Chemokine Receptors CCR1 and CCR2 on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Newly Diagnosed Patients with the CD38-Positive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Patients
2.2. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) DNA Load Quantification
2.3. Flow Cytometry Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis of ZAP70 Expression
3. Results
3.1. The Patient Groups
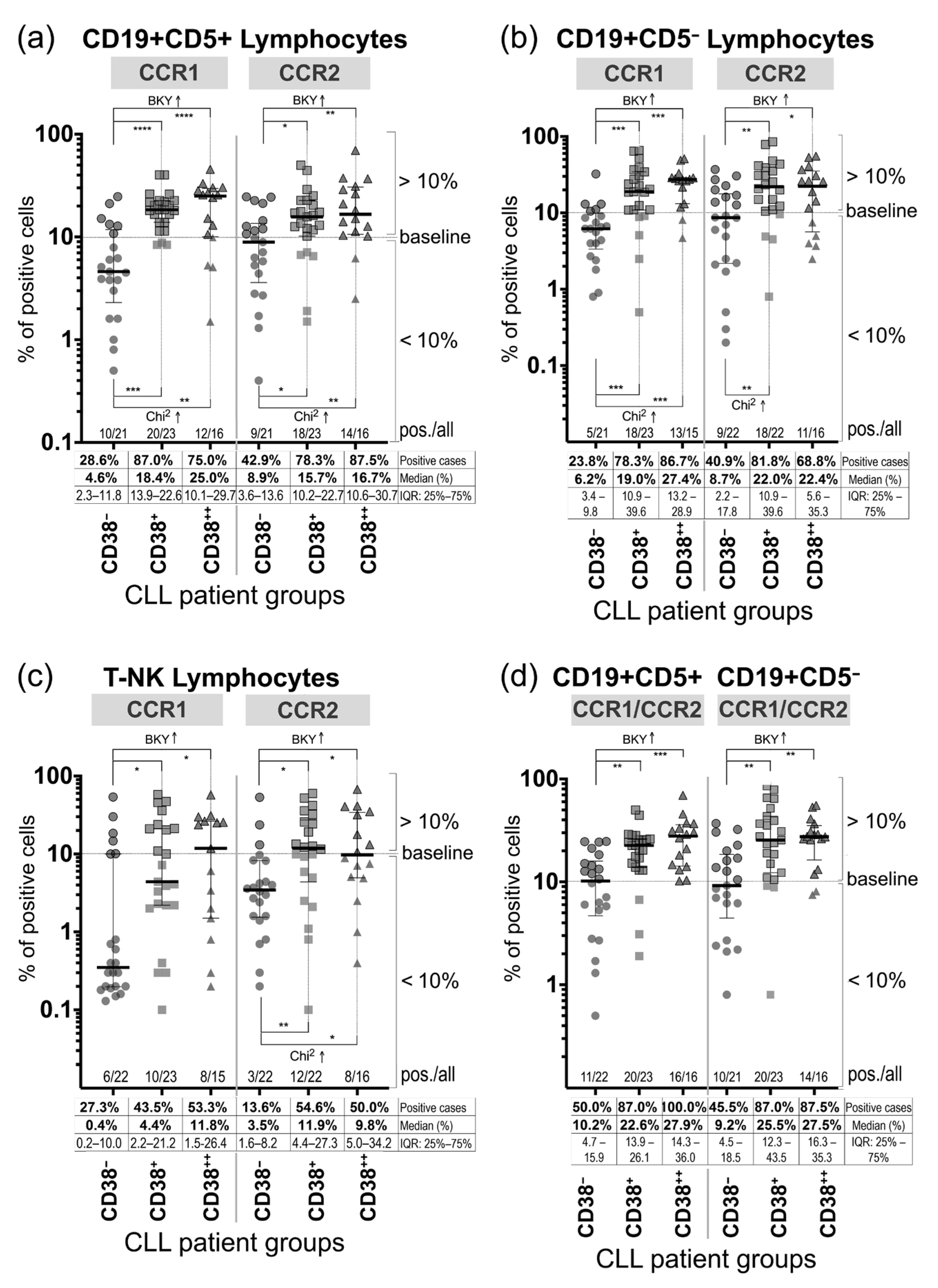
3.2. Expression of CCR1 and CCR2 on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
3.3. ZAP70 Relative mRNA Expression in the Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, G.E.; Iqbal, A.J.; Greaves, D.R. CC chemokine receptors and chronic inflammation-therapeutic opportunities and pharmacological challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 47–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, M.; Hayward, J.A.; Huang, C.E.; Huma, Z.; Sanchez, J. Mechanisms of Regulation of the Chemokine-Receptor Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabel, B.A.; Rott, A.; Butcher, E.C. Leukocyte chemoattractant receptors in human disease pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2015, 10, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frade, J.M.; Mellado, M.; del Real, G.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Lind, P.; Martinez, A.C. Characterization of the CCR2 chemokine receptor: Functional CCR2 receptor expression in B cells. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5576–5584. Available online: https://www.jimmunol.org/content/159/11/5576 (accessed on 3 February 2020). [PubMed]
- Corcione, A.; Tortolina, G.; Bonecchi, R.; Battilana, N.; Taborelli, G.; Malavasi, F.; Sozzani, S.; Ottonello, L.; Dallegri, F.; Pistoia, V. Chemotaxis of human tonsil B lymphocytes to CC chemokine receptor (CCR) 1, CCR2 and CCR4 ligands is restricted to non-germinal center cells. Int. Immunol. 2002, 14, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, C.; Ahlstedt, I.; Furubacka, S.; Johnsson, E.; Agace, W.W.; Quiding-Järbrink, M. Differential expression of chemokine receptors on human IgA+ and IgG+ B cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 141, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, E.L.; Esposito, J.A.; Todd, L.S. Wicker Multiplexed immunophenotyping of human antigen-presenting cells in whole blood by polychromatic flow cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, L.; Cabrelle, A.; Facco, M.; Carollo, D.; Miorin, M.; Tosoni, A.; Pizzo, P.; Binotto, G.; Nicolardi, L.; Zambello, R.; et al. Homeostatic chemokines drive migration of malignant B cells in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 2004, 104, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.W.; Zhao, S.; Ai, W.Z.; Tibshirani, R.; Levy, R.; Lossos, I.S.; Natkunam, Y. C-C chemokine receptor 1 expression in human hematolymphoid neoplasia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 133, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodnyuk, I.; Rudevica, Z.; Leonciks, A.; Ehlin-Henriksson, B.; Kashuba, E. Expression of the chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR2B is up-regulated in peripheral blood B cells upon EBV infection and in established lymphoblastoid cell lines. Virology 2017, 512, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipps, T.J.; Stevenson, F.K.; Wu, C.J.; Croce, C.M.; Packham, G.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; Gribben, J.; Rai, K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. IwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herth, I.; Dietrich, S.; Benner, A.; Hegenbart, U.; Rieger, M.; Stadtherr, P.; Bondong, A.; Tran, T.H.; Weide, R.; Hensel, M.; et al. The impact of allogeneic stem cell transplantation on the natural course of poor-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia as defined by the EBMT consensus criteria: A retrospective donor versus no donor comparison. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhla, P.S.; Butera, J.N.; Treaba, D.O.; Castillo, J.J.; Quesenberry, P.J. Spontaneous regression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to a monoclonal B-lymphocytosis or to a normal phenotype. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, W.; Bacher, U.; Schnittger, S.; Dicker, F.; Alpermann, T.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. Flow cytometric identification of 76 patients with biclonal disease among 5523 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL) and its genetic characterization. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.R.; Sawitsky, A.; Cronkite, E.P.; Chanana, A.D.; Levy, R.N.; Pasternack, B.S. Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1975, 46, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binet, J.L.; Leporrier, M.; Dighiero, G.; Charron, D.; Vaugier, G.; Beral, H.M.; Natali, J.C.; Raphael, M.; Nizet, B.; Follezou, J.Y. A clinical staging system for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Prognostic significance. Cancer 1977, 40, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Geyer, S.M.; Kay, N.E. Prognosis at diagnosis: Integrating molecular biologic insights into clinical practice for patients with CLL. Blood 2004, 103, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binet, J.L.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Catovsky, D.; Cheson, B.; Davis, T.; Dighiero, G.; Dohner, H.; Hallek, M.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; et al. Perspectives on the use of new diagnostic tools in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006, 107, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, R.N.; Wasil, T.; Fais, F.; Ghiotto, F.; Valetto, A.; Allen, S.L.; Buchbinder, A.; Budman, D.; Dittmar, K.; Kolitz, J.; et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F.K. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Orchard, J.A.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Davis, Z.; Stevenson, F.K. Immunoglobulin V genes and CD38 expression in CLL. Blood 2000, 95, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Poeta, G.; Maurillo, L.; Venditti, A.; Buccisano, F.; Epiceno, A.M.; Capelli, G.; Tamburini, A.; Suppo, G.; Battaglia, A.; Del Principe, M.I.; et al. Clinical significance of CD38 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001, 98, 2633–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavasi, F.; Deaglio, S.; Damle, R.; Cutrona, G.; Ferrarini, M.; Chiorazzi, N. CD38 and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A decade later. Blood 2011, 118, 3470–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, R.; Temburni, S.; Calissano, C.; Yancopoulos, S.; Banapour, T.; Sison, C.; Allen, S.L.; Rai, K.R.; Chiorazzi, N. CD38 expression labels an activated subset within chronic lymphocytic leukemia clones enriched in proliferating B cells. Blood 2007, 110, 3352–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassenti, L.; Huynh, L.; Toy, T.L.; Chen, L.; Keating, M.J.; Gribben, J.G.; Neuberg, D.S.; Flinn, I.W.; Rai, K.R.; Byrd, J.C.; et al. ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Peterson, L.C.; Dittman, D.; Evens, A.; Rosen, S.; Khoong, A.; Shankey, T.V.; Forman, M.; Gupta, R.; Goolsby, C.L. Comparative analysis of flow cytometric techniques in assessment of ZAP-70 expression in relation to IgVH mutational status in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 127, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.H.; Gao, R.; Xia, Y.; Gale, R.P.; Chen, R.Z.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Qu, X.Y.; Qiu, H.R.; Cao, L.; et al. Prognostic impact of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-DNA copy number at diagnosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grywalska, E.; Roliński, J.; Pasiarski, M.; Korona-Glowniak, I.; Maj, M.; Surdacka, A.; Grafka, A.; Stelmach-Gołdyś, A.; Zgurski, M.; Góźdź, S.; et al. High Viral Loads of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Associated with Unfavorable Prognosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, C.; Falisi, E.; Young, K.H.; Pascarella, M.; Perbellini, O.; Carli, G.; Novella, E.; Rossi, D.; Giaretta, I.; Cavallini, C.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is an independent predictor of clinical course and survival. Oncotarget 2015, 30, 18653–18663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozarowski, P.; Grabarek, J.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Current Protocols in Cell Biology; Bonifacino, J.S., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Chapter 18; pp. 18.8.1–18.8.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, A.A.; Potashnikova, D.M.; Tatarskiy, V., Jr.; Yastrebova, M.; Khamidullina, A.; Barteneva, N.; Vorobjev, I. Comparison of the mRNA expression profile of B-cell receptor components in normal CD5-high B-lymphocytes and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A key role of ZAP70. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2984–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valceckiene, V.; Kontenyte, R.; Jakubauskas, A.; Griskevicius, L. Selection of reference genes for quantitative polymerase chain reaction studies in purified B cells from B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 151, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelerie, F.; Ben-Baruch, A.; Charo, I.F.; Combadiere, C.; Farber, J.M.; Förster, R.; Graham, G.J.; Hills, R.; Horuk, R.; Locati, M.; et al. Chemokine receptors (version 2019.5) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. IUPHAR/BPS Guide Pharmacol. CITE 2019, 5, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodnyuk, I.; Kadisa, A.; Svirskis, S.; Gravelsina, S.; Studers, P.; Spaka, I.; Sultanova, A.; Lejniece, S.; Lejnieks, A.; Murovska, M. Proportion of the CD19-Positive and CD19-Negative Lymphocytes and Monocytes within the Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Set is Characteristic for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medicina (Kaunas Lith.) 2019, 55, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 6220. Human Protein Atlas available from http://www.proteinatlas.org (accessed on 18 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Kozireva, S.; Rudevica, Z.; Baryshev, M.; Leonciks, A.; Kashuba, E.; Kholodnyuk, I. Upregulation of the Chemokine Receptor CCR2B in Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Burkitt Lymphoma Cell Lines with the Latency III Program. Viruses 2018, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrussi, L.; Capitani, N.; Ulivieri, C.; Manganaro, N.; Granai, M.; Cattaneo, F.; Kabanova, A.; Mundo, L.; Gobessi, S.; Frezzato, F.; et al. P66Shc deficiency in the Eμ-TCL1 mouse model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia enhances leukemogenesis by altering the chemokine receptor landscape. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2040–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrussi, L.; Capitani, N.; Baldari, C.T. P66Shc: A Pleiotropic Regulator of B Cell Trafficking and a Gatekeeper in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassenti, L.Z.; Jain, S.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Grever, M.R.; Byrd, J.C.; Kay, N.E.; Brown, J.R.; Gribben, J.G.; Neuberg, D.S.; et al. Relative value of ZAP-70, CD38, and immunoglobulin mutation status in predicting aggressive disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008, 112, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.I.; Tam, C.S.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; Lerner, S.; Coombes, K.R.; Schlette, E.; Ferrajoli, A.; Barron, L.L.; et al. Relevance of the immunoglobulin VH somatic mutation status in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) or related chemoimmunotherapy regimens. Blood 2009, 113, 3168–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiestner, A.; Rosenwald, A.; Barry, T.S.; Wright, G.; Davis, R.E.; Henrickson, S.E.; Zhao, H.; Ibbotson, R.E.; Orchard, J.A.; Davis, Z.; et al. ZAP-70 expression identifies a chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype with unmutated immunoglobulin genes, inferior clinical outcome, and distinct gene expression profile. Blood 2003, 101, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppezzo, P.; Vasconcelos, Y.; Settegrana, C.; Jeannel, D.; Vuillier, F.; Legarff-Tavernier, M.; Kimura, E.Y.; Bechet, S.; Dumas, G.; Brissard, M.; et al. The LPL/ADAM29 expression ratio is a novel prognosis indicator in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Orchard, J.A.; Ibbotson, R.E.; Davis, Z.; Thomas, P.W.; Stevenson, F.K.; Oscier, D.G. CD38 expression and immunoglobulin variable region mutations are independent prognostic variables in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but CD38 expression may vary during the course of the disease. Blood 2002, 99, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.; Keating, M.; Do, K.A.; O’Brien, S.; Huh, Y.O.; Jilani, I.; Lerner, S.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Albitar, M. CD38 expression as an important prognostic factor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001, 98, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durig, J.; Naschar, M.; Schmucker, U.; Renzing-Kohler, K.; Holter, T.; Huttmann, A.; Duhrsen, U. CD38 expression is an important prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leuk. Off. J. Leuk. Soc. Am. Leuk. Res. Fund UK 2002, 16, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Krober, A.; Seiler, T.; Benner, A.; Bullinger, L.; Bruckle, E.; Lichter, P.; Dohner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S. V(H) mutation status, CD38 expression level, genomic aberrations, and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, P.D.; Fernandez, C.; Giustolisi, G.M.; Morilla, R.; Atkinson, S.; A’Hern, R.P.; Matutes, E.; Catovsky, D. CD38 expression as a prognostic indicator in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Hematol. J. Off. J. Eur. Haematol. Assoc. EHA 2004, 5, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchetto, A.; Bomben, R.; Dal Bo, M.; Bulian, P.; Benedetti, D.; Nanni, P.; Del Poeta, G.; Degan, M.; Gattei, V. CD49d in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Correlated expression with CD38 and prognostic relevance. Leuk. Off. J. Leuk. Soc. Am. Leuk. Res. Fund UK 2006, 20, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachtl, G.; Hofbauer, J.P.; Greil, R.; Hartmann, T.N. The pathogenic relevance of the prognostic markers CD38 and CD49d in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachtl, G.; Sahakyan, K.; Denk, U.; Girbl, T.; Alinger, B.; Hofbauer, S.W.; Neureiter, D.; Hofbauer, J.P.; Egle, A.; Greil, R.; et al. Differential bone marrow homing capacity of VLA-4 and CD38 high expressing chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetto, A.; Bomben, R.; Dal Bo, M.; Sonego, P.; Nanni, P.; Rupolo, M.; Bulian, P.; Dal Maso, L.; Del Poeta, G.; Del Principe, M.I.; et al. A scoring system based on the expression of six surface molecules allows the identification of three prognostic risk groups in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 207, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
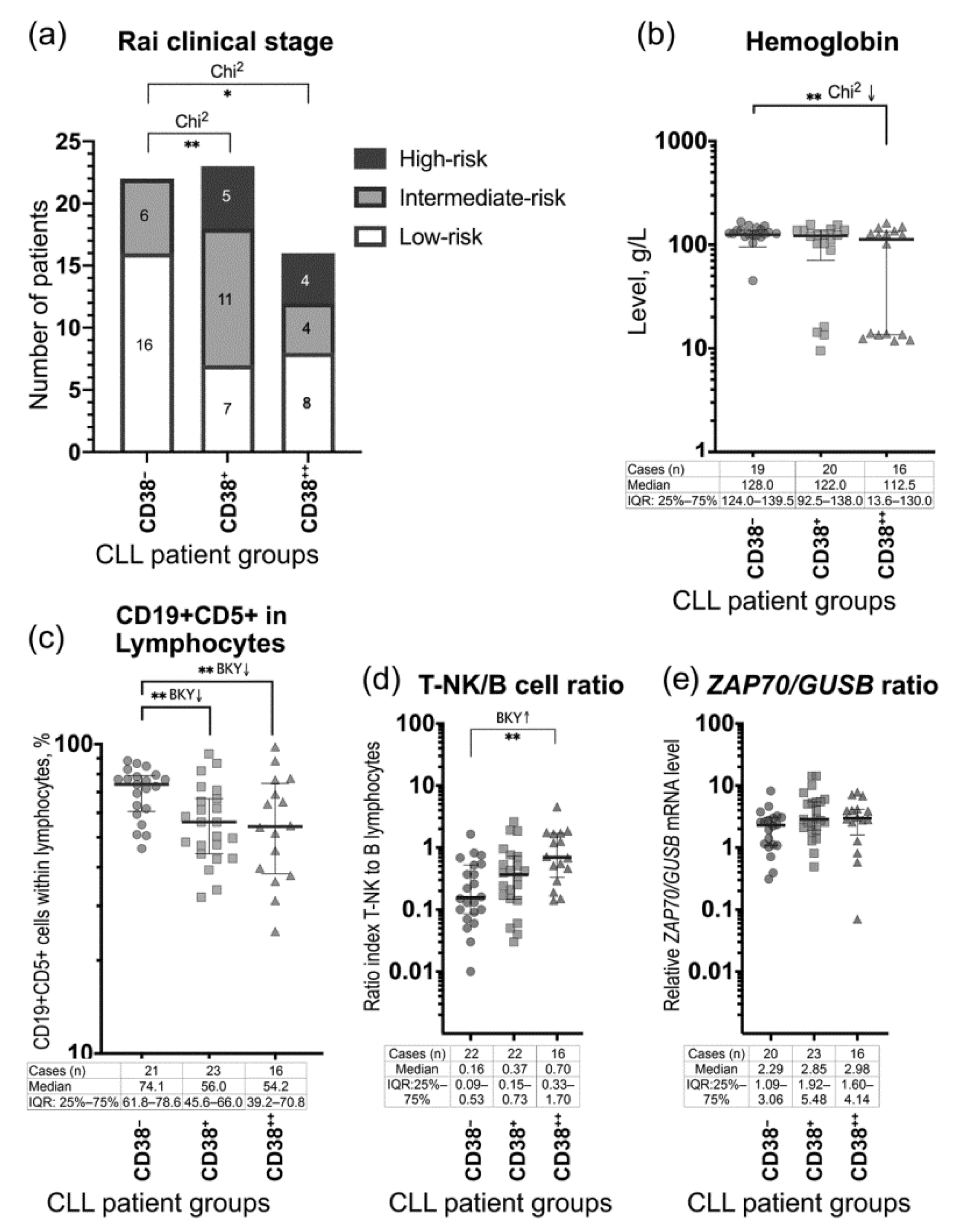

| Demographic and Clinical Parameters | CD38− Group (1) n = 22 | CD38+ Group (2) n = 23 | CD38++ Group (3) n = 16 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years: mean (range) | 69.3 (49–86) | 70.0 (54–88) | 65.6 (41–79) |
| Gender: Male number (%) Female number (%) | 10 (45.5%) 12 (54.5%) | 11 (47.8%) 12 (52.2%) | 11 (68.8%) 5 (31.2%) |
| Low-risk disease (Rai stage 0), n (%) | 16 (72.7%) | 7 (30.4%) | 8 (50.0%) |
| Intermediate-risk disease (Rai stages I–II), n (%) | 6 (27.3%) | 11 (47.8%) | 4 (25.0%) |
| High-risk disease (Rai stages III–IV), n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (21.7%) | 4 (25.0%) |
| Lymphadenopathy, n (%) | 2 (9.1%) | 8 (34.8%) | 5 (31.3%) |
| Splenomegaly, n (%) | 2 (9.1%) | 7 (30.4%) | 5 (31.3%) |
| Leukocytosis (white blood cells), 109/L: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 8.4–81.8 18.1 (12.6–42.5) | 9.3–142.7 18.5 (14.7–65.3) | 10.7–133.2 19.3 (15.0–33.3) |
| Lymphocytosis, 109/L: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 5.4–66.4 16.6 (7.8–40.8) | 2.7–99.0 13.5 (9.4–59.2) | 6.7–103.0 14.1 (9.5–32.9) |
| Monocytosis, 109/L: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 0.2–8.8 0.6 (0.4–1.9) | 0.4–16.1 1.0 (0.5–2.1) | 0.4–11.7 0.7 (0.6–1.9) |
| Neutrophilia, 109/L: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 1.1–21.9 3.4 (2.9–4.4) | 1.9–25.1 4.4 (3.1–6.4) | 2.4–10.8 3.7 (3.2–5.2) |
| Red blood cell count, 1012/L: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 1.1–5.2 4.1 (3.9–4.5) | 3.0–5.2 4.3 (3.8–4.6) | 3.3–4.8 4.2 (4.1–4.5) |
| Hemoglobin, g/L: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 45.0–167.0 128.0 (124.0–139.5) | 9.5–157.0 122.0 (92.5–138.0) | 11.8–162.0 ** 112.5 (13.6–130.0) |
| Platelets, 109/L: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 128.0–285.0 175.0 (147.0–218.0) | 57.0–335.0 221.5 (153.8–241.5) | 110.0–261.0 173.5 (141.8–206.0) |
| CD19+ cells (among lymphocytes), %: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 58.1–97.1 83.7 (76.2–91.1) | 47.0–95.9 82.0 (73.5–87.2) | 37.3–98.5 78.6 (66.5–85.7) |
| CD23+ cells (among lymphocytes), %: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 33.5–85.3 71.6 (59.3–78.6) | 10.8–84.6 56.5 (47.5–76.3) | 24.7–86.1 60.5 (46.9–71.1) |
| CD3+ cells (among lymphocytes), %: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 3.0–23.0 14.5 (7.7–19.8) | 3.0–49.0 12.1 (8.5–21.5) | 1.1–40.0 13.1 (9.0–22.1) |
| CD19+CD5+ (among lymphocytes), %: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 46.0–88.4 74.1 (61.8–78.6) | 32.0–93.0 ** 56.0 (45.6–66.0) | 24.8–98.0 ** 54.2 (39.2–70.8) |
| EBV DNA >50 copies/1 ug of PBMC DNA), n (copy number) | 0/(0.0) | 2/(441; 871) | 1/(430) |
| Relative ZAP70 mRNA level in PBMC: Range Median (IQR: Q1–Q3) | 0.31–8.18 2.29 (1.09–3.06) | 0.49–14.25 2.85 (1.92–5.48) | 0.07–7.79 2.98 (1.60–4.14) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kholodnyuk, I.; Rivkina, A.; Hippe, L.; Svirskis, S.; Kozireva, S.; Ventina, I.; Spaka, I.; Soloveichika, M.; Pavlova, J.; Murovska, M.; et al. Chemokine Receptors CCR1 and CCR2 on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Newly Diagnosed Patients with the CD38-Positive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072312
Kholodnyuk I, Rivkina A, Hippe L, Svirskis S, Kozireva S, Ventina I, Spaka I, Soloveichika M, Pavlova J, Murovska M, et al. Chemokine Receptors CCR1 and CCR2 on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Newly Diagnosed Patients with the CD38-Positive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072312
Chicago/Turabian StyleKholodnyuk, Irina, Alla Rivkina, Laura Hippe, Simons Svirskis, Svetlana Kozireva, Ildze Ventina, Irina Spaka, Marina Soloveichika, Jelena Pavlova, Modra Murovska, and et al. 2020. "Chemokine Receptors CCR1 and CCR2 on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Newly Diagnosed Patients with the CD38-Positive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072312
APA StyleKholodnyuk, I., Rivkina, A., Hippe, L., Svirskis, S., Kozireva, S., Ventina, I., Spaka, I., Soloveichika, M., Pavlova, J., Murovska, M., & Lejniece, S. (2020). Chemokine Receptors CCR1 and CCR2 on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Newly Diagnosed Patients with the CD38-Positive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072312







