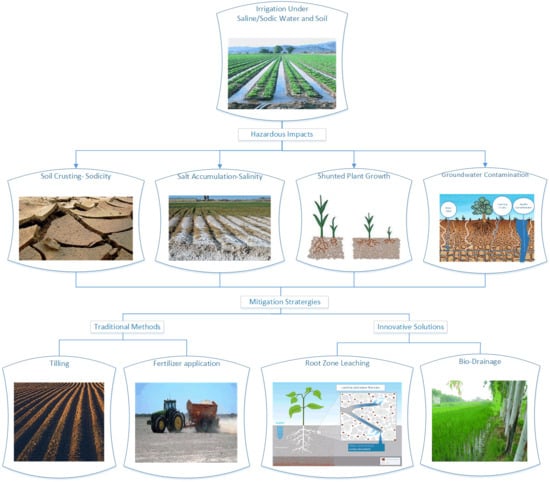
Irrigation Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts and Mitigation Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Global Distribution of Irrigation-Induced Salinity and Sodicity
3. Soil Salinity and Sodicity: Causes
4. Impacts of Salinity and Sodicity on Physicochemical Properties of Soil
5. Impacts of Salinity and Sodicity on Biological Activities in Soil
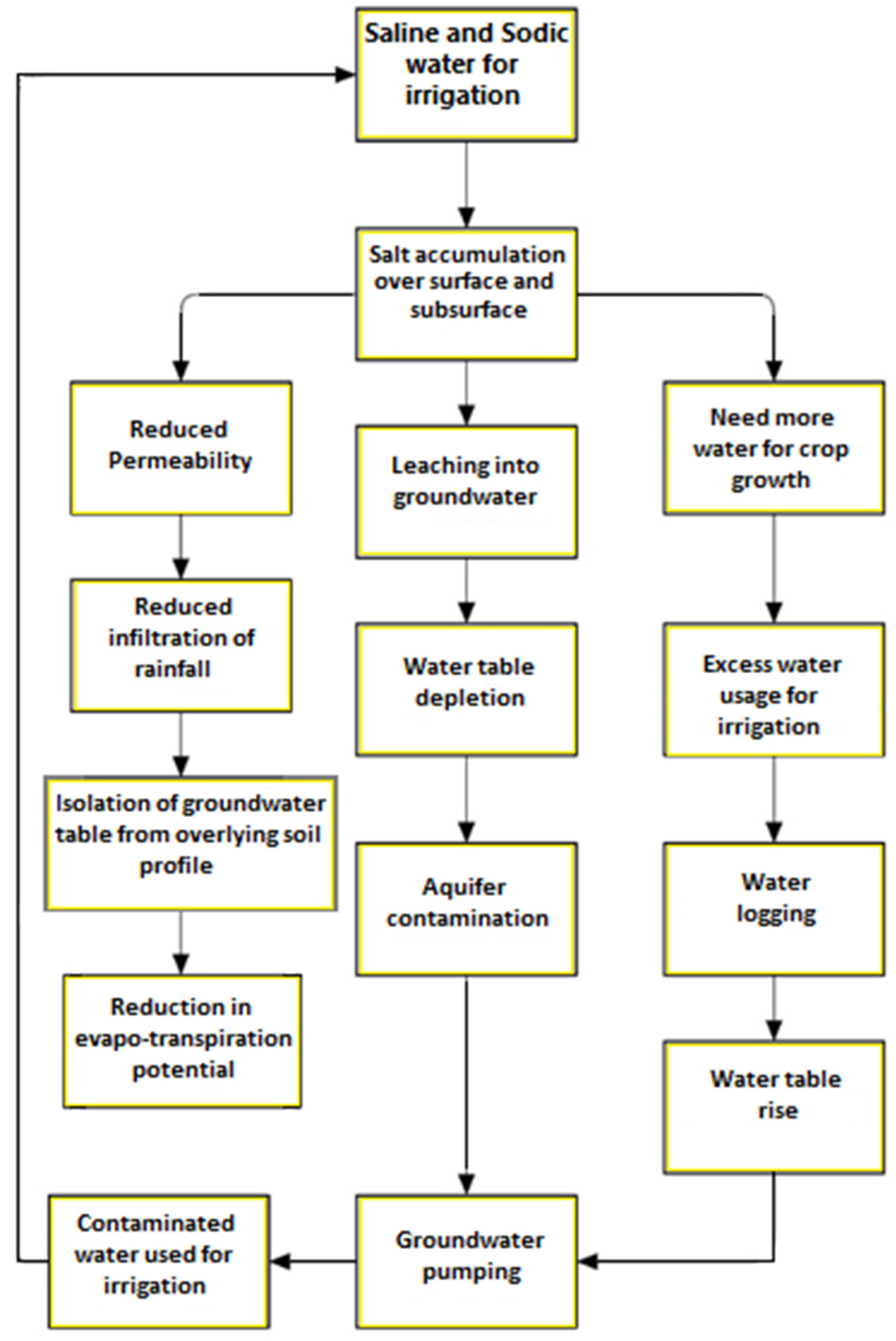
6. Effects of Irrigation-Induced Salinity and Sodicity on Groundwater
7. Traditional Strategies for Mitigating High Soil Salinity and Sodicity
8. Innovative Solutions to Manage Irrigation-Induced Salinity and Sodicity Crisis
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, S.J.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity and waterlogging as constraints to saltland pasture production: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil salinization. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Environmental Science; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Soil salinity: Historical perspectives and a world overview of the problem. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, M.M.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; García-Sánchez, E.; Mateu, J.; Juan, P. Spatial dynamics of soil salinity under arid and semi-arid conditions: Geological and environmental implications. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, F.; Čelková, A. Salinity and sodicity hazard in water flow processes in the soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Miyamoto, S. Testing soils for salinity and sodicity. In Soil Testing and Plant Analysis; Westerman, R., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990; pp. 299–336. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agriculture Handbook No. 60; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Northcote, K.H.; Srene, J. Australian Soils with Saline and Sodic Properties; Soil Publication No. 27; Transport and Road Research Laboratory: Crowthorne, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, T.F.; Seelig, B.; Franzen, D. Soil, Water and Plant Characteristics Important to Irrigation; NRCS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 14. Available online: https://library.ndsu.edu/ir/bitstream/handle/10365/9480/eb66_1996.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Alonge, T.; Ojo, O.; Adejumobi, A. Electrical conductivity based classification and mapping of salt affected soils in kampe-omi irrigation scheme. Glob. Sci. J. 2019, 6, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Odeh, I.O.A.; Onus, A. Spatial analysis of soil salinity and soil structural stability in a semiarid region of New South Wales, Australia. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Rahman, K. Soil salinity development, classification, assessment and management in irrigated agriculture. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.-Q.; Bañuelos, G.S. Soil salination indicators. In Environmental Indicators; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Introduction to soil salinity, sodicity and diagnostics techniques. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Waskom, R.M.; Bauder, T.; Davis, J.G.; Andales, A.A. Diagnosing Saline and Sodic Soil Problems; Colorado State University Extension Publications: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietz, D.N.; Haynes, R.J. Effects of irrigation-induced salinity and sodicity on soil microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrence, N.; Bauder, J.W.; Pearson, K.E. Basics of Salinity and Sodicity Effects on Soil Physical Properties; Department of Land Resources and Environmental Sciences, Montanta State University-Bozeman: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ezlit, Y.D.; Smith, R.J.; Raine, S.R. A Review of Salinity and Sodicity in Irrigation; CRC Irrigation Futures Irrigation Matters Series no. 01/10; CRC for Irrigation Futures: Cannon Hill, Australia, 2010; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Oster, J.D.; Shainberg, I. Soil responses to sodicity and salinity: Challenges and opportunities. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rengel, Z.; Veres, S. Soil salinisation and salt stress in crop production. In Abiotic Stress in Plants—Mechanisms and Adaptations; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/18402 (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Culverwell, T.L.; Swinford, J.M. Attempts at improving irrigation water quality in northern Zululand. In Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists Association, Mount Edgecombe, South Africa, 2–6 June 1986; pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J.; Rietz, D.N. Effect of irrigation-induced salinity and sodicity on sugarcane yields, soil chemical and microbial properties. In Proceedings of the 18th World Congress of Soil Science, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 15 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Salinity and sodicity adaptation and mitigation options. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 55–89. [Google Scholar]
- Minhas, P.S.; Qadir, M.; Yadav, R.K. Groundwater irrigation induced soil sodification and response options. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 215, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Feng, S.; Wang, J.; Huo, Z.; Ji, Q. Effects of irrigation water salinity on soil salt content distribution, soil physical properties and water use efficiency of maize for seed production in arid Northwest China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.; Serralheiro, R. Soil salinity: Effect on vegetable crop growth. Management practices to prevent and mitigate soil salinization. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, K.; Sharma, D.K.; Dagar, J.C.; Raju, R. Reclamation of salt-affected soils: Socioeconomic impact assessment. In Innovative Saline Agriculture; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 489–505. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Quillérou, E.; Nangia, V.; Murtaza, G.; Singh, M.; Thomas, R.J.; Drechsel, P.; Noble, A.D. Economics of salt-induced land degradation and restoration. Nat. Resour. Forum 2014, 38, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrich, J.C. Managing the Economics of Soil Salinity; Department of Agribusiness and Applied Economics, Agricultural Experiment Station, North Dakota State University: Fargo, ND, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Naifer, A.; Al-Rawahy, S.A.; Zekri, S. Economic impact of salinity: The case of al-batinah in Oman. Int. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madden, B.; Hayes, G.; Duggan, K. National Investment in Rural Landscapes: An Investment Scenario; The Virtual Consulting Group & Griffin-nrm Pty Ltd.: Canberra, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Abrol, I.P.; Yadav, J.S.P.; Massoud, F.I. Salt-Affected Soils and Their Management; FAO Soils Bulletin 39; FAO United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Mau, Y.; Porporato, A. A dynamical system approach to soil salinity and sodicity. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 83, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Varouchakis, A.E.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The threat of soil salinity: A European scale review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Predicting long-term dynamics of soil salinity and sodicity on a global scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33017–33027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentís, I.P. Advances in the prognosis of soil sodicity under dryland irrigated conditions. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014, 2, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mahmuduzzaman, M.; Ahmed, Z.U.; Nuruzzaman, A.K.M.; Ahmed, F.R.S. Causes of salinity intrusion in coastal belt of Bangladesh. Int. J. Plant Res. 2013, 4, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelgasim, A.; Ammad, R. Mapping soil salinity in arid and semi-arid regions using Landsat 8 OLI satellite data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockle, C.O. Environmental impact of irrigation: A review. In Proceedings of the IV International Congress of Agricultural Engineering, Chillan, Chile, 9–11 May 2001; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G. Salinity-related desertification and management strategies: Indian experience. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerma, J. Regional assessment of soil changes in Latin America and the Caribbean. In Status of the World’s Soil Resources; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, C.R.; Taboada, M.A.; Gutierrez Boem, F.H.; Bono, A.; Fernandez, P.L.; Prystupa, P. Topsoil properties as affected by tillage systems in the rolling pampa region of Argentina. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Vincent, B.; Yang, J.; Bouarfa, S.; Vidal, A. Remote Sensing monitoring of changes in soil salinity: A case study in inner Mongolia, China. Sensors 2008, 8, 7035–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Inoue, M.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, Z. The mitigation challenge of salt affected soils in Pakistan. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2007, 5, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Qureshi, A.S.; Cheraghi, S.A.M. Extent and characterisation of salt-affected soils in Iran and strategies for their amelioration and management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidov, A.; Helming, K.; Balla, D. Impact of agricultural land use in Central Asia: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Preez, C.C.; van Huyssteen, C.W. Threats to soil and water resources in South Africa. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankova, E.I. Salt-affected soils of Russia: Solved and unsolved problems. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamond, R.E.; Whitney, D.A. Management of Saline and Sodic Soils; Kansas State University: Manhattan, KS, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nauman, T.W.; Ely, C.P.; Miller, M.P.; Duniway, M.C. Salinity yield modeling of the Upper Colorado River Basin using 30-meter resolution soil maps and random forests. Water Resour. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardon, G.E. Salinity ISSUES in Colorado. Agron. News 1998, 12, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Seelig, B.D. Salinity and Sodicity in North Dakota Soils; North Dakota State University of Agriculture and Applied Science: Fargo, ND, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchi, C.; Cecchi, S. Soil salinisation in the grosseto plain (Maremma, Italy): An environmental and socio-economic analysis of the impact on the agro-ecosystem. In Coastal Water Bodies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Giambastiani, B.M.S. Predicting salinization trends in a lowland coastal Aquifer: Comacchio (Italy). Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, R.J.; Dell, B.; Ruprecht, J.K.; Sochacki, S.J.; Smettem, K.R.J. Salinity and the reclamation of salinized lands. In Soils and Landscape Restoration; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 193–208. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. Transient salinity and subsoil constraints to dryland farming in Australian sodic soils: An overview. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2002, 42, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyen, Z.; Moore, G.A.; Wrigley, R.J. Soil salinity and sodicity effects of wastewater irrigation in South East Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 99, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjra, M.A.; Blackwell, J.; Carr, G.; Zhang, F.; Jackson, T.M. Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: Implications for water governance and public policy. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, A.; Aslam Mirza, M.; Aziz Choudhary, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Raza, W.; Raza, N.; Soo Lee, S.; Zhang, M.; Lee, J.-H.; Sarfraz, M. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in crops in a wastewater irrigated zone and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Kharche, V.K. Soil salinity and sodicity. In Soil Science: An Introduction; Indian Society of Soil Science: New Delhi, India, 2018; pp. 353–384. [Google Scholar]
- Floerke, M.; Fink, J.; Malsy, M.; Voelker, J.; Alcamo, J. Implications of salinity pollution hotspots on agricultural production. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, EGU Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Renella, G.; Wirth, S.; Islam, R. Secondary salinity effects on soil microbial biomass. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjegunte, G.; Clark, J. Causes and management of root-zone salinity and sodicity in the arid west Texas: Field-scale experience. In Research Developments in Saline Agriculture; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 307–330. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L. Irrigation systems and zones of salinity development. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 91–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Hanati, G.; Danierhan, S.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Identifying seasonal accumulation of soil salinity with three-dimensional mapping—A case study in cold and semiarid irrigated fields. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Grattan, S.R.; Minhas, P.S. Sustainable crop production using saline and sodic irrigation waters. In Alternative Farming Systems, Biotechnology, Drought Stress and Ecological Fertilisation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 293–318. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, R.; Timms, W.; Rengasamy, P.; Arshad, M.; Cresswell, R. Soil and aquifer salinization: Toward an integrated approach for salinity management of groundwater. In Integrated Groundwater Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 377–412. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Rahmatullah, T.M.; Tahir, M.A. Contribution of shallow water table to salinity/sodicity development under fallow and cropped conditions. Pakistan J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 43, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane, D.J.; George, R.J.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G.; Gilfedder, M. Salinity in dryland agricultural systems: Challenges and opportunities. In Innovations in Dryland Agriculture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 521–547. [Google Scholar]
- Dunin, F.X. Integrating agroforestry and perennial pastures to mitigate water logging and secondary salinity. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 53, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkin, J.J. Terrain, groundwater and secondary salinity in Victoria, Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 1981, 4, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannell, D.J.; Ewing, M.A. Managing secondary dryland salinity: Options and challenges. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Soil pH and Organic Matter; Montana State University: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, T.L. Soil pH and the availability of plant nutrients. IPNI Plant Nutr. Today 2010, 2010, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein, M.; Plaut, Z.; Ben-Hur, M. Water salinity and sodicity effects on soil structure and hydraulic properties. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 24, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Klopp, H.W.; Daigh, A.L.M. Measured saline and sodic solutions effects on soil saturated hydraulic conductivity, electrical conductivity and sodium adsorption ratio. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2020, 34, 264–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelin, H.; Devi, T.S.; Gupta, S.; Kapoor, R. Mitigation of salinity stress in plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: Current understanding and new challenges. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy, P. Irrigation water quality and soil structural stability: A perspective with some new insights. Agronomy 2018, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, M.C.; Grand, S.; Verrecchia, É.P. Calcium-mediated stabilisation of soil organic carbon. Biogeochemistry 2018, 137, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.J.; Shainberg, I. Sodic soils. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 504–513. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K. Microbial and enzyme activities of saline and sodic soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Shah, S.H.H.; Vervoort, R.W. Root zone salinity and sodicity under seasonal rainfall due to feedback of decreasing hydraulic conductivity. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 9432–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UOC. Effects of Salinity and Sodicity on Physical and Hydraulic Properties. Available online: https://ucanr.edu/sites/Salinity/Salinity_Management/Effect_of_salinity_on_soil_properties/Effects_of_salinity_and_sodicity_on_physical_and_hydraulic_properties/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Rollins, L. Advanced Topics in Water Chemistry and Salinity; WateReuse Foundation: Alexandria, VA, USA; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Heydari, N.; Gupta, A.D.; Loof, R. Salinity and sodicity influences on infiltration during surge flow irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2001, 20, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shainberg, I.; Levy, G.J.; Goldstein, D.; Mamedov, A.I.; Letey, J. Prewetting rate and sodicity effects on the hydraulic conductivity of soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Environmental Soil Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchuk, A. Effect of Cations on Structural Stability of Salt-Affected Soils; The University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 2013; Available online: https://hekyll.services.adelaide.edu.au/dspace/bitstream/2440/92048/3/02whole.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Hanson, B.R.; Grattan, S.R.; Fulton, A. Agricultural Salinity and Drainage; Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources Publication 3375; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- ANZECC. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality; Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council and Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand: Canberra, Australia, 2000; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, G.; Chhabra, S.; Prasad, R. Role of soil microbes in biogeochemical cycle for enhancing soil fertility. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, N.; Marschner, P.; Cao, W.; Zuo, C.; Qin, W. Influence of salinity and water content on soil microorganisms. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Silva, C.M.M.; Francisconi, E. Effect of salinity on soil microorganisms. In Soil Health and Land Use Management; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/25277 (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Shi, S.; Tian, L.; Nasir, F.; Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Luo, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Tian, C. Response of microbial communities and enzyme activities to amendments in saline-alkaline soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, H.; Rao, D.L.N. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization from added organic matter in saline and alkali soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, G.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, K.S.; Joergensen, R.G. Immobilization and mineralization of nitrogen in a saline and alkaline soil during microbial use of sugarcane filter cake amended with glucose. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 45, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmajdoub, B.; Marschner, P. Salinity reduces the ability of soil microbes to utilise cellulose. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, R.A. Cellulolytic activity of some cellulose-decomposing fungi in salinized soils. Acta Mycol. 2014, 29, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Miao, F.; Li, Z.; Tang, W.; Sun, J. Assessing the effect of soil salinization on soil microbial respiration and diversities under incubation conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, M.S.; Marschner, P. Impact of salinity on respiration and organic matter dynamics in soils is more closely related to osmotic potential than to electrical conductivity. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, M.S.; Marschner, P.; Chittleborough, D.J.; Cox, J.W.; Sanderman, J. Salinity and sodicity affect soil respiration and dissolved organic matter dynamics differentially in soils varying in texture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmajdoub, B. Microbial Activity and Biomass in Saline Soils as Affected by Carbon Availability; The University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 2014; Available online: https://digital.library.adelaide.edu.au/dspace/bitstream/2440/86830/8/02whole.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Kaur, B.; Gupta, S.R.; Singh, G. Bioamelioration of a sodic soil by silvopastoral systems in northwestern India. Agrofor. Syst. 2002, 54, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.N.L.; Greene, R.S.B.; Dalal, R.C.; Murphy, B.W. Soil carbon dynamics in saline and sodic soils: A review. Soil Use Manag. 2010, 26, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Maheshwari, A.; Bengtson, P.; Rousk, J. Comparative toxicities of salts on microbial processes in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbaghan, M.E.; Lakzian, A.; Astaraei, A.R.; Fotovat, A.; Besharati, H. Salt and alkali stresses reduction in wheat by plant growth promoting haloalkaliphilic bacteria. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 1058–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Arezoo, T.; Mehran, H.; Khorsandi, F. Effect of salinity on free living—Diazotroph and total bacterial populations of two saline soils. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangming, L.; Xuechen, Z.; Xiuping, W.; Hongbo, S.; Jingsong, Y.; Xiangping, W. Soil enzymes as indicators of saline soil fertility under various soil amendments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 237, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Craats, D.; der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Sui, C.; Asten, P.J.A.; Cornelissen, P.; Leijnse, A. Soil sodicity originating from marginal groundwater. Vadose Zone J. 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Pedroli, B.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Shu, L. Soil salinity development in the yellow river delta in relation to groundwater dynamics. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mao, X.; Yang, X.; Tong, L.; Tang, M. Variation of groundwater salinity and its influence on crops in irrigation area of Northwest China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil processes affecting crop production in salt-affected soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijne, J.W.; Kuper, M. Salinity and sodicity in Pakistan’s Punjab: A threat to sustainability of irrigated agriculture? Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1995, 11, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.S.; McCornick, P.G.; Qadir, M.; Aslam, Z. Managing salinity and waterlogging in the Indus basin of Pakistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abliz, A.; Tiyip, T.; Ghulam, A.; Halik, Ü.; Ding, J.; Sawut, M.; Zhang, F.; Nurmemet, I.; Abliz, A. Effects of shallow groundwater table and salinity on soil salt dynamics in the Keriya Oasis, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishan, G. Groundwater Salinity. Curr. World Environ. 2019, 14, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, D. Managing Saline Soils in North. Dakota; North Dakota State University: Fargo, ND, USA, 2007; Available online: https://www.ndsu.edu/soilhealth/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Managing-saline-sodic-soils_2003.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Rubin, H. Pollution | Groundwater. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Mukate, S.V.; Panaskar, D.B.; Wagh, V.M.; Baker, S.J. Understanding the influence of industrial and agricultural land uses on groundwater quality in semiarid region of Solapur, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 3207–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C. Salinity and Sodicity Management; Montana State University-Bozeman: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2005; pp. 4481–4482. Available online: https://landresources.montana.edu/swm/documents/Final_Proof_SW2.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Mugwe, J.; Ngetich, F.; Otieno, E.O. Integrated soil fertility management in sub-Saharan Africa: Evolving paradigms toward integration. In Zero Hunger. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.; Pankova, E.I.; Balyuk, S.A.; Krasilnikov, P.V.; Khasankhanova, G.M. Handbook for Saline Soil Management; FAO of United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Kandiah, A.; Mashali, A.M. Management principles and practices for safe use of saline water. In The Use of Saline Waters for Crop Production; FAO of United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Effectiveness of organic wastes as fertilizers and amendments in salt-affected soils. Agriculture 2015, 5, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Kheir, A.M.S.; Ali, M.G.M.; Ali, O.A.M.; Abdelaal, A.I.N.; Lin, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.; He, Z. The integrated effect of salinity, organic amendments, phosphorus fertilizers, and deficit irrigation on soil properties, phosphorus fractionation and wheat productivity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Goyal, S.S.; Passioura, J. Salinity Stress and Its Mitigation; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P.; Chittleborough, D.; Helyar, K. Root-zone constraints and plant-based solutions for dryland salinity. Plant Soil 2003, 257, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Zeng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, J. Five-year experimental study on effectiveness and sustainability of a dry drainage system for controlling soil salinity. Water 2019, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin, Ö.; Akalp, E. Efficient use of water and fertilizers in irrigated agriculture: Drip irrigation and fertigation. Acta Hortic. Regiotect. 2019, 22, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Ashraf, M.; Al-Qurainy, F.; Harris, P.J.C. Salt tolerance in selected vegetable crops. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2012, 31, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, A.; Inal, A.; Bagci, E.G.; Coban, S.; Sahin, O. Silicon increases boron tolerance and reduces oxidative damage of wheat grown in soil with excess boron. Biol. Plant 2007, 51, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouni, Y.; Ghnaya, T.; Montemurro, F.; Abdelly, C.; Lakhdar, A. The role of humic substances in mitigating the harmful effects of soil salinity and improve plant productivity. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2014, 8, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letey, J.; Hoffman, G.J.; Hopmans, J.W.; Grattan, S.R.; Suarez, D.; Corwin, D.L.; Oster, J.D.; Wu, L.; Amrhein, C. Evaluation of soil salinity leaching requirement guidelines. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Rhoades, J.D.; Šimůnek, J. Leaching requirement for soil salinity control: Steady-state versus transient models. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D. Leaching requirement for exchangeable-sodium control. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1968, 32, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Oster, J.D.; Ingvalson, R.D.; Tucker, J.M.; Clark, M. Minimizing the salt burdens of irrigation drainage waters. J. Environ. Qual. 1974, 3, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D. Reclamation and management of salt affected soil after drainage. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Western Provincial Conference Rationalization of Water and Soil Research and Management, Lightbridge, Canada, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Van Schilfgaarde, J.; Rhoades, J.D. Water Quality in Relation to Irrigated Agriculture; U.S. Salinity Laboratory (USDA): Riverside, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bauder, T.A.; Davis, J.G.; Waskom, R.M. Managing Saline Soils; Colorado State University Extension Publications: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Alcívar, M.; Zurita-Silva, A.; Sandoval, M.; Muñoz, C.; Schoebitz, M. Reclamation of saline-sodic soils with combined amendments: Impact on quinoa performance and biological soil quality. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, M.A.; Hussain, S.; Aziz, T.; Ashraf, M. Sustainable agriculture through integrated soil fertility management on degraded lands. In Developments in Soil Salinity Assessment and Reclamation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 759–768. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.K.; Soni, R. Integrated soil fertility management. In Soil Fertility Management for Sustainable Development; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.A.; Al-Shankiti, A. Sustainable food production in marginal lands—Case of GDLA member countries. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2013, 1, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fipps, G. Irrigation Water Quality Standards and Salinity Management Strategies; The Texas A&M University System Extension Publications: College Station, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dehni, A.; Lounis, M. Remote sensing techniques for salt affected soil mapping: Application to the Oran region of Algeria. Procedia Eng. 2012, 33, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Setia, R.; Verma, V.K.; Arora, S.; Kumar, P.; Pateriya, B. Satellite remote sensing of salt-affected soils: Potential and limitations. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, E.; Suryabhagavan, K.V.; Argaw, M. Soil salinity modeling and mapping using remote sensing and GIS: The case of Wonji sugar cane irrigation farm, Ethiopia. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AQUA4D An Innovative Sustainable Solution to Soil Salinity. Available online: https://aqua4d.com/an-innovative-sustainable-solution-to-soil-salinity/ (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Cahn, M.; Bali, K. Drought Tip: Managing Salts by Leaching; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akramkhanov, A.; Ul Hassan, M.; Hornidge, A.-K. Redrawing soil salinity innovation-focused stakeholder interaction for sustainable land management in Khorezm Province, Uzbekistan. Water 2018, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, R. New Life for Saline Soil. Available online: https://www.agriculture.com/crops/cover-crops/new-life-for-saline-soil (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Christen, E.W.; Ayars, J.E. Subsurface Drainage System Design and Management in Irrigated Agriculture: Best Management Practices for Reducing Drainage Volume and Salt Load; CSIRO Land and Water: Griffith, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Christen, E.; Ayars, J.; Hornbuckle, J. Subsurface drainage design and management in irrigated areas of Australia. Irrig. Sci. 2001, 21, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Kashkouli, H.A.; Pazira, E. Sensitive variables controlling salinity and water table in a bio-drainage system. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.S. Bio-drainage: Potential and limitations. In Proceedings of the 9th International Drainage Workshop, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 10–13 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- George, S.J.; Harper, R.J.; Hobbs, R.J.; Tibbett, M. A sustainable agricultural landscape for Australia: A review of interlacing carbon sequestration, biodiversity and salinity management in agroforestry systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 163, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Blumwald, E. Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: Challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fita, A.; Rodríguez-Burruezo, A.; Boscaiu, M.; Prohens, J.; Vicente, O. Breeding and domesticating crops adapted to drought and salinity: A new paradigm for increasing food production. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, M.; Wani, S.P. Rhizobacterial-plant interactions: Strategies ensuring plant growth promotion under drought and salinity stress. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah; Dahlawi, S.; Naeem, A.; Rengel, Z.; Naidu, R. Biochar application for the remediation of salt-affected soils: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
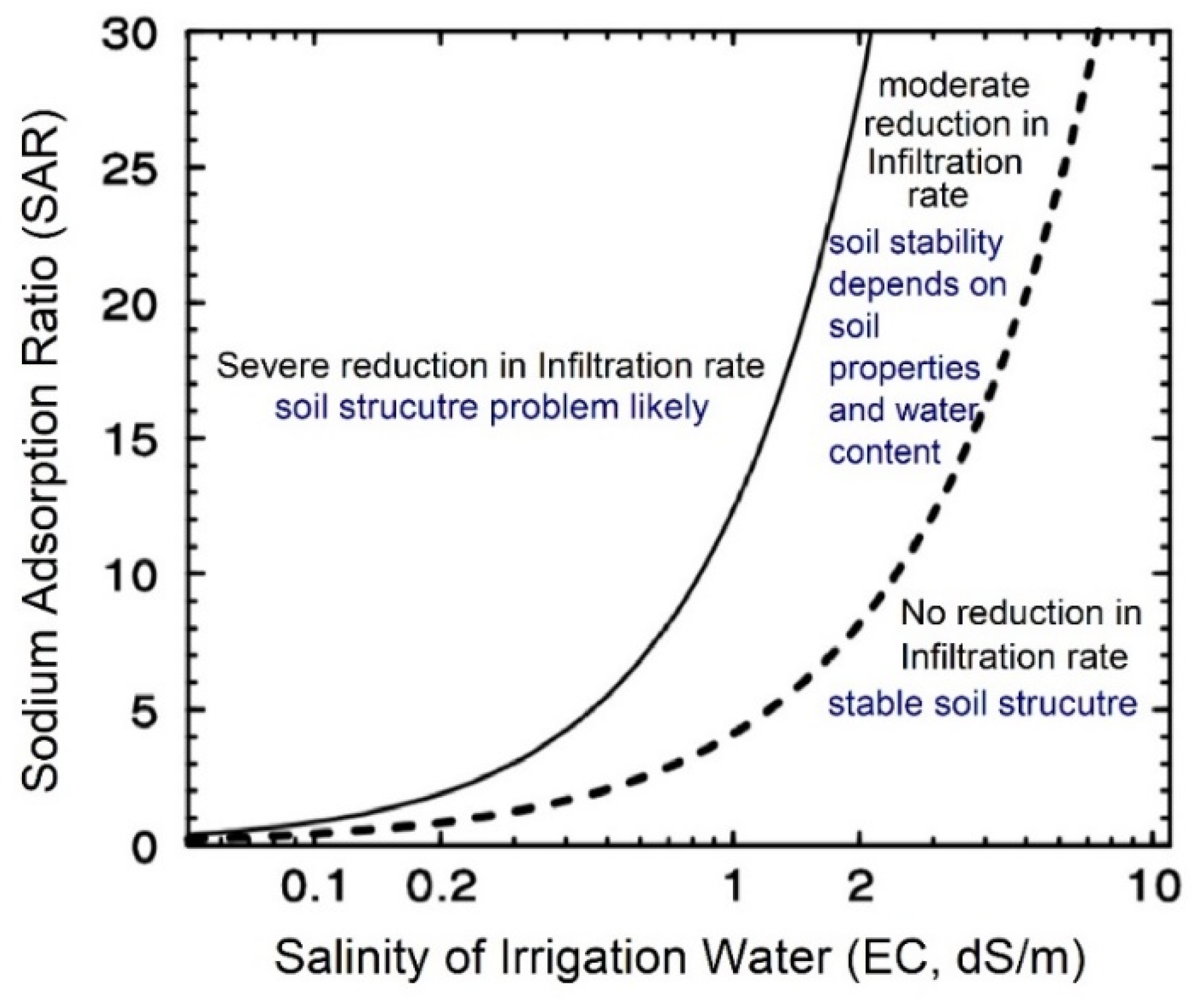
| Soil Classification | Electrical Conductivity (EC, dS/m) | pH | Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) (mmolc L−1)0.5 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal soil | EC < 4 | <8.5 | <13 | No visible salt accumulation on soil surface, uniform crop growth. |
| Saline soil | ||||
| Slightly saline | 4 < EC < 8 | <8.5 | <13 | Visible salts on soil surface, patchy and uneven crop growth. |
| Moderately saline | 8 < EC < 15 | Fairly visible salt layer on soil surface, restricted and very patchy crop growth. | ||
| Strongly saline | EC > 15 | Fluffy soil surface, fairly visible salt accumulation on surface, slow or no germination, patchy and highly restricted plant growth, etc. | ||
| Sodic soil | EC < 4 | 8.5–10 | >13 | Shallow plant root penetration, puddle formation with turbid water on soil surface, variability in crop growth rate, etc. |
| Saline-sodic soil | EC > 4 | <8.5 | >13 | Combined characteristics of saline and sodic soils. |
| Degraded sodic soils | 0.5 < EC < 2 | 5.5–8.5 | >14 | Contain excess exchangeable sodium and appreciable quantities of exchangeable hydrogen. ESP < 15. |
| Category | Types/options | Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Agronomic measures | Hydro-technical | |
| (a) Irrigation System | Sprinkling, drip irrigation, surface and sub-surface irrigation | |
| (b) Drainage Systems | Horizontal and vertical drainage | |
| Agro-technical | ||
| (a) Surface regulation | Levelling, Ridging, Furrowing | |
| (b) Subsurface regulation | Slitting, Moiling, Deep tilling | |
| Bio-chemical- Nutrient and manure application, soil acidification, etc. | Overall application, scattering, local, green manure, organic carbon sequestration | |
| Structural- amend the surface structure mainly in plough layer | Sand and clay application, Ditching, Deep ploughing | |
| Engineering | Increase storage | Construct supplemental water storage structures such as dams and reservoirs (e.g., ponds and tanks) |
| Improve drainage infrastructure | Develop artificial drainage structures (both surface and sub-surface), bio-drainage (e.g., planting eucalyptus) | |
| Reduce losses | Improve distribution systems (e.g., reduce canal seepage through the lining, opt for drip or sprinkler irrigation, etc.), reuse the drained water, find alternate discharge methods for the drainage effluent, employ rain water harvesting | |
| Policy | Regulation measures | Introduce soil health monitoring, water and power pricing, transferable water entitlements, set limits to groundwater pumping and recharge |
| Incentives | Increase the cost of hazardous fertilizers, provide funds to encourage soil reclamation, develop public water supply infrastructure (e.g., canal network) in hotspot regions | |
| Management | Optimal operation | Improve the operation of existing irrigation and drainage systems, manage irrigation logs, adopt innovative technologies, regularly monitor soil and groundwater |
| Technology application | Use sensor-based devices (e.g., soil moisture sensors), weather predictions, follow irrigation planning and forecasting | |
| Maintenance | Desilt the irrigation channels and drainage network |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohanavelu, A.; Naganna, S.R.; Al-Ansari, N. Irrigation Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts and Mitigation Strategies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11100983
Mohanavelu A, Naganna SR, Al-Ansari N. Irrigation Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts and Mitigation Strategies. Agriculture. 2021; 11(10):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11100983
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohanavelu, Aadhityaa, Sujay Raghavendra Naganna, and Nadhir Al-Ansari. 2021. "Irrigation Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts and Mitigation Strategies" Agriculture 11, no. 10: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11100983
APA StyleMohanavelu, A., Naganna, S. R., & Al-Ansari, N. (2021). Irrigation Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts and Mitigation Strategies. Agriculture, 11(10), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11100983