Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Plant (Vernonia amygdalina Delile) in Port Harcourt Metropolis, Nigeria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
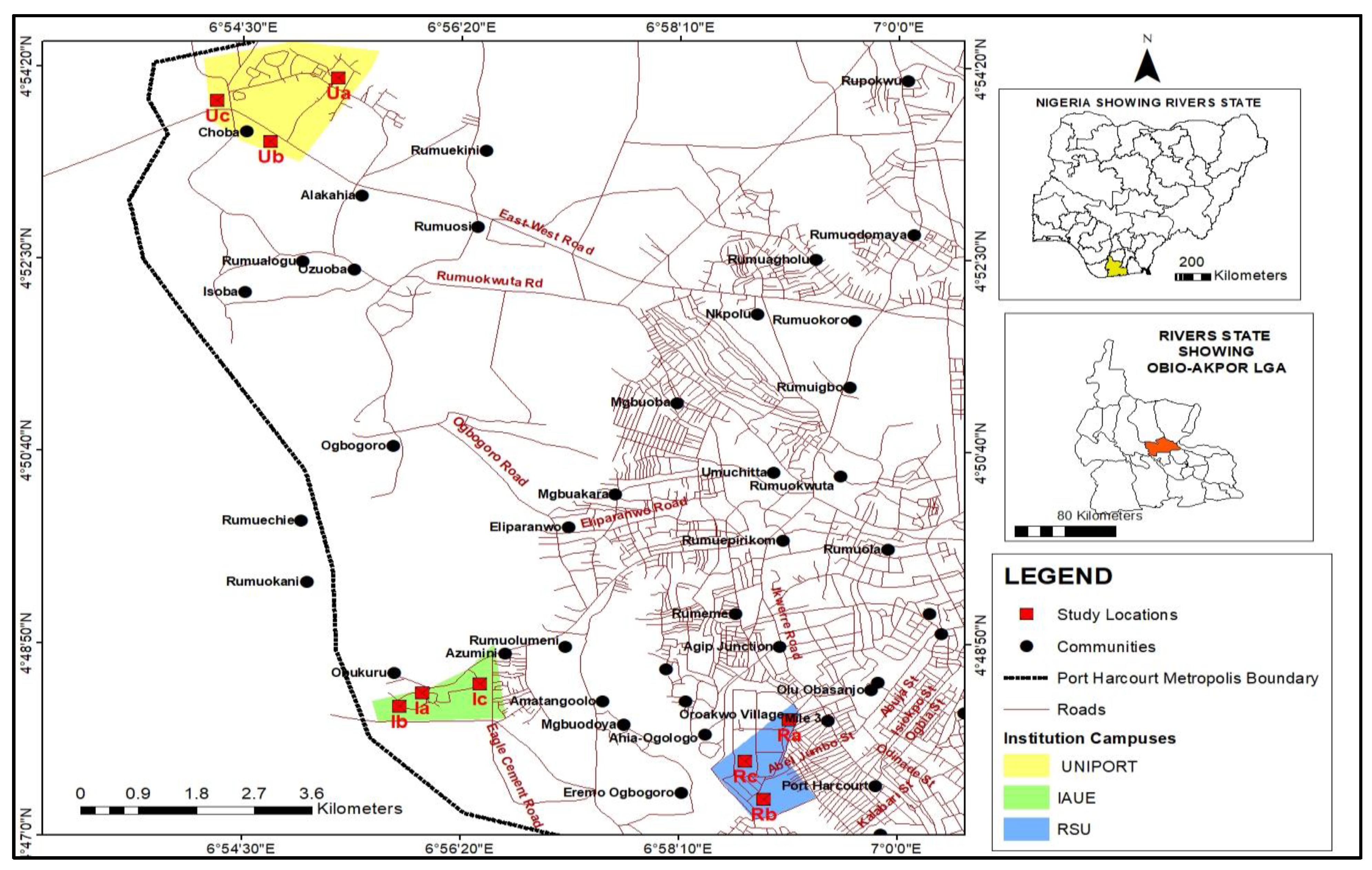
2.1. Study Stations
2.2. Sampling and Pre-Treatment Procedures
2.2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2.2. Vernonia Amygdalina Delile Sampling
2.3. Extraction Procedures
2.3.1. Agricultural Soil Extraction
2.3.2. Vernonia Amygdalina Delile Extraction
2.4. Analytical Procedures
2.5. Research and Sampling Designs
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Risk Assessment Models
- Transfer Factor (TF)
- 2.
- Contamination Factor (CF):
- 3.
- Pollution Load Index ():
- 4.
- Enrichment Factor (EF):
- 5.
- Ecological Risk Factor (ErF) and Potential Ecological Risk Factor (RI):
- 6.
- Chronic Daily Intake (CDIing) via ingestion:
- 7.
- Hazard Quotient (HQ):
- 8.
- Hazard Index (HI):
- 9.
- Carcinogenic Analysis (ILCR)
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Heavy Metal Concentration in Both Soils and Vernonia Amygdalina (Bitter Leaf)
3.2. Assessment of Pollution Indices and Health Risk Assessment for Heavy Metals in Soils and Bitter Leaf (Vernonia amygdalina)
3.2.1. Contamination Factor (CF)
3.2.2. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
3.2.3. Transfer Factor (TF)
3.2.4. Chronic Daily Intake (CDIing) for Both Soils and Bitter Leaf in Adults and Children
3.2.5. Health Risk (HQ and HI)
3.2.6. Carcinogenic Risk Analysis
3.2.7. Enrichment Factor (EF)
3.2.8. Ecological Risk Factor (ErF) and Risk Index (RI)
3.3. Statistical Analysis and Inter-Metal Correlation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, M.T.; Shaheen, B.; Khan, S. Pedo and biogeochemical studies of mafic and ultramafic rocks in the Mingora and Kabal areas, Swat, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekomo, C.B.; Nkurang, E.; Sousseau, D.P.; Lens, P.N. Fate of heavy metals in an urban natural wetland: The Nyabugogo Swamp (Rwanda). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 214, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rehman, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, M.T. Soils and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Shah, M.T.; Khan, S. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and their source apportionment in drinking water of Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchem. J. 2011, 98, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M.; Saleh, H.M. Introductory chapter: Introducing heavy metals. In Heavy Metals; Hosam El-Din, M., Saleh, R., Aglan, F., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/heavy-metals/introductory-chapter-introducing-heavy-metals (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Singh, M.R. Impurities-Heavy Metals: IR Perspective; Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission: Ghaziabad, India, 2007. Available online: http://www.usp.org/pdf/EN/meeting/asMeetingIndia/2008Session4track1.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Zhang, M.K.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, H. Use of single extraction methods to predict bioavailability of heavy metals in polluted soils to rice. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A Review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.C. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanko, C.R.; Dzombak, D.A. Remediation of Metals-Contaminated Soils and Groundwater; Ground-Water Remediation Technologies Analysis Center: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kafayatullah, Q.; Shah, M.T.; Irfan, M. Biogeochemical and environmental study of the chromite-rich ultramafic terrain of Malakand area, Pakistan. Environ. Geol. 2001, 40, 1482–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.; Lu, Y.; Khan, H.; Ishtiaq, M.; Khan, S.; Waqas, M.; Wei, L.; Wang, T. Heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops and their health risks in Swat District, northern Pakistan. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, F.A.; Ishaq, M.; Khan, S.; Ihsanullah, I.; Ahmad, I.; Shakirullah, M. A comparative study of human health risks via consumption of food crops grown on wastewater irrigated soil (Peshawar) and relatively clean water irrigated soil (lower Dir). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Bi, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, D. Assessment on environmental quality of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Chongming Island, Shanghai City. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.; Jin, T.; Bernard, A.; Fierens, S.; Buchet, J.P.; Ye, T.; Kong, Q.; Wang, H. Low bone density and renal dysfunction following environmental cadmium exposure in China. AMBIO 2002, 31, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkdogan, M.K.; Fevzi, K.; Kazim, K.; Ilyas, T.; Ismail, U. Heavy metal in soil, vegetables and fruits in the endemic upper gastrointestinal cancer region of Turkey. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.F.; Wang, F.H.; Wang, X.; He, W.; Wen, D.; Wang, Q.F.; Liu, X.X. Soil threshold values of total and available cadmium for vegetable growing based on field data in Guangdong Province, south China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhatt, K.; Pandey, K.; Rai, U.; Singh, K.P. Distribution of metals in the edible plants grown at Jajmau, Kanpur (India) receiving treated tannery waste water, relation with physicochemical properties of the soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 115, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echem, O.G.; Kabari, L.G. Heavy metal content in bitter leaf (Vernonia amygdalina) grown along heavy traffic routes in Port Harcourt. Agric. Chem. 2013, 12, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, M.A.; Salama, A.K. Market basket survey for some heavy metals in Egyptian fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echem, O.G. Analysis of heavy metals (Lead Pb, Cadmium Cd, Chromium Cr, and Cobalt Co) content of cassava (Manihot esculenta crantz) cultivated on oil polluted soil in Ogoni land, Nigeria. Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2010, 3, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Odukoya, A.M. Contamination assessment of toxic elements in the soil within and around two dumpsites in Lagos, Nigeria. Ife J. Sci. 2015, 17, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Edori, O.S.; Kpee, F. Index models assessment of heavy metal pollution in soils within selected abbattoirs in port harcourt, Rivers State, Nigeria. Singap. J. Sci. Res. 2017, 7, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhri, Y.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Conti, G.O.; Ferrante, M.; Khezri, A.; Darvishi, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Hasanzadeh, V.; Rahimizadeh, A.; Keramati, H.; et al. Probabilistic risk assessment (Monte Carlo simulation method) of Pb and Cd in the onion bulb (Alliumcepa) and soil of Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30894–30906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welz, B.; Sperling, M. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Adesodun, J.K.; Atayese, M.O.; Agbaje, T.; Osadiaye, B.A.; Mafe, O.; Soretire, A.A. Phytoremediation potentials of sunflowers (Tithonia diversifolia andHelianthusannuus) for metals ins oils contaminated with zinc and lead nitrates. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 207, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikumar, P.S.; Nasir, U.P.; Rahman, M.P.M. Distribution of heavy metals in the Core Sediments of Tropical Wetland System. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.H.; Li, L.Q.; Wu, X.M.; Pan, G.X. Distribution of Cu and Pb in particle size fractions of urban soils from different city zones of Nanjing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 482–487. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Meeresunters 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants. In Forty-First Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Series; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993; p. 837. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Environmental Protection Agency. Integrated Risk Information System. 2000. Available online: http://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/compare.cfm (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- IBGE. Censo Agropecuário 2006; Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2006.
- Gržetić, I.; Ghariani, A.R.H. Potential health risk assessment for soil heavy metal contamination in the central zone of Belgrade (Serbia). J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2008, 73, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Maghakyan, N.; Sahakyan, L.; Saghatelyan, A. Heavy metals pollution levels and children health risk assessment of Yerevan kindergartens soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiroma, T.M.; Ebewele, R.O.; Hymore, F.K. Comparative assessment of heavy metal levels in soil, vegetables and urban grey waste water used for irrigation in Yola and Kano. Int. Refereed J. Eng. Sci. 2014, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Edori, O.S.; Iyama, W.A. Assessment of physicochemical parameters of soils from selected abattoirs in Port Harcourt, Rivers state, Nigeria. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 4, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacholi, D.S.; Sahu, M. Levels and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil, water, and vegetables of dares salaam, Tanzania. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1402674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasrina, R.C.; Rowshon, A.; Mustafizur, A.M.R.; Rafiqul, I.; Ali, M.P. Heavy metals contamination in vegetables and its growing soil. J. Environ. Analytical. Chem. 2015, 2, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Folorunsho, J.O. Heavy metals concentration in soil and Amaranthusretroflexus grown on irrigated farmlands in the Makera Area, Kaduna, Nigeria. J. Geogr. Reg. Plan. 2015, 8, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fosu-Mensah, B.Y.; Addae, E.; Yirenya-Tawiah, D.; Nyame, F. Heavy metals concentration and distribution in soils and vegetation at Korle Lagoon area in Accra, Ghana. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2017, 3, 1405887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawal, A.O.; Audu, A.A. Analysis of Heavy Metals Found in Vegetables from Some Cultivated Irrigated Gardens in the Kano metropolis, Nigeria. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2011, 3, 142–148. Available online: https://academicjournals.org/article/article1380007572_Lawal%20and%20Audu.pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Towle, K.M.; Garnick, L.C.; Monnot, A.D. A human health risk assessment of lead (Pb) ingestion among adult wine consumers. Food Contam. 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kananke, T.; Wansapala, J.; Gunaratne, A. Heavy metal contamination in green leafy vegetables collected from selected market sites of Piliyandala Area, Colombo District, Sri Lanka. Am. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 2, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hange, K.; Awofolu, O.R. Assessment of anthropogenic influence on the level of selected heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) in soil. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2017, 8, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumbach, R.J.; Kipen, H.M. Respiratory health effects of air pollution: Update on biomass smoke and traffic pollution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhu, W.; Amombo, E.; Lou, Y.; Chen, L.; Fu, J. Effect of heavy metals pollution on soil microbial diversity and Bermudagrass genetic variation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edet, A.; Ukpong, A. The concentrations of potentially toxic elements and total hydrocarbon in soils of Niger Delta Region (Nigeria). J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO. Food additives and contaminants. In Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Program; ALI-NORM 01/12A; Codex Alimentarius Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2–7 July 2001; pp. 1–289. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, G.; Hermann, T.; Da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Tian, K.; Holm, P.E.; Zhang, Y. Heavy metals in intensive greenhouse vegetable production systems along Yellow Sea of China: Levels, transfer and health risk. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Afyuni, M.; Khademi, H.; Abbaspour, K.; Schulin, R. Mapping risk of cadmium and lead contamination to human health in soils of central Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 347, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartenkamp, A. Are cadmium and other heavy metal compounds acting as endocrine disrupters? Met. Ions Life Sci. 2011, 8, 305–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Damdimopoulou, P.; Stenius, U.; Adamsson, A.; Akesson, A.; Berglund, M.; Håkansson, H.; Halldin, K. Cadmium-induced effects on cellular signaling pathways in the liver of transgenic estrogen reporter mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 127, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MHSPE: Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment, The Netherlands. Environmental Standards. Circular on target values and intervention values for soil remediation. In Dutch Target and Intervention Values (the New Dutch List), 4th ed.; MHSPE: The Netherlands, 2000; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; Available online: http://www.who.int (accessed on 25 September 2021).
- DPR-EGASPIN. Department of Petroleum Resources (DPR) and Environmental Guidelines and Standards for the Petroleum Industry in Nigeria (EGASPIN); Review of the Environmental Guidelines and Standards for the Petroleum Industry in Nigeria (EGASPIN) Department of Petroleum Resources: Lagos, Nigeria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Abdu, N.; Agbenin, J.O.; Buerkert, A. Fractionation and mobility of cadmium and zincin urban vegetable gardens of Kano, northern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.A. Remedial Options for Metals-Contaminated Sites; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, K.A.; Oluwole, S.O. Heavy metal (Cu, Zn, Pb) contamination of vegetables in urban city: A case study in Lagos. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezejiofor, T.I.N.; Ezejiofor, A.N.; Udebuani, A.C.; Ezeji, E.U.; Ayalogbu, E.A.; Azuwuike, C.O.; Adjero, L.A.; Ihejirika, C.E.; Ujowundu, C.O.; Nwaogu, L.A.; et al. Environmental metals pollutants load of a densely populated and heavily industrialized commercial city of Aba, Nigeria. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2013, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adagunodo, T.A.; Sunmonu, L.A.; Emetere, M.E. Heavy metals’ data in soils for agricultural activities. Data Brief 2018, 18, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masona, C.; Mapfaire, L.; Mapurazi, S.; Makanda, R. Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in wastewater irrigated soil and uptake by maize plants (Zea Mays L.) at firle farm in harare. J. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, J.P. Understanding phytotoxicity thresholds for trace elementsin land-applied sewage-sludge. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadoust, A.P.; Reddy, K.R.; Maturi, K. Removal of nickel and phenanthrene from kaolin soil using different extractants. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2004, 21, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44584/9789241548151_eng.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2021).
- Saeki, S.; Kubota, M.; Asami, T. Determination of silver in soils by atomic absorption spectrometry. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 83, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigberua, A.; Tarawou, T. Speciation and mobility of selected heavy metals in sediments of the nun river system, Bayelsa State, Nigeria. Environ. Toxicol. Stud. J. 2018, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Moslen, M.; Ekweozor, I.K.E.; Nwoka, N.D. Assessment of heavy metals pollution in surface sediments of a tidal creek in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2018, 3, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, F.; Ou, J. Global pesticide consumption and pollution: With China as a focus. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 1, 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullateef, B.; Kolo, B.G.; Waziri, I.; Idris, M.A. Levels of heavy metals in soil as indicator of environmental pollution in Maiduguri, Borno state, Nigeria. Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 2014, 3, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkersdorfer, C.; Sartz, L.; Sillanpää, M.; Häkkinen, A. Enrichment and Geo accumulation of Pb, Zn, As, Cd and Cr in soils near New Union Gold Mine, Limpopo Province of South Africa. Available online: https://www.imwa.info/docs/imwa_2017/IMWA2017_Muzerengi_720.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2021).
- Manoj, K.; Padhy, P.K. Distribution, enrichment and ecological risk assessment of six elements in bed sediments of a tropical river, chottanagpur plateau: A spatial and temporal appraisal. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 5, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogundele, F.O.; Iwara, A.I.; Jeremiah, C.J. Heavy Metal Contents in the Soil and Leaves of Different Vegetables in Lagos State, Nigeria. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2019, 12, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.J.I.; Soni, H.; Kumar, R.N.; Bhatt, I. Hyperaccumulation and Mobility of Heavy Metals in Vegetable Crops in India. J. Agric. Environ. 2009, 10, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Eze, M.O.; Ekanem, E.O. Bioaccumulation and mobility of cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) in green spinach grown on dumpsite soils of different pH levels. Bull. Environ. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 2014, 4, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Farooq, R.; Shahbaz, S.; Khan, M.A.; Sadique, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals for population via consumption of vegetables. World Appl. Sci. J. 2009, 6, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from wastewater irrigated area, Beijing-Tianjin City cluster, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadia, C.D.; Fulekar, M.H. Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Recent techniques. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 921–928. [Google Scholar]
- Jaishankar, M.; Mathew, B.B.; Shah, M.S.; Gowda, K.R.S. Biosorption of heavy metal ions using agricultural wastes. J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health 2014, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, A.W.; Egejuru, N.J. pH variations and chemometric assessment of borehole water in Orji, Owerri Imo State, Nigeria. J. Environ. Anal Chem. 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Yi, X.; Dang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Luo, H.; Tang, J. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of a tailing pond in Gangdong, China. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Agrawa, M.; Marshall, F.M. Risk assessment of heavy metal toxicity through contaminated vegetables from waste water irrigated area of Varanasi. India Trop. Ecol. 2010, 51, 375–387. [Google Scholar]
- Isiuku, B.O.; Enyoh, C.E. Monitoring and modeling of heavy metal contents in vegetables collected from markets in Imo State, Nigeria. Environ. Anal Health Toxicol. 2020, 35, e2020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ametepey, S.T.; Cobbina, S.J.; Akpabey, F.J.; Abudu, B.D.; Zita, N.A. Health risk assessment and heavymetal contamination levels in vegetables from Tamale Metropolis, Ghana. Food Contam. 2018, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Z.J.; Liu, S.Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Yan, Y.L. Health risk assessment of heavy metals for edible parts of vegetables grown in sewage –irrigated soils in suburbs of Baoding City, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 3503–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortey-Sam, N.; Nakayama, S.M.; Ikenaka, Y.; Akoto, O.; Baidoo, E.; Yohannes, Y.B. Human health risks from metals and metalloid via consumption of food animals near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana: Estimation of the daily intakes and target hazard quotients (THQs). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 111, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karimi, A.; Naghizadeh, A.; Biglari, H.; Peirovi, R.; Ghasemi, A.; Zarei, A. Assessment of human health risks and pollution index for heavy metals in farmlands irrigated by effluents of stabilization ponds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2000, 27, 10317–10327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Ma, J.; Dong, T.; Huang, N.; Sun, C.; He, B.; Wei, F. Health risks from the exposure of children to As, Se, Pb and other heavy metals near the largest coking plant in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edith-Etakah, B.T.; Shapi, M.; Penaye, J.; Mimba, M.E.; NguemheFils, S.C.; Nadasan, D.S.; Davies, T.C.; Jordaan, M.A. Background concentrations of potentially harmful elements in soils of the Kette-Batouri Region, Eastern Cameroon. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 11, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osakwe, S.A. Contributions of abattoir activities in Delta State, Nigeria to the soil properties of their surrounding environment. J. Chem. Biol. Phys. Sci. 2016, 6, 982–991. [Google Scholar]
- Kieri, I.B.S.; Ekpete, O.A.; Edori, O.S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediments of Silver River, Southern Ijaw, Bayelsa State, Nigeria. Environ. Anal. Eco. Stud. 2021, 7, 186–193. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349549683_Assessment_of_Heavy_Metal_Pollution_in_Sediments_of_Silver_River_Southern_Ijaw_Bayelsa_State_Nigeria (accessed on 26 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, R. The accumulation and health risk of heavy metals in vegetables around a zinc smelter in northeastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 25114–25126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.M.; Xie, B.; Peng, G.; Huang, L. Heavy metal pollution status, spatial distribution and associated ecological risks within sediments of Yundang Lagoon catchment in Xianmen, China, after 30-years continuous ecological rehabilitation. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 27, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample Stations | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals(mg/kg) | I | Control (Ic) | R | Control (Rc) | U | Control | Mean (I, R, U) |
| Fe | 19.71 ± 1.77 | 22.51 ± 2.25 | 27.24 ± 3.56 | 27.57 ± 2.37 | 19.69 ± 1.78 | 20.55 ± 2.50 | 22.21 |
| Pb | 6.80 ± 0.86 | 7.36 ± 1.20 | 4.35 ± 0.87 | 5.35 ± 0.46 | 5.60 ± 0.01 | 6.40 ± 1.40 | 2.98 |
| Cd | 0.46 ± 0.28 | 0.50 ± 0.24 | 0.71 ± 0.11 | 0.75 ± 0.21 | 1.42 ± 0.40 | 2.40 ± 0.50 | 0.87 |
| Cr | 8.77 ± 0.88 | 8.78 ± 0.56 | 5.91 ± 1.14 | 6.56 ± 0.56 | 7.89 ± 0.26 | 8.20 ± 1.20 | 7.52 |
| Ni | 0.54 ± 3.38 | 0.48 ± 3.50 | 10.26 ± 3.50 | 11.15 ± 0.20 | 5.14 ± 0.12 | 5.50 ± 0.05 | 5.31 |
| Ag | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sample Stations | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals(mg/kg) | I | Control (Ic) | R | Control (Rc) | U | Control (Uc) | Mean |
| Fe | 14.86 ± 0.33 | 15.50 ± 0.50 | 12.95 ± 1.68 | 13.23 ± 0.54 | 18.18 ± 2.02 | 19.20 ± 1.00 | 15.33 |
| Pb | 0.98 ± 0.11 | 1.20 ± 0.20 | 0.24 ± 0.64 | 13.23 ± 0.54 | 2.19 ± 0.74 | 2.40 ± 0.50 | 1.14 |
| Cd | 0.17 ± 0.10 | 0.35 ± 0.25 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.05 | 0.42 ± 0.08 | 0.54 ± 0.26 | 0.30 |
| Cr | 5.92 ± 0.69 | 6.15 ± 0.50 | 4.88 ± 0.05 | 5.10 ± 0.03 | 4.04 ± 0.64 | 4.50 ± 0.45 | 4.95 |
| Ni | 0.04 ± 1.42 | 0.10 ± 1.60 | 3.30 ± 0.88 | 3.59 ± 0.10 | 2.80 ± 0.53 | 3.20 ± 0.10 | 2.05 |
| Ag | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sample Stations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals (mg/kg) | I | R | U | Mean |
| Fe | 0.0004 (0.310) | 0.0006 (0.270) | 0.0004 (0.379) | 0.0005 (0.320) |
| Pb | 0.3400 (3.273) | 0.2200 (0.790) | 0.2800 (7.297) | 0.2800 (3.787) |
| Cd | 1.5500 (0.830) | 2.3500 (1.595) | 4.7500 (2.095) | 2.8833 (1.507) |
| Cr | 0.1000 (2.576) | 0.0700 (2.120) | 0.0900 (1.757) | 0.0657 (2.151) |
| Ni | 0.0100 (0.028) | 0.1500 (2.197) | 0.0800 (1.865) | 0.0080 (1.363) |
| Ag | <0.001 (<0.001) | <0.001 (<0.001) | <0.001 (<0.001) | <0.001 (<0.001) |
| Sample Stations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U |
| Fe | A (2.7 × 10−5) C (2.5 × 10−4) | A (3.7 × 10−5) C (3.5 × 10−4) | A (2.7 × 10−5) C (2.5 × 102−4) |
| Pb | A (9.0 × 10−6) C (2.5 × 10−5) | A (6.0 × 10−6) C (5.6 × 10−5) | A (8.0 × 10−6) C (7.2 × 10−5) |
| Cd | A (6.0 × 10−7) C (6.0 × 10−6) | A (1.0 × 10−6) C (9.0 × 10−6) | A (2.0 × 10−6) C (1.8 × 10−5) |
| Cr | A (1.2 × 10−5) C (1.1 × 10−4) | A (8.0 × 10−6) C (7.6 × 10−5) | A (1.1 × 10−5) C (1.0 × 10−4) |
| Ni | A (7.0 × 10−7) C (2.5 × 10−6) | A (1.4 × 10−5) C (1.3 × 10−4) | A (7.0 × 10−6) C (6.6 × 10−5) |
| Sample Stations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U |
| Fe | A (2.0 × 10−5) C (1.9 × 10−4) | A (1.8 × 10−5) C (1.7 × 10−4) | A (2.5 × 10−5) C (2.3 × 10−4) |
| Pb | A (1.3 × 10−6) C (1.3 × 10−5) | A (3.0 × 10−7) C (3.0 × 10−6) | A (3.0 × 10−6) C (2.8 × 10−5) |
| Cd | A (2.0 × 10−7) C (2.1 × 10−6) | A (4.0 × 10−7) C (4.1 × 10−6) | A (6.0 × 10−7) C (5.4 × 10−6) |
| Cr | A (8.0 × 10−6) C (7.6 × 10−5) | A (6.7 × 10−5) C (6.2 × 10−5) | A (5.5 × 10−6) C (5.2 × 10−5) |
| Ni | A (6.0 × 10−8) C (5.4 × 10−7) | A (4.5 × 10−6) C (4.2 × 10−5) | A (3.8 × 10−6) C (3.6 × 10−5) |
| Sample Stations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U |
| Fe | (5.57 × 10−6) (5.14 × 10−4) | (7.57 × 10−5) (7.14 × 10−4) | (5.57 × 10−5) (5.14 × 10−4) |
| HQ/HI | (1.48 × 10−6) (1.42 × 10−5) | (3.0 × 10−6) (3.2 × 10−6) | (3.7 × 10−6) (3.7 × 10−6) |
| Pb | (0.74) (7.14) | (0.49) (4.57) | (0.65) (6.00) |
| HQ/HI | (0.20) (0.20) | (0.02) (0.02) | (0.04) (0.04) |
| Cd | (0.60) (6.00) | (1.00) (9.00) | (2.00) (18.0) |
| HQ/HI | (0.16) (0.17) | (0.04) (0.04) | (0.13) (0.13) |
| Cr | (1.33) (12.3) | (0.90) (8.33) | (1.23) (11.0) |
| HQ/HI | (0.35) (0.34) | (0.04) (0.04) | (0.08) (0.11) |
| Ni | (1.10) (10.8) | (22.5) (200) | (11.0) (104) |
| HQ/HI | (0.29) (0.30) | (0.90) (0.90) | (0.74) (0.75) |
| Sample Stations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U |
| Fe | (4.14 × 10−5) (3.86 × 10−4) | (3.71 × 10−5) (3.43 × 10−4) | (5.14 × 10−4) (4.71 × 10−4) |
| HQ/HI | (2.48 × 10−5) (2.38 × 10−6) | (2.57 × 10−6) (4.10 × 10−6) | (6.0 × 10−5) (5.9 × 10−6) |
| Pb | (0.11) (1.06) | (0.02) (0.25) | (0.25) (2.29) |
| HQ/HI | (0.07) (0.07) | (1.38 × 10−3) (2.99 × 10−3) | (0.03) (0.03) |
| Cd | (0.57) (6) | (0.11) (11.7) | (1.71) (15.43) |
| HQ/HI | (0.34) (0.37) | (7.61 × 10−3) (0.14) | (0.20) (0.19) |
| Cr | (0.9) (8.33) | (7.33) (6.67) | (0.6) (5.67) |
| HQ/HI | (10) (9.8) | (0.51) (0.08) | (0.07) (0.07) |
| Ni | (0.09) (0.85) | (7) (65) | (6) (56.3) |
| HQ/HI | (0.05) (0.05) | (0.48) (0.78) | (0.71) (0.71) |
| Sample Stations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U |
| Fe | (0) (0) | (0) (0) | (0) (0) |
| Pb | (1.06 × 10−3) (2.94 × 10−3) | (7.06 × 10−4) (6.59 × 10−3) | (9.41 × 10−4) (8.47 × 10−3) |
| Cd | (1.58 × 10−6) (1.58 × 10−5) | (2.63 × 10−6) (2.37 × 10−5) | (5.26 × 10−6) (4.74 × 10−5) |
| Cr | (2.4 × 10−5) (2.2 × 10−4) | (1.6 × 10−5) (1.52 × 10−4) | (2.26 × 10−5) (2.2 × 10−4) |
| Ni | (7.69 × 10−7) (2.75 × 10−6) | (1.54 × 10−5) (1.43 × 10−4) | (7.69 × 10−6) (7.25 × 10−5) |
| Sample Stations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U |
| Fe | (0) (0) | (0) (0) | (0) (0) |
| Pb | (1.53 × 10−4) (1.53 × 10−3) | (3.53 × 10−5) (3.53 × 10−4) | (3.53 × 10−4) (2.8 × 10−5) |
| Cd | (5.26 × 10−7) (5.53 × 10−6) | (1.05 × 10−6) (1.08 × 10−5) | (1.58 × 10−6) (1.42 × 10−5) |
| Cr | (1.6 × 10−5) (1.52 × 10−4) | (1.34 × 10−4) (1.24 × 10−4) | (1.1 × 10−5) (1.04 × 10−4) |
| Ni | (6.59 × 10−8) (5.93 × 10−7) | (4.94 × 10−6) (4.62 × 10−5) | (4.18 × 10−6) (3.96 × 10−5) |
| Sample Stations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U | Mean |
| Fe | - | - | - | - |
| Pb | 191 (10,229) | 88 (2821) | 157 (18,709) | 145 (10,586) |
| Cd | 3683 (2594) | 4057 (5696) | 11,302 (5372) | 6347 (4554) |
| Cr | 232 (8049) | 113 (7570) | 209 (4504) | 185 (6708) |
| Ni | 19 (88) | 260 (7848) | 180 (4783) | 153 (4240) |
| Sample Stations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | I | R | U | Mean |
| Fe | - | - | - | - |
| Pb | 1.70 (16.37) | 1.10 (3.95) | 1.400 (36.49) | 1.40 (18.94) |
| Cd | 46.50 (24.90) | 70.50 (47.85) | 142.5 (62.85) | 86.5 (45.20) |
| Cr | 0.20 (5.15) | 0.14 (4.24) | 0.180 (3.51) | 0.17 (4.30) |
| Ni | 0.05 (0.14) | 0.75 (10.99) | 0.400 (9.33) | 0.40 (6.82) |
| RI (Risk Index) | 48.45 (46.56) | 72.49 (67.03) | 144.5 (112.18) | 88.48 (75.26) |
| Statistics (Bitter Leaf) | |||||
| Heavy Metals (mg/kg) | Mean | Median | Min | Max | SD |
| Fe | 15.33 | 14.86 | 12.95 | 18.18 | 2.65 |
| Pb | 1.14 | 0.98 | 0.24 | 2.19 | 0.99 |
| Cd | 0.90 | 0.319 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.13 |
| Cr | 4.95 | 4.88 | 4.04 | 5.92 | 0.94 |
| Ni | 2.05 | 2.80 | 0.04 | 3.30 | 1.75 |
| Statistics (soil) | |||||
| Mean | Median | Min | Max | SD | |
| Fe | 22.21 | 19.71 | 19.70 | 27.24 | 4.35 |
| Pb | 5.59 | 5.60 | 4.35 | 6.80 | 1.23 |
| Cd | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.46 | 1.42 | 0.50 |
| Cr | 7.52 | 7.89 | 5.91 | 8.77 | 1.47 |
| Ni | 5.31 | 5.14 | 0.54 | 10.26 | 4.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iyama, W.A.; Okpara, K.; Techato, K. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Plant (Vernonia amygdalina Delile) in Port Harcourt Metropolis, Nigeria. Agriculture 2022, 12, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010027
Iyama WA, Okpara K, Techato K. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Plant (Vernonia amygdalina Delile) in Port Harcourt Metropolis, Nigeria. Agriculture. 2022; 12(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleIyama, William Azuka, Kingsley Okpara, and Kuaanan Techato. 2022. "Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Plant (Vernonia amygdalina Delile) in Port Harcourt Metropolis, Nigeria" Agriculture 12, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010027
APA StyleIyama, W. A., Okpara, K., & Techato, K. (2022). Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Plant (Vernonia amygdalina Delile) in Port Harcourt Metropolis, Nigeria. Agriculture, 12(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010027







