Assessment of Interactions between Yield Components of Common Vetch Cultivars in Both Conventional and Low-Input Cultivation Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
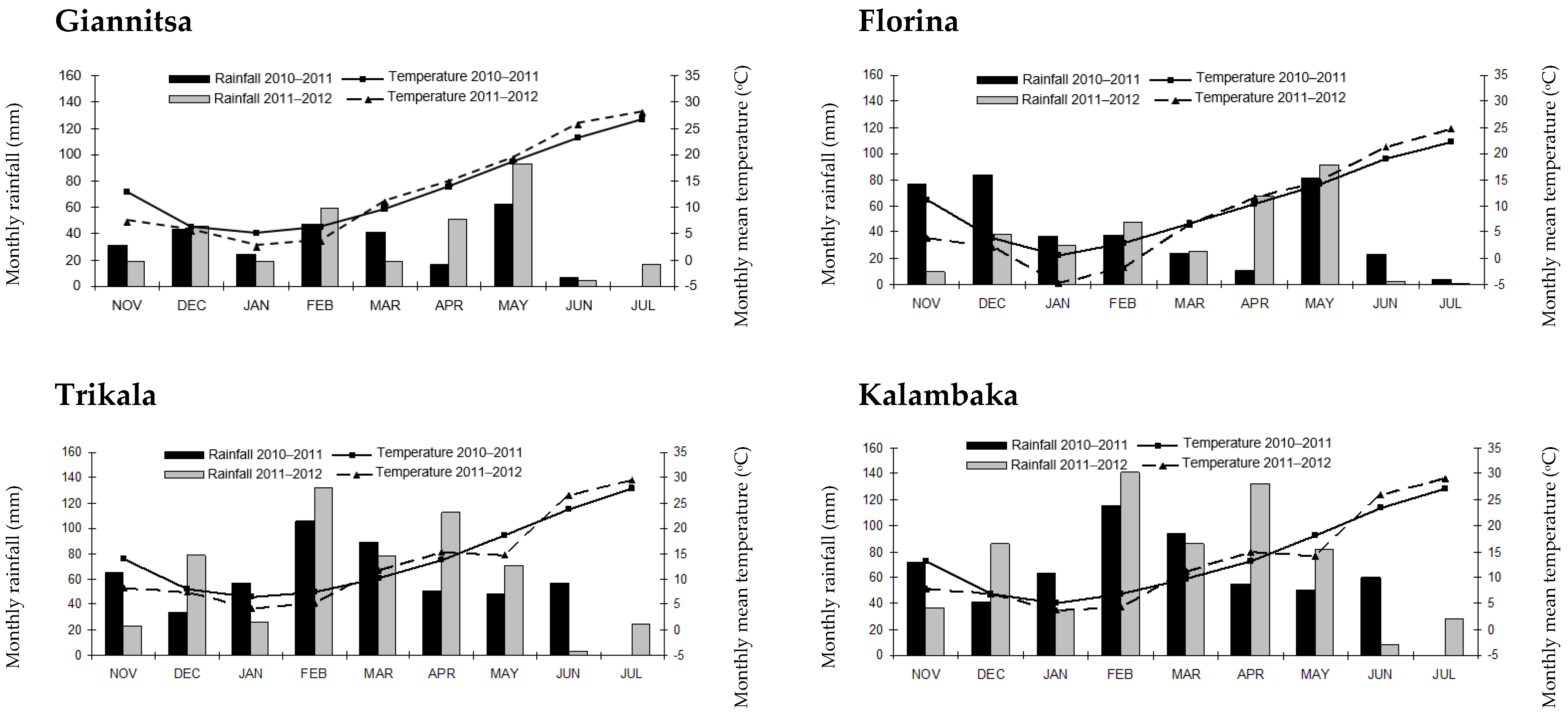
2.1. Crop Establishment and Experimental Procedures
- (A)
- In the farm of the Technological Educational Institute of Western Macedonia in Florina, Greece (latitude, 40°46′ N; longitude, 21°22′ E; elevation, 705 m a.s.l.). The soil type was characterized as sandy loam (SL): sand, 62%; silt, 26.9%; clay, 11.1%. The chemical properties of the soil were as follows: conventional: N-NO3, 16.1 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 26.4 mg kg−1; K, 236 mg kg−1; pHH20, 6.32; organic matter, 1.29%; and CaCO3, 1.7 (%). Low-input system: N-NO3, 17.4 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 25.1 mg kg−1; K, 224 mg kg−1; pHH20, 6,29; organic matter, 1.32%; and CaCO3, 1.9 (%).
- (B)
- In Trikala, Greece (latitude, 39°55′ N; longitude, 21°64′ E; elevation, 120 m a.s.l.). The soil type was characterized as sandy clay loam (SCL): sand, 48.6%; silt, 19.2%; clay, 32.2%. The chemical properties of the soil were as follows: conventional: N-NO3, 12.7 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 11.8 mg kg−1; K, 168 mg kg−1; pHH20, 8.15; organic matter, 2.21%; and CaCO3, 7.54 (%). Low-input system: N-NO3, 13.6 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 11.5 mg kg−1; K, 176 mg kg−1; pHH20, 8.11; organic matter, 2.39%; and CaCO3, 7.63 (%).
- (C)
- In Kalambaka, Greece (latitude, 39°64′ N; longitude, 21°65′ E; elevation, 190 m a.s.l.). The soil type was silty clay (SiC): sand, 14.6%; silt, 41.2%; clay, 44.2%. The chemical properties of the soil were as follows: conventional: N-NO3, 11.39 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 7.62 mg kg−1; K, 96.3 mg kg−1; pHH20, 8.05; organic matter, 2.14%; and CaCO3, 3.58 (%). Low-input system: N-NO3, 12.01 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 7.56 mg kg−1; K, 98.7 mg kg−1; pHH20, 8.08; organic matter, 2.21%; and CaCO3, 3.65 (%).
- (D)
- In Giannitsa, Greece (latitude, 40°77′ N; longitude, 22°39′ E; elevation, 10 m a.s.l.). The soil type was clay (C): sand, 9.1%; silt, 37.5%; clay, 53.8%. The chemical properties of the soil were as follows: conventional: N-NO3, 15.1 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 17.4 mg kg−1; K, 274 mg kg−1; pHH20, 7.69; organic matter, 3.26%; and CaCO3, 5.23 (%). Low-input system: N-NO3, 16.1 mg kg−1; P-Olsen, 15.9 mg kg−1; K, 261 mg kg−1; pHH20, 7.65; organic matter, 3.51%; and CaCO3, 5.37 (%).
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
Correlations between Characteristics
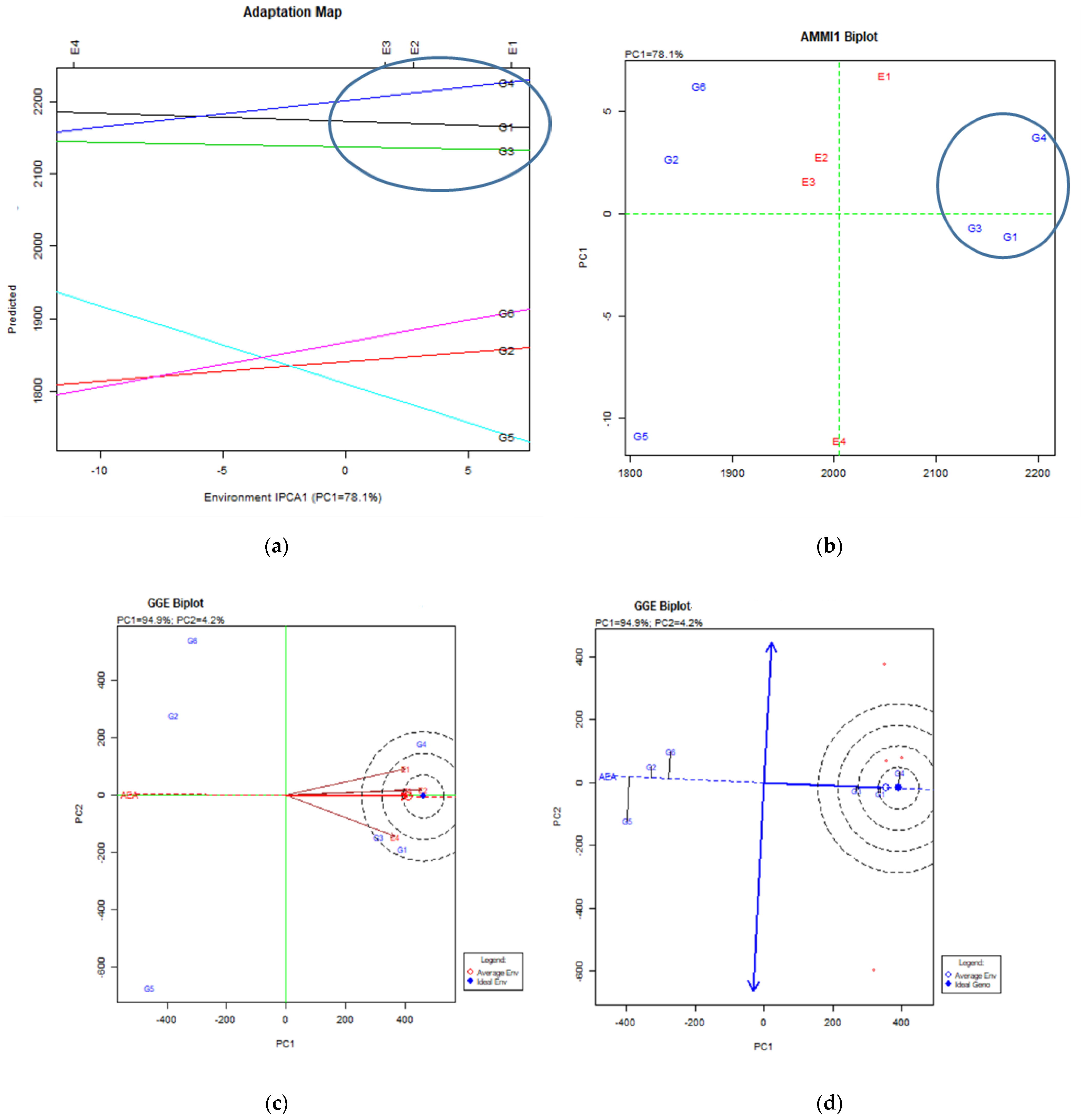
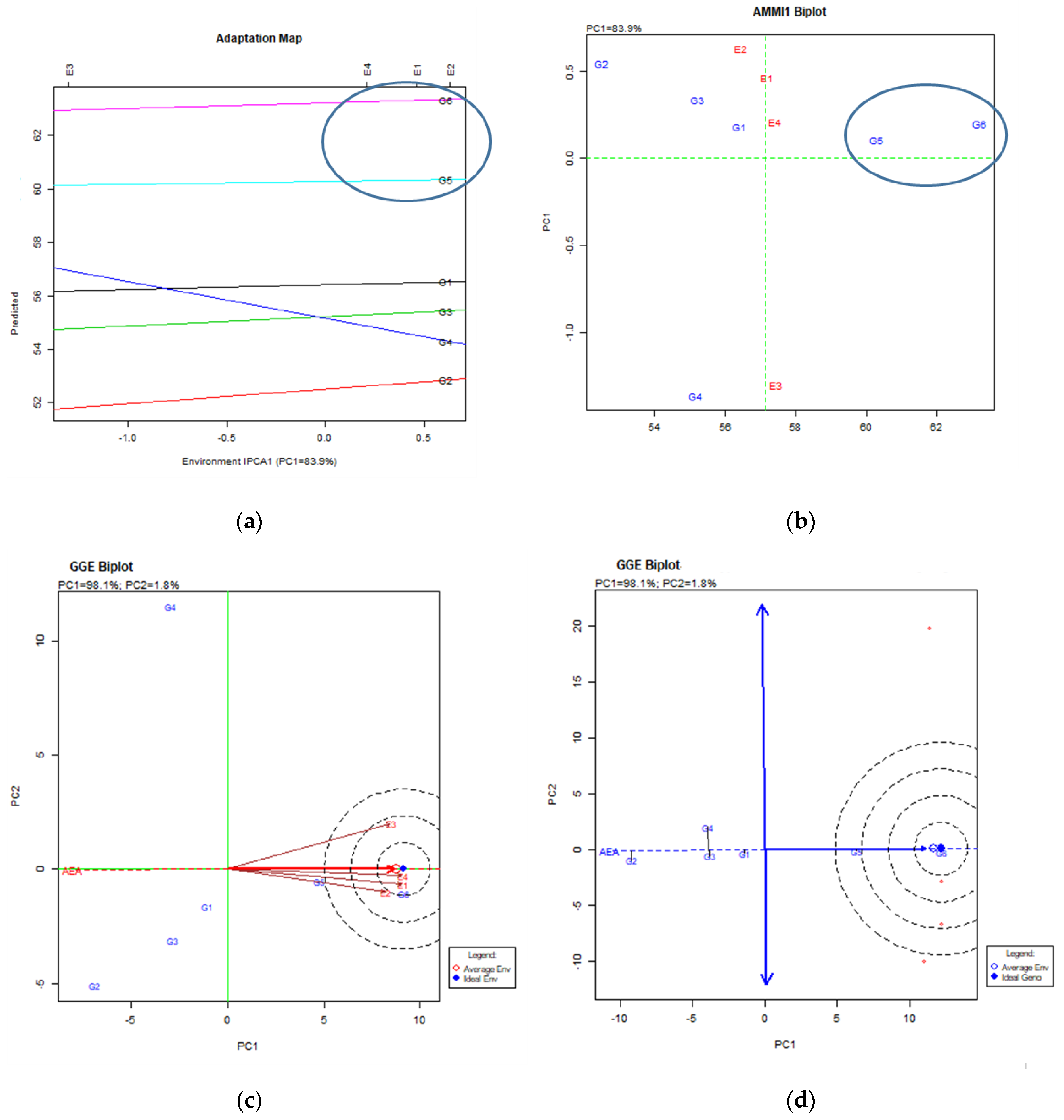
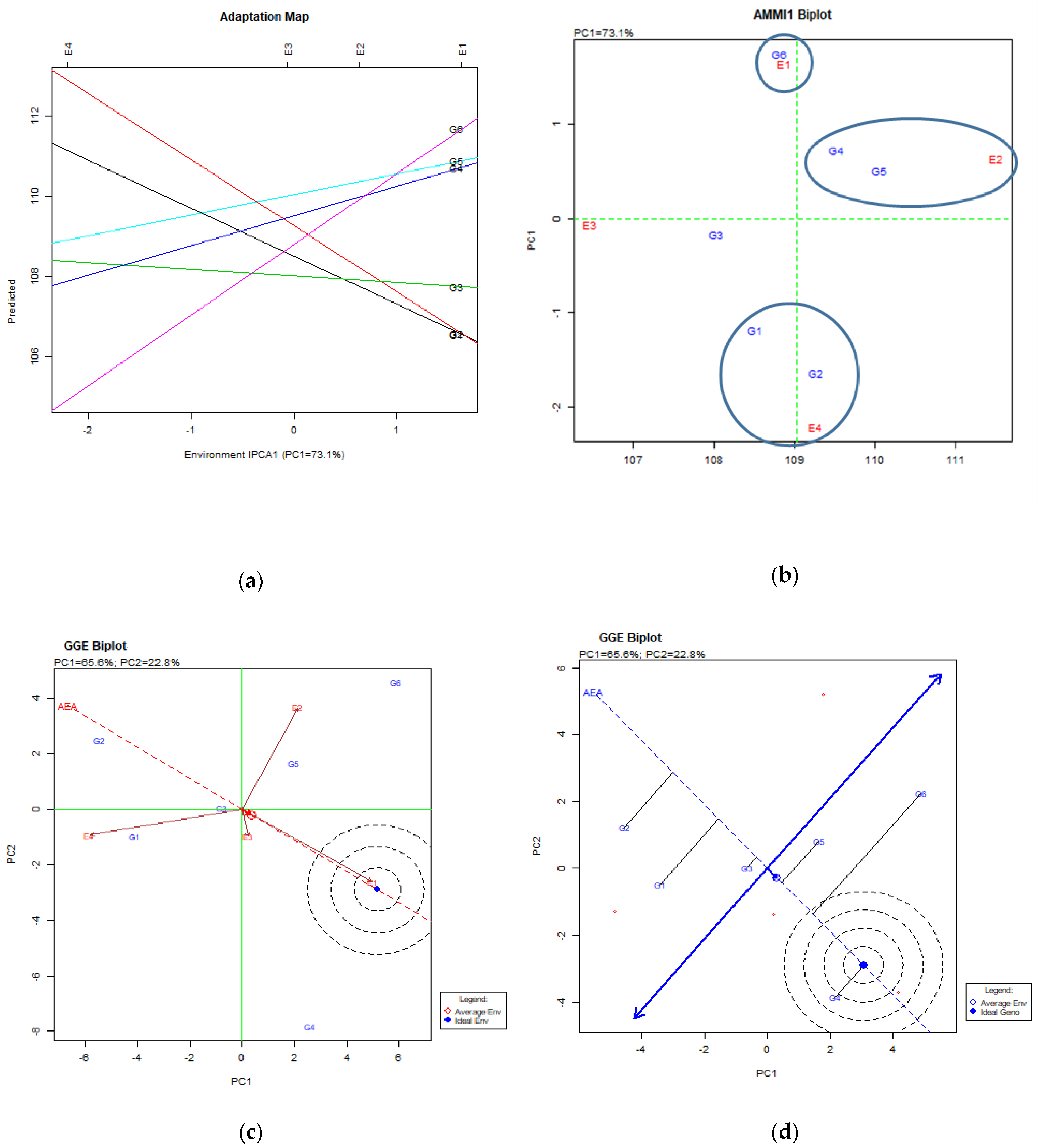
4. Stability Analysis, Total Results and Discussion
4.1. Seed Yielding Ability
4.2. Thousand Kernel Weight (TKW)
4.3. Number of Seeds per Plant
4.4. Hay Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fess, T.L.; Kotcon, J.B.; Benedito, V.A. Crop breeding for low input agriculture: A sustainable response to feed a growing world population. Sustainability 2011, 3, 1742–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachostergios, A.; Lithourgidis, A.; Korkovelos, A.; Baxevanos, D.; Lazaridou, T. Mixing ability of conventionally bred common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) cultivars for grain yield under low-input cultivation. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Dhima, K.V.; Lithourgidis, A.S.; Vasilakoglou, I.B.; Dordas, C.A. Competition indices of common vetch and cereal intercrops in two seeding ratio. Field Crops Res. 2007, 100, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolcu, H.; Gunes, A.; Dasci, M.; Turan, M.; Serin, Y. The effects of solid, liquid and combined cattle manure applications on the yield, quality and mineral contents of common vetch and barley intercropping mixture. Ekoloji 2010, 19, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2021: FAOSTAT Online Database. Available online: http://www.fao.org (accessed on 4 December 2020).
- Acikgoz, E. Annual forage legumes in the arid and semi-arid regions of Turkey. In Nitrogen Fixation by Legumes in Mediterranean Agriculture; Beck, D.B., Materon, L.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rinnofner, T.; Friedel, J.K.; de Kruijff, R.; Pietsch, G.; Freyer, B. Effect of catch crops on N dynamics and following crops in organic farming. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoulas, A.C. Principles of Crop Breeding; Fasoulas A.C.: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rédei, G.P. Genetics Manual: Current Theory, Concepts, Terms; Word Scientific: River Edge, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dechev, D. Genotype—Environment interaction and stability for some traits of durum wheat genotypes. Agrar. Sci. 2004, 2, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Fasoulas, A.C. The Honeycomb Methodology of Plant Breeding. Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding; Aristotle University of Thessaloniki: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fasoula, V.A. Prognostic Breeding: A new paradigm for crop improvement. Plant. Breed. Rev. 2013, 37, 297–347. [Google Scholar]
- Edmeades, G.E.; Deutsch, J.A. Stress Tolerance Breeding: Maize that Resists Insects, Drought, Low Nitrogen and Acid Soils; CIMMYT: Mexico City, Mexico, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tollenaar, M.; Wu, J. Yield improvement in temperate maize is attributable to greater stress tolerance. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmeades, G.O.; Daynard, T.B. The relationship between final yield and photosynthesis at flowering in individual maize plants. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1979, 59, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Shen, S.H.; Jahufer, M.Z.Z.; Dong, D.K.; Luo, D.; Zhou, Q.; Chai, X.T.; Luo, K.; Nan, Z.B.; Wang, Y.R.; et al. Effect of genotype and environment on agronomical characters of common vetch (Vicia sativa L.). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2019, 66, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoula, V.A. A novel equation paves the way for an everlasting revolution with cultivars characterized by high and stable crop yield and quality. In Proceedings of the 11th National Hellenic Conference in Genetics and Plant Breeding, Orestiada, Greece, 31 October–2 November 2006; pp. 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torie, H.; Dickey, D.A. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. A Biometrical Approach, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fasoula, V.A. Selection of High Yielding Plants Belonging to Entries of High Homeostasis Maximizes Efficiency in Maize Breeding. In Proceedings of the XXI International Eucarpia Conference in Maize and Sorghum Breeding in the Genomics Era, Bergamo, Italy, 21–24 June 2009; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, G. Evaluation of vetch species for yield, yield components and herbage quality in the central highlands of Ethiopia. Acad. Res. J. Agric. Sci. Res. 2016, 4, 264–278. [Google Scholar]
- Mikó, P.; Löschenberger, F.; Hiltbrunner, J.; Aebi, R.; Megyeri, M.; Kovács, G.; Molnár-Láng, M.; Vida, G.; Rakszegi, M. Comparison of bread wheat varieties with different breeding origin under organic and low input management. Euphytica 2014, 199, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, N.; Nikolova, I.; Delchev, G. Response of spring vetch (Vicia sativa L.) to organic production conditions. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 26, 520–526. [Google Scholar]
- Aydemir, S.K.; Karakoy, T.; Kokten, K.; Nadeem, M.A. Evaluation of yield and yield components of common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) genotypes grown in different locations of Turkey by GGE bıplot analysis. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 15203–15217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryaki, G.Y.; Cil, A.; Tiryaki, I. Revealing seed coat colour variation and their possible association with seed yield parameters in common vetch (Vicia sativa L.). Int. J. Agron. 2016, 2016, 1804108. [Google Scholar]

| Environments | Seed Yield (kg ha−1) | Thousand Kernel Weight (g) | Number of Pods per Plant | Number of Seeds per Pod | Number of Seeds per Plant | Pod Length (cm) | Pod Width (mm) | Pod Weight (g) | Hay Yield (kg ha−1) | Plant Height (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | Giannitsa | 49 | 175 | 38 | 89 | 951 | 225 | 755 | 46 | 43 | 241 |
| Florina | 47 | 210 | 67 | 62 | 937 | 320 | 455 | 26 | 47 | 311 | |
| Trikala | 37 | 198 | 59 | 60 | 588 | 211 | 669 | 47 | 30 | 270 | |
| Kalambaka | 37 | 178 | 59 | 79 | 598 | 253 | 481 | 60 | 33 | 365 | |
| Low-input | Giannitsa | 48 | 187 | 56 | 104 | 722 | 191 | 907 | 57 | 46 | 296 |
| Florina | 33 | 204 | 76 | 63 | 835 | 296 | 487 | 36 | 36 | 238 | |
| Trikala | 44 | 185 | 87 | 67 | 544 | 248 | 651 | 53 | 44 | 380 | |
| Kalambaka | 39 | 184 | 58 | 65 | 739 | 210 | 447 | 67 | 47 | 404 | |
| Conventional and low-input | Giannitsa | 37 | 167 | 44 | 97 | 827 | 172 | 778 | 51 | 42 | 269 |
| Florina | 30 | 192 | 68 | 63 | 887 | 282 | 471 | 30 | 34 | 273 | |
| Trikala | 27 | 175 | 66 | 64 | 554 | 214 | 617 | 51 | 26 | 318 | |
| Kalambaka | 23 | 171 | 54 | 72 | 645 | 215 | 452 | 64 | 28 | 387 |
| Genotypes | Seed Yield (kg ha−1) | Thousand Kernel Weight (g) | Number of Pods per Plant | Number of Seeds per Pod | Number of Seeds per Plant | Pod Length (cm) | Pod Width (mm) | Pod Weight (g) | Hay Yield (kg ha−1) | Plant Height (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | Filippos | 209 | 547 | 67 | 74 | 683 | 1126 | 1120 | 58 | 120 | 350 |
| Omiros | 175 | 1562 | 35 | 54 | 375 | 623 | 1119 | 75 | 284 | 331 | |
| Alexandros | 92 | 780 | 50 | 78 | 1101 | 585 | 708 | 67 | 33 | 296 | |
| Tempi | 37 | 521 | 53 | 80 | 1256 | 425 | 887 | 73 | 47 | 249 | |
| Zefyros | 46 | 1275 | 45 | 64 | 1435 | 859 | 1179 | 83 | 52 | 309 | |
| Pigasos | 30 | 1103 | 77 | 76 | 285 | 422 | 389 | 82 | 28 | 262 | |
| Low-input | Filippos | 145 | 474 | 71 | 69 | 771 | 524 | 1108 | 81 | 96 | 335 |
| Omiros | 351 | 1977 | 55 | 61 | 380 | 502 | 1261 | 96 | 341 | 367 | |
| Alexandros | 180 | 693 | 58 | 72 | 808 | 750 | 1263 | 70 | 75 | 298 | |
| Tempi | 46 | 385 | 52 | 90 | 699 | 457 | 1102 | 85 | 74 | 292 | |
| Zefyros | 26 | 945 | 47 | 66 | 1373 | 490 | 943 | 95 | 36 | 278 | |
| Pigasos | 44 | 1102 | 76 | 68 | 390 | 474 | 493 | 78 | 25 | 328 | |
| Conventional and low-input | Filippos | 40 | 418 | 63 | 72 | 723 | 538 | 1083 | 68 | 57 | 345 |
| Omiros | 43 | 1392 | 41 | 58 | 381 | 412 | 1190 | 86 | 70 | 353 | |
| Alexandros | 35 | 445 | 53 | 75 | 933 | 552 | 846 | 70 | 31 | 301 | |
| Tempi | 36 | 340 | 50 | 86 | 905 | 392 | 872 | 78 | 46 | 273 | |
| Zefyros | 28 | 650 | 42 | 66 | 1394 | 442 | 936 | 89 | 36 | 295 | |
| Pigasos | 35 | 889 | 72 | 73 | 327 | 380 | 433 | 81 | 25 | 289 |
| Genotypes | Seed Yield (kg ha−1) | Thousand Kernel Weight (g) | Number of Pods per Plant | Number of Seeds per Pod | Number of Seeds per Plant | Pod Length (cm) | Pod Width (mm) | Pod Weight (g) | Hay Yield (kg ha−1) | Plant Height (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Giannitsa | |||||||||||
| Conventional | Filippos | 472 | 694 | 36 | 78 | 8074 | 2079 | 750 | 69 | 555 | 366 |
| Omiros | 165 | 2265 | 127 | 86 | 746 | 2769 | 2983 | 77 | 494 | 245 | |
| Alexandros | 160 | 795 | 37 | 78 | 532 | 525 | 1917 | 73 | 40 | 299 | |
| Tempi | 70 | 887 | 51 | 68 | 2450 | 356 | 1059 | 94 | 64 | 217 | |
| Zefyros | 70 | 1192 | 66 | 126 | 2763 | 1136 | 1646 | 112 | 52 | 198 | |
| Pigasos | 57 | 1290 | 132 | 80 | 2835 | 304 | 664 | 83 | 69 | 213 | |
| Low-input | Filippos | 167 | 424 | 40 | 78 | 6655 | 741 | 1022 | 52 | 107 | 370 |
| Omiros | 700 | 2612 | 148 | 100 | 829 | 634 | 2417 | 102 | 454 | 272 | |
| Alexandros | 190 | 310 | 66 | 95 | 528 | 1070 | 2964 | 78 | 128 | 250 | |
| Tempi | 48 | 639 | 58 | 100 | 624 | 304 | 957 | 103 | 114 | 217 | |
| Zefyros | 38 | 1116 | 87 | 124 | 3830 | 722 | 2195 | 122 | 75 | 275 | |
| Pigasos | 47 | 1340 | 81 | 98 | 4683 | 313 | 2227 | 77 | 97 | 292 | |
| Florina | |||||||||||
| Conventional | Filippos | 233 | 977 | 117 | 77 | 5002 | 1389 | 2906 | 28 | 268 | 451 |
| Omiros | 179 | 1232 | 63 | 40 | 258 | 743 | 966 | 44 | 274 | 362 | |
| Alexandros | 149 | 568 | 84 | 68 | 4487 | 518 | 448 | 40 | 61 | 258 | |
| Tempi | 47 | 732 | 49 | 97 | 1682 | 867 | 714 | 44 | 78 | 264 | |
| Zefyros | 55 | 1186 | 129 | 47 | 51,452 | 864 | 3825 | 40 | 68 | 359 | |
| Pigasos | 39 | 937 | 78 | 91 | 42,065 | 958 | 187 | 76 | 74 | 327 | |
| Low-input | Filippos | 119 | 441 | 126 | 69 | 4699 | 998 | 1066 | 80 | 152 | 290 |
| Omiros | 473 | 2266 | 93 | 40 | 258 | 524 | 3095 | 66 | 383 | 301 | |
| Alexandros | 140 | 586 | 63 | 47 | 4713 | 1297 | 1323 | 38 | 102 | 172 | |
| Tempi | 32 | 652 | 65 | 80 | 528 | 689 | 1576 | 48 | 62 | 214 | |
| Zefyros | 30 | 853 | 66 | 69 | 35,609 | 1336 | 1521 | 59 | 28 | 176 | |
| Pigasos | 32 | 985 | 87 | 84 | 23,877 | 583 | 245 | 55 | 39 | 281 | |
| Trikala | |||||||||||
| Conventional | Filippos | 118 | 384 | 130 | 64 | 297 | 1600 | 1860 | 82 | 71 | 306 |
| Omiros | 258 | 1894 | 22 | 57 | 855 | 670 | 1230 | 85 | 183 | 372 | |
| Alexandros | 59 | 959 | 80 | 67 | 2233 | 1038 | 1564 | 76 | 19 | 324 | |
| Tempi | 24 | 441 | 87 | 57 | 736 | 529 | 1274 | 71 | 41 | 370 | |
| Zefyros | 31 | 1255 | 73 | 45 | 4774 | 637 | 754 | 87 | 71 | 350 | |
| Pigasos | 26 | 1274 | 87 | 55 | 294 | 317 | 1058 | 109 | 30 | 175 | |
| Low-input | Filippos | 119 | 502 | 111 | 71 | 280 | 1475 | 1517 | 99 | 135 | 351 |
| Omiros | 214 | 1989 | 62 | 57 | 362 | 564 | 1491 | 92 | 200 | 475 | |
| Alexandros | 181 | 1270 | 81 | 109 | 766 | 753 | 1243 | 89 | 51 | 503 | |
| Tempi | 53 | 301 | 125 | 80 | 2900 | 989 | 1539 | 66 | 124 | 360 | |
| Zefyros | 45 | 997 | 139 | 47 | 1936 | 975 | 574 | 124 | 115 | 251 | |
| Pigasos | 45 | 1083 | 125 | 48 | 308 | 506 | 1742 | 121 | 30 | 274 | |
| Kalambaka | |||||||||||
| Conventional | Filippos | 241 | 378 | 208 | 58 | 2764 | 780 | 1558 | 101 | 90 | 546 |
| Omiros | 117 | 1158 | 147 | 56 | 2952 | 627 | 797 | 94 | 509 | 394 | |
| Alexandros | 63 | 620 | 54 | 106 | 2538 | 998 | 1365 | 80 | 41 | 335 | |
| Tempi | 38 | 541 | 113 | 85 | 3512 | 438 | 1417 | 95 | 86 | 338 | |
| Zefyros | 33 | 1565 | 24 | 71 | 854 | 788 | 1270 | 142 | 73 | 344 | |
| Pigasos | 17 | 1154 | 74 | 73 | 341 | 690 | 2004 | 80 | 14 | 321 | |
| Low-input | Filippos | 159 | 395 | 87 | 51 | 1682 | 772 | 1903 | 121 | 115 | 341 |
| Omiros | 670 | 1499 | 115 | 77 | 2819 | 365 | 747 | 101 | 716 | 370 | |
| Alexandros | 165 | 1566 | 58 | 61 | 2830 | 405 | 1297 | 106 | 73 | 457 | |
| Tempi | 40 | 736 | 129 | 73 | 2525 | 759 | 1513 | 160 | 95 | 321 | |
| Zefyros | 23 | 1060 | 22 | 49 | 2424 | 453 | 871 | 107 | 110 | 433 | |
| Pigasos | 47 | 925 | 89 | 56 | 194 | 545 | 2675 | 71 | 24 | 354 | |
| Seed Yield (kg ha−1) | Thousand Kernel Weight (g) | Number of Pods per Plant | Number of Seeds per Pod | Number of Seeds per Plant | Pod Length (cm) | Pod Width (mm) | Pod Weight (g) | Hay Yield (kg ha−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thousand kernel weight (g) | −0.007 | ||||||||
| Number of pods per plant | 0.172 ** | 0.027 | |||||||
| Number of seeds per pod | 0.116 * | 0.057 | −0.106 * | ||||||
| Number of seeds per plant | −0.003 | 0.039 | 0.031 | −0.182 ** | |||||
| Pod length (cm) | 0.116 * | 0.079 | 0.042 | 0.064 | 0.024 | ||||
| Pod width (mm | −0.032 | −0.070 | −0.209 ** | 0.138 ** | −0.093 | 0.046 | |||
| Pod weight (g) | 0.109 * | 0.081 | 0.042 | 0.122 * | 0.017 | −0.104 * | −0.066 | ||
| Hay yield (kg ha−1) | 0.771 ** | 0.028 | 0.148 ** | 0.140 ** | 0.033 | 0.132 ** | −0.184 ** | 0.075 | |
| Plant height (cm) | 0.078 | 0.046 | 0.031 | 0.079 | −0.053 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.053 | 0.097 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Assessment of Interactions between Yield Components of Common Vetch Cultivars in Both Conventional and Low-Input Cultivation Systems. Agriculture 2021, 11, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11040369
Greveniotis V, Bouloumpasi E, Zotis S, Korkovelos A, Ipsilandis CG. Assessment of Interactions between Yield Components of Common Vetch Cultivars in Both Conventional and Low-Input Cultivation Systems. Agriculture. 2021; 11(4):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11040369
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreveniotis, Vasileios, Elisavet Bouloumpasi, Stylianos Zotis, Athanasios Korkovelos, and Constantinos G. Ipsilandis. 2021. "Assessment of Interactions between Yield Components of Common Vetch Cultivars in Both Conventional and Low-Input Cultivation Systems" Agriculture 11, no. 4: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11040369
APA StyleGreveniotis, V., Bouloumpasi, E., Zotis, S., Korkovelos, A., & Ipsilandis, C. G. (2021). Assessment of Interactions between Yield Components of Common Vetch Cultivars in Both Conventional and Low-Input Cultivation Systems. Agriculture, 11(4), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11040369





