Overview of the Side-Effects of FDA- and/or EMA-Approved Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies
Abstract
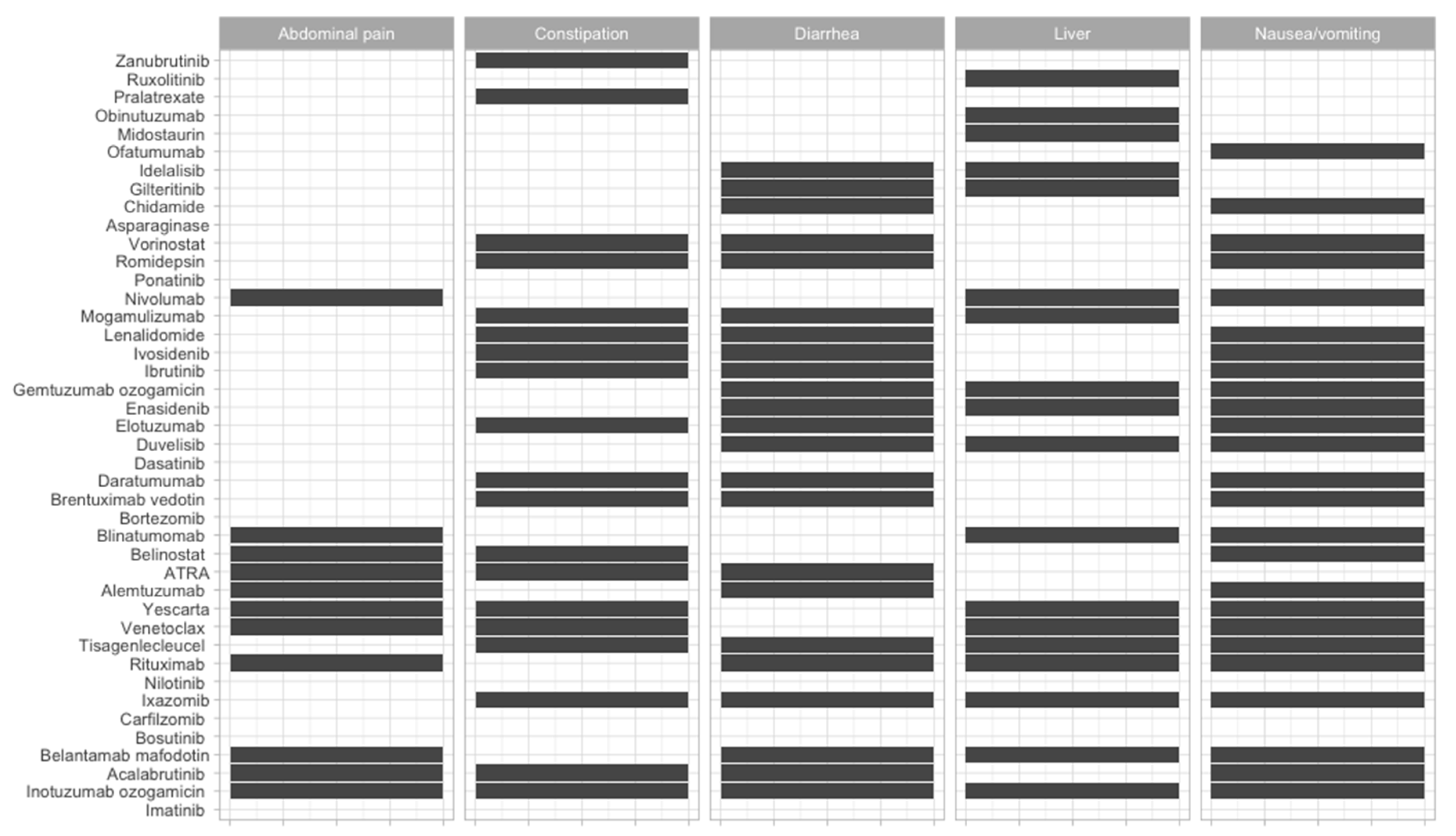
:1. Introduction
2. Specific Targets in Hematology
3. CAR-T Cells and Bispecific Antibodies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coller, B.S. Blood at 70: Its roots in the history of hematology and its birth. Blood 2015, 126, 2548–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, J.M. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Historical Perspective. Semin. Hematol. 2010, 47, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.J.E.; Stopforth, R.J.; Cragg, M.S. Therapeutic Antibodies: What Have We Learnt from Targeting CD20 and Where Are We Going? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makatsori, M.; Kiani-Alikhan, S.; Manson, A.L.; Verma, N.; Leandro, M.; Gurugama, N.P.; Longhurst, H.J.; Grigoriadou, S.; Buckland, M.; Kanfer, E.; et al. Hypogammaglobulinaemia after rituximab treatment--incidence and outcomes. QJM 2014, 107, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, N.; Chari, A.; Scott, E.; Mezzi, K.; Usmani, S.Z. B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in multiple myeloma: Rationale for targeting and current therapeutic approaches. Leukemia 2020, 34, 985–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, F.; Horenstein, A.L.; Costa, F.; Giuliani, N.; Pistoia, V.; Malavasi, F. CD38: A Target for Immunotherapeutic Approaches in Multiple Myeloma. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connors, J.M.; Jurczak, W.; Straus, D.J.; Ansell, S.M.; Kim, W.S.; Gallamini, A.; Younes, A.; Alekseev, S.; Illés, Á.; Picardi, M.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin with Chemotherapy for Stage III or IV Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, W.S. Brentuximab vedotin: Clinical updates and practical guidance. Blood Res. 2017, 52, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, J.C.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Alpers, J.D.; Croce, C.M.; Nowell, P.C. Regulation of bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression during normal human lymphocyte proliferation. Science 1987, 236, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, M.; Silini, E.; Kozak, C.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Croce, C.M. Molecular analysis of mbcl-2: Structure and expression of the murine gene homologous to the human gene involved in follicular lymphoma. Cell 1987, 49, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Bashir, M.M.; Givol, I.; Cossman, J.; Jaffe, E.; Croce, C.M. DNA rearrangements in human follicular lymphoma can involve the 5’ or the 3’ region of the bcl-2 gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, C.R. Classification of lymphoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1978, 102, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pollyea, D.A.; Stevens, B.M.; Jones, C.L.; Winters, A.; Pei, S.; Minhajuddin, M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Riemondy, K.A.; Gillen, A.E.; et al. Venetoclax with azacitidine disrupts energy metabolism and targets leukemia stem cells in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Salcedo, L.M.; Desai, V.; Dalia, S. Venetoclax: Evidence to date and clinical potential. DIC 2019, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledford, H.; Else, H.; Warren, M. Cancer immunologists scoop medicine Nobel prize. Nature 2018, 562, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, L.; Lemery, S.J.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Microsatellite Instability-High Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3753–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Gerber, D.E. Autoimmunity, checkpoint inhibitor therapy and immune-related adverse events: A review. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 64, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasanch, E.E.; Orlowski, R.Z. Proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nencioni, A.; Grünebach, F.; Patrone, F.; Ballestrero, A.; Brossart, P. Proteasome inhibitors: Antitumor effects and beyond. Leukemia 2007, 21, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotla, V.; Goel, S.; Nischal, S.; Heuck, C.; Vivek, K.; Das, B.; Verma, A. Mechanism of action of lenalidomide in hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holstein, S.A.; Suman, V.J.; McCarthy, P.L. Update on the role of lenalidomide in patients with multiple myeloma. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2018, 9, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daver, N.; Schlenk, R.F.; Russell, N.H.; Levis, M.J. Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: Review of current knowledge and evidence. Leukemia 2019, 33, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiyoi, H. FLT3 Inhibitors: Recent advances and problems for clinical application. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perl, A.E.; Daver, N.G.; Pratz, K.W.; Maly, J.; Hong, W.-J.; Bahceci, E.; Tong, B.; Tian, T.; Dilley, K. Venetoclax in Combination with Gilteritinib in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Phase 1b Study. Blood 2019, 134, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalipour, A.; Advani, R.H. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their clinical potential in the treatment of B-cell malignancies: Focus on ibrutinib. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2014, 5, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batlevi, C.L.; Younes, A. Revival of PI3K inhibitors in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2047–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Gisslinger, H.; Waltzman, R.; Stalbovskaya, V.; McQuitty, M.; Hunter, D.S.; Levy, R.; Knoops, L.; et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomuleasa, C.; Selicean, S.; Gafencu, G.; Petrushev, B.; Pop, L.; Berce, C.; Jurj, A.; Trifa, A.; Rosu, A.-M.; Pasca, S.; et al. Fibroblast dynamics as an in vitro screening platform for anti-fibrotic drugs in primary myelofibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieber, M.; Crispino, J.D.; Stein, B. Myelofibrosis in 2019: Moving beyond JAK2 inhibition. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Mattei, E.; Bayraktar, R.; Manshouri, T.; Silva, A.M.; Ivan, C.; Gulei, D.; Fabris, L.; Soares do Amaral, N.; Mur, P.; Perez, C.; et al. miR-543 regulates the epigenetic landscape of myelofibrosis by targeting TET1 and TET2. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selicean, S.E.; Tomuleasa, C.; Grewal, R.; Almeida-Porada, G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Mesenchymal stem cells in myeloproliferative disorders—Focus on primary myelofibrosis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, J.; Pasca, S.; Teodorescu, P.; Selicean, C.; Rus, I.; Zdrenghea, M.; Bojan, A.; Trifa, A.; Fetica, B.; Petrushev, B.; et al. Persistent Basophilia May Suggest an “Accelerated Phase” in the Evolution of CALR-Positive Primary Myelofibrosis toward Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstovsek, S.; Mesa, R.A.; Gotlib, J.; Levy, R.S.; Gupta, V.; DiPersio, J.F.; Catalano, J.V.; Deininger, M.; Miller, C.; Silver, R.T.; et al. A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Ruxolitinib for Myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, C.N.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Gisslinger, H.; Knoops, L.; Cervantes, F.; Jones, M.M.; Sun, K.; McQuitty, M.; et al. Long-term findings from COMFORT-II, a phase 3 study of ruxolitinib vs best available therapy for myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deak, D.; Pop, C.; Zimta, A.-A.; Jurj, A.; Ghiaur, A.; Pasca, S.; Teodorescu, P.; Dascalescu, A.; Antohe, I.; Ionescu, B.; et al. Let’s Talk about BiTEs and Other Drugs in the Real-Life Setting for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, C.; Pasca, S.; Tat, T.; Teodorescu, P.; Vlad, C.; Iluta, S.; Dima, D.; Tomescu, D.; Scarlatescu, E.; Tanase, A.; et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy in cytokine release syndrome following immunotherapy or cellular therapies? J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tat, T.; Li, H.; Constantinescu, C.-S.; Onaciu, A.; Chira, S.; Osan, C.; Pasca, S.; Petrushev, B.; Moisoiu, V.; Micu, W.-T.; et al. Genetically enhanced T lymphocytes and the intensive care unit. Oncotarget 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomuleasa, C.; Fuji, S.; Berce, C.; Onaciu, A.; Chira, S.; Petrushev, B.; Micu, W.-T.; Moisoiu, V.; Osan, C.; Constantinescu, C.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells for the Treatment of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliotou, A.N.; Papadopoulou, L.C. CAR T-cell Therapy: A New Era in Cancer Immunotherapy. CPB 2018, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.J.; Benani, D.J. A review of blinatumomab, a novel immunotherapy. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 22, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; Deininger, M.; Hochhaus, A. Management of adverse events associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasi, P.M.; Tawbi, H.A.; Oddis, C.V.; Kulkarni, H.S. Clinical review: Serious adverse events associated with the use of rituximab—A critical care perspective. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oak, E.; Bartlett, N.L. A safety evaluation of brentuximab vedotin for the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Pratz, K.; Pullarkat, V.; Jonas, B.A.; Arellano, M.; Becker, P.S.; Frankfurt, O.; Konopleva, M.; Wei, A.H.; Kantarjian, H.M.; et al. Venetoclax combined with decitabine or azacitidine in treatment-naive, elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajwa, R.; Cheema, A.; Khan, T.; Amirpour, A.; Paul, A.; Chaughtai, S.; Patel, S.; Patel, T.; Bramson, J.; Gupta, V.; et al. Adverse Effects of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (Programmed Death-1 Inhibitors and Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein-4 Inhibitors): Results of a Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2019, 11, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiers, L.; Coupe, N.; Payne, M. Toxicities associated with checkpoint inhibitors—An overview. Rheumatology 2019, 58, vii7–vii16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascones-Martinez, A.; Mattila, R.; Gomez-Font, R.; Meurman, J.H. Immunomodulatory drugs: Oral and systemic adverse effects. Med. Oral. 2014, e24–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Safyan, R.; Suzanne, L. Immunomodulatory Drugs (IMiDs) in Multiple Myeloma. CCDT 2017, 17, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-F.; Lin, L.; Xing, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Anderson, K.C.; Tai, Y.-T. BCMA-Targeting Therapy: Driving a New Era of Immunotherapy in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Sun, J. Overview of anti-BCMA CAR-T immunotherapy for multiple myeloma and relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunnery, S.E.; Mayer, I.A. Management of toxicity to isoform α-specific PI3K inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, x21–x26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Kanno, Y.; Villarino, A.; Ward, M.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J. Erratum: JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonbol, M.B.; Firwana, B.; Zarzour, A.; Morad, M.; Rana, V.; Tiu, R.V. Comprehensive review of JAK inhibitors in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2013, 4, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furumoto, Y.; Gadina, M. The Arrival of JAK Inhibitors: Advancing the Treatment of Immune and Hematologic Disorders. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
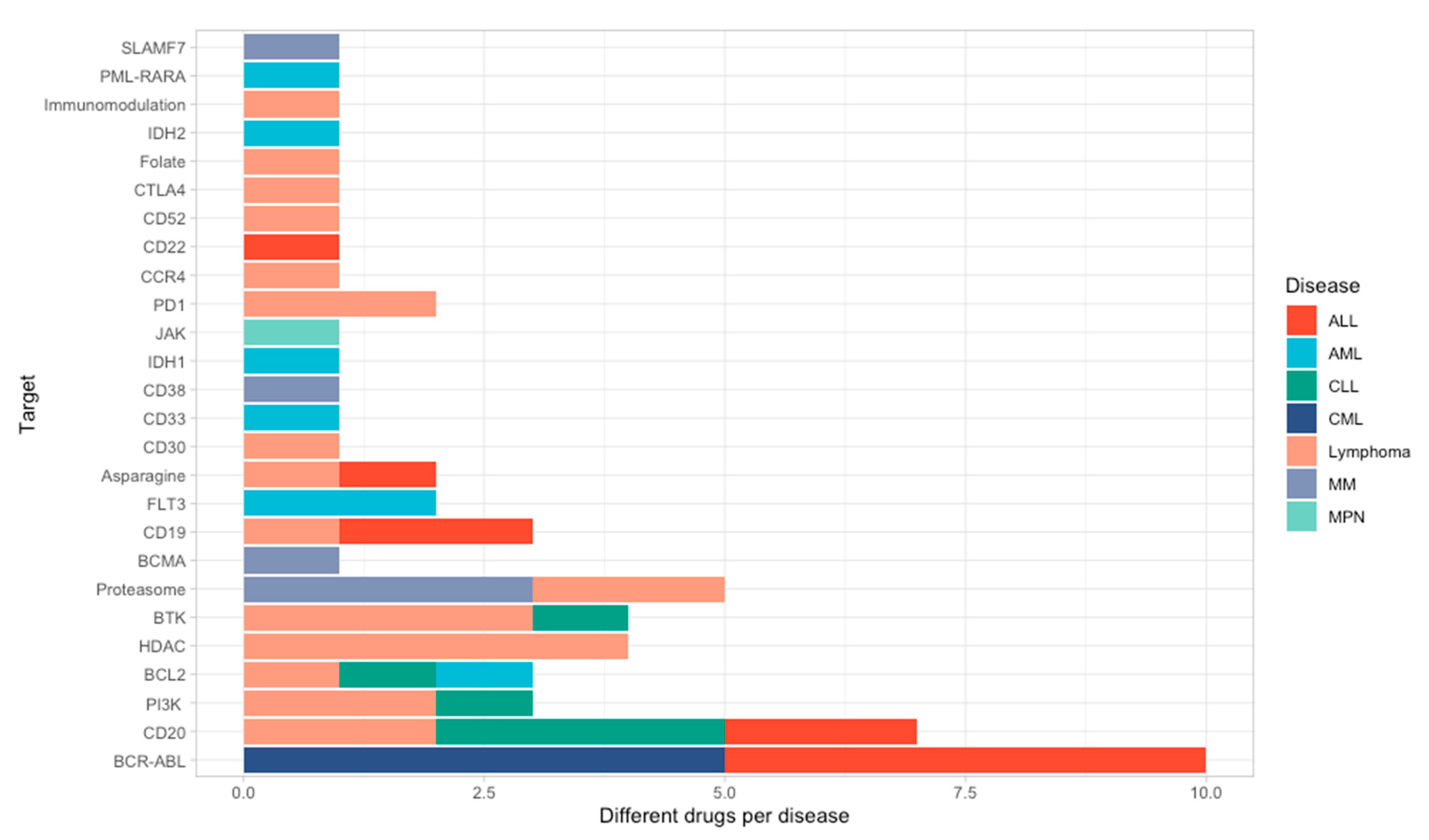
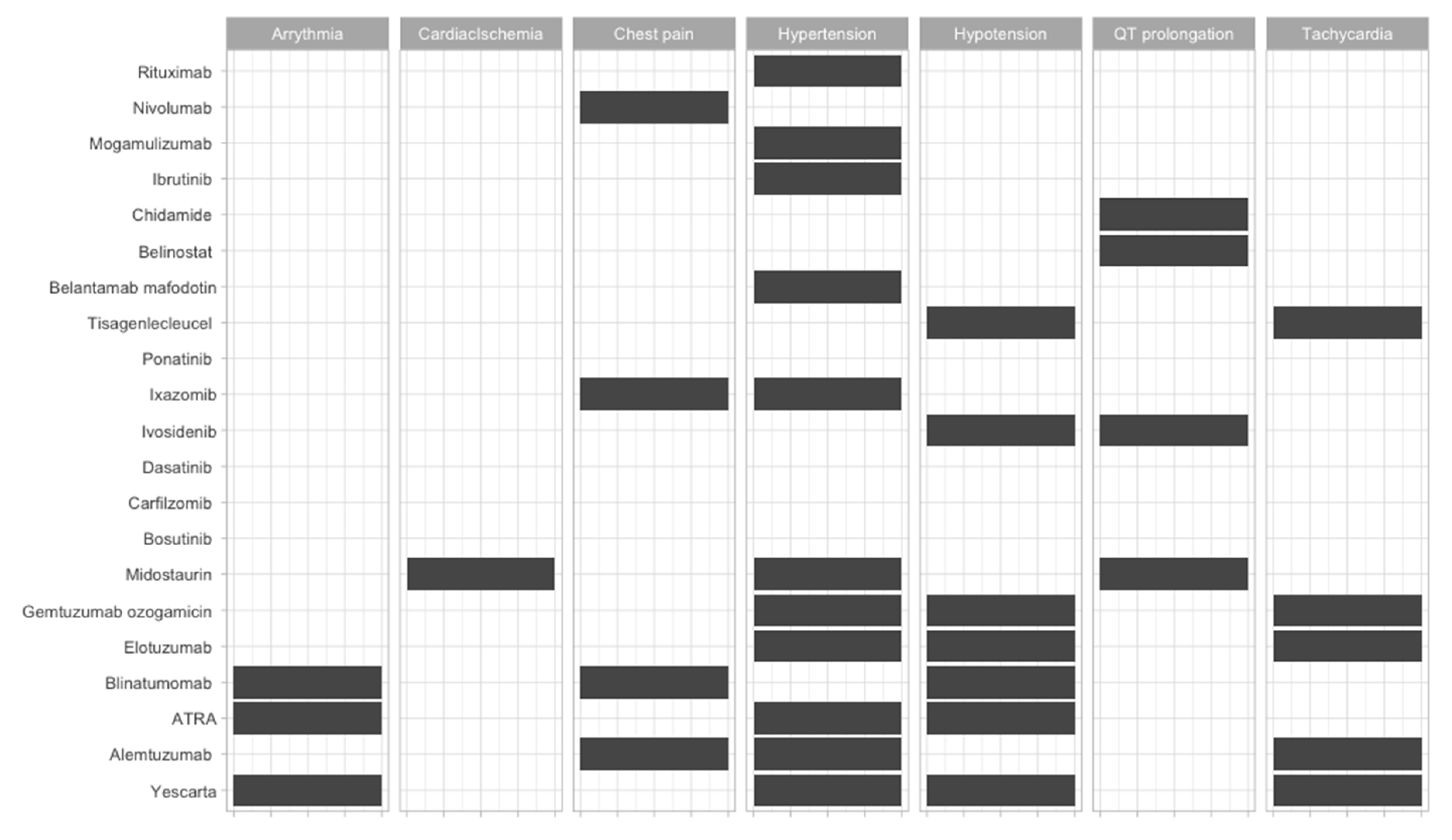


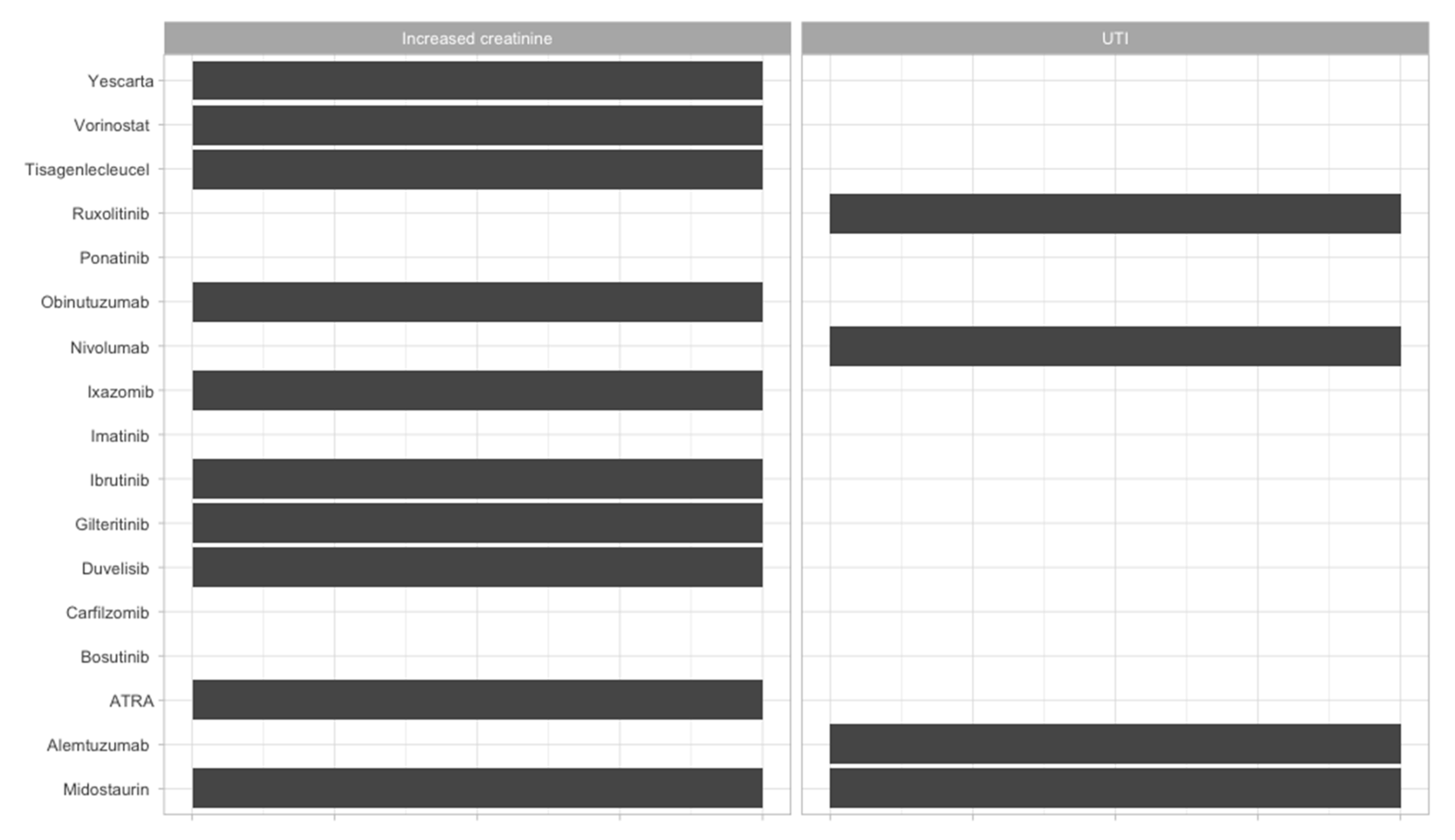
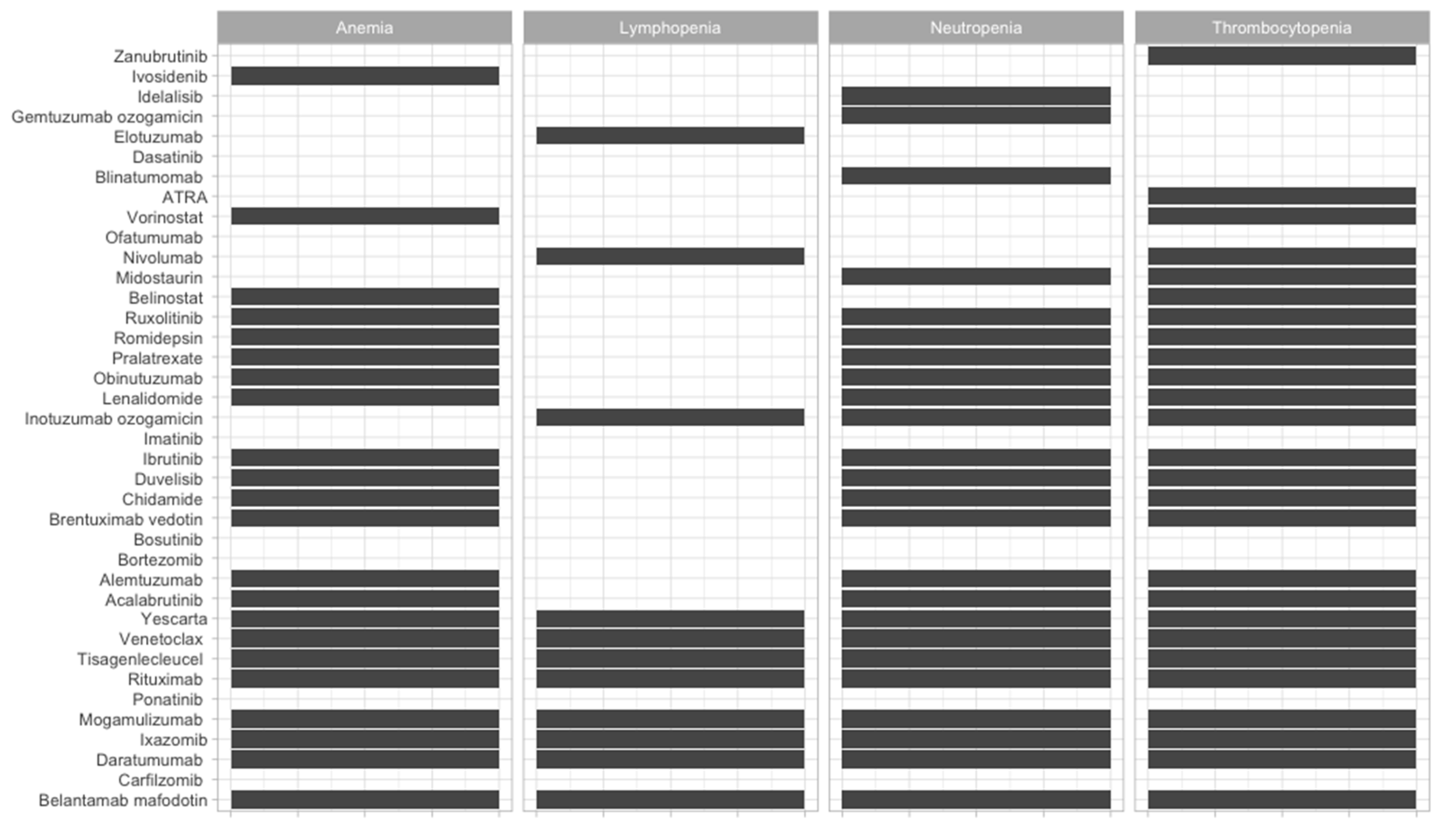

| Therapeutic Strategy | Type of Targeted Cell | Type of Hematological Malignancy | Mechanism behind Observed Side-Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCR-ABL inhibitor | Malignant myeloid cell, malignant lymphoid cells | Chronic myeloid leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia |
| [44] |
| anti-CD20 targets | B cell (malignant, as well as normal B cells) | B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, B-cell leukemias |
| [45] |
| anti-CD30 | Reed–Sternberg cells in Hodgkin lymphoma, LCL cells, other subtypes of NHL | Primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, B-cell lymphoma, multiple myeloma, adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma, mast cell malignancies |
| [46] |
| BCL2 inhibitors | chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) |
| [16,17,47] |
| immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD1) | T-cells and APCs, or T-cells and malignant cells | malignancies with high genomic instability |
| [48,49] |
| Immunomodulators (thalidomide, lenalidomide and pomalidomide,) | plasma cells | Multiple myeloma |
| [50,51] |
| anti-B-cell maturation antigen therapy | plasma cells | Multiple myeloma |
| [7,52,53] |
| PI3K inhibitors | B cells | Lymphoid diseases (especially of B-cell origin) |
| [29,54,55] |
| JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitors | megakaryocytes, but JAK1/JAK2 are ubiquitously expressed | Myelofibrosis, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. |
| [56,57,58] |
| CAR T cells | depending on the engineered target | Wide applications in hematological malignancies, depending on the engineered target |
| [39,40,41,42,53] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Constantinescu, C.; Pasca, S.; Zimta, A.-A.; Tat, T.; Rus, I.; Teodorescu, P.; Iluta, S.; Tanase, A.; Colita, A.; Sigurjonsson, O.; et al. Overview of the Side-Effects of FDA- and/or EMA-Approved Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092903
Constantinescu C, Pasca S, Zimta A-A, Tat T, Rus I, Teodorescu P, Iluta S, Tanase A, Colita A, Sigurjonsson O, et al. Overview of the Side-Effects of FDA- and/or EMA-Approved Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092903
Chicago/Turabian StyleConstantinescu, Catalin, Sergiu Pasca, Alina-Andreea Zimta, Tiberiu Tat, Ioana Rus, Patric Teodorescu, Sabina Iluta, Alina Tanase, Anca Colita, Olafur Sigurjonsson, and et al. 2020. "Overview of the Side-Effects of FDA- and/or EMA-Approved Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092903
APA StyleConstantinescu, C., Pasca, S., Zimta, A.-A., Tat, T., Rus, I., Teodorescu, P., Iluta, S., Tanase, A., Colita, A., Sigurjonsson, O., Einsele, H., & Tomuleasa, C. (2020). Overview of the Side-Effects of FDA- and/or EMA-Approved Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092903







