Abstract
Phenotypes are necessary for genomic evaluations and management. Sometimes genomics can be used to measure phenotypes when other methods are difficult or expensive. Prolificacy of bulls used in multiple-bull pastures for commercial beef production is an example. A retrospective study of 79 bulls aged 2 and older used 141 times in 4–5 pastures across 4 years was used to estimate repeatability from variance components. Traits available before each season’s use were tested for predictive ability. Sires were matched to calves using individual genotypes and evaluating exclusions. A lower-cost method of measuring prolificacy was simulated for five pastures using the bulls’ genotypes and pooled genotypes to estimate average allele frequencies of calves and of cows. Repeatability of prolificacy was 0.62 ± 0.09. A combination of age-class and scrotal circumference accounted for less than 5% of variation. Simulated estimation of prolificacy by pooling DNA of calves was accurate. Adding pooling of cow DNA or actual genotypes both increased accuracy about the same. Knowing a bull’s prior prolificacy would help predict future prolificacy for management purposes and could be used in genomic evaluations and research with coordination of breeders and commercial beef producers.
1. Introduction
The conceptual linking of genome to phenome is fundamental to animal improvement. Current genetic evaluation systems utilize many genotypes and associated phenotypes to accelerate improvement. Beyond the genome-to-phenome paradigm, some phenotypes used for management or inputs to genetic evaluation, particularly those notoriously difficult to be measured, may be best estimated by genomics. Bull prolificacy in multiple-bull pastures is one of those phenotypes.
Efficient use of bulls for mating cows in commercial beef production involves both the number of bulls maintained and pregnancy rates of the cows. Maintaining fewer bulls reduces costs, and greater pregnancy rates increase calves born. However, maintaining and using too few bulls can lower pregnancy rates. Using multiple bulls in breeding pastures is one technique used to simplify some aspects of management and may increase pregnancy rates without increasing the number of bulls [1]. Microsatellite and SNP markers have allowed calves resulting from multiple-bull breeding pastures to be matched to their sire [2,3,4,5] and fill in the sire-side of their pedigrees. Knowing calves’ sires allows evaluating bulls for prolificacy—their ability to sire calves in a multiple-bull pasture situation. Behavioral, physical, or other fertility factors may cause some bulls to sire more or fewer calves [2,6,7]. Cattle breeders could use a bull’s predicted prolificacy to help decide whether to keep, cull, or use the bull in a different way if predictions were accurate.
Genomic markers allow matching sires to calves, but the cost of genotyping all commercial calves may not be economical if prolificacy is the only use of the genotypes. The method of pooling DNA to estimate genomic differences between groups with different phenotypes is being studied for use in genomic association and prediction [8,9,10,11]. Another potential use is to estimate the number of calves for sires by pooling DNA from all calves, i.e., using DNA pooling to estimate phenotypic prolificacy differences.
One objective of this study is to estimate the repeatability of Bos taurus bull prolificacy across years in a temperate climate when used in multiple-bull breeding pastures and identify whether some bull traits could predict prolificacy before use. Another objective is to evaluate the potential for using the DNA pooling method to estimate prolificacy of bulls used in multiple-bull pastures at a lower cost.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Real Data
This retrospective study used 4 years of multiple-bull pasture breeding (2012 to 2015) and subsequent calving data (2013 to 2016). Cattle populations were purebred Angus and advanced generation composites MARC I, MARC II, and MARC III [12]. Only bulls and cows aged 2 and older at the time of breeding were included in data analyzed. In addition, only bulls passing breeding soundness exams for physical and semen traits were used in breeding pastures. A few bulls were removed for injury or other reasons and were replaced by different bulls unless it was late in the breeding season. Any bull not in the breeding pasture for at least 90% of the breeding season was eliminated from analyses. In 2012, some older cows in each of the 3 composite populations were synchronized and bred by AI 15 d after younger cows entered breeding pastures. The synchronized cows entered the same breeding pastures younger cows were in 9 d after AI and 39 d before the end of pasture breeding. Calves sired by AI were eliminated from data, but those sired by the pasture bulls were retained for analysis. Pastures and cow and bull assignments are described in Table 1. Assuming half of AI cows were open after timed AI, the average assigned open cows per bull was 23.6.

Table 1.
Natural service assignments of bulls and cows and resulting calves.
The patterns of bull usage in the edited data are shown in Table 2. Included were 79 unique bulls with 141 breeding opportunities, ranging from 38 bulls with one opportunity each to 4 bulls used each of the 4 years. Across years there were 27, 37, 37, and 40 breeding opportunities for calf years 2013, 2014, 2015, and 2016, respectively. Forty-one bulls had an average of 2.5 breeding opportunities, and 38 bulls had a single opportunity.

Table 2.
Patterns of edited bull usage by calf birth year.
Sires and calves were genotyped with 4 genotyping panels across 4 years. Two were low-density panels based on parentage markers [13] using the Bovine Parentage Panel (Eureka Genomics, Hercules, CA, USA) or implemented with TruSeq DNA technology (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Two were higher density panels with more than 50,000 SNP consisting of parentage, linkage, and functional SNP (BovineSNP50, Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA; GeneSeek Genomic Profiler F250, Neogen, Lansing, MI, USA). A higher proportion of calves born in early years were genotyped with only parentage panels. Most calves born in 2016 and all but 3 bulls (1 Angus, 1 MARC I, and 1 MARC II) were genotyped with GeneSeek Genomic Profiler F250.
A set of parentage SNP [13] in common across the 4 genotyping panels was identified. These SNP were used to identify sires based on exclusions [4]. Additional steps were taken to try to resolve some ambiguous sire identifications, including expanding exclusions to additional SNP if available, calculating the genotypic correlations between a calf and potential sires [14], and re-genotyping some animals. Calves genotyped with higher density panels (48.8%) were matched with sires genotyped with high density (33.8%) or only parentage (15.0%) genotyped with parentage panels were matched with sires genotyped with high density (15.6%) or only parentage (35.6%). Most genotyped calves were matched to a single sire, but several MARC II calves born in 2013 and 2015 and some Angus calves born in 2015 were not genotyped. Sires of 3 calves with <100 genotypes also were not identified.
The distribution of number-of-calves per bull opportunity (bull within pasture and year) was skewed (Table 3) as has been observed in other studies of sire prolificacy. The median and mode of the distribution is 18 with values from 0 to 57. A square root transformation was applied to the data before analysis.

Table 3.
Distribution of number of calves (CalfN) by bull within pasture and year.
Repeatability was estimated from the variance components for random effects for between bull (bull) and within bull across years and pastures (e) as . Variance components were estimated using PROC GLIMMIX (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) from the model , where is number of calves sired by bull k in pasture j () nested within year i (). Additional fixed categorical or continuous factors were individually added to this base model to test for possible explanatory variables for bull prolificacy. Based on results of individual variables, bull age category and scrotal circumference were added to the base model for testing jointly. All reported statistical probabilities are based on data transformed by square root, but reported means and regression coefficients of explanatory variables are from analyses of untransformed data.
2.2. Simulating Errors in Pooling Allele Frequency
The concept of using pooled calf DNA to estimate bulls’ prolificacies was tested by simulating DNA pooling of actual genotypes of calves born in 2016 and genotyped with the Genomic Profiler F250 and sired by bulls genotyped with the same panel. Five pastures (N, O, P, Q, and R; Table 1) with 189,165, 76, 89, and 198 calves and 9, 9, 5, 5, and 10 bulls, respectively, were used after removing bulls and calves without Genomic Profiler F250 genotypes. Simulations used 14,190 autosomal SNP common to both BovineSNP50 and GeneSeek Genomic Profiler F250 panels.
Simulation of pooling was a function of the actual allele frequencies for the calves in a pasture as well as pool construction and technical errors. Pool construction error or random unintended differences in the contribution of individual calves to the pool can result from incorrect DNA measurement or quantification; pipetting error; or cross contamination between pools, or between pools and individual animals. Technical error is the result of variation in the ratio of X (red dye intensity) to Y (green dye intensity) for samples with the same allele frequency (replicated pools) or the same genotype (replicated individuals or individuals of the same genotype). Standard deviations for pool construction error and technical error were estimated from replicated pools in earlier studies that have the same real or underlying allele frequency as if the animals in the pool had been individually genotyped [15,16]. Pooling allele frequency was estimated as the average of genotypes (copies of B allele) weighted by the random calf contribution divided by 2. Pool construction error was simulated as a Dirichlet distribution with SD = 0.0024 equivalent to using symmetric shape (alpha) parameter of 20 when pool size is 92. The Dirichlet distribution is parameterized by a shape parameter, alpha, for each calf in the pool. For example, for a pool size of 150 calves the parameterization included a vector of 150 elements all having the same value of 20. The magnitude of alpha determines how peaked the distribution of calf contributions is. Alpha = 10 would have less peaked and more variable animal contributions than alpha = 20. Simulated technical error was drawn from a normal distribution with a mean of zero and SD of 0.07.
Estimating the number of calves sired by a bull can be improved by knowing average genotype frequencies of the dams. Three levels of average dam allele frequency information were compared: (1) none, (2) a simulated, pooled estimate of allele frequencies from the 94.5% of dams with genotypes, and (3) average allele frequencies of the dams with genotypes. Quadratic programming [17] to compute sire contributions while both not adjusting and adjusting for dam pooling allele frequency is included in an R script that is part of the Supplemental Files.
When dam information was not included in the quadratic programming analysis, dam allele frequencies were proportional to the residual after subtracting predicted sire allele frequencies from calf pooling allele frequency (r2 ~0.8; data not shown). Adding dam frequencies would be expected to improve the accuracy of sire solutions at an additional cost of sampling cows and genotyping pools. Three levels of average dam allele frequency information were compared: (1) none, (2) pooled estimate of allele frequencies from the 94.5% of dams with genotypes with simulated pool construction and technical error incorporated, and (3) allele frequencies of the dams with genotypes.
3. Results
3.1. Repeatability Estimates
Estimated repeatability of bull prolificacy was 0.62 ± 0.09, and the SD of untransformed calf N was 13.6 (Table 4). The data used to estimate repeatability are in supplementary materials (Table S1) Previous numbers of calves from bulls used in multiple-bull pastures as 2-year-olds and older are good predictors of future numbers of calves. This result is consistent with or greater than other studies based on data from various pasture situations with different numbers of bulls and cows assigned to pastures, usually for fewer years and including yearling bulls [2,5]. It is also consistent with several studies observing bulls’ rankings across years [18,19].

Table 4.
Estimated repeatability of bull prolificacy and component variances.
3.2. Explanatory Variables
A bull’s life history and measurements made before entering the breeding pasture may explain some difference in bull prolificacy. Several retrospective variables were individually added to the statistical model for repeatability. Life history variables for bulls were (1) dam was 2 years old, (2) previously used for breeding as a yearling, (3) used for breeding any prior season, and (4) breeding age was >2. Bull measurements made during breeding soundness exams before each breeding season were included, such as bull weight and scrotal circumference.
None of the life history traits or bull measurements were significant when added individually to the model (Table 5). However, some measurements and life-history traits were partially confounded, especially bull measurements and breeding age. A model including breeding age category (2 years old vs. older than 2) and scrotal circumference measurement (at breeding soundness exam) resulted in significant effects for both. At the same scrotal circumference, bulls older than 2 years sired 6.33 more calves. At the same age classification, a 1.0 cm increase in scrotal circumference was associated with a decrease of 1.56 calves, possibly because only bulls that had scrotal circumferences greater than breeding soundness standards were used. The addition of these two variables accounted for less than 5% of variation in prolificacy and did not change estimated repeatability. The ability of individual bull measurements and life-history traits to predict prolificacy is limited compared to knowing a bull’s earlier prolificacy results, when available.

Table 5.
Patterns of edited bull usage by calf birth year.
3.3. Estimated Prolificacy
Genotypes of calves, dams and sires used to simulate pooling and estimate sire contributions are in supplementary materials (Tables S2–S6 for the 5 pastures N, O, P, Q, and R, respectively). Results of simulated pooling of calf DNA samples (Table 6; Figure 1) suggest that the concept of pooling to estimate prolificacy is valid. The accuracy of predicting actual proportions of calves is moderate to high regardless of whether cow allele frequencies are unknown, estimated by pooling, or known. Allele frequencies of dams estimated by pooling did increase accuracy and consistency across different pastures. There was little difference in either accuracy or consistency when allele frequencies of dams were estimated by individual cow or pooled genotyping.

Table 6.
Intercept, slope and r2 from regressing pooling estimates of sire progeny proportions on known proportions 100 simulated replicates using 14,190 autosomal.
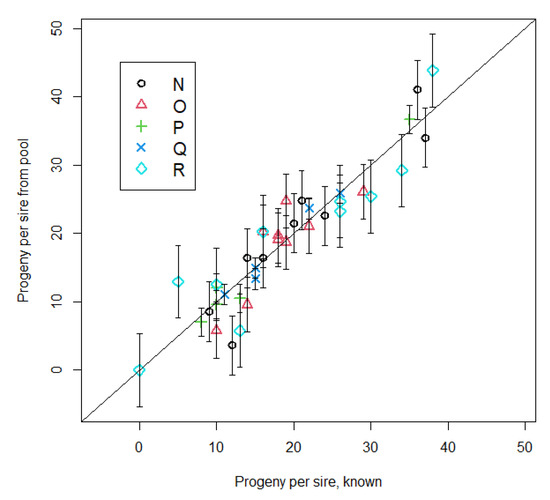
Figure 1.
Pooling estimates of sire progeny numbers for 2016 calf crop by known progeny numbers using 14,190 SNP. Dam allele frequencies were assumed unknown for this graph. Error bars are lack of fit SD between pooling sire progeny number and known progeny number. Symbols in the legend identify different pastures.
4. Discussion
A predicted number of calves should be useful for making management decisions about the number of bulls maintained and used. However, we are not aware of experimental evidence for making those management decisions. It seems likely that bulls that previously sired no or few calves should not subsequently be used in multiple-bull pastures. It is possible that these bulls would sire more calves in single-bull pastures or by AI, but culling them would also be a reasonable management strategy. Whether fewer bulls could be used in multiple-bull pastures if one-quarter of them are predicted to be above average (based on prior usage) and three-quarters are average (based on no prior information) is unknown. Any management strategy using predicted prolificacy would need to account for risks of injury, becoming unsound, or death before or during breeding. The estimated repeatability only applies to bulls 2 and older that passed breeding soundness exams prior to the breeding season and completed at least 90% of the breeding season.
Although not significant, prolificacy tended to increase from 2 through about 5 years of age in pastures with mixed-age bulls [5]. Our results showed a significant increase in prolificacy of bulls older than 2 compared with 2-year-olds when adjusted for scrotal circumference.
Scrotal circumference of older bulls measured in breeding soundness exams before breeding has shown little to moderate positive correlation with bull prolificacy in multiple-bull pastures. Results tended to be greater when breeding soundness exams were not rigorously applied [3,18]. Scrotal circumference breeding value was found to have some predictive ability across 2-year-old and older bulls [5].
Scrotal circumference combined with age had significant but small effects on prolificacy in this study. Life-history traits related to previous breeding experience had positive values, but a larger experiment would be needed to conclusively determine any trait effects of that size. Breeding exam live weights showed no indication of effects on prolificacy.
Pooling DNA can potentially reduce costs of accurately estimating bull prolificacy, essentially using genomics to measure phenotype if bull prolificacy is the only information desired by a cattle producer. A basic implementation of this method begins by individually sampling DNA from all bulls used in a multiple-sire pasture and maintaining correspondence between each sample and each bull. Blood from all calves would be individually sampled. Calf blood samples would need to be maintained individually but samples would not need to be connected to individual calves. For higher accuracy, cows assigned to a breeding pasture would need to be sampled sometime from pre-breeding through weaning if the cows were maintained as a group through that period. Like the calf samples, cow blood samples do not need to maintain connection with the individual cows. To make decisions on bull management in time for the current breeding season, samples would need to be collected well before breeding, likely at birth. Research has found that bulls siring large numbers of calves early in the calving period tended to sire more calves throughout [5,19]. This seems to be one likely approach for obtaining a prolificacy estimate early enough to be useful for the breeding season immediately following calving. This study has a few limitations with regards to relevance to commercial production. First, F1 crossbred dams are important in the commercial beef cattle sector. F1 dams might reduce precision of estimating sire contributions because alleles that are not inherited in calves would be part of dam allele frequencies but not part of calves. This is more complicated if dams are F1. We do not know how important this is currently. Second, pool construction and technical errors were simulated in the current study. The distribution of these errors may be different than real pooling data. We are planning future studies to rectify this limitation.
Once samples are collected, a genomics service provider would need to extract and separately pool calf DNA and cow DNA. Other ways of constructing pools are possible [16]. Then, the individual bull samples and each pool would need to be genotyped with a moderate-to-high density panel. A service provider would need to estimate prolificacy from the genotypes. This approach to estimating prolificacy may facilitate additional research on factors affecting bull prolificacy using industry cooperators.
Other benefits from a pooled sample of calves are possible but would require additional technical support and industry coordination. It should be possible to estimate average breed composition from pooled alleles, predicted heterosis from differences between weighted sire allele frequencies and pooled cow allele frequencies, and average performance levels from those two inputs. Estimated performance might be enhanced through genomic prediction of commercial bulls based on their individual genotypes. This could be useful for marketing calves or managing them through the feedlot or as breeding heifers. Estimated bull prolificacy could be used as phenotypic data for genomic evaluation with information transfer to breeding value prediction organizations based on careful documentation of commercial bulls, their use in pastures, and their genotypes. Claims-based marketing programs could be verified for things such as breed composition or genetic potential based on markers associated with large effects for carcass traits, e.g., beef tenderness [20] or carcass leanness [21]. A pool including heifers could be genetically evaluated for reproductive traits, e.g., pubertal age, antral follicle count, and heifer pregnancy rate [22,23], and for common genetic disorders [24] or disease susceptibility to avoid inappropriate matings.
5. Conclusions
The repeatability of bull prolificacy in multi-bull breeding pastures is high. Bull prolificacy is accurately estimated using DNA pools of calves and genotyping the calves at a lower cost compared to individually genotyping. Genotyping pools of dams improves the accuracy of estimating bull prolificacy which requires samples of dams.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture11070603/s1, Table S1: Data used for repeatability estimates, Table S2: Genotypes of calves, bulls and dams in Pasture N, Table S3: Genotypes of calves, bulls and dams in Pasture O, Table S4: Genotypes of calves, bulls and dams in Pasture P, Table S5: Genotypes of calves, sires and dams in Pasture Q, Table S6: Genotypes of calves, sires and dams in Pasture R, quadratic ProgramSireProportions. R: An R script to estimate sire proportions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L.B. and J.W.K.; methodology, G.L.B., J.W.K., and L.A.K.; validation, G.L.B., J.W.K., L.A.K., and W.M.S.; formal analysis, G.L.B. and J.W.K.; resources, G.L.B., W.M.S., and T.G.M.; data curation, D.L., A.M.D., and T.G.M.; writing—original draft preparation, G.L.B. and J.W.K.; writing—review and editing, L.A.K., W.M.S., T.G.M., A.M.D., D.L., and R.A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Archival pedigrees, genotypes, animal data, and blood samples from research protocols approved and monitored by the USDA, Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Meat Animal Research Center Institutional and Animal Care Committee following the Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Agricultural Research and Teaching [25] were used in this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the supplementary tables.
Acknowledgments
Mention of the trade name, proprietary product, or specific equipment does not constitute a guarantee or warranty by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and does not imply approval to the exclusion of other products that may be suitable. The USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. We acknowledge Richard G. Tait, Jr., for contributions to determining pedigree in the early stages of this research while employed by the U.S. Meat Animal Research Center.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lunstra, D.D.; Laster, D.B. Influence of single-sire and multiple-sire natural mating on pregnancy rate of beef heifers. Theriogenology 1982, 18, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, A.R.; Brown, M.B.; Schindler, H.; Holzer, Z.; Larsen, B. Paternity tests in multi-sired beef herds by blood grouping. Acta Vet. Scand. 1977, 18, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holroyd, R.G.; Doogan, V.J.; De Faveri, J.; Fordyce, G.; McGowan, M.R.; Bertram, J.D.; Vankan, D.M.; Fitzpatrick, L.A.; Jayawardhana, G.A.; Miller, R.G. Bull selection and use in northern Australia: 4. Calf output and predictors of fertility of bulls in multiple-sire herds. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2002, 71, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Weaber, R.L.; Drake, D.J.; Penedo, M.C.T.; Quaas, R.L.; Garrick, D.J.; Pollak, E.J. DNA-based paternity analysis and genetic evaluation in a large, commercial cattle ranch setting. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Weber, K.L.; Drake, D.J. Evaluation of bull prolificacy on commercial beef cattle ranches using DNA paternity analysis. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ologun, A.G.; Chenoweth, P.J.; Brinks, J.S. Relationships among production traits and estimates of sex drive and dominance value in yearling beef bulls. Theriogenology 1981, 15, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, W.A.; Forrest, D.W.; Sprott, L.R.; Holloway, J.W.; Warrington, B.G. Physical, and mating behavior traits of bulls on number of calves sired per bull in a multisire herd. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2008, 24, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keele, J.W.; Kuehn, L.A.; McDaneld, T.G.; Tait, R.G., Jr.; Jones, S.A.; Smith, T.P.L.; Shackelford, S.D.; King, D.A.; Wheeler, T.L.; Lindholm-Perry, A.K.; et al. Genomewide association study of lung lesions in cattle using sample pooling. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baller, J.L.; Kachman, S.D.; Kuehn, L.A.; Spangler, M.L. Genomic prediction using pooled data in a single-step genomic best linear unbiased prediction framework. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa184:1–skaa184:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverter, A.; Porto-Neto, L.R.; Fortes, M.R.S.; McCulloch, R.; Lyons, R.E.; Moore, S.; Nicol, D.; Henshall, J.; Lehnert, S.A. Genomic analyses of tropical beef cattle fertility based on genotyping pools of Brahman cows with unknown pedigree. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 4096–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, P.A.; Porto-Neto, L.R.; Karaman, E.; Lehnert, S.A.; Reverter, A. Pooled genotyping strategies for rapid construction of genomic reference populations. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 4761–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, K.E.; Cundiff, L.V.; Koch, R.M. Breed effects and heterosis in advanced generations of composite populations for preweaning traits of beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, M.P.; Harhay, G.P.; Bennett, G.L.; Stone, R.T.; Grosse, W.M.; Casas, E.; Keele, J.W.; Smith, T.P.; Chitko-McKown, C.G.; Laegreid, W.W. Selection and use of SNP markers for animal identification and paternity analysis in U.S. beef cattle. Mamm. Genome 2002, 13, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- amap: Another Multidimensional Analysis Package. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/amap/index.html (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Kuehn, L.A.; McDaneld, T.G.; Keele, J.W. Quantification of genomic relationship from DNA pooled samples. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Auckland, New Zealand, 11–16 February 2018; Volume 11, p. 631. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, A.N.; McDaneld, T.G.; Keele, J.W.; Chitko-McKown, C.G.; Kuehn, L.A.; Gonda, M.G. Evaluating accuracy of DNA pool construction based on white blood cell counts. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 635846:1–635846:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- quadprog: Functions to Solve Quadratic Programming Problems. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=quadprog (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- McCosker, T.H.; Turner, A.F.; McCool, C.J.; Post, T.B.; Bell, K. Brahman bull fertility in a north Australian rangeland herd. Theriogenology 1989, 27, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, K.M.; Theurer, M.E.; Larson, R.L.; White, B.J.; Hardin, D.K.; Randle, R.F.; Cushman, R.A. Calving distributions of individual bulls in multiple-sire pastures. Theriogenology 2017, 93, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, R.G., Jr.; Shackelford, S.D.; Wheeler, T.L.; King, D.A.; Keele, J.W.; Casas, E.; Smith, T.P.; Bennett, G.L. CAPN1, CAST, and DGAT1 genetic effects on preweaning performance, carcass quality traits, and residual variance of tenderness in a beef cattle population selected for haplotype and allele equalization. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 5382–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.L.; Tait, R.G., Jr.; Shackelford, S.D.; Wheeler, T.L.; King, D.A.; Casas, E.; Smith, T.P.L. Enhanced estimates of carcass and meat quality effects for polymorphisms in myostatin and mu-calpain genes. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelling, W.M.; Cushman, R.A.; Fortes, M.R.S.; Reverter, A.; Bennett, G.L.; Keele, J.W.; Kuehn, L.A.; McDaneld, T.G.; Thallman, R.M.; Thomas, M.G. How single nucleotide polymorphism chips will advance our knowledge of factors controlling puberty and aid in selecting replacement beef females. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushman, R.A.; Tait, R.G., Jr.; McNeel, A.K.; Forbes, E.D.; Amundson, O.L.; Lents, C.A.; Lindholm-Perry, A.K.; Perry, G.A.; Wood, J.A.; Cupp, A.S.; et al. A polymorphism in myostatin influences puberty but not fertility in beef heifers, whereas µ-calpain affects first calf birth weight. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OMIA-Online Mendelian Inheritance in Animals. Available online: http://omia.org/home/ (accessed on 4 May 2021).
- FASS. Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Agricultural Research and Teaching, 1st ed.; Federation of Animal Science Societies: Savoy, IL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).