Biosystematic Study on Some Egyptian Species of Astragalus L. (Fabaceae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxonomy Study
2.1.1. Taxon Sampling and Collection of Plant Specimens
2.1.2. Taxonomical Studies
2.1.3. Morphological Studies
2.2. Molecular Study
2.2.1. Genomic DNA Extraction, PCR and Sequencing
2.2.2. Clustering Analysis for SCoT Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Data Analysis
3.2. Molecular Data Analysis
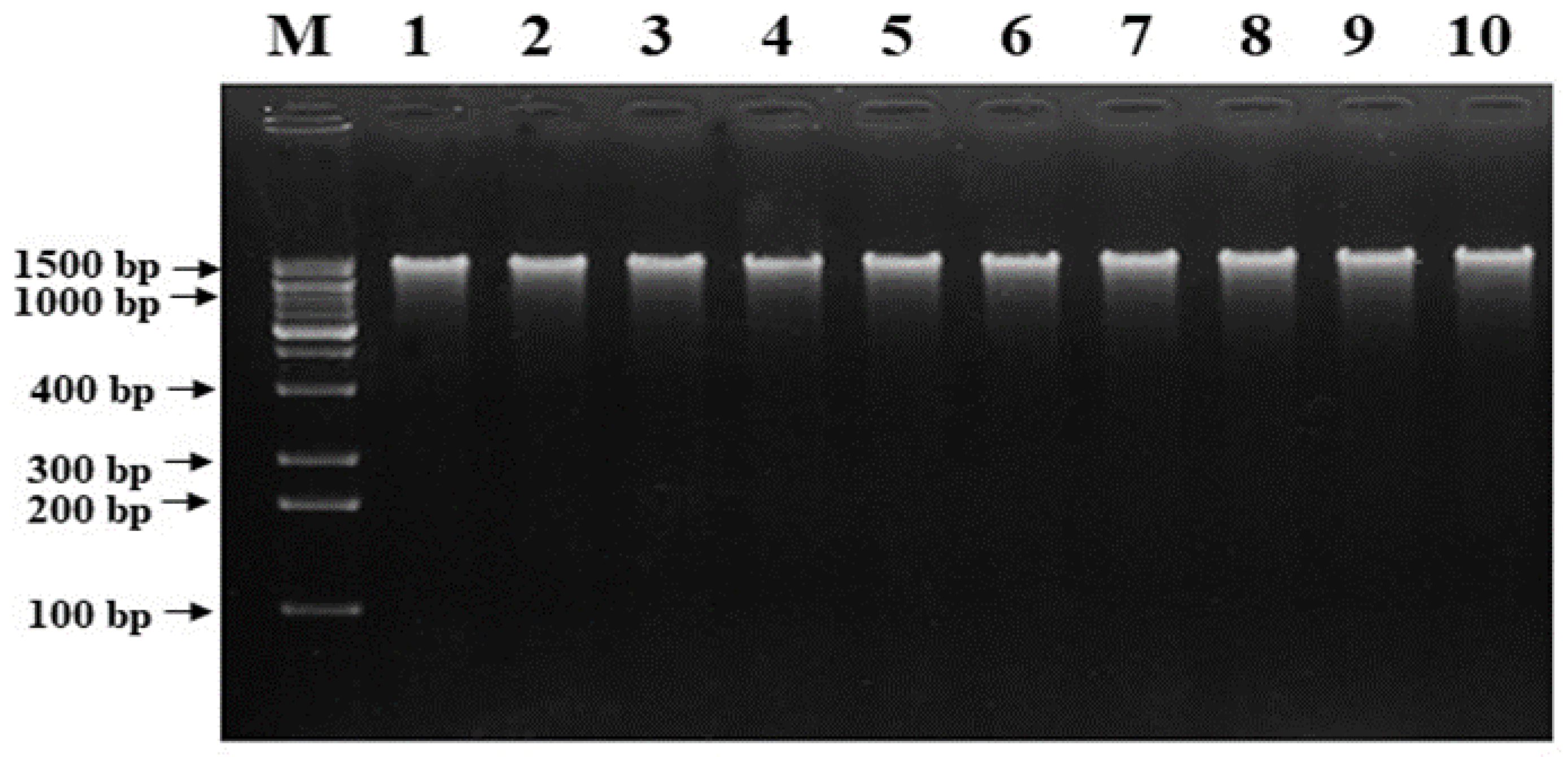
3.2.1. DNA Extraction
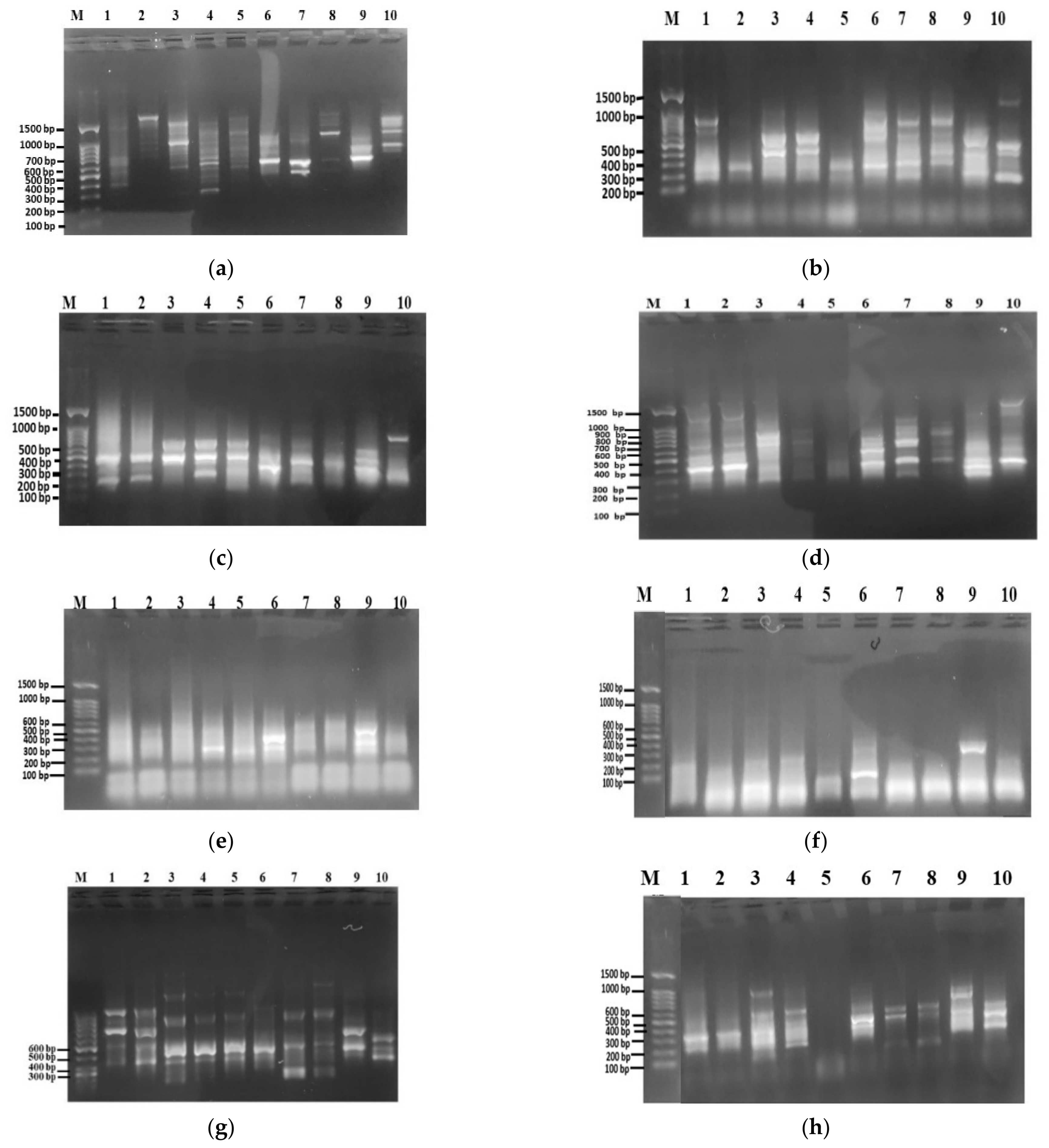
3.2.2. Amplification of SCoT Region
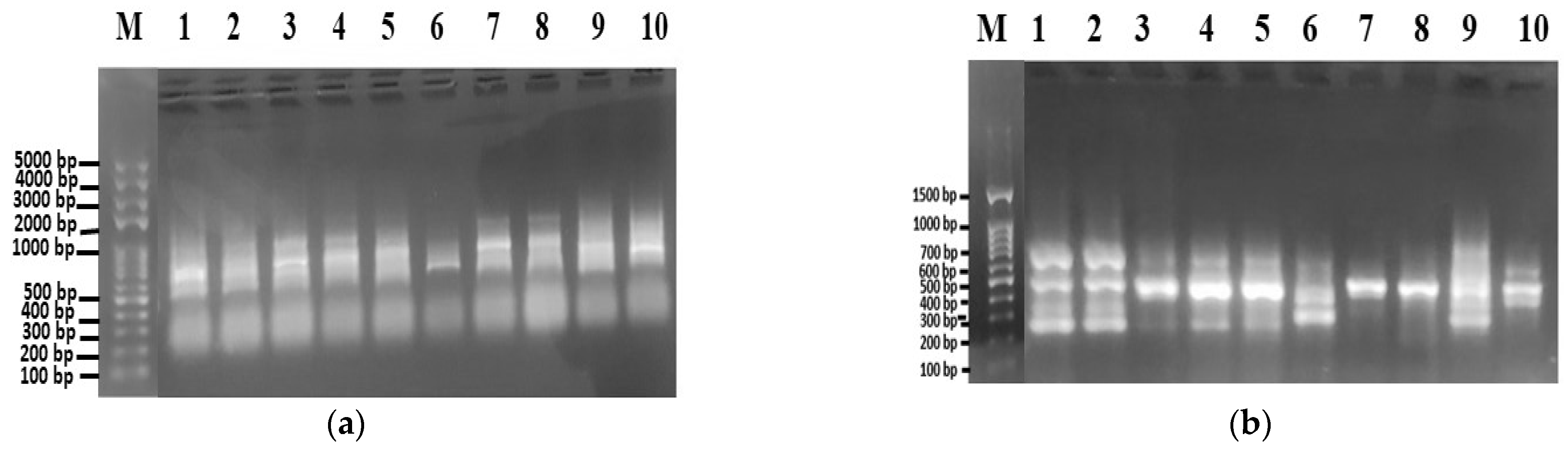
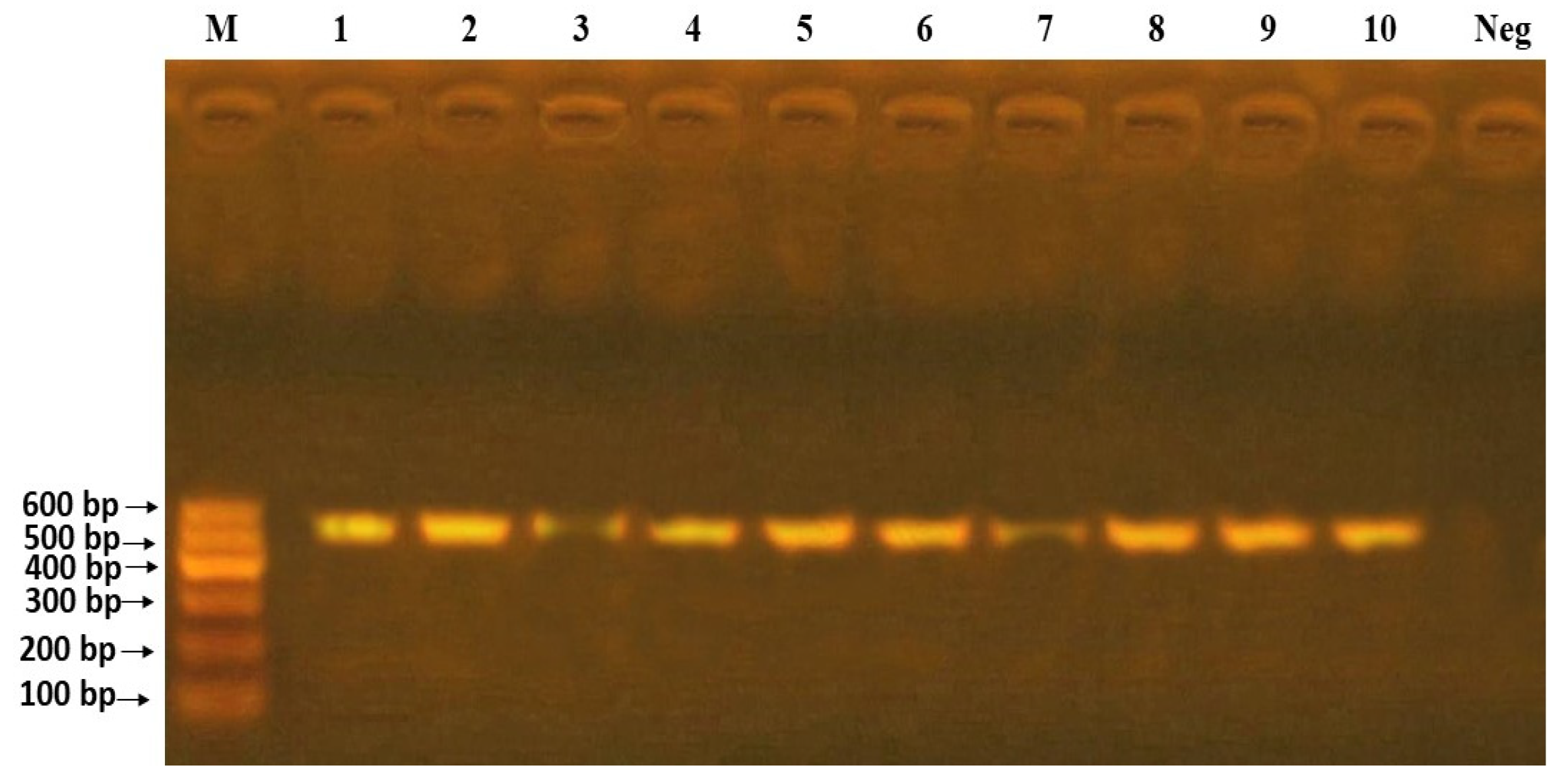
3.2.3. Amplification of ITS Region Using Universal ITS2 Primers
3.2.4. SCoT Polymorphism in Astragalus
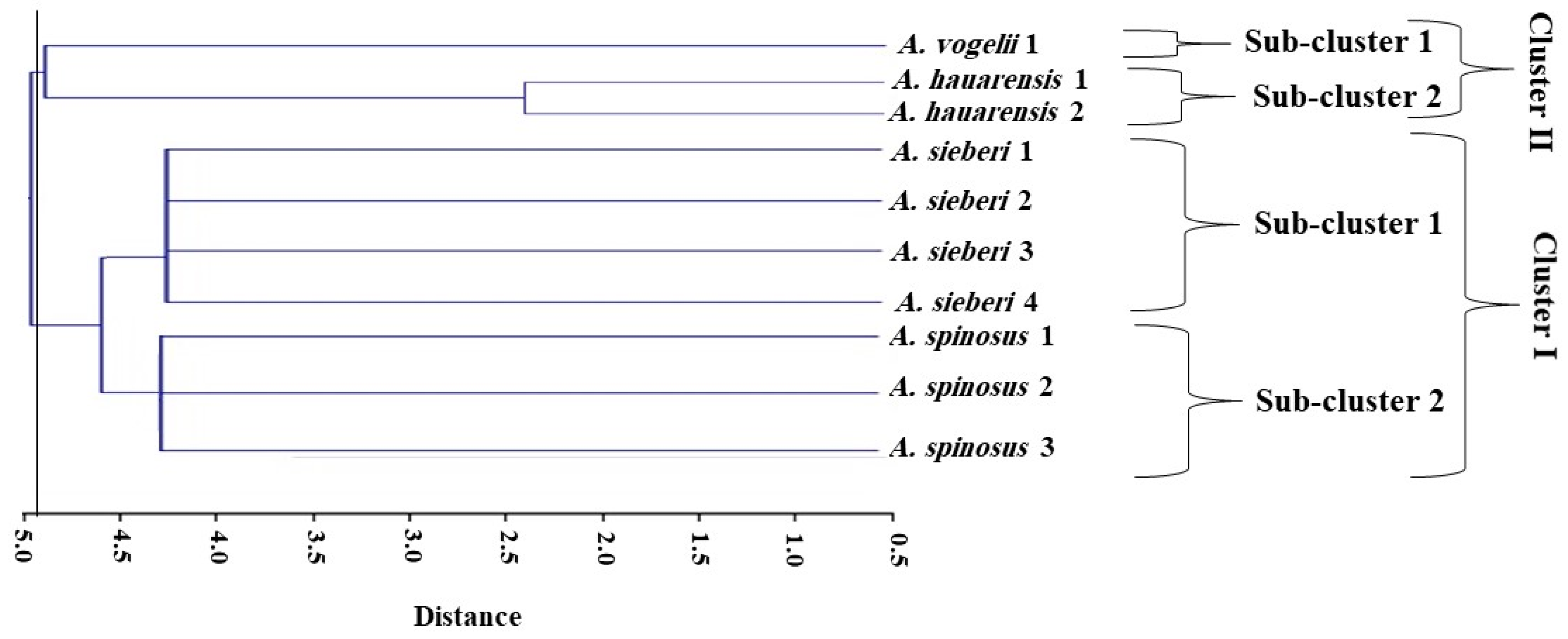
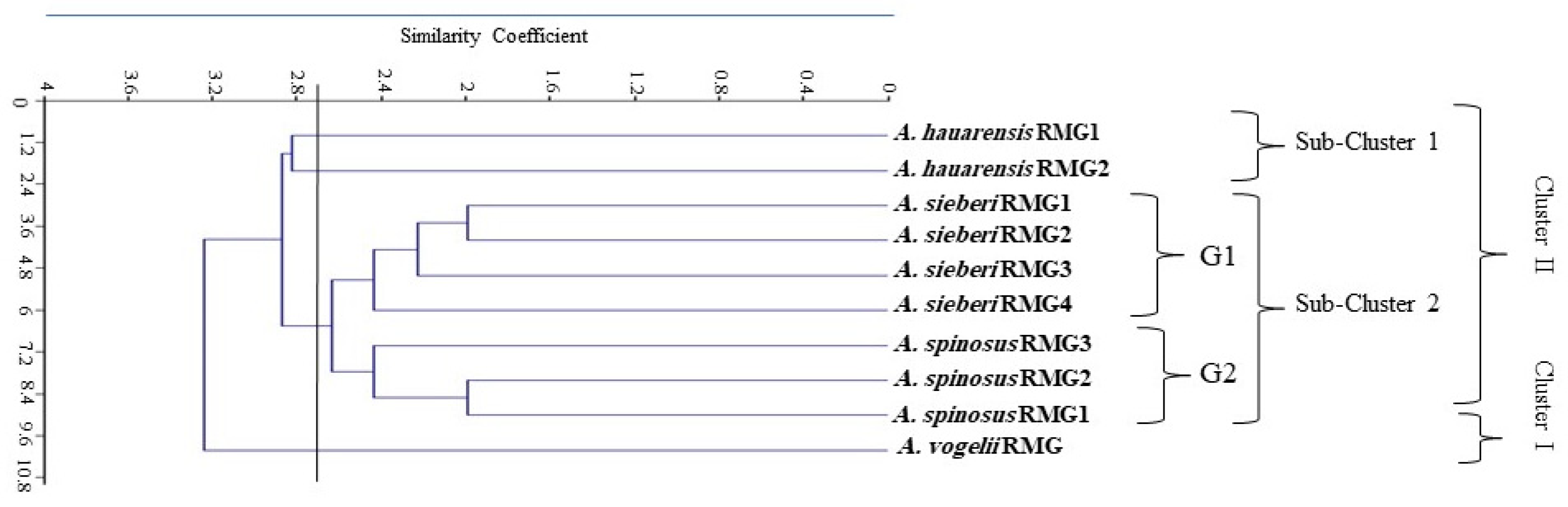
3.2.5. Clustering Analysis
3.2.6. Molecular Identification of Specimens by Using ITS2 Gene Sequence
3.2.7. Sequences Submission
3.2.8. Comparison between Results of Morphological Identification and ITS2 Identification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statement
References
- Mabberley, D.J. The Plant-Book: A Potable Dictionary of the Vascular Plants, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; p. 858. [Google Scholar]
- Haerinasab, M.; Rahiminejad, M. A taxonomic revision of the genus Trifolium L. sect. Fragifera Koch (Fabaceae) in Iran. Iran. J. Bot. 2012, 18, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ceter, T.; Karaman, S.; Aytac, Z.; Baser, B. Pollen morphology of the genus Oxytropis in Turkey. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2013, 42, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.; Desai, T.; Patel, R. Pharmacognostic Evaluation of Melilotus officinalis Linn. Pharmacognjournal 2016, 8, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Grusak, M. Structure and development of Medicago truncatula pod wall and seed coat. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallón, S.A.; Sanderson, M.J. Absolute diversification rates in angiosperm clades. Evolution 2001, 55, 1762–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, W.S.; Campbell, C.S.; Kellogg, E.A.; Stevens, P.F.; Donoghue, M.J. Plant systematics: A phylogenetic approach. Sinauer Axxoc. 2002, 2, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Rendle, A.B. Classification of Flowering Plants, 2nd ed.; Institute of Terrestrial Ecology: Cambridge, UK, 1952; pp. 348–370. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, J.C. A Dictionary of the Flowering Plants and Ferns, 7th ed.; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1967; pp. 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, R.J.; Johnson, K.R. South American paleobotany and the origins of neotropical rainforests. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.P.; Schrire, B.D.; Mackinder, B.A.; Lock, M. Legumes of the World; Royal Botanic Gardens: Kew, India, 2005; pp. 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- Maassoumi, A.A. Astragalus L. in the Old World, Check-List; Research Institute of Forests and Rangeland: Tehran, Iran, 1998; p. 618. [Google Scholar]
- Maassoumi, A.A. The genus Astragalus in Iran. Tehran 2005, 5, 785. [Google Scholar]
- Taeb, F.; Zarre, S.; Podlech, D.; Tillich, H.; Kazempour Osaloo, S.; Maassoumai, A.A. A contribution to the phylogeny of annual species of Astragalus (Fabaceae) in the Old-World using hair micromorphology and other morphological characters. Feddes Repert. 2007, 118, 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPNI. The International Plant Names Index; Royal Botanic Gardens: Kew, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lock, M.; Schrire, B.D. Galegeae. In Legumes of the World; Lewis, G.P., Schrire, B.D., Mackinder, B.A., Lock, M., Eds.; Royal Botanic Gardens: Kew, India, 2005; pp. 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, M.J.; Wojciechowski, M.F. Improved bootstrap confidence limits in large-scale phylogenies with an example from Neo-Astragalus (Leguminosae). Syst. Biol. 2000, 49, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlech, D. The genus Astragalus L. (Fabaceae) in Europe with exclusion of the former Soviet Union. Feddes Repert. 2008, 119, 310–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidarlord, M.; Ghahremaninejad, F.; Maassoumi, A.A. A new species of the genus Astragalus (Leguminosae) from Northwest Iran. Phytotaxa 2016, 252, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, M.F. Astragalus (Fabaceae): A molecular phylogenetic perspective. Brittonia 2005, 57, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeckholm, V. Students’ flora of Egypt, 2nd ed.; Cairo University: Cairo, Egypt, 1974; pp. 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, L. Flora of Egypt. In Azollacae-Oxalidacae; Al-Hadara Publishing: Cairo, Egypt, 1999; Volume 1, pp. 320–336. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, J.; Abdul Majid, S.; Allan, D.G.; Alsafran, M.; Boer, B.; Richer, R. An Illustrated Checklist of the Flora of Qatar; Browndown Publications: Gosport, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, S.A. Flora of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; Ministry of Agriculture: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2000.
- Alshammari, A.M.; Sharawy, S.M. Wild plants diversity of the Hema Faid Region (Ha’il Province, Saudi Arabia). Asian J. Plant Sci. 2010, 9, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Llewellyn, O.A.; Hall, M.; Miller, A.G.; Al-Abbasi, T.M.; Al-Wetaid, A.H.; Al-Harbi, R.J.; Al-Shammari, K.F. Important plant areas in the Arabian Peninsula: 4. Jabal Aja. Edinb. J. Bot. 2011, 68, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremaninejad, F.; Joharchi, M.R. 840th species of genus Astragalus (Fabaceae) for the flora of Iran from Khorassan Province as a new record: A. globiceps Bunge. J. Plant Res. 2020, 32, 906–910. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.H.; Li, P.; Dong, T.T.X.; Tsim, K.W.K. Molecular diversity of 5S-rRNA spacer domain in Fritillaria species revealed by PCR analysis. Planta Medica 1999, 65, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, F.; Guiry, M.D.; López-Bautista, J.M. Distribution, morphology, and phylogeny of Klebsormidium (Klebsormidiales, Charophyceae) in urban environments in Europe. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, R.S.; Lagu, M.D.; Chaudhary, L.B.; Ranjekar, P.K.; Gupta, V.S. Assessment of genetic diversity in Trigonella foenum-graecum and Trigonella caerulea using ISSR and RAPD marker. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, P.Y.; Kwan, H.S. Molecular identification of Astragalus membranaceus at the species and locality levels. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 106, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B. ITS1 region of the rDNA of Pythium megacarpum sp. Nov., its taxonomy, and its comparison with related species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 186, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazempour Osaloo, S.; Maassoumi, A.A.; Murakani, N. Molecular systematics of the genus Astragalus L. (Fabaceae): Phylogenetic analysis of nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacers and chloroplast gene ndhF sequences. Plant Syst. Evol. 2003, 242, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazempour Osaloo, S.; Maassoumi, A.A.; Murakami, N. Molecular systematics of the old world Astragalus (Fabaceae) as inferred from nrDNA ITS sequence data. Brittonia 2005, 57, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, B.C.Y.; Mackill, D.J. Start Codon Targeted (SCoT) polymorphism: A simple, novel DNA marker technique for generating gene-targeted markers in plants. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 27, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.Q.; Tang, R.H.; Chen, Z.L.; Pan, L.H.; Zhuang, W.J. SCoT: A novel gene-targeted marker technique based on the translation start codon. Mol. Plant Breed 2009, 7, 635–638. [Google Scholar]
- Podlech, D. The systematics of annual species of the genus Astragalus L. (Leguminosae). Flora et. Veg. Mundi 1991, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, L. Flora of Egypt. In Geraniaceae-Boraginaceae; Al-Hadara Publishing: Cairo, Egypt, 2000; Volume 2, p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, L. Flora of Egypt. In Verbenaceae Compositae; Al Hadara Publishing: Cairo, Egypt, 2002; Volume 3, p. 373. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics. Cessadoem 2001, 25, 2009. Available online: www.uv.es/~pardomv/pe/2001_1/past/pastprog/past.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2001).
- Padmalatha, K.; Prasad, M.N.V. Optimization of DNA isolation and PCR protocol for RAPD analysis of selected medicinal and aromatic plants of conservation concern from Peninsular India. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Mohamed, N.M.; Safan, S.; Yassin, M.A.; Shaban, L.; Shindia, A.; Ali, G.S.; Sitohy, M. Restoring the biosynthetic machinery of taxol of Aspergillus terreus via cocultivation with the endophytic microbiome of Podocarpus gracilior Pilger. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Ali, G.A. Aspergillus flavipes is a novel efficient biocontrol agent of Phytophthora parasitica. Biol. Control 2020, 140, 104072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Yassin, M.A.; Ali, G.S. Transcriptional and proteomic profiling of Aspergillus flavipes in response to sulfur starvation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Safan, S.; Mohamed, N.Z.; Shaban, L.; Ali, G.S.; Sitohy, M.Z. Induction of Taxol biosynthesis by Aspergillus terreus, endophyte of Podocarpus gracilior Pilger, upon intimate interaction with the plant endogenous microbes. Process Biochem. 2018, 71, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Akbar, A.; Iqrar, I.; Ali, R.; Norman, D.; Brennan, M.; Ali, G.S. A Glucanolytic Pseudomonas sp. associated with Smilax bona-nox L. displays strong activity against Phytophthora parasitica. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Ruff, L.E.; Ghany, S.E.A.; Ali, G.S.; Esener, S. Molecular and Spectroscopic Characterization of Aspergillus flavipes and Pseudomonas putida L-Methionine γ-Lyase in Vitro. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 1513–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.T.; El-Sayed, A.S.A. Biocidal Activity of Metal Nanoparticles Synthesized by Fusarium solani against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Mycotoxigenic Fungi. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Shindia, A.A.; Zeid, A.A.A.; Yassin, A.M.; Sitohy, M.Z.; Sitohy, B. Aspergillus nidulans thermostable arginine deiminase-Dextran conjugates with enhanced molecular stability, proteolytic resistance, pharmacokinetic properties and anticancer activity. Enzym. Microbiol. Technol. 2019, 131, 109432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; George, N.M.; Bolbol, A.A.; Mohamed, M.S. Purification and biochemical characterization of Aspergillus terreus ornithine decarboxylase: Curcumin is a potent enzyme inhibitor. Molecules 2019, 24, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yao, H.; Han, J.; Liu, C.; Song, J.; Shi, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, X.; Gao, T.; Pang, X.; et al. Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yao, H.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Song, J.Y. Identification of Astragalus plants in China using the region ITS2. World Sci. Technol. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Med. 2010, 12, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. NTSYS-pc. In Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, Version 2.10; Exeter Software: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sneath, P.H.A.; Sokal, R.R. Numerical Taxonomy; W. H. Freeman and Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Mohamed, A. Comparative anatomical studies on some species of Astragalus growing in Egypt. Ann. Agric. Sci. 1988, 33, 745–760. [Google Scholar]
- Sharawy, S.M. Taxonomic Studies on Interspecific and Intraspecific Relationships in the Genus Astragalus in Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University Cairo, Cairo, Egypt, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, A.; Sharawy, S.M. Karyotype analysis and systematic relationships in the Egyptian Astragalus L. (Fabaceae). Int. J. Bot. 2007, 3, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- CBOL (Consortium of Barcode of Life). A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12794–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, R.S.; Chase, M.W.; Kress, W.J.; Savolainen, V. 300,000 species to identify problems, progress, and prospects in DNA barcoding of land plants. Taxon 2006, 55, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, M.F.; Sanderson, M.J.; Baldwin, B.G.; Donoghue, M.J. Monophyly of aneuploid Astragalus (Fabaceae): Evidence from nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences. Am. J. Bot. 1993, 80, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulpuri, S.; Muddanuru, T.; Francis, G. Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism in toxic and non-toxic accessions of Jatropha curcas L. and development of a codominant SCAR marker. Plant Sci. 2013, 207, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Studied Taxa | Abb. | Section | Sites of Collection | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Astragalus hauarensis Boiss. | A.hau.1 | Harpilobus Bge. | The Red Sea road, Kafer Homodyne (a distance 40 km from Safage to El-Quseir or before 20 km from El-Quseir). | May 2019 |
| 2 | Astragalus hauarensis Boiss. | A.hau.2 | The Red Sea road, El-Quseir before 60 km from Marsa-Alam. | May 2019 | |
| 3 | Astragalus sieberi DC. | A.sie.1 | Chronopus Bge. | Matrouh road (before about 8 Km from El-Alamein or before about 52km from El-Dabaa Gate. | May 2018 |
| 4 | Astragalus sieberi DC. | A.sie.2 | Alexandria El-Alamein desert road, courage village at a distance 25 km after El-Alamein Gate. | March 2019 | |
| 5 | Astragalus sieberi DC. | A.sie.3 | Wadi El-Natron El-Alamein desert before 65 km from the entrance to the El-Alamein. | March 2019 | |
| 6 | Astragalus sieberi DC. | A.sie.4 | Matrouh road, North Coast, Aleamid direction. | March 2019 | |
| 7 | Astragalus spinosus (Forssk.) Muschl. | A.spi.1 | Poterium Bge. | Matrouh road, North Coast, El-Alamein before El-Dabaa axis or after 40 km from El-Hammam. | May 2018 |
| 8 | Astragalus spinosus (Forssk.) Muschl. | A.spi.2 | Alexandria El-Alamein desert road, courage village at a distance 25 km after El-Alamein Gate. | March 2019 | |
| 9 | Astragalus spinosus (Forssk.) Muschl. | A.spi.3 | Matrouh road, North Coast, El-Omeid direction. | March 2019 | |
| 10 | Astragalus vogelii (Webb) Bornm. | A.vog.1 | Herpocaulos Bge. | The Red Sea road, Kafr Homodyne (a distance 40 km from safaga to El-Quseir or before 20 km from El-Quseir). | May 2019 |
| Morphological Characters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | Serial Number | Characters | State | Code |
| Whole plant | 1 | Lifespan | Annual | 0 |
| Perennial | 1 | |||
| 2 | Life form | Herb | 0 | |
| Spiny shrub | 1 | |||
| 3 | Succulence | Succulent | 0 | |
| Non-succulent | 1 | |||
| 4 | Habit | Climbing | 0 | |
| Not climbing | 1 | |||
| 5 | Conservation | Threatened | 0 | |
| Not threatened | 1 | |||
| 6 | Spines | Absent | 0 | |
| Present | 1 | |||
| 7 | Height (cm) | 5–30 | 0 | |
| 40–60 | 1 | |||
| stem | 8 | Habit | Erect | 0 |
| Prostrate | 1 | |||
| 9 | Surface | Smooth | 0 | |
| Rough | 1 | |||
| 10 | Status | Winged | 0 | |
| Not winged | 1 | |||
| 11 | Spines on internodes | Absent | 0 | |
| Present | 1 | |||
| 12 | Tipped of lateral branches | Spiny | 0 | |
| Not spiny | 1 | |||
| Rachis | 13 | Detection | Absent | 0 |
| Present | 1 | |||
| 14 | Spines | Turned | 0 | |
| Not turned | 1 | |||
| Leaf stipules | 15 | Detection | Absent | 0 |
| Present | 1 | |||
| 16 | Adnation | Free | 0 | |
| Adnate | 1 | |||
| 17 | Length (mm) | 3 or less | 0 | |
| 7 or less | 1 | |||
| 18 | Shape | Triangle | 0 | |
| Lanceolate | 1 | |||
| 19 | Apex | Acute | 0 | |
| Acuminate | 1 | |||
| leaf | 20 | Leaf midrib | Turned spines | 0 |
| Not turned spines | 1 | |||
| 21 | Length (cm) | 6 or less | 0 | |
| 10 or less | 1 | |||
| 22 | Width (cm) | 1 or more | 0 | |
| 2 or more | 1 | |||
| Petal | 23 | Color | White | 0 |
| Not white | 1 | |||
| Leaf or leaflet | 24 | shape | Elliptical-oblong | 0 |
| Ovate-oblong | 1 | |||
| 25 | Margin | Entire | 0 | |
| Not entire | 1 | |||
| 26 | Status | Evergreen | 0 | |
| Deciduous | 1 | |||
| 27 | Upper surface | Hairy | 0 | |
| Glabrous | 1 | |||
| 28 | Lower surface | Hairy | 0 | |
| Glabrous | 1 | |||
| Pod | 29 | Texture | Hairy | 0 |
| Glabrous | 1 | |||
| 30 | Curvature | Curved | 0 | |
| Not curved | 1 | |||
| 31 | Pedicle | Absent | 0 | |
| Stipitate | 1 | |||
| Long | 2 | |||
| Seed | 32 | Length (cm) | 0.4 or less | 0 |
| 0.5 or more | 1 | |||
| 33 | Shape | Reniform | 0 | |
| Quadrate | 1 | |||
| 34 | Surface | Smooth | 0 | |
| Irregular | 1 | |||
| 35 | Color | Brown | 0 | |
| Yellow | 1 | |||
| Region. | Primer Name | Base Pair Primers (bp) | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCOT | SCOT 7 | 18 bp | ACAATGGCTACCACTGAC | Collard and Mackill, [37], Xiong et al., [38] |
| SCOT 9 | 18 bp | ACAATGGCTACCACTGCC | ||
| SCOT 10 | 18 bp | ACAATGGCTACCACCAGC | ||
| SCOT 11 | 18 bp | ACAATGGCTACCACTACC | ||
| SCOT 14 | 18 bp | ACCATGGCTACCAGCGCG | ||
| SCOT 24 | 18 bp | CCATGGCTACCACCGCAG | ||
| SCOT 28 | 18 bp | CAACAATGGCTACCACCA | ||
| SCOT 32 | 18 bp | CAACAATGGCTACCACGC | ||
| SCOT 35 | 18 bp | AACCATGGCTACCACCAC | ||
| SCOT 46 | 18 bp | ACCATGGCTACCACCGCC | ||
| ITS2 | ITS2 2F | 20 bp | ATGCGATACTTGGTGTGAAT | Chen et al., [53] |
| ITS2 3R | 21 bp | GACGCTTCTCCAGACTACAAT | Gao et al., [54] |
| No. | Studied Taxa | Lifespan | Life Form | Succulence | Habit | Conservation | Spines | Height (cm) |
| 1 | A.hau.1 | Annual | Herb | Succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Absent | 8–30 |
| 2 | A.hau.2 | Annual | Herb | Succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Absent | 9–30 |
| 3 | A.sie.1 | Perennial | Spiny shrub | Non-succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Present | 18–40 |
| 4 | A.sie.2 | Perennial | Spiny shrub | Non-succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Present | 19–40 |
| 5 | A.sie.3 | Perennial | Spiny shrub | Non-succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Present | 22–40 |
| 6 | A.sie.4 | Perennial | Spiny shrub | Non-succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Present | 20–40 |
| 7 | A.spi.1 | Perennial | Spiny shrub | Non-succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Present | 20–60 |
| 8 | A.spi.2 | Perennial | Spiny shrub | Non-succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Present | 22–60 |
| 9 | A.spi.3 | Perennial | Spiny shrub | Non-succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Present | 24–60 |
| 10 | A.vog.1 | Annual | Herb | Succulent | Not climbing | Not threatened | Absent | 10–40 |
| No. | Studied Taxa | Stem Characters | Leaf Stipule Characters | |||||
| Habit | Surface | Status | Spines on Internodes | Tipped of Lateral Branches | Detection | Adnation | ||
| 1 | A.hau.1 | Prostrate | Smooth | Not winged | Absent | Not winged | Present | Free |
| 2 | A.hau.2 | Prostrate | Smooth | Not winged | Absent | Not winged | Present | Free |
| 3 | A.sie.1 | Erect | Smooth | Not winged | Absent | Not winged | Present | Adnate |
| 4 | A.sie.2 | Erect | Smooth | Not winged | Absent | Not winged | Present | Adnate |
| 5 | A.sie.3 | Erect | Smooth | Not winged | Absent | Not winged | Present | Adnate |
| 6 | A.sie.4 | Erect | Smooth | Not winged | Absent | Not winged | Present | Adnate |
| 7 | A.spi.1 | Erect | Smooth | Not winged | Present | Not winged | Present | Adnate |
| 8 | A.spi.2 | Erect | Smooth | Not winged | Present | Not winged | Present | Adnate |
| 9 | A.spi.3 | Erect | Smooth | Not winged | Present | Not winged | Present | Adnate |
| 10 | A.vog.1 | Prostrate | Smooth | Not winged | Absent | Not winged | Present | Free |
| No. | Studied Taxa | Leaf Stipules Characters | Rachis | Leaf Characters | ||||
| Shape | Apex | Length (mm) | Detection | Spines | Length (cm) | width (cm) | ||
| 1 | A.hau.1 | Triangle | Acute | 3 or less | Present | Not turned | 10 or less | 1 or more |
| 2 | A.hau.2 | Triangle | Acute | 3 or less | Present | Not turned | 10 or less | 1 or more |
| 3 | A.sie.1 | Lanceolate | Acuminate | 7 or less | Present | Turned | 10 or less | 2 or more |
| 4 | A.sie.2 | Lanceolate | Acuminate | 7 or less | Present | Turned | 10 or less | 2 or more |
| 5 | A.sie.3 | Lanceolate | Acuminate | 7 or less | Present | Turned | 10 or less | 2 or more |
| 6 | A.sie.4 | Lanceolate | Acuminate | 7 or less | Present | Turned | 10 or less | 2 or more |
| 7 | A.spi.1 | Triangle | Acute | 5 or less | Present | Turned | 5 or less | 2 or more |
| 8 | A.spi.2 | Triangle | Acute | 5 or less | Present | Turned | 5 or less | 2 or more |
| 9 | A.spi.3 | Triangle | Acute | 5 or less | Present | Turned | 5 or less | 2 or more |
| 10 | A.vog.1 | Triangle | Acuminate | 3 or less | Present | Not turned | 5 or less | 1 or more |
| No. | Studied Taxa | Petal Color | Leaf Midrib Spines | Leaf or Leaflet Characters | ||||
| Shape | Upper Surface | Lower Surface | Margin | Status | ||||
| 1 | A.hau.1 | White | Not turned | Elliptical | Hairy | Hairy | Entire | Evergreen |
| 2 | A.hau.2 | White | Not turned | Elliptical | Hairy | Hairy | Entire | Evergreen |
| 3 | A.sie.1 | Not white | Turned | Ovate | Glabrous | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| 4 | A.sie.2 | Not white | Turned | Ovate | Glabrous | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| 5 | A.sie.3 | Not white | Turned | Ovate | Glabrous | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| 6 | A.sie.4 | White | Turned | Ovate | Glabrous | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| 7 | A.spi.1 | White | Not turned | Ovate | Glabrous | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| 8 | A.spi.2 | White | Not turned | Ovate | Glabrous | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| 9 | A.spi.3 | White | Not turned | Ovate | Hairy | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| 10 | A.vog.1 | Not white | Not turned | Ovate | Hairy | Hairy | Entire | Deciduous |
| No. | Studied Taxa | Pod Characters | Seed Characters | |||||
| Texture | Curvature | Pedicle | Length (cm) | Shape | Surface | Color | ||
| 1 | A.hau.1 | Hairy | Curved | Absent | 0.5 or less | Quadrate | Smooth | Brown |
| 2 | A.hau.2 | Hairy | Curved | Absent | 0.5 or less | Quadrate | Smooth | Brown |
| 3 | A.sie.1 | Glabrous | Curved | Long | 0.4 or less | Quadrate | Irregular | Brown |
| 4 | A.sie.2 | Glabrous | Curved | Long | 0.4 or less | Quadrate | Irregular | Brown |
| 5 | A.sie.3 | Glabrous | Curved | Long | 0.4 or less | Quadrate | Irregular | Brown |
| 6 | A.sie.4 | Glabrous | Curved | Long | 0.4 or less | Quadrate | Irregular | Brown |
| 7 | A.spi.1 | Hairy | Not curved | Stipitate | 0.4 or less | Reniform | Smooth | Brown |
| 8 | A.spi.2 | Hairy | Not curved | Stipitate | 0.4 or less | Reniform | Smooth | Brown |
| 9 | A.spi.3 | Hairy | Not curved | Stipitate | 0.4 or less | Reniform | Smooth | Brown |
| 10 | A.vog.1 | Hairy | Not curved | Long | 0.5 or less | Reniform | Irregular | Brown |
| SI No. | Primer ID. | M. Morph. Bands | P. Morph. (without Unique Bands) | Unique Bands | P. Morph. (with Unique Bands) | TNB | P. Morphism Ratio (%) | MBF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Scot 7 | 0 | 3 | 34 | 37 | 37 | 100 | 0.11 |
| 2 | Scot 9 | 0 | 2 | 26 | 28 | 28 | 100 | 0.11 |
| 3 | Scot 10 | 0 | 3 | 14 | 17 | 17 | 100 | 0.12 |
| 4 | Scot 11 | 0 | 5 | 21 | 26 | 26 | 100 | 0.13 |
| 5 | Scot 14 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 100 | 0.10 |
| 6 | Scot 24 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 87.5 | 0.21 |
| 7 | Scot 28 | 0 | 6 | 20 | 26 | 26 | 100 | 0.12 |
| 8 | Scot 32 | 0 | 3 | 16 | 19 | 19 | 100 | 0.12 |
| 9 | Scot 35 | 0 | 2 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 100 | 0.11 |
| 10 | Scot 46 | 1 | 3 | 15 | 18 | 19 | 94.7 | 0.17 |
| Total | 2 | 27 | 183 | 210 | 212 | - | - | |
| NO. | Studied Taxa | Region | Length/b | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Astragalus hauarensis RMG1 | ITS2 | 434 | MT367587.1 |
| 2 | Astragalus hauarensis RMG2 | 431 | MT367591.1 | |
| 3 | Astragalus sieberi RMG1 | 426 | MT367593.1 | |
| 4 | Astragalus sieberi RMG2 | 433 | MT367585.1 | |
| 5 | Astragalus sieberi RMG3 | 427 | MT367586.1 | |
| 6 | Astragalus sieberi RMG4 | 445 | MT367588.1 | |
| 7 | Astragalus spinosus RMG1 | 421 | MT160347.1 | |
| 8 | Astragalus spinosus RMG2 | 428 | MT367590.1 | |
| 9 | Astragalus spinosus RMG3 | 443 | MT367589.1 | |
| 10 | Astragalus vogelii RMG | 420 | MT367592.1 |
| NO. | Morphologically Identification after Reinvestigation | BLAST Search Match Identified as | BLAST Similarity (%) | Sequence Submission |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Astragalus hauarensis 1 | Astragalus hauarensis | 97.51 | Astragalus hauarensis RMG1 |
| 2 | Astragalus hauarensis 2 | Astragalus hauarensis | 96.60 | Astragalus hauarensis RMG2 |
| 3 | Astragalus sieberi 1 | Astragalus sieberi | 96.76 | Astragalus sieberi RMG1 |
| 4 | Astragalus sieberi 2 | Astragalus sieberi | 96.76 | Astragalus sieberi RMG2 |
| 5 | Astragalus sieberi 3 | Astragalus sieberi | 97.70 | Astragalus sieberi RMG3 |
| 6 | Astragalus sieberi 4 | Astragalus sieberi | 99.31 | Astragalus sieberi RMG4 |
| 7 | Astragalus spinosus 1 | Astragalus spinosus | 89.28 | Astragalus spinosus RMG1 |
| 8 | Astragalus spinosus 2 | Astragalus spinosus | 94.66 | Astragalus spinosus RMG2 |
| 9 | Astragalus spinosus 3 | Astragalus spinosus | 96.70 | Astragalus spinosus RMG3 |
| 10 | Astragalus vogelii | Astragalus vogelii | 95.30 | Astragalus vogelii RMG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd El-Ghani, M.M.; El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Moubarak, A.; Rashad, R.; Nosier, H.; Khattab, A. Biosystematic Study on Some Egyptian Species of Astragalus L. (Fabaceae). Agriculture 2021, 11, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11020125
Abd El-Ghani MM, El-Sayed ASA, Moubarak A, Rashad R, Nosier H, Khattab A. Biosystematic Study on Some Egyptian Species of Astragalus L. (Fabaceae). Agriculture. 2021; 11(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11020125
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd El-Ghani, Monier M., Ashraf S. A. El-Sayed, Ahmed Moubarak, Rabab Rashad, Hala Nosier, and Adel Khattab. 2021. "Biosystematic Study on Some Egyptian Species of Astragalus L. (Fabaceae)" Agriculture 11, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11020125
APA StyleAbd El-Ghani, M. M., El-Sayed, A. S. A., Moubarak, A., Rashad, R., Nosier, H., & Khattab, A. (2021). Biosystematic Study on Some Egyptian Species of Astragalus L. (Fabaceae). Agriculture, 11(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11020125






