethyl disulfide fumigation on soil microbial community in continuous cropping in protected area. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2011, 19, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yan, D.; Cheng, H.; Fang, W.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Ouyang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of multi-year biofumigation on soil bacterial and fungal communities and strawberry yield. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y. Effects of Dimethyl Disulfide and Chloropicrin on Soil Microbial Community Structure and Its Restoration Dynamics in Continuous Cropping. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.D.; Zhao, P.Y.; Li, X.J.; Yan, P.M.; Ren, T.Z.; Li, Y.T. Response characteristics of soil fungi to fumigation of metham sodium. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 580–590. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X.P. Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, D.; Huang, B.; Song, Z.; Ren, L.; Hao, B.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Fang, W.; Yan, D.; et al. Organic fertilizer improves soil fertility and restores the bacterial community after 1,3-dichloropropene fumigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.R.; Li, W.J.; Li, Q.J.; Zhang, D.Q.; Fang, W.S.; Yan, D.D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.X.; Cao, A.C. Effects of different fumigants compounds on ginger soil borne diseases and yield. Agrochemicals 2022, 61, 674–678. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Bu, D.X.; Zhang, C.; Bi, Y.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, J.X. The toxicity of four soil fumigants against Phytophthora capsici and Meloidogyne incognita. J. Plant Prot. 2013, 40, 463–467. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.R.; Hao, J.L.; Hao, Y.F.; Bai, W.B.; Zhang, J.H.; Guo, R.F.; Liu, Y. Effects of four kinds of Bacillus agents on Yield and quality of sweet potato in different periods. Crops 2022, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, J.M.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.M.; Su, W.J.; Wu, D.R. Antibacterial activity and antioxidant activity of fermentation broth of Bacillus amylolyticus. J. Jimei Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 27, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, D.; Defago, G. Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.P. Study on the Control effect and Mechanism of Tomato Fusarium wilt Mediated by Biomass Carbon. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, R.Q.; Gai, Y.P.; Deng, M.G.; Chen, X.L.; Xu, D.G.; Ji, C.Y. A new peanut disease worthy of attention: Peanut new scabby rot. J. Plant Prot. 2012, 38, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Zhong, J.P.; Li, D.B. Antagonistic effect of Trichoderma on soil borne pathogenic fungi. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 1993, 1, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Daryaei, A.; Jones, E.; Glare, T.; Falloon, R. PH and water activity in culture media affect biological control activity of Trichoderma atroviride against Rhizoctonia solani. Biol. Control 2016, 92, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Fumigant (Abbreviation) | Laboratory Dose | Equivalent to Weight Consumption | Main Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chloropicrin (PIC) | 51.3 μL | 40 g/m2 | Broad-spectrum antimicrobial, fungicide, herbicide, nematicide and insecticide |
| Metham sodium (MS) | 152.7 μL | 40 g/m2 | Pesticide, herbicide, and fungicide. |
| Dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) | 51.3 μL | 50 g/m2 | Control of nematodes, weeds and soil-borne plant pathogens |
| Soil | Sand | Clay | Silt | A-N | K | P | OM | ES | PH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | g/kg | μm/cm | 1:2.5 | ||||||
| Fangshan, Beijing (N 39°6″, E 115°9″) | 69.2 | 4.0 | 26.8 | 4.3 | 215.8 | 242.8 | 33.4 | 918 | 7.1 |
| Shunyi, Beijing (N 40°13″, E 116°65″) | 66.65 | 3.53 | 29.82 | 5.16 | 142 | 85 | 16.4 | 175 | 8.26 |
| Daxing, Beijing (N 39°73″, E 116°33″) | 58.28 | 4.86 | 36.86 | 2.55 | 165 | 62.5 | 30 | 229 | 8.42 |
| Wenshan, Yunnan (N 23°06″, E 103°43″) | 12.03 | 14.23 | 73.74 | 15.8 | 255 | 61 | 68 | 681 | 5.5 |
| Xinxiang, Henan (N 35°31″, E 113°85″) | 8.32 | 12.78 | 78.9 | 8.5 | 155 | 41 | 8 | 474 | 8.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Cao, A.; Fang, W.; Yan, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Effects of Chloropicrin, Dimethyl Disulfide and Metham Sodium Applied Simultaneously on Soil-Born Bacteria and Fungi. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121982
Shi Z, Zhu J, Wu J, Cao A, Fang W, Yan D, Wang Q, Li Y. Effects of Chloropicrin, Dimethyl Disulfide and Metham Sodium Applied Simultaneously on Soil-Born Bacteria and Fungi. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121982
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhaoai, Jiahong Zhu, Jiajia Wu, Aocheng Cao, Wensheng Fang, Dongdong Yan, Qiuxia Wang, and Yuan Li. 2022. "Effects of Chloropicrin, Dimethyl Disulfide and Metham Sodium Applied Simultaneously on Soil-Born Bacteria and Fungi" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121982
APA StyleShi, Z., Zhu, J., Wu, J., Cao, A., Fang, W., Yan, D., Wang, Q., & Li, Y. (2022). Effects of Chloropicrin, Dimethyl Disulfide and Metham Sodium Applied Simultaneously on Soil-Born Bacteria and Fungi. Agriculture, 12(12), 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12121982









