Quantification of Death Risk in Relation to Sex, Pre-Existing Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors in COVID-19 Patients: Let’s Take Stock and See Where We Are
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Process
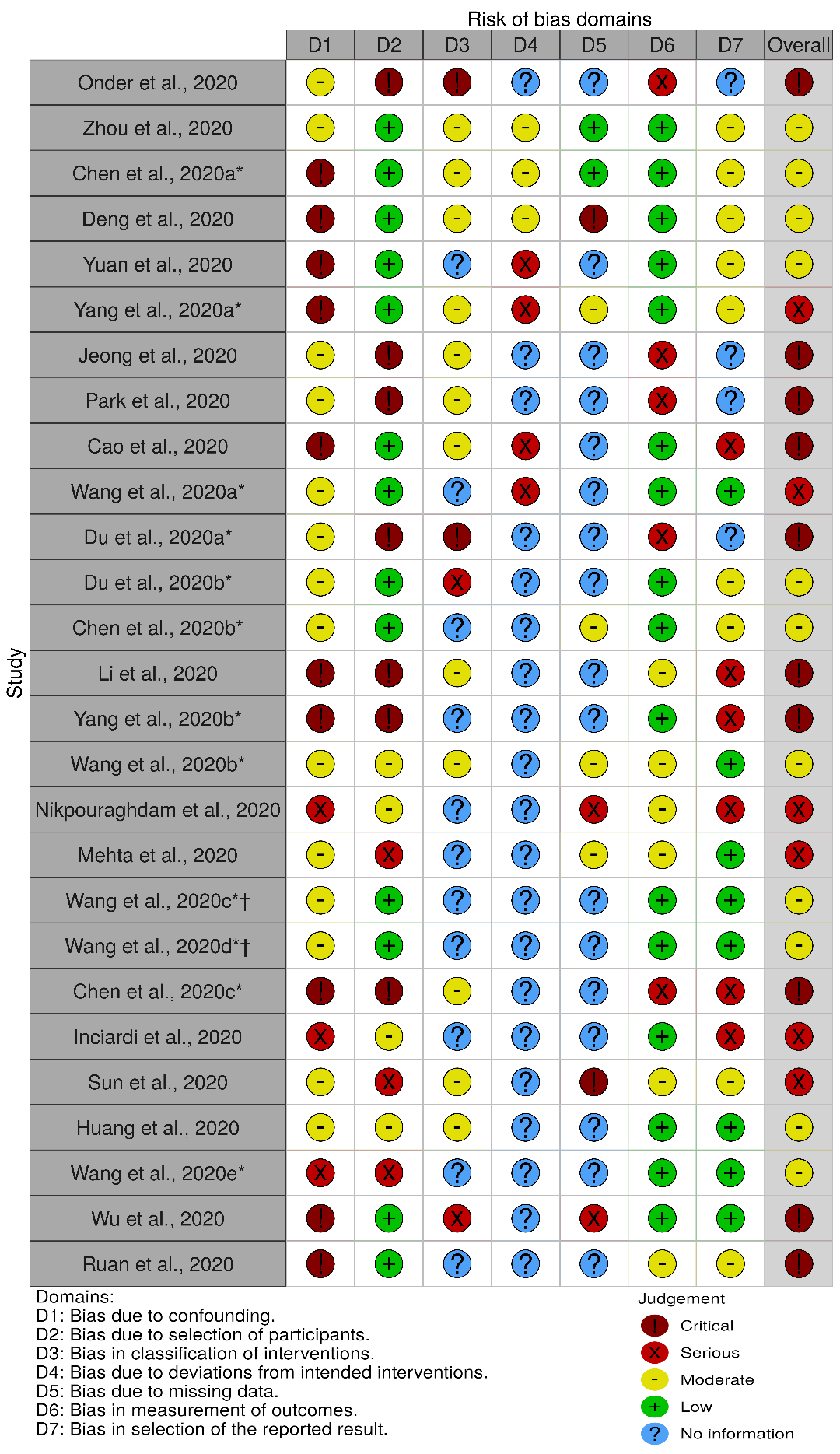
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Endpoints
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
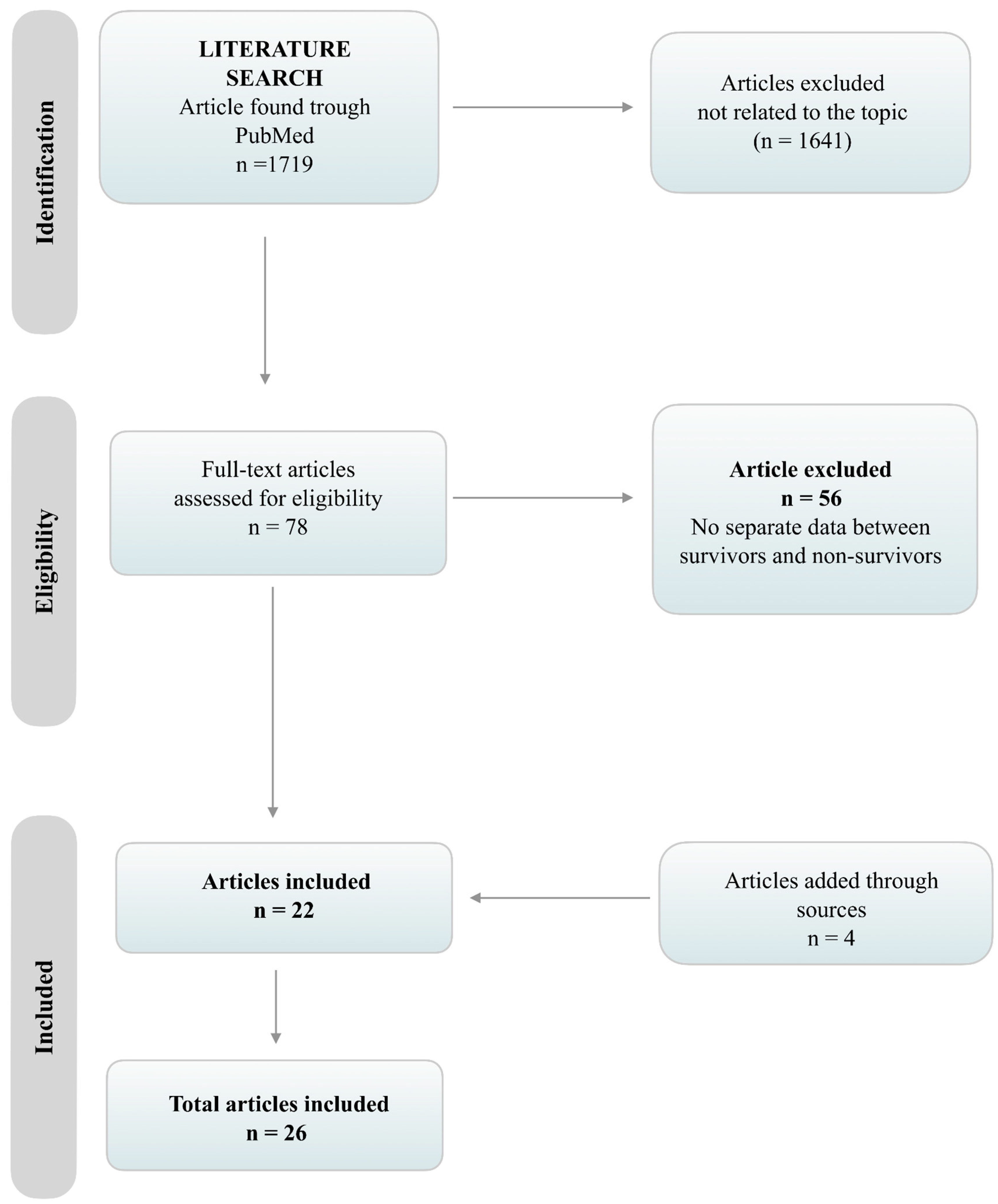
3.1. Search Results and Characteristics of the Studies
3.2. Assessment of Bias
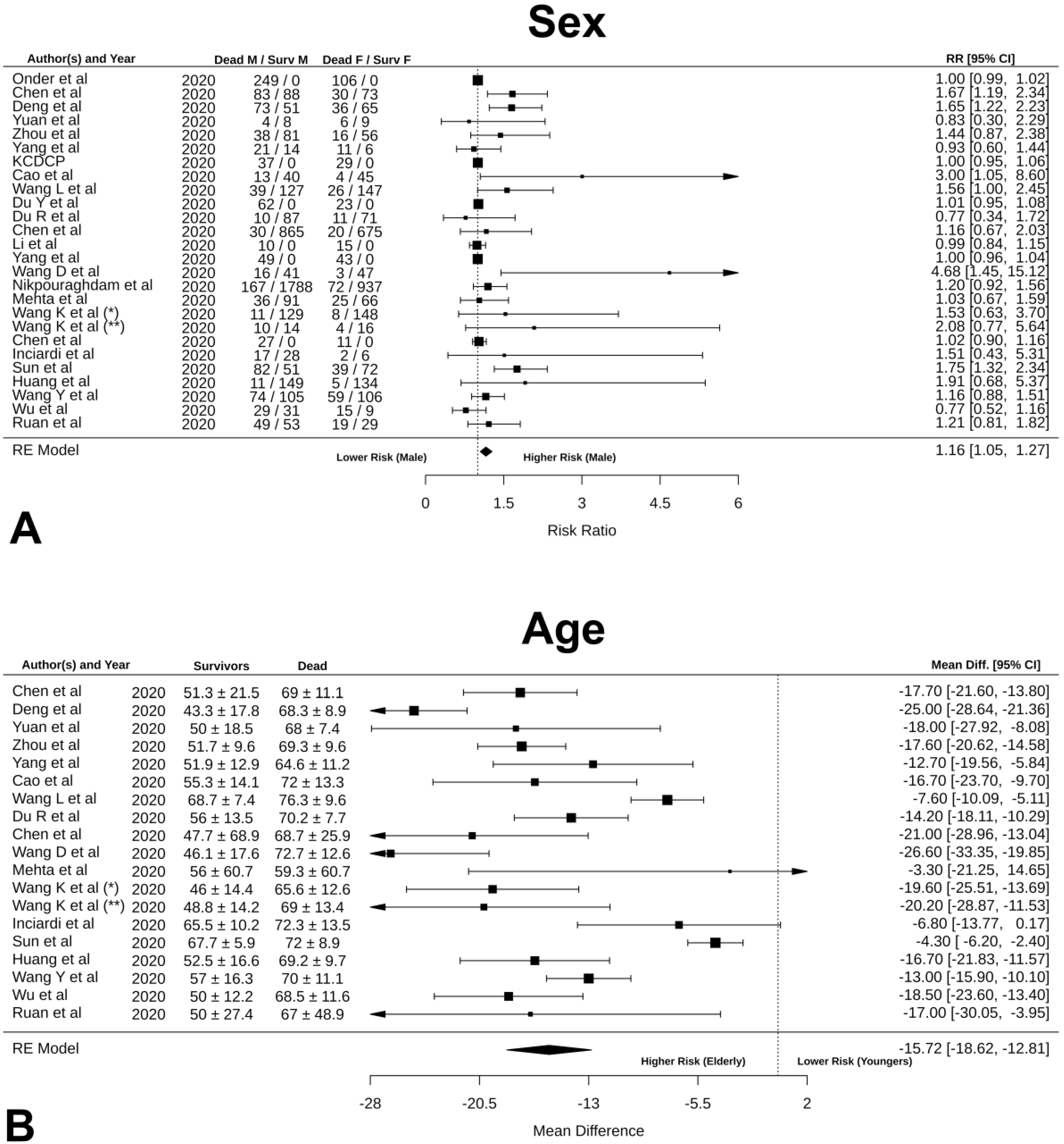
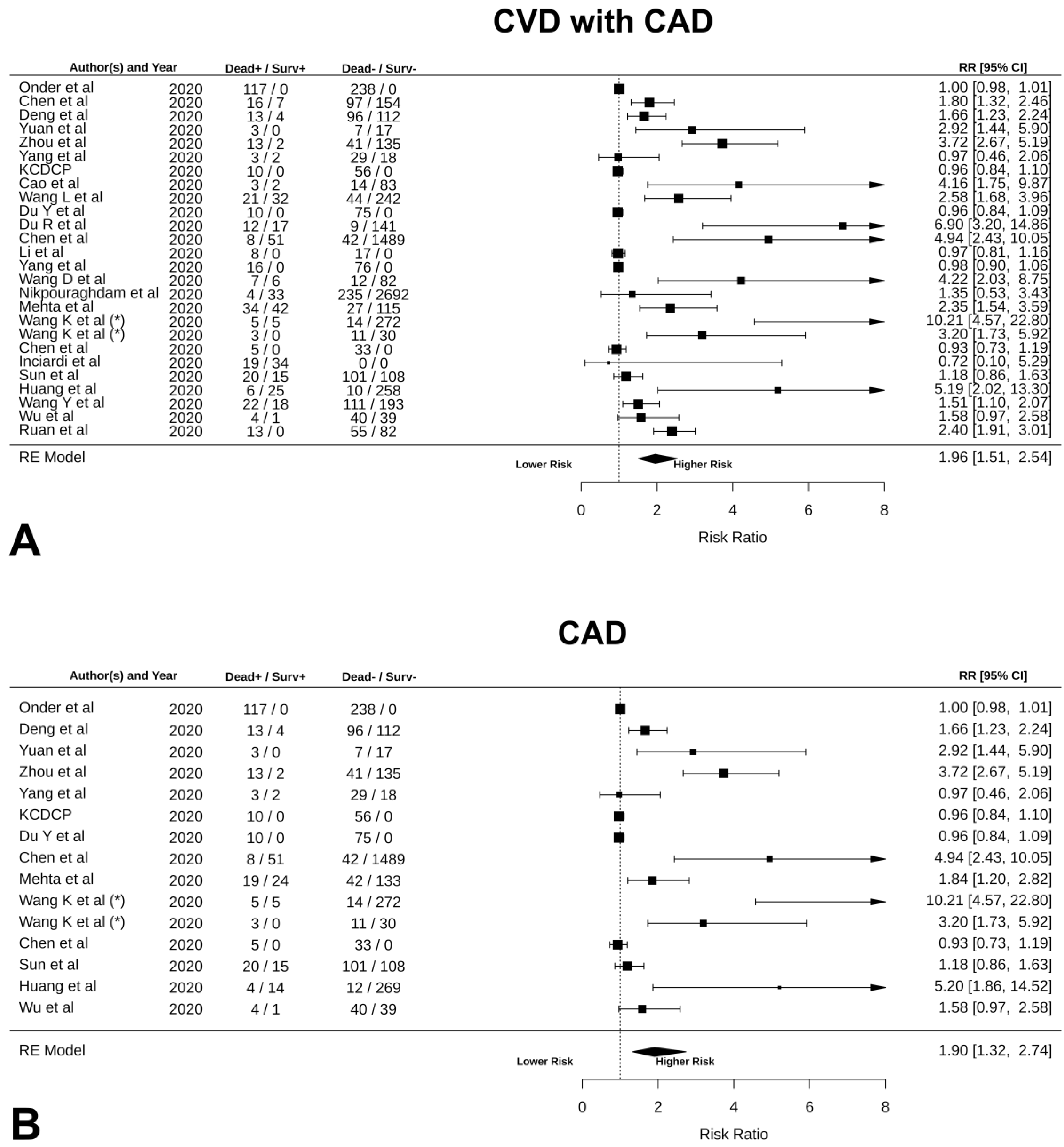
3.3. Prognostic Factors for Mortality
4. Discussion
4.1. Increased Mortality in Males and Elderlies
4.2. Increased Mortality in Patients with Pre-Existing CVD
4.3. Increased Mortality in Patients with Diabetes
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shereen, M.A.; Khan, S.; Kazmi, A.; Bashir, N.; Siddique, R. COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, P.; Anderson, M.; Mossialos, E. Health system, public health, and economic implications of managing COVID-19 from a cardiovascular perspective. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2516–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhi, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Bi, Z.; Zhao, Y. Prevalence and impact of cardiovascular metabolic diseases on COVID-19 in China. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerkin, K.J.; Fried, J.A.; Raikhelkar, J.; Sayer, G.; Griffin, J.M.; Masoumi, A.; Jain, S.S.; Burkhoff, D.; Kumaraiah, D.; Rabbani, L.; et al. COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2020, 141, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, G.; Cheruiyot, I.; Aggarwal, S.; Wong, J.; Lippi, G.; Lavie, C.J.; Henry, B.M.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Association of Cardiovascular Disease With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Severity: A Meta-Analysis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2020, 45, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; A Welch, V.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Hu, X.; Cheng, W.; Yu, L.; Tu, W.; Liu, Q. Correction to: Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 18 patients with corona virus disease 2019 in intensive care unit. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Liang, W.; Jiang, M.; Guan, W.; Zhan, C.; Wang, T.; Tang, C.; Sang, L.; Liu, J.; Ni, Z.; et al. Risk Factors of Fatal Outcome in Hospitalized Subjects With Coronavirus Disease 2019 From a Nationwide Analysis in China. Chest 2020, 158, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Yan, W.; Yang, D.; Chen, G.; Ma, K.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: Retrospective study. BMJ 2020, 368, m1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wu, Y.; Zang, S. Epidemiological analysis of the early 38 fatalities in Hubei, China, of the coronavirus disease 2019. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Fang, Y.-Y.; Shang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, K.; Leng, F.; Wei, S.; Chen, L.; et al. Clinical characteristics of fatal and recovered cases of coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective study. Chin. Med J. 2020, 133, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.-H.; Liang, L.-R.; Yang, C.-Q.; Wang, W.; Cao, T.-Z.; Li, M.; Guo, G.-Y.; Du, J.; Zheng, C.-L.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Predictors of mortality for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2: A prospective cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Tu, L.; Zhu, P.; Mu, M.; Wang, R.; Yang, P.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.; Ping, R.; Hu, P.; et al. Clinical Features of 85 Fatal Cases of COVID-19 from Wuhan: A Retrospective Observational Study. SSRN Electron. J. 2020, 201, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cheng, A.; Kumar, R.; Fang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, S. Hypoalbuminemia predicts the outcome of COVID-19 independent of age and co-morbidity. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inciardi, R.M.; Adamo, M.; Lupi, L.; Cani, D.S.; Di Pasquale, M.; Tomasoni, D.; Italia, L.; Zaccone, G.; Tedino, C.; Fabbricatore, D.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 and cardiac disease in Northern Italy. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Yan, S.; Yang, F.; Xiang, L.; Zhu, J.; Shen, B.; Gong, Z. Clinical characteristics of 25 death cases with COVID-19: A retrospective review of medical records in a single medical center, Wuhan, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Goel, S.; Kabarriti, R.; Cole, D.; Goldfinger, M.; Acuna-Villaorduna, A.; Pradhan, K.; Thota, R.; Reissman, S.; Sparano, J.A.; et al. Case Fatality Rate of Cancer Patients with COVID-19 in a New York Hospital System. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpouraghdam, M.; Farahani, A.J.; Alishiri, G.; Heydari, S.; Ebrahimnia, M.; Samadinia, H.; Sepandi, M.; Jafari, N.J.; Izadi, M.; Qazvini, A.; et al. Epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in IRAN: A single center study. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, G.; Rezza, G.; Brusaferro, S. Case-Fatality Rate and Characteristics of Patients Dying in Relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 2763667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Ning, R.; Tao, Y.; Yu, C.; Deng, X.; Zhao, C.; Meng, S.; Tang, F.; Xu, D. Risk Factors for Mortality in 244 Older Adults With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68, E19–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yin, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Jian, M.; Xu, H.; Prowle, J.R.; Hu, B.; et al. Clinical course and outcome of 107 patients infected with the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, discharged from two hospitals in Wuhan, China. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zuo, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, C. Clinical and laboratory predictors of in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19: A cohort study in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, W.; Yu, X.; Hu, D.; Bao, M.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, H. Coronavirus disease 2019 in elderly patients: Characteristics and prognostic factors based on 4-week follow-up. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Shi, S.; Zhu, J.; Shi, J.; Dai, K.; Chen, X. Analysis of 92 deceased patients with COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, M.; Yin, W.; Tao, Z.; Tan, W.; Hu, Y. Association of radiologic findings with mortality of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Su, N.; Huang, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Yan, F.; et al. Clinical Course and Outcomes of 344 Intensive Care Patients with COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, Q.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Song, J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, E.K.; Park, O.; Park, Y.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Jo, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Kweon, S. Coronavirus disease-19: The first 7,755 cases in the Republic of Korea. Osong. Public Health Res. Perspect 2020, 11, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Kwak, Y.; Kwon, K.; Park, J.; Shin, B.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y. Analysis on 54 mortality cases of coronavirus disease 2019 in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 10, 2020. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e132. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.-M.; Bai, P.; He, W.; Wu, F.; Liu, X.-F.; Han, D.-M.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.-K. Gender Differences in Patients With COVID-19: Focus on Severity and Mortality. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhard, C.; Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Neuhauser, H.K.; Morgan, R.; Klein, S.L. Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, T.; Mohiddin, S.A.; DiMarco, A.; Patel, V.; Savvatis, K.; Marelli-Berg, F.M.; Madhur, M.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; Maffia, P.; D’Acquisto, F.; et al. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system: Implications for risk assessment, diagnosis, and treatment options. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1666–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Volgman, A.S.; Michos, E.D. Sex Differences in Mortality From COVID-19 Pandemic. JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 1407–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.C. Clinical Relevance of Age-Related Immune Dysfunction. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sargiacomo, C.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. COVID-19 and chronological aging: Senolytics and other anti-aging drugs for the treatment or prevention of corona virus infection? Aging 2020, 12, 6511–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, M.R.; Ruschitzka, F. COVID-19 Illness and Heart Failure. JACC: Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; et al. Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 766–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.-C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vankadari, N.; Wilce, J.A. Emerging COVID-19 coronavirus: Glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driggin, E.; Madhavan, M.V.; Bikdeli, B.; Chuich, T.; Laracy, J.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Brown, T.S.; Der Nigoghossian, C.; Zidar, D.A.; Haythe, J.; et al. Cardiovascular Considerations for Patients, Health Care Workers, and Health Systems During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2352–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, J.; Argudo, E.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; Ferrer, R. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Adults with Refractory Septic Shock. ASAIO J. 2019, 65, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gheblawi, M.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2: A Double-Edged Sword. Circulation 2020, 142, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Karakiulakis, G.; Roth, M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, R.; Gubbi, S. COVID-19 pandemic, coronaviruses, and diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2020, 318, E736–E741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Author, Year | Study Design | No. of Patients | F/M | Age | CVD | CAD | Hypertension | Diabetes | Cerebrovascular Disease | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | S | NS | S | NS | S | NS | S | NS | S | NS | S | NS | S | NS | S | NS | ||
| Onder et al., 2020 [21] | – | 355 | 0 (0) | 355 (100) | 0 | 106/249 | – | 79.5 ± 8.1 | 0 (0) | 117 (33) | 0 (0) | 117 (33) | – | – | 0 (0) | 126 (35.5) | 0 (0) | 34 (9.6) |
| Zhou et al., 2020 [29] | MRCS | 191 | 137 (71.7) | 54 (28.3) | 56/81 | 16/38 | 52.0 (45.0–58.0) | 69.0 (63.0–76.0) | 2 (1.5) | 13 (24.1) | 2 (1.5) | 13 (24.1) | 32 (23.4) | 26 (48.2) | 19 (13.9) | 17 (31.5) | – | – |
| Chen et al., 2020 * [11] | RCsSr | 274 | 161 (58.8) | 113 (41.2) | 73/88 | 30/83 | 51.0 (37.0–66.0) | 68.0 (62.0–77.0) | 7 (4.3) | 16 (14.2) | – | – | 39 (24.2) | 54 (47.8) | 23 (14.3) | 24 (21.3) | 0 (0) | 4 (3.5) |
| Deng et al., 2020 [13] | RCS | 225 | 116 (51.6) | 109 (48.4) | 65/51 | 36/73 | 40.0 (33.0–57.0) | 69.0 (62.0–74.0) | 4 (3.4) | 13 (11.9) | 4 (3.4) | 13 (11.9) | 18 (15.5) | 40 (36.7) | 9 (7.8) | 17 (15.6) | – | – |
| Yuan et al., 2020 [28] | RCS | 27 | 17 (63.0) | 10 (37.0) | 9/8 | 6/4 | 55.0 (35.0–60.0) | 68.0 (63.0–73.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (30.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (30.0) | 0 (0) | 5 (50.0) | 0 (0) | 6 (60.0) | 0 (0) | 1 (10.0) |
| Yang et al., 2020 * [27] | SROS | 52 | 20 (38.5) | 32 (61.5) | 6/14 | 11/21 | 51.9 ± 12.9 | 64.6 ± 11.2 | 2 (10.0) | 3 (9.4) | 2 (10.0) | 3 (9.4) | – | – | 2 (10.0) | 7 (21.9) | 0 (0) | 7 (21.9) |
| Jeong et al., 2020 (KCDCP) [33] | 66 | 0 (0) | 66 (100) | 0 | 29/37 | – | 77 (35–93) | 0 (0) | 10 (15.2) | 0 (0) | 10 (15.2) | 0 (0) | 30 (45.5) | 0 (0) | 23 (34.8) | 0 (0) | 5 (7.6) | |
| Park et al., 2020 (KSID) [34] | 54 | 0 (0) | 54 (100) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 16 (29.6) | – | – | |
| Cao et al., 2020 [9] | – | 102 | 85 (83.3) | 17 (16.7) | 45/40 | 4/13 | 53.0 (47.0–66.0) | 72.0 (63.0–81.0) | 2 (2.4) | 3 (17.6) | – | – | 17 (20.0) | 11 (64.7) | 5 (5.9) | 6 (35.3) | 3 (3.5) | 3 (17.6) |
| Wang et al., 2020 * [25] | RCS | 339 | 274 (80.2) | 65 (19.8) | 147/127 | 26/39 | 68.0 (64.0–74.0) | 76.0 (70.0–83.0) | 32 (11.7) | 21 (32.3) | – | – | 106 (38.7) | 32 (49.2) | 43 (15.7) | 11 (16.9) | 11 (4.0) | 10 (15.4) |
| Du et al., 2020 * [15] | ROS | 85 | 0 (0) | 85 (100) | 0 | 23/62 | – | 65.8 ± 14.2 | 0 (0) | 10 (11.8) | 0 (0) | 10 (11.8) | 0 (0) | 32 (37.6) | 0 (0) | 19 (22.4) | 0 (0) | 7 (8.2) |
| Du et al., 2020 * [14] | PCS | 179 | 158 (88.3) | 21 (11.7) | 71/87 | 11/10 | 56.0 ± 13.5 | 70.2 ± 7.7 | 17 (10.8) | 12 (57.1) | – | – | 45 (28.5) | 13 (61.9) | 27 (17.1) | 6 (28.6) | – | – |
| Chen et al., 2020 * [10] | RCS | 1590 | 1540 (96.9) | 50 (3.1) | 675/865 | 20/30 | 48.0 (1.0–94.0) † | 69.0 (51.0–86.0) † | 51 (3.3) | 8 (16.0) | 51 (3.3) | 8 (16.0) | 241 (15.6) | 28 (56.0) | 117 (7.6) | 13 (26.0) | 24 (1.6) | 6 (12.0) |
| Li et al., 2020 [18] | ROS | 25 | 0 (0) | 25 (100) | 0 | 15/10 | – | 73.0 (55.0–100.0) | 0 (0) | 8 (32.0) | – | – | 0 (0) | 16 (64.0) | 0 (0) | 10 (40.0) | 0 (0) | 4 (16.0) |
| Yang et al., 2020 * [26] | ROS | 92 | 0 (0) | 92 (100) | 0 | 43/49 | – | 69.8 ± 14.5 (30.0–97.0) | 0 (0) | 16 (17.4) | – | – | 0 (0) | 51 (55.4) | 0 (0) | 13 (14.1) | – | – |
| Wang et al., 2020 * [23] | RCsSr | 107 | 88 (82.2) | 19 (17.8) | 47/41 | 3/16 | 44.5 (35.0–58.8) | 73.0 (64.0–81.0) | 6 (6.8) | 7 (36.8) | – | – | 16 (18.2) | 10 (52.6) | 6 (6.8) | 5 (26.3) | 3 (3.4) | 3 (15.8) |
| Nikpouraghdam et al., 2020 [20] | SRCS | 2964 | 2725 (91.9) | 239 (8.1) | 937/1788 | 72/167 | – | 65.0 (57.0–75.0) | 33 (1.2) | 4 (1.7) | – | – | 51 (1.9) | 8 (3.3) | 102 (3.7) | 11 (4.6) | – | – |
| Mehta et al., 2020 [19] | SROS | 218 | 157 (72.0) | 61 (28.0) | 66/91 | 25/36 | 66.0 (10.0–92.0) | 76.0 (10.0–92.0) | 42 (26.8) | 34 (55.7) | 24 (15.3) | 19 (31.1) | 100 (63.7) | 47 (77.0) | 53 (33.8) | 27 (44.3) | – | – |
| Wang et al., 2020a *‡ [24] | – | 296 | 277 (93.6) | 19 (6.4) | 148/129 | 8/11 | 46.0 ± 14.4 | 65.6 ± 12.6 | 5 (1.8) | 5 (26.3) | 5 (1.8) | 5 (26.3) | 33 (11.9) | 9 (47.4) | 24 (8.7) | 6 (31.6) | 4 (1.4) | 3 (15.8) |
| Wang et al., 2020b *‡ [24] | – | 44 | 30 (68.2) | 14 (31.8) | 16/14 | 4/10 | 48.8 ± 14.2 | 69.0 ± 13.4 | 0 (0) | 3 (21.4) | 0 (0) | 3 (21.4) | 7 (23.3) | 4 (28.6) | 5 (16.7) | 4 (28.6) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (7.1) |
| Chen et al., 2020 * [12] | RCS | 38 | 0 (0) | 38 (100) | 0 | 11/27 | – | 70.0 (36.0-89.0) | 0 (0) | 5 (13.2) | 0 (0) | 5 (13.2) | 0 (0) | 15 (39.5) | 0 0 (0) | 11 (28.9) | 0 (0) | 4 (10.5) |
| Inciardi et al., 2020 [17] | – | 53 | 34 (64.2) | 19 (35.8) | 6/28 | 2/17 | 65.5 ± 10.2 | 72.3 ± 13.5 | 34 (100) | 19 (100) | – | – | 27 (79.4) | 13 (68.4) | 7 (20.0) | 9 (47.4) | – | – |
| Sun et al., 2020 [22] | RCC | 244 | 123 (50.4) | 121 (49.6) | 72/51 | 39/82 | 67.0 (64.0–72.0) | 72.0 (66.0–78.0) | 15 (12.9) | 20 (16.5) | 15 (12.9) | 20 (16.5) | 62 (50.4) | 76 (62.8) | 24 (19.5) | 27 (22.3) | – | – |
| Huang et al., 2020 [16] | RCS | 299 | 283 (94.6) | 16 (5.4) | 134/149 | 5/11 | 52.5 ± 16.6 | 69.2 ± 9.7 | 25 (8.8) | 6 (37.5) | 14 (4.9) | 4 (25.0) | 63 (22.3) | 11 (68.8) | 31 (11.0) | 4 (25.0) | – | – |
| Wang et al., 2020 * [30] | – | 344 | 211 (61.3) | 133 (38.7) | 106/105 | 59/74 | 57.0 (47.0–69.0) | 70.0 (62.0–77.0) | 18 (8.5) | 22 (16.5) | – | – | 72 (34.1) | 69 (51.9) | 34 (16.1) | 30 (22.6) | – | – |
| Wu et al., 2020 [31] | RCS | 84 | 40 (47.6) | 44 (52.4) | 9/31 | 15/29 | 50.0 (40.3–56.8) | 68.5 (59.3–75.0) | 1 (2.5) | 4 (9.1) | 1 (2.5) | 4 (9.1) | 7 (17.5) | 16 (36.4) | 5 (10.0) | 11 (25.0) | – | – |
| Ruan et al., 2020 [32] | MRCS | 150 | 82 (54.7) | 68 (45.3) | 29/53 | 19/49 | 50.0 (44.0–81.0) | 67.0 (15.0–81.0) | 0 (0) | 13 (19.1) | – | – | 23 (28.0) | 29 (42.6) | 13 (15.9) | 12 (17.6) | 5 (6.1) | 7 (10.3) |
| Mean Difference | Relative Risk | Heterogeneity | Publication Bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD [95% CI] | p-Value | RR [95% CI] | p-Value | I2 (%) | p-Value | Egger’s Intercept [95% CI] | p-Value | |
| Sex | NA | NA | 1.16 [1.05, 1.27] | 0.003 | 90.79 | <0.0001 | 2.67 [−0.01, 0.03] | 0.002 |
| Age | −15.72 [−18.62, 12.81] | <0.0001 | NA | NA | 86.74 | <0.0001 | −6.44 [−12.05, 0.81] | 0.00 |
| CVD with CAD | NA | NA | 1.96 [1.51, 2.54] | <0.0001 | 97.87 | <0.0001 | −0.03 [−0.06, 0.01] | 0.00 |
| CAD | NA | NA | 1.90 [1.32, 2.74] | 0.0005 | 97.79 | <0.0001 | −0.02 [−0.06, 0.01] | 0.00 |
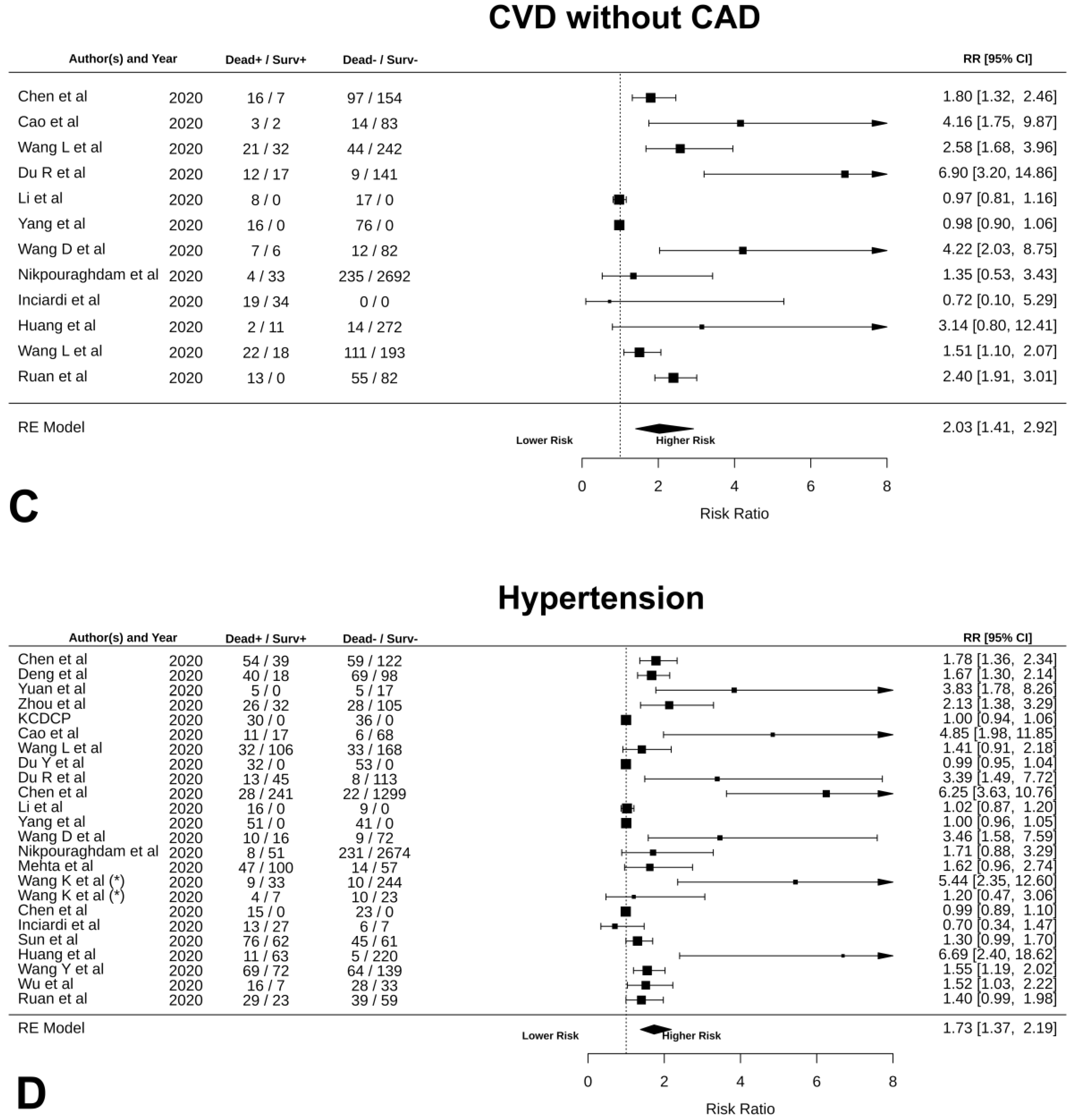
| CVD without CAD | NA | NA | 2.03 [1.41, 2.92] | 0.0002 | 93.25 | <0.0001 | −0.11 [−0.34, 0.13] | 0.00 |
| Hypertension | NA | NA | 1.73 [1.37, 2.19] | <0.0001 | 98.01 | <0.0001 | −0.08 [−0.13, 0.03] | 0.00 |
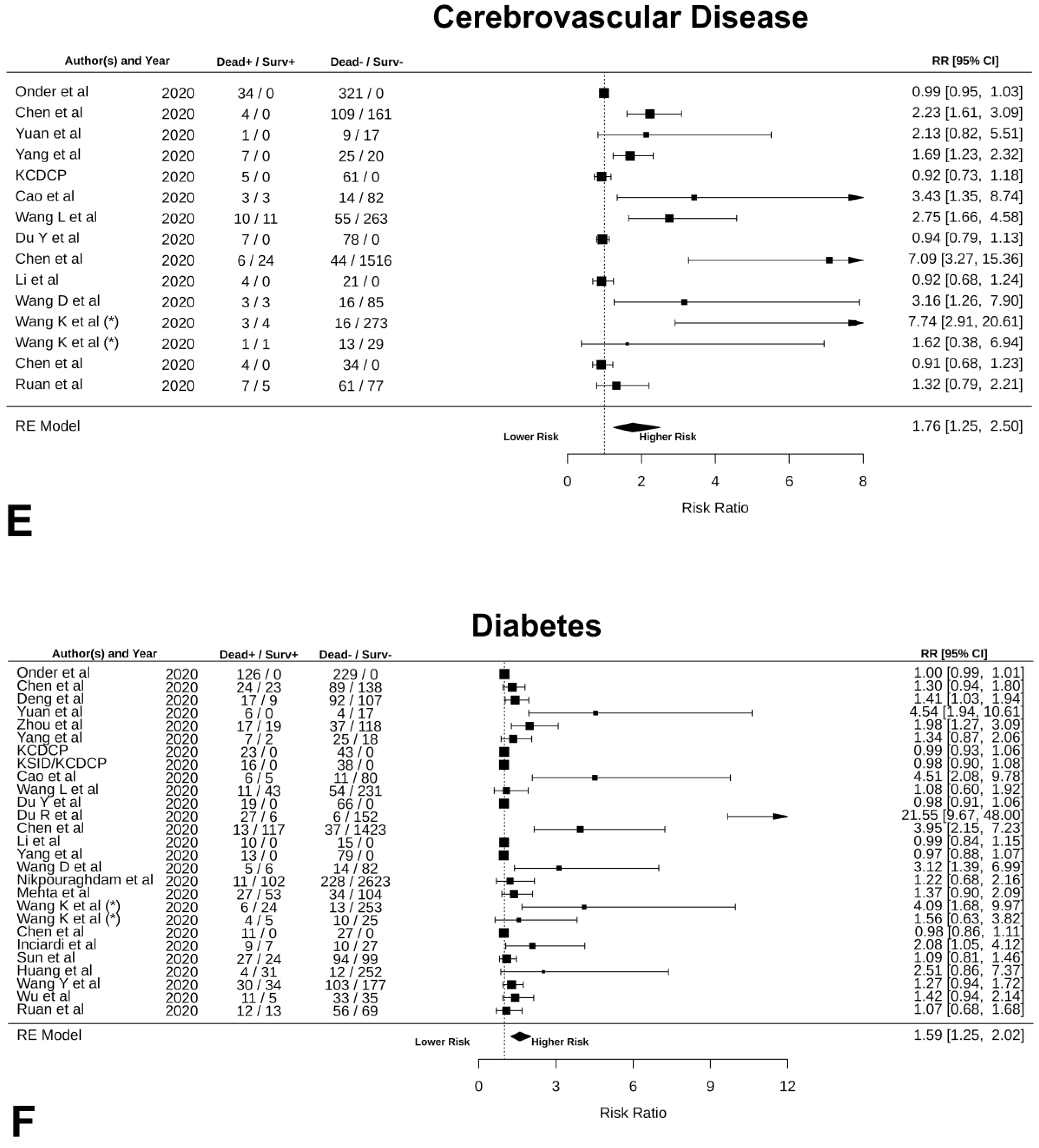
| Cerebrovascular diseases | NA | NA | 1.76 [1.25, 2.50] | <0.0001 | 98.01 | <0.0001 | −0.07 [−0.16, 0.01] | 0.01 |
| Diabetes | NA | NA | 1.59 [1.25, 2.02] | <0.0001 | 98.71 | <0.0001 | −0.02 [−0.04, 0.00] | 0.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moula, A.I.; Micali, L.R.; Matteucci, F.; Lucà, F.; Rao, C.M.; Parise, O.; Parise, G.; Gulizia, M.M.; Gelsomino, S. Quantification of Death Risk in Relation to Sex, Pre-Existing Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors in COVID-19 Patients: Let’s Take Stock and See Where We Are. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092685
Moula AI, Micali LR, Matteucci F, Lucà F, Rao CM, Parise O, Parise G, Gulizia MM, Gelsomino S. Quantification of Death Risk in Relation to Sex, Pre-Existing Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors in COVID-19 Patients: Let’s Take Stock and See Where We Are. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092685
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoula, Amalia Ioanna, Linda Renata Micali, Francesco Matteucci, Fabiana Lucà, Carmelo Massimiliano Rao, Orlando Parise, Gianmarco Parise, Michele Massimo Gulizia, and Sandro Gelsomino. 2020. "Quantification of Death Risk in Relation to Sex, Pre-Existing Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors in COVID-19 Patients: Let’s Take Stock and See Where We Are" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092685
APA StyleMoula, A. I., Micali, L. R., Matteucci, F., Lucà, F., Rao, C. M., Parise, O., Parise, G., Gulizia, M. M., & Gelsomino, S. (2020). Quantification of Death Risk in Relation to Sex, Pre-Existing Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors in COVID-19 Patients: Let’s Take Stock and See Where We Are. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092685





