Performance Evaluation of Soil Moisture Sensors in Coarse- and Fine-Textured Michigan Agricultural Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Experiment
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Field Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
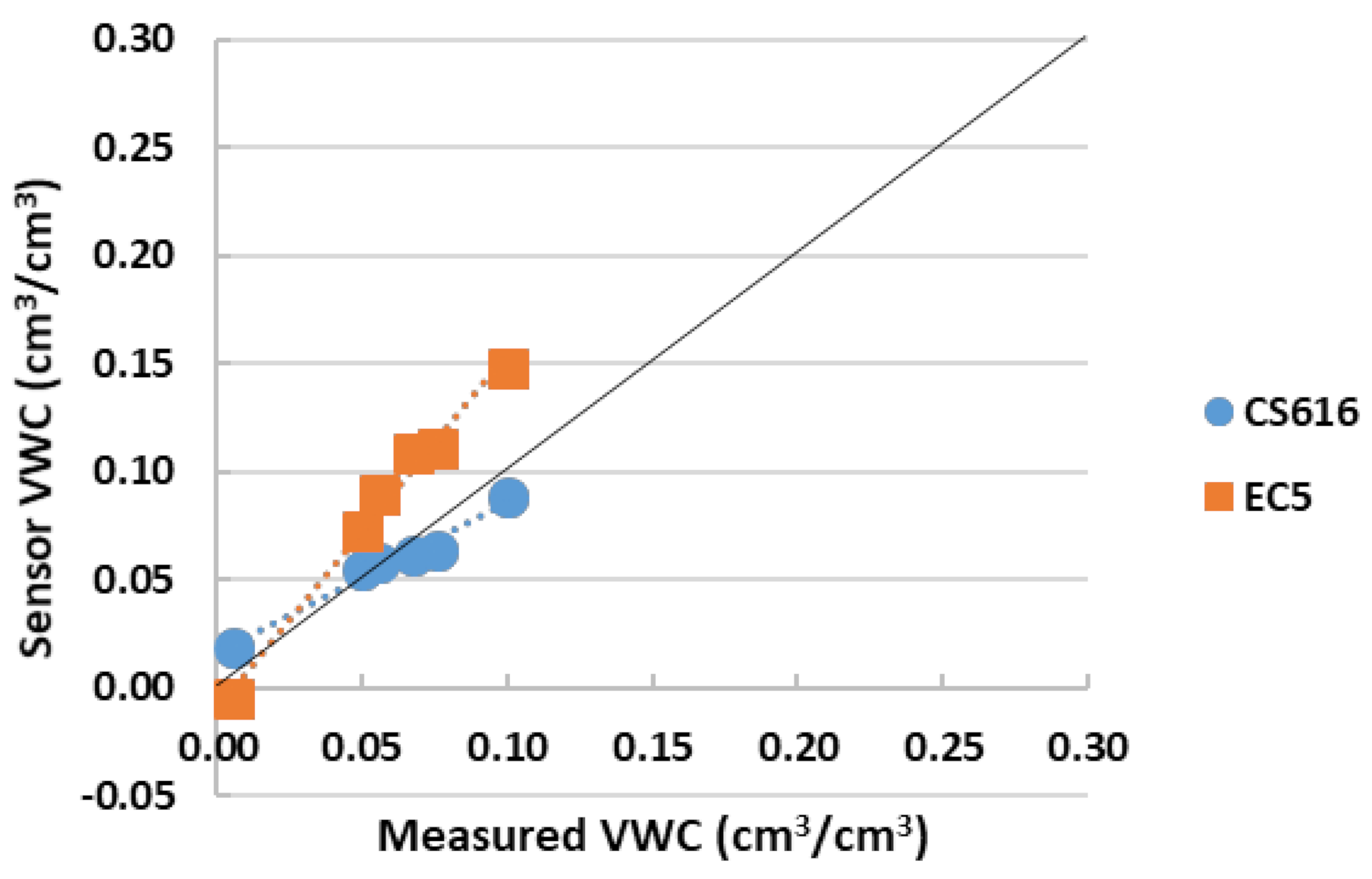
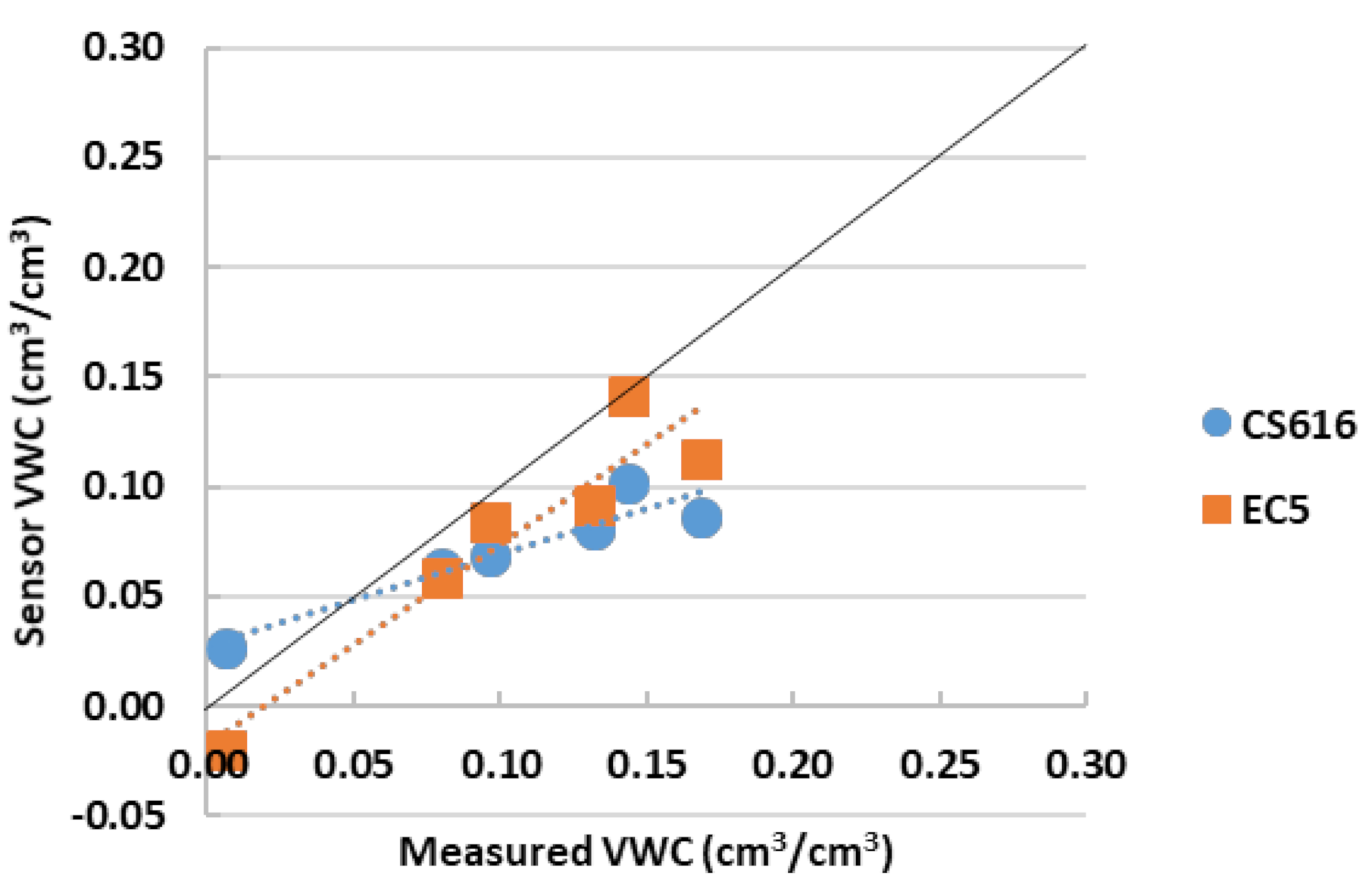
3.1. Performance Evaluation of Factory-Based Calibrated CS616 and EC5
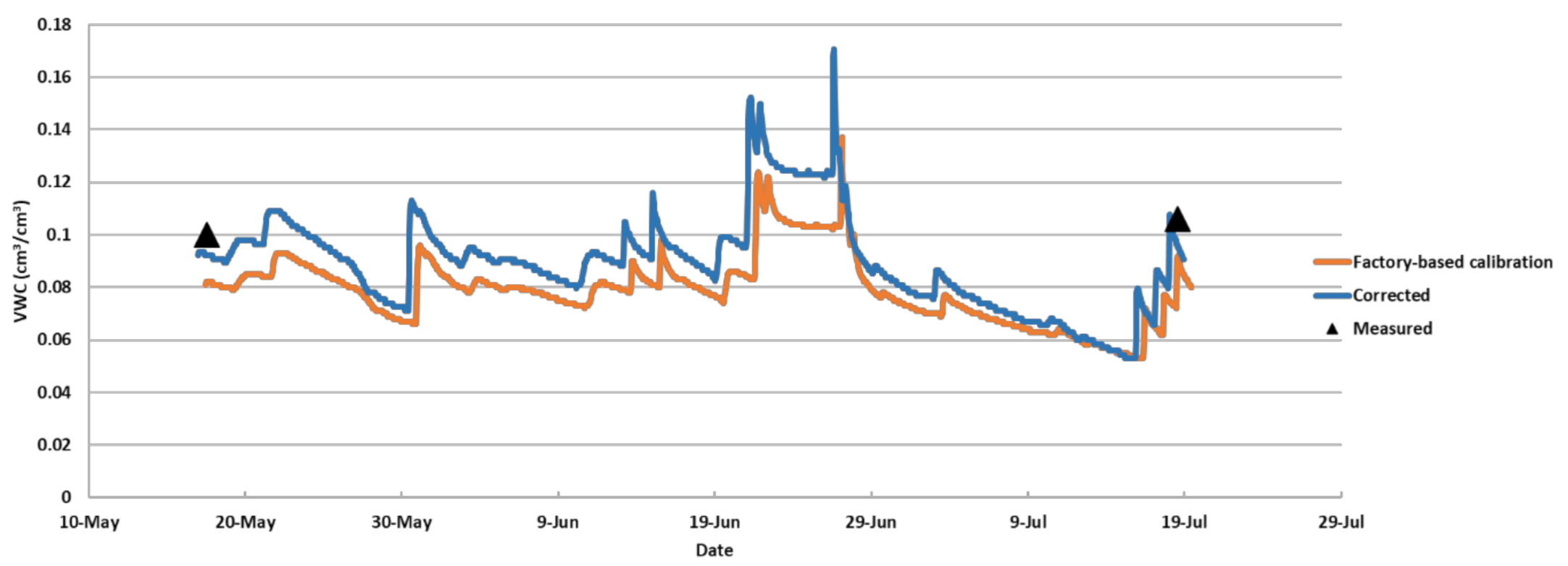
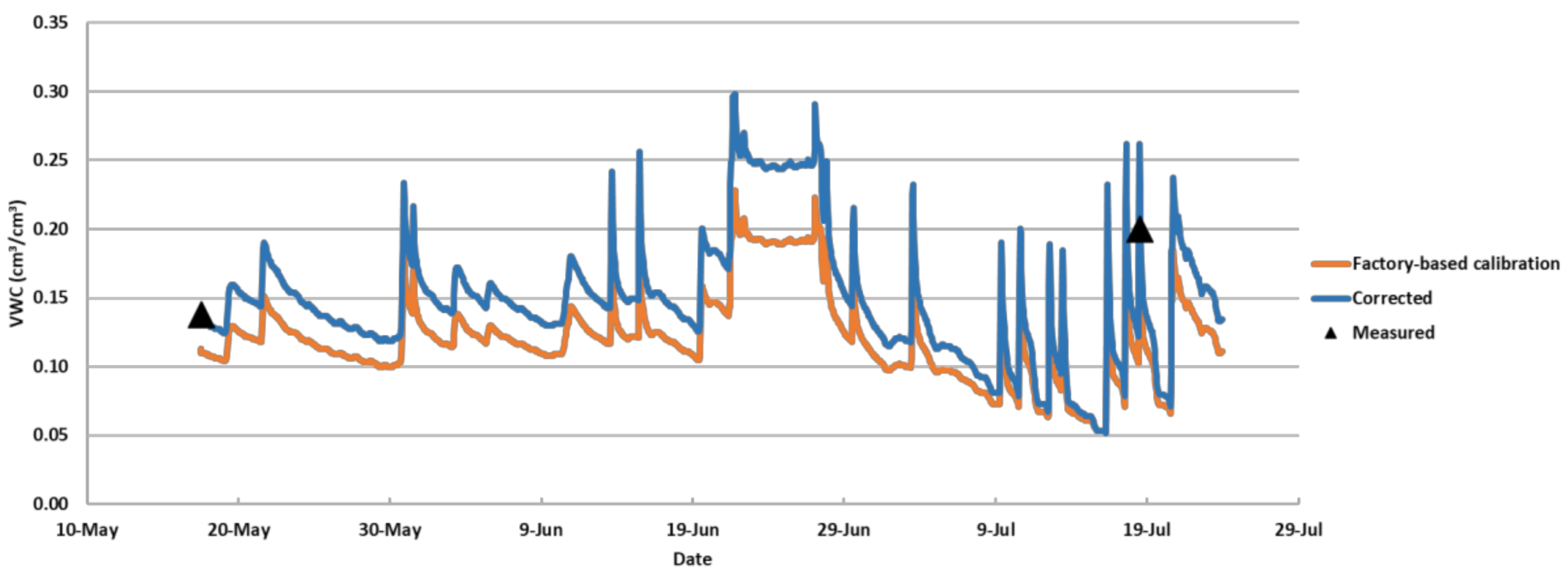
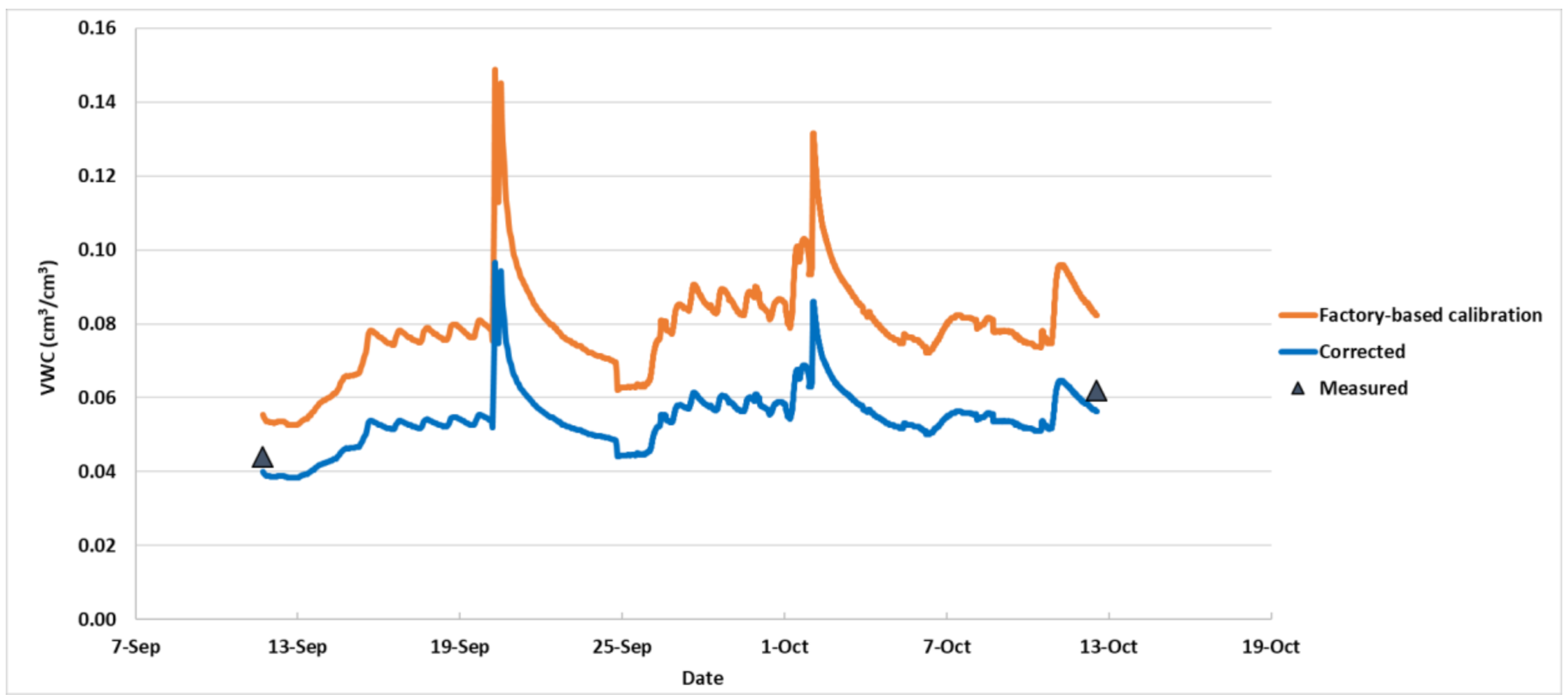
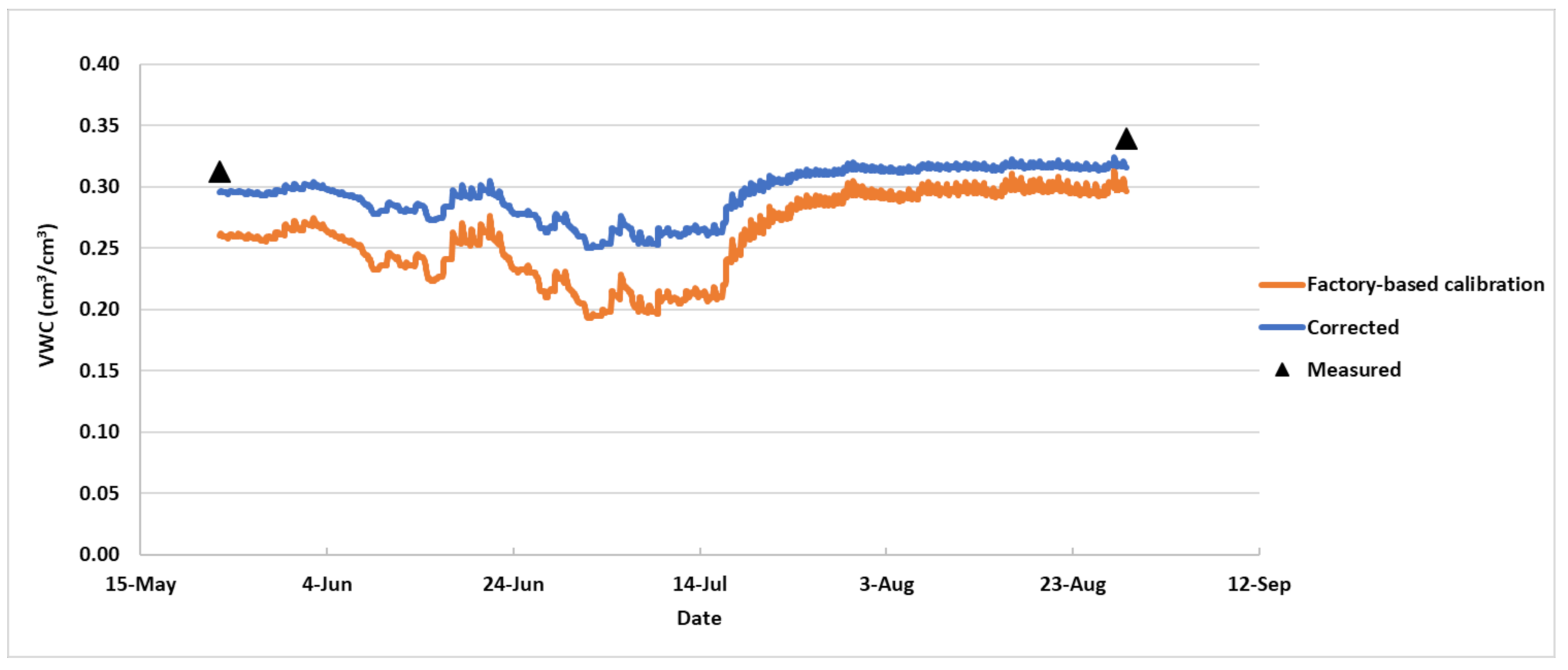
3.2. Validation of Correction Equations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Engman, E.T. Applications of microwave remote sensing of soil moisture for water resources and agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Stuntebeck, E.P. Wireless underground sensor networks: Research challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2006, 4, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Lunadei, L.; Barreiro, P.; Robla, J.I. A Review of Wireless Sensor Technologies and Applications in Agriculture and Food Industry: State of the Art and Current Trends. Sensors 2009, 9, 4728–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, F.; Pallottino, F.; Costa, C.; Rimatori, V.; Giorgi, S.; Papetti, P.; Menesatti, P. Development of a Rapid Soil Water Content Detection Technique Using Active Infrared Thermal Methods for In-Field Applications. Sensors 2011, 11, 10114–10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Jones, S.B.; Wraith, J.M.; Or, D.; Friedman, S.P. A Review of Advances in Dielectric and Electrical Conductivity Measurement in Soils Using Time Domain Reflectometry. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 444–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazueta, F.; Xin, J. Soil moisture sensors. Soil Sci. 1994, 73. [Google Scholar]
- S.U., S.L.; Singh, D.; Baghini, M.S. A critical review of soil moisture measurement. Measurement 2014, 54, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, G. Water Content; American Society of Agronomy-Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas-Lailhacar, B.; Dukes, M.D. Precision of soil moisture sensor irrigation controllers under field conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, T.; Limsuwat, A.; Smits, K.M.; Illangasekare, T.H. Empirical two-point α -mixing model for calibrating the ECH2 O EC-5 soil moisture sensor in sands. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzli, K.; Manana, N.; Oad, R. Comparison of Laboratory and Field Calibration of a Soil-Moisture Capacitance Probe for Various Soils. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanato, L.; Baroni, G.; Cohen, Y.; Fontana, C.L.; Gatto, S.; Lunardon, M.; Marinello, F.; Moretto, S.; Morselli, L. A Novel Cosmic-Ray Neutron Sensor for Soil Moisture Estimation over Large Areas. Agriculture 2019, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, H.; Lehner, I.; Seneviratne, S.I. Comparison of four soil moisture sensor types under field conditions in Switzerland. J. Hydrol. 2012, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varble, J.; Chávez, J.L. Performance evaluation and calibration of soil water content and potential sensors for agricultural soils in eastern Colorado. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 101, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.J.A.; Bonfim-Silva, E.M.; Pacheco, A.B.; Duarte, T.F.; Sousa, H.H.D.F.; José, J.V. Evaluation of Various Soil Moisture Sensors in Four Different Soil Types. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2018, 34, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hignett, C.; Evett, S. Direct and surrogate measures of soil water content. In Field Estimation of Soil Water Content; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell Scientific CS616. Available online: https://www.campbellsci.com/cs616-reflectometer (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- METER Group ECH2O EC-5. Available online: https://www.metergroup.com/environment/products/ec-5-soil-moisture-sensor/ (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- Kargas, G.; Soulis, K.X. Performance Analysis and Calibration of a New Low-Cost Capacitance Soil Moisture Sensor. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Marek, G.W.; Marek, T.H.; Heflin, K.R.; Porter, D.O.; Moorhead, J.E.; Brauer, D. Soil Water Sensor Performance and Corrections with Multiple Installation Orientations and Depths under Three Agricultural Irrigation Treatments. Sensors 2019, 19, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Willgoose, G.R.; Kalma, J.D. In situ measurement of soil moisture: a comparison of techniques. J. Hydrol. 2004, 293, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.R. Field Estimation of Soil Water Content: A Practical Guide to Methods, Instrumentation and Sensor Technology. Vadose Zone J. 2009, 8, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics: Fundamentals, Applications, and Environmental Considerations. In Environmental Soil Physics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.; Dean, T.; Hodnett, M. Soil moisture measurement by an improved capacitance technique, part II. Field techniques, evaluation and calibration. J. Hydrol. 1987, 93, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, A.; Kreutzer, K.; Matthies, D.; Hess, U.; Ansorge, B.; Weis, W. Changes in soil structure caused by the installation of time domain reflectometry probes and their influence on the measurement of soil moisture. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Miller, S.; Kelley, L. Improving Irrigation Water Use Efficiency: Using Soil Moisture Sensors. Available online: https://www.egr.msu.edu/bae/water/irrigation/sites/default/files/content/E3445_ImprovingIrrigationWaterUse.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- Nagahage, E.A.A.D.; Nagahage, I.; Fujino, T. Calibration and Validation of a Low-Cost Capacitive Moisture Sensor to Integrate the Automated Soil Moisture Monitoring System. Agriculture 2019, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Container | Class | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sand | 1.71 | 89.5 | 4 | 6.5 |
| 2 | Loamy Sand | 1.64 | 83.2 | 7.2 | 9.6 |
| 3 | Sandy Clay Loam | 1.42 | 63.4 | 12.4 | 24.2 |
| Sensor | Class | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS616 | Sand | 91.9 | 3.7 | 4.4 |
| Loamy Sand | 87.9 | 5.8 | 6.3 | |
| Sandy Clay Loam | 54.8 | 23.6 | 21.6 | |
| EC5 | Sand | 92.3 | 1.3 | 6.4 |
| Loamy Sand | 86.8 | 4.8 | 8.4 | |
| Sandy Clay Loam | 53.3 | 26.6 | 20.1 |
| Soil Type | Sensor | RMSE | IA | MBE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | CS616 | 0.010 | 0.96 | −0.01 |
| EC5 | 0.035 | 0.82 | 0.03 | |
| Loamy Sand | CS616 | 0.046 | 0.74 | −0.03 |
| EC5 | 0.032 | 0.91 | −0.03 | |
| Sandy Clay Loam | CS616 | 0.040 | 0.88 | −0.02 |
| EC5 | 0.063 | 0.62 | −0.05 |
| Soil Type | Sensor | Equation Type | Equation | RMSE | IA | MBE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | CS616 | Linear | 0.005 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.97 | |
| Exponential | 0.031 | 0.84 | 0.004 | 0.88 | |||
| Logarithmic | 0.008 | 0.97 | 0.001 | 0.92 | |||
| Quadratic | 0.005 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.97 | |||
| EC5 | Linear | 0.003 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.99 | ||
| Exponential | 0.020 | 0.92 | 0.002 | 0.93 | |||
| Logarithmic | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| Quadratic | 0.002 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.99 | |||
| Loamy Sand | CS616 | Linear | 0.016 | 0.97 | −0.001 | 0.89 | |
| Exponential | 0.061 | 0.78 | 0.006 | 0.85 | |||
| Logarithmic | 0.017 | 0.56 | 0.001 | 0.88 | |||
| Quadratic | 0.016 | 0.97 | −0.001 | 0.89 | |||
| EC5 | Linear | 0.059 | 0.76 | −0.057 | 0.89 | ||
| Exponential | 0.055 | 0.81 | 0.005 | 0.85 | |||
| Logarithmic | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| Quadratic | 0.017 | 0.97 | 0.001 | 0.90 | |||
| Sandy Clay Loam | CS616 | Linear | 0.011 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.97 | |
| Exponential | 0.017 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.99 | |||
| Logarithmic | 0.015 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.94 | |||
| Quadratic | 0.016 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.99 | |||
| EC5 | Linear | 0.037 | 0.88 | −0.001 | 0.65 | ||
| Exponential | 0.043 | 0.87 | −0.011 | 0.49 | |||
| Logarithmic | 0.024 | 0.89 | −0.011 | 0.67 | |||
| Quadratic | 0.034 | 0.89 | 0.020 | 0.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Miller, S.; Kelley, L. Performance Evaluation of Soil Moisture Sensors in Coarse- and Fine-Textured Michigan Agricultural Soils. Agriculture 2020, 10, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120598
Dong Y, Miller S, Kelley L. Performance Evaluation of Soil Moisture Sensors in Coarse- and Fine-Textured Michigan Agricultural Soils. Agriculture. 2020; 10(12):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120598
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Younsuk, Steve Miller, and Lyndon Kelley. 2020. "Performance Evaluation of Soil Moisture Sensors in Coarse- and Fine-Textured Michigan Agricultural Soils" Agriculture 10, no. 12: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120598
APA StyleDong, Y., Miller, S., & Kelley, L. (2020). Performance Evaluation of Soil Moisture Sensors in Coarse- and Fine-Textured Michigan Agricultural Soils. Agriculture, 10(12), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120598






