Early Vigor of a Pyramiding Line Containing Two Quantitative Trait Loci, Phosphorus Uptake 1 (Pup1) and Anaerobic Germination 1 (AG1) in Rice (O. Sativa L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
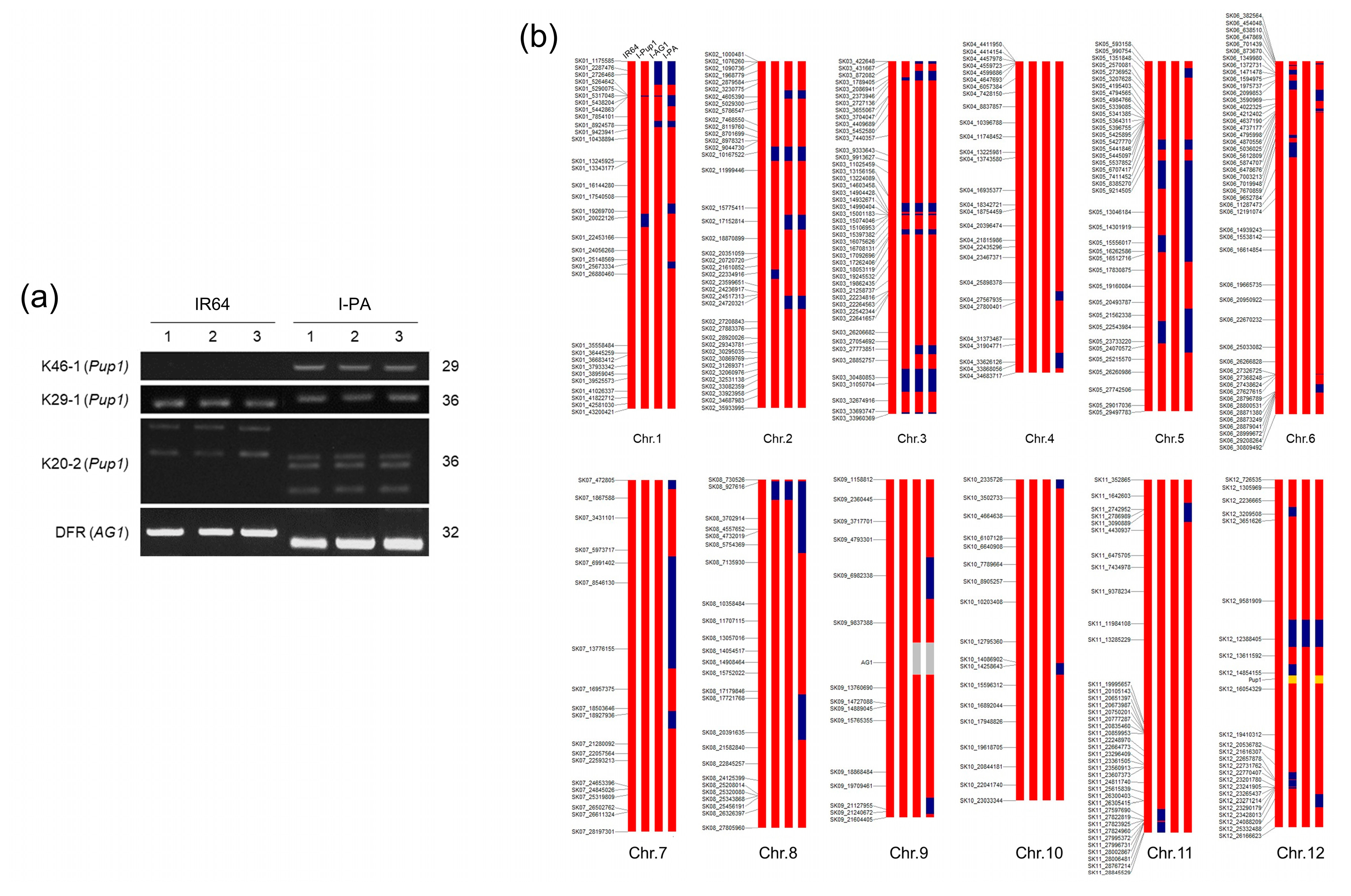
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Genotyping
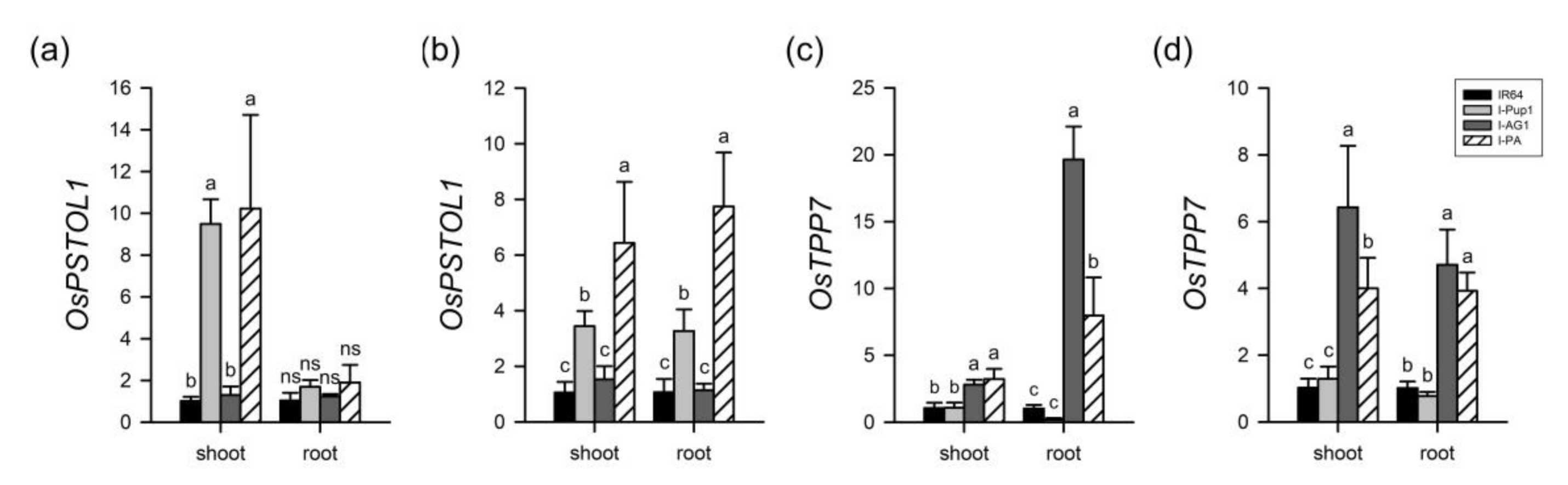
2.3. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis of Pup1 and AG1
2.4. Phenotyping under Different P Concentrations of Soil and Hydroponic Conditions
2.5. Phenotyping Germinability under Anaerobic Conditions
2.6. Plant Growth Conditions in Paddy Field
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Structure of I-PA
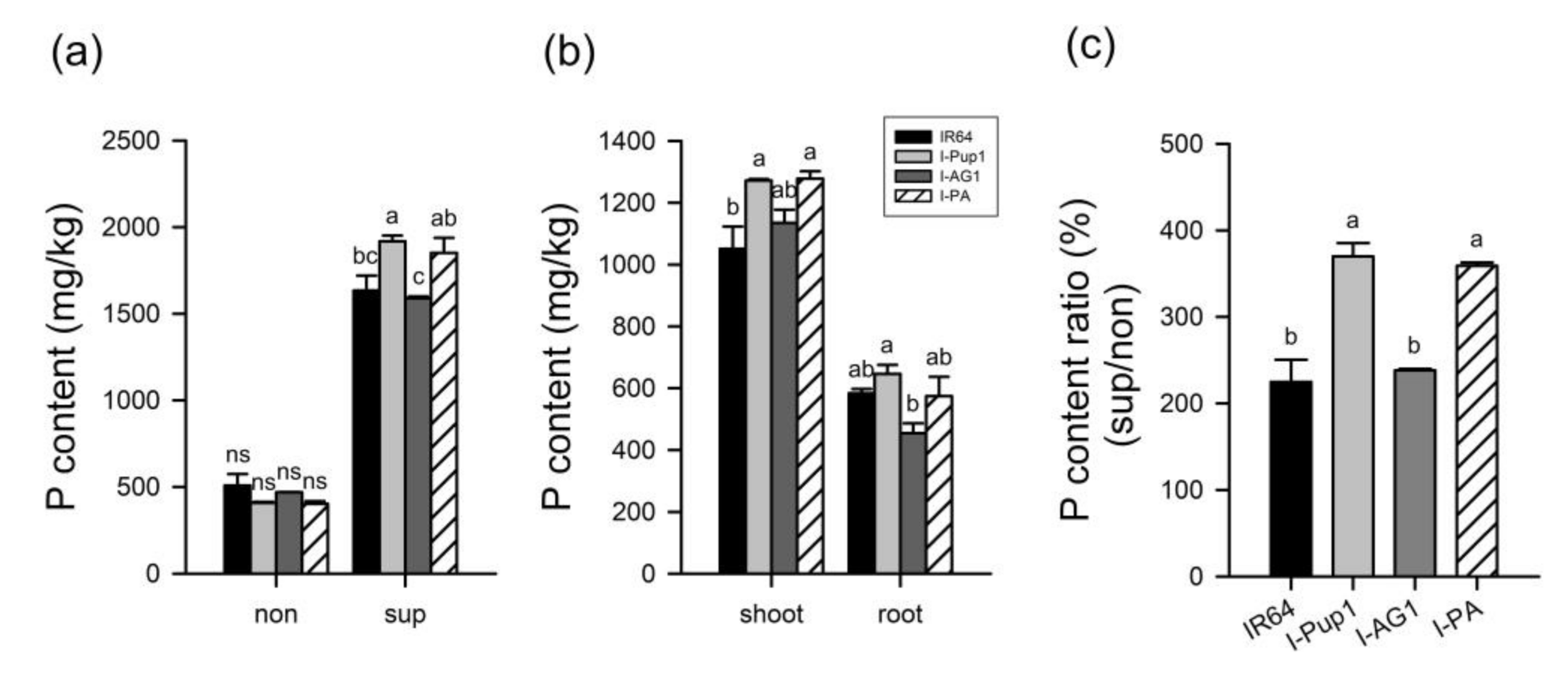
3.2. Independent Pup1 Function of I-PA under Different P Supply Conditions
3.3. Independent AG1 Function of I-PA under Anaerobic Conditions at the Germination Stage
3.4. Improved Tillering Ability of I-PA during the Early Growth Stage in the Paddy Field
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farooq, M.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Rehman, H.; Aziz, T.; Lee, D.J.; Wahid, A. Rice direct seeding: Experiences, challenges and opportunities. Soil Till. Res. 2011, 111, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, B.; Ismail, A.M. Tolerance of anaerobic conditions caused by flooding during germination and early growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, T.; Pelayo, M.A.F.; Trijatmiko, K.R.; Gabunada, L.F.M.; Alam, R.; Jimenez, R.; Mendioro, M.S.; Slamet-Loedin, I.H.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Bailey-Serres, J.; et al. A trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase enhances anaerobic germination tolerance in rice. Nat Plants 2015, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angaji, S.A.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Mackill, D.J.; Ismail, A.M. QTLs associated with tolerance of flooding during germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 2010, 172, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissuwa, M. Combining a modelling with a genetic approach in establishing associations between genetic and physiological effects in relation to phosphorus uptake. Plant Soil 2005, 269, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissuwa, M.; Wegner, J.; Ae, N.; Yano, M. Substitution mapping of Pup1: A major QTL increasing phosphorus uptake of rice from a phosphorus-deficient soil. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamuyao, R.; Chin, J.H.; Pariasca-Tanaka, J.; Pesaresi, P.; Catausan, S.; Dalid, C.; Slamet-Loedin, I.; Tecson-Mendoza, E.M.; Wissuwa, M.; Heuer, S. The protein kinase Pstol1 from traditional rice confers tolerance of phosphorus deficiency. Nature 2012, 488, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.H.; Lu, X.; Haefele, S.M.; Gamuyao, R.; Ismail, A.; Wissuwa, M.; Heuer, S. Development and application of gene-based markers for the major rice QTL Phosphorus uptake 1. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.H.; Gamuyao, R.; Dalid, C.; Bustamam, M.; Prasetiyono, J.; Moeljopawiro, S.; Wissuwa, M.; Heuer, S. Developing rice with high yield under phosphorus deficiency: Pup1 sequence to application. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chithrameenal, K.; Alagarasan, G.; Raveendran, M.; Robin, S.; Meena, S.; Ramanathan, A.; Ramalingam, J. Genetic enhancement of phosphorus starvation tolerance through marker assisted introgression of OsPSTOL1 gene in rice genotypes harbouring bacterial blight and blast resistance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, A.M.U.; Ignacio, J.C.I.; Casal, C.; Gonzaga, Z.J.; Mendioro, M.S.; Septiningsih, E.M. Development of improved Ciherang-Sub1 having tolerance to anaerobic germination conditions. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mondal, S.; Khan, M.I.R.; Entila, F.; Dixit, S.; Sta Cruz, P.C.; Panna Ali, M.; Pittendrigh, B.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Ismail, A.M. Responses of AG1 and AG2 QTL introgression lines and seed pre-treatment on growth and physiological processes during anaerobic germination of rice under flooding. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid Isolation of High Molecular-Weight Plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, K.-S.; Baek, J.; Cho, Y.-I.; Jeong, Y.-M.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Oh, J.; Won, Y.J.; Kang, D.-Y.; Oh, H.; Kim, S.L. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery and kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) marker development with Korean japonica rice varieties. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Forno, D.A.; Cock, J.H. Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice. In Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice; International Rice Research Institute: Laguna, Philippines, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Alia, N.; Durranib, S.; Abbasc, M.; Ullaha, I.; Ishfaqa, M.; Akbara, N.; Rehmana, A.; Waheedc, A. Different approaches in direct seeded rice system to avert weed infestation. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2018, 9, 1538–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, R.A.; Purugganan, M.D.; Zhang, Q.F. The rice genome revolution: From an ancient grain to Green Super Rice. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Rao, G.J.N.; Varier, M.; Prakash, A.; Prasad, D. Improved Tapaswini having four BB resistance genes pyramided with six genes/QTLs, resistance/tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses in rice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissuwa, M.; Kretzschmar, T.; Rose, T.J. From promise to application: Root traits for enhanced nutrient capture in rice breeding. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3605–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Conditions | Germination | Low P and Aerobic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NILs | Anoxia | Hypoxia | ||
| I-Pup1 | poor | poor | good | |
| I-AG1 | good | good | poor | |
| I-PA | good | good | good | |
| IR64 | poor | poor | poor | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, N.-H.; Han, J.-H.; Jang, S.; Song, K.; Koh, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoo, S.; Chin, J.H. Early Vigor of a Pyramiding Line Containing Two Quantitative Trait Loci, Phosphorus Uptake 1 (Pup1) and Anaerobic Germination 1 (AG1) in Rice (O. Sativa L.). Agriculture 2020, 10, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100453
Shin N-H, Han J-H, Jang S, Song K, Koh H-J, Lee J-H, Yoo S, Chin JH. Early Vigor of a Pyramiding Line Containing Two Quantitative Trait Loci, Phosphorus Uptake 1 (Pup1) and Anaerobic Germination 1 (AG1) in Rice (O. Sativa L.). Agriculture. 2020; 10(10):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100453
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Na-Hyun, Jae-Hyuk Han, Su Jang, Kihwan Song, Hee-Jong Koh, Jong-Hee Lee, Soocheul Yoo, and Joong Hyoun Chin. 2020. "Early Vigor of a Pyramiding Line Containing Two Quantitative Trait Loci, Phosphorus Uptake 1 (Pup1) and Anaerobic Germination 1 (AG1) in Rice (O. Sativa L.)" Agriculture 10, no. 10: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100453
APA StyleShin, N.-H., Han, J.-H., Jang, S., Song, K., Koh, H.-J., Lee, J.-H., Yoo, S., & Chin, J. H. (2020). Early Vigor of a Pyramiding Line Containing Two Quantitative Trait Loci, Phosphorus Uptake 1 (Pup1) and Anaerobic Germination 1 (AG1) in Rice (O. Sativa L.). Agriculture, 10(10), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100453






