Modeling for the Prediction of Soil Moisture in Litchi Orchard with Deep Long Short-Term Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
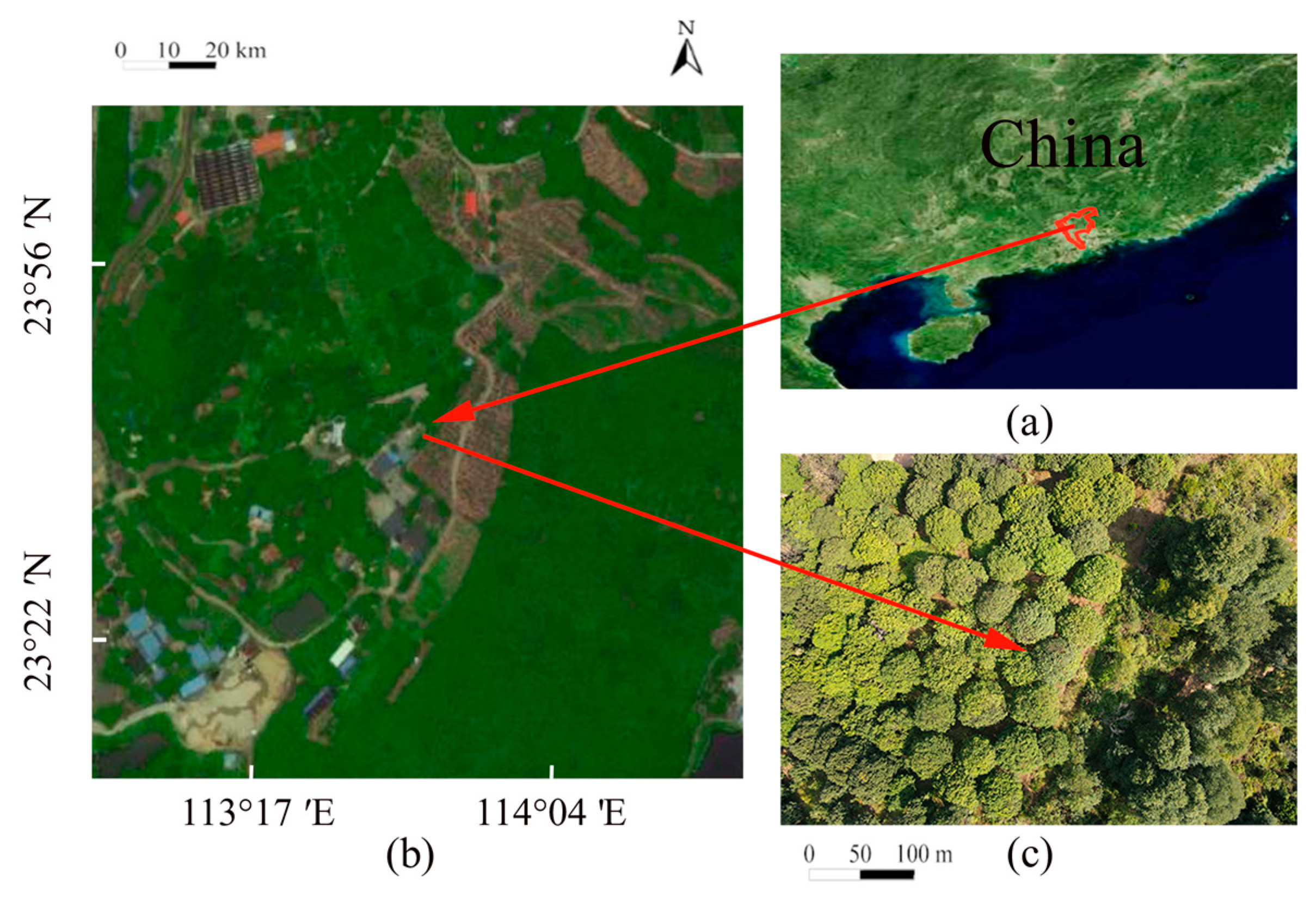
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Data Denoising
2.2.1. Wavelet Decomposition
2.2.2. Threshold Optimization
2.2.3. Wavelet Reconstruction
2.3. Evapotranspiration Estimation of Litchi Orchard
2.4. Data Preprocessing
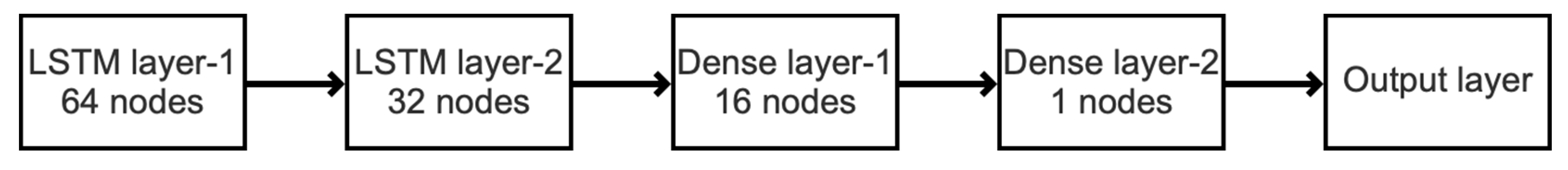
2.5. Time Series Model Based on Deep-LSTM Model
2.6. Classic Models to Compare with Deep-LSTM
2.6.1. Elman Neural Network
2.6.2. Generalized Regression Neural Network (GRNN) Model
3. Results
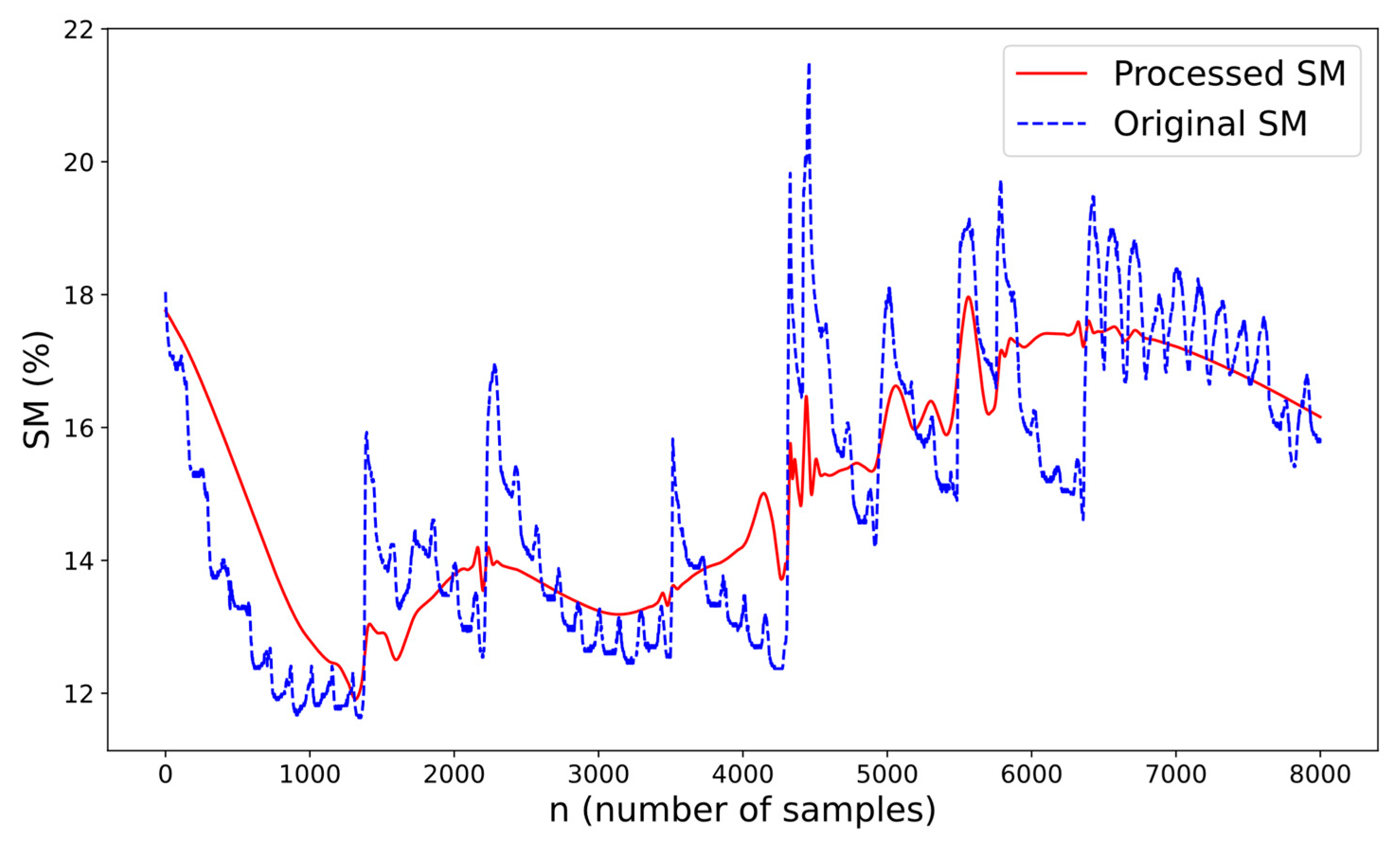
3.1. Results of Wavelet Denoising
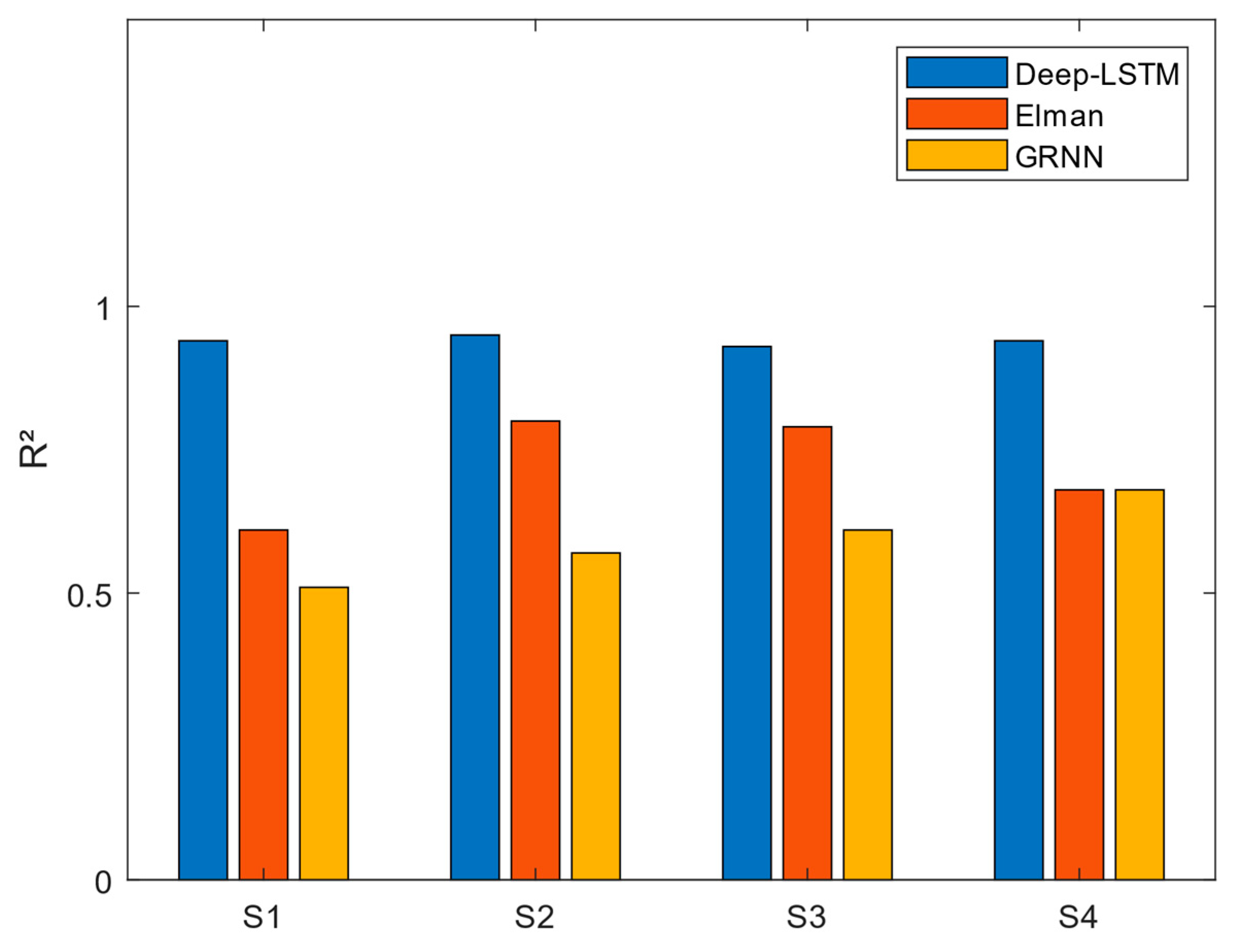
3.2. Performance of Models
3.3. Model Fitting Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, X.; Lin, H.; Shi, J.; Neethirajan, S.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y. Effects of a Novel Chitosan Formulation Treatment on Quality Attributes and Storage Behavior of Harvested Litchi Fruit. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, Z. A Visual Detection Method for Nighttime Litchi Fruits and Fruiting Stems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lü, E.; Lu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Quality Detection of Litchi Stored in Different Environments Using an Electronic Nose. Sensors 2016, 16, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.P. World Trade in Litchi: Past, Present and Future. Acta Hortic. 2001, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Ge, H.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, M.; Meng, Y.; Li, X. The Characteristics of Oestrone Mobility in Water and Soil by the Addition of Ca-Biochar and Fe–Mn-Biochar Derived from Litchi chinensis sonn. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, M.B.; Dukes, M.D. Validation of Landscape Irrigation Reduction with Soil Moisture Sensor Irrigation Controllers. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.K.V.; Menzel, C.M. The Water Relations and Irrigation Requirements of Lychee (Litchi chinensis sonn.): A Review. Exp. Agric. 2014, 50, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gurav, M.; Sarik, S.; Singh, K.; Pendharkar, G.; Baghini, M.S. IITB_TDR: A Portable TDR System with DWT Based Denoising for Soil Moisture Measurement. Sens. Actuator Phys. 2018, 283, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Hu, G.; Lin, C.; Gao, P.; Sun, D.; Xue, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, W. Irrigation Prediction Model with BP Neural Network Improved by Genetic Algorithm in Orchards. In Proceedings of the 2019 Eleventh International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Guilin, China, 7–9 June 2019; pp. 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Spatial Prediction of Soil Moisture Content Using Multiple-Linear Regressions in a Gully Catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.K.; Asefa, T.; Kemblowski, M.W.; McKee, M. Soil Moisture Prediction Using Support Vector Machines1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Grove, I.; Peets, S.; Domun, Y.; Norton, T. Dynamic Neural Network Modelling of Soil Moisture Content for Predictive Irrigation Scheduling. Sensors 2018, 18, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Xie, J.; Yang, M.; Zhou, P.; Chen, W.; Liang, G.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, W. Improved Soil Moisture and Electrical Conductivity Prediction of Citrus Orchards Based on IoT Using Deep Bidirectional LSTM. Agriculture 2021, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.C.; Shukla, S.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Chen, L.-C. Do Climate Forecast System (CFSv2) Forecasts Improve Seasonal Soil Moisture Prediction? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xie, Z.; Wu, L.; Yu, Z.; Li, R. Data Prediction Model in Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Bidirectional LSTM. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Li, N. Automated Recognition of Epileptic EEG States Using a Combination of Symlet Wavelet Processing, Gradient Boosting Machine and Grid Search Optimizer. Sensors 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiranyaz, S.; Ince, T.; Zabihi, M.; Ince, D. Automated Patient-Specific Classification of Long-Term Electroencephalography. J. Biomed. Inform. 2014, 49, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, F.M.; Kozakevicius, A.J.; Cintra, R.J. An Iterative Wavelet Threshold for Signal Denoising. Signal Process. 2019, 162, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, D.; Sun, H.; Yang, L. Estimation of Chlorophyll Content in Maize Canopy Using Wavelet Denoising and SVR Method. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.-M.; Cui, H. Improved Threshold Denoising Method Based on Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC), Sousse, Tunisia, 18–20 December 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.-J.; Huang, X.-Y.; Fang, M.-C. MRI Denoising by NeighShrink Based on Chi-Square Unbiased Risk Estimation. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 97, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, I.A.; Allen, R.G.; Elliott, R.; Jensen, M.E.; Itenfisu, D.; Mecham, B.; Howell, T.A.; Snyder, R.; Brown, P.; Echings, S.; et al. ASCE’s Standardized Reference Evapotranspiration Equation. In Proceedings of the Watershed Management and Operations Management 2000, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 20–24 June 2000; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.G.; Kang, S. An Improved Evapotranspiration Model for an Apple Orchard in Northwestern China. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Italy, Rome, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Rallo, G.; González-Altozano, P.; Manzano-Juárez, J.; Provenzano, G. Using Field Measurements and FAO-56 Model to Assess the Eco-Physiological Response of Citrus Orchards under Regulated Deficit Irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 180, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Peng, Y.; Cui, N.; Gong, D.; Zhang, K. Modeling Reference Evapotranspiration Using Extreme Learning Machine and Generalized Regression Neural Network Only with Temperature Data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Shukla, S.; Wadhvani, R. Dynamic Selection of Normalization Techniques Using Data Complexity Measures. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 106, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, B. Investigating the Impact of Data Normalization on Classification Performance. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, M.; Jin, L. Data Normalization to Accelerate Training for Linear Neural Net to Predict Tropical Cyclone Tracks. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 931629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Lin, W.; Raghavan, N. A Novel Framework for Semiconductor Manufacturing Final Test Yield Classification Using Machine Learning Techniques. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 197885–197895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, H.; Sak, H.; Tripathi, A.; McDermott, E.; Koo, S.; Kumar, S. Transformer Transducer: A Streamable Speech Recognition Model with Transformer Encoders and RNN-T Loss. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 7829–7833. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Shi, Z.H.; Zhu, H.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ai, L.; Yin, W. Soil Moisture Dynamics within Soil Profiles and Associated Environmental Controls. Catena 2016, 136, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T. A Review on Time Series Data Mining. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2011, 24, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, F.-M.; Yu, H.-C.; Tzeng, G.-H. Combining Neural Network Model with Seasonal Time Series ARIMA Model. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2002, 69, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Bu, S.; Kim, I. An Enhanced Algorithm of RNN Using Trend in Time-Series. Symmetry 2019, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Network. Phys. Nonlinear Phenom. 2020, 404, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, B.B.; Jha, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, D. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Recurrent Neural Network for Low-Flow Hydrological Time Series Forecasting. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, J.L. Finding Structure in Time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Adeloye, A.J.; Shankar, V.; Rustum, R. Neural Computing Modelling of the Crop Water Stress Index. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, D.F. A General Regression Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomandl, D.; Schober, A. A Modified General Regression Neural Network (MGRNN) with New, Efficient Training Algorithms as a Robust ‘Black Box’-Tool for Data Analysis. Neural Netw. 2001, 14, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H. Water Quality Prediction in the Luan River Based on 1-DRCNN and BiGRU Hybrid Neural Network Model. Water 2021, 13, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubaidi, S.L.; Al-Bugharbee, H.; Ortega-Martorell, S.; Gharghan, S.K.; Olier, I.; Hashim, K.S.; Al-Bdairi, N.S.S.; Kot, P. A Novel Methodology for Prediction Urban Water Demand by Wavelet Denoising and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Approach. Water 2020, 12, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahage, E.A.A.D.; Nagahage, I.S.P.; Fujino, T. Calibration and Validation of a Low-Cost Capacitive Moisture Sensor to Integrate the Automated Soil Moisture Monitoring System. Agriculture 2019, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, X.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y. Soil Water Simulation and Predication Using Stochastic Models Based on LS-SVM for Red Soil Region of China. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2823–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, T.; Wang, F. Time Series Prediction Model of Soil Moisture Based on Wavelet De-Noising. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Management and Service Science, Wuhan, China, 16–18 September 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Kim, S. Wavelet Analysis of Soil Moisture Measurements for Hillslope Hydrological Processes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; DeChant, C.M.; Moradkhani, H. Improving Soil Moisture Profile Prediction with the Particle Filter-Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6134–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.X.; Li, R.F.; Huang, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, H.B. Effect of Ground Mulching on Flowering and Fruit Development of Litchi. Acta Hortic. 2014, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Kalbarczyk, Z.; Iyer, R.K. A Data-Driven Approach to Soil Moisture Collection and Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), St Luis, MO, USA, 18–20 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Gao, P.; Mo, H.; Yu, G.; Hu, J.; Wang, W. Design and Optimization of Intelligent Irrigation Decision System in Litchi Orchard Based on Fuzzy Controller. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Growth Season (Month) | Mean of Soil Moisture (%) | Std of Soil Moisture (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Processed | Original | Processed | |
| Season 1 (2–4) | 17.59 | 17.53 | 2.97 | 1.34 |
| Season 2 (5–7) | 21.38 | 21.14 | 3.81 | 2.81 |
| Season 3 (8–10) | 15.79 | 15.74 | 3.10 | 2.43 |
| Season 4 (11–12) | 15.66 | 15.63 | 1.52 | 1.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, P.; Qiu, H.; Lan, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Han, X.; Lu, J. Modeling for the Prediction of Soil Moisture in Litchi Orchard with Deep Long Short-Term Memory. Agriculture 2022, 12, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010025
Gao P, Qiu H, Lan Y, Wang W, Chen W, Han X, Lu J. Modeling for the Prediction of Soil Moisture in Litchi Orchard with Deep Long Short-Term Memory. Agriculture. 2022; 12(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Peng, Hongbin Qiu, Yubin Lan, Weixing Wang, Wadi Chen, Xiongzhe Han, and Jianqiang Lu. 2022. "Modeling for the Prediction of Soil Moisture in Litchi Orchard with Deep Long Short-Term Memory" Agriculture 12, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010025
APA StyleGao, P., Qiu, H., Lan, Y., Wang, W., Chen, W., Han, X., & Lu, J. (2022). Modeling for the Prediction of Soil Moisture in Litchi Orchard with Deep Long Short-Term Memory. Agriculture, 12(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010025









