Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4—A Circulating Protein Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease in Diabetic Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Baseline Measurements
2.4. PAD Assessment and Sample Processing
2.5. FABP4 Multiplex Assay
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description
3.2. Regression Analysis
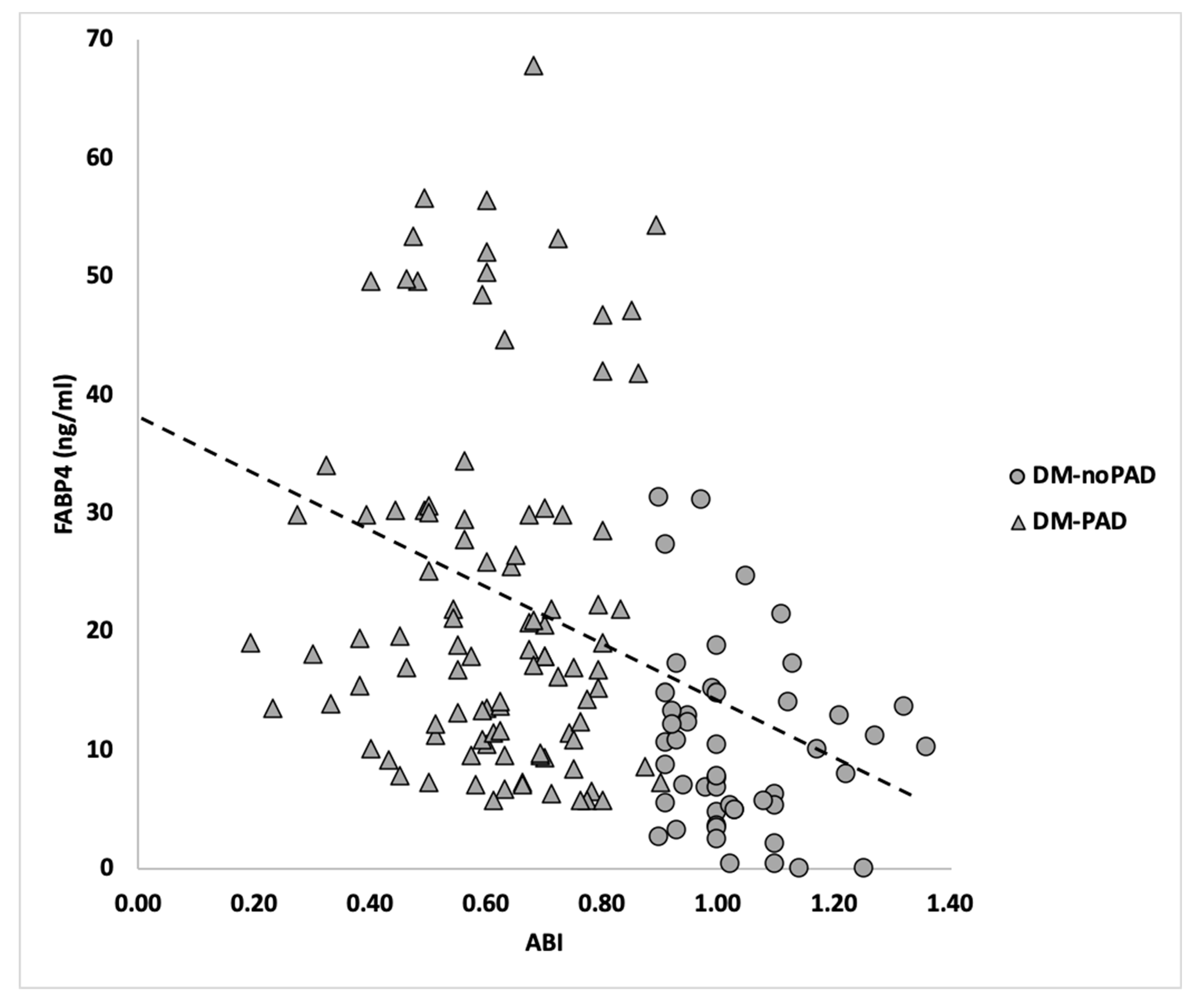
3.3. Hemodynamic Association between FABP4 and DM-PAD
3.4. Diagnostic Potential of FABP4 for PAD within Diabetic Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasmauski, K. Type 2 diabetes: The urgent need to protect young people. Lancet 2018, 392, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, A.; Arora, R.R. Medical management and cardiovascular risk reduction in peripheral arterial disease. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2008, 13, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, P.E.; Davis, W.A.; Bruce, D.G.; Davis, T.M. Peripheral arterial disease and risk of cardiac death in type 2 diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marso, S.P.; Hiatt, W.R. Peripheral arterial disease in patients with diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freisinger, E.; Malyar, N.M.; Reinecke, H.; Lawall, H. Impact of diabetes on outcome in critical limb ischemia with tissue loss: A large-scaled routine data analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oguntibeju, O.O. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation: Examining the links. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 11, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Gong, Y.L.; Li, C.J.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, Q.M.; Yu, D.M. Circulating MiRNA biomarkers serve as a fingerprint for diabetic atherosclerosis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glatz, J.F.; van der Vusse, G.J. Cellular fatty acid-binding proteins: Their function and physiological significance. Prog. Lipid Res. 1996, 35, 243–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernlohr, D.A.; Simpson, M.A.; Hertzel, A.V.; Banaszak, L.J. Intracellular lipid-binding proteins and their genes. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smathers, R.L.; Petersen, D.R. The human fatty acid-binding protein family: Evolutionary divergences and functions. Hum Genom. 2011, 5, 170–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabre, A.; Lazaro, I.; Girona, J.; Manzanares, J.M.; Marimon, F.; Plana, N.; Heras, M.; Masana, L. Plasma fatty acid binding protein 4 is associated with atherogenic dyslipidemia in diabetes. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, K.; Cao, H.; Kono, K.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Furuhashi, M.; Uysal, K.T.; Cao, Q.; Atsumi, G.; Malone, H.; Krishnan, B.; et al. Adipocyte/macrophage fatty acid binding proteins control integrated metabolic responses in obesity and diabetes. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furuhashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; Shimamoto, K.; Miura, T. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4): Pathophysiological Insights and Potent Clinical Biomarker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2014, 8, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, R.; Okura, T.; Fujioka, Y.; Sumi, K.; Matsuzawa, K.; Izawa, S.; Ueta, E.; Kato, M.; Taniguchi, S.I.; Yamamoto, K. Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4) concentration is associated with insulin resistance in peripheral tissues, A clinical study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, R.; Qasim, A.N.; Mehta, N.N.; Terembula, K.; Kapoor, S.; Braunstein, S.; Schutta, M.; Iqbal, N.; Lehrke, M.; Reilly, M.P. Relation of plasma fatty acid binding proteins 4 and 5 with the metabolic syndrome, inflammation and coronary calcium in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trojnar, M.; Patro-Malysza, J.; Kimber-Trojnar, Z.; Leszczynska-Gorzelak, B.; Mosiewicz, J. Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4(-)A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2019, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeung, D.C.; Xu, A.; Tso, A.W.; Chow, W.S.; Wat, N.M.; Fong, C.H.; Tam, S.; Sham, P.C.; Lam, K.S. Circulating levels of adipocyte and epidermal fatty acid-binding proteins in relation to nephropathy staging and macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, A.; Tso, A.W.; Cheung, B.M.; Wang, Y.; Wat, N.M.; Fong, C.H.; Yeung, D.C.; Janus, E.D.; Sham, P.C.; Lam, K.S. Circulating adipocyte-fatty acid binding protein levels predict the development of the metabolic syndrome: A 5-year prospective study. Circulation 2007, 115, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.S.; Tso, A.W.; Xu, A.; Yuen, M.M.; Fong, C.H.; Lam, T.H.; Lo, S.V.; Tse, H.F.; Woo, Y.C.; Yeung, C.Y.; et al. Elevated circulating adipocyte-fatty acid binding protein levels predict incident cardiovascular events in a community-based cohort: A 12-year prospective study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e004176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyoshi, T.; Onoue, G.; Hirohata, A.; Hirohata, S.; Usui, S.; Hina, K.; Kawamura, H.; Doi, M.; Kusano, K.F.; Kusachi, S.; et al. Serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein is independently associated with coronary atherosclerotic burden measured by intravascular ultrasound. Atherosclerosis 2010, 211, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, E.J.; Lee, W.Y.; Park, C.Y.; Oh, K.W.; Kim, B.J.; Sung, K.C.; Kim, B.S. The association of serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein with coronary artery disease in Korean adults. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, D.C.; Xu, A.; Cheung, C.W.; Wat, N.M.; Yau, M.H.; Fong, C.H.; Chau, M.T.; Lam, K.S. Serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein levels were independently associated with carotid atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobaus, C.; Herz, C.T.; Pesau, G.; Wrba, T.; Koppensteiner, R.; Schernthaner, G.H. FABP4 and Cardiovascular Events in Peripheral Arterial Disease. Angiology 2018, 69, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Rand, M.L.; Singh, K.; Hussain, M.A.; Jain, S.; Khan, H.; Verma, S.; Al-Omran, M.; Abdin, R.; et al. Altered coagulation profile in peripheral artery disease patients. Vascular 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.H.; Zamzam, A.; Valencia, J.; Khan, H.; Jain, S.; Singh, K.K.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. MicroRNA Profile of Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azab, S.M.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Serum Metabolic Signatures of Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Non-PAD (n = 49) | PAD (n = 119) | p-Value α |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) † | |||
| ABI | 1.03 (0.11) | 0.61 (0.15) | 0.001 |
| Age in years | 68.3 (12.8) | 69.1 (9.29) | 0.628 |
| Frequency (%) ‡ | |||
| Sex-male n (%) | 38 (79) | 82 (70) | 0.159 |
| Hypertension n (%) | 38 (79) | 101 (86) | 0.214 |
| Hypercholesteremia n (%) | 38 (79) | 98 (83) | 0.350 |
| Renal Insufficiency n (%) | 6 (13) | 13 (11) | 0.789 |
| Smoking n (%) | 35 (76) | 90 (78) | 0.494 |
| CAD n (%) | 15 (32) | 63 (53) | 0.016 |
| Stroke n (%) | 7 (21) | 21 (18) | 0.803 |
| Ulceration n (%) | 0 (0) | 17 (10) | 0.001 |
| ASA n (%) | 28 (57) | 76 (64) | 0.485 |
| ACEi/Arb n (%) | 19 (56) | 78 (71) | 0.142 |
| Beta-Blocker n (%) | 9 (27) | 48 (43) | 0.108 |
| CCB n (%) | 9 (27) | 33 (30) | 0.830 |
| Insulin n (%) | 7 (21) | 25 (23) | 0.820 |
| Oral Hypoglycemia n (%) | 18 (55) | 76 (69) | 0.145 |
| Mean Blood Work mean (SD) | |||
| Cr (mmol/L) | 87.0 (29.9) | 92.8 (54.7) | 0.934 |
| INR | 1.39 (0.95) | 1.15 (0.26) | 0.148 |
| WBC (×109) | 8.30 (2.09) | 9.32 (2.50) | 0.033 |
| Platelet count (×103) | 213 (64.1) | 230 (66.5) | 0.179 |
| HbA1c (%) | 0.07 (0.02) | 0.07 (0.01) | 0.409 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 0.99 (0.23) | 0.99 (0.25) | 0.815 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 1.49 (0.37) | 1.76 (0.80) | 0.143 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 8.3 (2.49) | 7.9 (2.59) | 0.197 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 2.03 (1.64) | 2.35 (3.09) | 0.893 |
| Regression Models | Odds Ratio (95% CI) ‡ | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1, adjusted for age and sex | 2.74 (1.80–4.18) | 0.001 |
| Model 1 + CAD | 2.76 (1.79–4.29) | 0.001 |
| Model 1 + CAD + WBC | 2.77 (1.81–4.31) | 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Greco, E.; Wheatcroft, M.; Jain, S.; Khan, H.; Singh, K.K.; Forbes, T.L.; Rotstein, O.; Abdin, R.; et al. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4—A Circulating Protein Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease in Diabetic Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092843
Zamzam A, Syed MH, Greco E, Wheatcroft M, Jain S, Khan H, Singh KK, Forbes TL, Rotstein O, Abdin R, et al. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4—A Circulating Protein Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease in Diabetic Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092843
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamzam, Abdelrahman, Muzammil H. Syed, Elisa Greco, Mark Wheatcroft, Shubha Jain, Hamzah Khan, Krishna K. Singh, Thomas L. Forbes, Ori Rotstein, Rawand Abdin, and et al. 2020. "Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4—A Circulating Protein Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease in Diabetic Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092843
APA StyleZamzam, A., Syed, M. H., Greco, E., Wheatcroft, M., Jain, S., Khan, H., Singh, K. K., Forbes, T. L., Rotstein, O., Abdin, R., & Qadura, M. (2020). Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4—A Circulating Protein Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease in Diabetic Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092843










