Autism and COVID-19: A Case Series in a Neurodevelopmental Unit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Setting
2.2. Participants and Ethics
2.3. Collected Variables
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, M.; Chen, Q. Insight into 2019 novel coronavirus-An updated interim review and lessons from SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kang, J.M.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, E.Y. Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.S.; Hung, I.F.; Chan, P.P.; Lung, K.C.; Tso, E.; Liu, R.; Ng, Y.Y.; Chu, M.Y.; Chung, T.W.H.; Tam, A.R.; et al. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Virus Load in Fecal Samples From a Hong Kong Cohort: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.K.; Webster, R.K.; Smith, L.E.; Woodland, L.; Wessely, S.; Greenberg, N.; Rubin, G.J. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: Rapid review of the evidence. Lancet 2020, 395, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.A.; O’Connor, R.C.; Perry, V.H.; Tracey, I.; Wessely, S.; Arseneault, L.; Ballard, C.; Christensen, H.; Silver, R.C.; Everall, P.; et al. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: A call for action for mental health science. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzisi, A. Handle the Autism Spectrum Condition During Coronavirus (COVID-19) Stay At Home period: Ten Tips for Helping Parents and Caregivers of Young Children. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango, C. Lessons Learned From the Coronavirus Health Crisis in Madrid, Spain: How COVID-19 Has Changed Our Lives in the Last 2 Weeks. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 88, e33–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevance, A.; Gourion, D.; Hoertel, N.; Llorca, P.M.; Thomas, P.; Bocher, R.; Moro, M.-R.; Laprévote, V.; Benyamina, A.; Fossati, P.; et al. Ensuring mental health care during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in France: A narrative review. Encephale 2020, 46, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslandes, A.; Berti, V.; Tandjaoui-Lambotte, Y.; Alloui, C.; Carbonnelle, E.; Zahar, J.R.; Brichler, S.; Cohen, Y. SARS-CoV-2 was already spreading in France in late December 2019. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinchat, V.; Cravero, C.; Diaz, L.; Perisse, D.; Xavier, J.; Amiet, C.; Gourfinkel-An, I.; Bodeau, N.; Wachtel, L.; Cohen, D.; et al. Acute behavioral crises in psychiatric inpatients with autism spectrum disorder (ASD): Recognition of concomitant medical or non-ASD psychiatric conditions predicts enhanced improvement. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 38, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, J.; Cohen, D.; Herman, C.; Verloes, A.; Guinchat, V.; Diaz, L.; Cravero, C.; Mandel, A.; Gozes, I. Developmental Phenotype of the Rare Case of DJ Caused by a Unique ADNP Gene De Novo Mutation. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 68, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravero, C.; Guinchat, V.; Xavier, J.; Meunier, C.; Diaz, L.; Mignot, C.; Doummar, D.; Chantot-Bastaraud, S.; Consoli, A.; Cohen, D. Management of Severe Developmental Regression in an Autistic Child with a 1q21.3 Microdeletion and Self-Injurious Blindness. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2017, 2017, 7582780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravero, C.; Guinchat, V.; Barete, S.; Consoli, A. Cornelia de Lange and Ehlers-Danlos: Comorbidity of two rare syndromes. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2015210925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinchat, V. Multidisciplinary Treatment Plan for Challenging Behaviors in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. In Handbook of Neurocognitive Development: Disorders and Disabilities; Gallagher, C.B.A., Bulteau, C., Cohen, D., Michaud, J.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; in press. [Google Scholar]
- COVID19-APHP Group. Assistance Publique-Hopitaux de Paris’ response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1760–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Royal College of Physicians. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) 2|RCP London. Available online: https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/projects/outputs/national-early-warning-score-news-2 (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santé Publique France. Infection au Nouveau Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), COVID-19, France et Monde. 2020. Available online: https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/maladies-et-traumatismes/maladies-et-infections-respiratoires/infection-a-coronavirus/articles/infection-au-nouveau-coronavirus-sars-cov-2-covid-19-france-et-monde (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Stoecklin, S.B.; Rolland, P.; Silue, Y.; Mailles, A.; Campese, C.; Simondon, A.; Mechain, M.; Meurice, L.; Nguyen, M.; Bassi, C. First cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in France: Surveillance, investigations and control measures, January 2020. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000094. [Google Scholar]
- Hyman, S.L.; Levy, S.E.; Myers, S.M. Identification, Evaluation, and Management of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20193447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ASD Symptoms Prior COVID | COVID-19 Acute Symptoms (JX; Y Days) ** | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Age | Social Interaction | Stereotypic, Restricted Behaviors | Challenging Behaviors | Language | Autism * Severity | General Cognition | Psychiatric Comorbidity | Medical Comorbidity | Fever | Oral-Facial | Respiratory | Fatigue | Gastro-Intestinal | Brain | Atypical Behaviors | |
| Case 1 | F | 23 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Touching people, page flipping | No | Few spoken words | Level 2 | Moderate ID | No | Class I obesity (BMI = 30) | No | Possible dysgeusia (J1; 5); epistaxis (J4; <15 min) | No | No | No | No | Irrepressible licking behavior (J1; 5), puts her index finger to her mouth (J1; 5) |
| Case 2 | F | 26 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity, no nonverbal communicative behaviors | Strolling | SIB | Nonverbal | Level 3 | Profound ID | Bipolar disorder | Recurrent urinary tract infections, chronic constipation | No | Rhinitis (J1; 7) | No | No | No | No | Crying, irritability, head blows in the walls (J3; 4) |
| Case 3 | F | 43 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Body swings, hand clapping | Mild SIB, mild hetero-aggressivity | Short sentences echolalia | Level 3 | Moderate ID | Bipolar disorder | Prematurity, repetitive infections (urine, skin, breast), constipation, tooth decay | Yes (J1; 1) | Rhinitis (J2; a few days) | Dry cough (J5; 3) | Yes (J6; 10) | Diarrhea (J3; a few days) | No | Increased hetero-aggressivity and sleep disorders the week before (associated with an urinary tract infection 5 days before fever) |
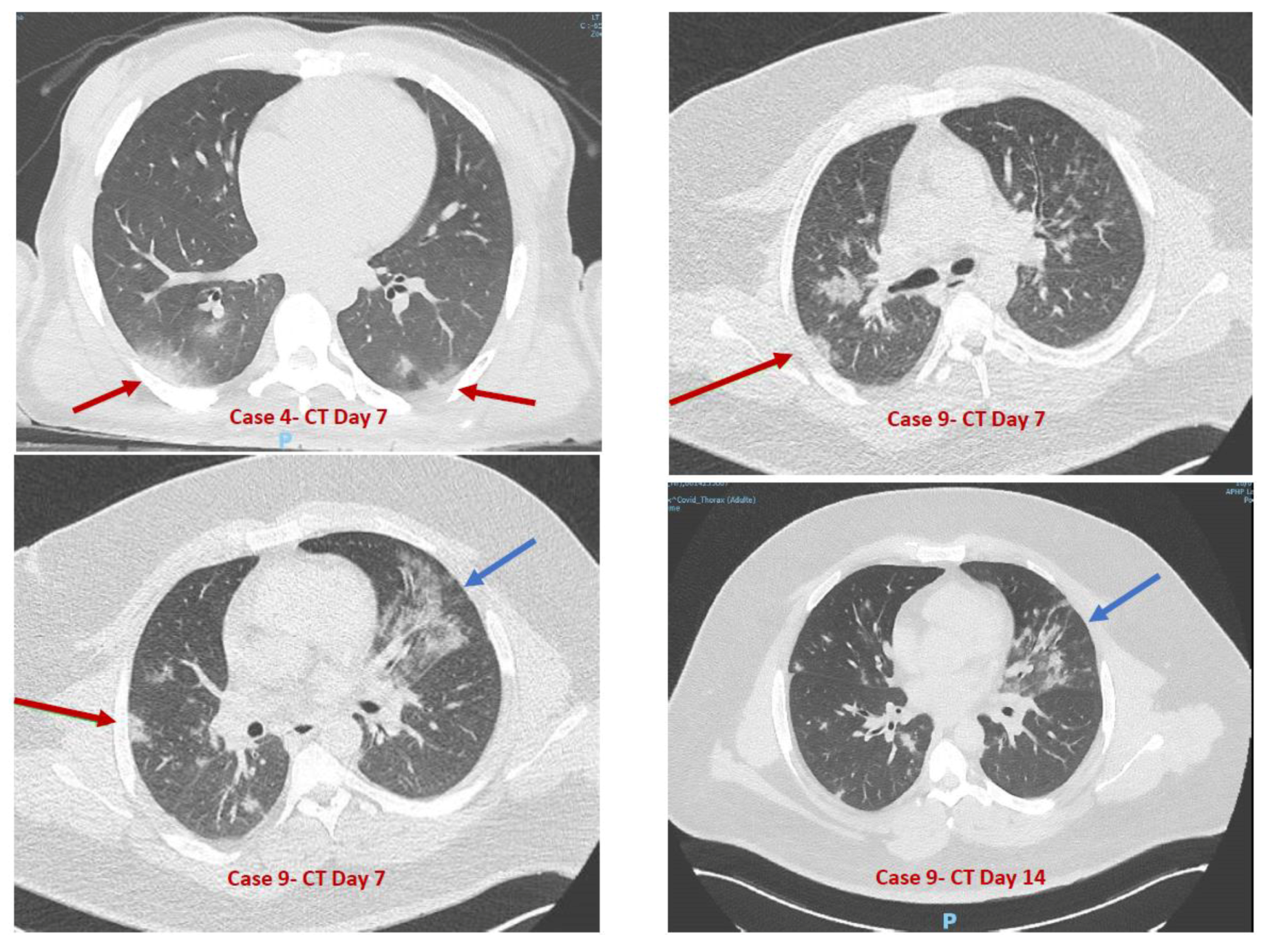
| Case 4 | M | 24 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Invasive food search, echopraxia | Mild SIB, hetero-aggressivity | Few spoken words, echolalia | Level 3 | Severe ID | No | Epilepsy, neuropathic pain, gastroparesis surgery | Yes (J3; 1) | Rhinitis (J1; 12) | Productive cough, polypnea (J4; 5) | Yes (J3; 10) | Diarrhea (J3; 1) | No | No |
| Case 5 | M | 16 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity, limited facial expressions, some interest in maintaining verbal relationships | Pseudo OCD, echolalia, smells food before eating | Moderate hetero-aggressivity | Functional language | Level 2 | Mild ID | Bipolar disorder | Meningitis, horizontal nystagmus | No | Anosmia, dysgeusia (J1; <10) | No | No | No | No | Threw away his meal trays (J1; 3) |
| Case 6 | M | 16 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors, significant autism withdrawal | Puts objects in his ears and nose | Hetero-aggressivity | Nonverbal few Makaton signs | Level 3 | Severe ID | Major depressive disorder | Epilepsy, Behcet’s syndrome, chronic constipation | Yes (J1; 1) | Rhinitis (J1; 6) | No | Yes (J1; 4) | Diarrhea (J2; 3 then J9; 2) | No | No |
| Case 7 | M | 20 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Upper body motor stereotypies, pseudo OCD | SIB | Nonverbal few Makaton signs | Level 3 | Severe ID | Major depressive disorder with catatonic features | Pharmacoresistant epilepsy, gastritis, severe chronic constipation | No | No | Dry cough (J1; 5) | Yes (J3; 10) | Diarrhea (J3; 3 then J8; 6) | No | Stool spread during episodes of diarrhea; increase in SIB (J6; 10) |
| Case 8 | M | 15 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity, no nonverbal communicative behaviors | Strolling, pica, spitting and spreading saliva | No | Nonverbal | Level 3 | Severe ID | No | Epilepsy, gastric mastocytosis, delayed puberty | No | Rhinitis (J1; 3) | No | Yes (J1; 3) | Diarrhea (J4; 4 then J10; 5) | No | No |
| Case 9 | M | 28 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | No | No | Nonverbal | Level 3 | Severe ID | No | Epilepsy, class III obesity (BMI = 55), HBP | Yes (J1; <36 h) | No | Dry cough (J1; 2), polypnea (J1; >9 days) needing oxygen | No | No | Epilepsy (J7, 1 episode) | No |
| Case 10 | M | 16 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Motor stereotypies, OCD | Moderate hetero-aggressivity | Few sentences echolalia | Level 3 | Severe ID | No | Seronegative autoimmune encephalitis (responsive to immuno-suppressive drug) | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Case 11 | M | 16 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Flapping, pseudo OCD | Mild SIB, hetero-aggressivity | Nonverbal few Makaton signs | Level 3 | Severe ID | Major depressive disorder | Epilepsy, gastric ulcer, chronic hives, constipation | No | No | Dry cough (J1; 3) | No | No | No | No |
| Case 12 | F | 13 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Body swings, tiptoeing | No | Few spoken words | Level 3 | Severe ID | No | Severe constipation | No | Rhinitis (J1; 2) | No | Yes (J1; 2) | Diarrhea (J3; 7) | No | No |
| Case 13 | M | 12 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity, some effective nonverbal communicative behaviors | Strolling | Severe SIB | Nonverbal sign language | Level 2 | Moderate ID | No | CHARGE syndrome, unilateral cecity, deafness, anosmia | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Case 14 | M | 16 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Attention search | Sexual behaviors | Functional language | Level 3 | Severe ID | Bipolar disorder, anxiety disorder | Migraine, hiatal hernia, esophagitis, gastritis, class I obesity (BMI = 31), inflammatory bowel disease | No | Rhinitis (J1; 4) | No | Yes (J1; 4) | No | No | No |
| Case 15 | M | 14 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity, limited facial expressions, difficulties adjusting behavior to suit various social contexts, some interest in peers | Attention search | No | Functional language | Level 1 | Moderate ID | No | Chronic myeloid leukemia (immuno-suppressive drug) | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Case 16 | M | 34 | Limited social-emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors | Wandering, vocalizations | Punctual hetero-aggressivity | Few spoken words | Level 3 | Severe ID | Anxiety disorder | PRODH gene deletion, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, restless legs syndrome, gastritis, constipation | No | No | No | No | Diarrhea (J1; 5) | No | No |
| Close Exposition to a PCR+ COVID-19 Patient * | SARS-CoV2 PCR Screening | SARS-CoV2 IgG Screening | Chest CT Scan | Other Imaging | Blood Test | COVID-19 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Yes | Positive | Not performed | No | No | At Day 2: Neutropenia (1.78 × 10⁹/L), Aspartate AminoTransferase elevation (×2 N) | Yes |
| Case 2 | Yes | Positive | Not performed | No | No | At Day 4: Anemia (11.2 g/dL), Elevated C-Reactive Protein (8.78 mg/L) | Yes |
| Case 3 | Yes | Positive | Not performed | No | No | At Day 1: Elevated C-Reactive Protein (51 mg/L) | Yes |
| Case 4 | Yes | Positive | Not performed | Yes | No | At Day 6: Anemia (12.9 g/dL), Neutropenia (1.58 × 10⁹/L), Elevated C-Reactive Protein (9.59 mg/L) | Yes |
| Case 5 | No (psychiatric secure room) | Positive | Not performed | No | No | Not performed as paucisymptomatic | Yes |
| Case 6 | Yes | Positive | Not performed | No | No | At Day 7: Elevated C-Reactive Protein (6.07 mg/L), Lactate Dehydrogenase elevation (×1.5 N) | Yes |
| Case 7 | Yes | Positive | Not performed | Yes | No | At Day 7: Anemia (12.7 g/dL), Neutropenia (1.75 × 10⁹/L), Elevated C-Reactive Protein (6.04 mg/L) | Yes |
| Case 8 | Yes | Positive | Not performed | No | No | At Day 7: Neutropenia (1.70 × 10⁹/L), Lactate Dehydrogenase elevation (×1.1 N) | Yes |
| Case 9 | Yes | Negative | Positive | Yes | No | At Day 6: Elevated C-Reactive Protein (22.4 mg/L), Aspartate AminoTransferase elevation (×1.5 N) | Yes |
| Case 10 | Yes | Negative | Negative | No | No | Under immunosuppressive regimen: Anemia (11.7 g/dL), Leukopenia (3.51 × 10⁹/L), Lymphopenia (0.76 × 10⁹/L) | No |
| Case 11 | Yes | Negative | Negative | No | No | At Day 9: Lymphocytosis (4.46 × 10⁹/L) | No |
| Case 12 | Yes | Negative | Negative | No | No | Not performed as paucisymptomatic | No |
| Case 13 | Yes | Negative | Negative | No | No | Not performed as asymptomatic | No |
| Case 14 | Yes | Negative | Positive | No | No | Not performed as paucisymptomatic | Yes |
| Case 15 | Yes | Negative | Negative | No | No | Under immunosuppressive regimen: Anemia (12.0 g/dL), Lactate Dehydrogenase elevation (×1.1 N) | No |
| Case 16 | No (psychiatric secure room) | Positive | Not performed | No | No | Not performed | Yes |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nollace, L.; Cravero, C.; Abbou, A.; Mazda-Walter, B.; Bleibtreu, A.; Pereirra, N.; Sainte-Marie, M.; Cohen, D.; Giannitelli, M. Autism and COVID-19: A Case Series in a Neurodevelopmental Unit. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092937
Nollace L, Cravero C, Abbou A, Mazda-Walter B, Bleibtreu A, Pereirra N, Sainte-Marie M, Cohen D, Giannitelli M. Autism and COVID-19: A Case Series in a Neurodevelopmental Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092937
Chicago/Turabian StyleNollace, Leslie, Cora Cravero, Alice Abbou, Brice Mazda-Walter, Alexandre Bleibtreu, Nathalie Pereirra, Myriam Sainte-Marie, David Cohen, and Marianna Giannitelli. 2020. "Autism and COVID-19: A Case Series in a Neurodevelopmental Unit" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092937
APA StyleNollace, L., Cravero, C., Abbou, A., Mazda-Walter, B., Bleibtreu, A., Pereirra, N., Sainte-Marie, M., Cohen, D., & Giannitelli, M. (2020). Autism and COVID-19: A Case Series in a Neurodevelopmental Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092937





